Dental radiology class
1/138
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
139 Terms
Radiation
Energy that is radiated in the form of rays or waves or particles.
X-radiation
A high-energy radiation produced by the collision of a beam of electrons with a metal target in an x-ray tube
X-ray
a beam of energy that has the power the penetrate substances. could also record images on receptors
radiograph
2D image representation of a 3D object
image receptor
A recording medium; examples include x-ray film, phosphor plate, or digital sensor
why do we take dental radiographs?
documentation, , patient education, treatment plan, localize disease, detect lesions, classify disease, evaluate growth and development, get a baseline
who is father of x-ray?
Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen
Pariapical radiograph
taken to assess bone levels
bitewing x-rays
looking at interproximal spaces to assess for caries
occlusal exam
-examine large areas of the maxilla or mandible on one image
complete/full mouth series
a series of intraoral dental images that show all the tooth-bearing areas of both jaws
images ranges from 14-20
Extraoral imaging examination
inspection used to examine large areas of the skull or jaws
descriptive terminology terms used for lesions
appearance, size, and location
Radiolucent
appears dark on a x-ray due to x-ray being able to pass through space or tissue
Radiopaque
white or light grey on a image due to x-ray not being able to penetrate it
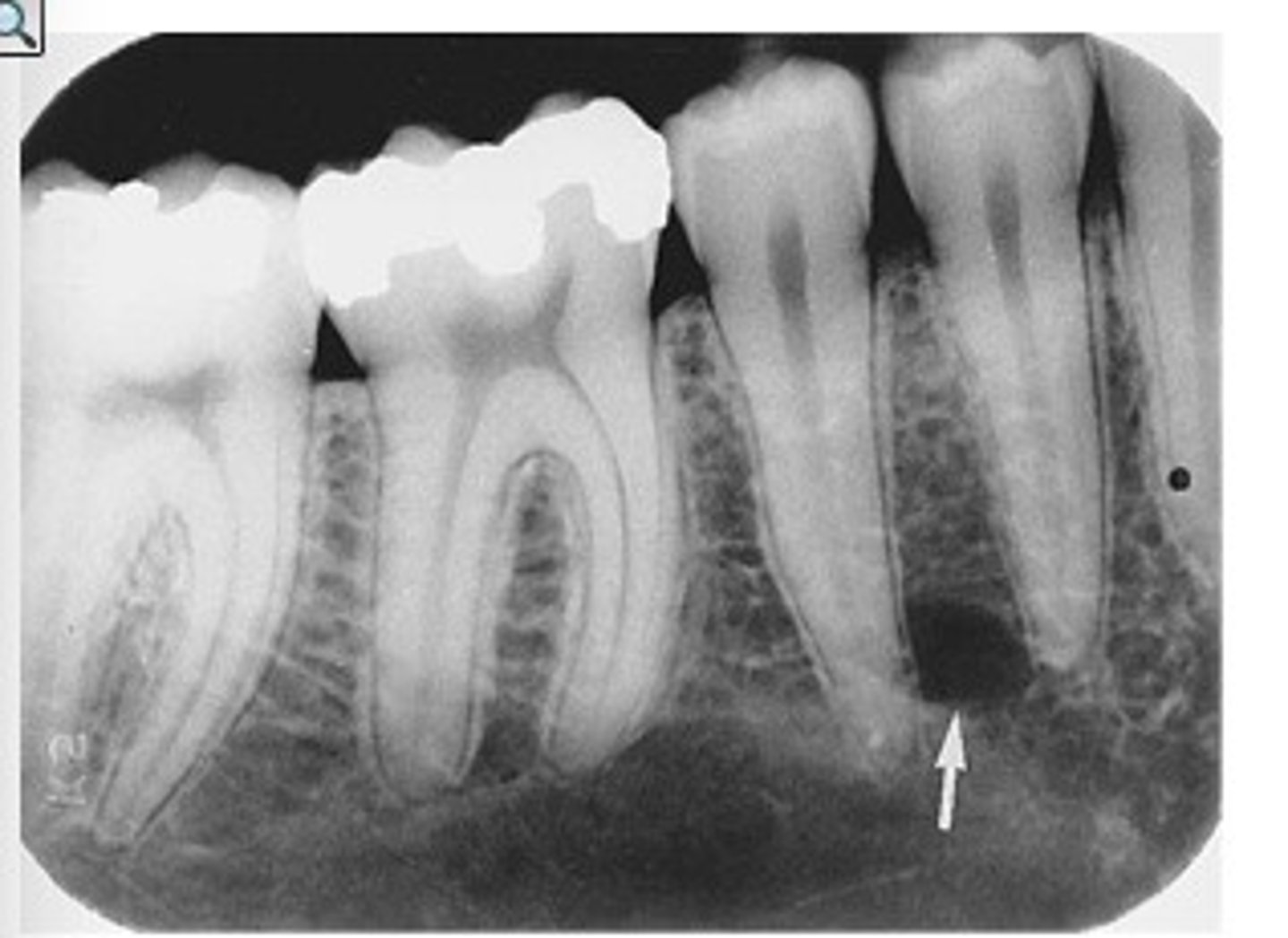
radiolucent lesions
corticated or non corticated
corticated
thin, well-defined radiopaque rim of bone around radiolucent lesion
non corticated
No well-defined outline around a radiolucent lesion

Unilocular
having a single cavity/bubble
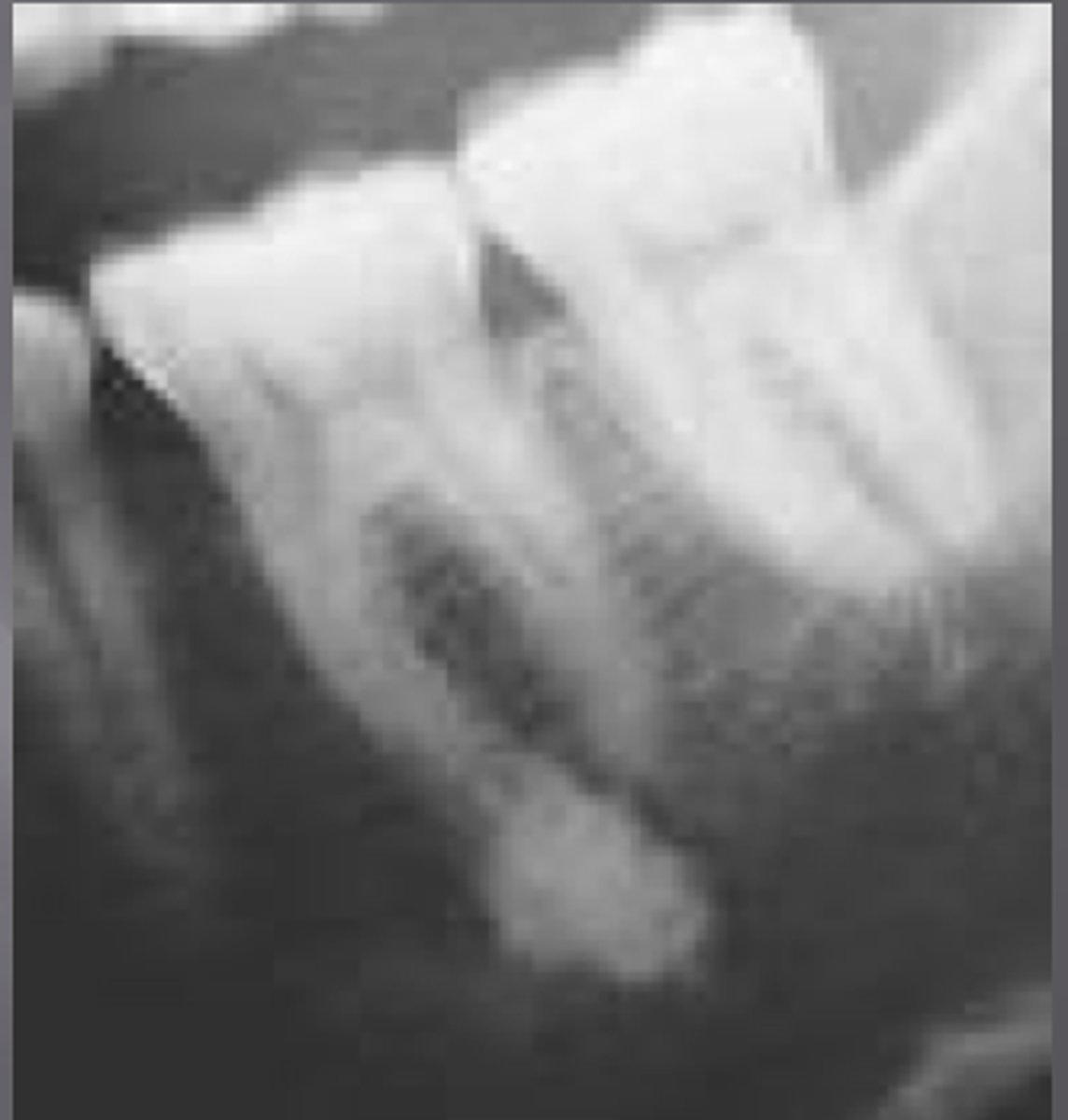
multilocular
multiple cavieties/bubbles
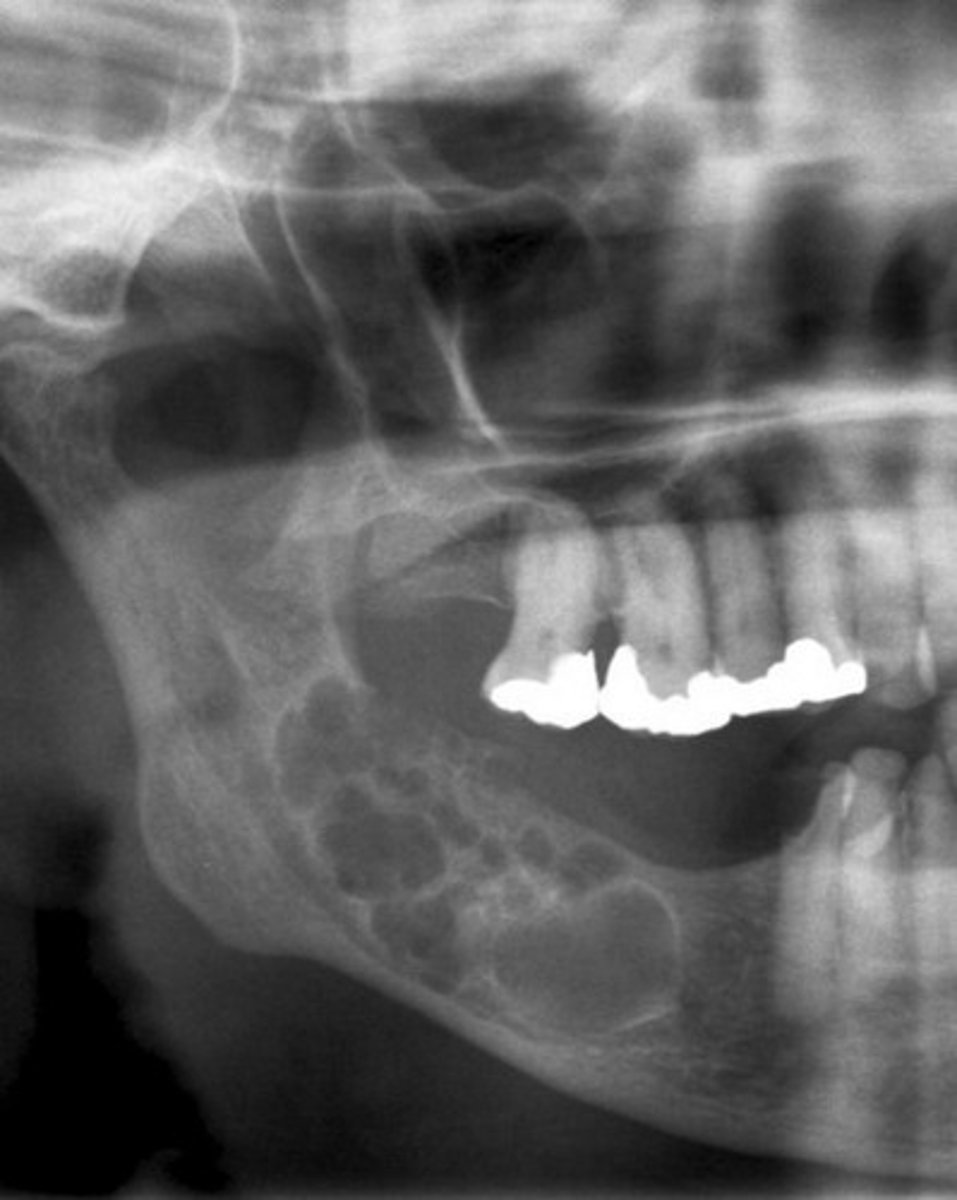
moth-eaten
full of small holes
focal opacity
well-defined, localized radiopaque lesion
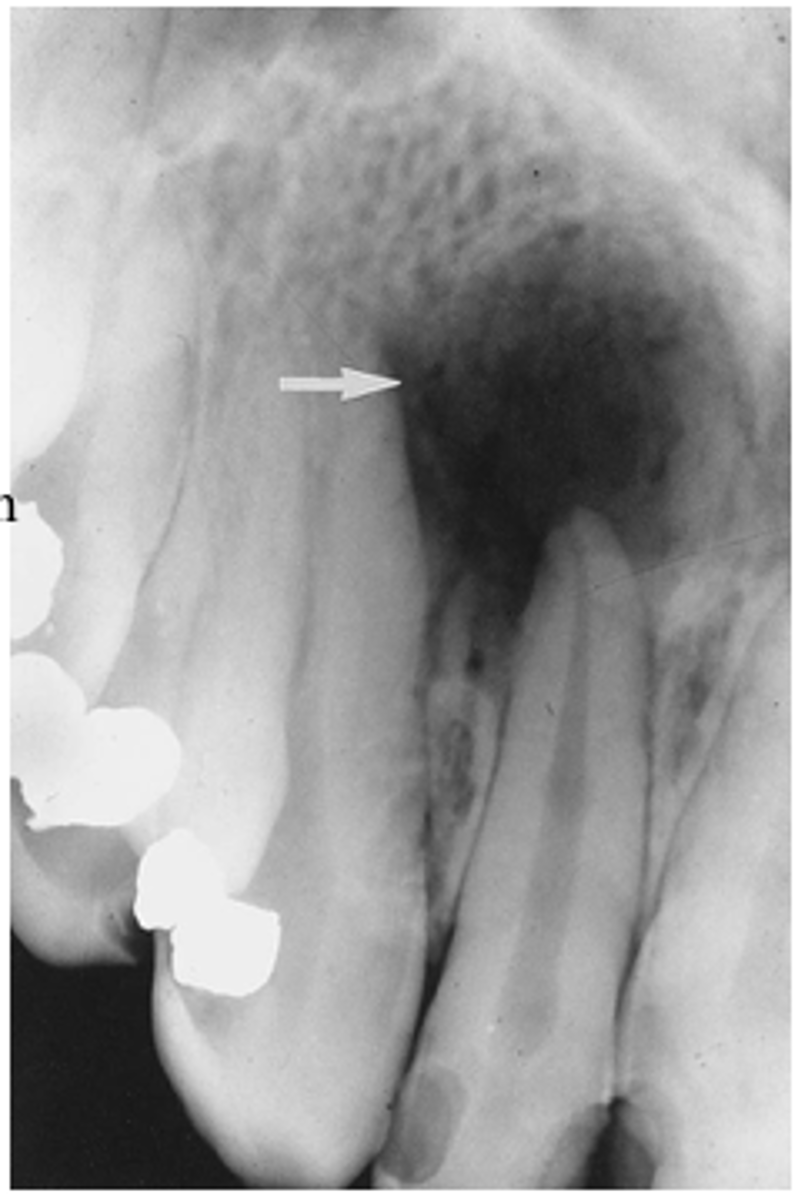
target lesion
has a radiolucent rim and has radiopaque inside
multifocal confluent pattern
multiple radiopacities that appear to overlap or flow together
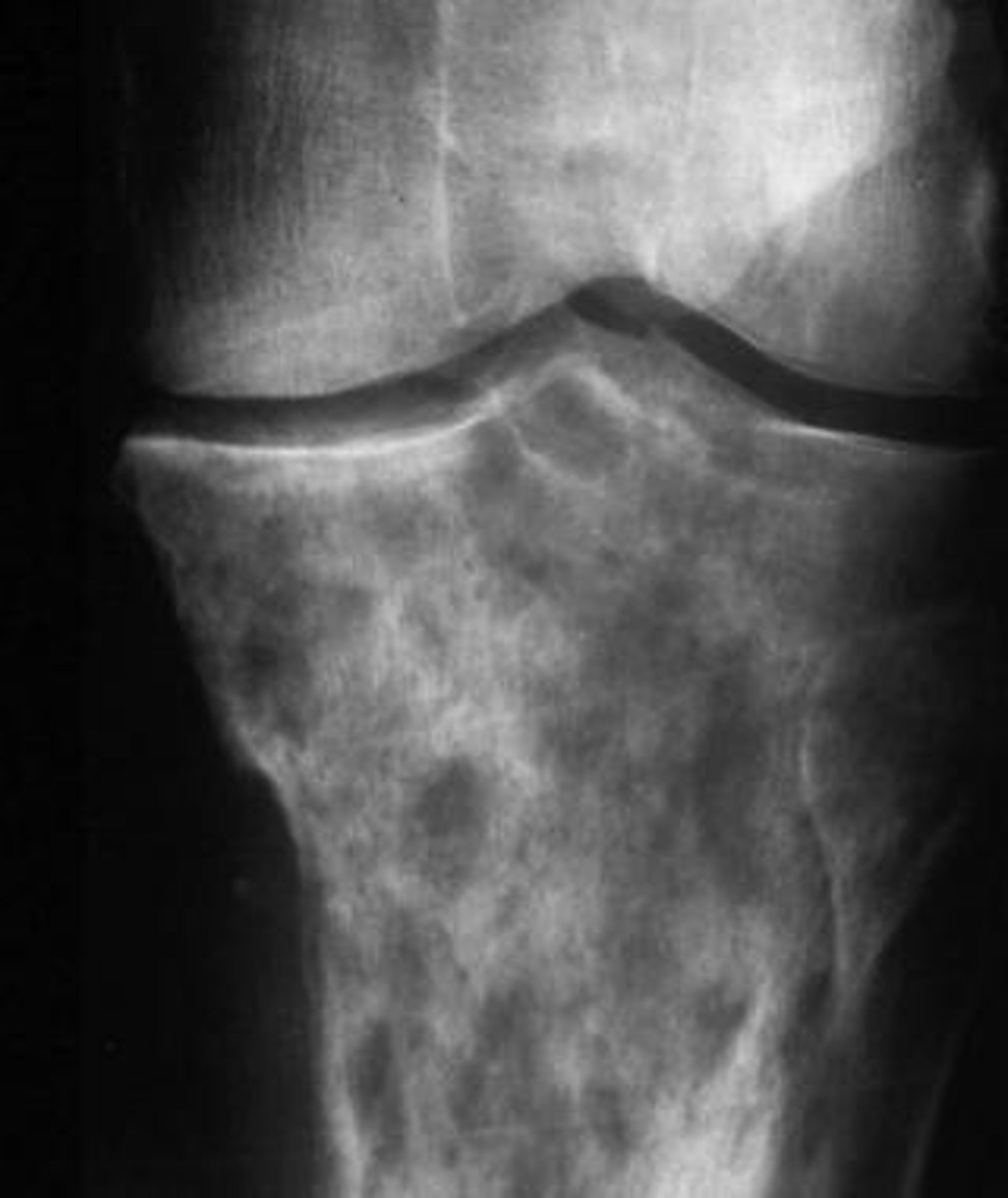
ground glass opacity
granular or pebbled radiopacity, resembling pulverized glass. Gives an "Orange Peel" appearance.
Mixed lucent-opaque lesion
Exhibits both a radiopaque and a radiolucent component
periapical
Around the apex of the tooth
inter-radicular
between the roots of two adjacent teeth
pericoronal
around crown of unerupted tooth
Edentulous zone
tooth bearing area that do not have teeth
cortical bone intraoral images
normally looks radiopaque
cancellous bone intraoral images
radiolucent
process (radiopaque)
any bony prominence or projection of bone
ridge (radiopaque)
linear prominence
spine (radipaque)
tubercle (radiopaque)
A small bump or nodule of bone
Tuberosity ( radiopaque)
rounded prominence
canal (radiolucent)
tube like passage
cavity (radiolucent)
compartment of bone
formane (radiolucent)
small little hole
fossa ( not so dense)
shallow depression
sinus (radiolucent)
hollow space or cavity in bone
suture ( radiolucent)
immovable joint the represents the union of two bones
septum ( radiopaque)
bony wall that separates cavities
pulp chamber is:
radiolucent
incisive foramen is :
radiolucent
the median palatine suture is :
radiolucent
the nasal cavity is:
radiolucent
the nasal septum is:
radiopaque
the lateral fossa is :
radiolucent
inferior nasal conchea is:
radiopaque
the lamina dura is:
radiopaque
lingual foramen is:
radiolucent
mental fossa is:
radiolucent
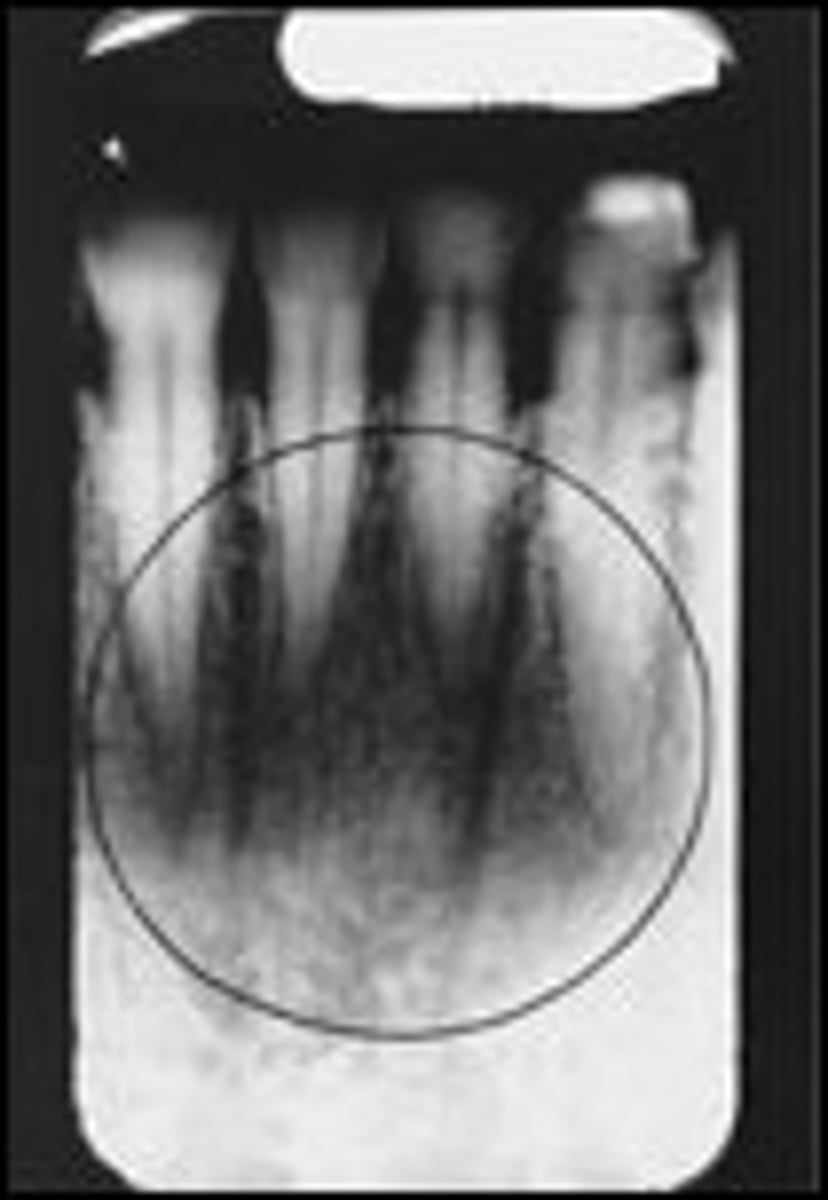
hamulus
hook-like bone that is radiopaque
who developed the first x-ray unit?
William H. Rollins
Dental Radiographer
Any person who positions, exposes, and processes dental x-ray imagereceptors
what are the three types of Intraoral Imaging Examinations?
periapical, interproximal, and occlusal technique
what is a corticated radiolucent lesion indicative of?
benign, slow-growingprocess
what is a non-corticated radiolucent lesion indicative of?
benign or malignant process
what is a Multifocal confluent pattern?
multiple radiopacities that appear to overlap or flow together
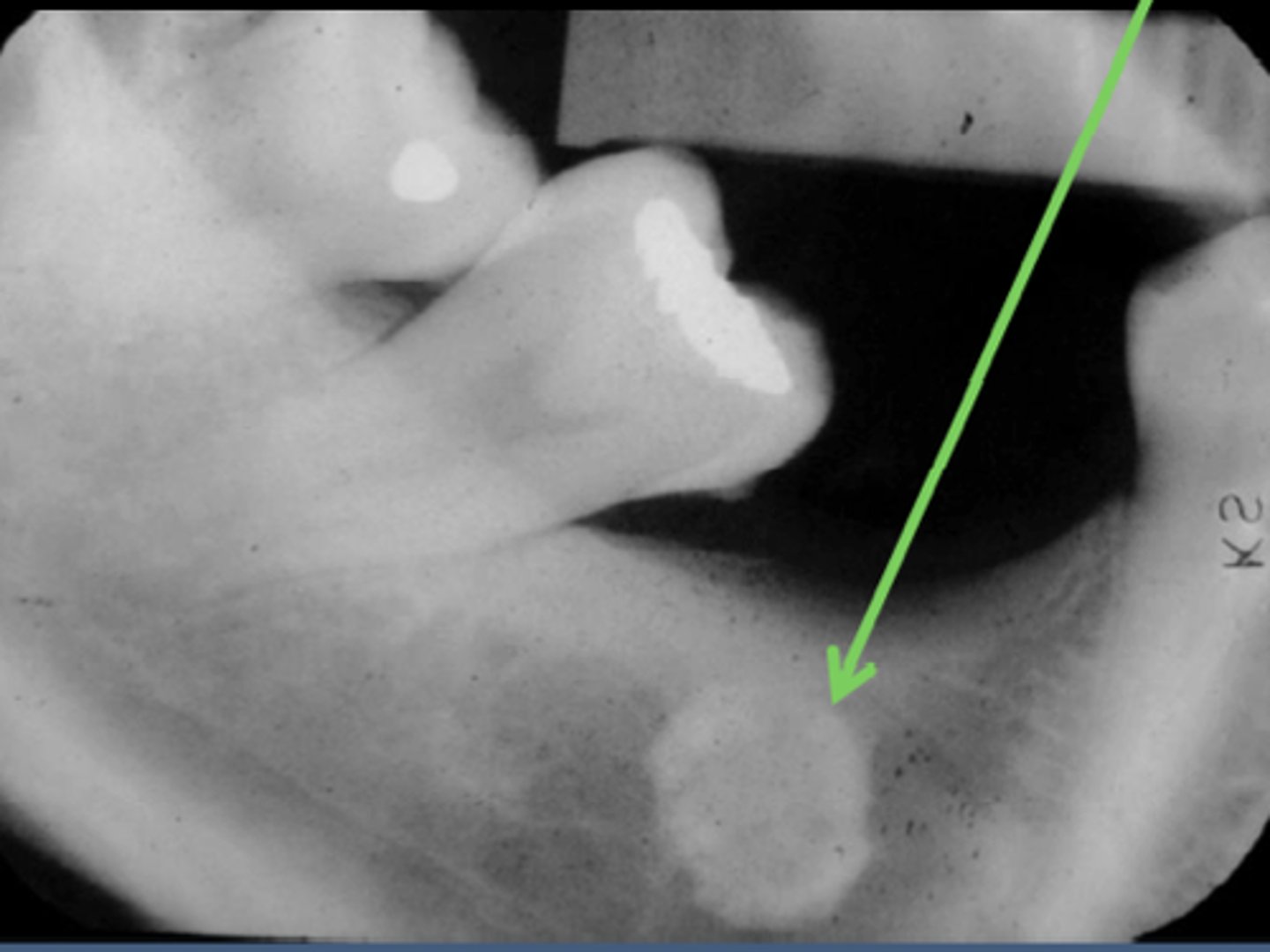
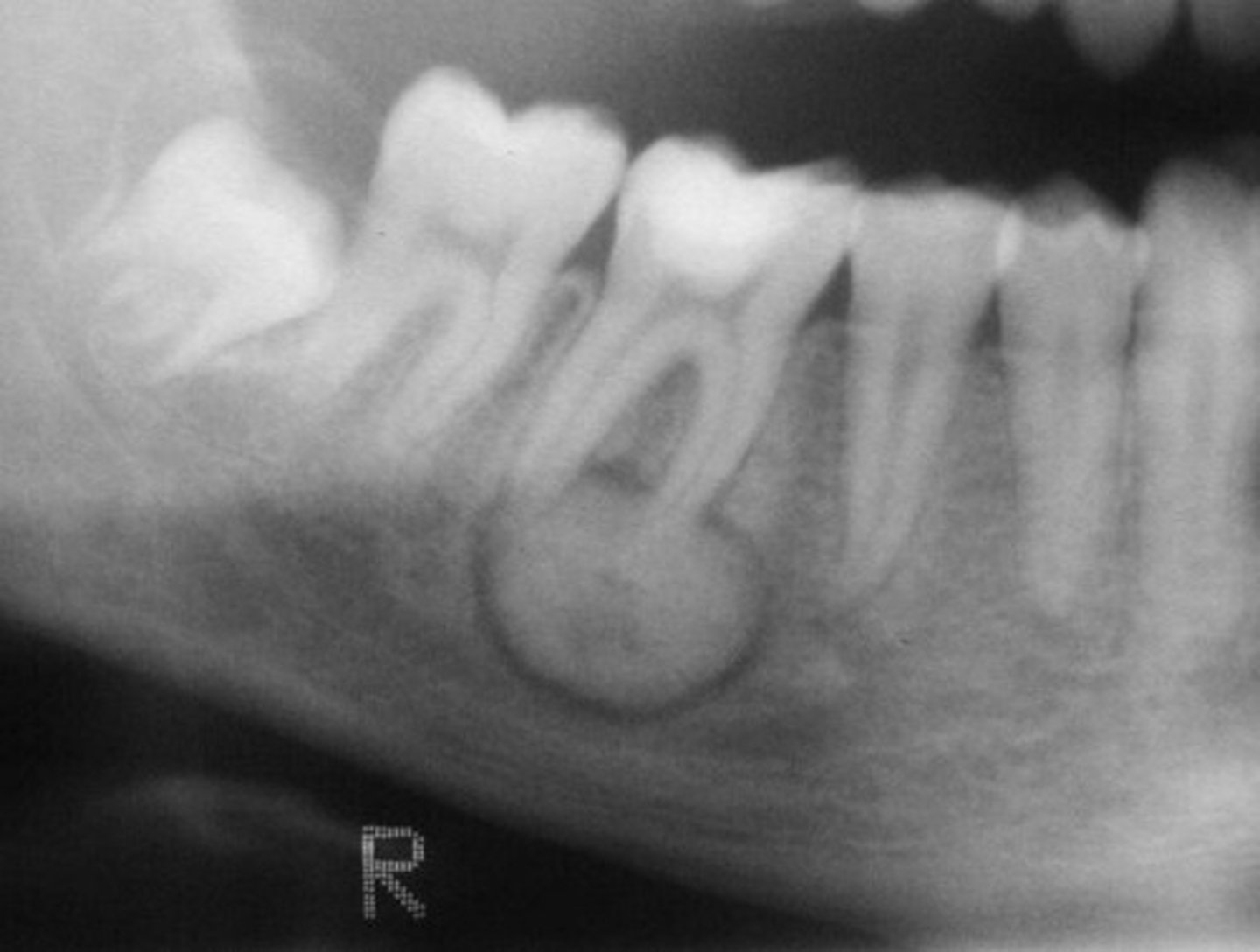
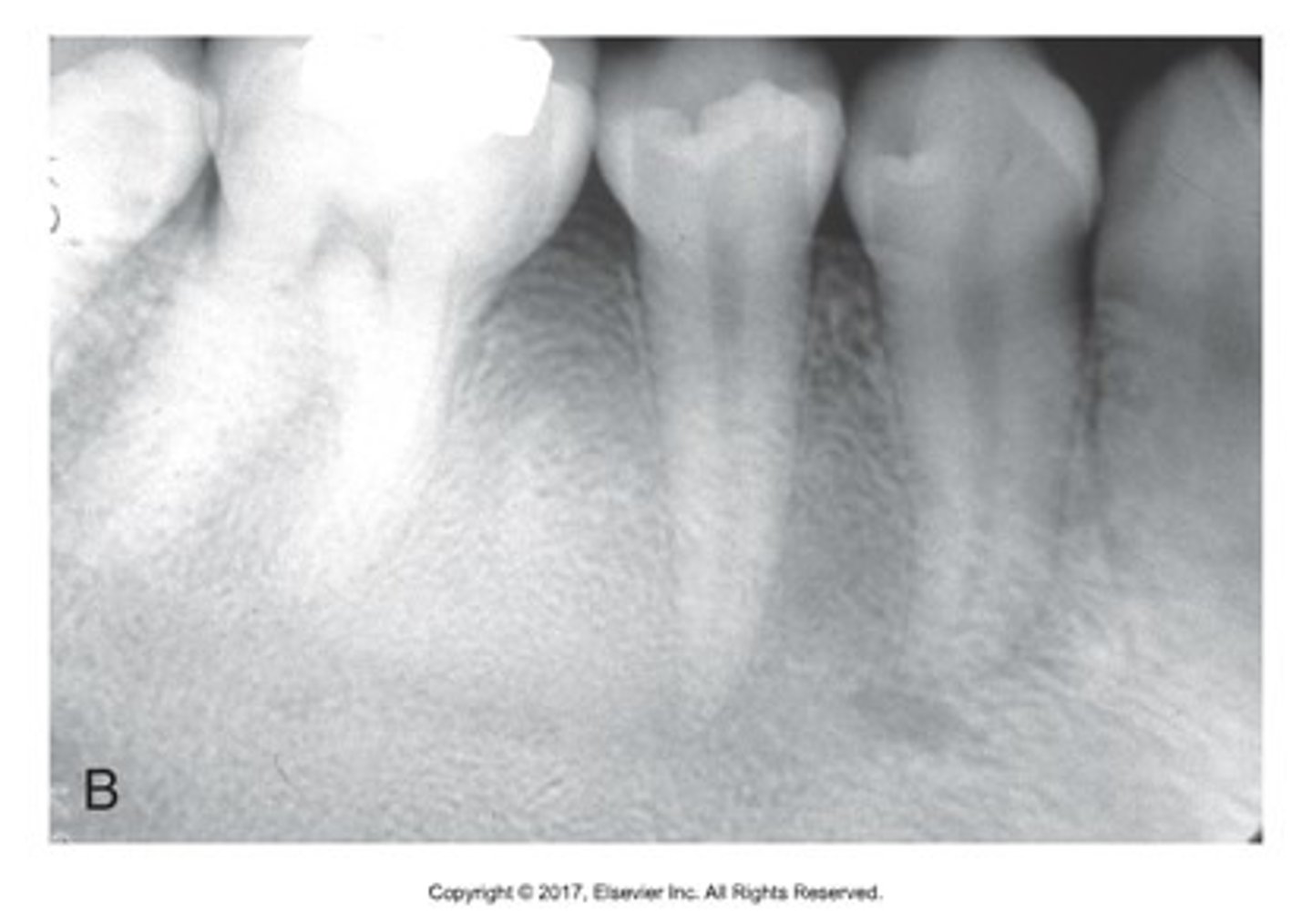
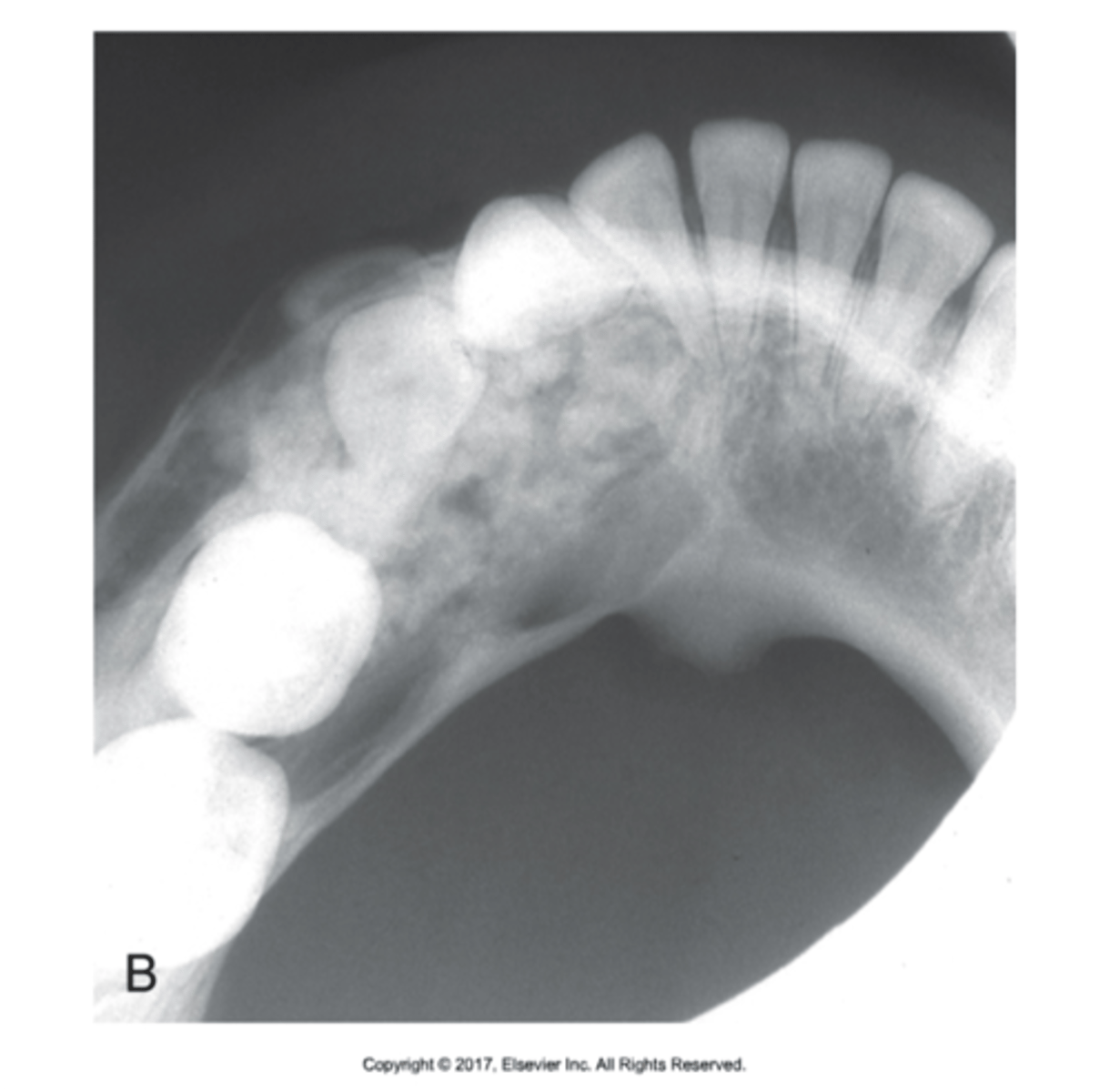
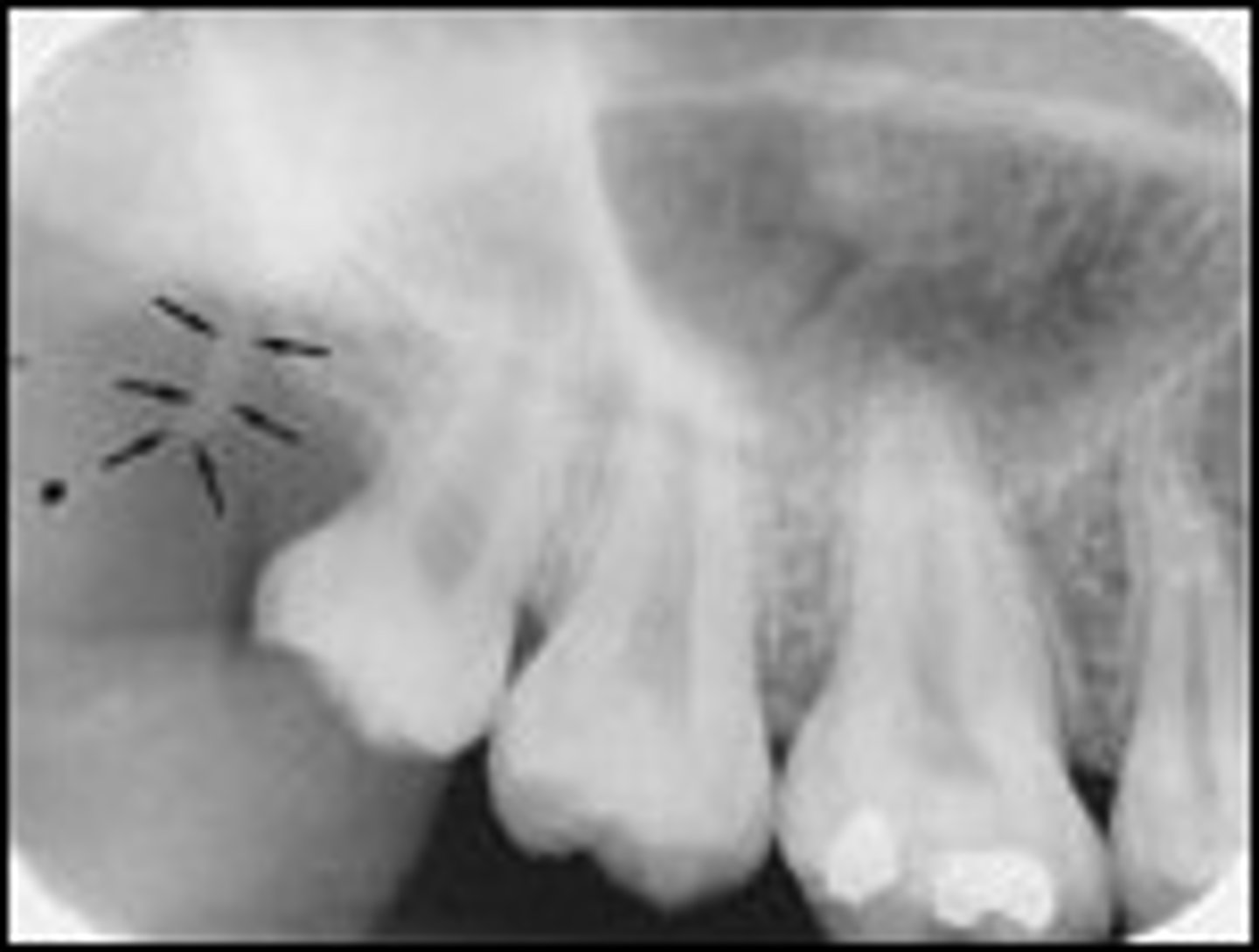
what is this?
what is this?
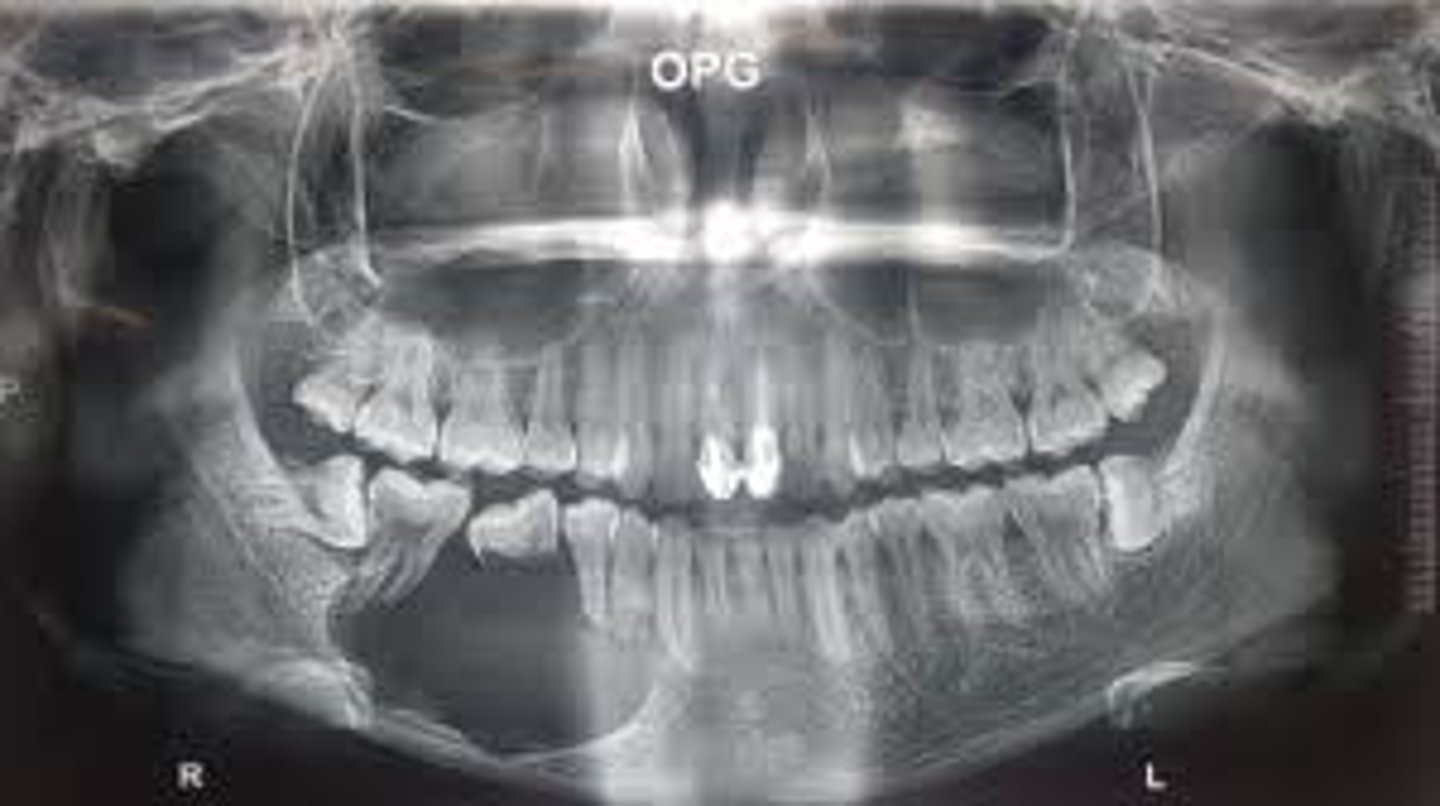
what is this?
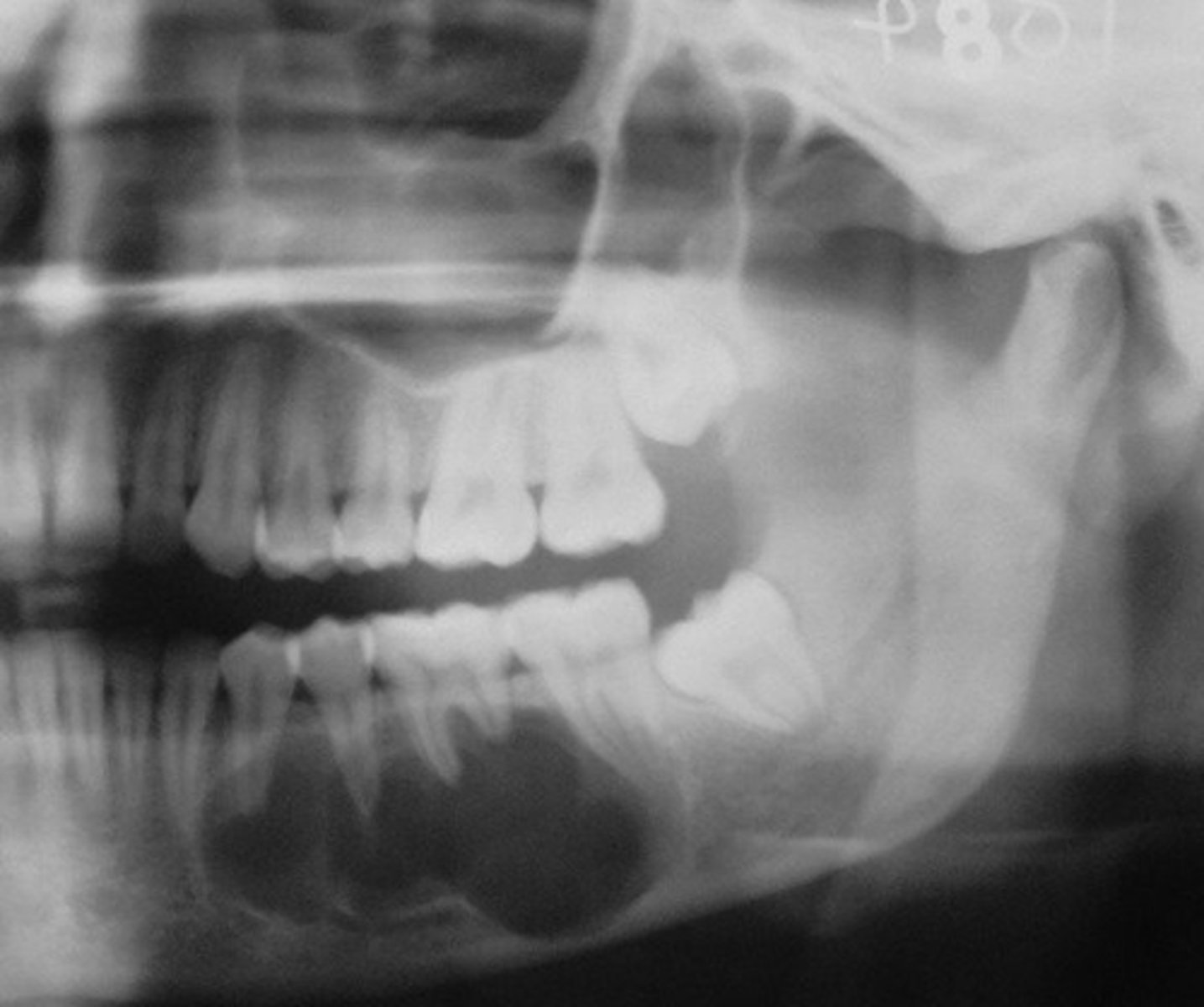
what is this?
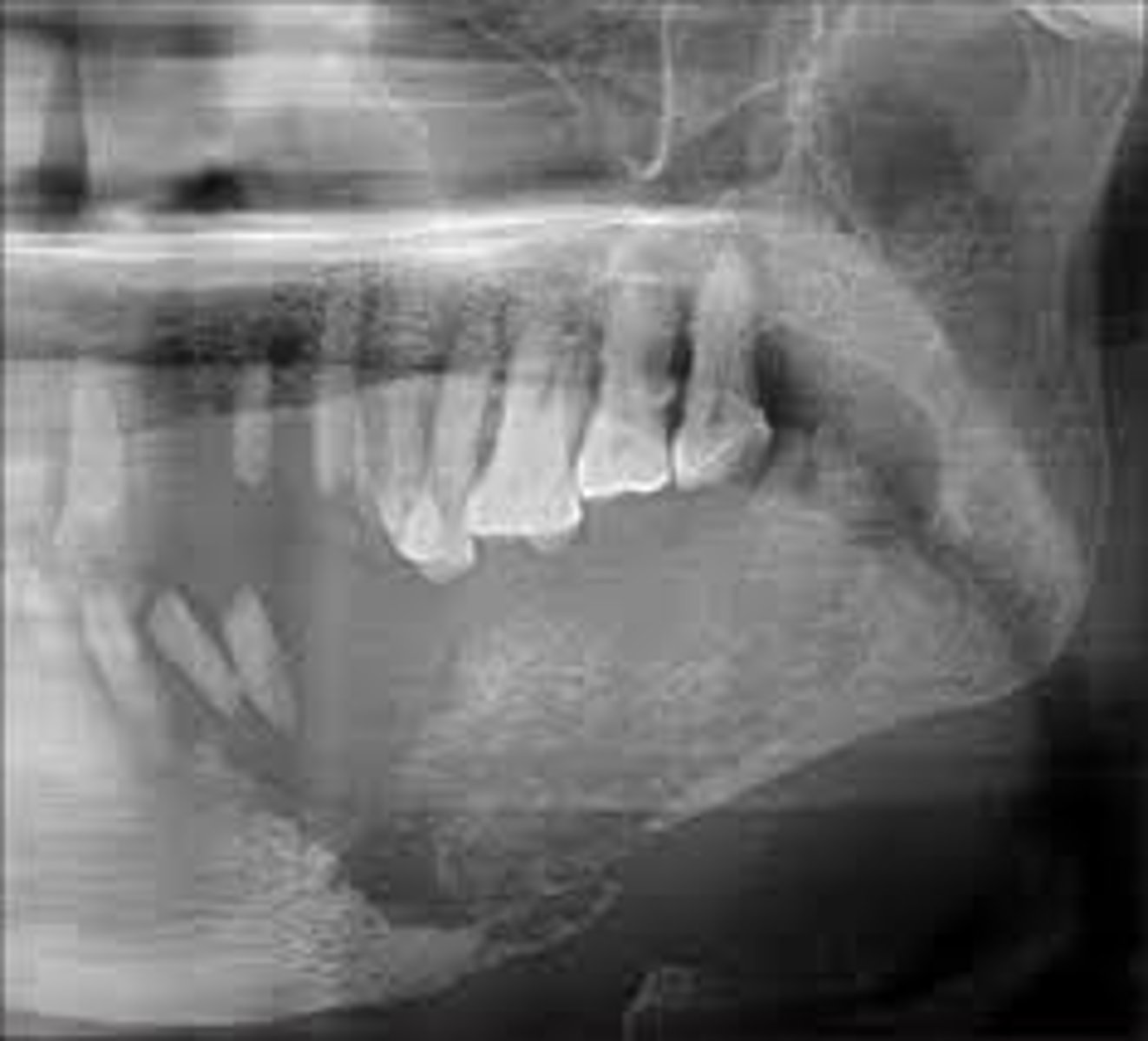
what is this?
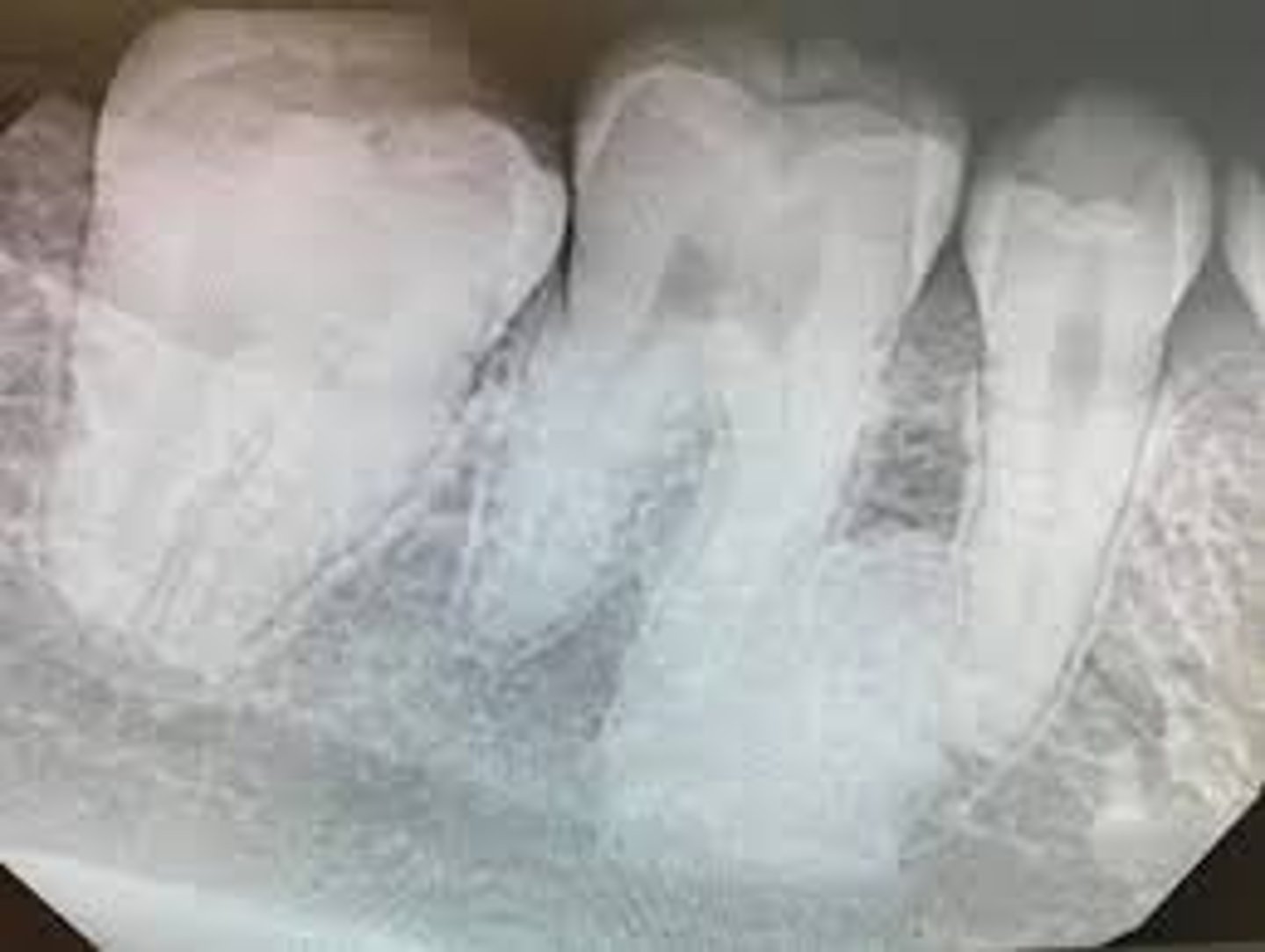
what is this?
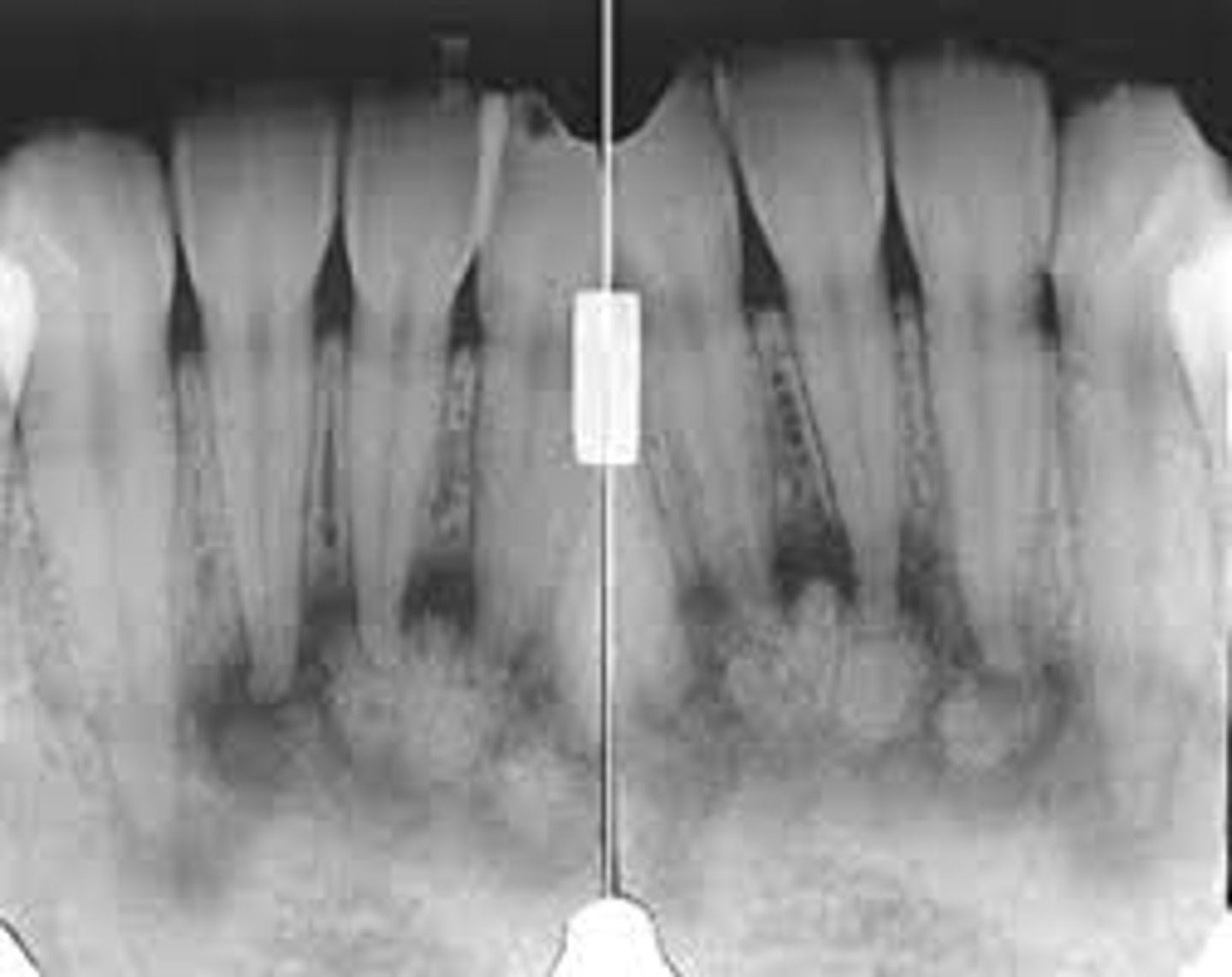
what is this?
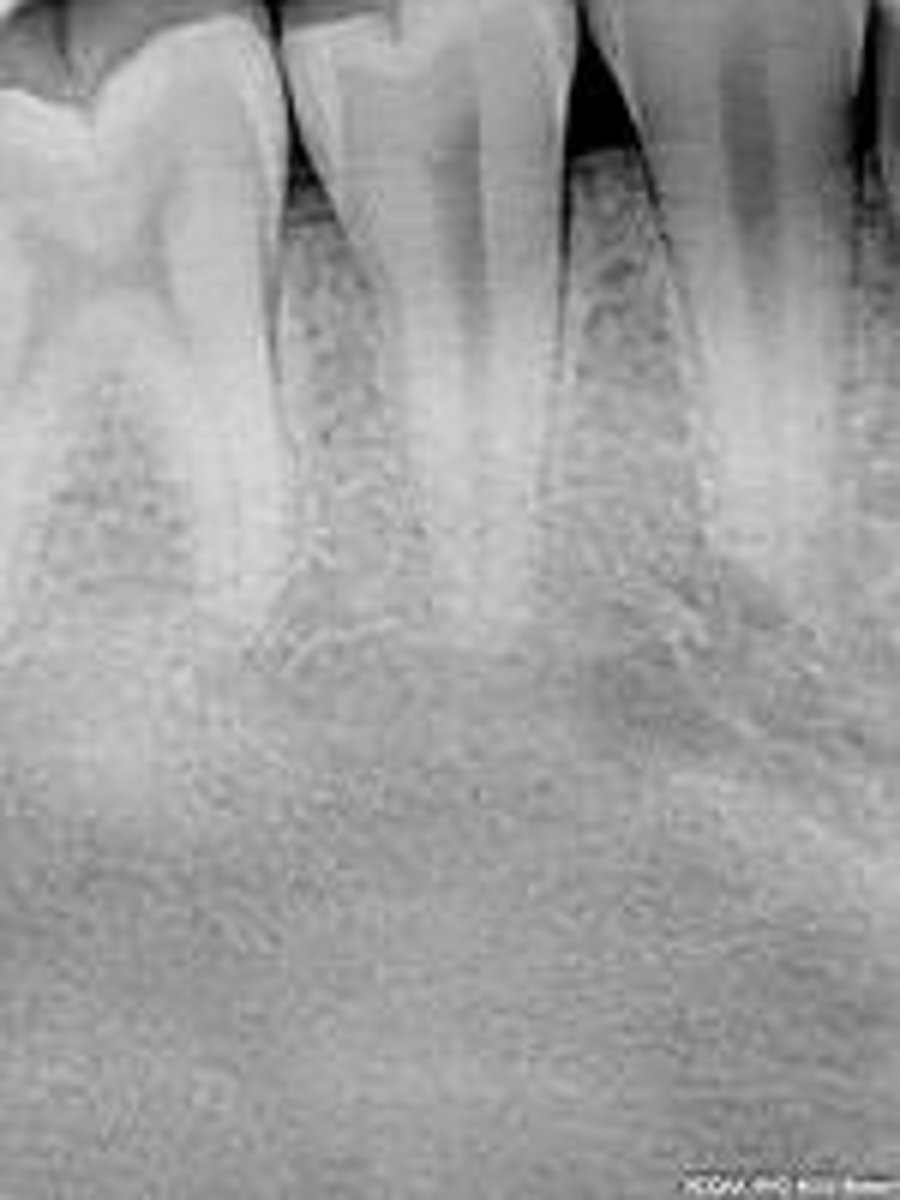
what is this?
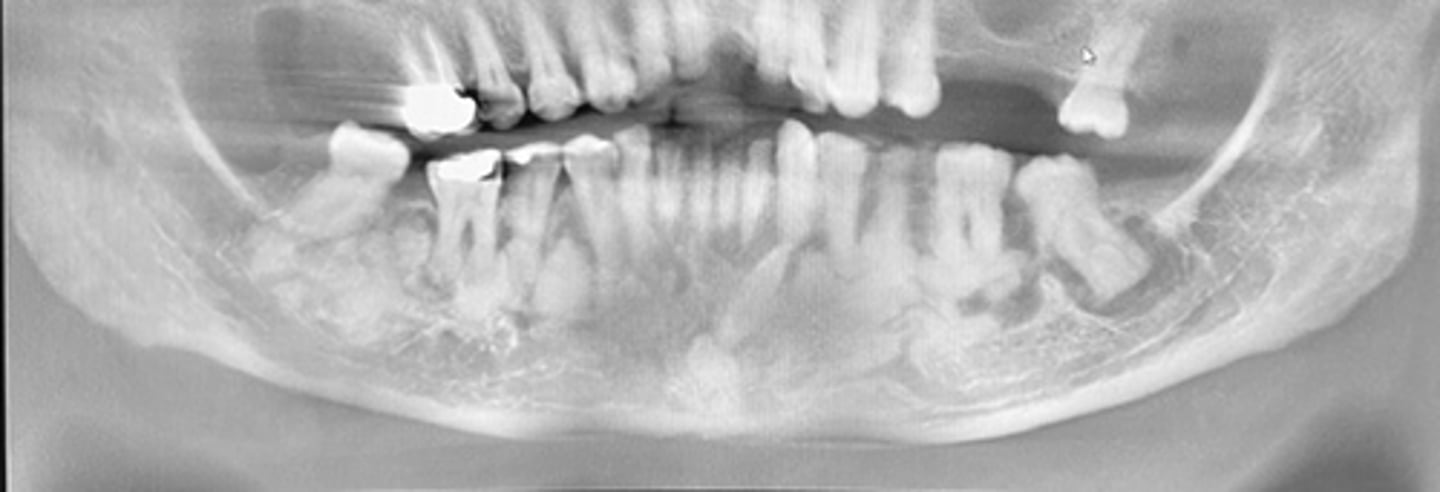
what normal anatomies are radiolucent?
canals, sinuses, foramen, fossas, sutures, and cavities
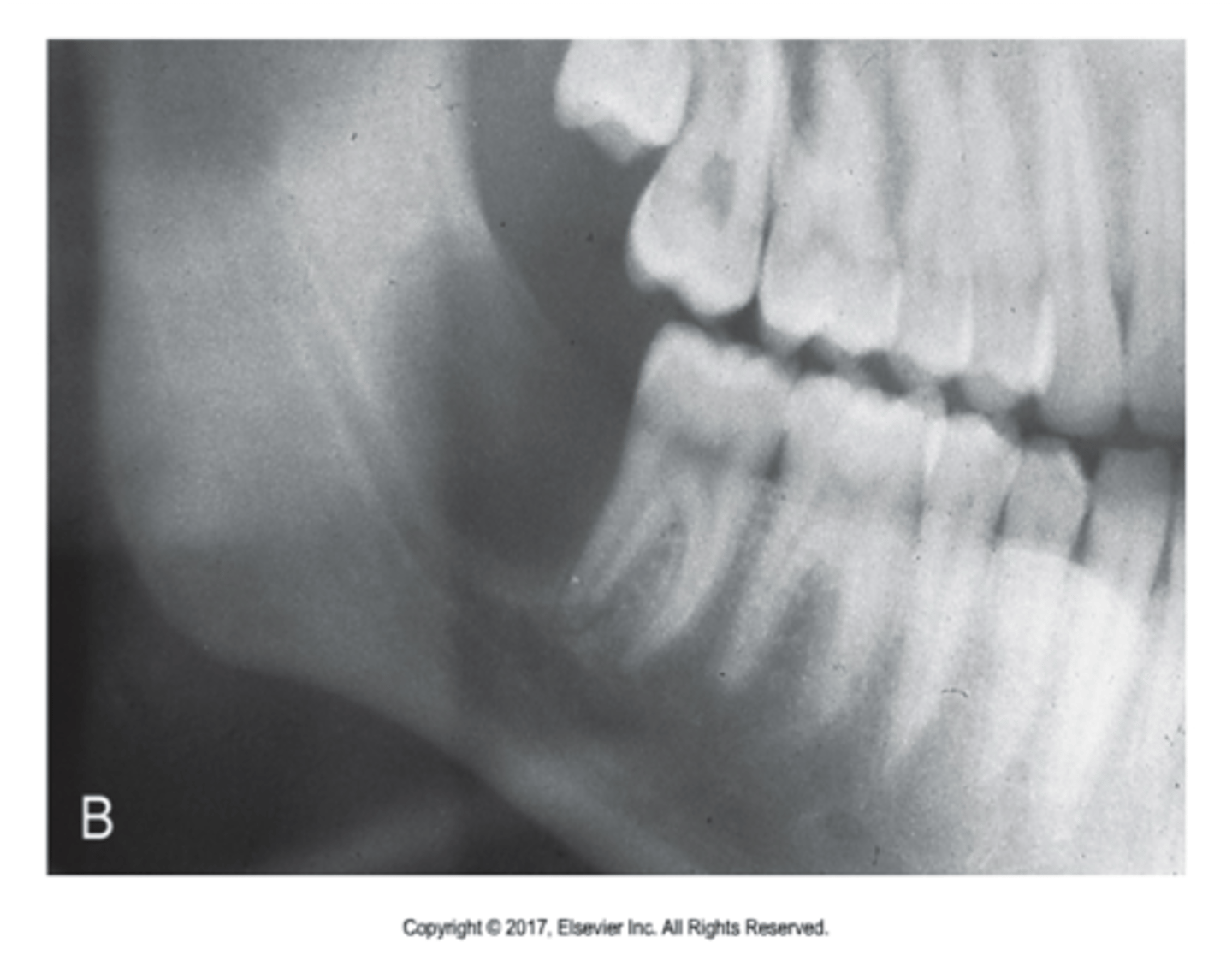
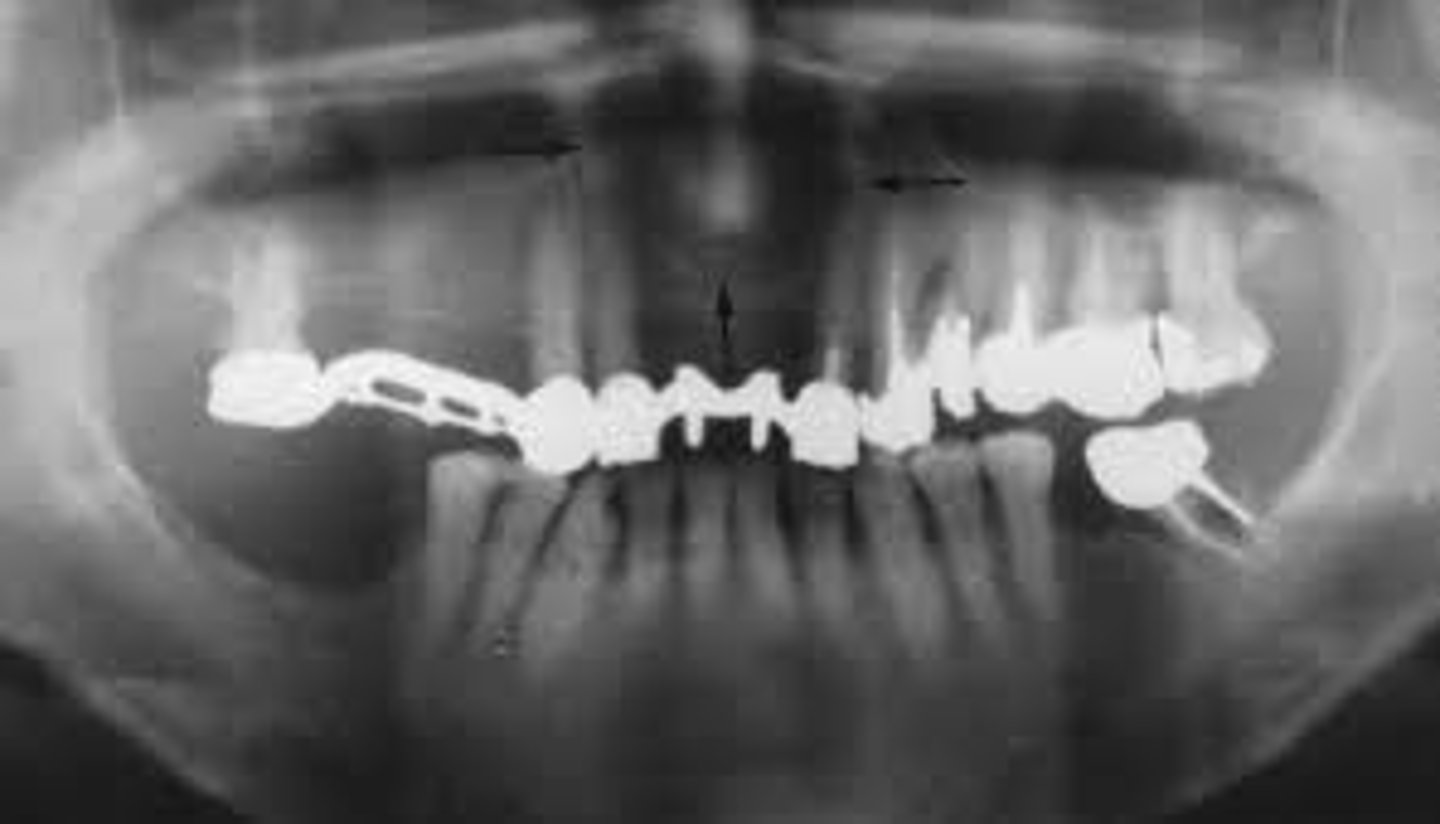
what is this?
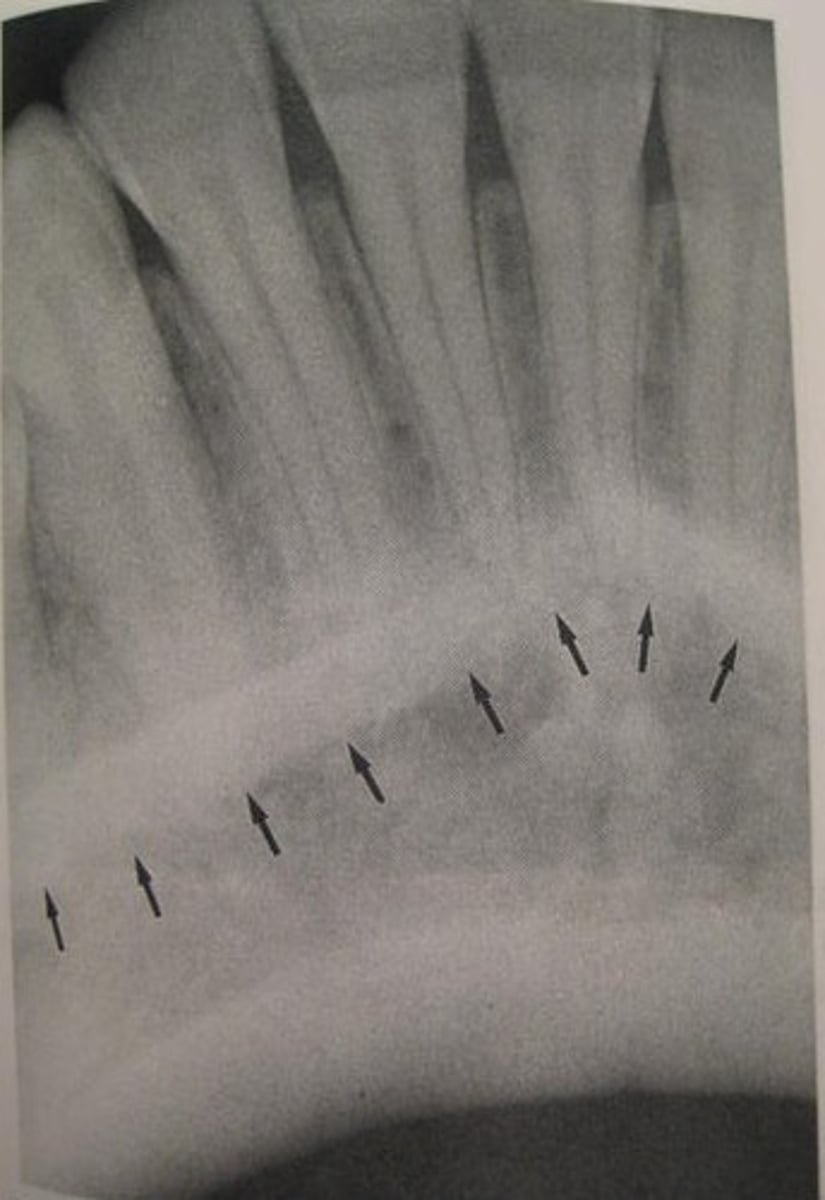
what is this?
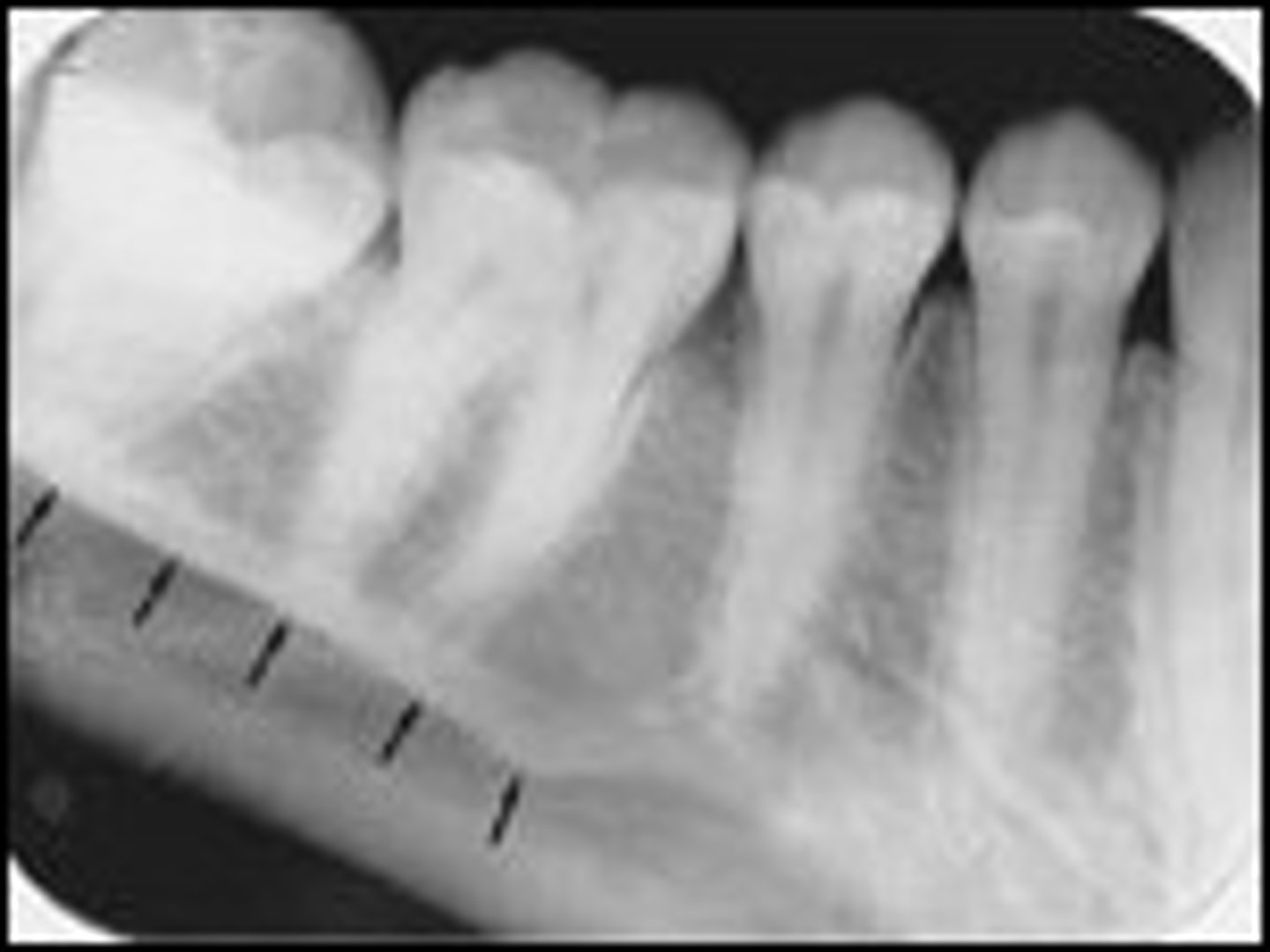
what is this?
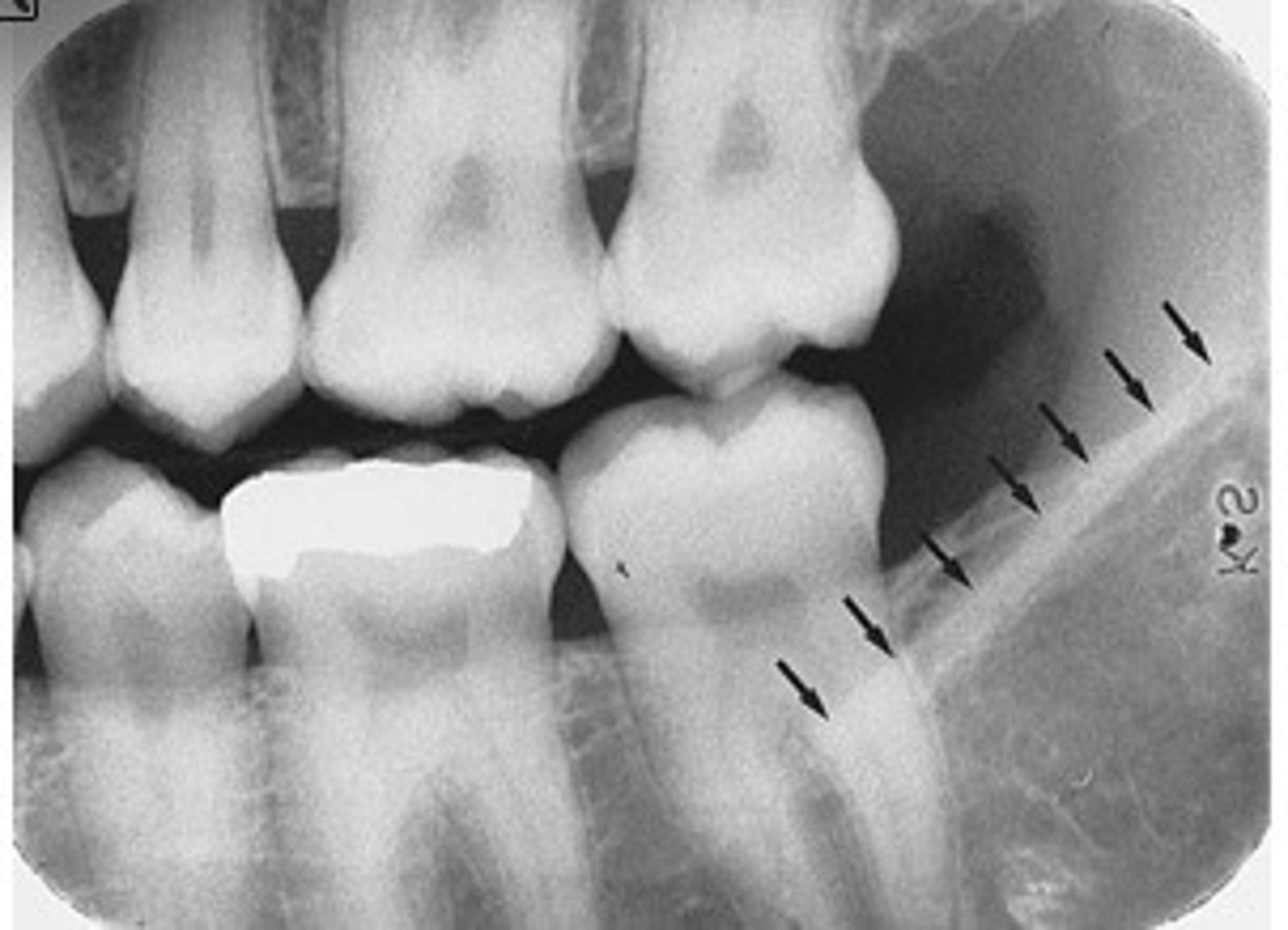
what is this?
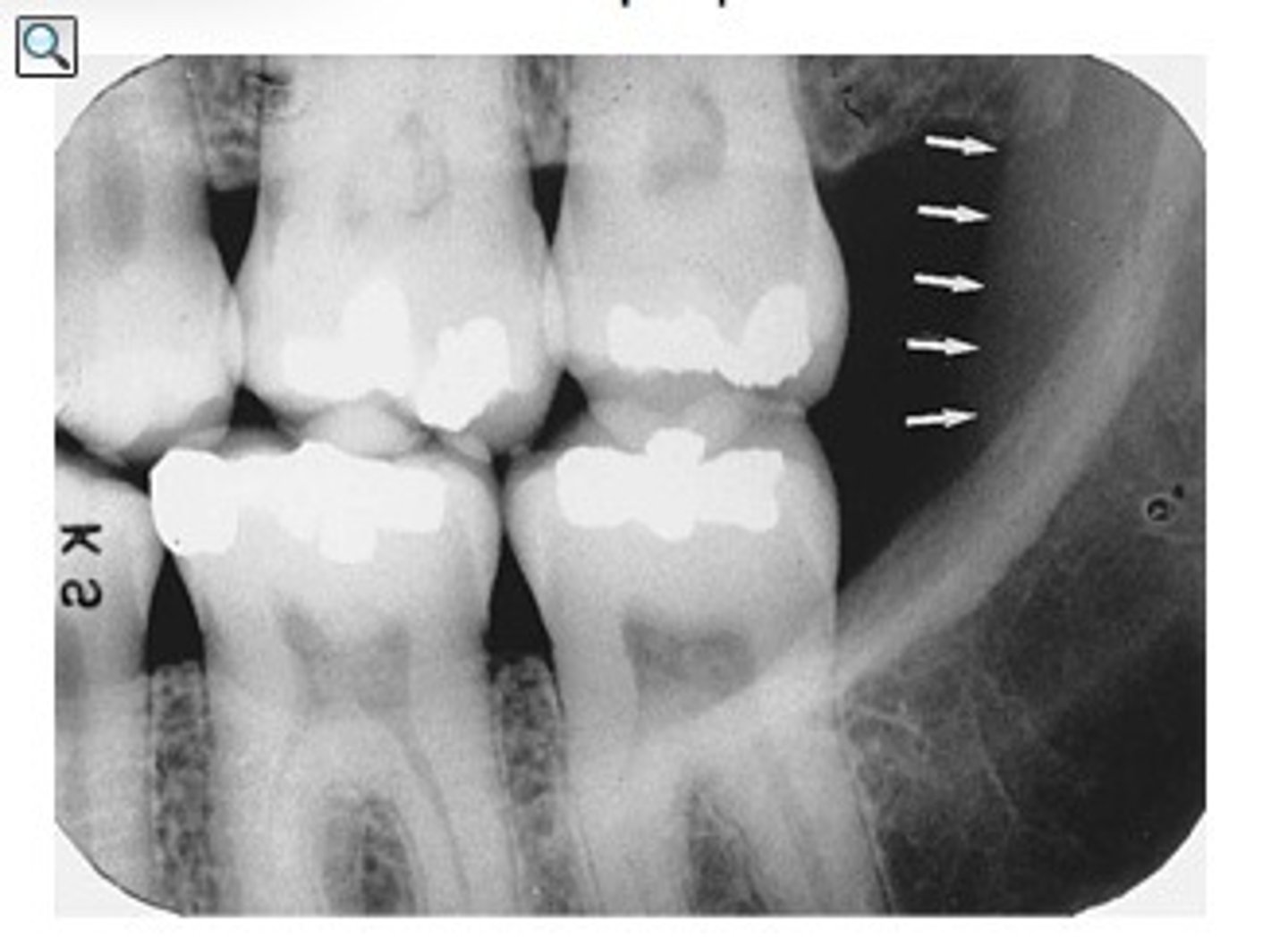
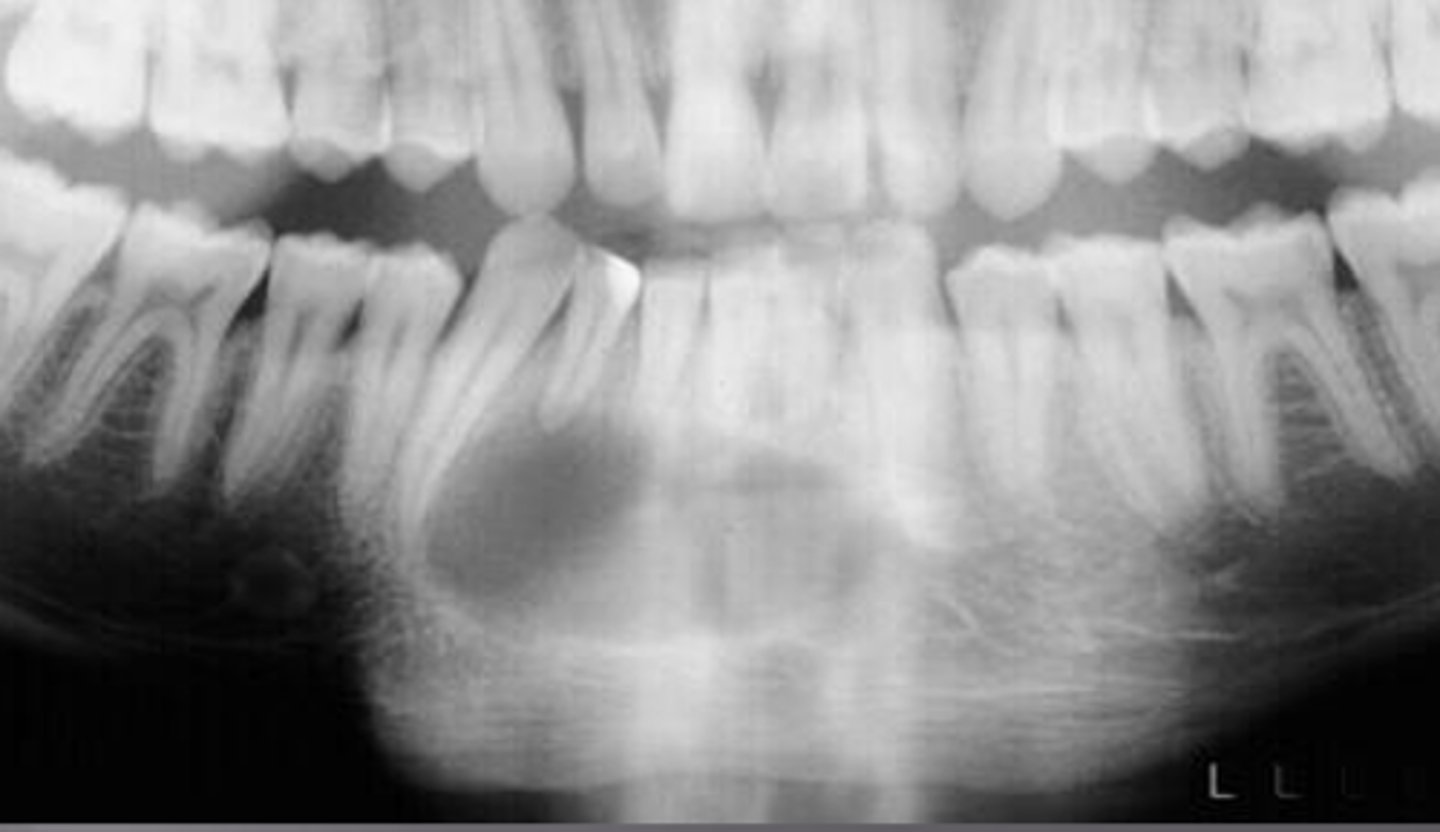
what is this radiolucent area in the image?
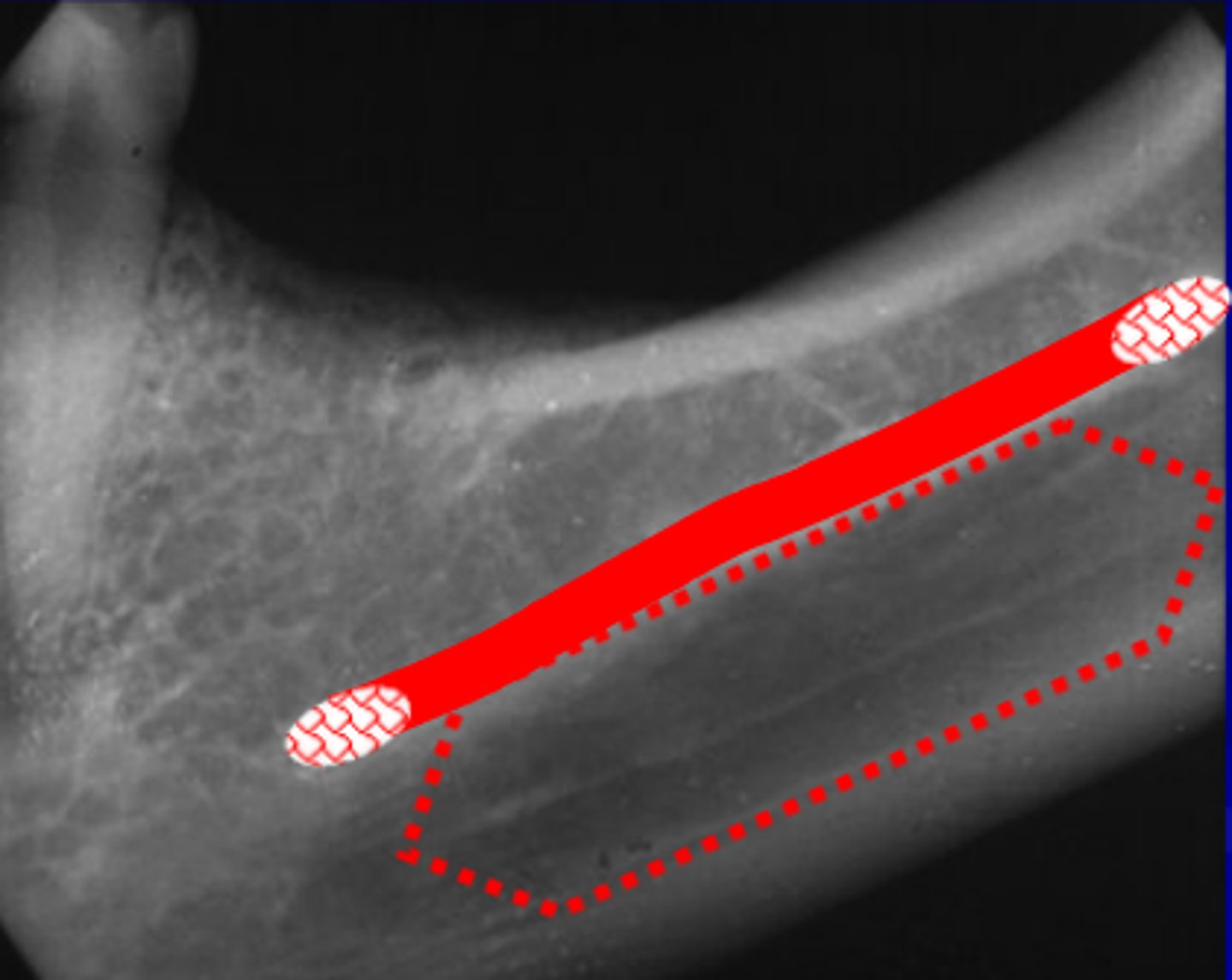
When images are properly prescribed and exposed, their benefit
far outweighs the risk of small doses of x-radiation
what does a complete/Full Mouth Series do?
show all tooth-bearing areas of both jaws
Descriptive terminology is
NOT A DIAGNOSIS
purpose of radiation protection
to protect patient and operator from unnecessary exposure
What can X-Radiation cause?
biologic changes in living cells
inherit filtration
filtration built up in the glass envelope and protective housing, average about 0.5 - 1.0 mm Al/Eq
-glass envelope (and glass window)
-oil
added filtration
The filtration that is added to the port of the x-ray tube.
added in half millimeter increments
what does added filtration do?
filters out longer wave length filtration which have less energy
half-value layer
Thickness of aluminumrequired to reduce beamintensity by 1/2
what is total filtration?
Inherent filtration + Added filtration
Regulated by state and federal laws
at or below 70 kV require minimum
at least 1.5 mm aluminum filtration
above 70 kV filtration requires
at least 2.5 mm aluminum filtration
three characteristics of collimater
restricts size and shape of beam, reduces patient exposure, made of lead
two shapes of collimator
circle and rectangular
preferred shape of collimator
a rectangular shape, which reduce radiation by 60%
what might a rectangular collimator do?
cause more possible errors due to limited space
size of circular collimator
2.75 inches in diameter
what does is the PID?
Extension of the tubehead, Directs the x-ray beam, Lead-lined, open-ended
two lengths of the PID
8 and 16 inches
preferred length of PID
16 inches because longer = less radiation
although the longer PID is better, why would we use the shorter one?
easier to aim and less awkward
what the THE best way to reduce radiation exposure?
the use of a digital sensor
whys to protect patient from radiation exposure
shielding, digital sensors or fast film, BID's, exposure factors, and good technique
At least ___mm thickness of lead or lead equivalent
.25 mm of lead or lead equivalent for lead apron
placed over pt's chest and lap to protect ______ &______ tissues from scatter
reproductive organs and blood forming tissues