Mgmt 200-FInal Exam Purdue questions with complete verified solutions already graded A+
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
liability
an obligation of a company to transfer some economic benefit in the future
Which liabilities require payment in the future?
Accounts payable
Notes Payable
Salaries Payable
When does deferred revenue arise?
when companies receive payment in advance
What is a current liability?
A liability expected to be paid within 1 year of balance sheet date
What is a long-term liability?
payable in more than one year from balance sheet date
What is the operating cycle?
the length in time from spending cash to provide goods/services to a customer until collection of cash from that customer
What does a company with a 3 month operating cycle do with their liabilities?
classifies current liabilities as those due in 1 year
What does a company with a 15 month operating cycle do with their liabilities?
classifies current liabilities as those due within 15 months
What is notes payable?
A written promise made by the business to pay a debt, usually involving interest, in the future.
How to calculate Interest on notes payable?
Face Value x Annual Interest Rate x Fraction of the year
How do you record Notes Payable?
debit cash, credit notes payable
Southwest Airlines borrows $100,000 from Bank of America on September 1,2024, signing a 6%, six-month note for the amount borrowed plus accrued interest due six months later on March 1, 2025.
On September 1, 2024, Southwest will receive $100,000 in cash and record the following:
debit cash 100,000
credit notes payable 100,000
Southwest Airlines borrows $100,000 from Bank of America on September 1,2024, signing a 6%, six-month note for the amount borrowed plus accrued interest due six months later on March 1, 2025.
How do you calculate the Interest for the 6 month period?
100,000 X.06 X 6/12 = 3000
Southwest Airlines borrows $100,000 from Bank of America on September 1,2024, signing a 6%, six-month note for the amount borrowed plus accrued interest due six months later on March 1, 2025.
How do you calculate the Interest for the 4 month period? What would be the Adjusted journal Entry?
100,000 x .06 x 4/12 = 2000, Debit to Interest Expense 2000 and Credit to interest Payable 2000
How do you record the repayment of Notes Payable?
Debit to Notes Payable, Interest Expense, Interest Payable
Credit to Cash
What are the payroll costs for employees?
Federal and state income taxes
FICA taxes
Health, Dental, Disability, Life insurance
Investments in retirement/savings plan
What are the payroll employer costs?
federal and state unemployment taxes
employer matching portion of Social Security and Medicare
Health, Dental, Disability, Life insurance
Contributions to retirements or savings plan
What is the journal entry for employee salary expense, withholdings, and salaries payable?
debit to salaries expense
credit to employee income tax payable, FICA Tax payable, Salaries Payable
What is the journal entry for posting fringe benefits?
Debit to salaries expense
Credit to Fringe Benefits Payable(depending on company)
How do you record employer payroll taxes?
Debit to Payroll Tax Expense
Credit to FICA Tax Payable
Credit to Unemployment Tax Payable
What are some other current liabilities?
- Deferred Revenues
- Sales Tax Payable
- Current portion of long-term debt
how to record deferred revenue
debit to cash, credit to sales revenue
Apple sells gift card to customer for $100
What is the journal entry?
Debit to cash for 100
Credit o deferred revenue for 100
Apple sells gift card to customer for $100
Customer spends $15 of it
what is the journal entry apple makes?
debit to deferred revenue for 15
credit to sales revenue for 15
What account classification is deferred revenue?
liability
What is the journal entry for sales tax payable?
Debit to cash
Credit to sales revenue
Credit to sales tax payable
A customer bought lunch in an airport for $15 plus 10% sales tax
What is the journal entry?
Debit to cash for 16.5
Credit to sales revenue for sales revenue
Credit to sales tax payable for 1.5
Suppose a company has a long-term note payable of $1,000,000. At the balance sheet date, the company determines that $200,000 of the note is due within the next 12 months (2025), while the remaining $800,000 is due in later periods (2026 and beyond). The company needs to reclassify $200,000 of the long-term note to current notes payable
Debit to Notes payable (long term)
Credit to Notes Payable (short term)
What is contingency?
uncertain situations that can result in a win or loss for a company
What is a contingent liability?
existing uncertain situation that might result in a loss
When do you report contingent liabilities?
when a loss is probable and the amount is reasonably estimable
How do you record a Contingent liability?
debit loss
credit contingent liability
If it is probable that Jeeps, Inc., will lose a $100 million lawsuit at some pointin the future, Jeeps records the following entry:
Debit to loss 100 mil
Credit to contingent liability for 100 mil
What is capital structure?
the mixture of debt and equity maintained by a firm
What are the 2 types of capital structure?
debt and Equity financing
What is debt financing?
funds raised through various forms of borrowing that must be repaid
What is equity financing?
obtaining investment from stockholders
Cost of Financing
-Debt: interest expense (tax-deductible)
-Equity: dividends (not tax-deductible)
examples of debt
notes, leases, and bonds
What is one advantage of debt financing?
interest on borrowed funds is tax-deductible
What is an installment note?
a debt that requires the borrower to make equal periodic payments to the lender for the term of the note
What do installment notes include?
interest on borrowed amount
Reduction of outstanding loan balance
How do companies normally borrow cash?
using installment notes
What is the amortization schedule for an installment notes?
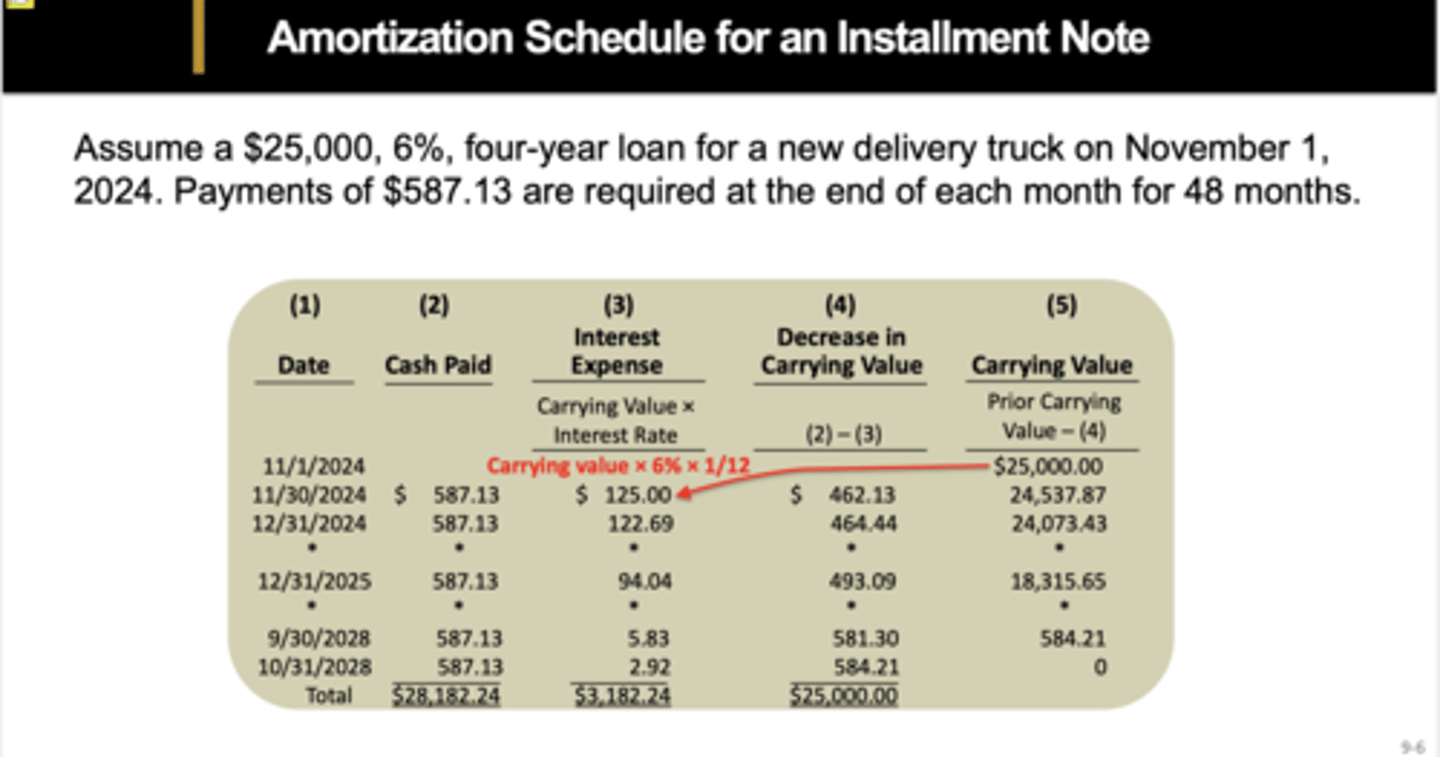
Installment note transaction establishment of the note payable
debit to cash
credit to notes payable
what is a lease?
an agreement by which the owner allows users to use an asset for a period of time
What is the transaction for a lease by the owner?
debit to lease asset
credit to lease payable
How do you calculate present value of lease payments?
ordinary annuity x monthly lease payment
What is a bond?
a formal debt instrument issued by a company to borrow money
How to record a bond issue?
debit to cash
credit to bonds payable
How to record an interest payment?
debit to interest expense
credit to cash
how to retire a bond?
debit bonds payable
credit to cash
Future Value
how much the money today will grow in the future
Present Value
the amount of money you would need to deposit now in order to have a desired amount in the future
annuity
payment received every year
What are the characteristics of bonds?
Secured
Unsecure
Term
Serial
Callable
Convertible
Secured Bonds
are backed by collateral
Unsecure Bonds
not backed by collateral
Term Bonds
bonds that all mature at the same time
serial bonds
bonds issues matures in installments
Callable Bonds
Issuing company can pay off bonds early
Convertible Bonds
investor can convert bonds to common stock
Debt to Equity Ratio
the higher debt to equity ratio, the higher the risk of bankruptcey
What are the stages of equity financing?
1) investment by the founders of business
2) investment by friends and family of founders
3) outside investment by "angel" investors and venture capital firms
4) initial Public Offering (IPO)
What are the types of common stock?
authorized, issued, outstanding, treasury
Authorized stock
shares available to sell (issued+unissued)
Issued stock
Shares actually sold (outstanding+treasury)
Outstanding stock
shares issued and held by investors
Treasury stock
shares issued and repurchased by the company
Purchase of Treasury Stock journal Entry
debit treasury stock, credit cash
Resale of treasury stock journal entry(above cost)
debit cash, credit treasury stock, credit additional paid-in capital
Resale of treasury stock journal entry(below cost)
debit cash, debit additional paid in capital, credit treasury stock
Journal entry for authorized stock
no journal entry
journal entry for common stock no par value
debit cash, credit common stock
journal entry for common stock par value
debit cash, credit common stock, credit additional paid-in capital
Journal entry for preferred stock
debit cash
credit preferred stock
credit additional paid in capital
What 2 stocks make up issued stock?
outstanding stock and treasury stock
par value
the amount that an investor pays to purchase a bond and that will be repaid to the investor at maturity
How does preferred stock differ from common stock?
1. Preferred stock allows different voting rights
2. Dividends on preferred stock, if any, may be paid at a fixed rate
3. Preferred stock carries priority over common stock
What are the features of preferred stock?
Convertible- shares can be exchanged for common stock
Redeemable- shares can be returned to the corp. at a fixed price
Cumulative- shares receive priority for future dividends if dividends are not paid in a given year
Why do corporations have treasury stock?
1. to boost underpriced stock
2. to distribute surplus cash without paying dividends
3. to boost earnings per share
4. to satisfy employee stock ownership
Retained Earnings
An amount earned by a corporation and not yet distributed to stockholders.
What is the formula for retained earnings?
all net income - dividends
Does retained earnings differ from cash?
yes
cash dividend
a cash distribution of earnings by a corporation to its shareholders
What is the journal entry for cash dividends?
debit dividends, credit dividends payable
What is the jounral entry for when the dividend gets paid?
debit to dividends payable, credit to cash
Stock dividend
Corporation's distribution of its own stock to its stockholders without the receipt of any payment.
Journal entry for stock dividend
debit used to reduce retained earnings and credit records items distributed (cash or stock)
Stock split
the division of a single share of stock into more than one share
How does a stock split effect SE?
it does not
How does a stock split impact a stock price?
A stock split lowers the stock price
How do you calculate stockholders equity?
Stockholders' Equity = Common Stock + Retained Earnings
Operating Activities
cash receipts and cash payments for transactions relating to revenue and expense activities
investing activities
transactions involving the purchase and sale of long-term assets and current investments
Financial Activities
cash inflows and outflows from transactions with creditors and owners
Operating activities involving the indirect method
1. Begin with net income
2. list adjustments to net income to arrive at operating cash flows
3. most popular
4. easier and less costly
Vertical Analysis
expressing each item in a financial statement as a percentage of the same base amount
horizontal analysis
analyzing trends in financial statement data for a single company over time
Formula for horizantal analysis
(current year-base year)/base year