Chem 103 Exam 4
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Describe the structure of ionic compounds
3 dimension crystal lattice structure with positively charged and negative charged ions held together.
What determines the force of attraction in ionic compounds
Higher charge and smaller ions both result in stronger attractions. Stronger attraction= greater lattice energy
Does forming ion-ion interactions absorb or release energy?
Energy is released when and ionic lattice forms in the gas phase (lattice energy)
Why do ionic compounds have high boiling points
It takes a lot of energy to overcome the attractions between the opposite charges in lattice
Why do ionic compounds have a hard and brittle structure
The ions are stuck together making it hard, its brittle bc when forces make the layers move the shift of like charges near one another can cause shattering.
Explain the conductivity of ionic compounds
Not conductive in solids bc ions cannot move, but in melted or aqueous states ions are free to move and carry an electric current
Relationship and difference between temp, KE, and thermal energy
Temp=avg KE of particles and is not dependent upon the number of particles. Thermal energy= Total KE of all particles so it’s dependent upon the # of particles. (inc in particles=inc in TE)
Why do particles move w/a range of diff velocities at a given temp
Particle collisions transfer energy at random so there’s a range of speeds
Boltzmans distribution
Lower temp = Lower avg particle velocity = higher # of particles at lower speeds, resulting in a tall, narrow graph.
Higher temp=Higher average particle velocity = fewer particles moving at the same speeds = spread out distribution
Properties of ideal gases
Particles have no volume, exert no forces on each other, and KE is unchanged when gases collide with each other or the surroundings
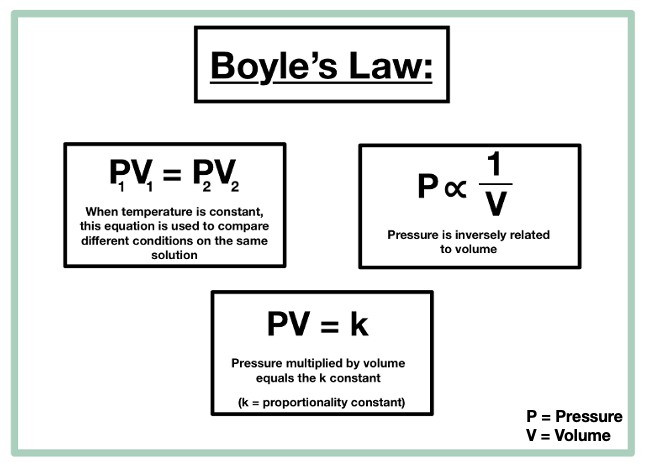
Boyles law
At a constant temp, volume and pressure have an inverse relationship
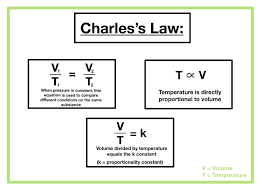
Charles law
At a constant pressure volume and temp have a direct relationship
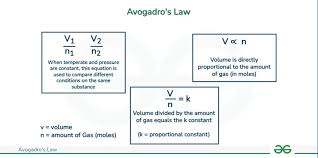
Avogadros law
At a constant temp and pressure moles and volume have a direct relationship
Ideal gas law
PV=nRT (t is in kevlins)
Open system
can transfer energy and matter (biological systems)
Closed system
Can transfer energy but not matter (container)
Isolated system
No transfer of energy or matter
sign of Energy out of a system into surroundings
negative
sign of energy into system from surroundings
positive
Thermal energy
molecular KE
Molecular motion in solid state
Free Vibration
Molecular motion in liquid state
Free vibration, restricted rotation and translation
Molecular motion in gas state
free vibration, translation and rotation
Exothermic
Energy is released from the system into the surroundings
Endothermic
Energy is absorbed into the system from the surroundings
Heat (q)
The amount of energy that flows spontaneously from a hotter system to a colder system
First law of thermodynamics
energy cannot be created or destroyed only transformed or transferred
Sign of q when interactions are broken
Energy is input so q>0
Sign of q of the system when interactions are broken
Energy is released so q<0
Enthalpy
The way in which energy flows as heat under conditions of constant pressure
Solid-fusion-vaporization-gas
Endothermic (sublimation)
gas-condensation-crystalization-solid
Exothermic (deposition)
Explain relative magnitudes of heats for phase changes
stronger imfs= higher hvap and hfusion but hvap is always higher than hfusion bc fusion is a phase change while in vap imfs are fully overcome.
Heat capacity
How much energy is needed to inc the temp of a substance.
Relationship between heat capacity and thermal energy
Higher heat capacity=more thermal energy to inc temp (less steep slope)
Lower heat capacity=less thermal energy to inc temp (steeper slope)
Relationship between mass and heat capacity and imfs and heat capacity
Greater mass=greater heat capacity (greater mass=more particles thus more energy needed)
Stronger imfs=higher heat capacity
Formula to find the amount of heat energy required to change temp
q=mCT (Celsius for T) (c=heat capacity) (m=mass)
Why doesn’t the temperature change during a phase change
That energy is being used to break or form imfs instead of inc KE.
Explain the difference between slopes in a heating or cooling curve
Liquid has a higher heat capacity than gas meaning it requires more energy to inc the temp so the slope isnt as steep (imfs are stronger in liquid than in gas)
Why does it take more energy to boil water compared to melting
Imfs aren’t fully overcome in melting
Explain why water has a high MP/BP
Strong h-bonds require a lot of energy to overcome
Explain why water has lower density (ice floating in water)
In ice h-bonds form a open spread out structure where the molecules are further apart making it less dense
Explain why water has a high heat capacity
It takes a lot of energy to overcome the H-bonds
Explain why water has high Hvap
All h-bonds must be broken to turn into vapor which takes a lot of energy
Interactions as they pertains to solutes and solvents prior to solution
Solute: ion-ion interactions, Solvent(H2O): h-bonds, dipole-dipole, and LDFS
Interactions as it pertains to solute and solvents after the solution
Ion-dipole interactions between the solute and solvent
Process of dissolution as it pertains to enthalpy
1.) Interaction between solutes are overcome- endothermic
2.) Some interactions between solvents are overcome- endothermic
3.) New interactions between solute and solvent are formed- exothermic
What does it mean if the the temp inc when a solution formed
The new solute-solvent interactions release more energy than it took to break the og solutions (exothermic)
What does it mean if the temp dec when a solution is formed
The energy required to break to solute-solvent interactions is greater than the energy required when forming them. (endothermic)
Define a chemical change and its evidence
A change to the molecular structure resulting in the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances, which results from bonds being broken and new ones forming.
Evidence: color change, energy absorbed or released, new compound w/diff properties, gas or precipitate
Define a phase change and its evidence
Physical transformation that doesn’t alter the molecular structure
Evidence: substance is the same in all states of matter, temperature doesn’t change in a phase change, energy isn’t released or absorbed to overcome imfs between molecules
Entropy
A measure of disorder within a system that signifies the dispersion of energy (more dispersion=more thermodynamically stable)
Key things about entropy
s>gas>liquid>solid,
temp inc=entropy inc,
heavier atoms= higher entropy at a given temp
Inc in #of moles in molecules=inc in entropy
Entropy of a mixture of 2 or more types of particles is > than that of a pure substance
Spontaneous process
Physical(chemical process) which results in a lower more stable energy state
2nd law of thermodynamics
For any process to be spontaneous entropy of the universe must inc. Stotal=Ssystem+Ssurroundings
When is a reaction always spontaneous
A reaction is always spontaneous if its exothermic and has an inc in entropy of the system. (exothermic processes lower the energy of the system)
Equation for spontaneity
G=H-TS when g<0 it’s spontaneous when g>0 it is not spontaneous.
How can you determine ionic radius from a potential energy (PE) graph?
The x-value at the minimum of the PE curve represents the distance between ions. A larger x-value (further from 0) indicates a greater distance between the ions, meaning the ions have larger radii.
How can you determine the boiling point of salts from a PE graph?
A more negative potential energy minimum means stronger attractions between ions (greater lattice energy), making the salt more stable and requiring more energy to separate the ions—resulting in a higher melting/boiling point.
Process of determining the final temp of a solution
Convert solute to moles
Use q=moles*h to find q and convert to J if necessary
Find total mass
Use q=mct to find t
Solve for final temp: finaltemp=intital temp+t
At a constant volume explain why more molecules results in higher pressure and vise versa
More molecules result in more collisions with the walls inc the pressure, less molecules=less collisions, dec the pressure
How do gas molecules behave when they occupy more volume
More volume allows the molecules to be more spread out resulting in less collisions
How do gas molecules behave when they occupy less volume
Less volume = molecules packed tighter, so more collisions