TEST FOR PULMONARY MECHANICS
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Spiromtery, Recording system
Equipments needed for pulmonary test
Forced Vital Capacity Maneuver
Most frequently used method for assessing dynamic pulmonary function.
Volume-time curve
A curve which has volume on vertical axis, and time on horizontal axis
FVC
The volume change of the lung between a full inspiration to total lung capacity and a maximal expiration to residual volume. (FORCED)
4 to 6 seconds
What is the total expiratory time needed to completely exhale the FVC in a normal lung function
IVC (Inspiratory Vital Capacity)
The volume change of the lung between a maximal expiration to residual volume and a full inspiration to total lung capacity.
EVC (Expiratory Vital Capacity)
The volume change of the lung between a full inspiration to total lung capacity and a maximal expiration to residual volume but not forced
FEVt
An indication of the average flow rate over a time interval
60%
In normal lung function, the percentage of total FVC exhaled in FEV0.5
83%
In normal lung function, the percentage of total FVC exhaled in FEV1
94%
In normal lung function, the percentage of total FVC exhaled in FEV2
97%
In normal lung function, the percentage of total FVC exhaled in FEV3
FEV1
The volume exhaled during the first second of a forced expiratory maneuver started from the level of total lung capacity.
FEFx%
Maximum expiratory flow when x% of the FVC has been exhaled
FEF200-1200
Measures flow early in the expiratory maneuver, First 200-1200mL
8 L/sec (480 L/min)
In normal lung function, the average FEF200-1200 for men ages 20-30
5.5 L/sec (330 L/min)
In normal lung function, the average FEF200-1200 for women ages 20-30
as low as 1 L/sec
In abnormal lung function, the FEF200-1200 is
FEF25%-75%
Measures expiratory flow rates at a later point in the maneuver than FEF 200-1200
4.5 L/sec (270 L/min)
In normal lung function, FEF25%-75% for men ages 20 to 30 is
3.5 L/sec (210 L/min)
In normal lung function, FEF25%-75% for women ages 20 to 30 is
as low as 0.3 L/sec
In abnormal lung function, FEF25%-75% IS
FEF 75%-85%
Measures expiratory flow rates towards the end of the maneuver
Flow-Volume Loop
Flow on vertical axis; volume on horizontal axis, Allow for inspiratory and expiratory peak flow rates to be read directly from graph
Peak Expiratory Flow
flow generated during expiration performed with maximal force and started after a full inspiration
10 L/sec (600/Lmin)
In normal lung function, the average PEFR for men ages 20 to 30 is
7.5 L/sec (450 L/min)
In normal lung function, the average PEFR for women ages 20 to 30 is
FIVC
The volume change of the lung between a maximal expiration to residual volume and a full inspiration to total lung capacity. FORCEFULLY
FIV1
The volume that can be forcefully inhaled in the first second during a forced inspiratory maneuver started from residual volume.
Small Airway Obstruction
The latter portion of the expiratory loop begins to take on a concave appearance
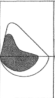
Fixed Large Airway Obstruction
causes relatively equal decreases in both expiratory and inspiratory flow rates

Intrathoracic Variable Large Airway Obstruction
causes a flattening of the expiratory portion of a flow/volume loop caused by the limitations of expiratory flow.
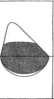
Extrathoracic Variable Large Airway Obstruction
cause a flow limitation on inspiration, with a characteristic flattening of the flow/volume loop's inspiratory portion

Low-Density Gas spirometry
Measuring FVC maneuver after the subject has breathed a helium/ oxygen
80%He / 20%O2
Percentage of Helium and O2 mixture if heliox
Volume of Isoflow
Maximum or earliest flow rate that is controlled by density- independent flow through small, peripheral airway
Peak Expiratory Flow Monitoring
This test requires a peak expiratory flow meter: a small handheld device with a mouthpiece at one end and a scale with a moveable indicator
Green Zone
80 to 100 percent of the usual or normal peak flow readings are clear.
Asthma is under good control.
Yellow Zone
50 to 79 percent of the usual or normal peak flow readings
Indicates caution.
Red Zone
➔ Less than 50 percent of the usual or normal peak flow readings
➔ Indicates a medical emergency.
80-100%
Green zone Percentage for peak expiratory flow monitoring
50-79%
Yellow zone percentage for peak expiratory flow monitoring
less than 50%
Red zone percentage for peak expiratory flow monitoring
Maximum Voluntary Ventilation
➔ Largest volume that a subject can breathe in and out of the lungs in one minute with maximum voluntary effort.
10-15 seconds
What is the amount of time for measurement during MVV
170 L/min
The average MVV for normal lung function for men ages 20 to 30
110 L/min
The average MVV for normal lung function for women ages 20 to 30
Airway Resistance
The drive pressure required to create a flow of air through a subject's airway.
Elastic Recoil Pressure/Compliance
An indication of the elastic force that is generated by the thoracic / lung system when the lungs are expanded.
Compliance
The amount of transpulmonary pressure change required to produce a certain change in lung volume.
Dynamic Compliance
Distensibility of the lungs and thorax during breathing
Maximum Inspiratory and Expiratory pressure
measures subject's ventilatory muscle strength.
MIP
is a measure of the most negative (subatmospheric) pressure that can be generated with an inspiratory effort.
MEP
is the greatest positive pressure that a subject can generate.
three-way directional breathing valve or a shutter mechanism
Equipment needed for maximum inspiratory and expiratory pressure
-20 cmH20 or smaller
MIP value that needs mechanical ventilatory support
less than +40cmH20
MIP value = difficulty in coughing and clearing secretions. = generalized neuromuscular disorders