Chapter 11: Population Growth
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
in presence of abundant resources
populations can grow at geometric or exponential rates, but cannot continue indefinitely
unlimited resources leads to
max reproductive rate leads to pop. growth accelerates
geometric population growth
pop. growth in which generations do not overlap and successive generations differ in size by constant ratio
(pulsed reproduction)
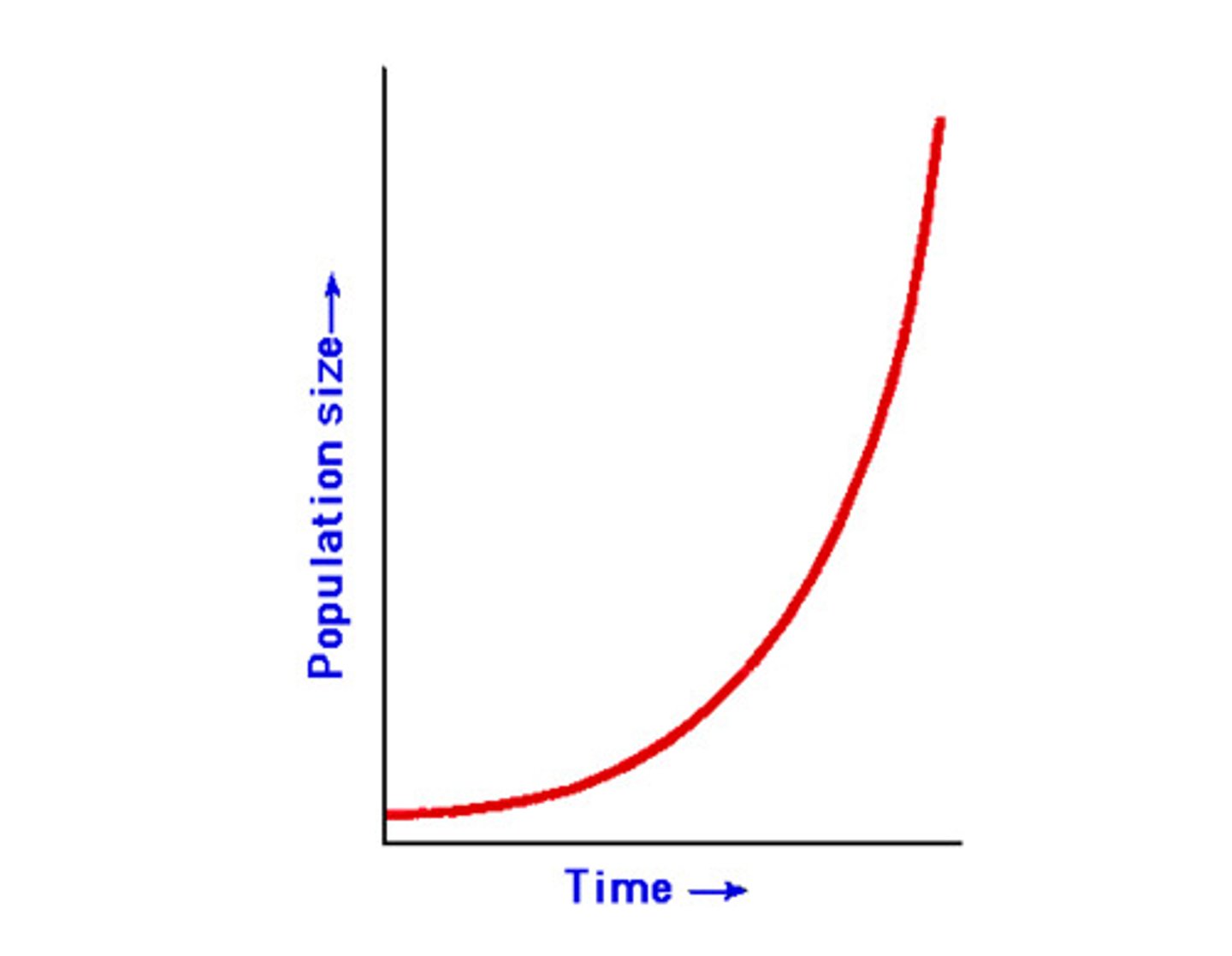
geometric population growth equation
Nt = N0λ^t
(Nt = # of individuals at any time
N0 = inital number of individuals
λ = geometric rate of increase
t = number of time intervals or generations)
exponential population growth
pop. growth in which generations overlap and the per capita rate of increase (r) is constant
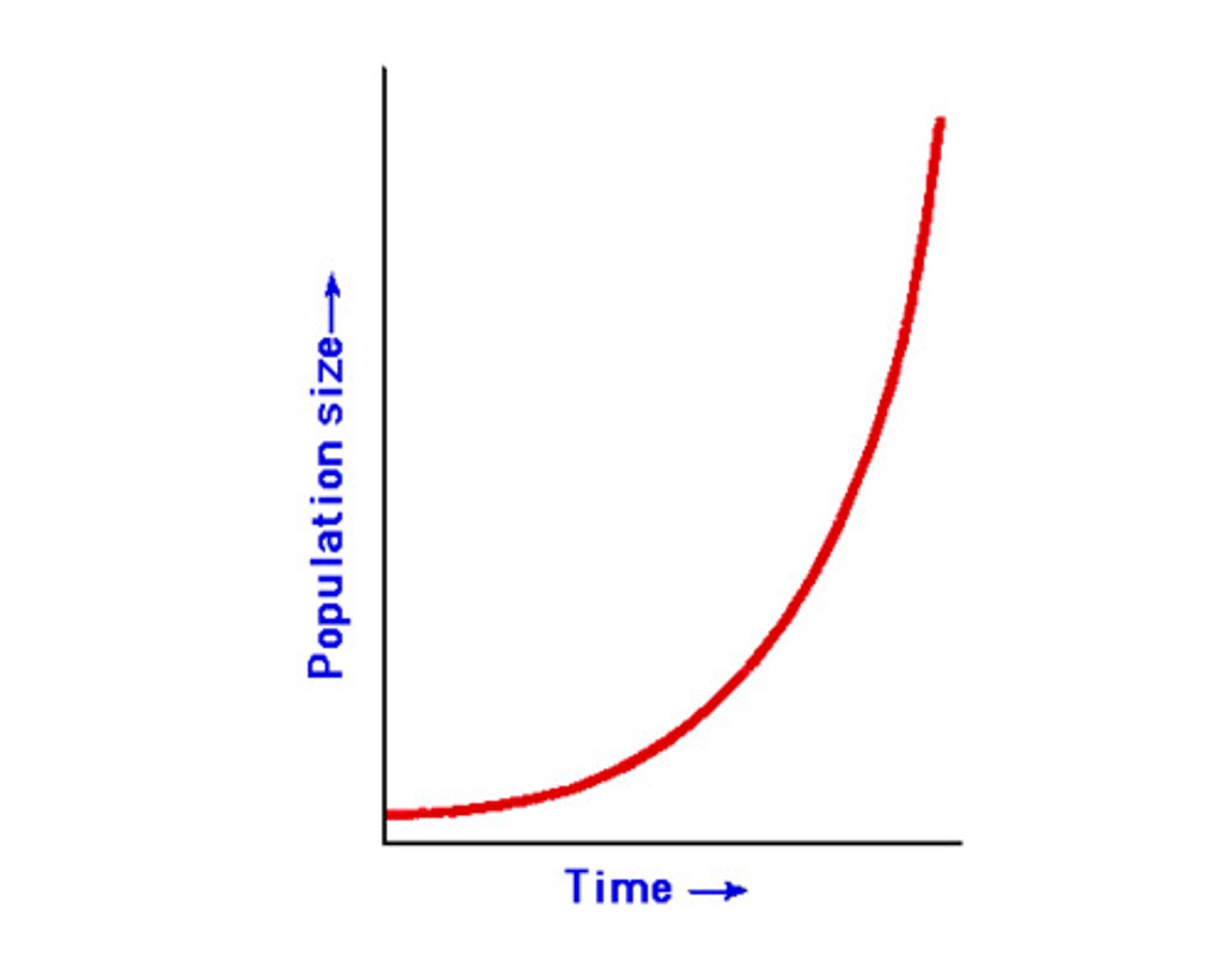
exponential population growth equation
Nt=Noe^rt
(Nt = # of indiv. at any time
N0 = inital number of individuals
r = per capita rate of increase
t = number of time intervals or generations)
exponential growth in nature
natural populations may grow exponentially for short period of time when resources are abundant
(ex: Scots pine: pollen in lake sediments showed following colonization, population grew exponentially for 500 years)
exponential growth is important process in
establishment of new environments, during favorable env. conditions, recovery from exploitation (or other threats)
logistic population growth
pop. growth that occurs when resources are limited and produces a sigmoidal (S-shaped) curve
pop. size stabilizes at carrying capacity (K)
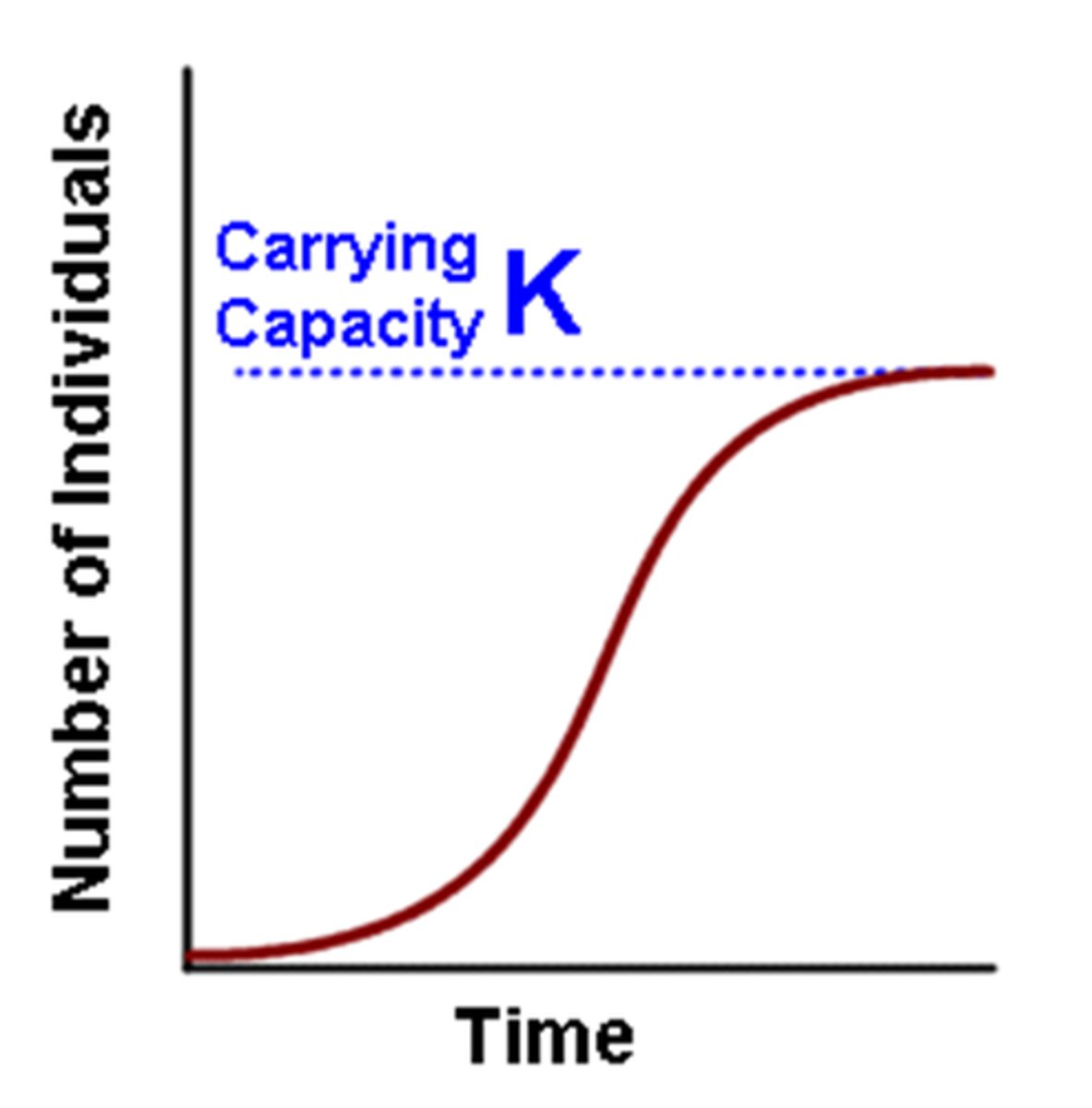
logistic population growth equation
dN/dt= rmaxN(1-N/K)
(dN/dt = # individuals per unit time
rmax = intrinsic rate of increase
N = pop. size
K = carrying capacity)
density-dependent factors
biotic factors that limit pop. growth and are influenced by pop. density
tend to regulate a pop. at relatively constant size near K
ex: competition, disease, predation
density-independent factors
abiotic factors that limit pop. growth and are not influenced by pop. density, unpredictable
ex: weather events, habitat destruction, etc