GI System Review
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
What is the shape of the stomach?
J shaped
What are the 3 major roles of the stomach?
•Reservoir for food
•Breaks down solid food- chyme
•Controls rate of emptying gastric content into the duodenum
What is the anatomy order of the stomach?
mouth, esophagus, stomach, duodenum, jejunum, illium, cecum, large intestine, anus
How does the fundus sit in the stomach?
site proximal and more posterior
Hoe does the antrum sit in the stomach?
sits distal and mroe anterior
What is the small intestine divided into?
divied into the duodenum, jejunum, ileum
What is the anntomy of the large intesttne
cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, decending colon, sigmoid colon, retum
What are the causes of delayed gastric emptying?
diseases, surgucal procedures, medications
What is gastroparesis?
condition thats effects ability of the stomach to empty it contents, but there is no obstuction
Gastroparesis can either be…?
acute or chronic
What are the clinical symptoms for gastroparesis?
early postprandial satiety, bloating, nausea, vomiting
What are the treatment options for gastroparesis?
various pharmaceuticals, numerous side effects associated with these drugs
What are the indications for gastric emptying?
diebetics with persitent postprandial symptoms, severe reflux, unexplained nuasea and vomiting, asses response to motility drug
What are the clinical symptoms?
nausea, vomiting, abdominal fullness, distention, wieght loss
What are the types of gastric emptying?
solid, liquid, both
What are the food options for the solid gastric emptying study?
eggs (most common), meat, potatoes, oatmeal,pancakes, cornflakes, chicken liver, french toast
What is the patient prep?
NPO after midnight, discontinuation of any medications that may affect motility, refrain from smokin, diebetics should be done first thing in AM 2/3 usual insulin dose
What radiopharmaceuticals do we use for gastric emptying study?
Tc99m Sulfur Colliod, In-111 DTPA
What is the dose for when we use Tc99m SC? solid or liquid?
dose is 0.5-1mci and we put into the eggs (solid); 1mci into water or orange juice (liquid)
What is the dose we give when using In-111 DTPA? solid or liquid?
75-125uci (liquid)
When usung both TC SC and In-111 DTPA, which one is for solid and liquid?
Tc99m SC is for solid and In-111 DTPA is for liquid
How long does the patient have to complete the meal?
10 min
How should the patient be imaged?
upright or supine for at least 90 min
When should we take static images?
every 5-15 min
When should we take dynamic images?
30-60 second/frame
How are the images acquierd?
LAO with single head camera and Anterior and Posterior images with dual head camera
Why is LAO the best view when doing a gastric emptying study?
bc the stomach is not just anterior, fundus is posterior and antrum is more anterior
What the the normal values for solid and liquid?
soild is 90 min and liquid is 10-45 min
What are the advantages of doing a gastric emptying study?
non invasive, sensitive, accurate, quanititaive, simple to perform
What are the disadvantages or advantages for a gastric emptying study?
connot differentiate an anatomical obstruction form functional gastroparesis, and mechanical causes of such as obstruction by tumor have to be excluded by endoscopy
Grastro refulx results from what?
transient sphincter relaxation not associated with swallowing, transient increases in intra-abdominal pressure, free reflux across atonic sphinter.
When dose reflux occur in pedi patients?
7-8 months
What are some common symptoms pedi’s experience?
faliure to thrive, respiratory symptoms, iron deficiency
How long should an adult patient be NPO for a reflux study?
8 hours
How long should an infant be NPO for a reflux study?
one scheduled feeding
What radiopharmacutical do we use for a reflux study?
Tc99m Sulfur colloid
What is the dose for adult patients for a reflux?
200-300uci in 150ml of orange juice and 150ml of hydrochloric acid
What is the dose for infants for a reflux?
200-1000uci in formula
What are the 4 ways for inducce reflux?
oral administration of acidified solution, increased pressure to abdomen, supine position, at least 300ml of volume of liquid
What is the adult procedure for a ruflux study
have patient be supine with camera positioned anteriorly, stomach has to be on bottom of FOV, static images 30sec/frame at following pressure points(0,20,40,60,80,100 mm or Hg)
What is the pedi patient procedure for a reflux study?
patient has to be supine with the camera postioned posteriorly, stomach at bottom of FOV, dynamic images acquierd 5-10 sec/frame for 60 min
What is sensitivity for reflux and aspiration?
reflux: 75-100% and aspiration: 0-25%
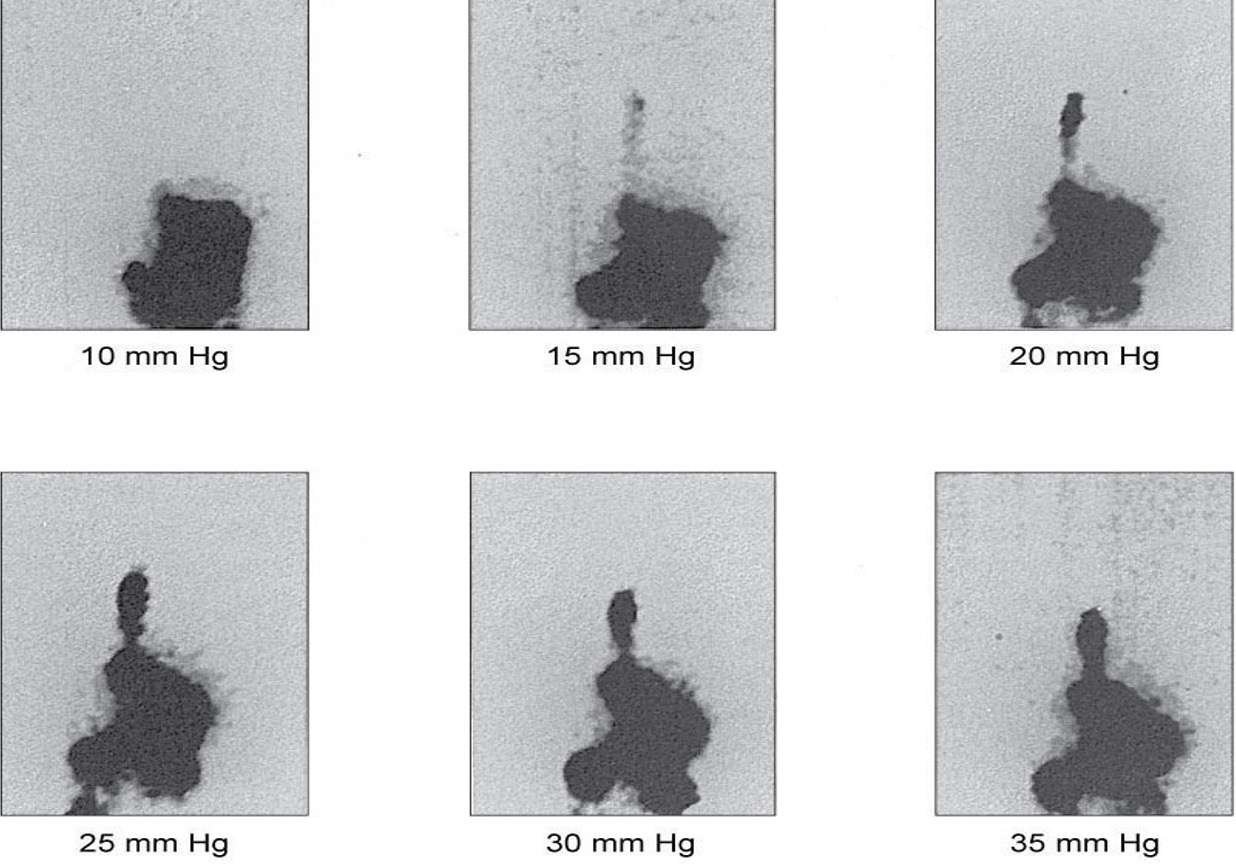
is this a pedi or adult?
adult with abdominal cuff
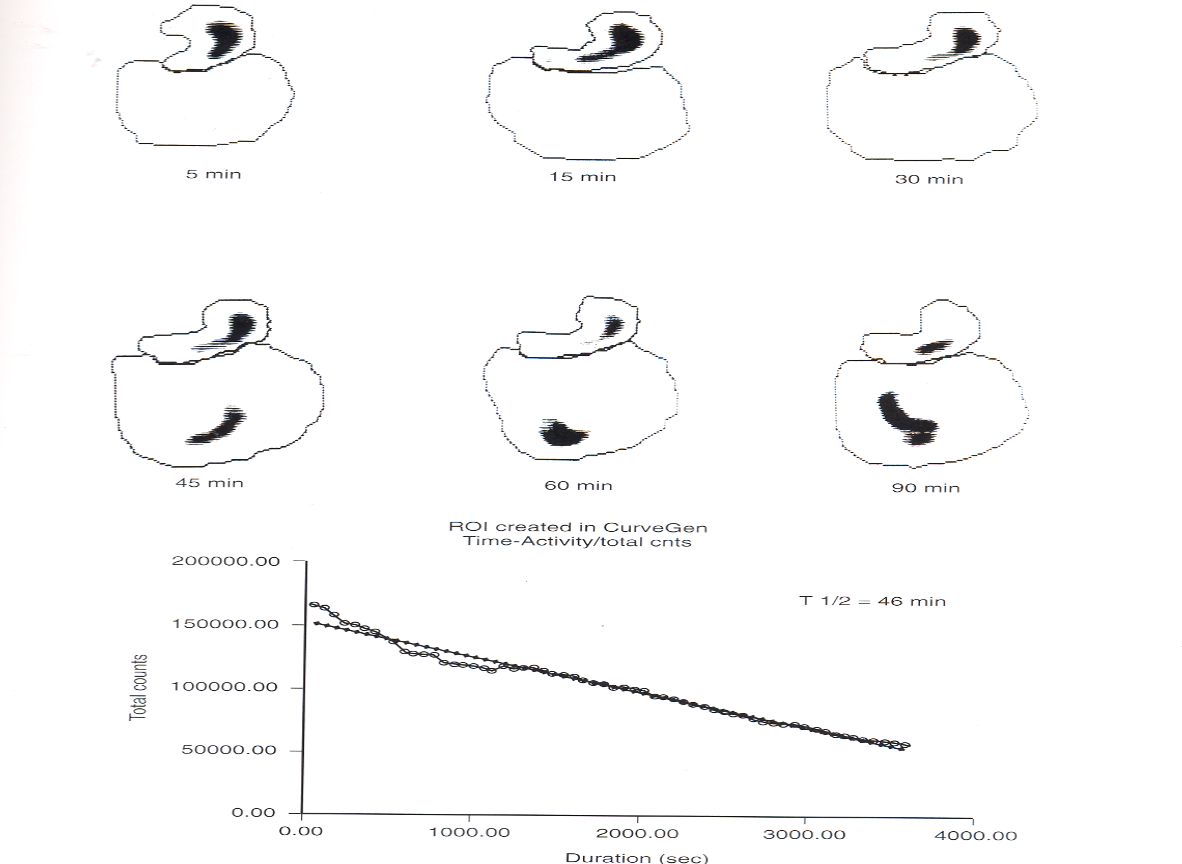
what is this pictuer showing?
a normal gastric image
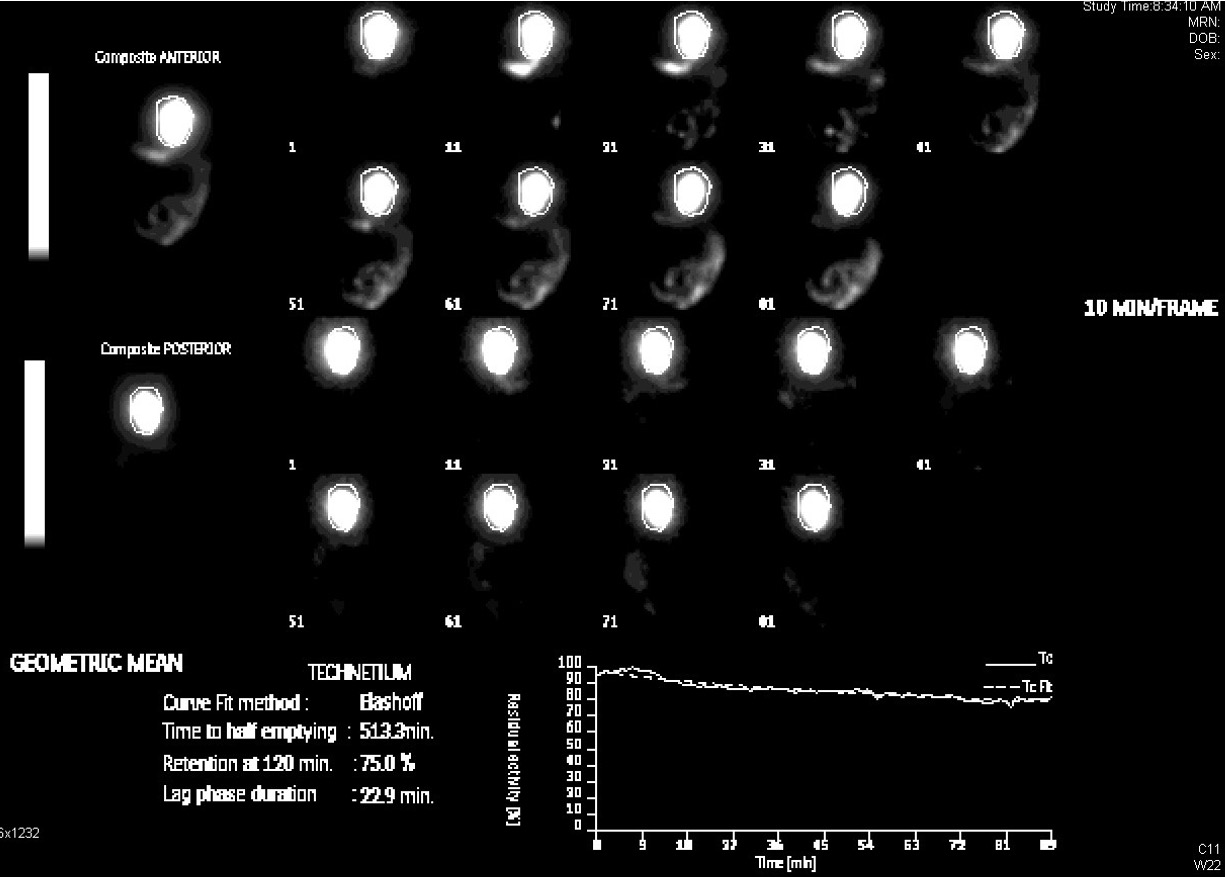
what is this picture showing?
abnormal-gastroparesis
What are the cuases for an upper GI bleed?
esophageal varies, gastric and duodenal ulcers, gastritis, esophagitis,mallory-weiss tear, neoplasm
What are the causes of a lower GI bleed?
angiodysplasia, diverticular, neoplasms, inflammatory owel diseases, meckels diverticulum
What are the most common sites for GI bleeds?
cecum, hepatic flexure, decending colon, sigmiod colon, rectum
What is the paitne prep for GI bleed?
none
What radiopharmaceutical do we use for Gl Bleed?
Tc99m labeld RBC’s and Tc99m sulfur colloid
What is the dose when we use Tc99m labeled RBC’s?
20-30mci
What is the dose when we use Tc99m SC?
10 mci
How fast can Tc99m labeled RBC’s detect rates?
0.1-0.35ml/min
Why is Tc99m labeled RBC’s the best choice?
for intermittent bleeds because of long intravasular half life (48 hours)
When using Tc99m labeled RBC’s where can it visualize bleeds?
liver and spleen
What is the sensitivity for intermittent bleeding?
>90%
What is the disadvantage when using Tc99m labeled RBS’s?
Free tech is excreated in the kidneys and gastric mucossa and passes into the bladder, small bowel, and colon
When using Tc99m labeled RBC’s imaging can be perfomed up to how many hours post injection?
24 hours post inj
Which tag should be done to prevent free tech?
in vitro or modified invitro
What does In Vivo mean?
inside the body
What is the prodcedure when using the in vivo method?
Inject stannous ion, wait 20-30 min, inject Tc99m-Pertechnetate
For in vivo method the labeling efficency is?
60-90%
What is the procedure when using In vivo/In vitro method?
IV injection of stannous ion, blood sample is collected into a syringe containg Tc99m-pertechnetate and anticoagulant, then re-inejcted
What is the labeling efficiently for In vivo/In vitro?
95%
What is a Pro when doing the In vivo/In vitro method?
Absence of blood manipulation
What does In virto mean?
labeling done outside the body
What is the procedure when doing thr in vitro method?
blood 1-3ml is collected into a syringe containg the anticoagulant, then let it sit for 5 min, then add ACD, then add Tc99m pertechnetate, then wait 20 min and inject
What method has the highest lableing efficiency and superior for image quality?
In vitro method
Which radiopahrmacutical isnt commonly used for GI bleeds?
Tc99m SC
Why is Tc99m SC the best choice for active bleeds?
bc it clears rapdily form intrsvasular space via RE system and maybe cleared before next bleeding episode
What is the disadvantage when using Tc99m SC for GI bleeds?
it clears so rapidly that intermittent bleeding might be missed and the liver and spleen activity
How should the patient be positioned and the camera?
supine, camera is positioned anteriorly over the suspected bleeding site
What normal bisdistribution do we see when we use Tc99m RBC’s?
liver, spleen, abnormal vessles, kidneys, bladder, genitals, stomach
What does normal biodistributuon look like when we use Tc99m SC?
liver, spleen, bone morrow
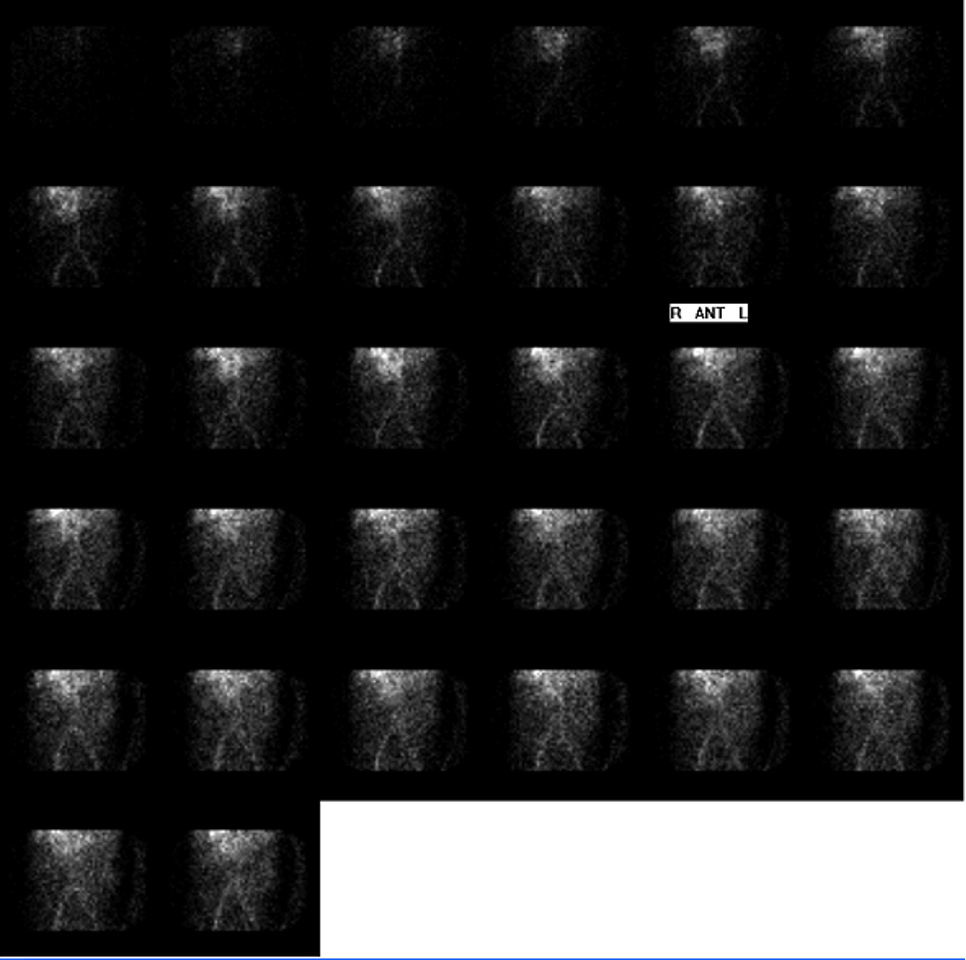
what is picture showing?
flow phase for GI bleed
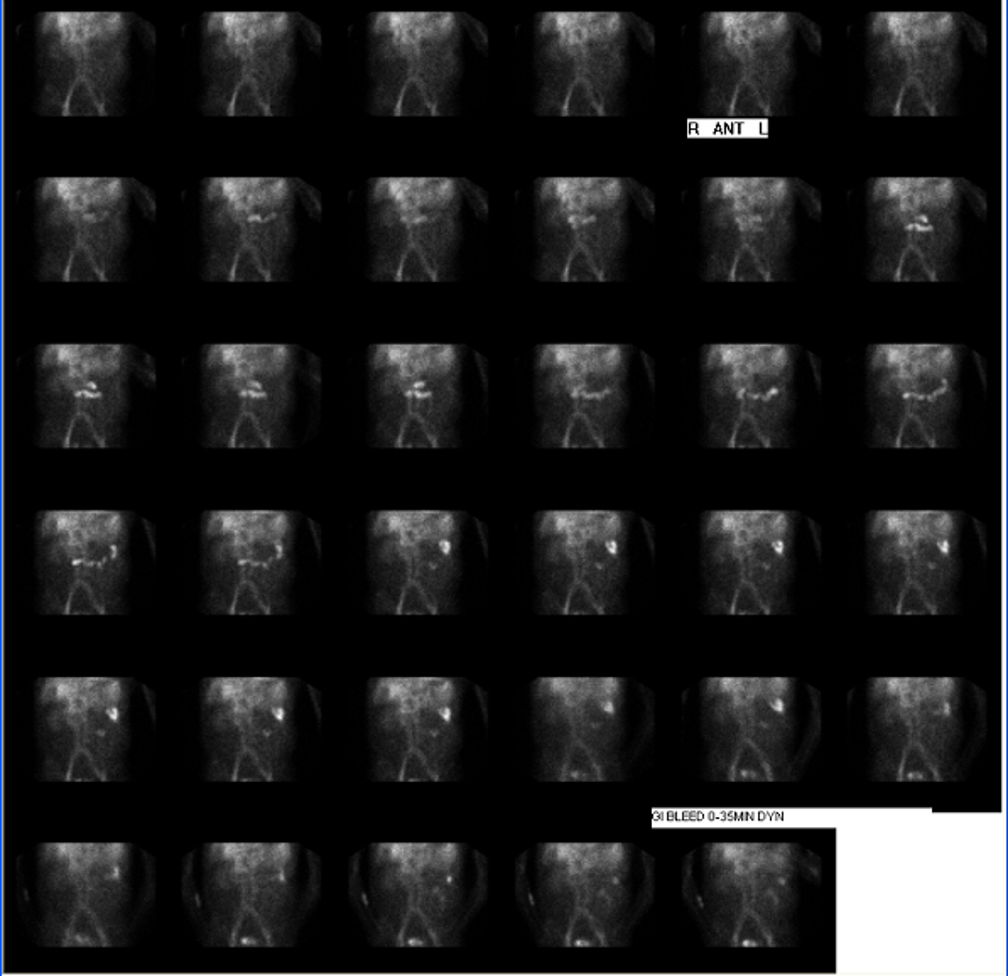
what is this pictuer showing?
0-35min dynamic for GI bleed
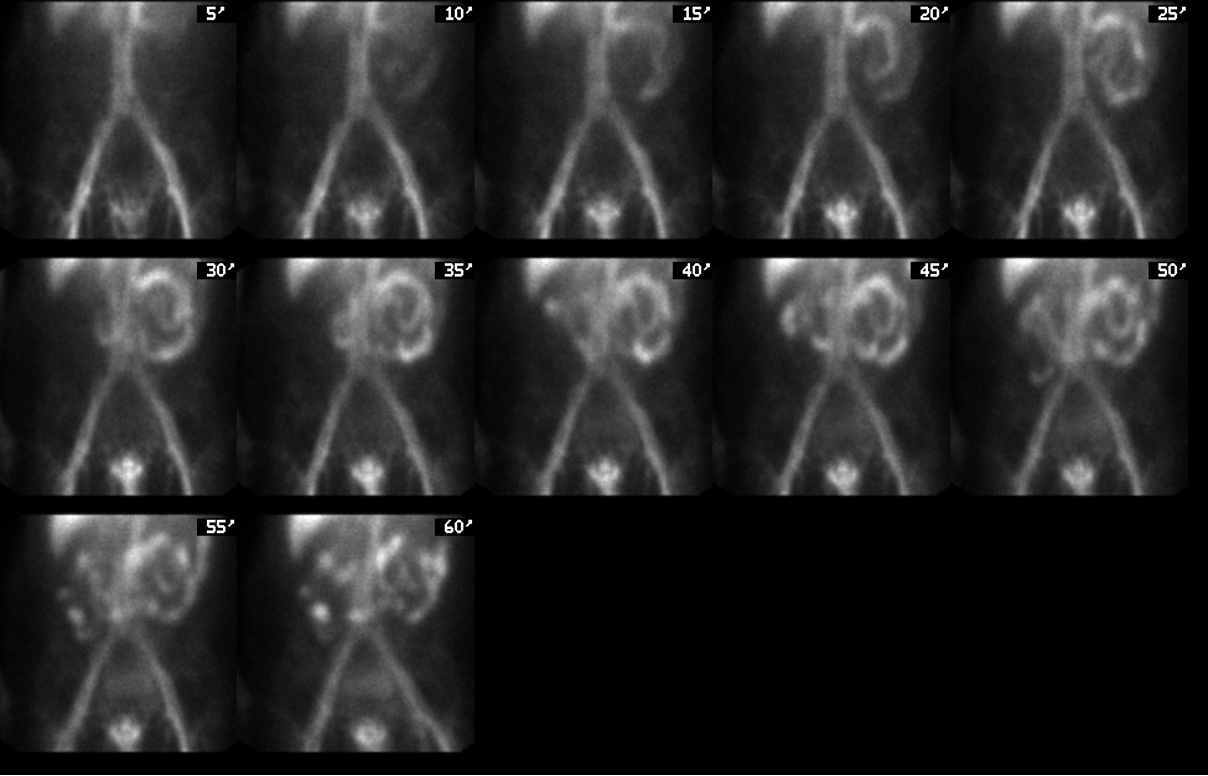
is this using Tc-RBC’s or Tc-SC?
Tc-RBC’s
is this using Tc-RBC’s or Tc-SC?
Tc-RBC’s
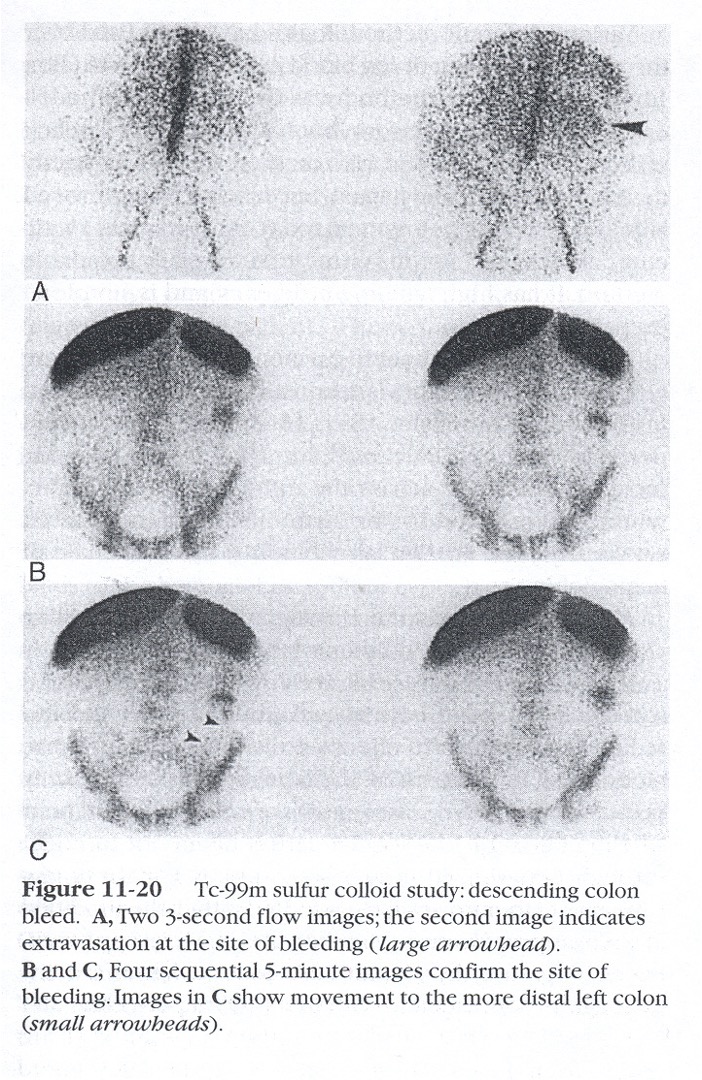
is this using Tc-RBC’s or Tc-SC?
Tc-SC
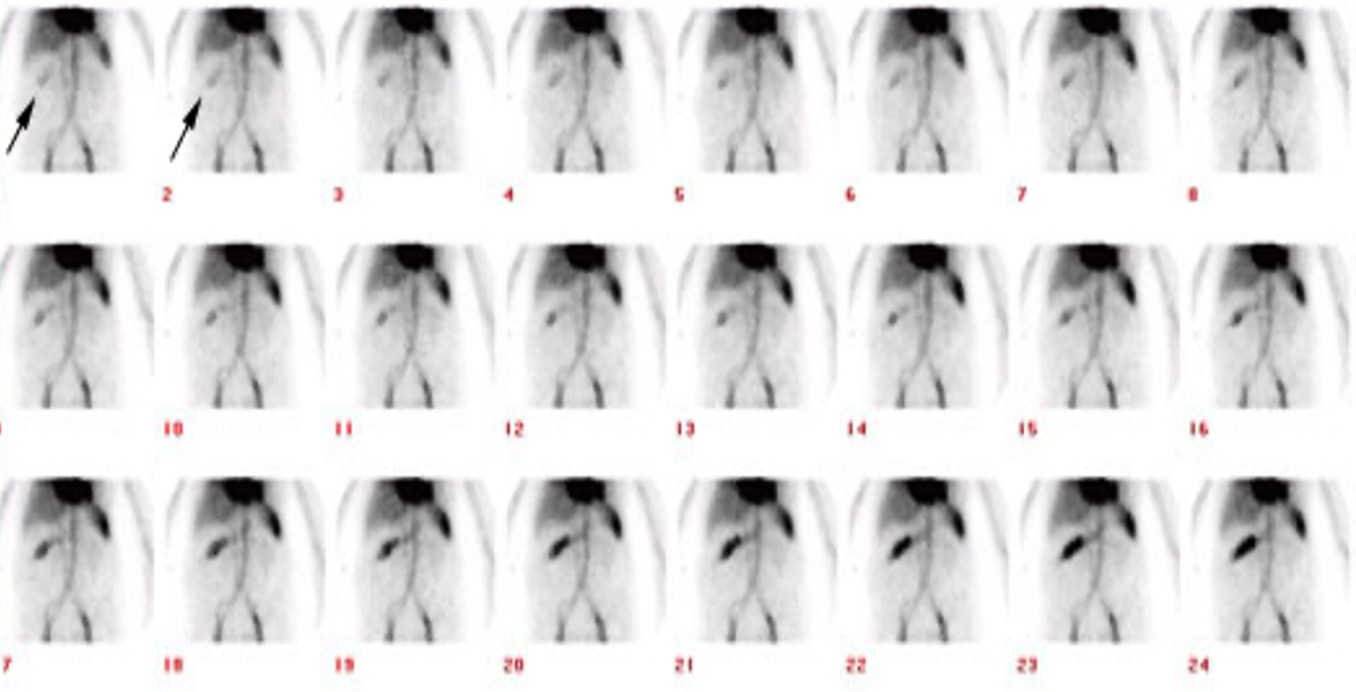
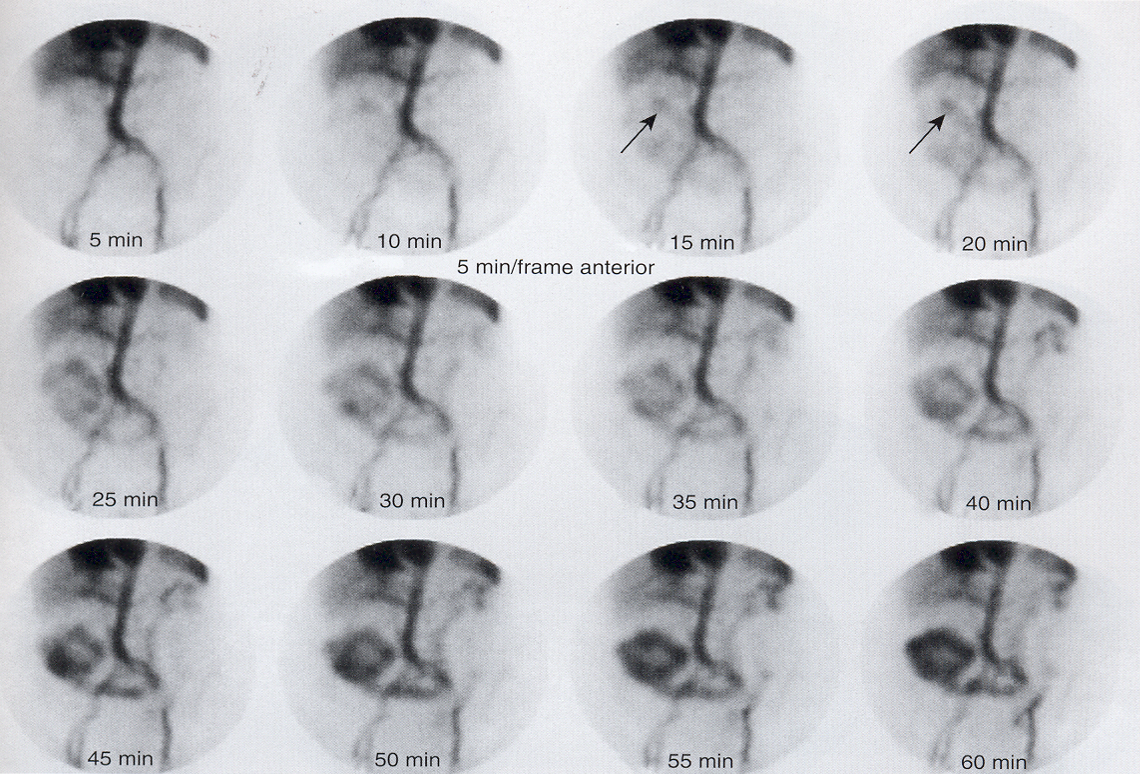
what is this picture showing and is this using Tc-RBC’s or Tc-SC?
shows and active bleed in the region for the heptatic flexure and this uses Tc-RBC’s
What is the most common benign tumor of the liver?
cavernous hemangioma
Cavernous hemangiomas are often found on CT as what?
an accidental finding
What radiopharmacutical do we use for a liver hemangioma?
Tc99m labeled RBC’s
What is the dose and what is the critical organ?
25mci and the heart
What is the imaging protocol for liver hemangioma?
flow(optional) 1 frame/sec for 60 frames, blood pool(optional) 750-1000k views vary, Delayed imaging 45-180 min post injection (SPECT if indicated)
What is cholecystokinin (CCK)?
a hormone produced by the duodenum
What are the indications for hepatobiliary imaging?
acute or chronic cholecysitits, calculation of GB function, evaluation of bile, jaundice, biliary atresia, biliary leak
What is the peatient prep for a HIDA scan?
pain med that containopium or morphine should be discontinued for at least 4 hours, patient should fast for 4 hours no longer than 24 hours, no recent barrium studies
What radiopharmaceuticals do we use for a HIDA scan?
Tc99m Mebrofenin(choletec) and Tc99m Disofenin(hepatolite)
What is the method of localizeation for radiopahrmaceuticals for a HIDA scan?
active transport
If a patient has a severe hepatocelluar function IDA will be cleared though what?
the kidneys
What is uptake dependent on for a HIDA scan?
chemical structure of IDA compund, hepatic blood flow, viability of hepatocytes, bilirubin level
Whats is the critcal orgna in a HIDA scan?
large intestine
What is the dose for a HIDA scan?
1-5 mci IV
What camera is used for a HIDA scan?
LEAP and LEHR
If a patient has high levels of bilirubin >than 20-30mg/dl, does the dose change?
yes
What is the acquisition protocol for a HIDA scan?
Imaging begins, immediately after injection, liver in upper left hand corner of FOV, optional 60 second flow, dynamic 1-5min/frame for 45-60 min, after forst hours AO’s and right lateral, delay images up to 24 hours post injection
Right lateral position GB lies anteriorly or posteriorly?
anteriorly
What structuers should be seen within one hour?
hepatic parenchyma, biliary ductal system, gallbladder, duodenum
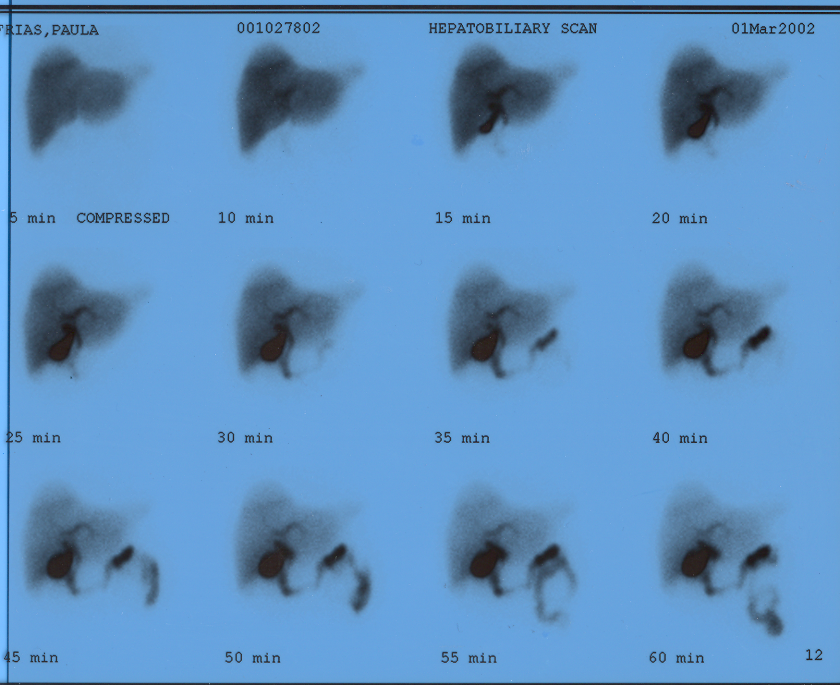
what is this pictuer showing?
normal hepatobiliary