Ch. 8 Articulations Lecture PP
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
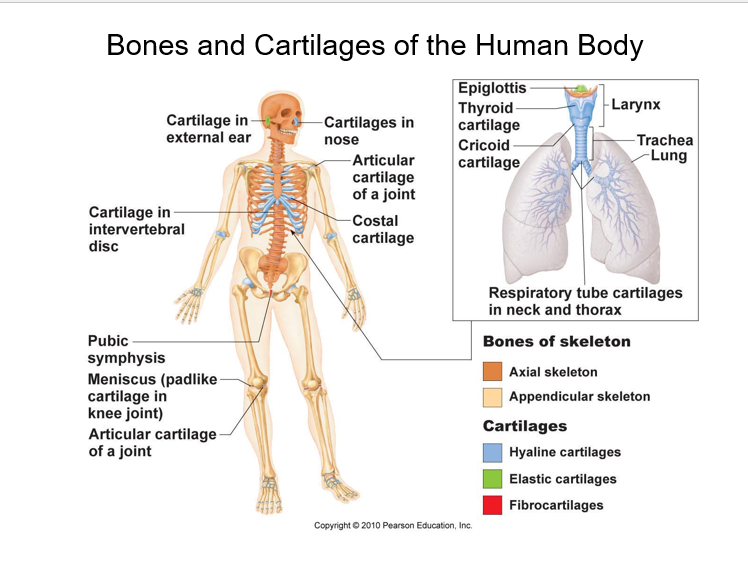
Bones and Cartilages of the Human Body
Joint (articulation) classifications
A. definition:
site at which 2 or more bones meet
joint (articulation) classifications
B. classification by movement:
S = Synarthrosis (none)
A = Amphiarthrosis (little)
D = Diarthrosis (freely)
joint (articulation) classifications
C. classification by structure:
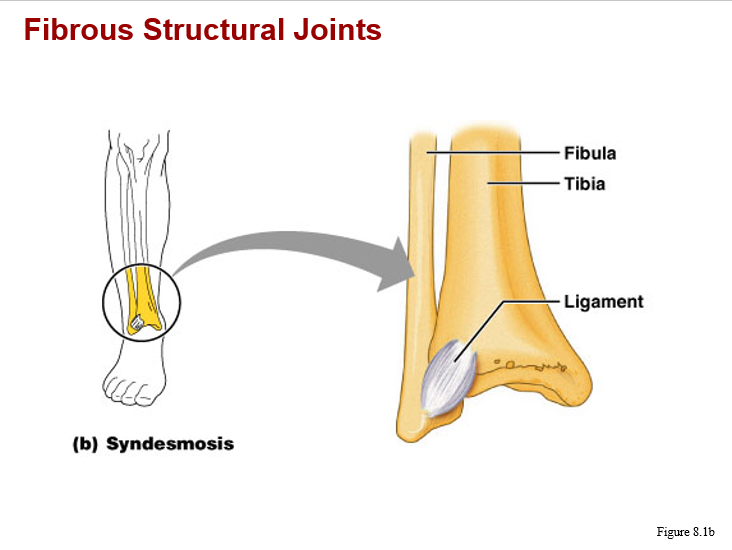
fibrous
cartilagenous
synovial
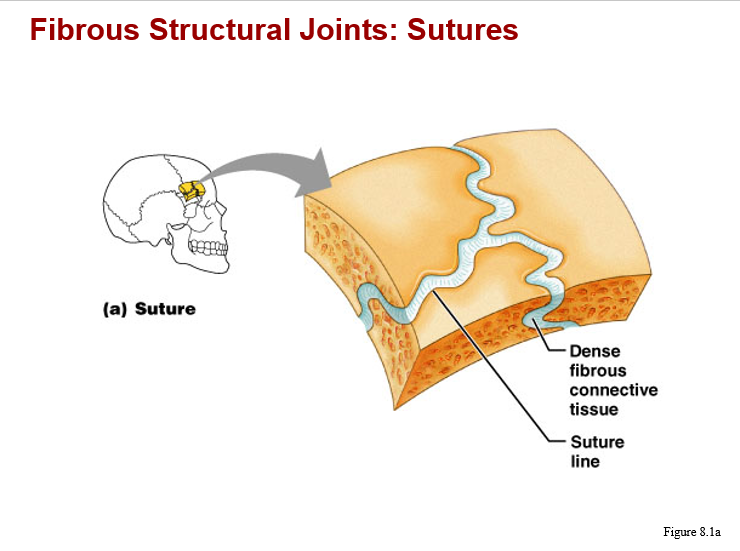
fibrous structural joints: sutures image
fibrous structural joints image
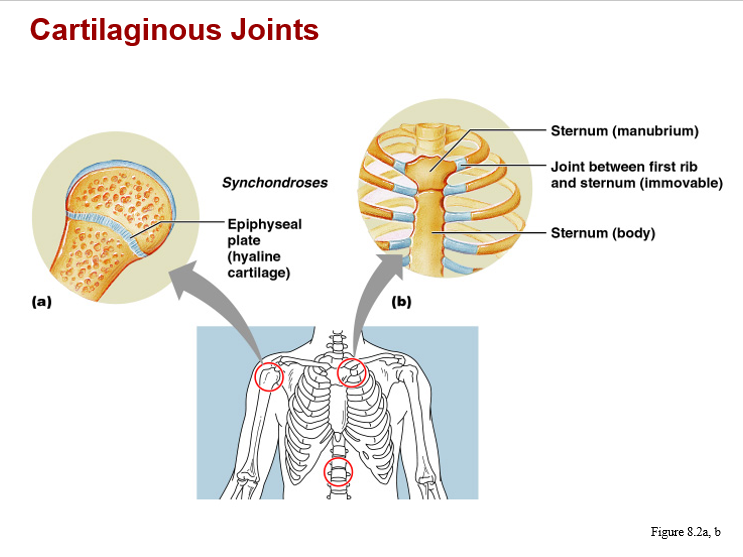
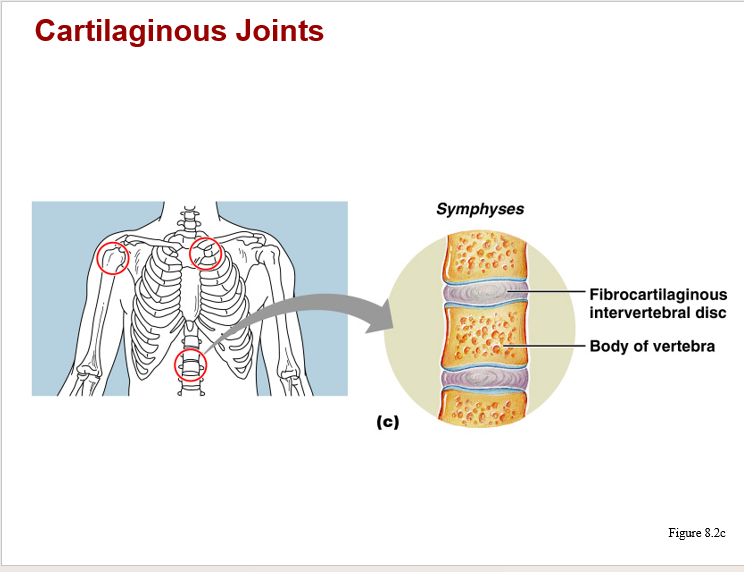
cartilaginous joints image
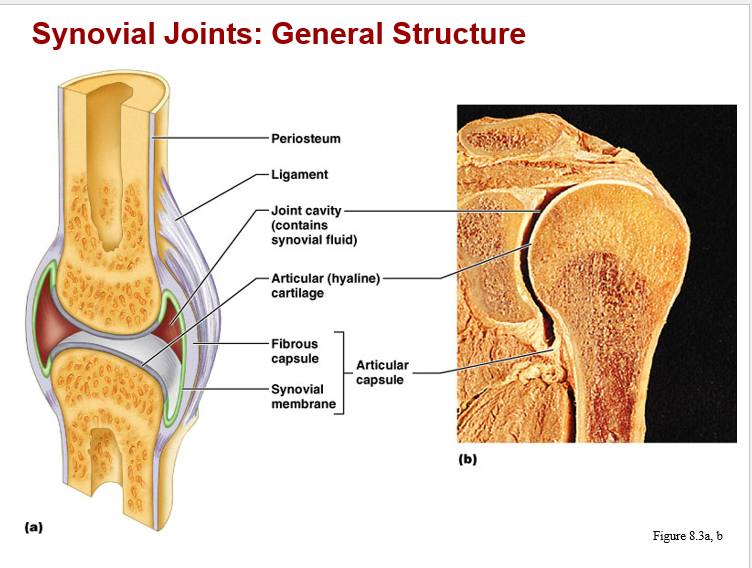
synovial joints: general structure image
structure and function of synovial joints
articular cartilage:
covers ends of bones, specialized hyaline (incr. water content)
structure and function of synovial joints
joint cavity:
potential space
structure and function of synovial joints
articular capsule:
fibrous joint covering, inner lining is a synovial membrane
structure and function of synovial joints
synovial fluid:
present in cavity to assist lubrication, will be pumped in/out of matrix, across synovial membrane
structure and function of synovial joints
reinforcing ligaments:
a. intrinsic: thickening of the joint capsule
b. extracapsular: outside capsule
c. intracapsular: inside capsule
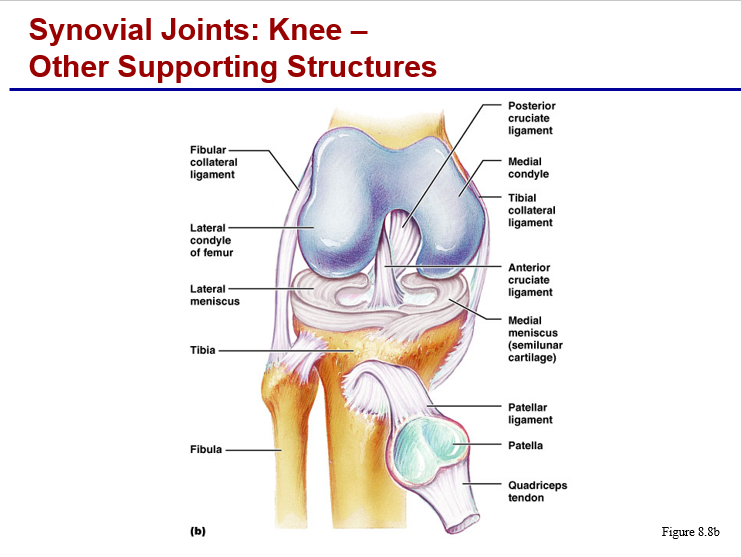
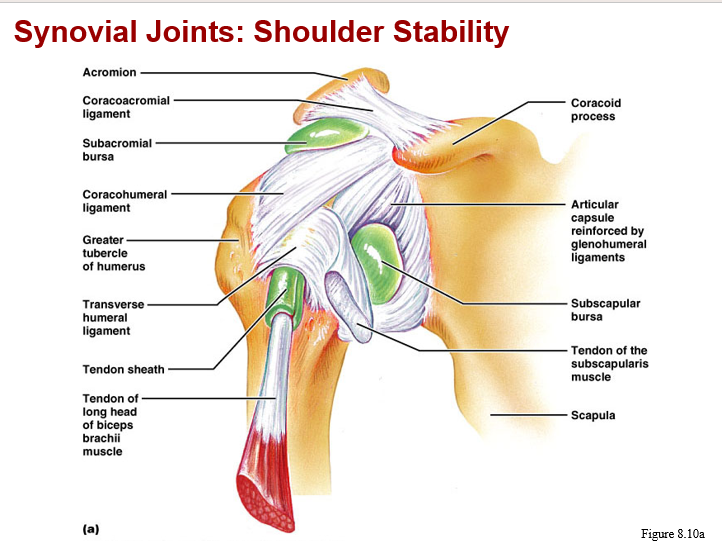
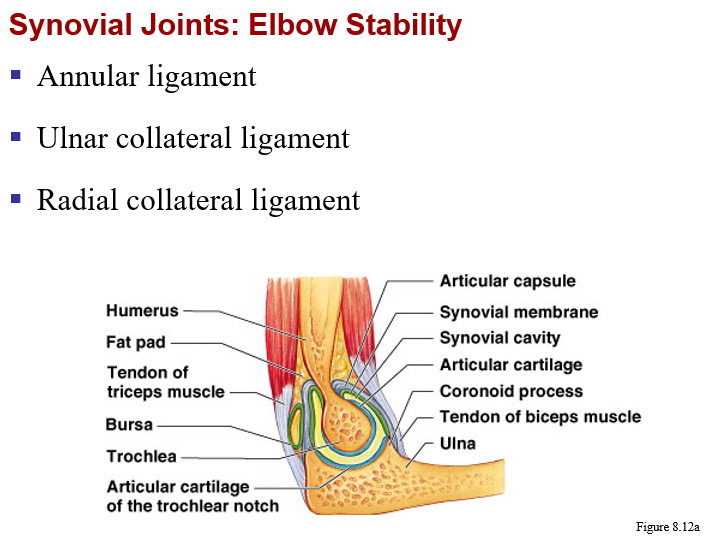
synovial joints: knee - other supporting structures
structure and function of synovial joints
meniscus:
articular disc, exists as a fibrocartilage pad between
structure and function of synovial joints
bursae:
small pockets of synovial fluid at the interface of ligaments and tendons with surrounding tissue
structure and function of synovial joints
tendon sheath:
elongated bursa, wraps around the tendon
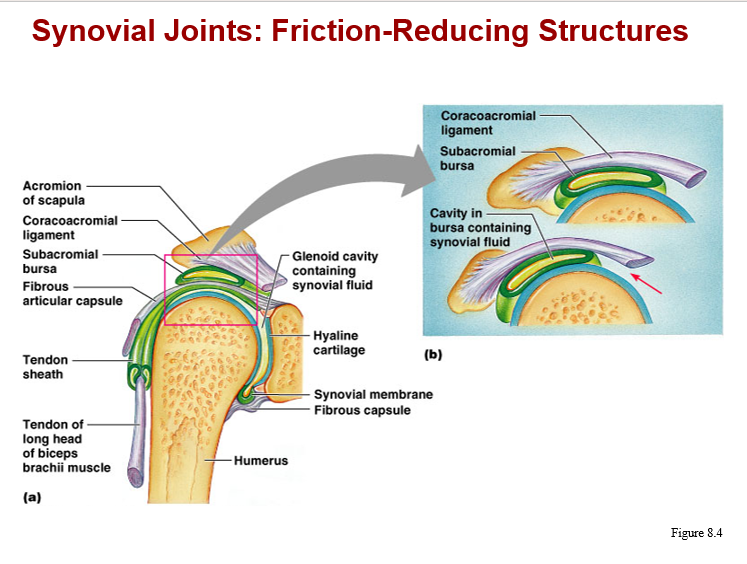
synovial joints: friction-reducing structures image
structure and function of synovial joints
c. joint stabilization -
reinforcing ligaments
shapes of bones at articular surfaces
muscle tone
NOTE: bone may still move out of alignment= dislocation (luxation)
*when articular surfaces forced out of position
*”subluxation”= partial dislocation
*”double-jointed”= joints are weekly stabilized
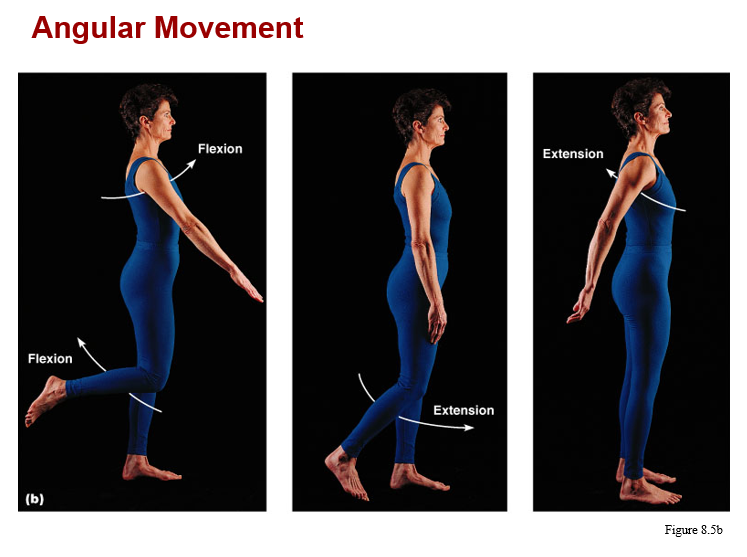
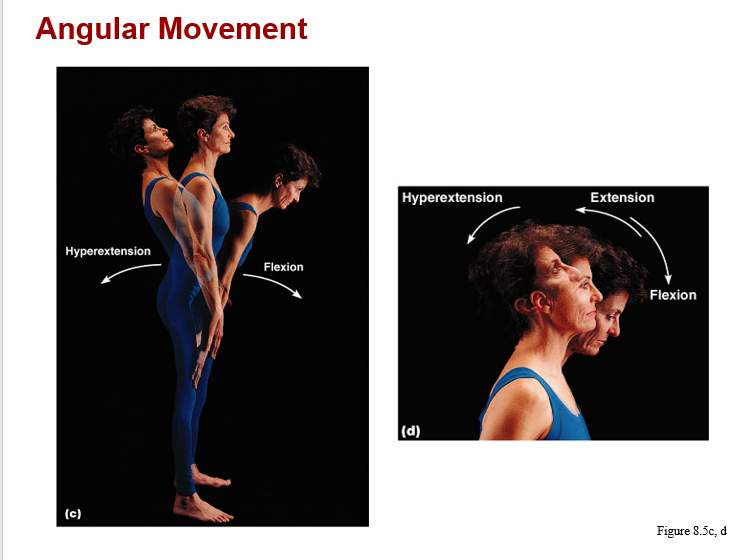
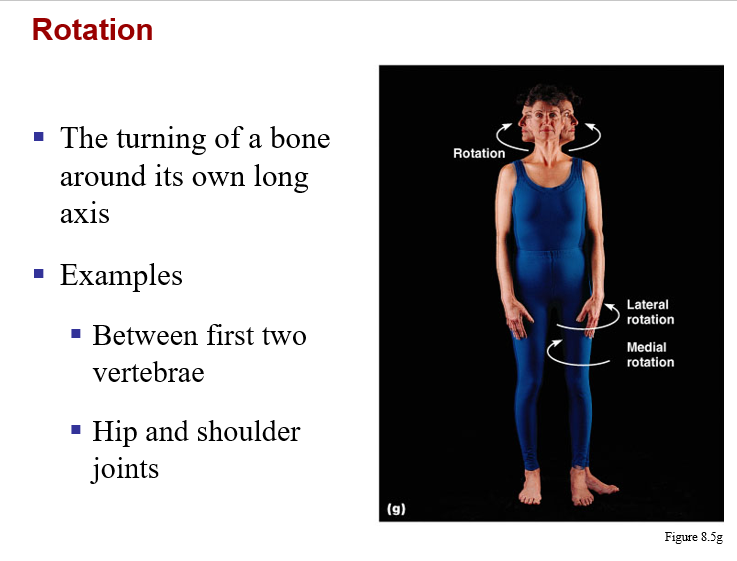
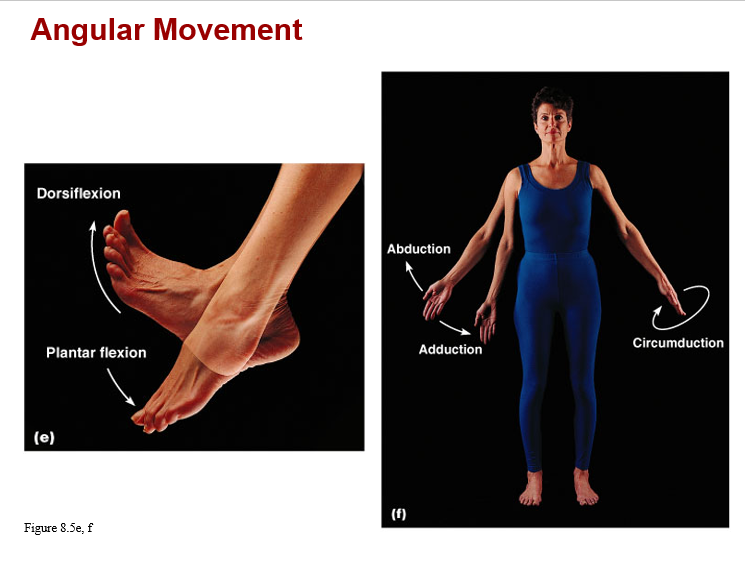
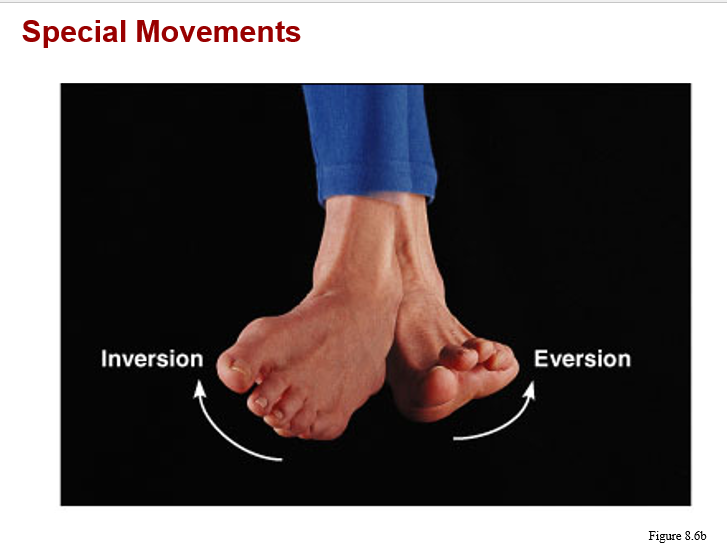
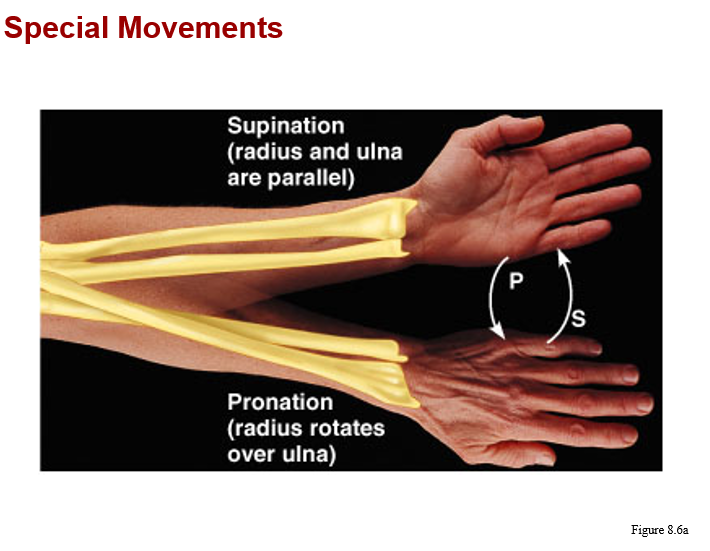
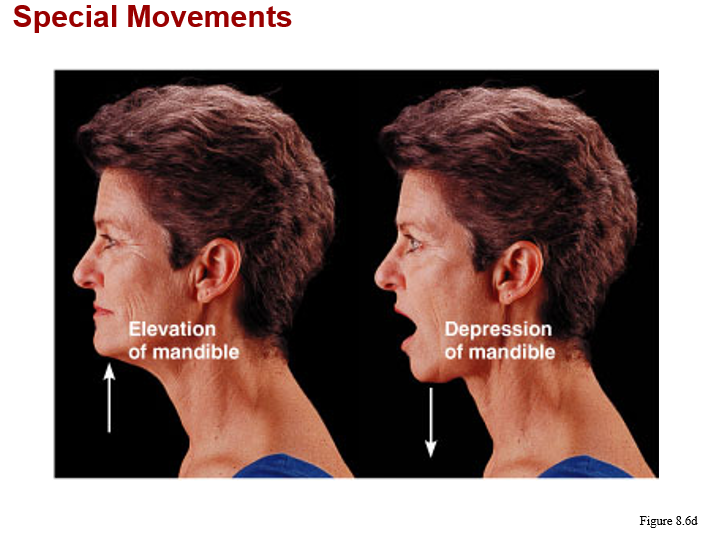
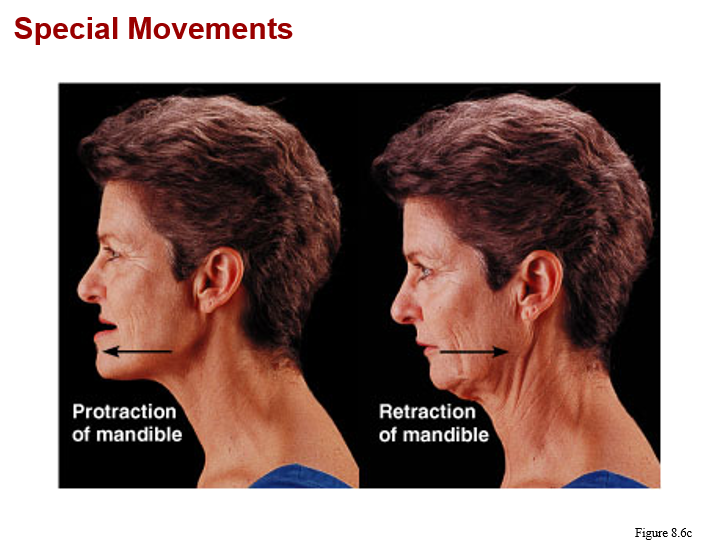
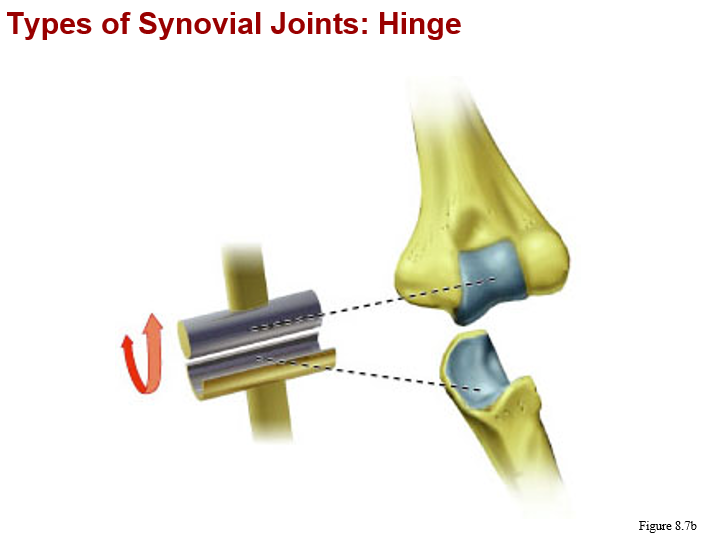
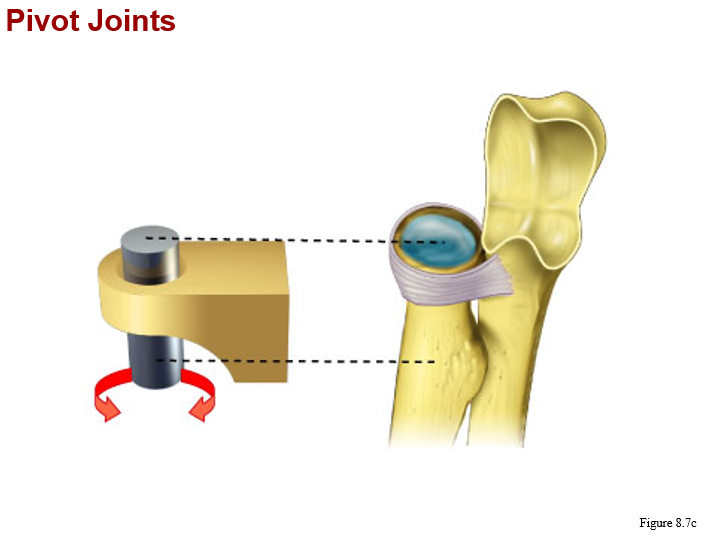
monaxial joints:
a. hinge (knee and elbow)
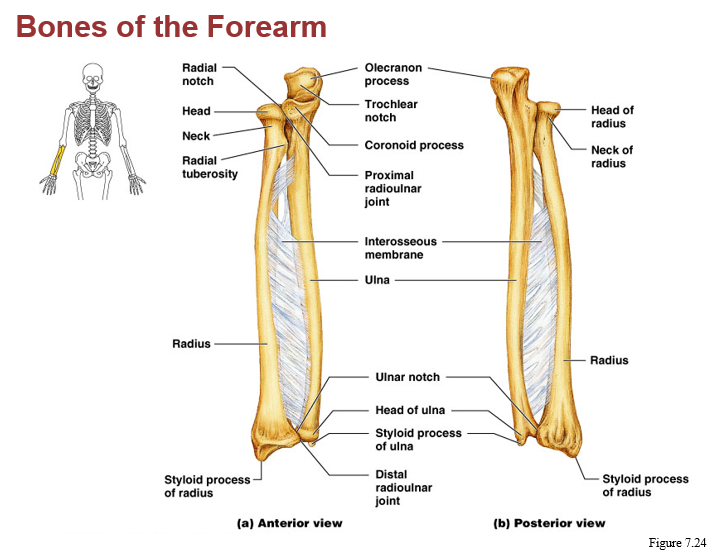
b. pivot (between atlas & axis, radius & ulna)
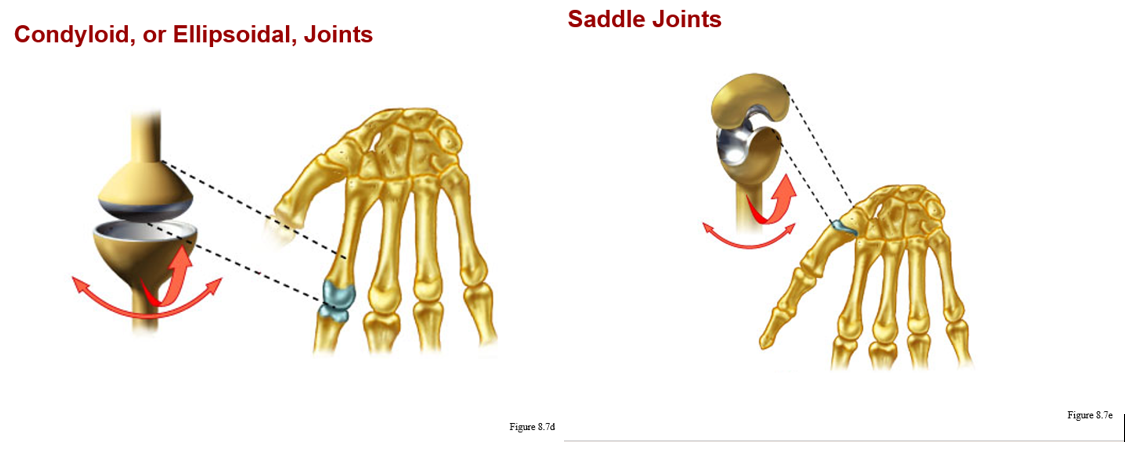
biaxial:
a. gliding (plane): wrist and vertebrae (flat surfaces)
b. coldyloid: metacarpals and phalanges (knuckles)
c. saddle: at base of thumb (metacarpal with carpal)

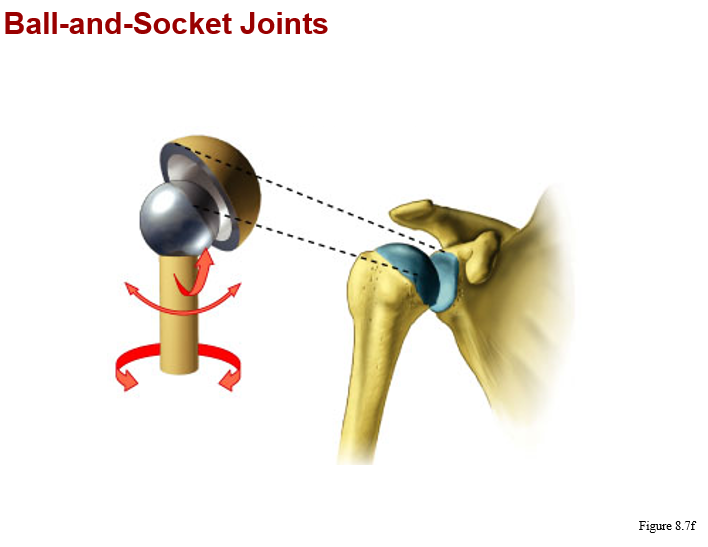
triaxial:
all ball and socket joints (shoulder, hip)