Pain Plasticity
0.0(0)Studied by 0 people
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:42 AM on 12/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
what are nociceptors
receptors that terminate free nerve endings and respond to noxious stimulus and generate nerve impulses that the brain perceive as pain signals
2
New cards
what do nociceptors respond to
noxious stimulus
3
New cards
what do nociceptors generate
nerve impulses that the brain perceive as pain signals
4
New cards
what stimuli do nociceptors respond to
thermal-mechanical and chemical
5
New cards
what are the 4 neural steps in the processing of pain signals
transduction, transmission, modulation, and perception
6
New cards
transduction
noxious stimuli are converted to electrical signals in sensory nerve endings
7
New cards
transmission
neural events which relay the information from the periphery to the cortex
8
New cards
modulation
the nervous system can selectively inhibit the transmission of pain signals
9
New cards
perception
subjective interpretation by the cortex of the noxious stimulus
10
New cards
what are the 2 components of perception
sensory component and affective component
11
New cards
what is the therapeutic goal for pain
eliminate abnormal pain without interfering with normal - protective pain
12
New cards
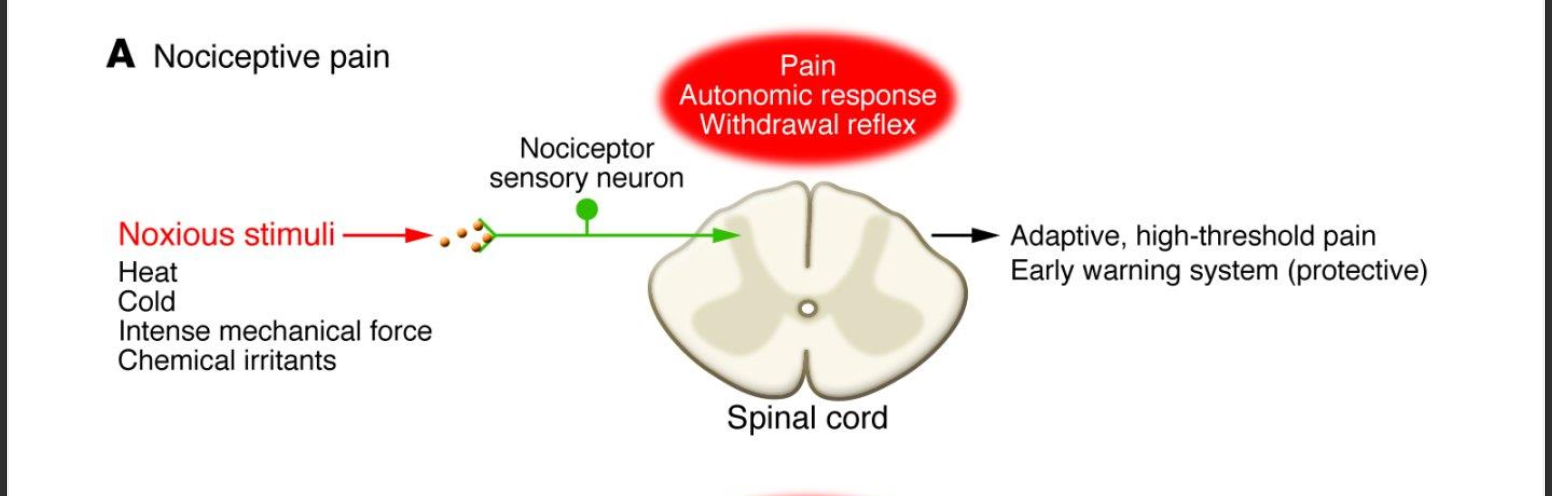
nociceptive pain processing
Noxious stimuli (Heat, cold, intense mechanical force, chemical irritants) -> nociceptor -> spinal cord -> adaptive, high-threshold pain early warning system (protective)
13
New cards
what is the response to nociceptive pain
autonomic response withdrawal reflex
14
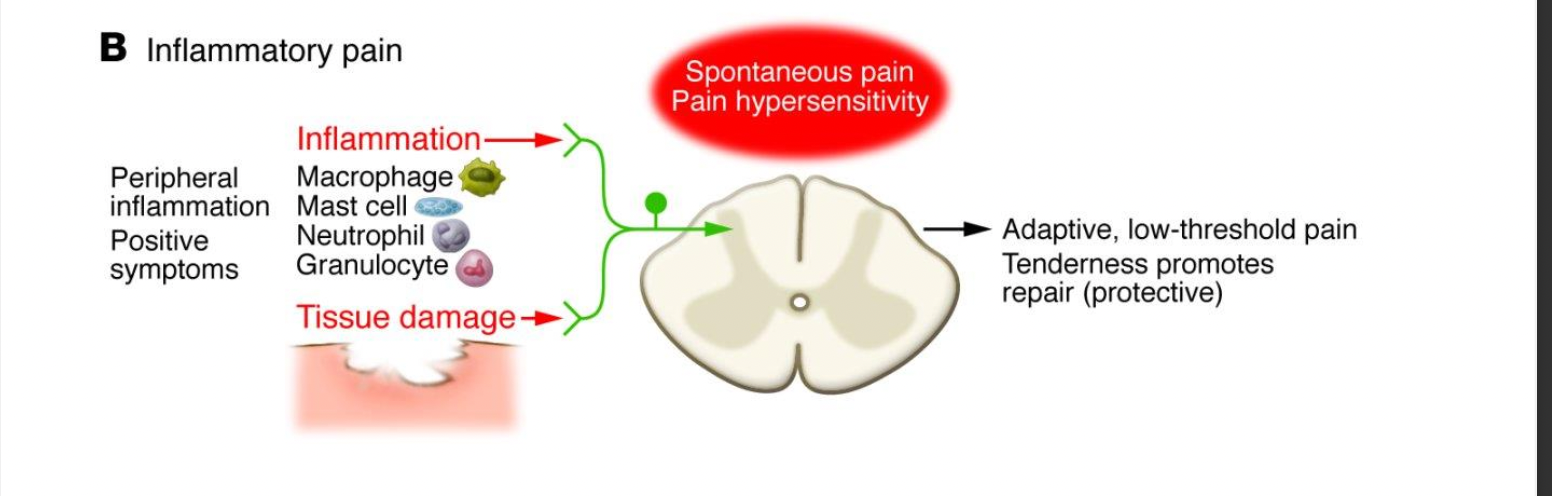
New cards
inflammatory pain processing
peripheral inflammation & tissue damage -> spinal cord -> adaptive, low-threshold pain; tenderness promotes reapari (protection)
15
New cards
what are the 4 potential
macrophage, mast cell, neutrophil, and Granulocyte
16
New cards
name the 2 paths for pathological pain processing
neuropathic pain and dysfunctional pain
17
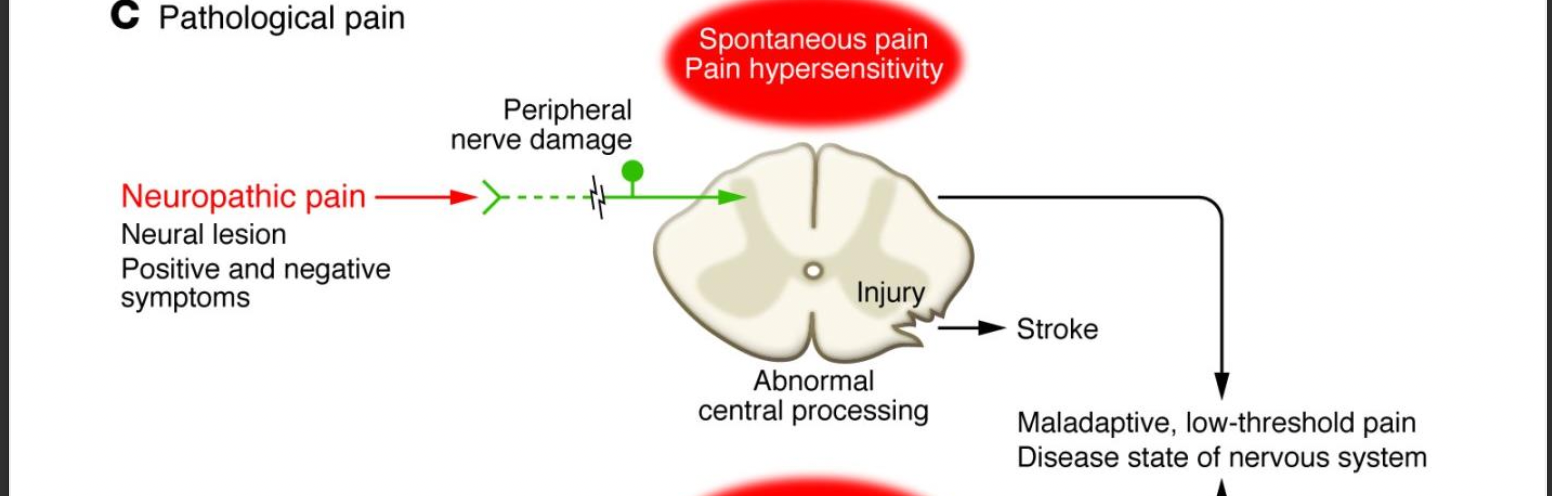
New cards
neuropathic pain pathway
neural lesion, positive and negative symptoms -> peripheral nerve damage -> abnormal central spinal processing -> stroke
OR
-> maladaptive , low-threshold pain disease state of nervous system
OR
-> maladaptive , low-threshold pain disease state of nervous system
18
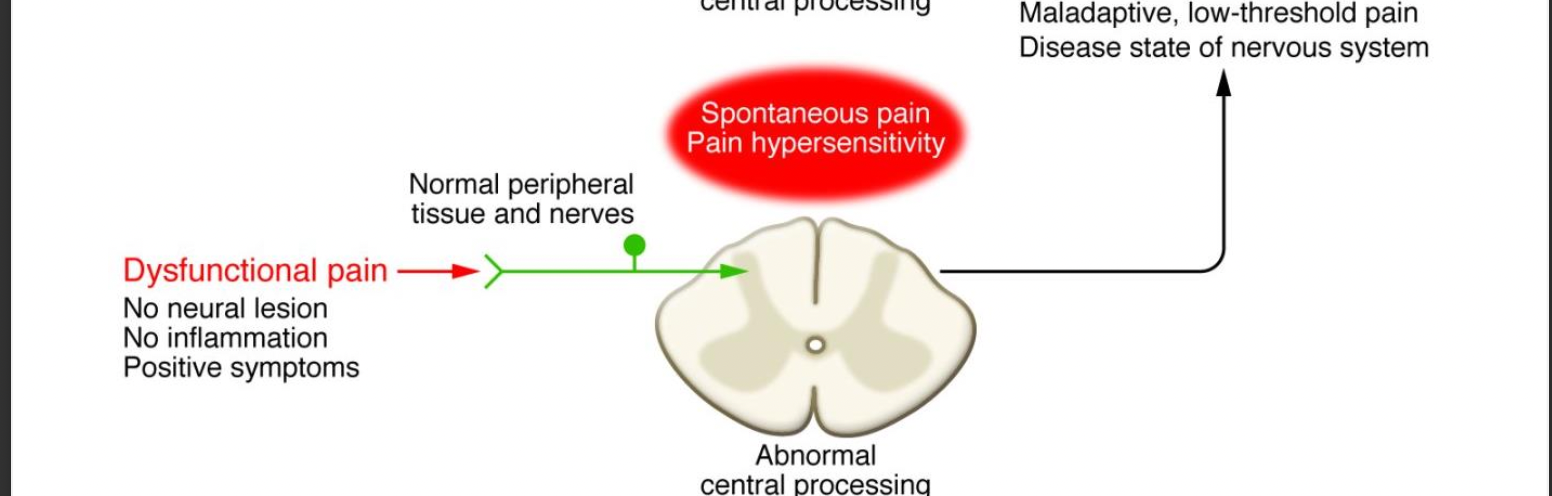
New cards
dysfunctional pain pathway
no neural lesion, no inflammation, positive symptoms -> normal peripheral tissue and nerves -> abnormal central spinal processing -> maladaptive, low-threshold pain disease state of nervous system
19
New cards
what kind types of pain and their central processing goes with spontaneous pain & pain hypersensitivity
inflammatory and pathological pain
20
New cards
what is familial erythromelalgia
autosomal-dominant condition with painful spontaneous burning pain of feet and/or hands, increased skin temp
21
New cards
what mutation causes Erythema
mutations in SCN9A - encoding a sodium channel alpha subunit
22
New cards
characteristics of Aß-fibers
Myelinated Non-nociceptive; Vary Fast conduction; convey light touch and vibration; may become nociceptive after nerve injury
23
New cards
what do Aß-fibers convey
light touch and vibration
24
New cards
what can afferent nerve fiber can become nociceptive after injury
Aß-fibers
25
New cards
characteristics of Aδ-fibers
Myelinated Nociceptors; fast conduction; convey fast "picking" pain, punctate stimuli, cold, thermal
26
New cards
what do Aδ-fibers convey
fast "picking" pain, punctate stimuli, cold, thermal
27
New cards
Characteristics of Nociceptive C-fibers
UNmyelinated nociceptors; slow conduction; convey slow "burning" and "aching" pain - polymodal (high-threshold mechanical, thermal, cold)
28
New cards
what afferent nerve fibers are nociceptors
Aδ-fibers and C-fibers
29
New cards
what do Nociceptive C-fibers convey
slow "burning" and "aching" pain - polymodal (high-threshold mechanical, thermal, cold)
30
New cards
TRP channels (transient receptor potential)
respond to a number of strong stimuli
31
New cards
what does TRPM8 stimulated by
cool temperature and menthol
32
New cards
what happens when TRPM8 is stimulated by menthol
since TRPM8 responds to both cool temp and menthol - response is same as cold temp
33
New cards
what does TRPV1 stimulated by
capsaicin and noxious heat
34
New cards
what happens when TRPV1 is stimulated by capsaicin
a noxious heat is felt
35
New cards
what kind of surface receptors can nociceptors also express? and what does it lead to
GPCRs and Try receptors - sensitization of the nerve endings
36
New cards
what is allodynia
perception of pain from a normally non-painful stimulus
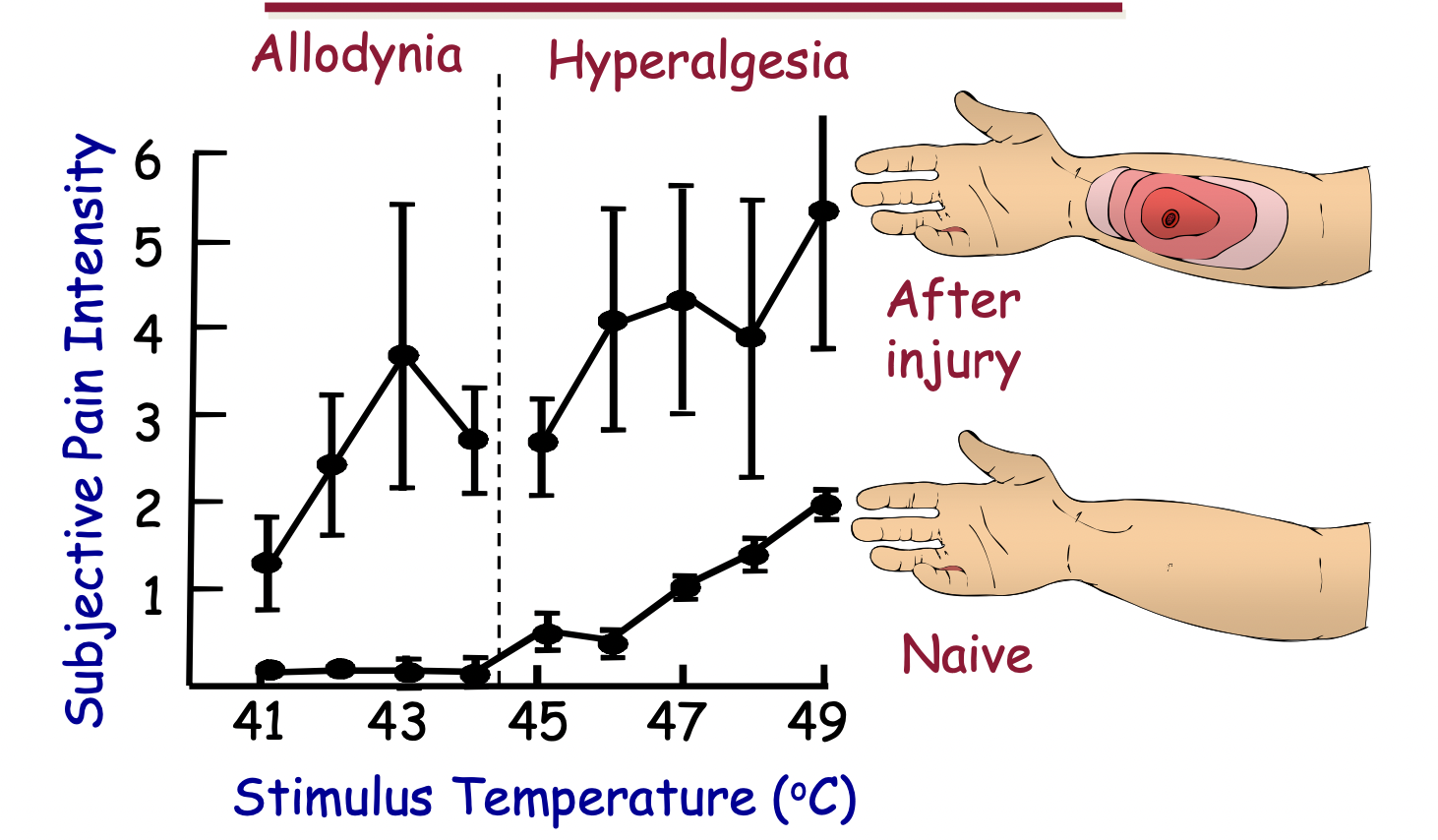
37
New cards
what is hyperalgesia
exaggerated perception of pain from a normally painful stimulus
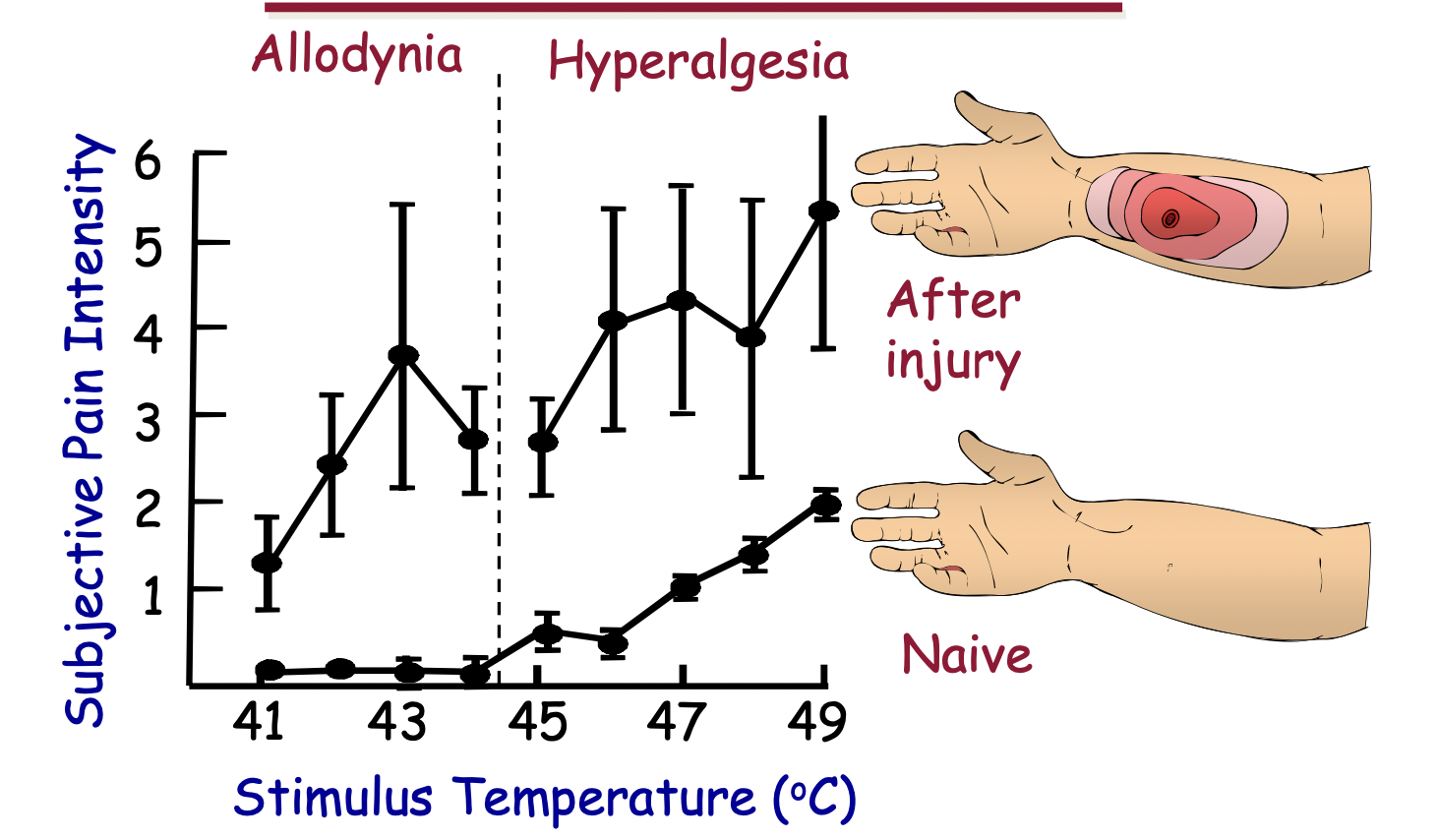
38
New cards
where is the Dorsal Root Ganglion (DRG)
spinal cord
39
New cards
ascending pain system
transmits information from nerve endings to the brain (peripheral -> CNS)
40
New cards
Descending pain system
allows the brain to modulate incoming information by sending projections down to the spinal cord (CNS -> peripheral)
41
New cards
what are opioids
Highly effective analgesics
42
New cards
what do presynaptic opioids do
block Ca++ influx; open K+ channels - K+ efflux (leave cell making more negative); decrease excitatory neurotransmitter release
43
New cards
what do postsynaptic opioids do
open K+ channels; hyper polarize 2 degree - order neuron; inhibit action potential generation
44
New cards
what does Acetaminophen do
inhibits COX, But different from NSAIDss
45
New cards
side effects of Acetaminophen overdose
kidney and liver failure
46
New cards
what do NSAIDs do
inhibit COX1 and COX2
47
New cards
what does inhibiting COX enzymes do
stop the process of converting Archidonic acid to Prostaglandins
48
New cards
some notable NSAIDs
aspirin, diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen, ketorolac, celecoxib, ketoprofen, and indomethacin
49
New cards
side effects of NSAIDs over usage
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea/constipation, rash, ULCERS, kidney failure, liver failure, and prolonged bleeding
50
New cards
what can aspirin in children and teenagers with chickenpox or influenza do
develop Reye's syndrome - acute pressure in the brain and massive accumulations of fat on the liver
51
New cards
What are the 3 types of opioid receptors
Mu, Delta, and Kappa
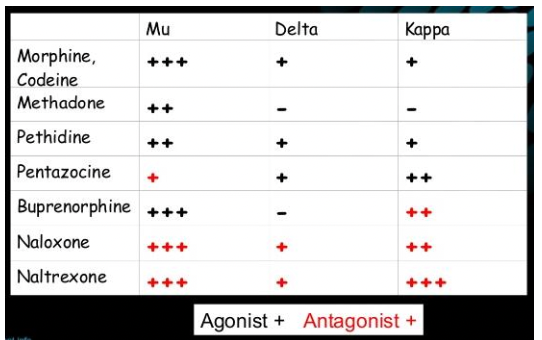
52
New cards
Morphine
Mu opined agonist (codeine is less potent morphine)
53
New cards
fentanyl
100 times more potent than morphine
54
New cards
methadone
orally available, long half life
55
New cards
buprenorphine
partial Mu opioid agonist
56
New cards
Pentazocine
Kappa and Mu opioid agonist