Chapter 21: Sex Chromosome Haplotyping and Gender Identification
21.1: Y Chromosome Haplotyping
Human Y Chromosome Genome
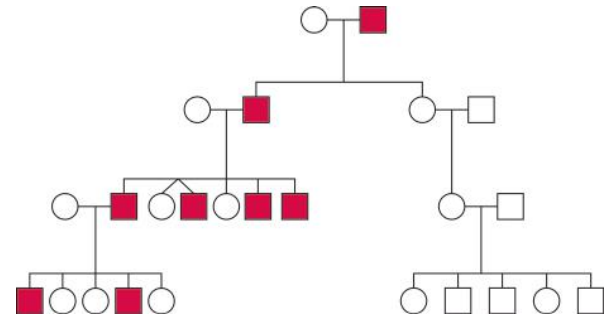
Patrilineage: The Y chromosome is inherited from the father and is passed on to all male offspring.
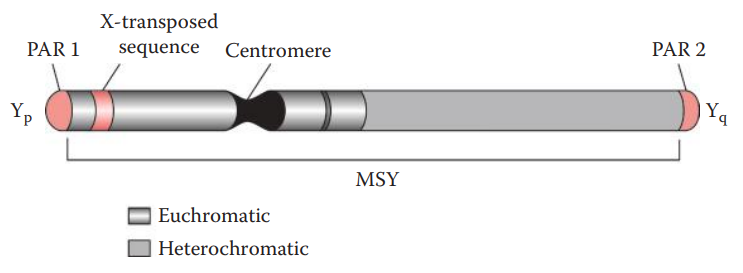
Pseudoautosomal Regions (PARs): Homologous nucleotide sequences that are present on the X and Y chromosomes.
- PAR1: It is located on the terminal region of the short arm. It comprises 2.6 Mb. Twenty-four genes have been identified within the PAR1.
- PAR2: It is located at the tip of the long arm. It comprises 320 kb, with only four genes identified so far.
Male-Specific Y Region: The remainder of the Y chromosome.
Polymorphic Sequences
- DYF155S1: The first characterized VNTR at the human Y chromosome.
- It consists of an array of AT-rich repeats at 25 bp per unit repeat.
Y-STR
- Y-STRs used in forensic DNA testing are male specific and are thus useful in the investigation of sexual assault cases involving male suspects.
- The technique can be used for paternity testing and the identification of missing persons.
- The major disadvantage of Y-STR loci is that their discriminating power is lower than that of autosomal loci. Because Y chromosome loci are linked, the product rule for statistical calculations for profile probability does not apply.
- Haplotypes: Alleles of Y-STR loci linked or inherited together.
- In 1997, the European minimal haplotype locus set, also known as the minimal haplotype loci, was recommended by the International Y-STR User Group for forensic applications.
21.2: X Chromosome Haplotyping
- X-chromosomal STR (X-STR) profiling is a useful tool in kinship testing in forensic investigations.
- Homologous recombination between the X and Y chromosomes is restricted to the homologous PARs.
- The paternal X chromosome is inherited by daughters as haplotypes.
- Homologous recombination can occur between two X chromosomes in the mother– child transmission.
- Recombination Fraction: The percentage of recombinants resulting from chromosomal crossover between two loci during meiosis among all the offspring.
21.3: Sex Typing for Gender Identification
Amelogenin Locus
This region encodes extracellular matrix proteins involved in tooth enamel formation.
Amelogenesis Imperfecta: A disorder that causes abnormal formation of tooth enamel in both primary and permanent teeth.
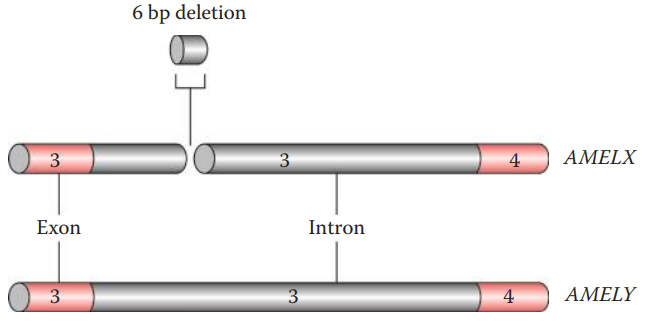
The AMEL locus has two homologous genes:
- AMEL X: AMEL locus which is located on the human X chromosome.
- AMEL Y: AMEL locus which is located on the human Y chromosome.
Other Loci
- Sex-determining region Y (SRY) gene: Encodes a transcription factor that plays a role in the regulation of sex determination toward male development.
- The SRY protein contains a DNA-binding domain known as the HMG box.
- SOX3: An SRY-related HMG box-containing gene, has been identified at Xq27.1 of the X chromosome, which shares sequence homology with SRY.
- TSPY Locus: It encodes the testis-specific protein Y-encoded gene that is only expressed in the testis and may play a role in spermatogenesis.
- DYS14: A marker utilized for the characterization of the TSPY locus.
- TSPY-like (TSPYL) gene: It has been identified on the short arm of the X chromosome and is designated as TSPYL2.
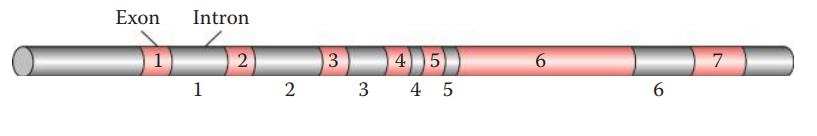
- TSPYL2: A single-copy gene per X chromosome and is 6.3 kb in length, consisting of 7 exons and 6 introns.
- DXYS156: A polymorphic pentanucleotide STR. It is located at the pseudo-autosomal region of both X and Y chromosomes, is another candidate marker used for sex typing.
- DXYS156 Y: Alleles that have an additional adenine insertion in the repeat units of STR.
- Steroid sulfatase (STS) gene: Encodes an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of sulfated steroid precursors to biologically active steroids such as estrogens and androgens.