670 Upper and lower ext. trauma
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
B in BOLTS
breaks in cortical surface
O in BOLTS
opacities
L in BOLTS
lucencies
T in BOLTS
trabeculae disruption
S in BOLTS
soft tissue abnormality
displacement is described in terms of
distal fragment at fracture site
angle is described in terms of
distal fragment at most distal end
soft tissue signs
soft tissue emphysema, fat pads, fat-fluid levels
When to look for fat fluid levels
cross table lateral knees
soft tissue emphysema
air in soft tissue
sail sign
anterior fat pad of the elbow visible
why are fat pads visible in fx elbows
blood pushes the fat pads out
hemoarthrosis
blood in the joint from fracture or dislocation
subluxation
partial loss of normal joint alignment, bones remain partially intact
bones can _____ and joints cannot
displace
joints can ____ and bones cannot
dislocate
diastasis
abnormal widening of a fibrous joint
name the pediatric fractures
greenstick, buckle, bowing, torus, salter harris
what type of fracture affects the physis only
Salter Harris 1
what type of fracture affects the ohysis and metaphysis
salter harris 2
what type of fracture affects the physis and epiphysis
salter harris 3
What type of fracture affects the physis, metaphysis, and epiphysis
salter harris 4
What type of fracture crushes the physis
salter harris 5
Step one of fracture healing
hematoma → granulation of tissue
step two of fracture healing
soft callus
What happens in the granulation of tissue phase of a fracture?
fibroblast and new vessels form
step three of the fracture healing process is
hard callus
whats step 4 of a healing fracture
remodeling and replacing
the remodeling phase takes
months to years
factors that delay healing
poor blood supply, infection, motion/overuse, age, smoking
non-union
fracture doesn’t heal
mal-union
The fracture heals, but not within clinical alignment standards
Fx of the distal 2.5 inches of the radius with dorsal displacement or angulation (often accompanied by ulnar styloid fx)
Colles
Fx of the distal 2.5 inches of the radius with anterior displacement or angulation
smith AKA reverse colles
Fracture of the distal radius with radioulnar joint disruption
Galezzi
important note for Galezzi fx
do the radius and ulna remain aligned?
Fx of the proximal ulna with radiocapitellar dislocation
Monteggia
oblique intra-articular fx at the base of the thumb metacarpal and extends to trapezium joint
Bennet
Oblique intraarticular comminuted fx at the base of the thumb metacarpal and extends to trapezium joint
Rolando
fx of the distal end of the 5th metacarpal (typically transverse and angulated anteriorly)
Boxers
injury to the ulnar side of the thumb MCP involving ulnar collateral ligament
Game keepers
injury of the anteroinferior portion of the glenoid labrum
Bankart
usual cause of bankart injurues
anteroinferior glenohumeral dislocation
fx of the superiolateral portion of the humeral head
Hills-sachs
common cause of hills-sachs injuris
humeral head impacted on anteroinferior portion of glenoid
complication of bankart
predisposes to frequent injury
injury at tarsometatarsal junction of midfoot (can be fx of metatarsal bases, adjacent cunieforms, and cuboids, can be multiple joint disruption of MTs)
Lisfranc
Transverse fx of the 5th MT base
Jones
Transverse intra-articular fx of the 5th MT base
dancer
ankle injury with proximal fibula fracture
Maisonneuve
common causes of Colles, Smith, scaphoid, and carpal fractures
FOOSH
Ring Trauma
rings of bone will always have a second injury site
common places for ring of bone injuries
pelvis, tib fib, radius ulna
often creates comminuted, displaced, severly angled, open fractures
direct blow injuries
common causes of spiral and oblique fractures
twisting or rotational forces
insufficient injuries
fracture of weakened bone
stress fractures
injuries of normal bone due to abnormal repetitive stress
FOOSH on the extended wrist (palm of hand hts the ground)
Colles
FOOSH on flexed wrist (back of hand hits ground)
Smith
common causes of direct blow injuries
MVA, fall from height, sports collision
lower extremity axial loading injuries
calcaneus and tibial plateau
Dashboard injury aka
posterior force on flexed knee (MVC)
common dashboard injuries
posterior hip dislocation, acetabulum and femoral head fx
associated complication of pelvis injuries
bladder/urethra injurymajor vascular injury, pelvic hematoma
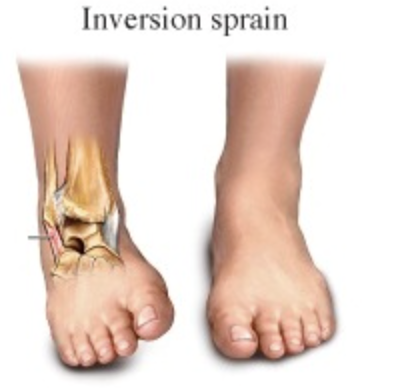
Ankle Inversion
foot turns medially putting pressure on lateral ankle
Ankle inversion common injuries
lateral malleolus and other lateral structure fx
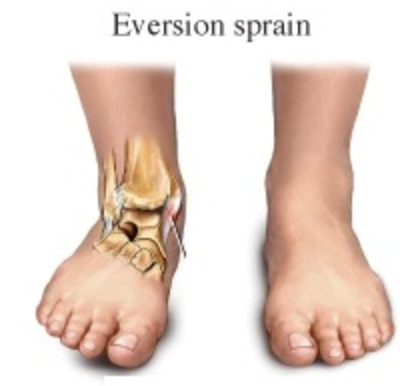
Ankle Eversion
foot turned laterally putting pressure on medial ankle
Ankle Eversion injuries
medial malleolus fx, fibular fracture