16-coronary artery dominance + hypokalemia
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pg 66-68
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
the artery that supplies the _________________ determine the coronary dominance
posterior descending artery
in 85% of the population, the ____________ gives off the PDA (_________ dominant)
right coronary artery… right
in 15% of the population, the ____________ gives off the PDA (_________ dominant)
left circumflex artery… left
__________&_________ + _________ on ecg → hypOkalemia
muscle weakness…cramps… U wave
important reason for hypokalemia
thiazide like diuretics (bendroflumethiazide)
loop diuretics (furosemide)
__________,___________,__________ → hyperkalemia
__________,___________→ hypokalemia
spionolactone, ARB(losartan), ACEi
loop diuretics, thiazide like diuretics
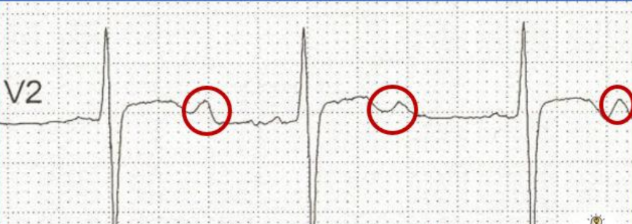
U wave (hypokalemia) - an additional wave after T wave
management of hypokalemia
oral/IV K chloride (<2.5 then IV)
stop the cause (furosemide or thiazide like diuretics)
causes of hypokalemia
thiazide like diuretic
loop diuretic
vomit/diarrhoea
villous adenoma
renal tubular failure
cushing syndrome
conns disease (1ry hyperaldosteronism)
causes of hyperkalemia
ARB
ACEi
K sparing diuretics (spironolactone, eplerenone)
addison’s (primary adrenal insufficiency)
CKD/acute renal failure
congenital adrenal hyperplasia
____________ wave → hyperkalemia
____________ wave → hypokalemia
tall tented T
U wave
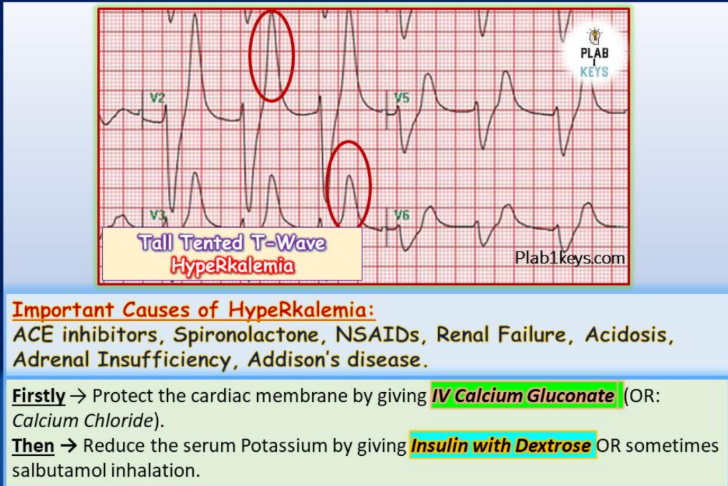
treatment of hyperkalemia
-IV calcium gluconate/ CaCl (protect cardiac membrane)
-insulin with dextrose/salbutamol inhalation (reduce K serum)