Topic 3.3 - Haloalkanes
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Are halogenoalkanes
soluble in water?
Insoluble as C-H bonds are non-polar, not
compensated for enough by C-X bond polarity
Do halogenoalkanes have a
polar bond? why?
Yes polar, as halogen has a higher
electronegativity than C ( halogen is δ-, carbon is
δ+)
Which intermolecular forces
do they have? why?
Permanent dipole-dipole and van der Waals
forces of attraction
C-X bond polarity creates permanent dipoles
When would they have
higher boiling points?
Increase Carbon chain length
Halogen further down group 7
How would the mass of a
haloalkane compare with
the mass of an alkane of the
same chain length?
Greater as mass of halogen > mass of H
What is the most important
factor in determining their
reactivity?
Carbon-halogen bond enthalpy
What is the order of
reactivity of
halogenoalkanes?
Although C-F is the most polar bond, the bond
enthalpy of C-X decreases down the group, so
reactivity increases down the group
What is a nucleophile?
A negatively charged ion/δ− atom with a lone pair
of electrons which can be donated to an electron
deficient atom
Give 3 examples of
nucleophiles
:OH -
:CN -
:NH 3
What is nucleophilic
substitution?
A reaction where a nucleophile donates a lone
pair of electrons to δ+ C atom, δ− atom leaves
molecule (replaced by nucleophiles)
Draw the mechanism for the
reaction of bromoethane
with NaOH (aq).
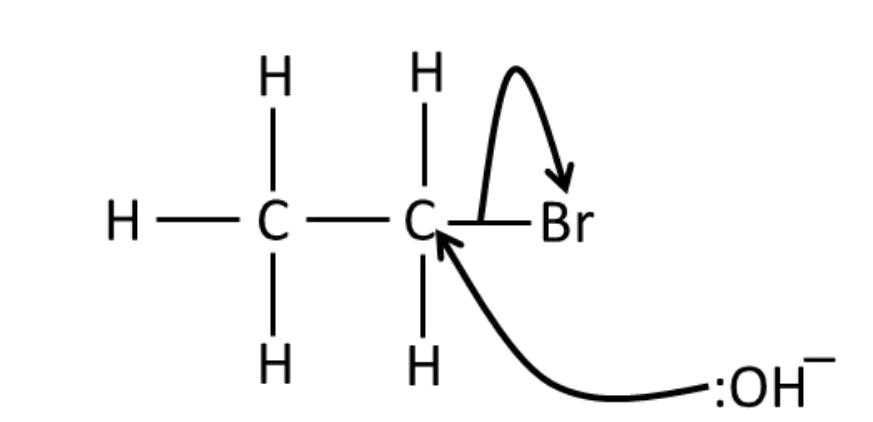
Draw the mechanism for the
reaction of bromoethane
with KCN
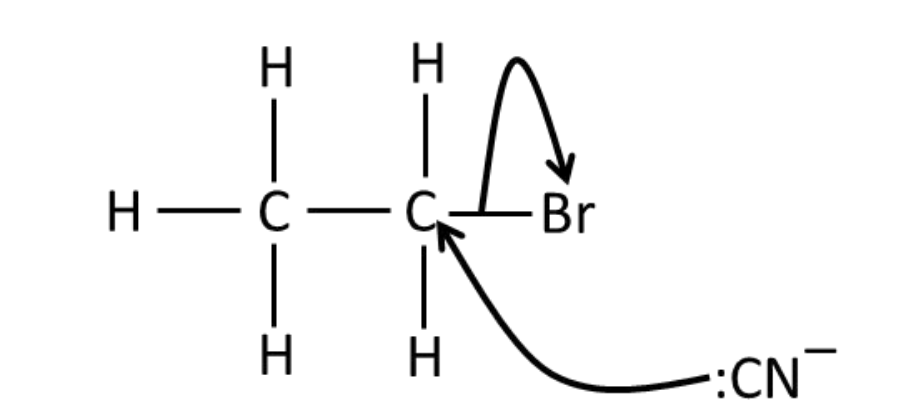
Draw the mechanism for the
reaction of bromoethane
with NH

Draw a mechanism for the
reaction of bromoethane
with NaOH in ethanol
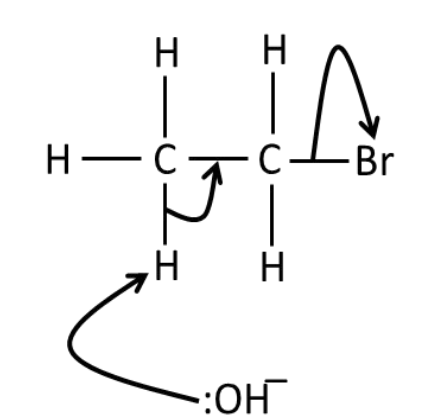
What are CFCs?
Chlorine-fluoro-carbons - haloalkanes containing
C, F and Cl only (no H)
What is the problem with
CFCs?
Although unreactive under normal conditions,
they catalyse the breakdown of ozone in the
atmosphere via free radical substitution
What are CFCs being
replaced with?
HCFCs (hydrogen, chlorine, fluorine, carbon)
HFCs (hydrogen, fluorine, carbon)
What are the conditions/
reactants needed for the
elimination reaction of
haloalkanes?
NaOH or KOH dissolved in ethanol (no water
present)
Heated
What is formed in the
elimination reaction of
haloalkanes?
An alkene, water and halogen ion