Wk Two - Perfusion & Blood Pressure & Homeostasis & VSS
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Adequate Perfusion
WPD, 60-100bpm, >100mmHg systolic, Alert & Orientatetd
Borderline Perfusion
CPC, 50-100bpm, 80-100mmHg systolic, Alert & Orientatetd
Inadequate Perfusion
CPC, <50, >100bpm, 60-80mmHg systolic, Alert & Orientatetd OR ALTERED
Extremely Poor Perfusion
CPC, <50, >110bpm, <60mmHg systolic,Altered or Unconscious
No Perfusion
CPC, No pulse, ,No BP, Unconscious
Perfusion definition
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system to an organ or a tissue.
Function of perfusion
Provide tissues with an adequate oxygenated blood supply to meet their functional demands at that time and to effectively remove the associated metabolic waste products.
All the components for maintaining perfusion
Heart: Pumping Force
Arteries: Distribution (high pressure)
Arterioles: Flow and Pressure Regulation (control conduits)
Capillaries: Exchange fluid, nutrients, electrolytes, hormones, and other substances between the blood and the interstitial fluid
Venules: Collection
Veins: conduit of transport back to the heart and blood reservoir
Pressure equation
Pressure = Force/Area
Blood Pressure Def.
the pressure the circulating blood is exerting on the blood vessel walls
What artery is typically used to measure BP?
Brachial A
Mean Arterial Presure Equations
MAP = Diasoltic BP + (1/3 x Pulse Pressure)
OR
MAP = HR x SV x R
Pulse pressure equation
Systolic BP - Diastolic BP
Flow Equation
Change in Pressure/Resistance
Fancy flow equation
Q (Flow) = MAP/Resistance
What is ‘flow’ also known as?
Cardiac Output
Cardiac Output EquationS
CO = HR x SV
OR
CO = MAP/R
What is resistance & what is it effected by?
total peripheral resistance (TPR) - how much opposition to flow there is. It is affected by length, viscosity and radius.
How does length affect resistance?
Double the length - double the resistance. Linear, cannot be changed.
Viscosity def.
measure of a fluids resistance to flow.
How can we change vessel radius to increase blood flow?
Vasodialtors
What relationship does radius have to blood flow?
Parabolic
Stroke Volume Definition
The amount of blood pumped by the left ventricle of the heart in one contraction, measured in mls/beat
Stroke Volume Equation
SV = EDV - ESV
End diastolic volume def.
how much blood is in the ventricle at end of diastole (ie when fullest) = Preload
End systolic volume def. & what it relies on
how much blood in the ventricle at end of systole (ie when emptiest). relies on contractility and afterload
Afterload def.
the pressure the heart needs to work against in order to eject blood during systole
What is Homeostasis
describes any self-regulating process by which biological systems tend to maintain stability. Homeo = similar to, Stasis = standing still.
Hypotension/Hypoperfusion
Low blood pressure, the force of the blood pushing against the arterial ealls is too low. Slower blood flow, can decrease the delivery of O2 and nutrients to vital organs.
Normotension
the state of having normal blood pressure, characterized by values within the healthy range
Hypertension
when the pressure in your blood vessels is too high
BP equation (again?)
BP = HR x (EDV - ESV) x TPR
Neurohormonal factors
Substances that mediate the transmission of nerve impulses or influence physiological processes. (baroreceptors & chemoreceptors)
What affects SVR, HR, Intropy, Venous Compliance & Renal Na and H2O
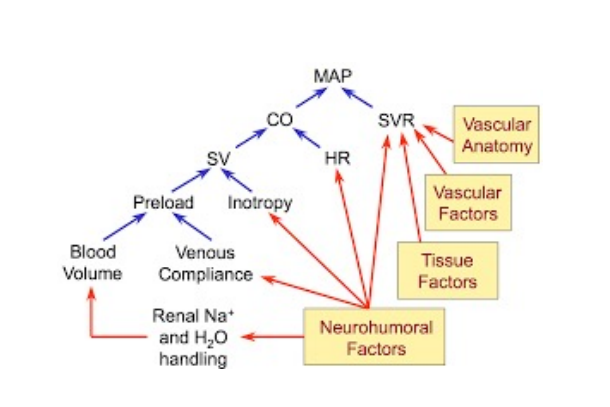
Feedback Loop
A feedback loop is a biological occurence where in the outpit of a system amplifies the system (positive) or inhibits the system (negative).
Hypovolemia Loop
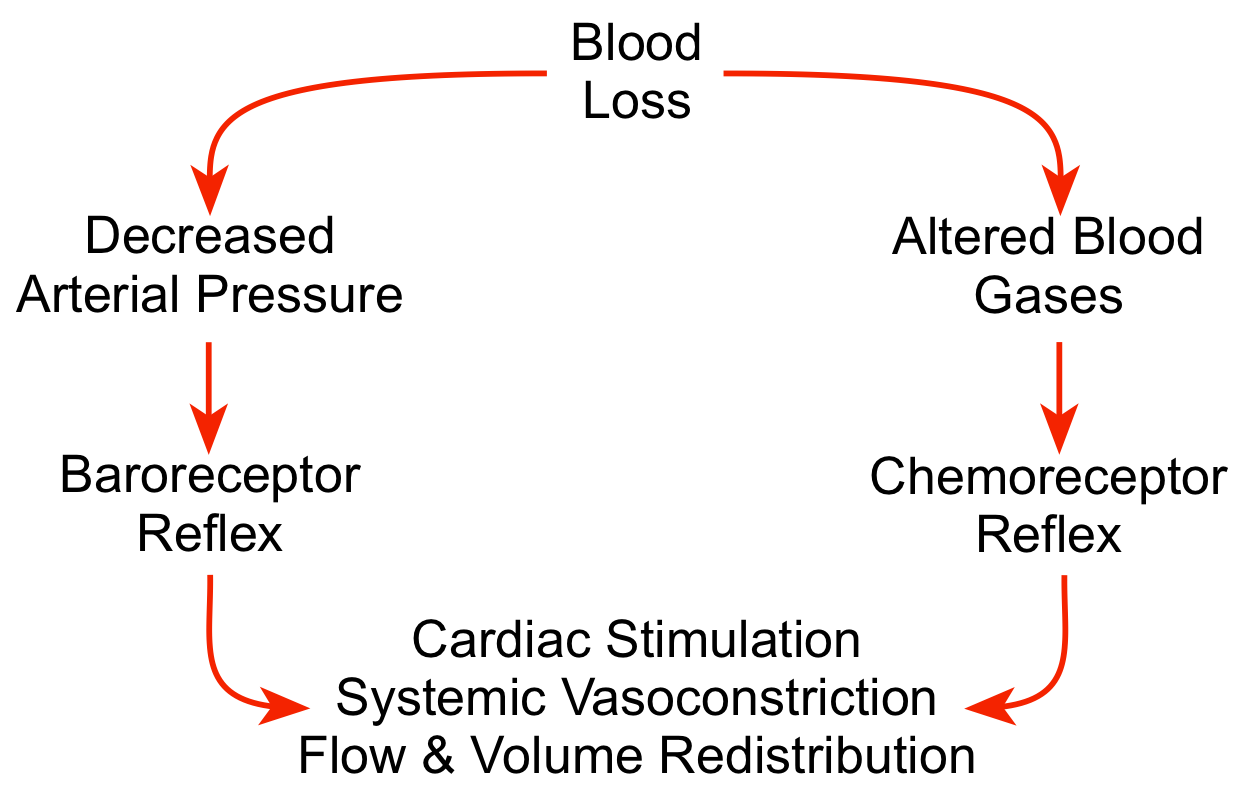
What is a baroreceptor?
They sense arterial stretch. Most important ones are in the cartoid sinus in the aortic arch.
Cartoid Sinus Massage
A procedure that stimulates baroreceptors in the carotid sinus to help lower heart rate and blood pressure. Gentle pressure to the cartoid sinus in circles.
Renin-Angiotensin-ALdosterone System
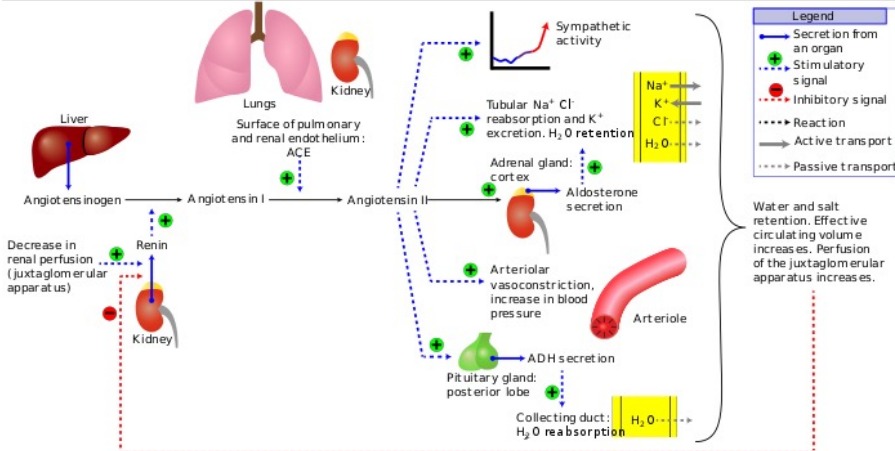
Adrenaline Presentation
1mg in 1mL or 1mg in 10mL
What does adrenaline do?
Increases HR by increasing SA node firing
Increases conduction velocity through the AV node
Increases myocardial contractility
Increases the irratablility of the ventricles
Causes bronchodialation
Causes peripheral vasoconstriction
Adrenaline indications, pres, & contras
(Cardiac Arrest, Shock, Bradycardia w poor perfusion, Anaphalaxis, Severe Asthma, and Croup)
CONTRAED IN HYPOVOLEMIC SHOCK WITH NO FLUID REPLACEMENT
Precs = Elderly/frail, patients with cardiovascular disease or with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and patients on beta blockers.
Adrenaline Side Effects & onset/peaks
(Sinus Tachy, Supraventricular arrhythmias, Ventricular arrhythmias, hypertension, pupilliary dialation, may increase MI, anxiety/palpitations)

GTN Sheet
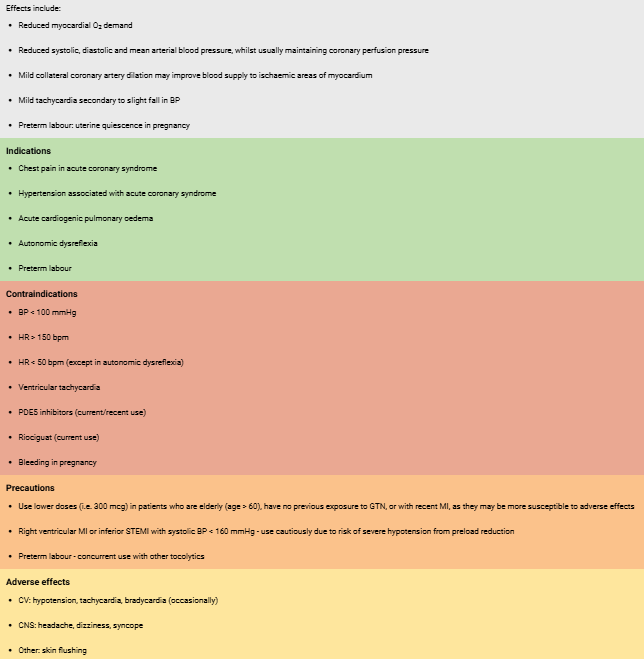
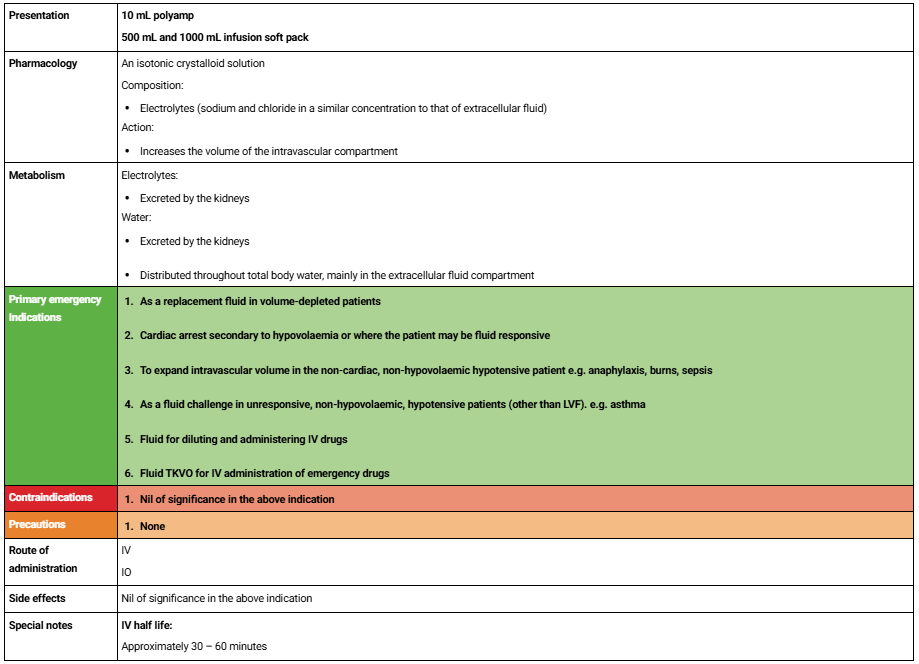
Saline Sheet
GTN onset & presentation
