Energy Flow and Climate Change Overview
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
What is the biosphere
All of Earth's ecosystems, including all living things (flora, fauna, and microorganisms), within a 20 km thick layer of the Earth.
What is the maximum depth and height of the biosphere?
Deepest ocean depths are 11 km below sea level, and the highest mountain is 9 km above sea level.
What is the hydrosphere?
The hydrosphere contains all water on Earth, which is essential for life.
What percentage of Earth's water is saltwater and freshwater?
Approximately 97% of Earth's water is saltwater, while only 3% is freshwater.
Where is most of Earth's freshwater found?
Most freshwater is found frozen in glaciers, underground as groundwater, or in the atmosphere as humidity.
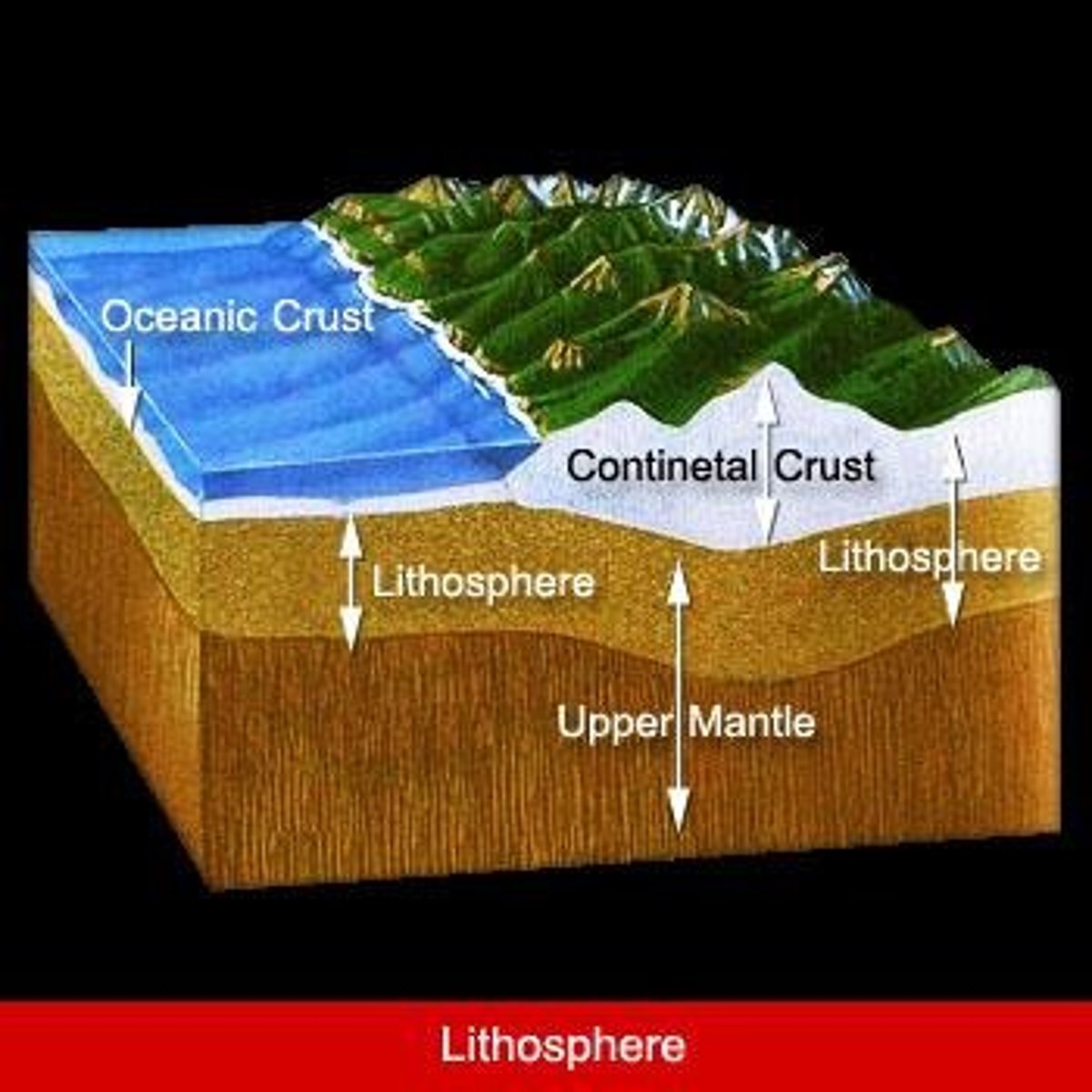
What is the lithosphere?
The lithosphere, also known as the geosphere, is the 100 km thick layer of rock surrounding the Earth.
What are the two layers of the lithosphere?
The crust (uppermost layer) and the upper mantle (contains partially molten rocks where magma forms).
What is the composition of the atmosphere?
The atmosphere consists mostly of Nitrogen (78%) and Oxygen (21%), with traces of other gases such as argon, methane, and carbon dioxide.
How do the four spheres (biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere) interact?
They are closely linked and often interact, supporting living organisms in the biosphere.
What is biodiversity?
Biodiversity is the total of all living organisms, including the variety of different plants, animals, and microorganisms.
What are the two main components of an ecosystem?
Biotic factors (living or once living) and abiotic factors (non-living).
Give examples of biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem.
Biotic: rotting logs, fungi, bacteria, animals, plants. Abiotic: temperature, wind, water, soil, sun.
What does genetic diversity refer to?
Variation within a species, such as different eye colors, heights, or abilities to retain water in plants.
What is species diversity?
The variety of species on Earth, including the number of species and the populations of individuals within each species.
What roles do different species fulfill in ecosystems?
Insects act as pollinators, birds spread seeds, and plants provide shelter and food.
What is ecosystem diversity?
The variety of different types of habitats, such as rainforests, coral reefs, polar ice caps, and deserts.
How does human activity impact biodiversity?
Land clearing for cities and farmland destroys ecosystems, and human activities spread invasive plant species.
What is an example of a species with limited habitat?
The large-eared pika is only found in the Himalayas.
What is the significance of undiscovered species?
Many undiscovered species are usually microorganisms (bacteria) or fungi, and there are more species of beetles than any other animals.
What is the relationship between habitat variety and ecosystem diversity?
The greater the variety of habitats, the higher the ecosystem diversity, leading to a greater variety of animals and plants.
What human activities contribute to the spread of invasive plant species?
Human activities such as illegal dumping can help spread weeds and invasive plants that outcompete and kill native species.
What percentage of its original grassland does Victoria have left?
Less than 5% of its original grassland.
What event in 2022 affected the rare Kangaroo grass in Truganina?
Illegal dumping over grassland destroyed the rare Kangaroo grass.
What are the five layers of the atmosphere?
Troposphere, Stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere, Exosphere.

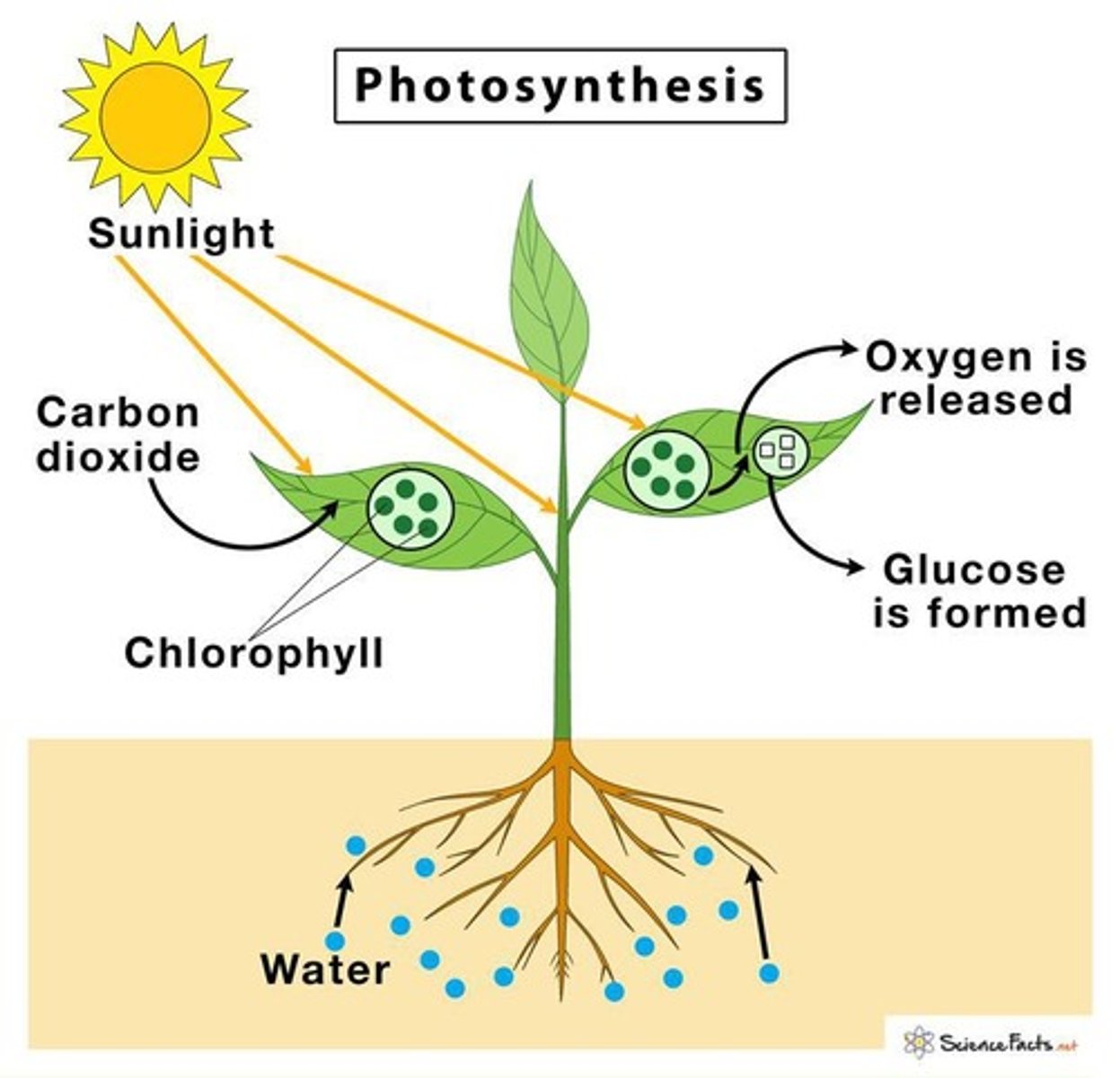
What is photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process where carbon dioxide and water react in the presence of sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen gas.
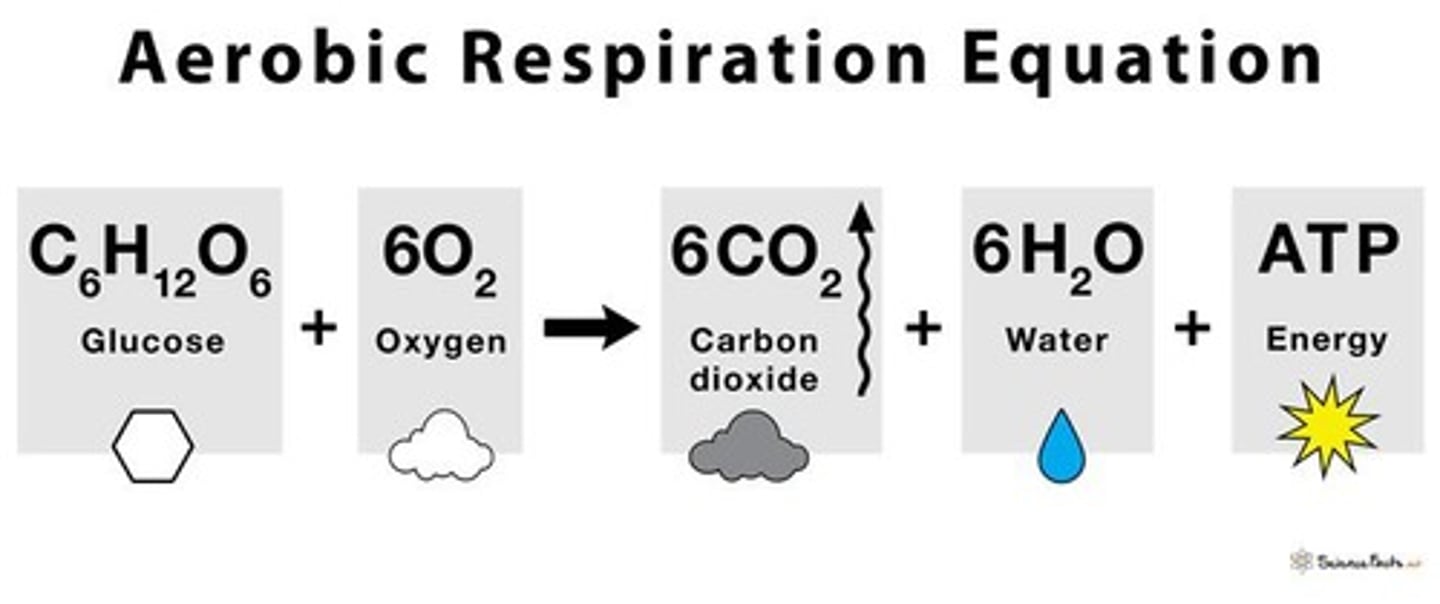
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process where oxygen is taken up and carbon dioxide is released to produce energy.
Which organisms perform photosynthesis?
Plants and certain micro-organisms.
What is the carbon-oxygen cycle?
The carbon-oxygen cycle involves the cycling of carbon and oxygen between biotic and abiotic environments, where carbon dioxide is used in photosynthesis and returned to the atmosphere in respiration.
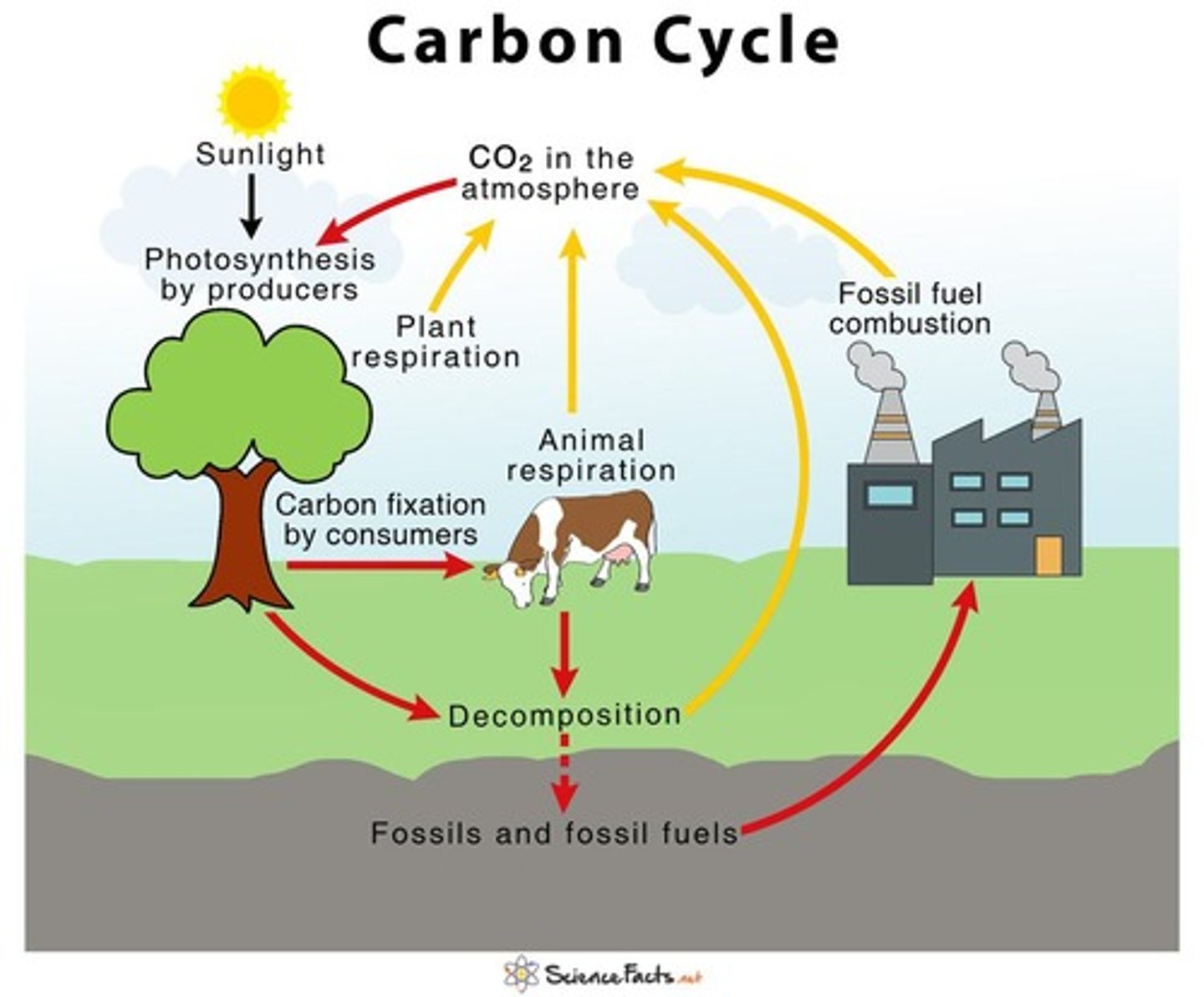
How is carbon stored in the food chain?
Carbon is stored as part of glucose and starch, which moves up the food chain when animals eat plants.
What human activities disturb the carbon cycle?
Burning fossil fuels and deforestation disturb the balance of the carbon cycle.
What is the effect of burning fossil fuels on the carbon cycle?
Burning fossil fuels releases CO2 into the atmosphere, increasing CO2 levels.
How does deforestation affect CO2 levels?
Deforestation reduces the amount of CO2 absorbed by trees, leading to increased CO2 in the atmosphere.
What is the water cycle?
The water cycle collects, purifies, and distributes the Earth's water.
What happens to water over the oceans in the water cycle?
Evaporation exceeds precipitation, resulting in movement of water vapor over land.
What is evaporation?
Evaporation is the process where liquid water turns into gas due to heat from the Sun.
What is transpiration?
Transpiration is the process where water evaporates from plant leaves.
What is condensation?
Condensation is the process where rising water vapor cools and changes back into liquid, forming tiny water droplets and clouds.
What occurs during precipitation?
Precipitation occurs when condensed water droplets become too heavy for the air to hold, falling as rain, snow, or sleet.
What is infiltration in the water cycle?
Infiltration is the process where water soaks into the ground and is collected in layers of rock, sand, or gravel.
How does groundwater contribute to rivers?
Groundwater eventually seeps into rivers, providing a steady flow of water.
What happens to water that is locked up in snow and ice?
Some precipitation becomes locked up in snow and ice for long periods of time.
What is the role of the Sun in the water cycle?
The Sun provides heat that breaks hydrogen bonds between water molecules during evaporation.
What is the ultimate destination of water in the water cycle?
Water will eventually reach the ocean.
What factors influence the rate of infiltration in the water cycle?
The rate of infiltration is dependent on the soil and rock types.
What human activities increase surface water run-off?
Concrete roads and buildings increase the rate of surface water run-off.
What is run-off in the context of the water cycle?
Run-off occurs when water does not enter the soil but flows across the land, collecting pollutants.
What are the consequences of run-off on waterways?
Run-off collects pollutants such as fuel, rubbish, and toxins, causing contamination of waterways.
How does human groundwater usage impact water resources?
Humans are constantly taking up groundwater for domestic, stock, and agricultural uses, leading to depletion.
What is soil compaction and its effects?
Soil compaction is the compression of soil particles due to heavy machinery and livestock, leading to fewer air and water pockets.
What are the three major groups of rocks?
Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
How are igneous rocks formed?
Igneous rocks are formed by the cooling of molten magma.
What is the difference between basalt and granite?
Basalt has fine grains formed from quick cooling of magma, while granite has coarse grains formed from slow cooling.
How are sedimentary rocks formed?
Sedimentary rocks are formed from deposits of smaller rock particles that solidify due to pressure.
What are some examples of sedimentary rocks?
Examples include sandstone, limestone, and coal.
What characterizes metamorphic rocks?
Metamorphic rocks are igneous or sedimentary rocks altered by heat, pressure, and chemical change.
What is the Albedo effect?
Albedo refers to the fraction of solar energy reflected from the Earth back into space, ranging from 0 to 1.
Which surfaces have low albedo?
Ocean surfaces and rainforests have low albedos, absorbing most of the sun's radiation.
Which surfaces have high albedo?
Deserts, ice, and clouds have high albedo, reflecting a large portion of the sun's energy.
How does the color of an object influence its albedo?
Darker-colored objects have lower albedo, absorbing more light and heat than lighter-colored objects.
What is terrestrial radiation?
Terrestrial radiation is the process by which absorbed heat energy is released back into the atmosphere and space.
What percentage of the Sun's energy is absorbed by water, soil, plants, and animals on Earth?
Approximately 51% of the Sun's energy is absorbed.
What is the Earth's Energy Budget?
The Earth's Energy Budget refers to the total amount of energy Earth receives and sends back to space.
What role do certain gases play in the atmosphere regarding heat?
Certain gases can trap heat in the atmosphere for longer periods.
What is the greenhouse effect?
A natural process where some terrestrial radiation is trapped in the troposphere, keeping Earth's surface temperature around 15 degrees Celsius instead of -15 degrees.
What are greenhouse gases (GHGs)?
Chemicals in the atmosphere that trap heat, including carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), water vapour, and nitrous oxide (N2O).
Which greenhouse gas is the most abundant?
Water vapour is the most abundant greenhouse gas, followed by carbon dioxide.
How has human activity impacted greenhouse gas levels?
Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have drastically increased carbon dioxide emissions, leading to more heat being trapped in the atmosphere.
What are some sources of carbon dioxide emissions?
Sources include agriculture, industry/manufacturing, transportation, and residential/commercial buildings.
What is one major effect of global warming on tropical regions?
Global warming may lead to reduced rainfall and humidity, transforming rainforests into savannahs and potentially deserts.
What happens to coral reefs due to global warming?
Coral bleaching occurs when corals expel algae from their tissues due to stress from temperature and carbon dioxide increases, making them more susceptible to starvation and disease.
How does global warming affect weather patterns?
It leads to more extreme weather patterns, such as heavy rainfall and flooding, as seen in Australia.
What are some potential positives of global warming?
Warmer climates may allow countries near the poles to grow more crops and create new habitats in high-altitude areas.
Why are the negative effects of global warming considered to outweigh the positives?
Many biodiversity hotspots and densely populated areas are in tropical regions, which are at risk of destruction from high global temperatures.
What are some solutions to combat the increase of carbon dioxide?
Solutions include capturing and storing carbon dioxide, decreasing emissions through renewable energy, and using carbon capture techniques.
What is carbon capture?
Techniques developed to capture and store carbon dioxide during fossil fuel burning before it reaches the atmosphere.
What is geological sequestration?
Storing carbon dioxide deep underground in areas where fossil fuel gas was originally extracted, requiring stable, impermeable rock formations.
What is biological sequestration?
Storing carbon dioxide through seaweed farms, which utilize photosynthesis to capture carbon.
What is renewable energy?
Energy derived from natural sources that are replenished at a higher rate than they are consumed, such as solar, wind, geothermal, hydropower, and bioenergy.
What are some examples of renewable energy sources?
Solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, hydropower, and bioenergy.
What is the relationship between carbon dioxide and global warming?
Increased levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere are linked to global warming, as they trap more heat.
What is the average surface temperature of Earth due to the greenhouse effect?
Approximately 15 degrees Celsius.
What would Earth's average surface temperature be without the greenhouse effect?
About -15 degrees Celsius.
How does carbon dioxide affect ocean temperatures?
Increased carbon dioxide levels lead to higher ocean temperatures, contributing to global warming.
What is the impact of global warming on ecosystems?
It can drastically reshape ecosystems, affecting biodiversity and species distribution.
What is the significance of the Industrial Revolution in relation to carbon dioxide levels?
The Industrial Revolution marked a drastic increase in carbon dioxide emissions due to industrial activities.
What are the consequences of coral bleaching?
Bleached corals are not dead but are more vulnerable to starvation and disease.