Nomenclature of Alkanes (Flashcards)
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key concepts, rules, prefixes, substituents, and cycloalkane nomenclature from the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
suffix -ane
Suffix used for alkanes
meth
1 carbon
eth
2 carbons
prop
3 carbons
but
4 carbons
pent
5 carbons
hex
6 carbons
hept
7 carbons
oct
8 carbons
non
9 carbons
dec
10 carbons
Longest linear chain
The main uninterrupted chain chosen as the base for naming; it is the longest possible and can be numbered in either direction.
Monosubstituted alkane
An alkane with a single substituent; substituents use the suffix -yl.
yl suffix
Suffix for alkyl substituents (methyl, ethyl, etc.) derived from the base alkane.
Multiply-substituted alkane
An alkane with two or more substituents on the main chain.
tie for longest chain
If multiple longest chains exist, choose the one with the most substituents.
multiplicity prefixes di-, tri-, tetra-
Prefixes used to indicate more than one substituent of the same type (dimethyl means 2 methyl groups, trimethyl means 3 methyl groups attached to the main carbon chain)
alphabetical order of substituents
Substituents are listed in alphabetical order in the name; prefixes di/tri/tetra are not considered for ordering.
Halogen substituents
Fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo-; substituents derived from halogens.
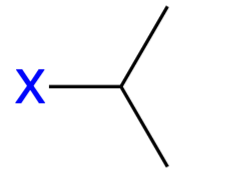
isopropyl (iPr)
An alkyl substituent (CH3-CH-CH3)
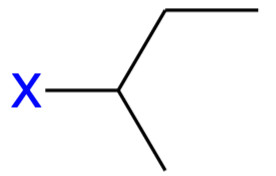
sec-butyl (sBu)
Secondary-butyl substituent;
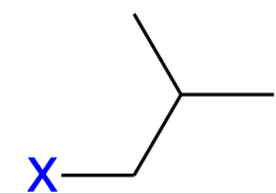
isobutyl (iBu)
Branched butyl substituent;
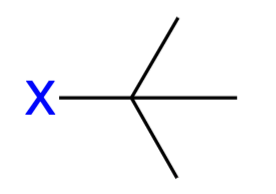
tert-butyl (tBu)
Tertiary-butyl substituent;
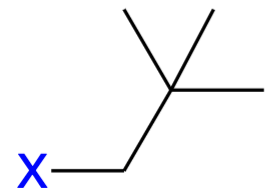
neopentyl (neop)
A branched-chain alkyl group derived from neopentane, consisting of a five-carbon chain with a central carbon attached to two methyl groups.
alphabetization note for iso/neo
In alphabetizing, count 'iso' and 'neo' but ignore 'sec' and 'tert' as separate letters.
cycloalkanes
Nomenclature for cyclic alkanes uses the prefix 'cyclo-' before the base name (cycloalkane). Everything else is the same as linear alkanes in terms of substituent placement and numbering.
one substituent on cycloalkane exception
If only one substituent is present on a cycloalkane, a number is not required.
ring can be substituent when chain longer
If the side chain has more carbons than the ring, the ring is named as a substituent on the chain.
Bicycloalkanes
Complex hydrocarbons with two fused rings, using the 'bicyclo-' prefix in naming.
Numbers in bicycloalkanes
are assigned to indicate the position of the bridges and the connected carbon atoms between the fused rings.
spirobicyclos
are bicyclic compounds where two rings share one carbon atom, forming a unique structure that is distinct from typical bicycloa. lkanes only has 1 bridge carbon so 2 paths. Replace “bicyclo” with “spiro”
lowest-locants rule
When numbering substituents, select the numbering that yields the smallest set of locants, read from left to right.
Alcohol Nomenclature
An alcohol group (-OH group) is a priority group, must be part of the principal chain
Principal chain for alcohol nomenclature
Before it was the longest carbon chain, now it is the longest chain that contains the -OH group. (in red)
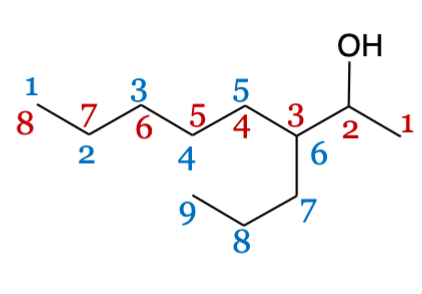
Numbering groups (alcohol)
Alcohol is given priority and is numbered first so it is on the lowest locant, regardless of other groups attached.
Suffix for SIMPLE alkane derived alcohols
-anol (keeps -an from -ane dropping e and is replaced with -ol)
locant number placement
as per the alkane rules any substitutes are numbered at the front of the name and separated by a comma to indicate the position of each substituent on the principal chain HOWEVER for alcohol the number indicating the position of the OH group is placed after the substitutes but before the name of the principal chain
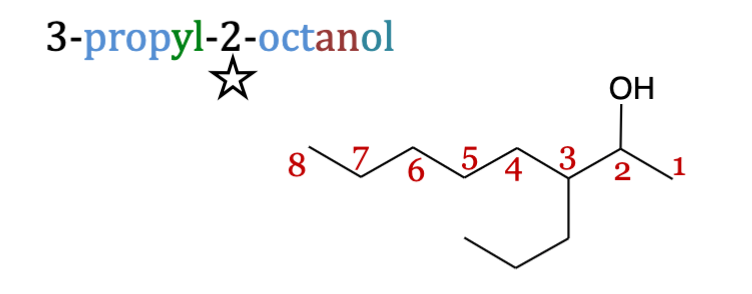
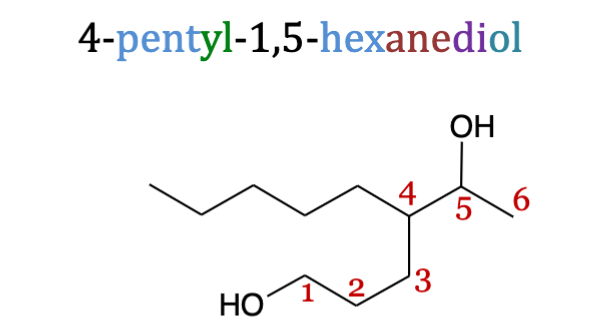
Polyols
are alcohols containing multiple hydroxyl groups
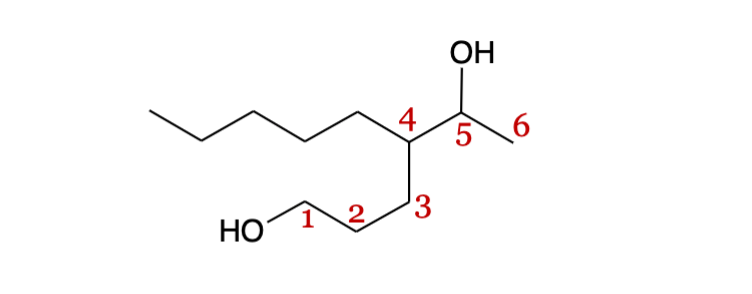
Polyols principal chain
all alcohols should be on the principal chain
Suffix for polyols
-ane_iol (di, tri, tetra correlating to the number of -OH groups)
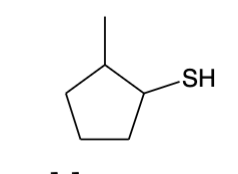
Thiols (-SH) nomenclature
Name in the same way as alcohol but the suffix -thiol is used instead of -ol

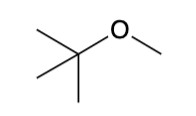
Ethers (R-O-R) nomenclature
Named by arranging the groups bound to the OXYGEN in alphabetical order and adding the word ether
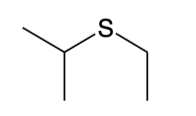
Sulfides (R-S-R)
named in the same way as ethers, except sulfide replaces the word ether
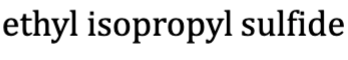
Phenyl
Ph
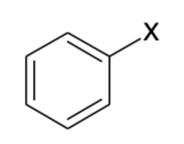
Benzyl
Bn
Vinyl
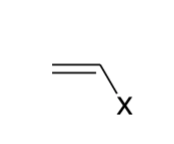
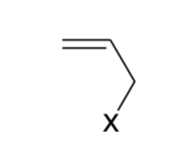
Allyl
Halides exception
Halides are sometimes named like an inorganic compound i.e. butylbromide and bromobutane
Trihalomethanes
are organic compounds that contain three halogen atoms bonded to a single carbon atom. They do not apply to halide exception and will always be named as a haloform i.e. fluoroform = HCF3