Marketing Test 1- Chapter 3
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Steps in the marketing research process
Step 1: Establish the need for marketing research
Step 2: Define the problem
Step 3: Establish research objectives
Step 4: Determine research design
Step 5: Identify information types and sources
Step 6: Determine methods of accessing data
Step 7: Design data collection forms
Step 8: Determine the sample plan and size
Step 9: Collect data
Step 10: Analyze data
Step 11: Communicate the insights.
The “Step-by-Step Process”
Not always presented as an 11-step process
Not all studies use all 11 steps
Few studies follow the steps in order
Step 1: Establish the need for marketing research
•Is there a real need for marketing research?
•Research takes time and costs money
•Cost of information may outweigh value of information
Is there a real need for marketing research?
marketing research is not always neeeded
we often have the information
When is marketing research not needed?
•The information is already available
•The timing is wrong to conduct marketing research
•Funds are not available for marketing research
•Costs outweigh the value of marketing research
the information is already available
can we obtain the information from past studied?
Can we get the information from internal reports from the Marketing Intellegence SYstem (MIS)?
the timing is wrong
Do we need to act immediately to remain competitive?
Is the product at the end of its life cycle?
costs outweigh the value
Have we conducted a cost benefit analysis?
What is the marketing return on investment of the market research project?
Step 2: Define the problem
The need to make a decision requires decision alternatives. If there are no alternatives, no decision is necessary.
Step 3: Establish research objectives
Research objectives state what the researchers must do.
Research objectives, when achieved, provide the information necessary to solve the problem identified in step 2.
Exploratory research
collecting information in an unstructured and informal manner
Descriptive research
research that descries the phenomena of interest
Casual studies
attempt to uncover what factor or factors cause some event
Step 4: Determine research design
exploratory, descriptive, casual
Step 5: Identify information types and sources
Primary and Secondary Information
Primary information
inforamtion collected specifically for the problem at hand
Secondary information
information already collected
Step 6: Determine methods of accessing Data
Secondary and Primary data
secondary data
relatively easy to access
primary data
more complex
refers to information that is developed or gathered by the researcher specifically for the research project at hand
Step 7: Design Data Collection Forms
•The questionnaire must be worded objectively, clearly, and without bias in order to communicate with respondents.
•If a focus group is used, a focus group guide must be developed.
•If we observe respondents, the form is called an observation form.
•Software programs are available to assist marketing researchers in preparing data collection forms.
Step 8: Determine sample plan and size
•A sample is drawn from an entire group or population. The sample plan describes how each sample element, or unit, is to be drawn from the total population. Gives you representativeness!
Sample size
refers to determining how many elements of the population should be included in the sample. Gives you accuracy!
Step 9: Collect Data
•Researchers aim to minimize this possibility by undertaking a control referred to as validation.
•Companies that specialize in data collection are referred to as field service firms.
Step 10: analyze data
data analysis
data analysis
involves entering data into computer files, inspecting data for errors, and running tabulations and various statistical tests.
Step 11: Communicate the insights
•Communicating the results, the last step, is one of the most important phases of marketing research.
•Its importance cannot be overstated because it is the report, or its presentation, that properly communicates the results to the client.
Defining the problem: problems
situations calling for managers to amke choices among decision alternatives
most important step in the marketing research process
defining the problem
Process for defining a problem
Recognize the problem, understand the backround of the problem, determine the decision alternatives
Recognize the problem
Is it a failure to meet an objective or identification of an oppurtunity
Understand the Backround of the Problem
-conduct a situation analysis
-clarify the symptoms
-determine the probable causes of the symptoms
Determine the decision alternatives
specify decision alternatives
weigh the alternatives
Formulate the problem statement
develop a concise description of the problem
Research Objectives
Are specific and tell the researcher exactly what information must be collected to solve the problem by facilitating selection of an alternative.
•They are goal-oriented statements or questions that specify what information is needed.
The Research Objective
•Specify from whom information is to be gathered
•Specify what information is needed
•Specify the unit of measurement used to gather information
•Word questions used to gather information using the respondents’ frame of reference
Hypotheses
statements that are taken as true for the purposes of argument or investigation.
Construct
an abstract idea or concept composed of a set of attitudes or behaviors that are thought to be related.
–What is the unit of measurement?
–What is the proper frame of reference?
Variables
elements of constructs that can be measured or quantified
action standard
a predesignation of some quantity of a measured attribute or characteristic that must be achieved for a research objective for a predetermined action to take place.
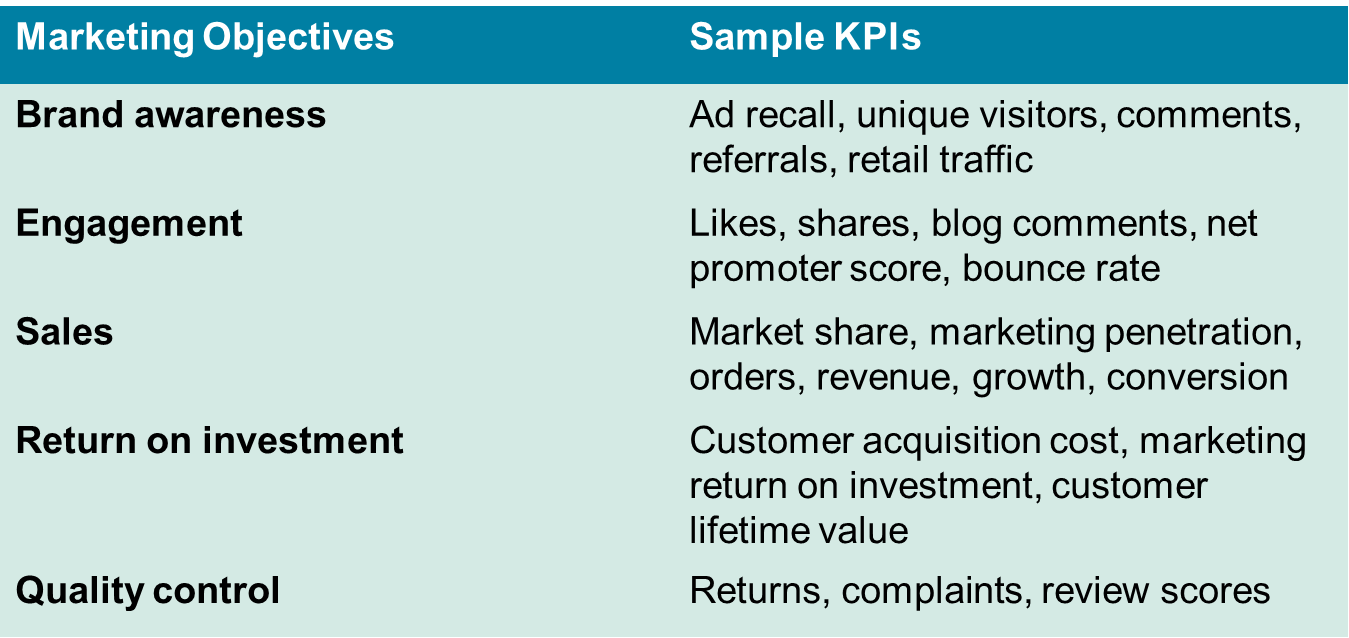
Sample Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
marketing research proposal
serves as the basis of a contract as it documents what the marketing researcher proposes to deliver to the client for some consideration, typically a fee.
invitation to bid (ITB) or Resequest for proposal (RFP)
When a client first contacts a marketing research supplier to conduct research, the client will generally request a proposal prior to agreeing to work with the firm in this process