Neoplasms of the Nervous System - Clin Med
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
148 Terms
What does this refer to

Neoplasms Overview
What does this refer to

Epidemiology Neoplasms Overview
What does this refer to
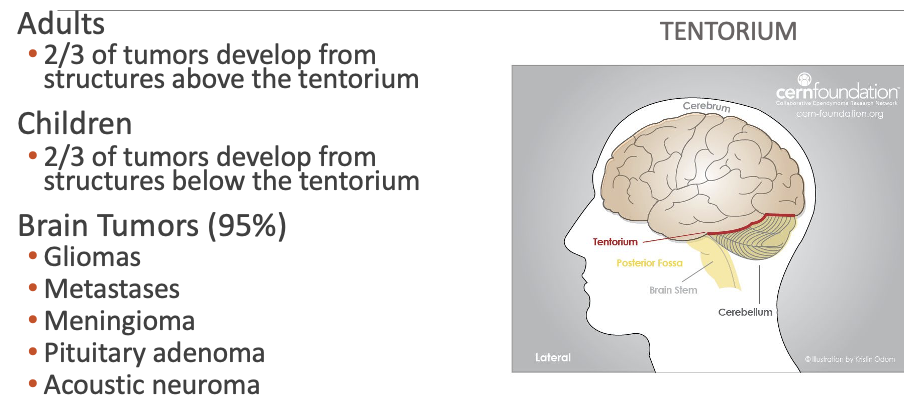
Etiology Neoplasms of the Brain
What does this refer to
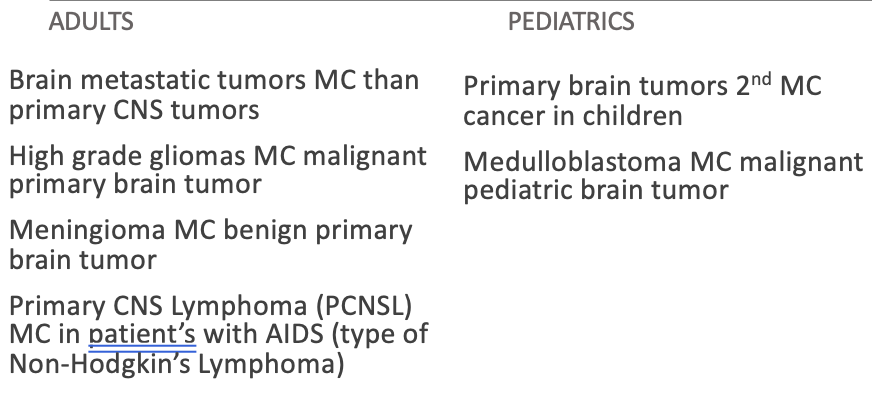
Adult-pediatric neoplasms
What does this refer to

Malignant neoplasms of the brain
What does this refer to
“Worst HA of my life”
Progressive HA
Onset > 50 yo
Worse at night/early morning
Marked exacerbation with straining
Focal neurologic dysfunction
Clinical Features Of HA Suggestive Of Structural Brain Lesion
What does this refer to
Nuchal rigidity
Fever
Papilledema
Pathologic reflexes or reflex asymmetry
Altered state of consciousness
Physical Exam Of HA Suggestive Of Structural Brain Lesion
What does this refer to
Headache is common (Tension)
Dull/constant
Throbbing
Followed by migrainous type
MC bifrontal location
Worse on same side as tumor
Sx severity worsens over time
Clinical history Neoplasms Overview
What does this refer to

Clinical presentation Neoplasms Overview
What does this refer to
Tumor-related seizures - repetitive and are stereotyped
Ictal event may be preceded by an aura
Aura brief focal seizure
Postictal sequelae
Period of fatigue and an urge to sleep
Focal seizures, a postictal paresis (also known as a Todd’s paralysis) may be present
Malignant Brain Neoplasm Seizures
What does this refer to
Muscle weakness
UMN lesion
Frequent response to glucocorticoids
Sensory loss
Cortical sensory deficit
Aphasia
Word finding/word substitution
Severe expressive-receptive aphasia
Visual spatial dysfunction
Tumor related compression optic chiasm
Bitemporal hemianopsia
Central Scotoma (early)
Unilateral hemianopsia contralateral
Cognitive dysfunction
Memory problems
Mood – personality change
↑ ICP
Physical exam findings Neoplasms
What does this refer to

Workup Neoplasms
What does this refer to
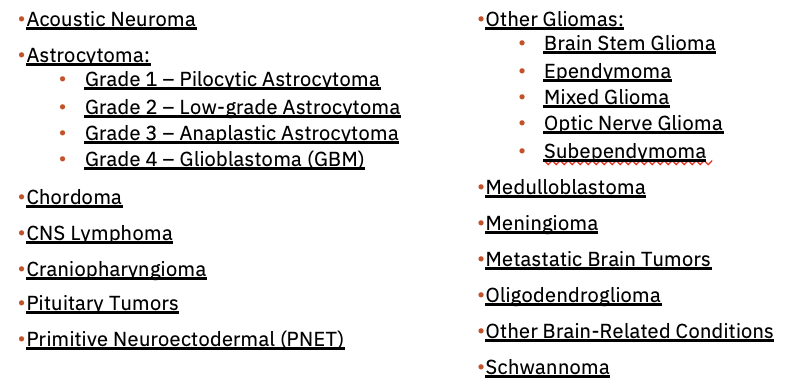
Types of Brain Neoplasms
What does this refer to
Brain Stem Glioma
Craniopharyngioma
Ependymoma
Juvenile Pilocytic Astrocytoma (JPA)
Medulloblastoma
Optic Nerve Glioma
Pineal Tumor
Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors (PNET)
Rhabdoid Tumor
Types of brain tumors more common in children than adults
What does this refer to
Neoplasm arising from the meninges
Benign Neoplasm
What does this refer to
Risk factors
Age > 50
Family hx of brain tumors
Genetic condition that increases risks
Previous radiation therapy
Especially head or neck
Epidemiology Benign Neoplasm
What does this refer to
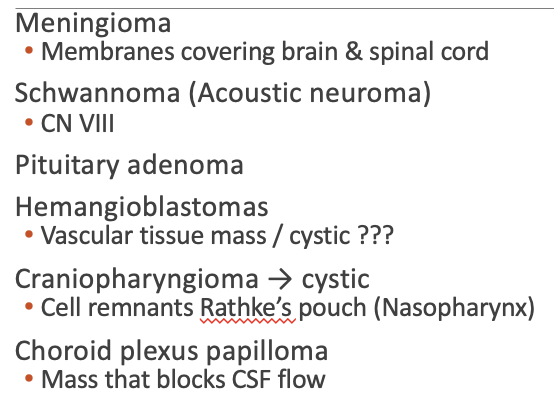
Etiology Benign Neoplasm
What does this refer to
Vision problems
Hearing problems
Balance problems
Changes in mental abilities
Change in sense of smell
Nausea/vomiting
Facial paralysis
HA
Numbness in extremities
Clinical history Benign Neoplasm
What does this refer to
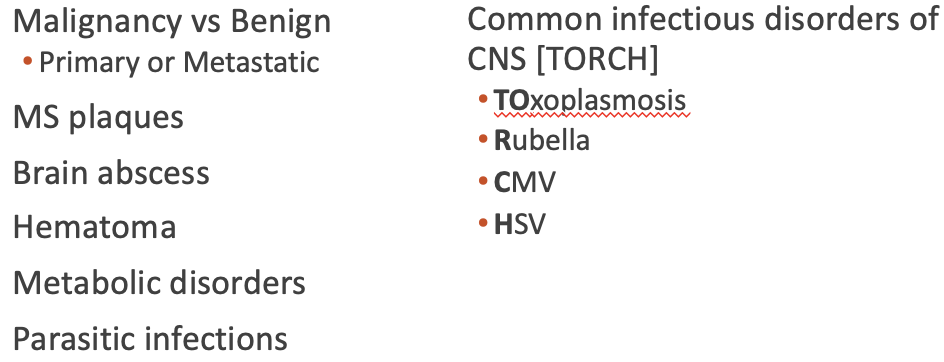
Differential diagnosis Benign Neoplasm
What does this refer to

Workup Benign Neoplasm
What does this refer to
90% are benign
Forms on membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord just inside the skull
Forms on the three layers of membranes that are called meninges
Slow-growing
Meningioma
What does this refer to
Account for 20% of primary brain tumors
MC African Americans
F > M
Incidence increases with age
Median age of dx 65yo
Epidemiology Meningioma
What does this refer to
Childhood exposure to diagnostic head CTs ↑ risk of brain tumor
Genetic predisposition Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)
Atomic bomb exposure
Estrogen therapy
Obesity
Breast CA
Etiology/Risk Factors Meningioma
What does this refer to\
Irritation → Seizures
Compression → Headache
Invading soft tissues
Inducing vascular injury
Clinical history Meningioma
What does this refer to

Most often correlate with tumor location
Seizures/muscle jerking (30% of cases)
Obstructive hydrocephalus (tumor in posterior cranial fossa)
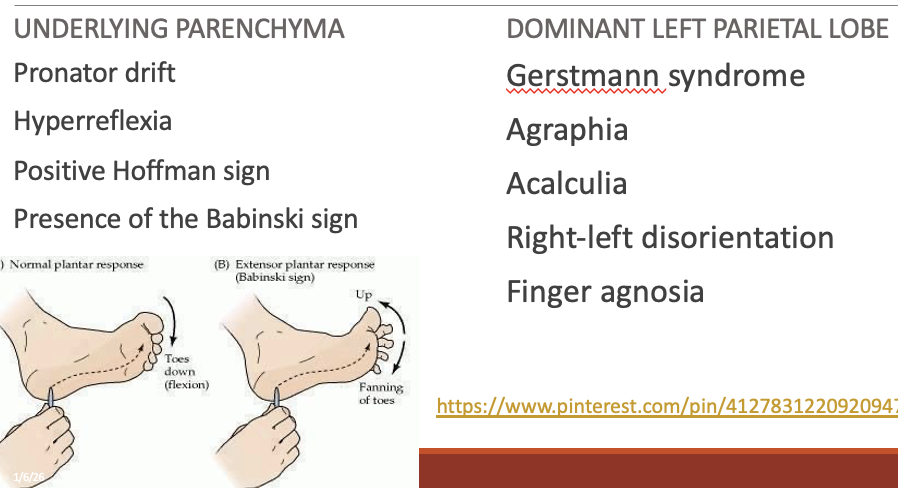
Physical exam Meningioma
What does this refer to
Benign brain neoplasms
What does this refer to
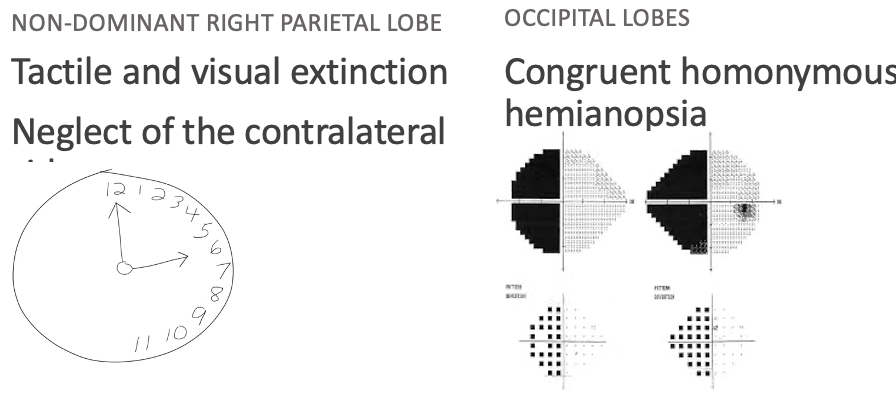
Benign brain neoplasms
What does this refer to
Brainstem glioma
Glioblastoma multiforme
Frontal lobe syndrome
Neurofibromatosis Type 1/Type 2
Differential diagnosis Meningoma
What does this refer to
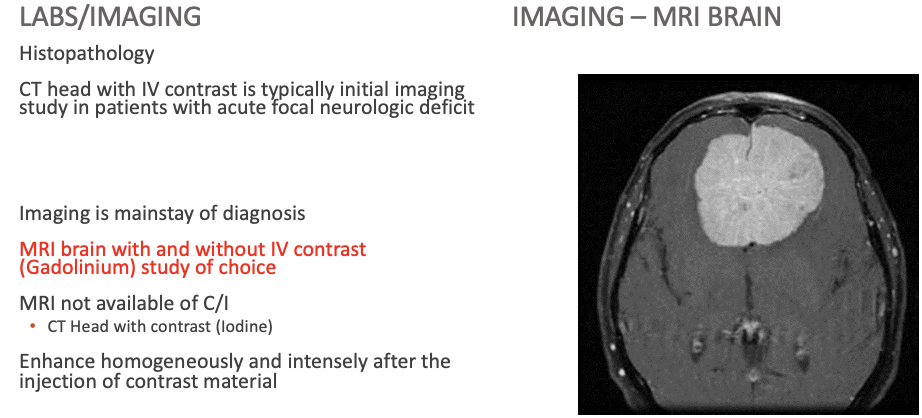
Workup Meningioma
What does this refer to
Referral to neurosurgery
Medical
Radiation therapy for nonaccessible meningiomas
May be post-op tx
Surgical resection
Clinical intervention Meningioma
What does this refer to
Pre-op/post-op Corticosteroids
Dexamethasone (Decadron)
Antiepileptic drugs
Started preoperatively in supratentorial surgery
Continued postoperatively for no less than 3 months
Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Meningioma
What does this refer to
5-year survival usually range from 73-94%
May produce severe morbidity before death due to the slow growing nature
High post-op morbidity
Advanced age
Hx Diabetes or CAD
Preoperative neurologic status
Tumor characteristics – size/location/vascularity, etc
Prognosis Meningioma
What does this refer to
Hemangioma – abnormal buildup of blood vessels in the skin or internal organs
Hemangioblastoma – arises from the blood vessel lining
Slow growing and well defined
MC posterior fossa
Hemangioma/Hemangioblastoma
What does this refer to
MC > 40 yo
Hemangioblastoma
M > F
Epidemiology Hemangioma/Hemangioblastoma
What does this refer to
Hemangioma – abnormal buildup of blood vessels in the skin or internal organs
Hemangioblastoma – arises from the stromal cells of the blood vessel lining
Retinal hemangioblastoma associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
Hemangiopericytoma – originates from cells surrounding blood vessels & meninges
Etiology Hemangioma/Hemangioblastoma
What does this refer to

Clinical history Hemangioblastoma
What does this refer to
Loss of visual acuity
Abnormal gait
Poor coordination in extremities
Clinical presentation Retinal Hemangioblastoma
What does this refer to
Ependymoma
Subependymoma
Cerebral neuroblastoma
Astrocytoma
Oligodendroglioma
Meningioma
Cranial Nerve-Choroid plexus papilloma
AVM
Differential diagnosis Hemangioma/Hemangioblastoma
What does this refer to
Labs
Biopsy
Imaging
CT scan or MRI w/ contrast
Workup Hemangioma/Hemangioblastoma
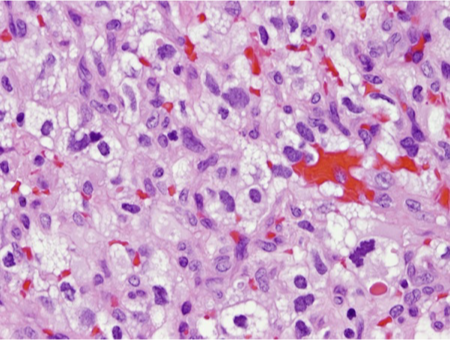
What does this refer to
Diagnostics Hemangioma/Hemangioblastoma
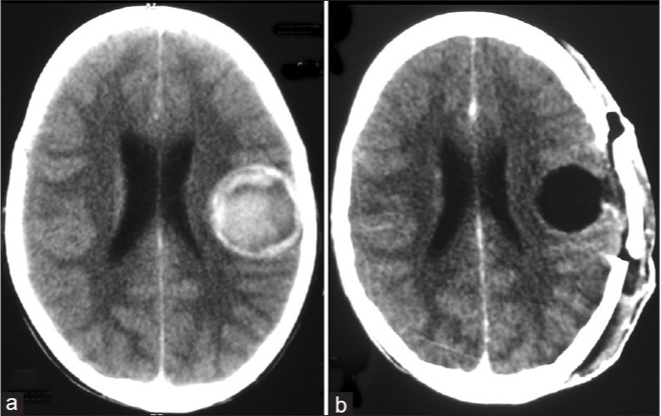
What does this refer to
WORKUP – IMAGING Hemangioma/Hemangioblastoma
What does this refer to
Referral to neurosurgery
Surgical resection
Radiation tx —> tumor attached to brainstem
Clinical intervention Hemangioma/Hemangioblastoma
What does this refer to
Very good prognosis if surgical extraction is successful
Minimal neurologic deficit
Poorer prognosis with retinal hemangioblastoma + VHL
Prognosis Hemangioma/Hemangioblastoma
What does this refer to
Specific type of astrocytoma
Grade 1 Astrocytoma
Originates in glial cells
Type of glioma
Derived from astrocytes
Slow growing
Pilocytic Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
M > F (minimal prevalence)
MC Caucasians than AA
Glioma tumors account for 33% of all brain tumors
MC glial tumor in children
Epidemiology Pilocytic Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
Astrocytes
Can appear in any part of the brain
MC in cerebellum
Etiology Pilocytic Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
Juvenile astrocytoma
Typically localized
Considered the most benign of all astrocytomas
Includes cerebellar astrocytoma and desmoplastic infantile
Etiology Pilocytic Astrocytoma (Grade I)
What does this refer to
Low grade
Types
Fibrillary
Gemistocytic
Protoplasmic
Tend to invade surrounding tissue
Grows at relatively slow rate
Etiology Diffuse astrocytoma (Grade II)
What does this refer to
Rare, but very aggressive
Etiology Anaplastic Astrocytoma (Grade III)
What does this refer to
MC primary CNS tumor in adults
Etiology Glioblastoma multiforme (Grade IV)
What does this refer to
Ventricular tumors associated with tuberculous sclerosis
Etiology Subependymal Giant Cell Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
Headache
Nausea
Vomiting
Lethargy
Clinical history Pilocytic Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
Physical exam Pilocytic Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
Other malignant brain neoplasms
Brain abscess
Brain metastasis
Cardioembolic stroke
Multiple sclerosis
Differential diagnosis Pilocytic Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
Workup Pilocytic Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
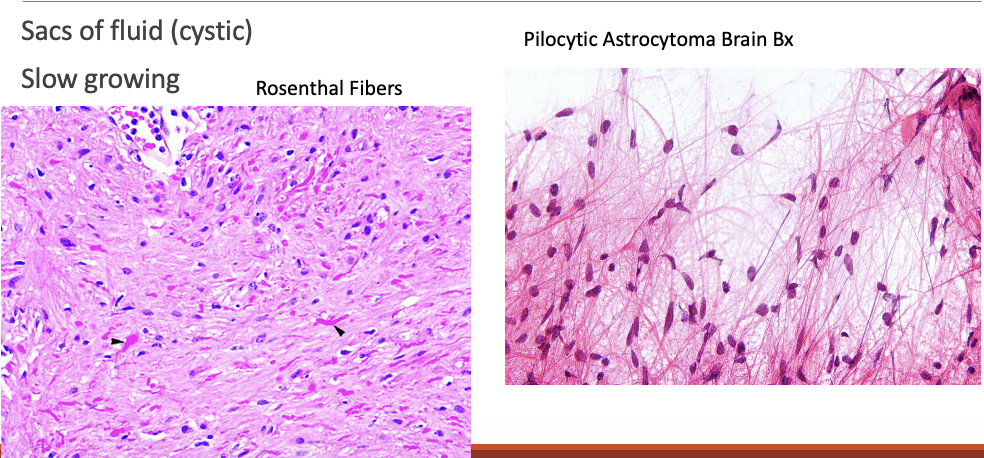
DIAGNOSTICS Brain Biopsy – Pilocytic Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
Contain microcysts and mucus-like fluid
Grouped by appearance and behavior of the cells for which they are named
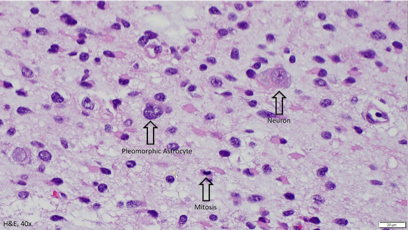
DIAGNOSTICS Brain Biopsy – Diffuse Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
Tentacle-like projections grow into surrounding tissues
Growth into surrounding tissues makes them difficult to remove during operative procedure
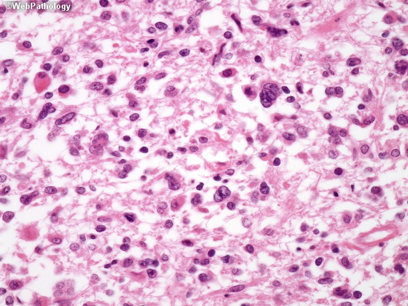
DIAGNOSTICS Brain Biopsy – Anaplastic Astrocytoma
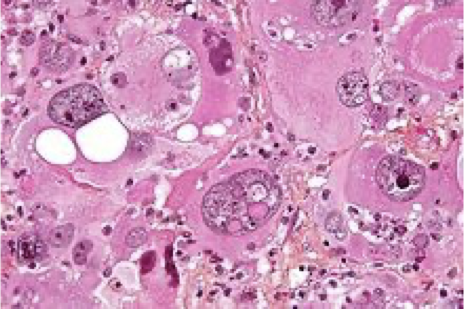
What does this refer to
May contain cystic material, calcium deposits, blood vessels and/or mixed grade of cells
DIAGNOSTICS Brain Biopsy – Astrocytoma Grade IV (Glioblastoma)
What does this refer to
Pilocytic astrocytoma
Surgical excision
+ radiation in older children and adults
Diffuse astrocytoma
Surgical excision
+/- radiation tx
Anaplastic astrocytoma
Surgical excision —> rad tx
+/- chemo
Astrocytoma grade IB
Surgical excision —> rad tx
PLUS chemo
Clinical intervention for Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
Degree of atypia (tumor grade) on histopathology is the best prognostic indicator
Childhood survival Grade I and II
5 yr survival 90%
Low grade – average survival after surgery is 6-8 yrs
> 40% live more than 10 yrs
Grade IV Glioblastoma
Average survival 12-18 months
Only 25% survive > 1 yr
Prognosis Astrocytoma
What does this refer to
A 63-year-old man is brought to the physician's office by his son due to progressively worsening headache and weakness.
His headache began approximately 3 months prior to presentation and is described as diffuse but worse on the right-side of the head.
The headache worsens with coughing and lifting heavy objects and is associated with nausea, multiple episodes of vomiting, and left-sided weakness.
He previously worked for the synthetic rubber industry for over 30 years.
Physical Exam: 3/5 strength in the left upper and lower extremities
Glioblastoma
What does this refer to
Highly malignant (grade IV) Astrocytoma
Most lethal & most common primary brain tumor
Highly vascular/extensively irregular and infiltrative tumor
MC in frontal lobes & cerebral hemispheres
Primary and secondary origin
Glioblastoma
What does this refer to

Epidemiology of Giloblastoma
What does this refer to
Arise from poorly differentiated neoplastic astrocytes
Familial gliomas
Etiology Giloblastoma
What does this refer to
Primary glioblastoma multiforme (MC)
60% in adults older than 50 years
Secondary glioblastoma multiforme
40% in adults < 45 yo
Variants
Classic – extra copies of epidermal growth factor receptor gene (EGFR)
Mesenchymal – TP53 mutation and mutation/alteration of gene encoding for neurofibromatosis
Etiology – Glioblastoma Primary and Secondary Tumor
What does this refer to

Clinical History Glioblastoma
What does this refer to
Headache (50-60%)
New onset seizures (20-50%)
Focal neurologic symptoms (10-40%)
Presentation High Grade Glioblastoma (GBM)
What does this refer to
Focal neurologic deficit (dependent on tumor location) is MC
Papilledema on fundoscopic exam
Hemiparesis
Dysphasia
Dyspraxia
CN Palsies
Visual field deficits
AMS
Physical Exam Glioblastoma
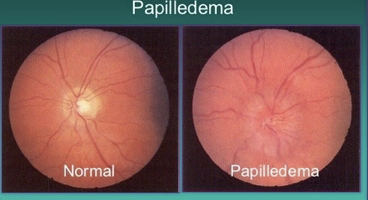
What does this refer to
Occurs when the Optic nerve is swollen due to pressure in or around the brain
Symptoms
Visual disturbances
Headaches & nausea
Fundoscopic Exam- Papilledema Glioblastoma
What does this refer to
Anaplastic Astrocytoma
Cerebral Abscess
Demyelination disease
Encephalitis
ICH
Metastasis
Differential Diagnosis Giloblastoma
What does this refer to
Workup Glioblastoma
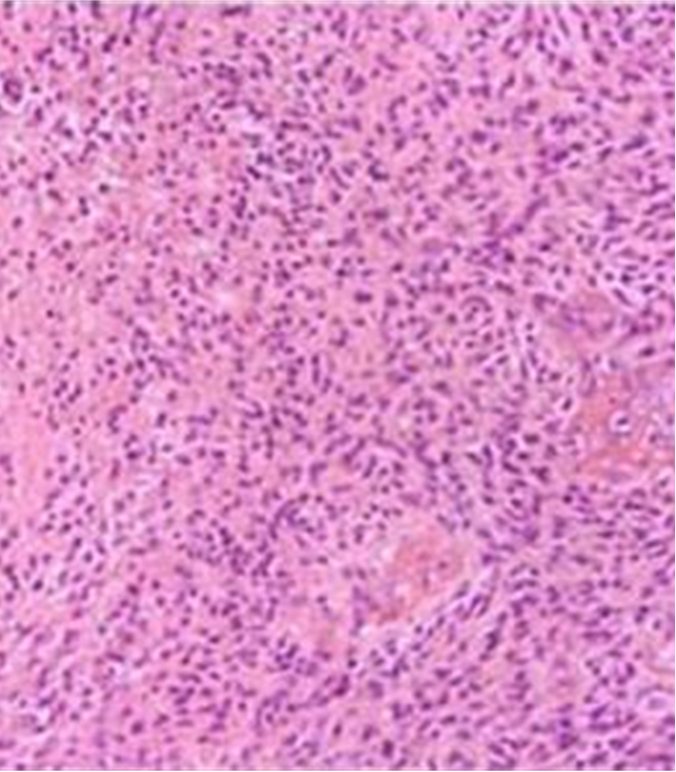
What does this refer to
Confirms dx
Malignant astrocytes +necrotizing hemorrhagic center surrounded by pseudopalisading (tumor cells lining necrotic cells)
Diagnostics - Histopathology Glioblastoma
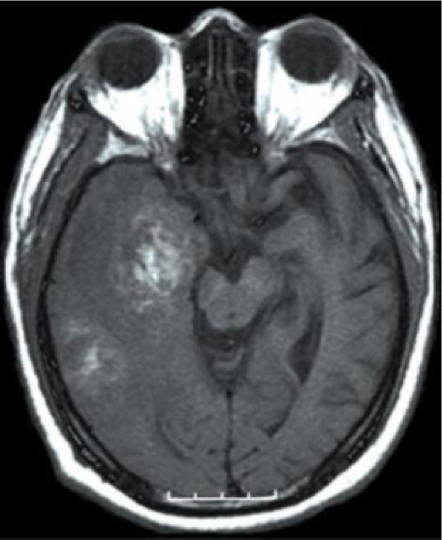
What does this refer to
DIAGNOSTICS – MRI Glioblastoma
What does this refer to
Butterfly gliomas
High grade astrocytoma
Usually a glioblastoma
Crosses the midline via the corpus callosum.
May involve other white matter commissures
The term butterfly refers to the symmetric wing-like extensions across the midline.
WORKUP – MRI Butterfly Glioma
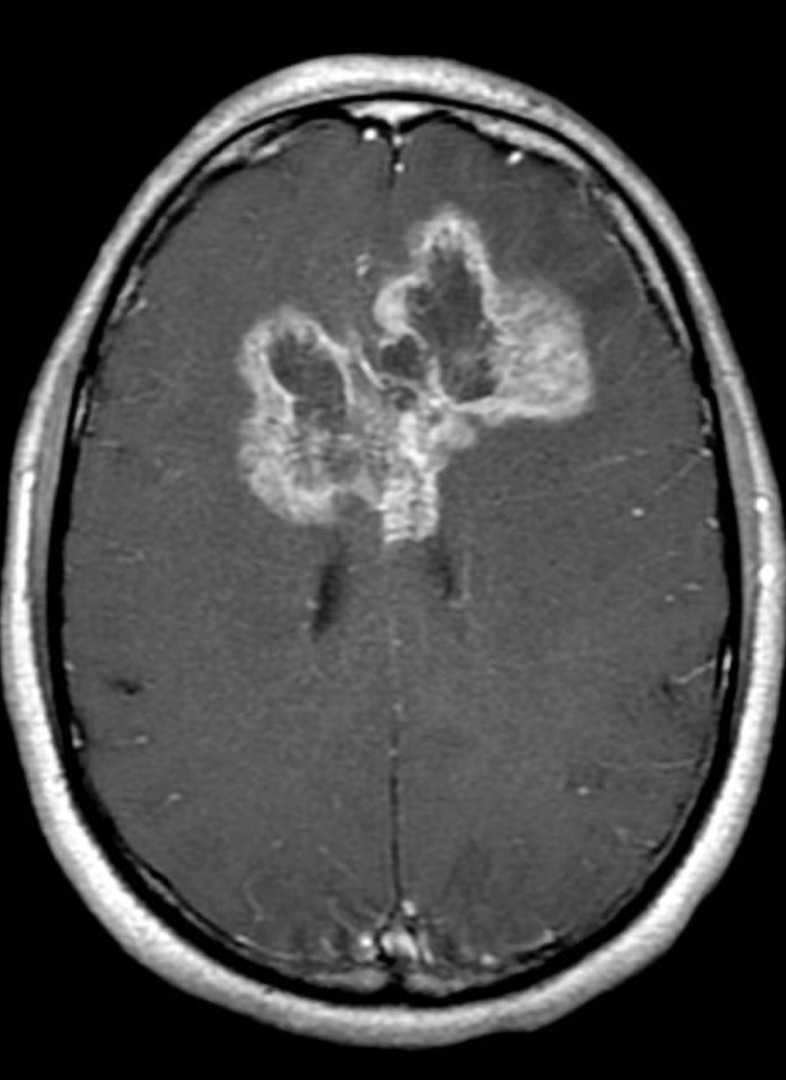
What does this refer to **PICTURE WILL BE ON EXAM
Butterfly Glioma
What does this refer to
Maximal surgical resection
Adjuvant radiation – not curative (after surgery)
Concurrent and adjuvant chemotherapy
Antineoplastic – Temozolomide (Temodar) [PO or IV]
Clinical Intervention Glioblastoma
What does this refer to
Most of the medications used to treat Sx 2° to GBM
Seizures
Levetiracetam (Keppra) 1st line tx
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
Vasogenic Cerebral Edema
Dexamethasone (Decadron) + Famotidine
Antineoplastics with radiation tx – POST-OP
Temozolomide (Temodar) 1st line tx
Carmustine (BiCNU)
Clinical Pharmacotherapeutics Glioblastoma
What does this refer to
There is no cure
Significant overall survival improvement in patients treated with temozolomide and radiation compared with radiotherapy alone
Without tx – die within 3 months
Optimal combination tx – 12 month survival
2 year survival – less than 25%
5 year survival – less than 10%
Survivors may have cognitive deficits/focal neuro deficits/personality changes
Prognosis Glioblastoma
What does this refer to
Type of embryonal tumor
Starts in fetal brain cells
Occurs in cerebellum
Specific etiology is unknown
Wingless/Integrated (WNT) signaling pathway
Sonic Hedge Hog (SHH) protein
Meduloblastoma
What does this refer to
MC malignant pediatric brain tumor
Accounts for 64% of embryonal tumors in patients 0-19 yo
M > F and most common in boys 1 – 10 yo
Peak age of dx is 5-9yo
MC Caucasian and Asian/Pacific Islander race
Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to
4 molecular subgroups
WNT
Sonic hedgehog (SHH) protein
Group 3
Group 4
Etiology Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to
Sx of ↑ ICP & cerebellar dysfunction
Nocturnal or morning headaches
Nausea/vomiting
Altered mental status
Tumors in midline
Gait ataxia
Truncal instability
Tumors in lateral cerebellar hemispheres
Limb clumsiness/incoordination
Clinical History Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to
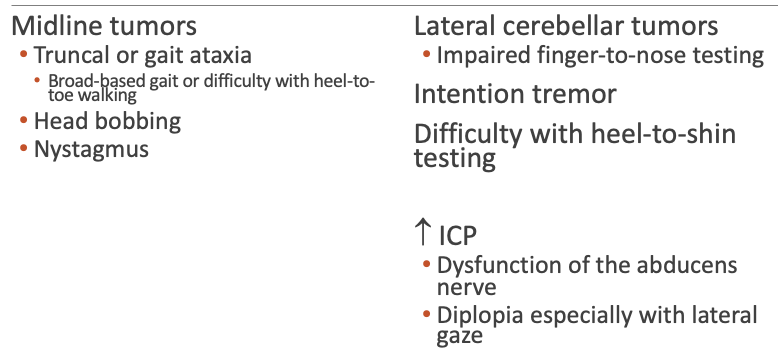
Physical Exam Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to
Pilocytic astrocytoma
Ependymoma
Atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumors (ATRT)
Differential diagnosis Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to
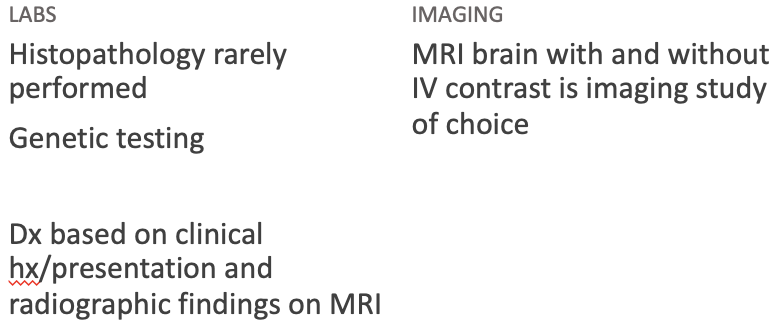
Workup Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to
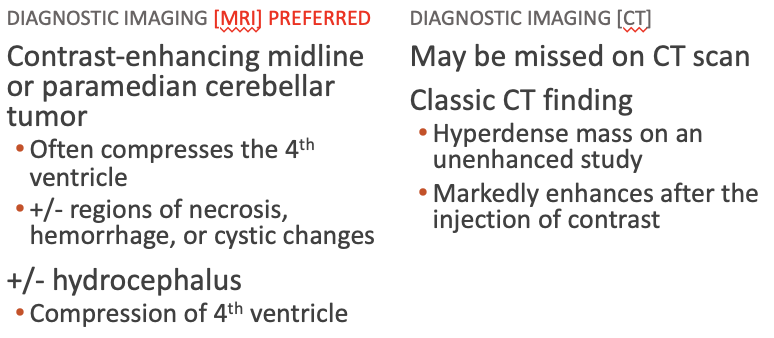
Diagnostic Imaging Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to
Consult/referral pediatric neurosurgery, pediatric oncology/neuro-oncology
Surgical resection, radiation and chemotherapy
Placement of CSF shunt for ICP ↑
Minimal neurologic signs and no hydrocephalus – preop workup can be done outpatient
Impending hydrocephalus
Decreased mental status 1st sign
Initiated within 28 days of dx
Macroscopic complete tumor resection THEN
Craniospinal irradiation
Post-op MRI
Clinical Intervention for Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to

Clinical pharmacotherapeutics Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to
Hydrocephalus
Cerebellar dysfunction
Brainstem invasion of the tumor was the only risk factor identified as having a positive correlation with the development of cerebellar mutism
Morbidity Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to
Prognosis correlates with age of dx, post procedure residual deficit, bio-molecular marker
Survival rates in children depend on the patient's age and how much the tumor spreads
5 yr survival rate child < 3yo is 40-50%
Has not spread to spinal cord
Survival rate into adulthood are ~75%
Spread to the spinal cord
Survival rate ~60%
Within 1.5 yrs after tx
GH deficiency noted (94%)
TSH deficiency noted (10%)
Prognosis Medulloblastoma
What does this refer to
Rare malignant tumor of the retina that affects young children
A 2-year-old boy presents to his pediatrician for strabismus. Family history is notable for osteosarcoma in his father. Physical examination is notable for strabismus and bilateral leukocoria. He is referred to a pediatric ophthalmologist for further evaluation.
Retinoblastoma
What does this refer to
MC primary ocular cancer of childhood
Accounts for 13% of cancer in the first year of life
Median age dx 18-20 months
Unilateral and bilateral 40%
Heritable and non-heritable
Epidemiology Retinoblastoma
What does this refer to
Arises from the retina
Heritable
Germline mutations in the RB1 gene
Usually leads to bilateral disease
Non-heritable
Somatic mutations in the RB1 gene
Typically leads to unilateral disease
Mutation in the long arm of chromosome 13
Normal gene suppresses Retinoblastoma
Etiology Retinoblastoma
What does this refer to

Clinical History/Physical Exam Retinoblastoma
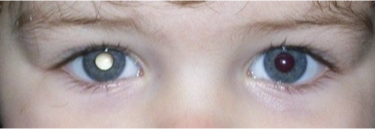
What does this refer to
Leukocoria
Strabismus
Red, painful eye with glaucoma
Nystagmus
Orbital cellulitis
Physical Exam Retinoblastoma
What does this refer to

Screening Retinoblastoma
What does this refer to
Congenital cataract
Exudative Retinal Detachment
Retinopathy of Prematurity
Anterior Uveitis of Childhood
Differential Diagnosis Retinoblastoma
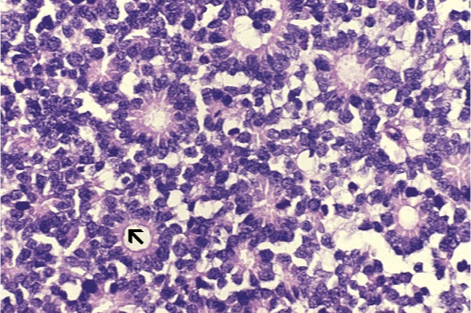
What does this refer to
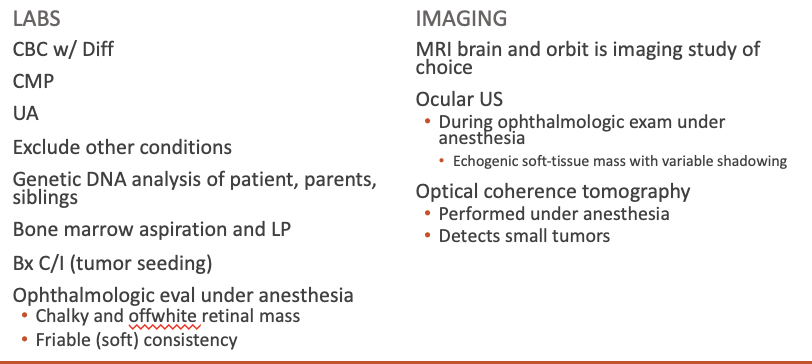
Histology
Classic histologic finding (ocular tissue)
Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes
Spoke and wheel shaped cell formation
Workup Retinoblastoma
What does this refer to
Immediate consult with Pediatric Oncologic Ophthalmologist
Exam with dilation
Control of tumor size/vision preservation
Radioactive Isotope plaques
Chemotherapy
Clinical Intervention Retinoblastoma