Topic 5: Enzymes
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is an enzyme?
A biological catalyst (protein in nature) that increases the rate of chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy and remaining unchanged at the end of the reaction.
What is a catalyst?
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction and is not changed by the reaction.
Why are enzymes important?
They are important to all living organisms as they maintain reaction speeds of all metabolic reactions at a rate that can sustain life.
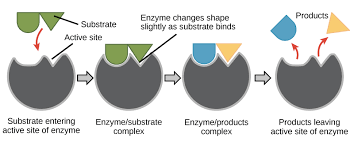
What is enzyme action?
Each enzyme has an active site with a specific shape that is complementary to its substrate. When the substrate fits into the active site, an enzyme-substrate complex forms. The enzyme then catalyzes the reaction, breaking down or building up molecules, and releases the products. The enzyme itself remains unchanged and can be reused for further reactions.
What is the specificity of enzymes?
Enzymes are specific because each enzyme’s active site has a unique shape that fits only one particular substrate. The substrate’s shape is complementary to the active site, allowing them to fit together like a key in a lock. This ensures that each enzyme catalyses only one specific reaction.
What effect does temperature have on enzyme activity?
Enzymes are proteins with a specific shape held together by bonds, especially around the active site, which allows the substrate to fit and the reaction to proceed. As temperature increases towards the optimum temperature (37°C in humans), molecules gain more kinetic energy, leading to a higher number of enzyme-substrate collisions, increasing the reaction rate. If the temperature rises above the optimum, the bonds holding the enzyme’s shape break. This changes the shape of the active site, meaning the substrate no longer fits. The enzyme becomes denatured, and because this change is irreversible, enzyme activity stops completely.
What effect does pH have on enzyme activity?
Most enzymes work best at an optimum pH of around 7, although some enzymes are adapted to acidic conditions (e.g., pepsin in the stomach, pH 2) or alkaline conditions (e.g., enzymes in the duodenum, pH 8–9). If the pH becomes too high or too low, it can break the bonds that hold the enzyme’s protein structure together. This changes the shape of the active site, meaning the substrate can no longer fit properly. As a result, the rate of enzyme activity decreases. If the pH moves far from the optimum, the enzyme becomes denatured, making this change permanent and stopping the reaction completely.
How do temperature affect enzymes?
When there is a high temperature, it increases the kinetic energy of substrate & enzymes so they collide more. When there is a low temperature the kinetic energy decreases hence slow movement of molecules slowing down reaction.
What temperature do enzymes work best at?
Enzymes work faster as the temperature increases up to 40°C, but are eventually denatured at about 60°C.This is because the shape of the active site is lost.
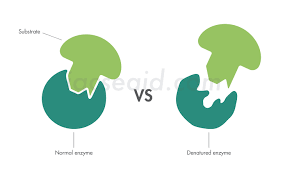
What happens when the the temperature and pH changes sufficiently beyond an enzyme’s optimum?
It denatures. The shape of the enzyme irreversibly changes, this affects the shape of the active site and means that the enzyme will no longer work.
How do pH affect enzyme action?
Each enzyme works best at a particular pH. This is known as the optimum pH. Extremes levels of pH will cause the active site to denature.
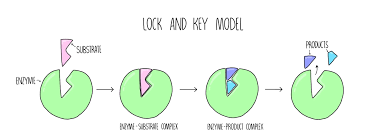
What is the lock and key mechanism in enzymes?
The lock and key mechanism explains how enzymes work. The substrate fits into the enzyme, the same way a key would fit into a lock. Each enzyme has an active site complementary to the substrate. When the substrate fits into the active site (enzyme-substrate complex), the enzyme catalyzes the reaction, turning the substrate into products.
What is activation energy?
The minimum amount of energy required for a given chemical reaction to occur.
Which pH does starch work best at?
ph7, produced in the salivary glands and pancreas
Which pH does proteins work best at?
ph3, produced in the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine
Which pH does lipids work best at?
ph8, being produced in the pancreas
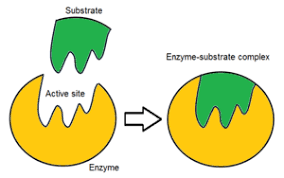
What is a substrate?
The substance that an enzyme causes to react.
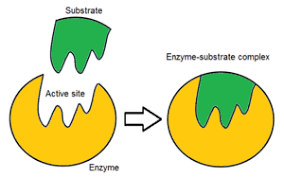
Define an active site.
The part of an enzyme molecule to which the substrate temporarily binds