Lab Exam 2
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
143 Terms
The cranial bones are classified as _____ bones
Flat
Most carpal and tarsal bones are classified as ____ bones
Short
Bones found within tendons are classified as
Sesamoid
Bones of the forearm are classified as ___ bones
Long
A bone that will not fit into any other category is called
Irregular
The tough outer covering of a bone is called the __
Periosteum
The hollow cavity within the diaphysis of a long bone is called the ___
Medullary Cavity
____ marrow is primarily fat
Yellow
The expanded ends of a long bone are called the ____
Epiphysis
The shaft of the long bone is called the ____
Diaphysis
The ___ is the band of cartilage present in bones that have not fully ossified.
Epiphyseal Plate
_____ Cartilage covers the ends of a typical long bone
Articular
Location of Skeletal tissue
Mostly attached to skeleton
Location of cardiac tissue
Heart
Location of smooth tissue
walls of hollow organs, skin & eyes
Movement of skeletal tissue
Voluntary
Movement of cardiac tissue
Involuntary
Movement of smooth tissue
Involuntary
Structure of skeletal tissue
Long, cylindrical, striated, multinucleated
Structure of cardiac tissue
short, wide, branching, striated with intercalated discs, single or two nuclei.
Structure of smooth tissue
thin, spindle-shaped, non-striated, single nuclei.
Function of skeletal tissue
produces movement of the body
Function of cardiac tissue
produces beating of the heart
Function of smooth tissue
changes diameter of hollow organs, erect hairs, adjust shape of lens & size pupil
Timmy is an 8-year-old baseball player who recently suffered a simple fracture in his distal tibia. Doctor is concerned that it’s near the epiphyseal plate. Why?
The epiphyseal plate/growth plate is responsible for the increased growth of a long bone. If damaged, could interfere with bone growth
Patient suffers form sever and persistent anemia, doctor orders a test that inserts a needle into a bone to withdraw tissue. Will the needle enter the spongy or compact bone?
Spongy bone contributes to bone strength, but its primary function is hematopoiesis. (formation of blood cells)
Rickets weakens bones. Legs bow due to not enough vitamin D or calcium. Why would loss of calcium make bones less strong & more flexible?
Calcium is the main mineral maintaining bone density and strength. Less calcium & vitamin D would weaken the bone
Osteoporosis leads to weakened & porous bones, common in post-menopausal women. What change in bone cell activity causes osteoporosis
osteoclasts maintain their activity & osteoblasts decrease their activity.
Neuroglial Cells
form myelin
Peripheral Nervous System contains: (2 types)
Schwann Cells and Satellite Cells
Multipolar neurons:
1 axon, 2+ dendrites, motor/efferent neurons.
Bipolar neurons:
1 axon, 1 dendrite, afferent special sense organs
Pseudounipolar neurons:
single short process splits into 2 axons, touch, pain, vibration sensations
Nissl bodies
rough ER and ribosomes for protein synthesis
Neurons
primary signaling units
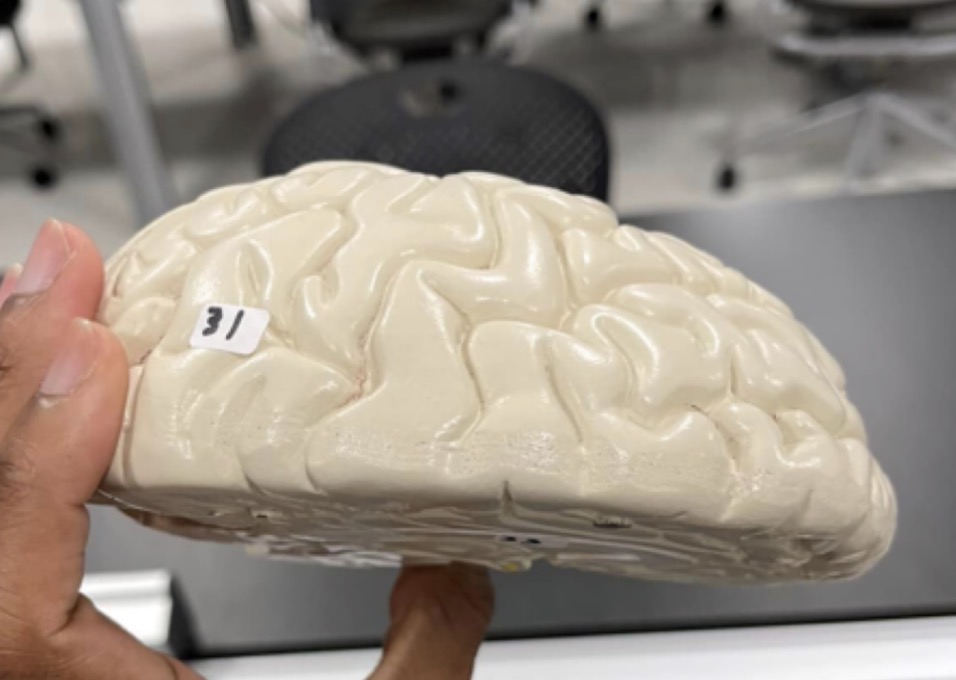
31
Cerebrum of the brain
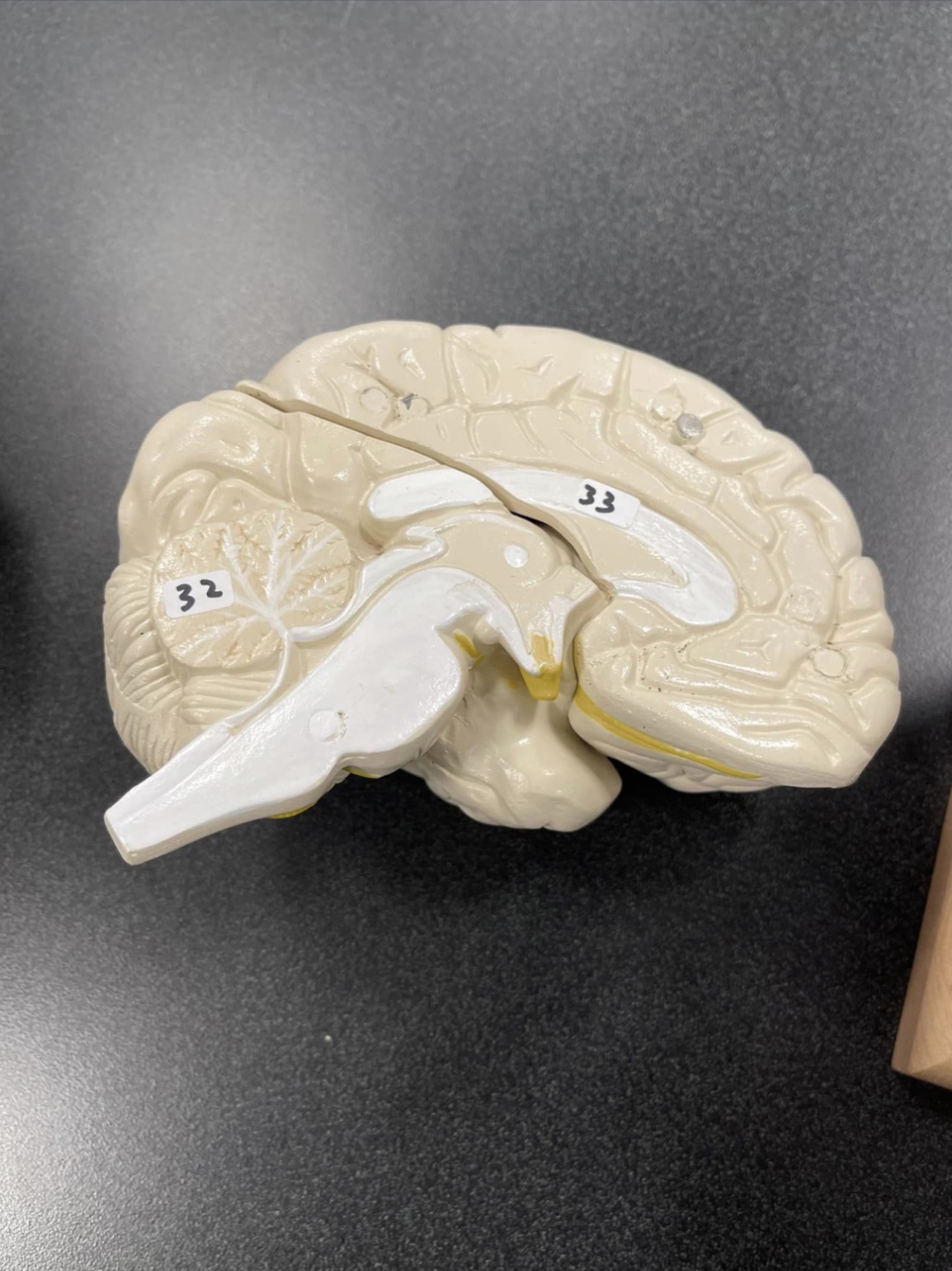
32
Cerebellum of the brain
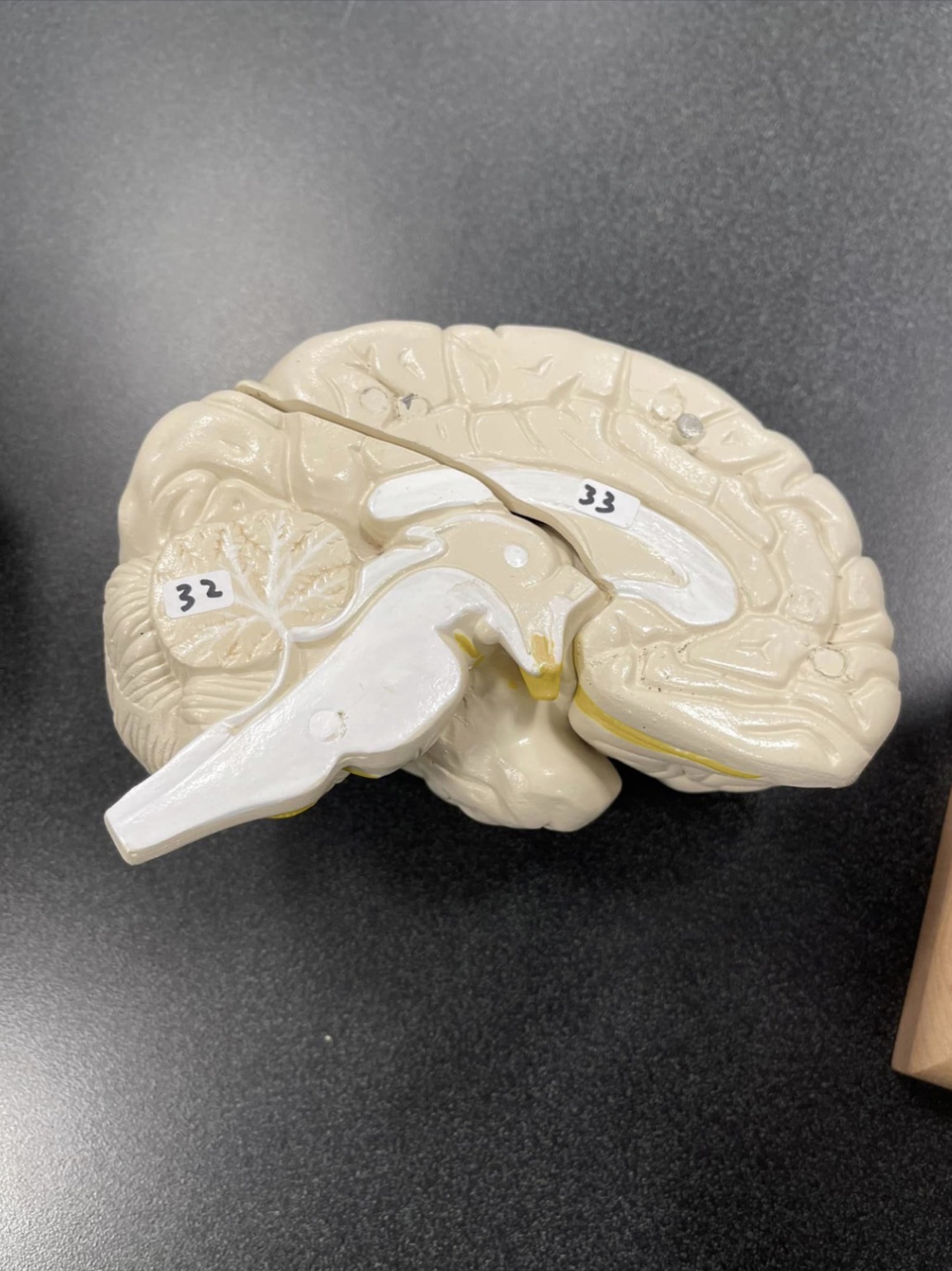
33
Corpus Callosum of the brain
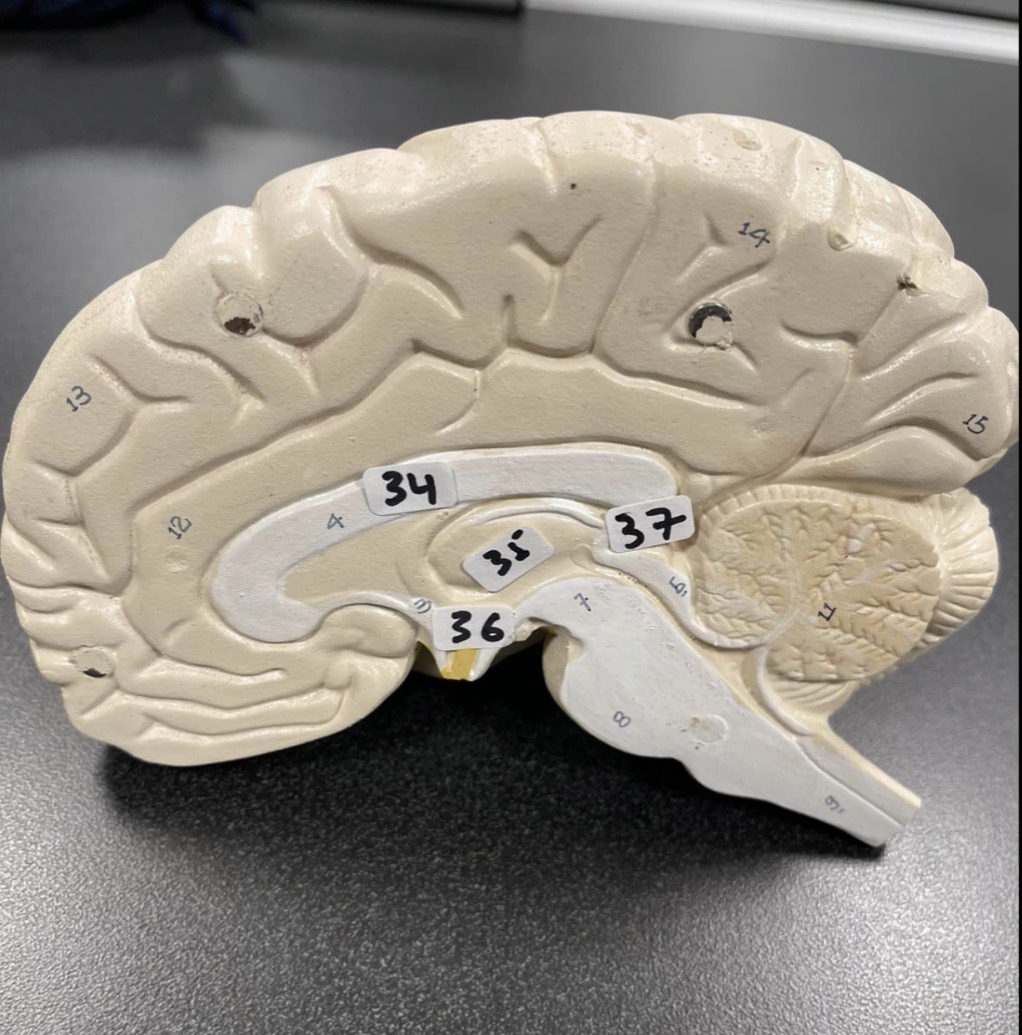
34
Corpus Callosum of the brain
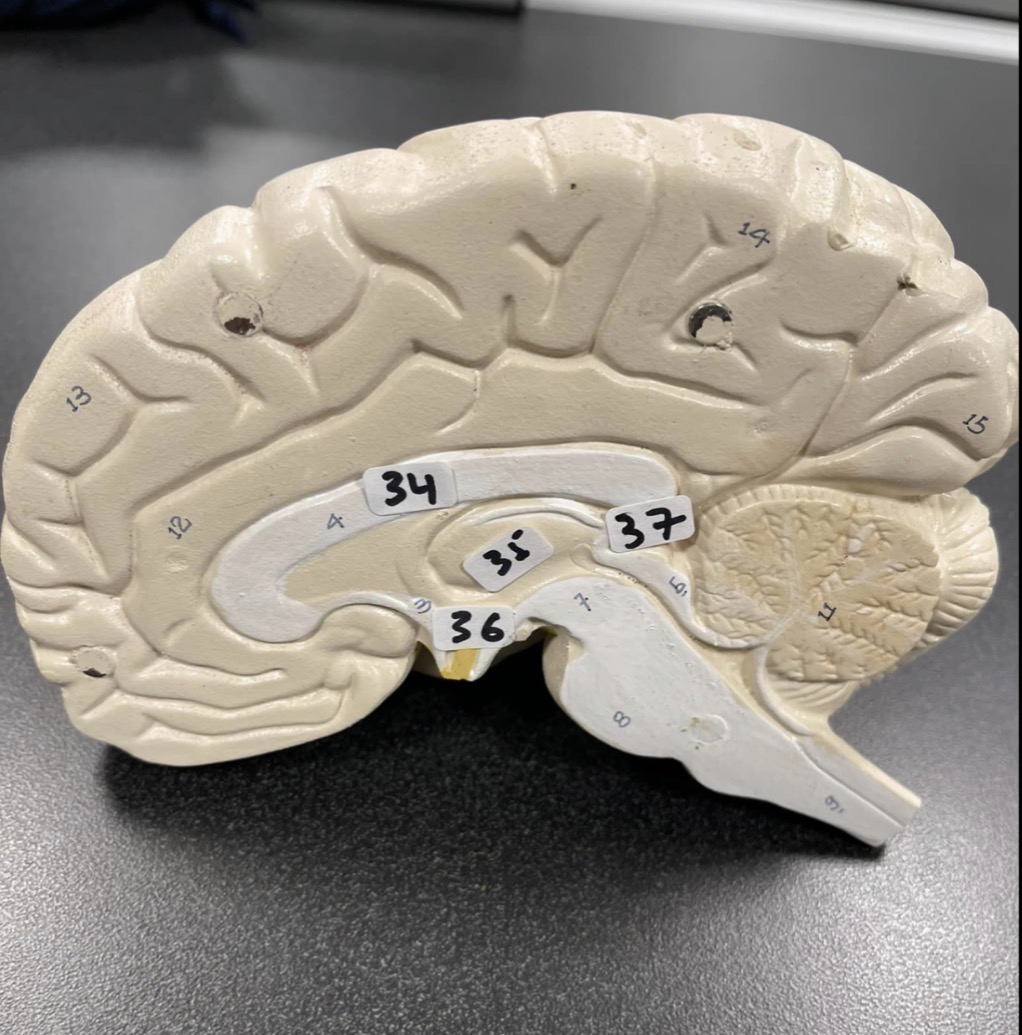
35
Thalamus of the brain
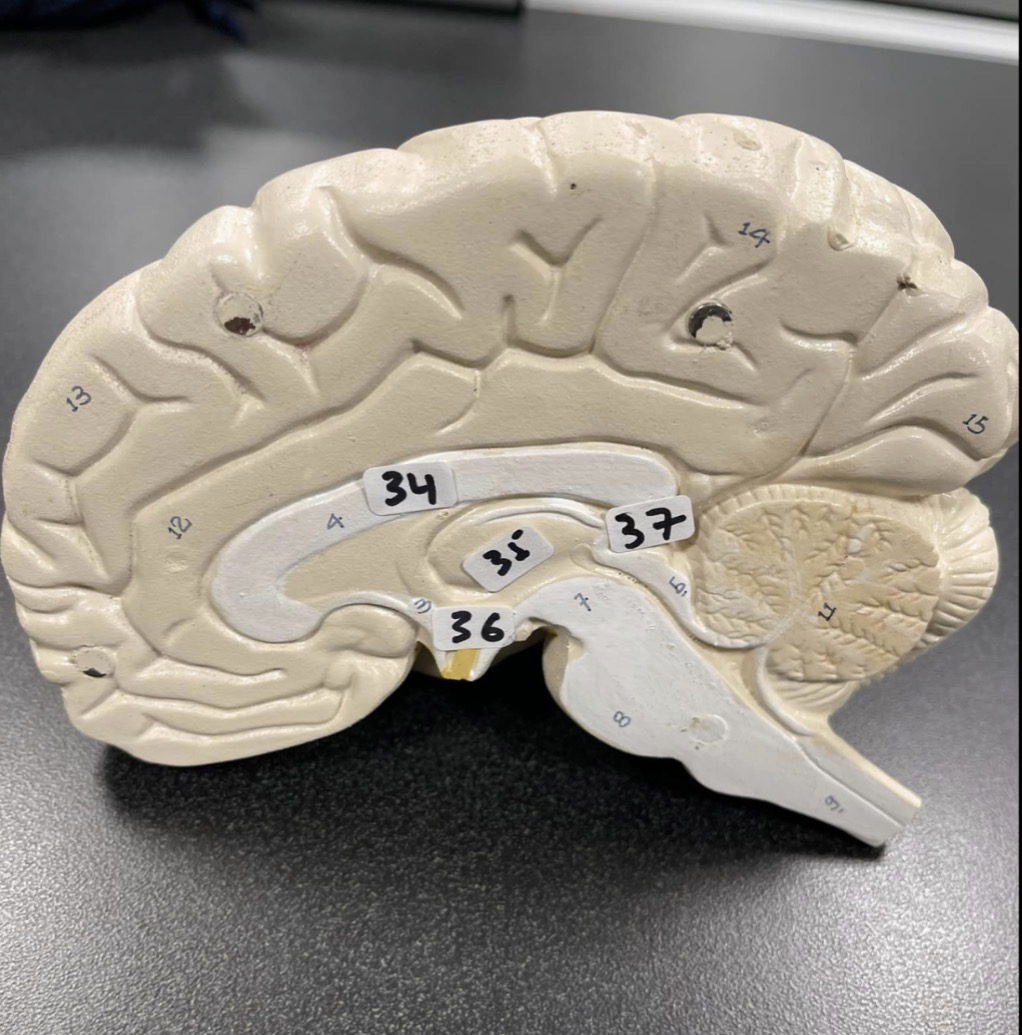
36
Hypothalamus of the brain
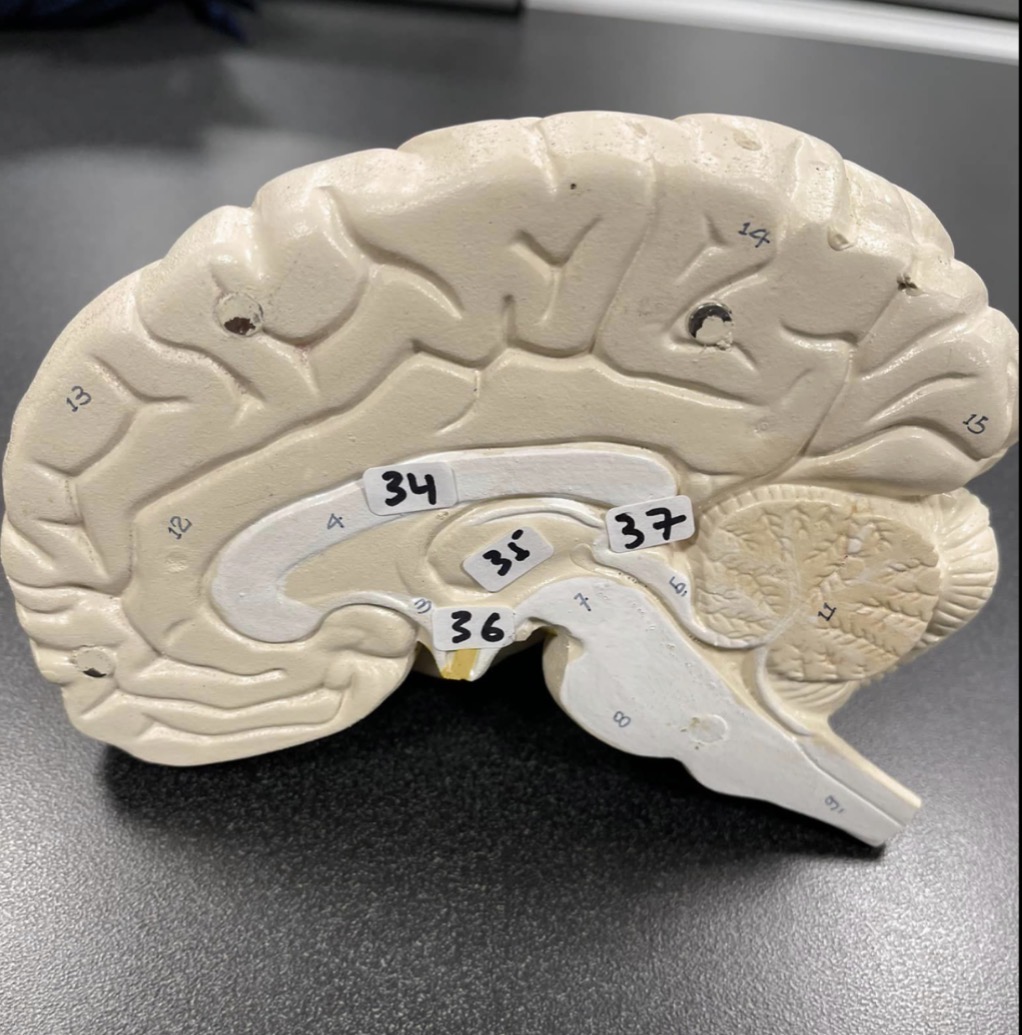
37
Pineal gland of the brain
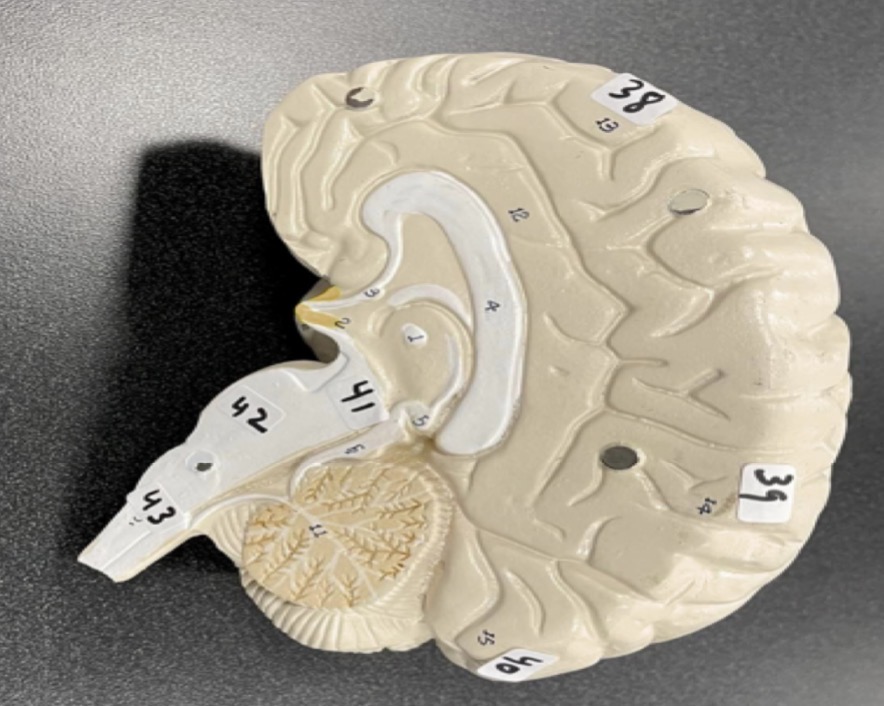
38
Frontal lobe of the cerebrum
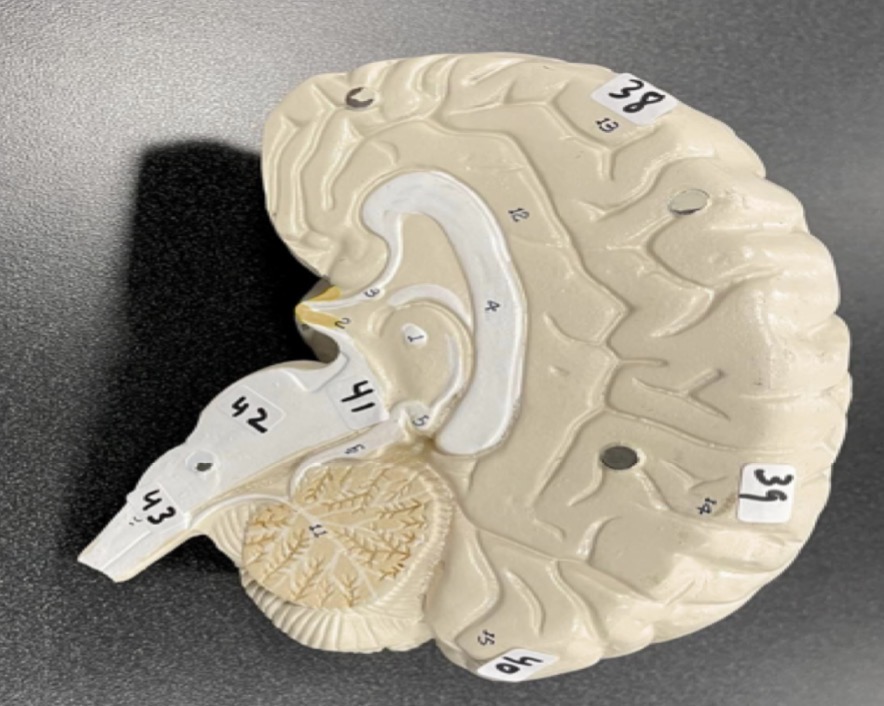
39
Parietal lobe of the cerebrum
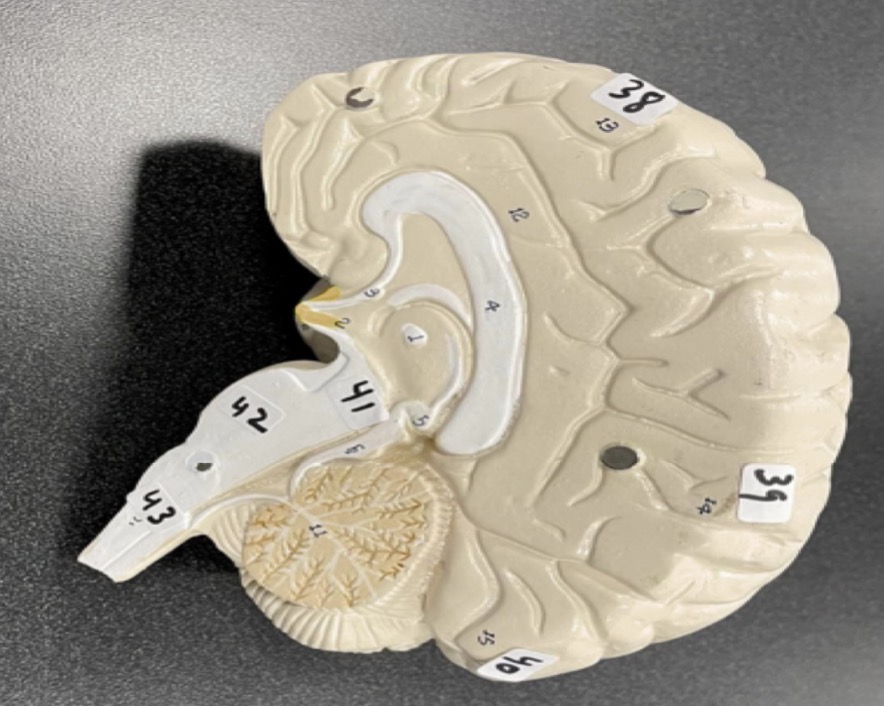
40
Occipital lobe of the cerebrum
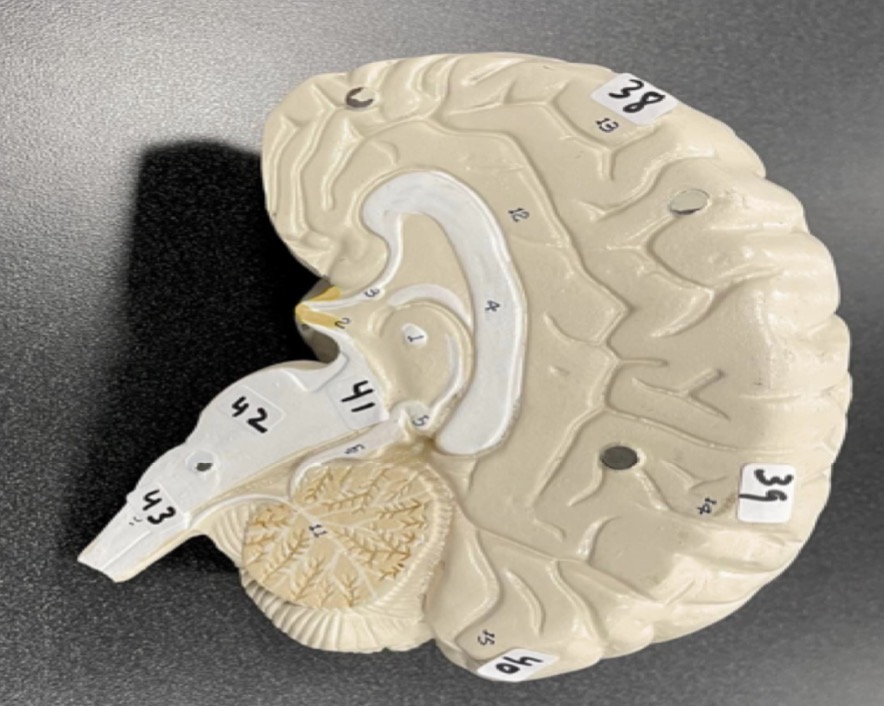
41
Midbrain of the brain stem
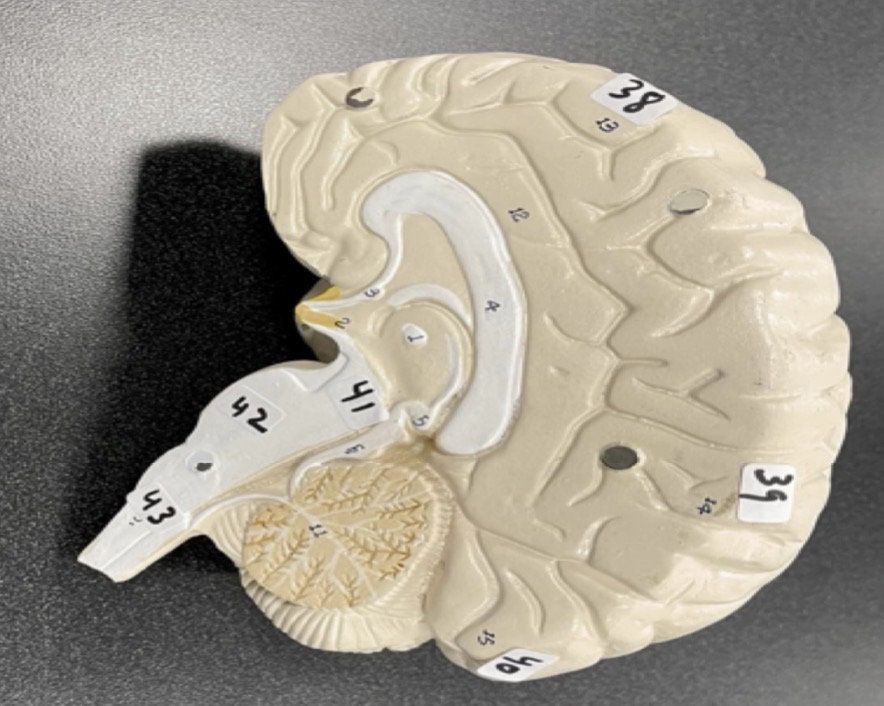
42
Pons of the brain stem
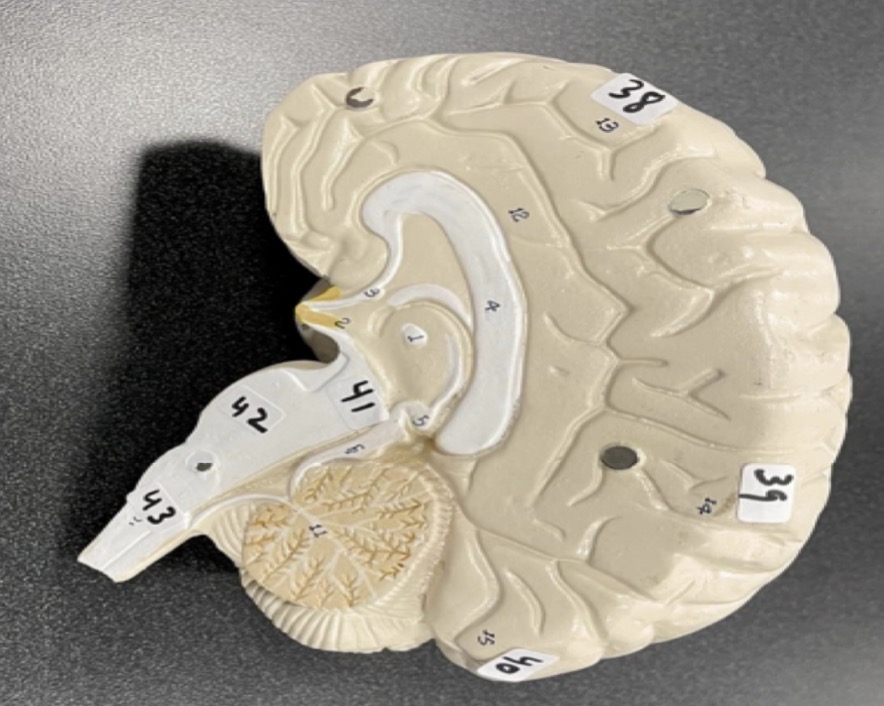
43
Medulla of the brain stem
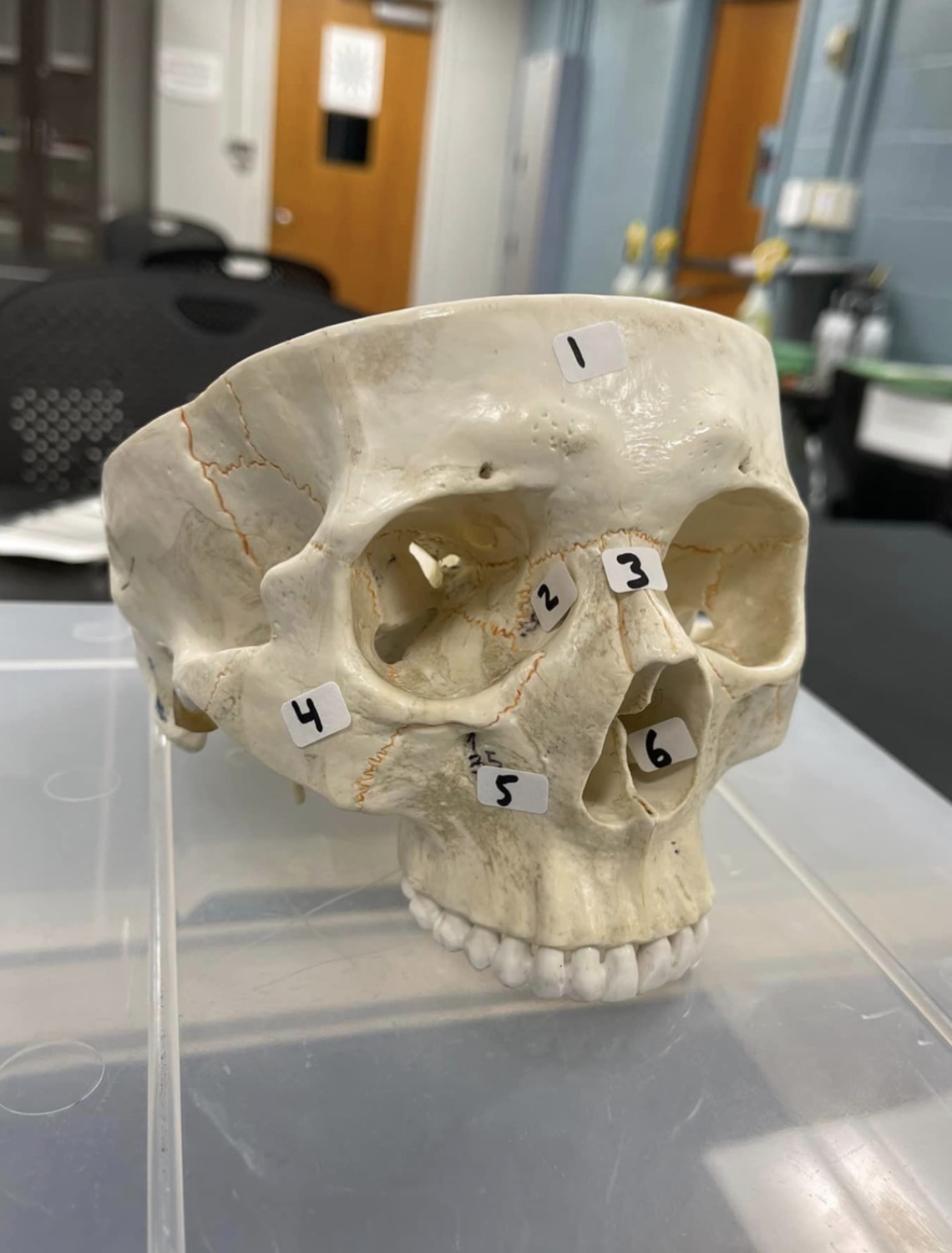
1
frontal bone of the skull
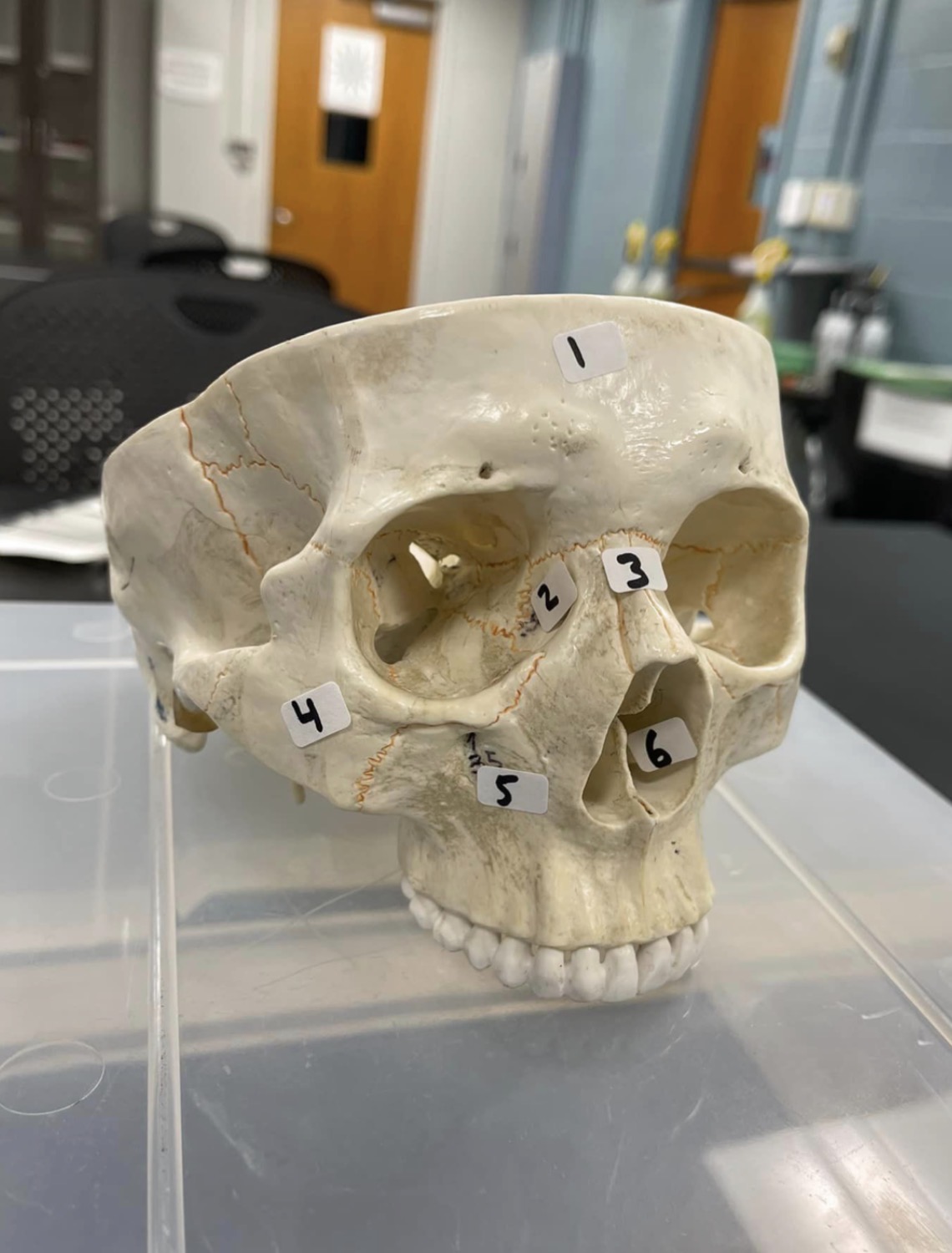
2
Lacrimal bone of the skull
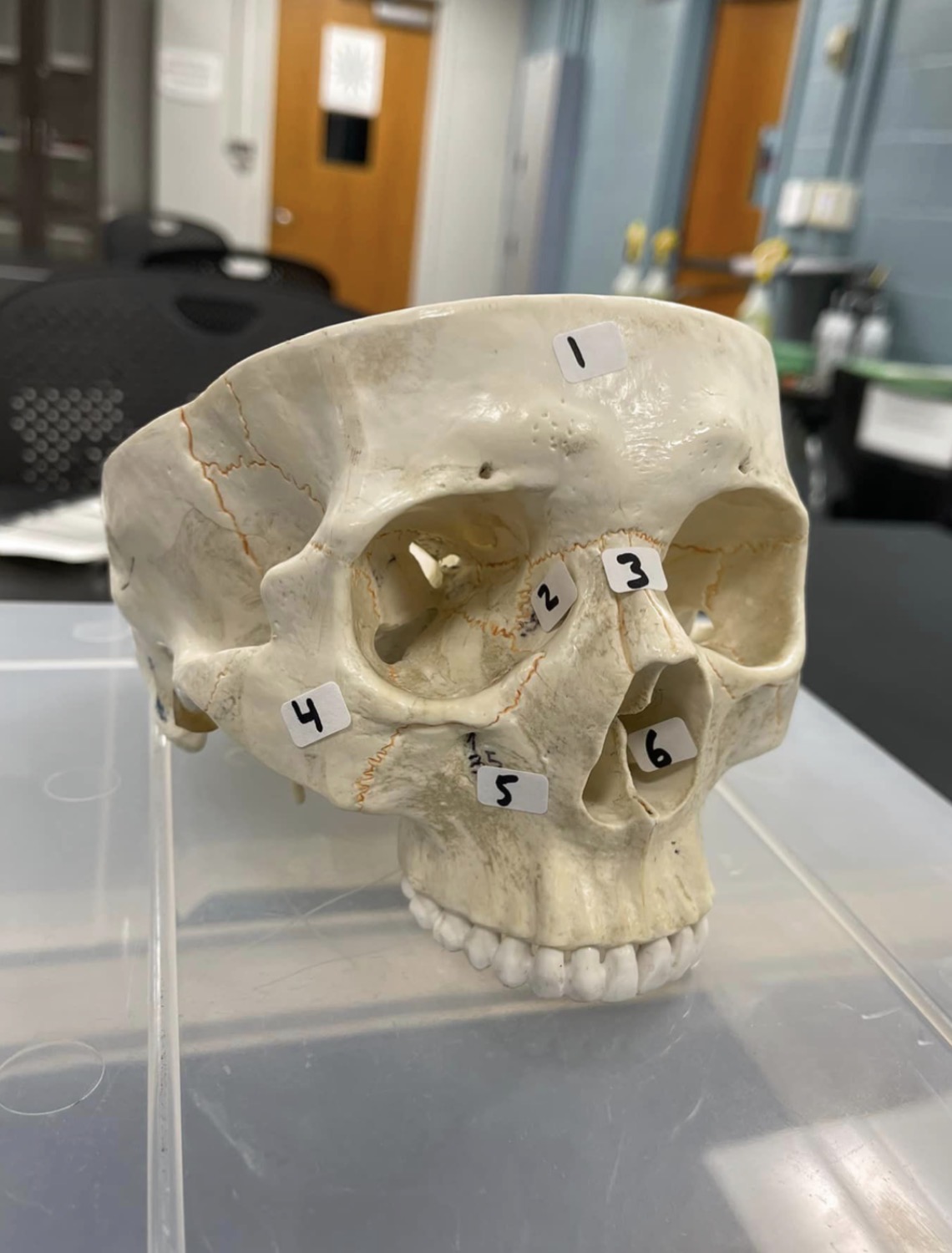
3
Nasal bone of the skull
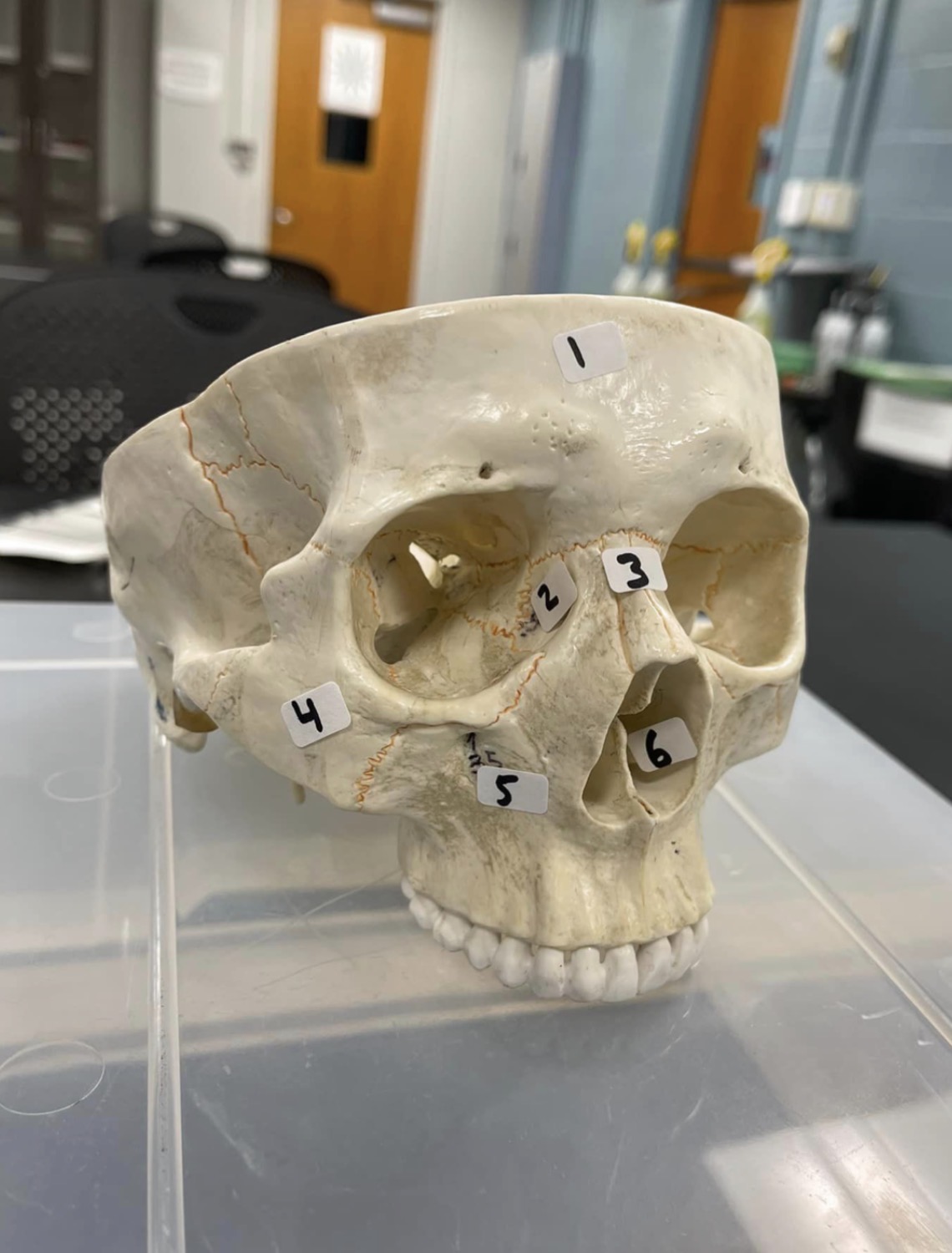
4
Zygomatic bone of the skull
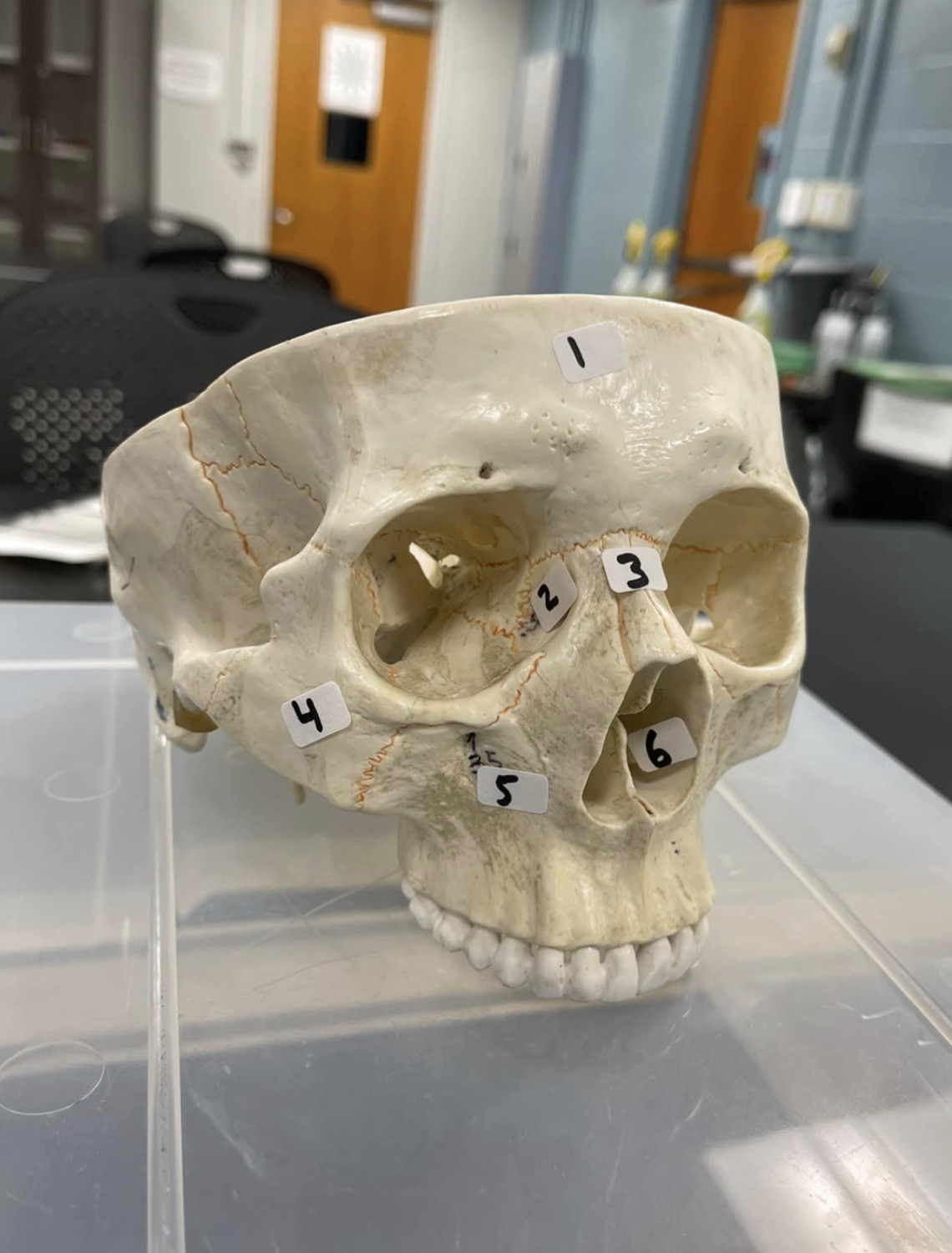
5
Maxilla of the skull
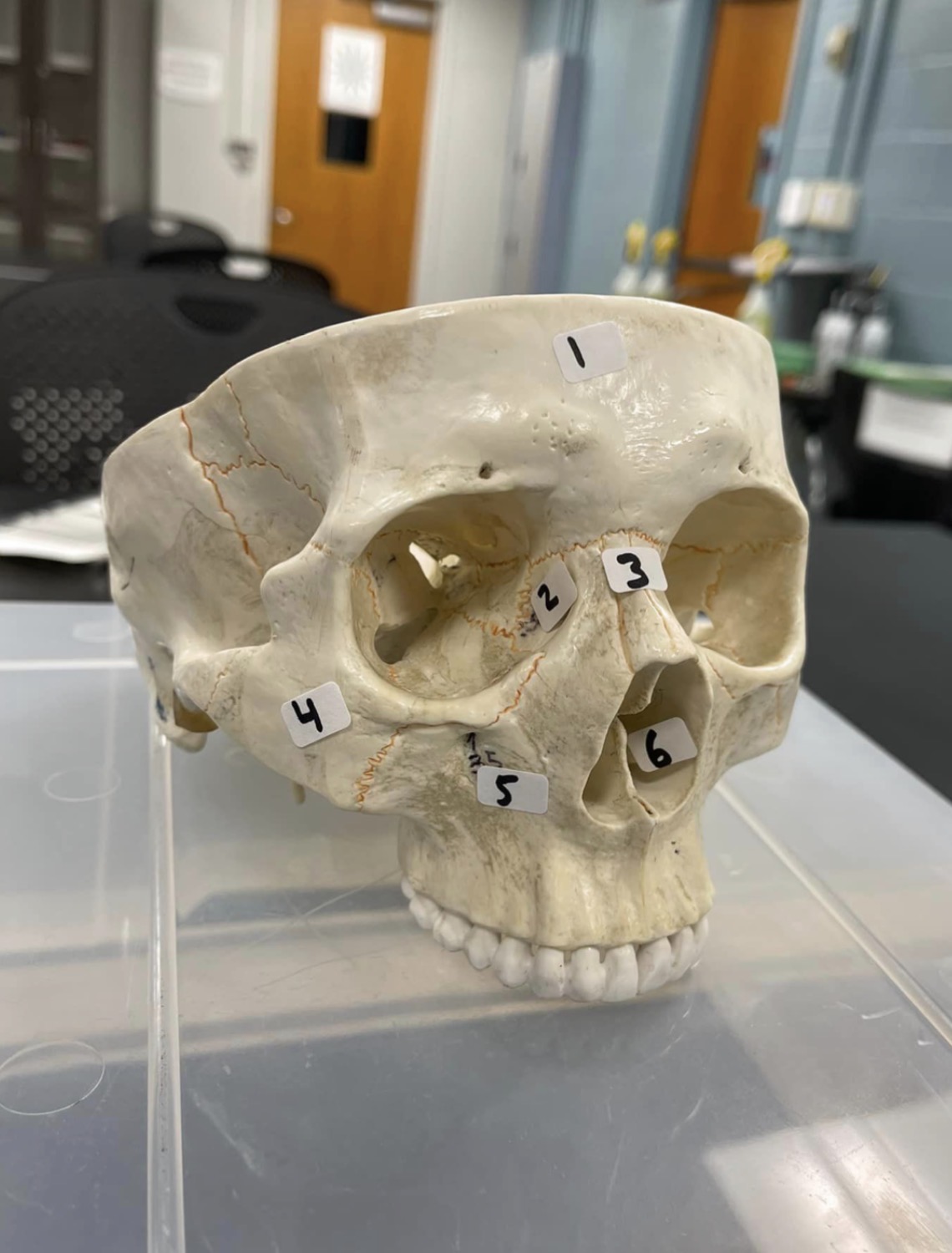
6
inferior nasal concha of the skull
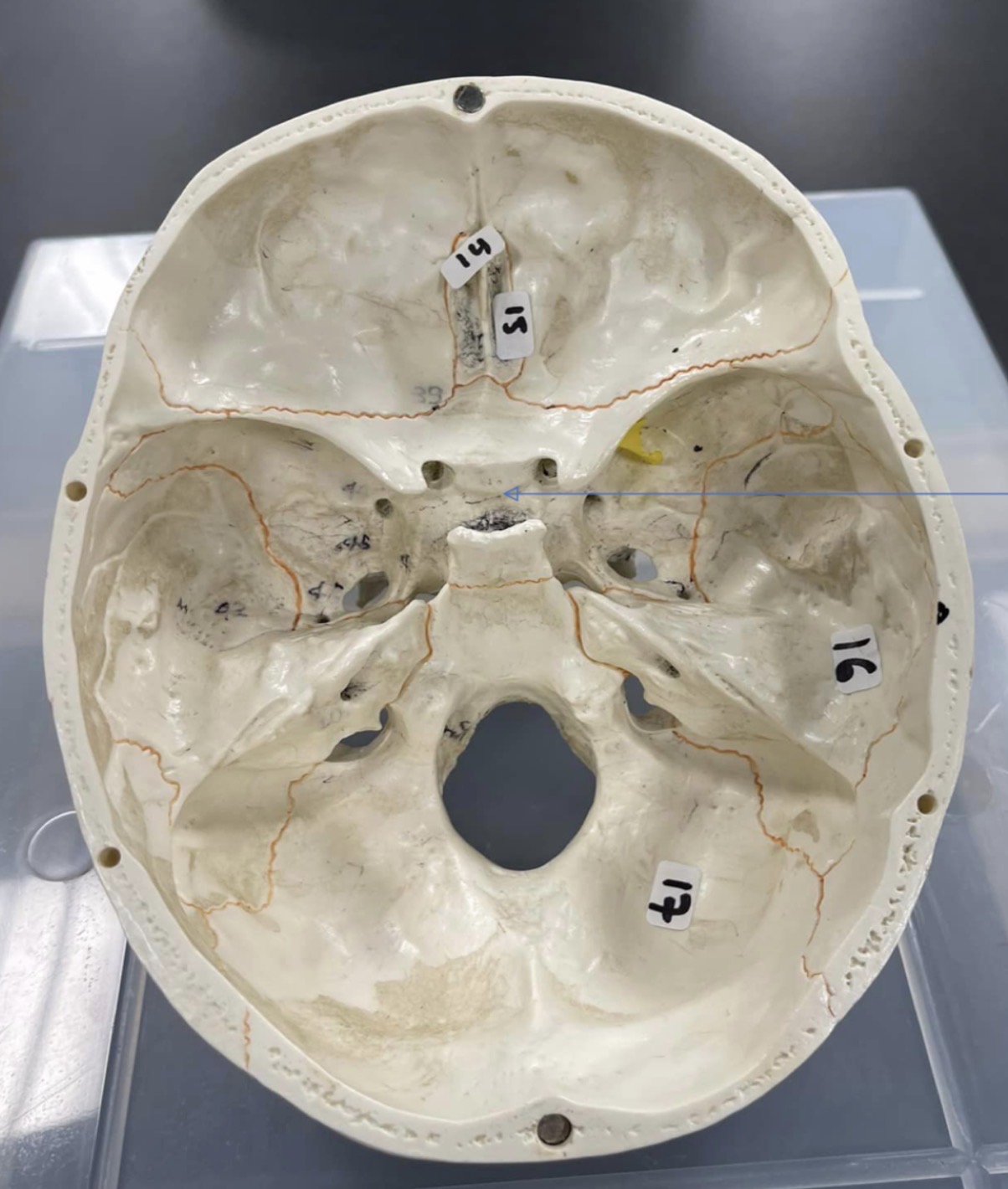
14
ethmoid bone
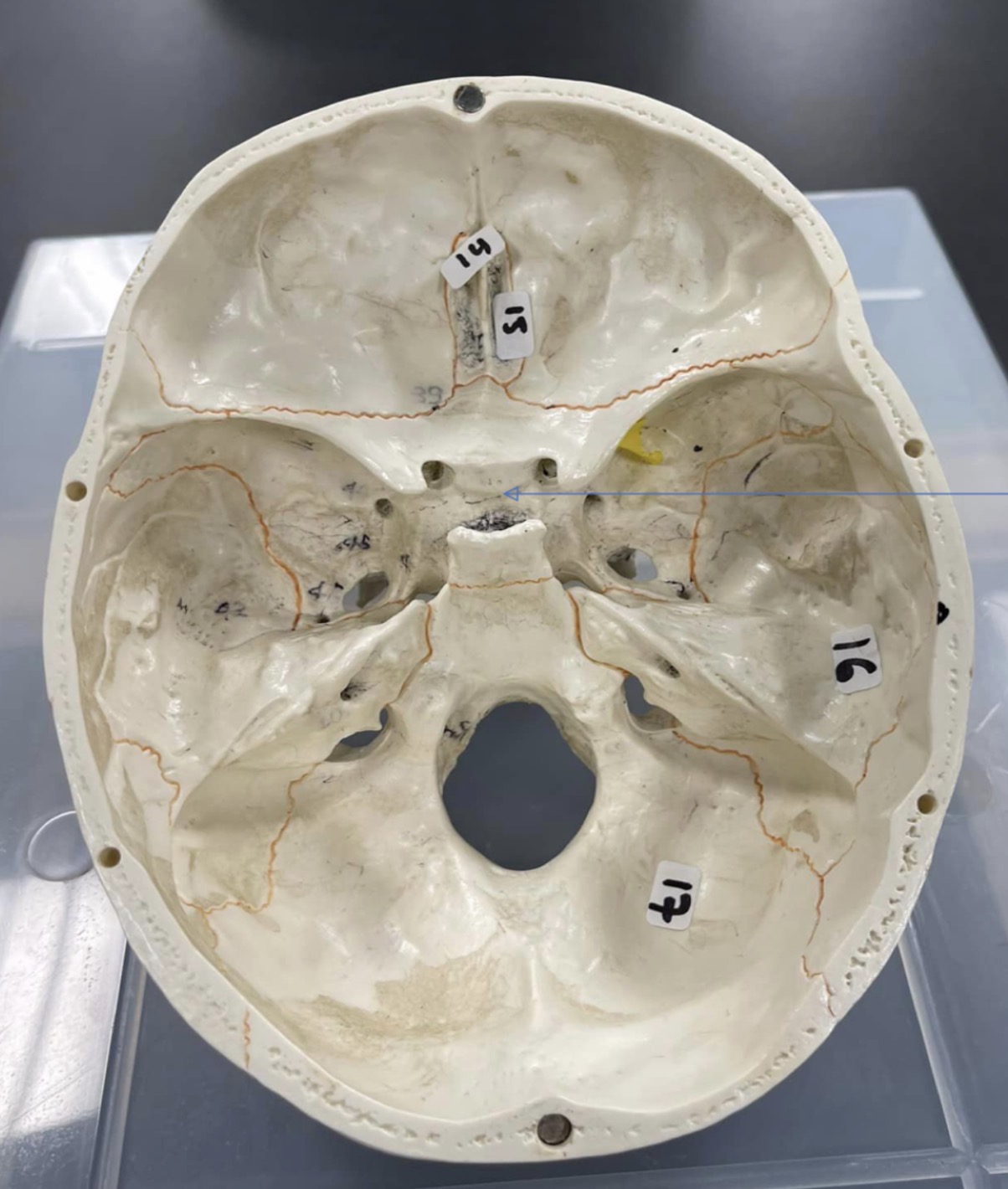
15
Cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
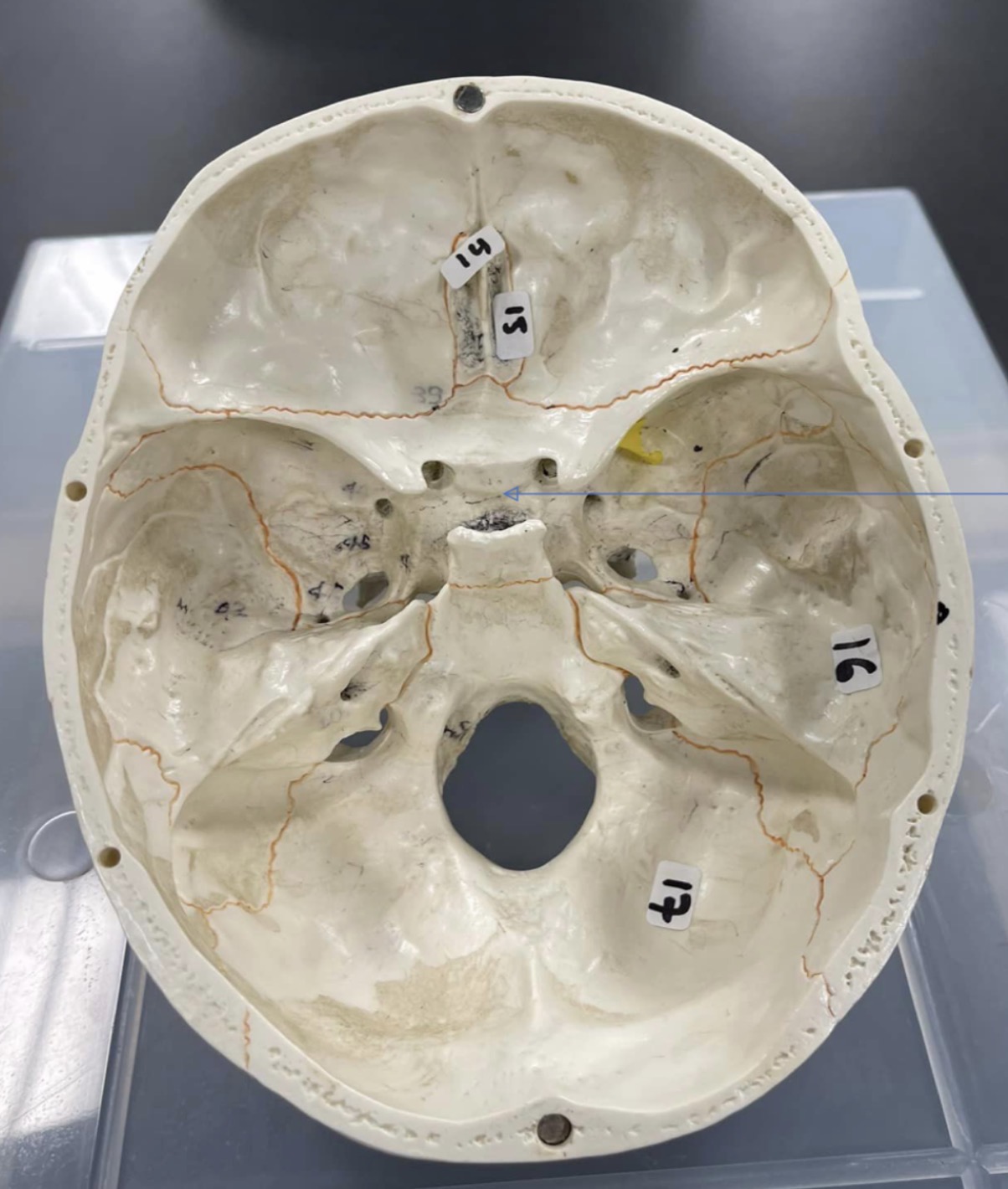
16
temporal bone of the skull
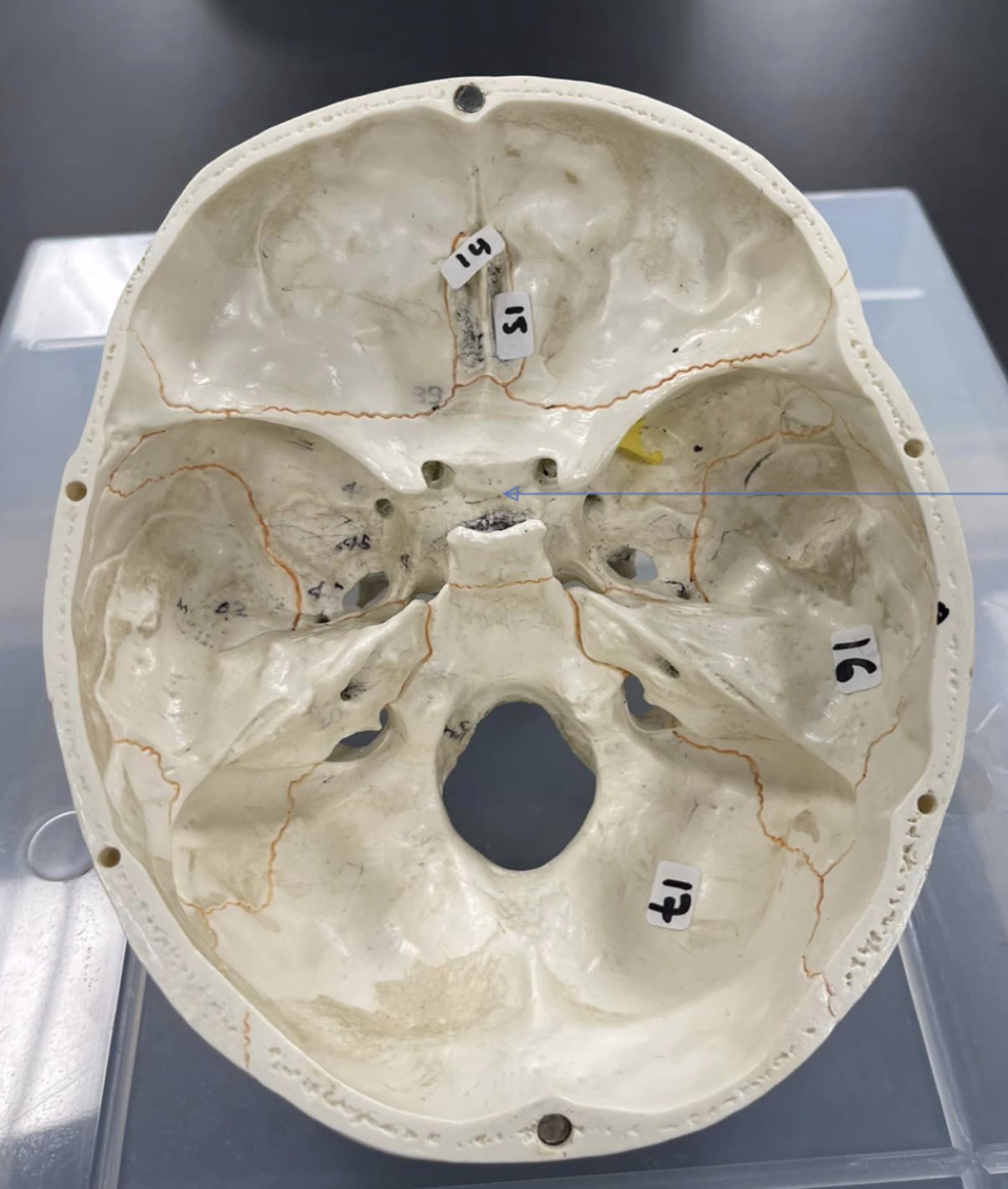
17
occipital bone of the skull
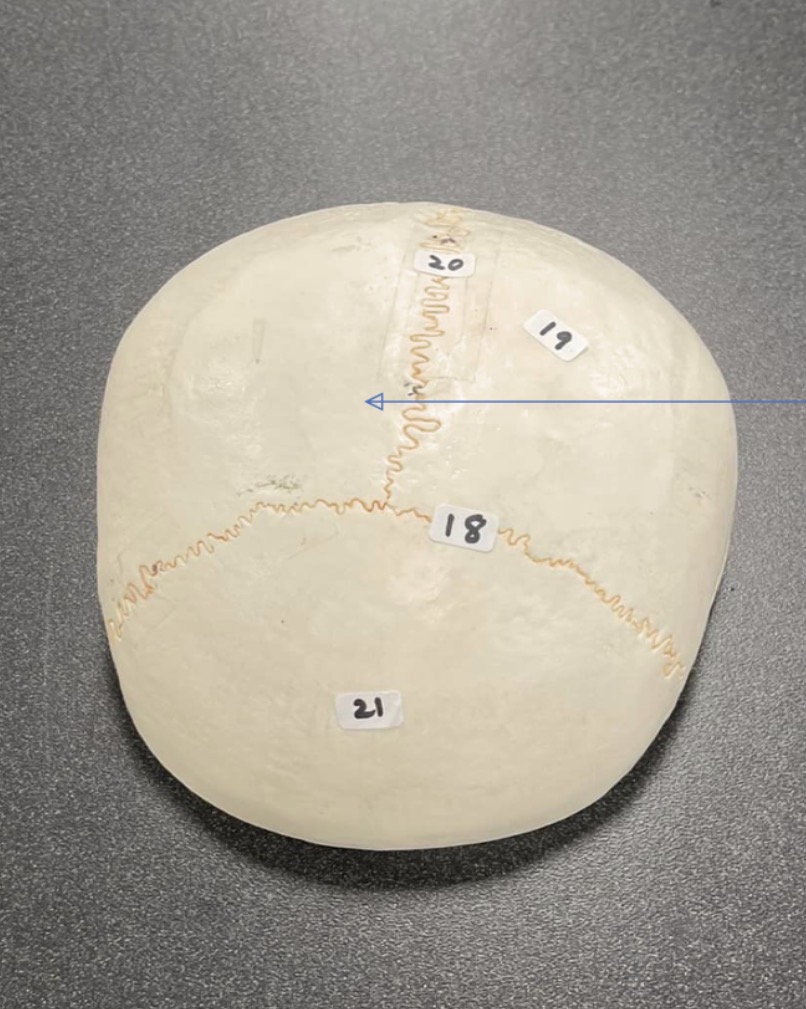

18
coronal suture of skull
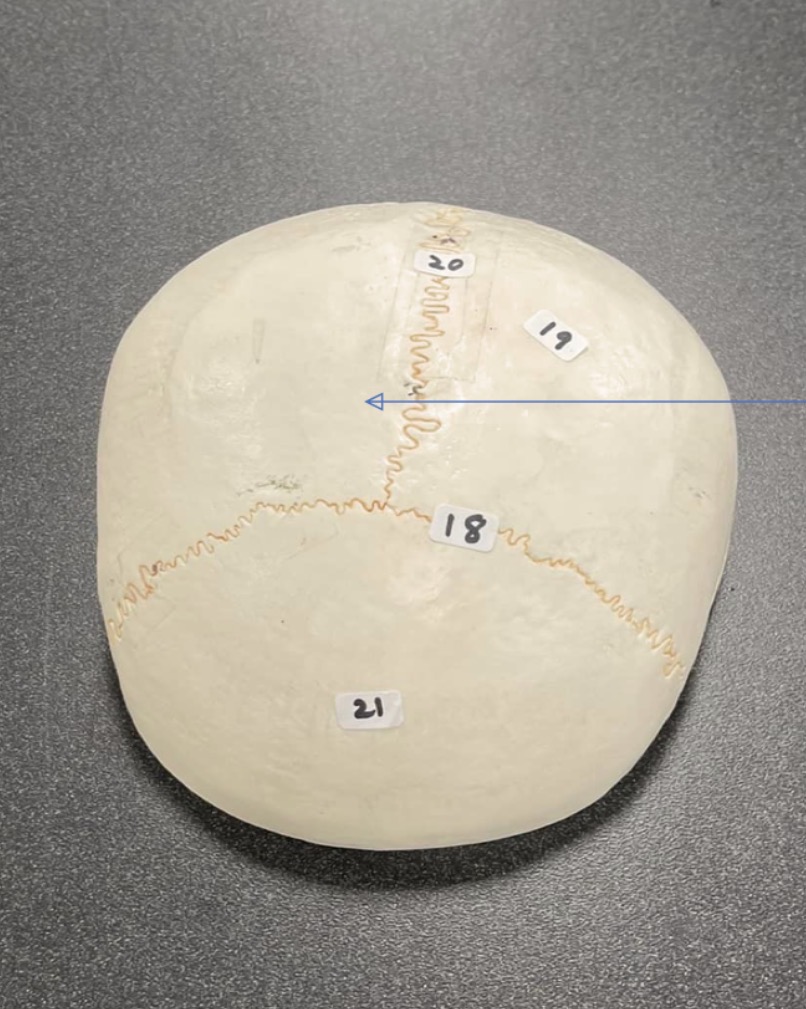

19
Parietal bone of the skull
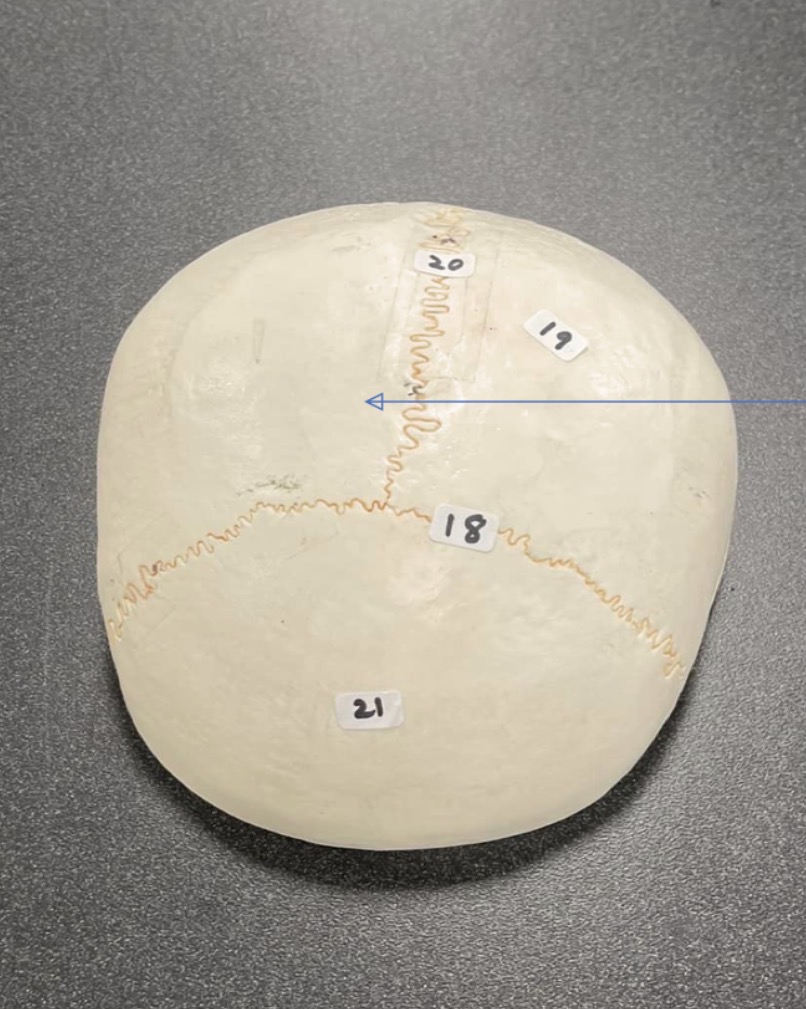

20
Sagittal suture of skull
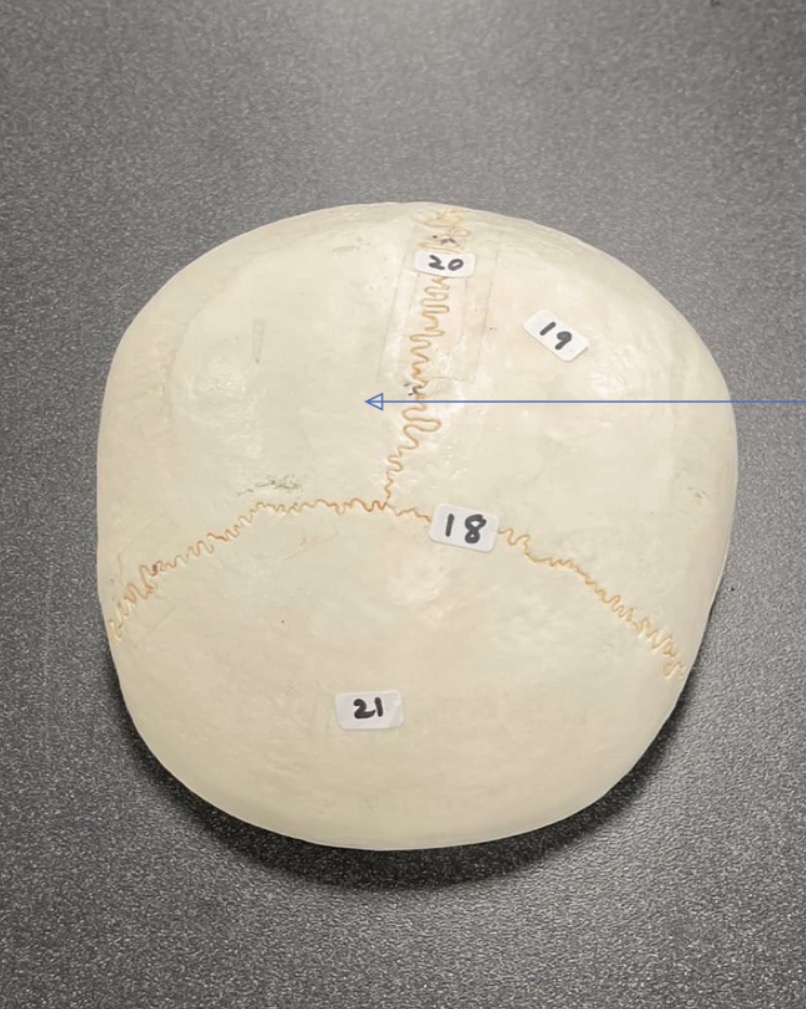

21
Frontal bone of the skull
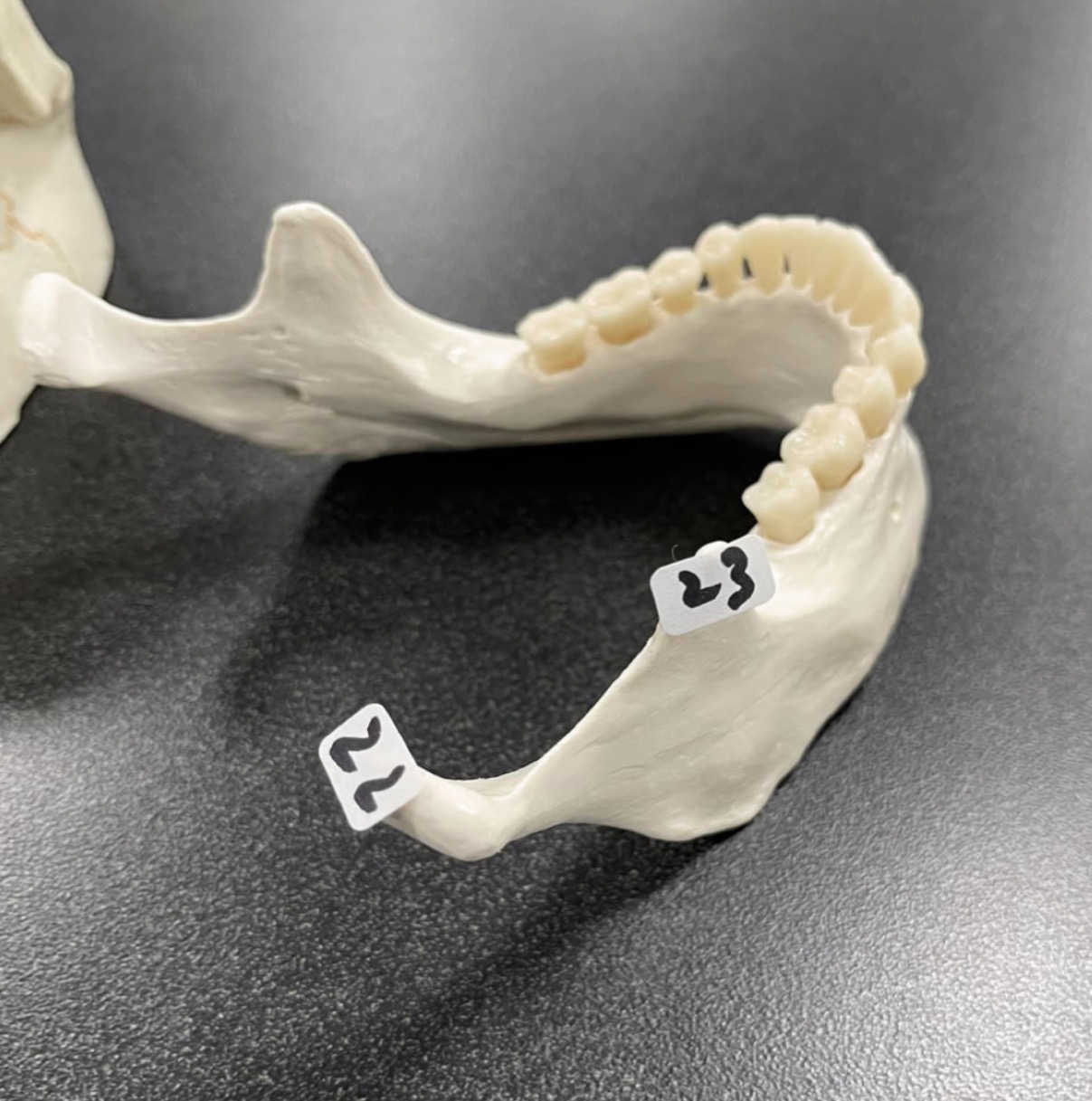
22
Mandibular condyle of the skull
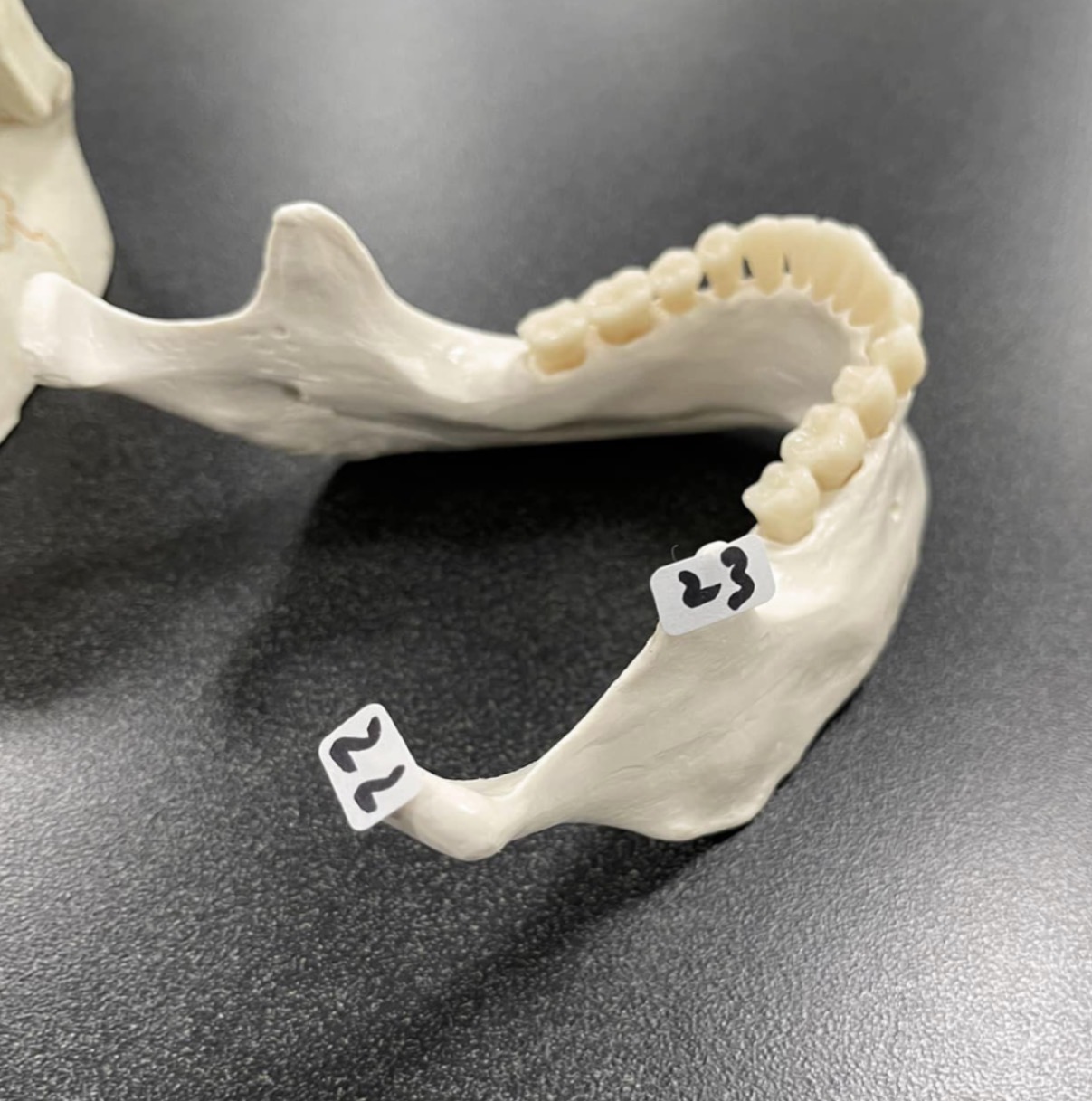
23
Coronoid process of the skull
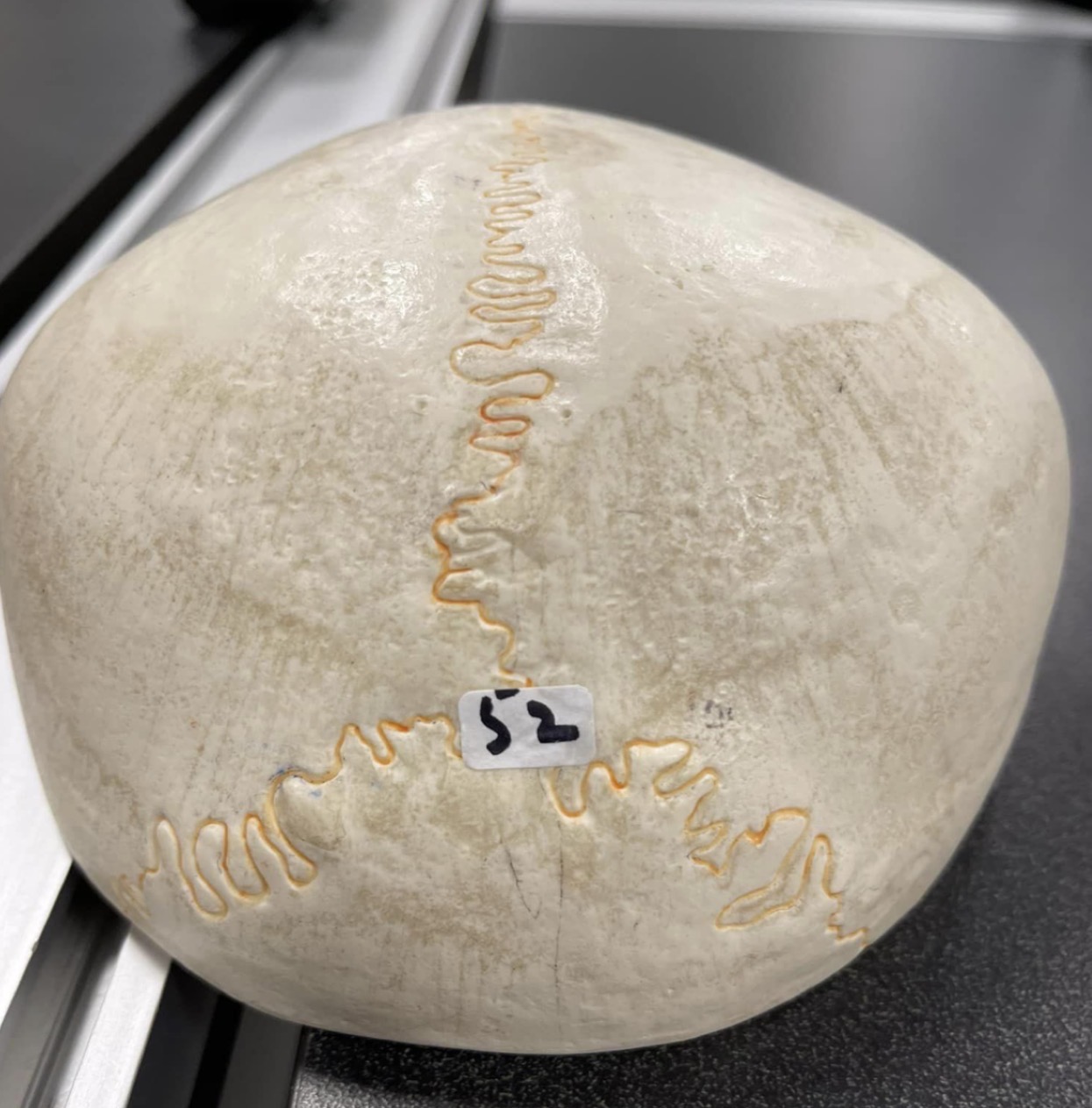

52
Lambdoid suture of skull
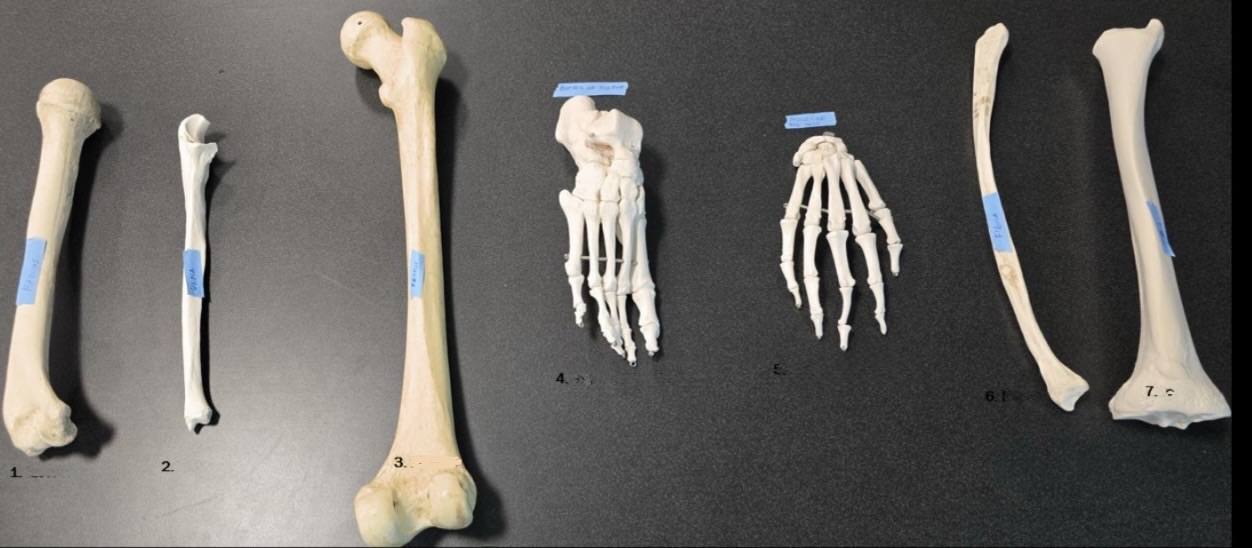
1
Radius
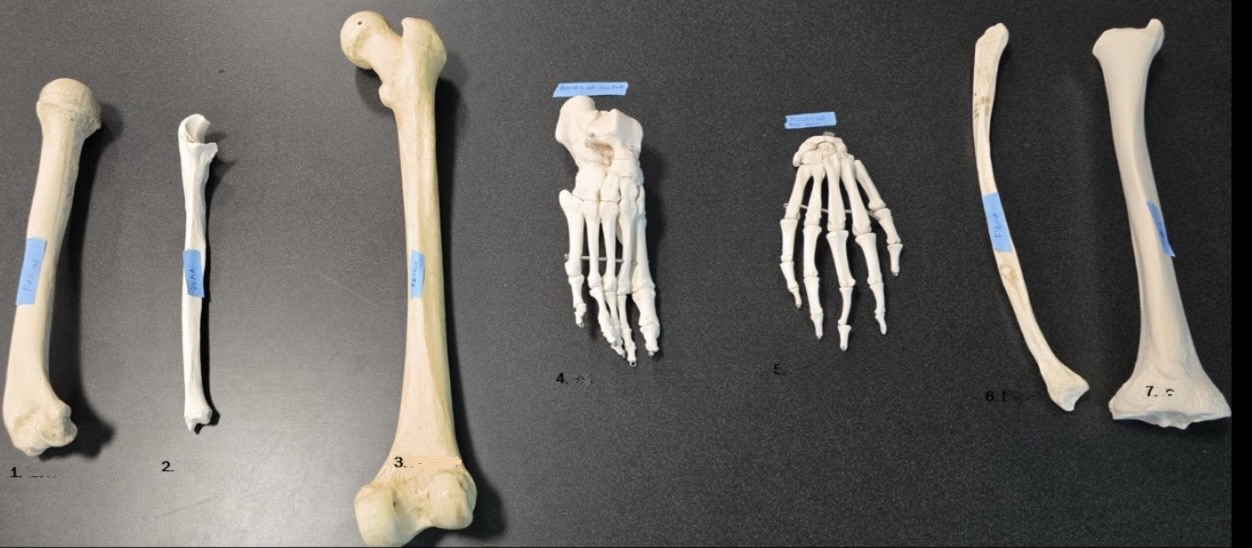
2
Ulna
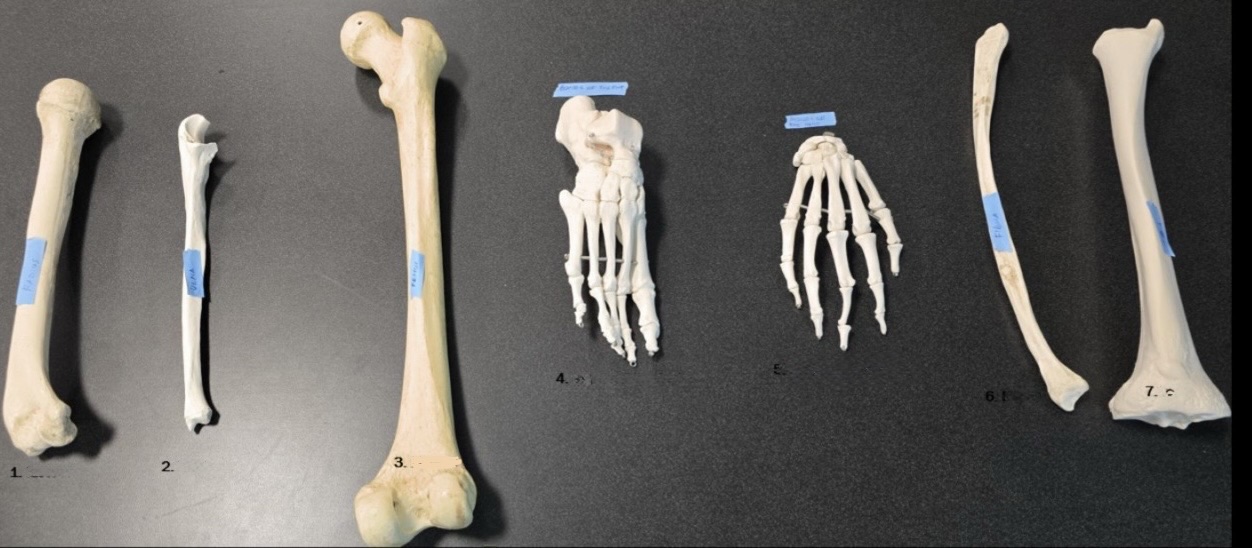
3
Femur
4
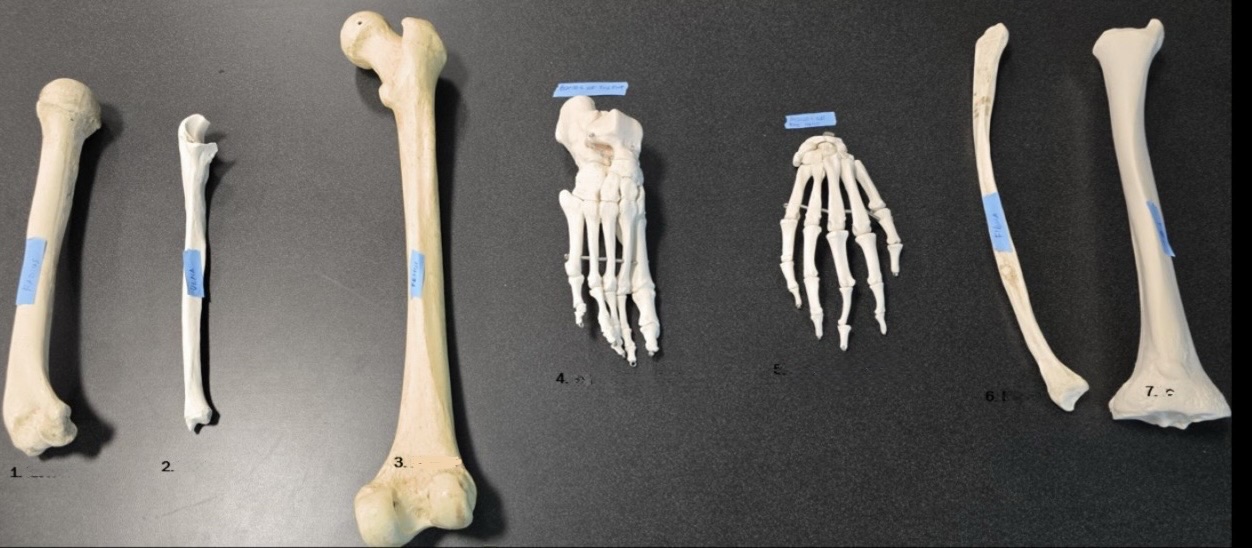
Bones of the foot
5
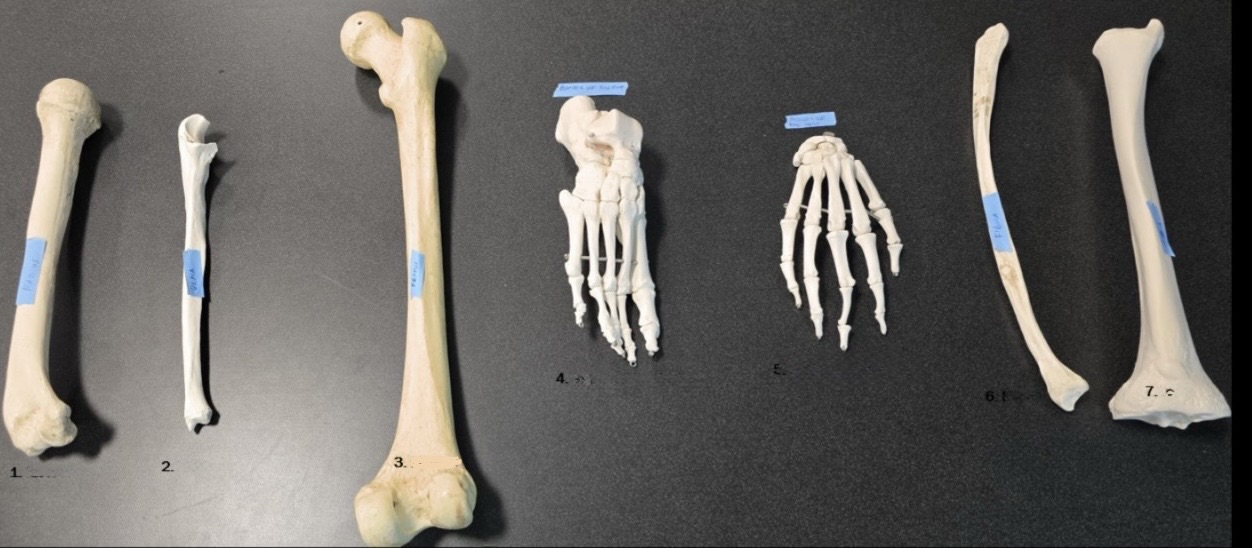
Bones of the hand
6
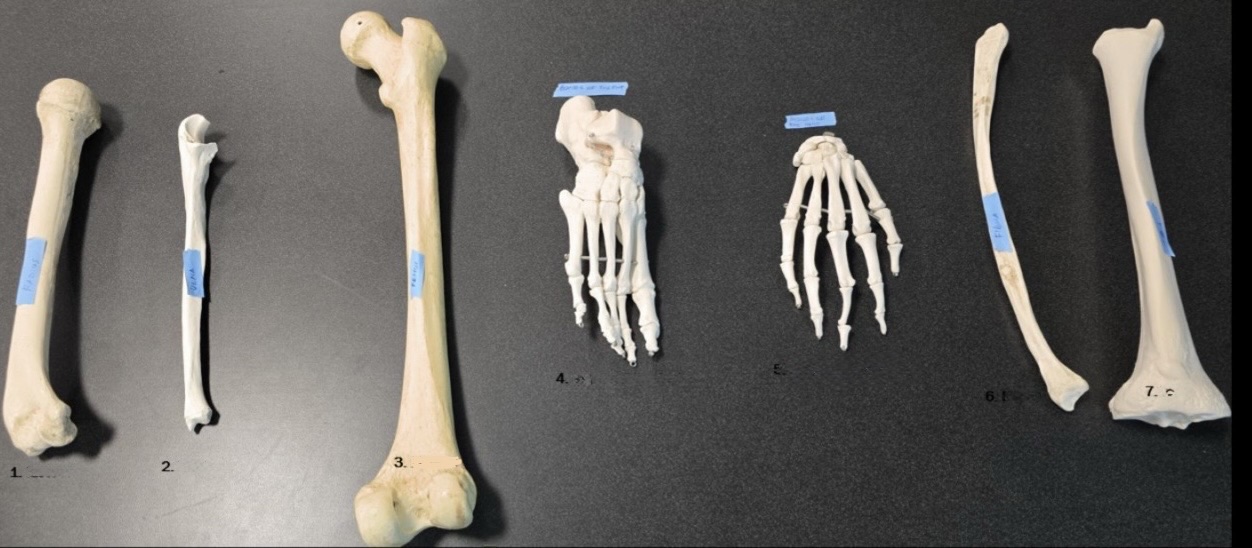
Fibula
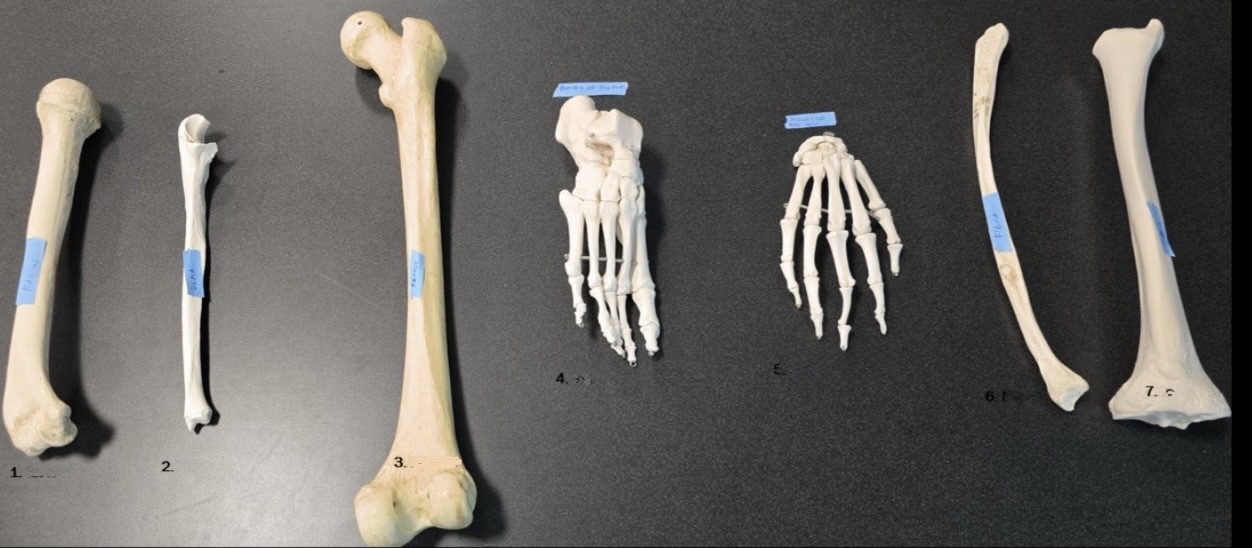
7
Tibia
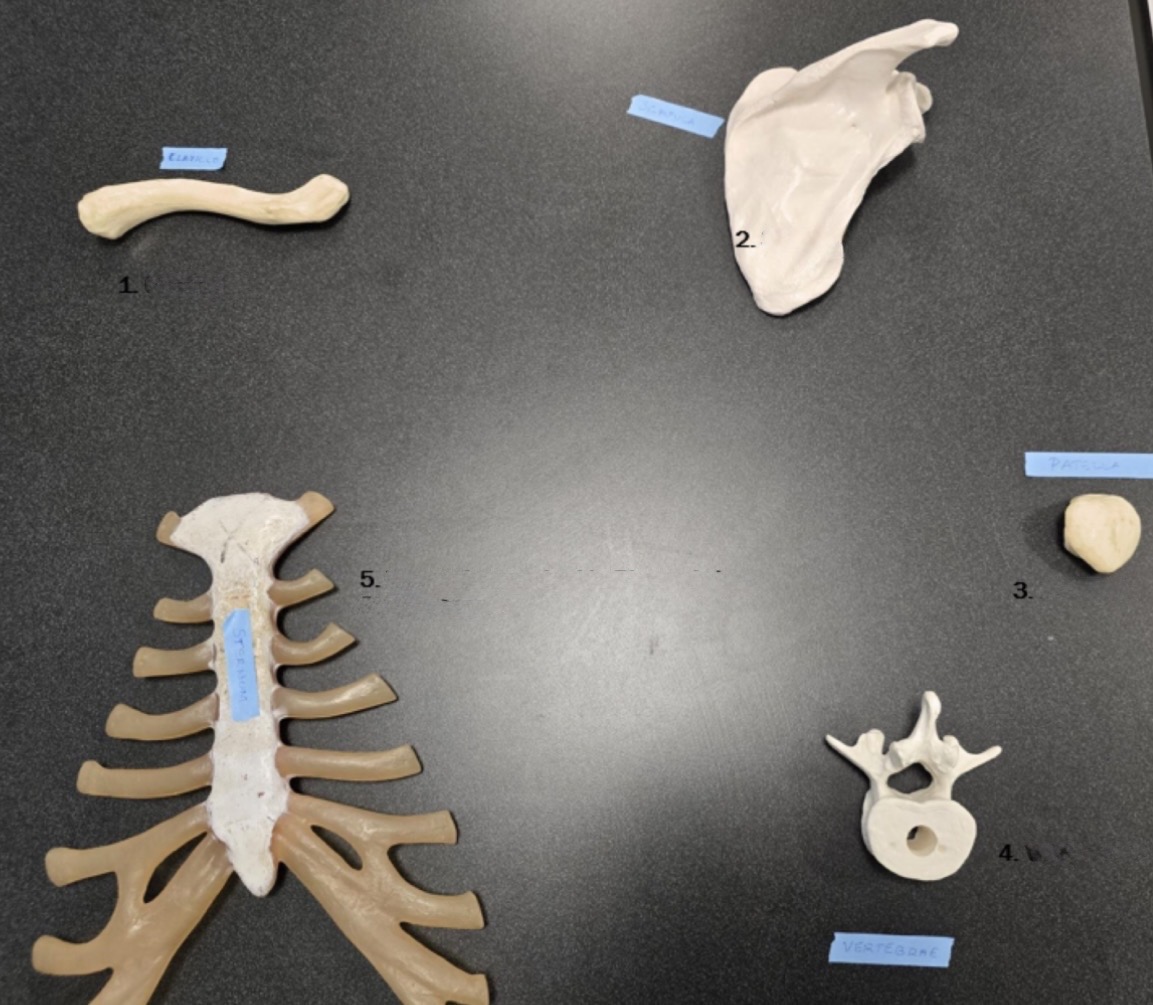
1
Clavicle
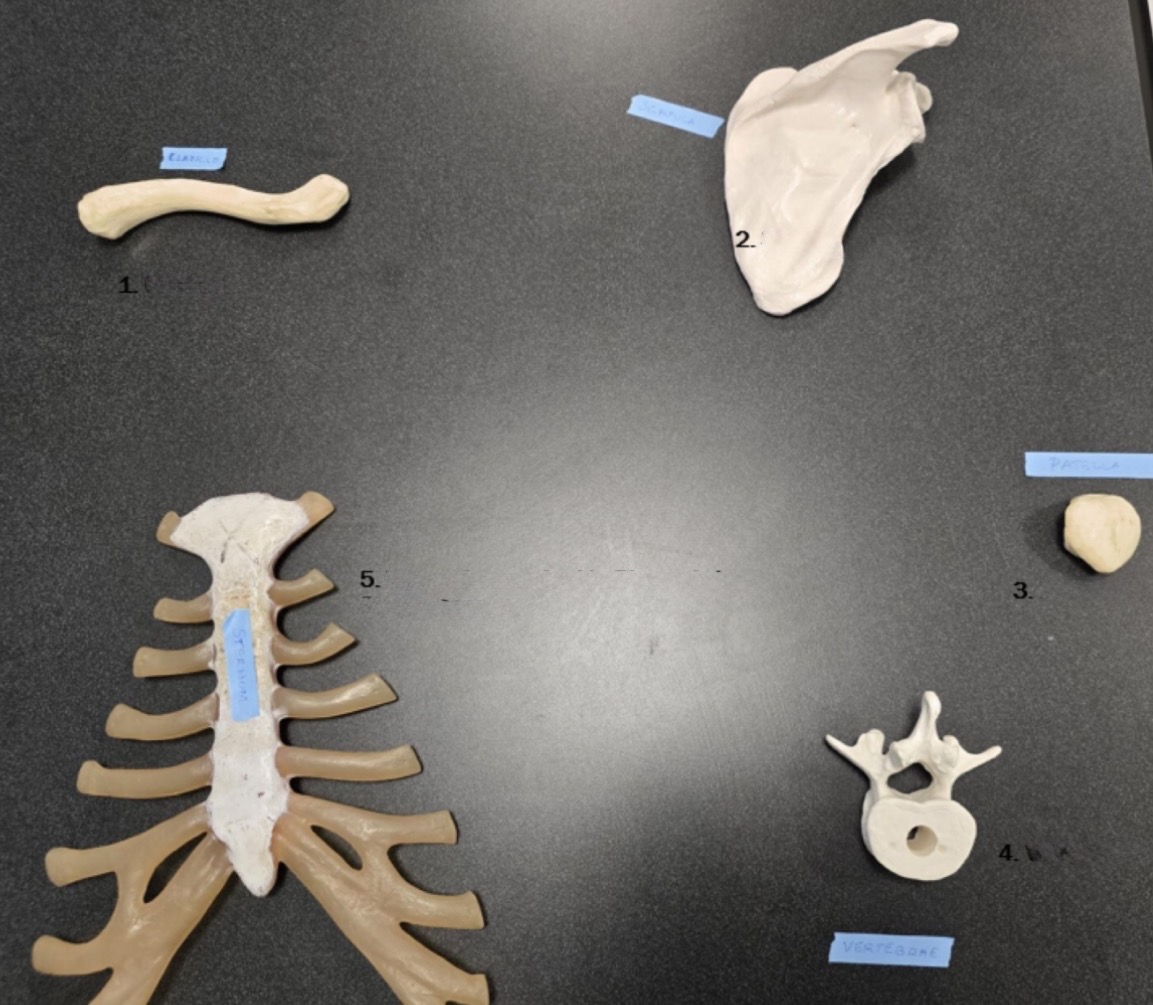
2
Scapula
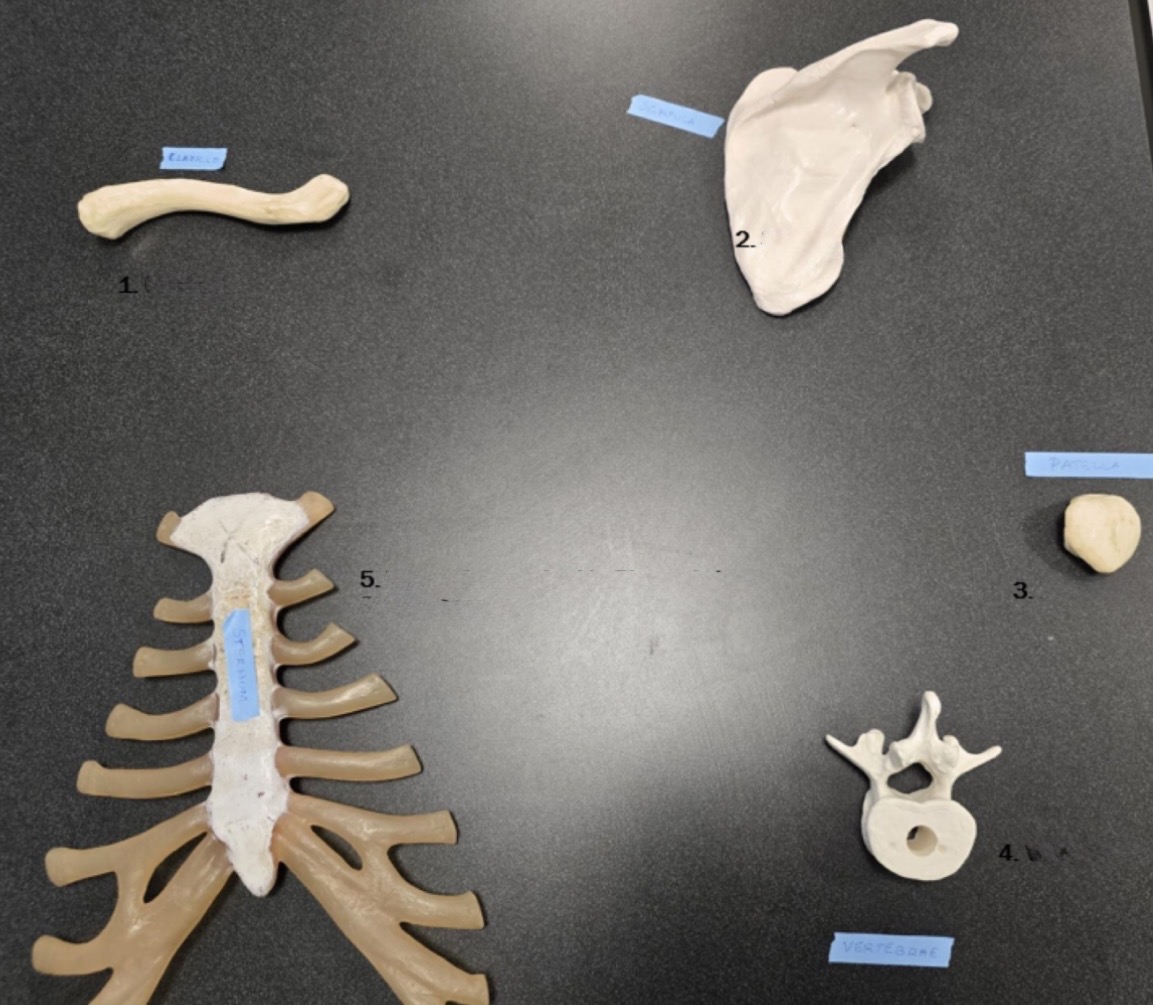
3
Patella
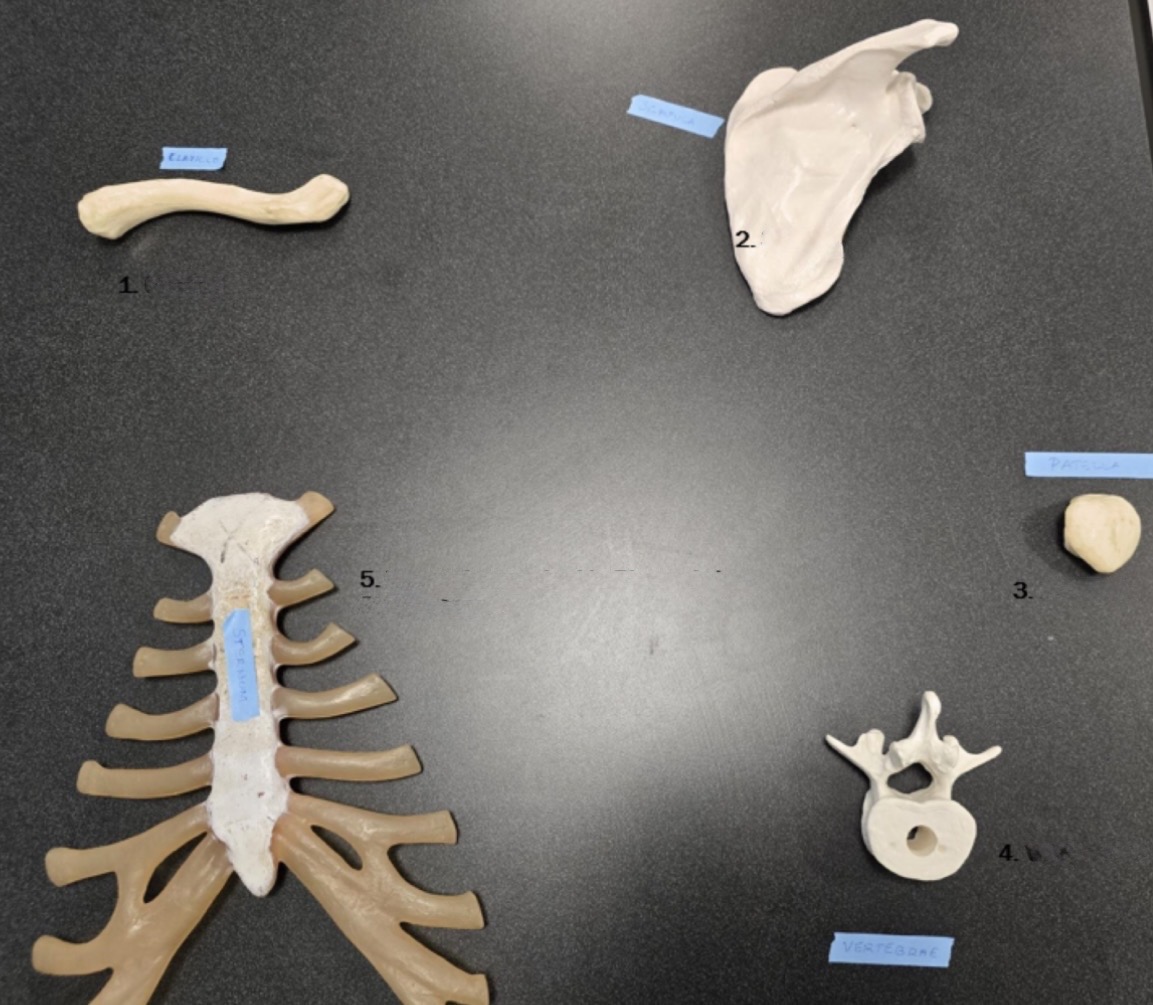
4
Vertebrae
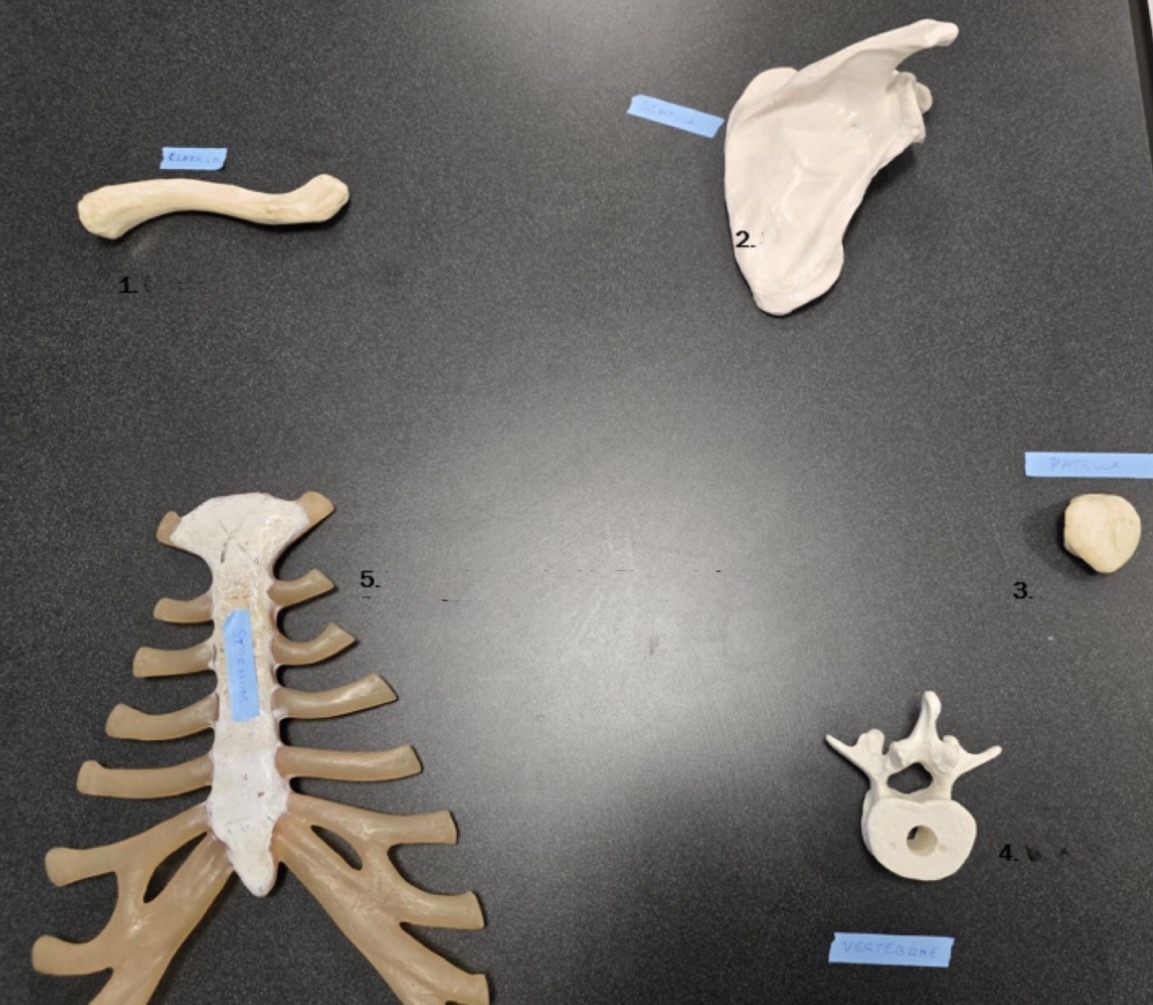
5
Sternum
Lamellae
Provide strength to your bone
Trabecula
Air-filled cavity within spongy bone
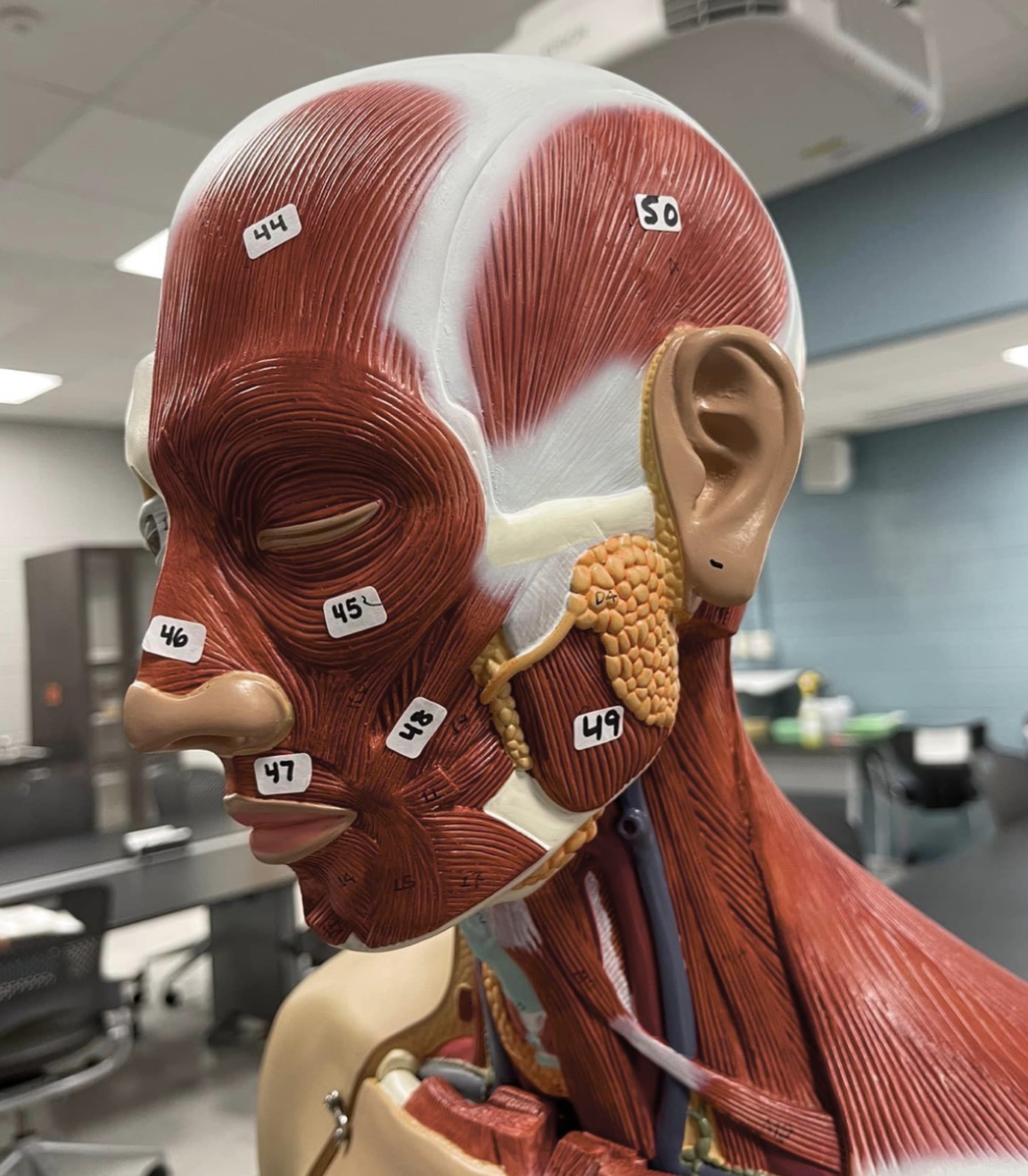
44
Frontalis muscle of the face
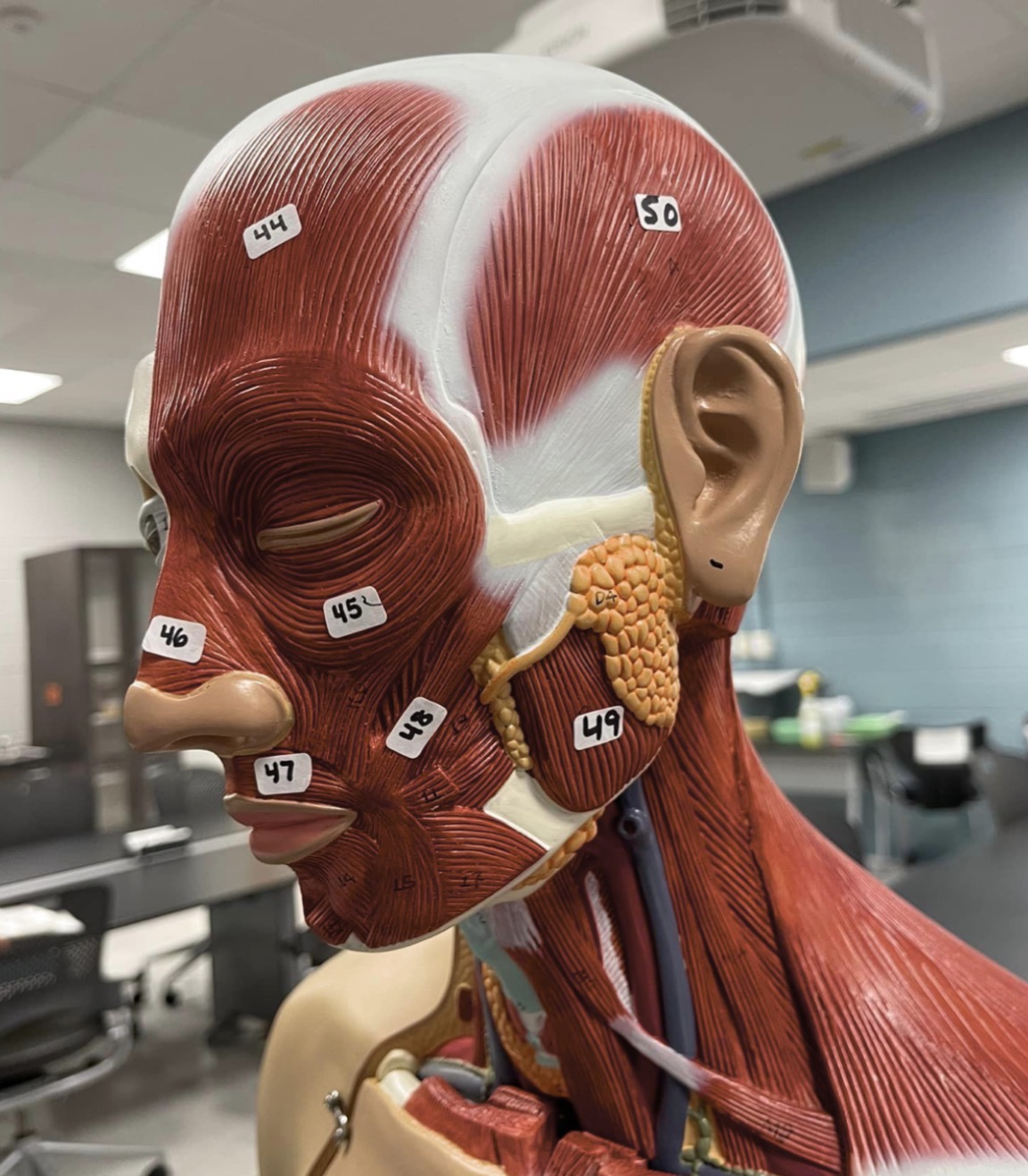
45
Orbicularis oculi muscle of the face
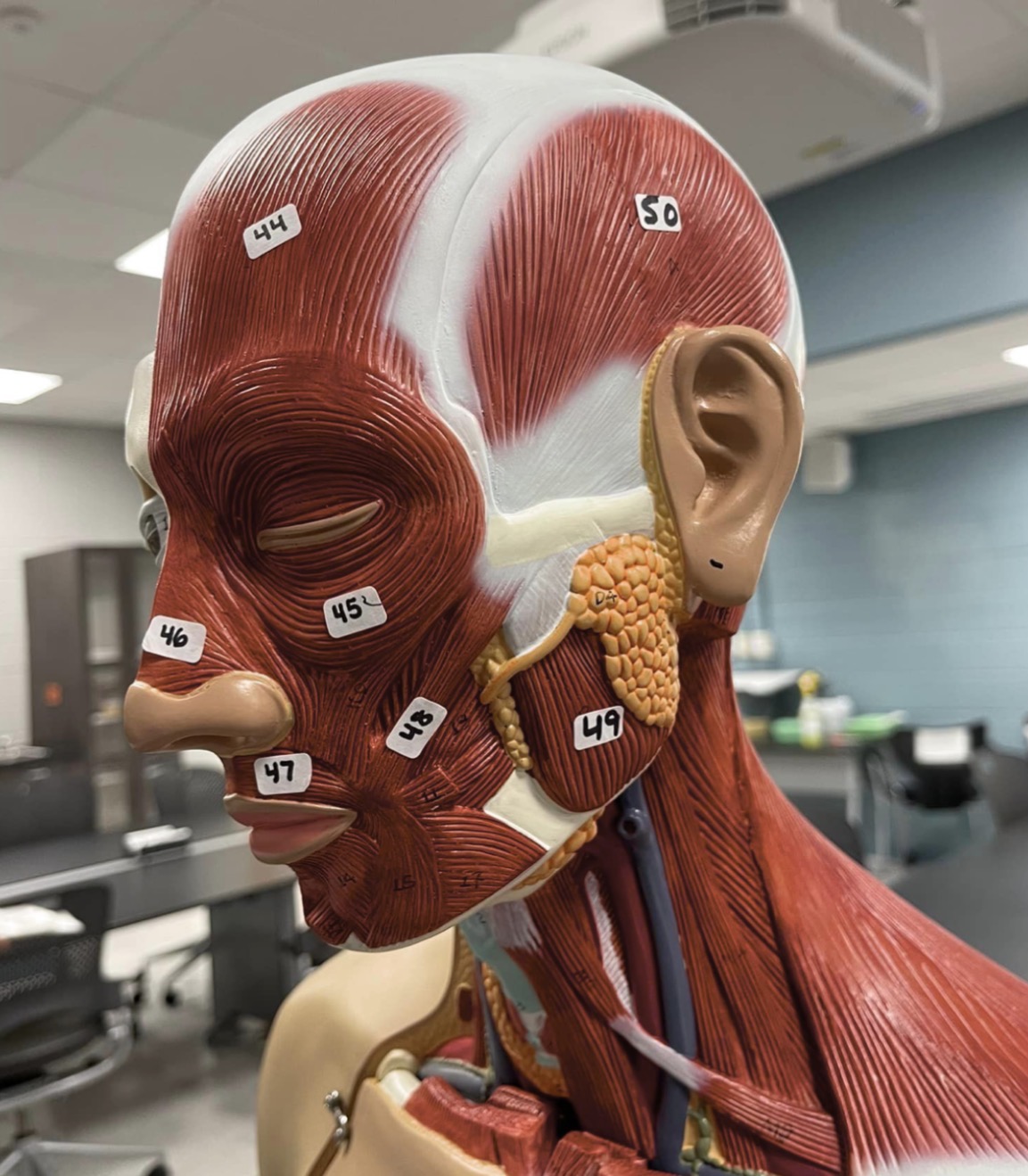
46
Nasalis muscle of the face
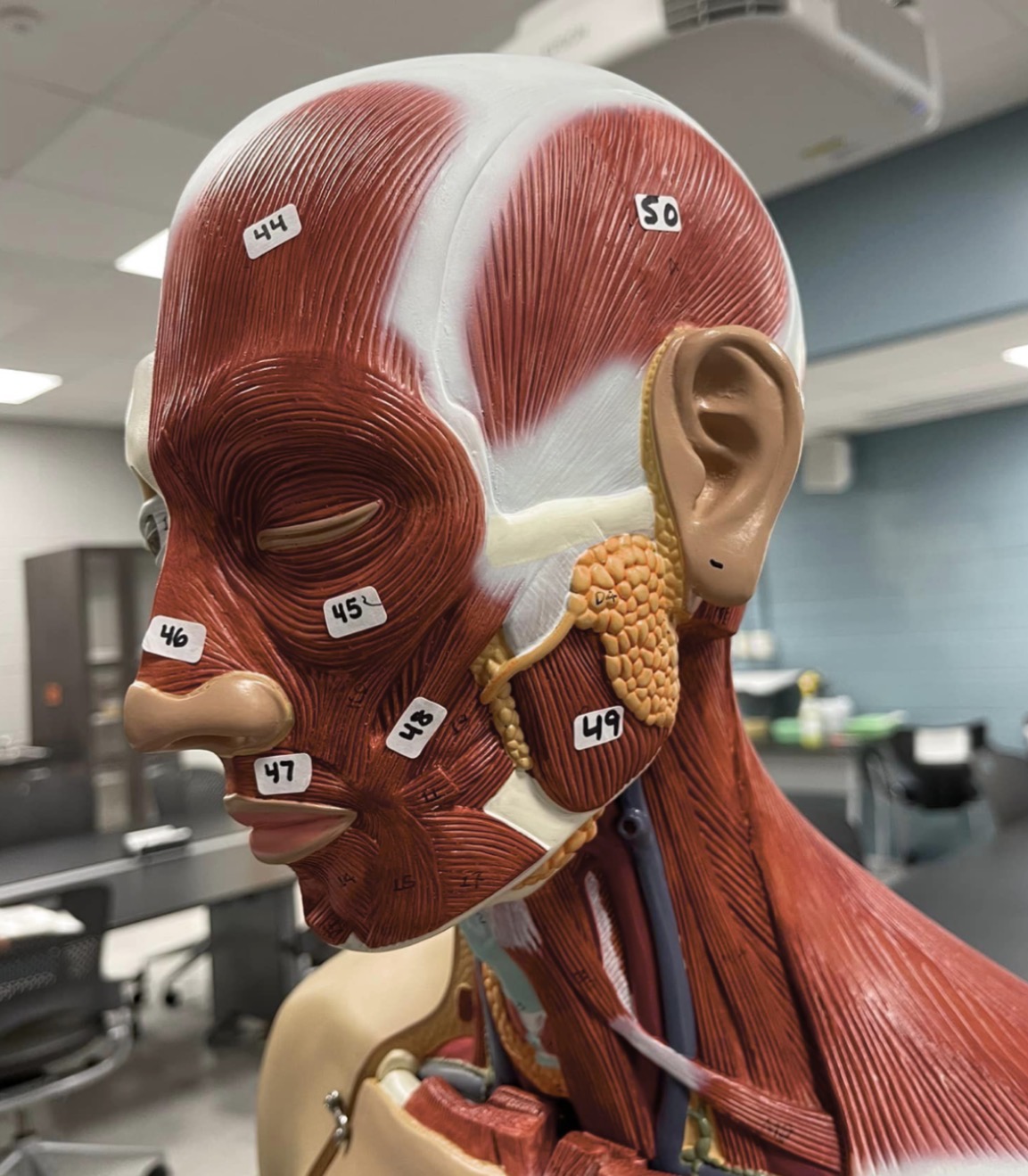
47
Orbicularis oris of the face
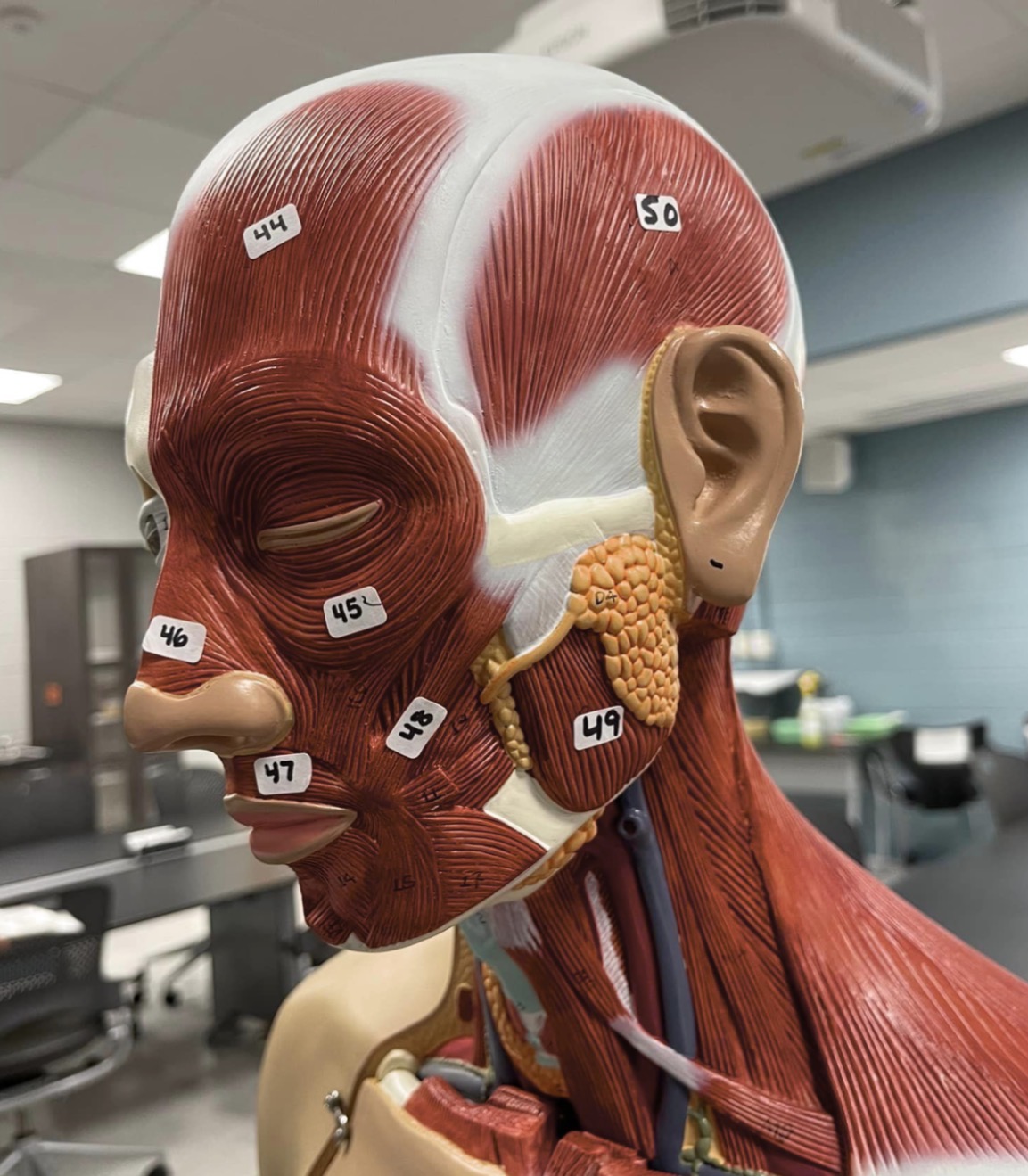
48
Zygomaticus muscle of the face
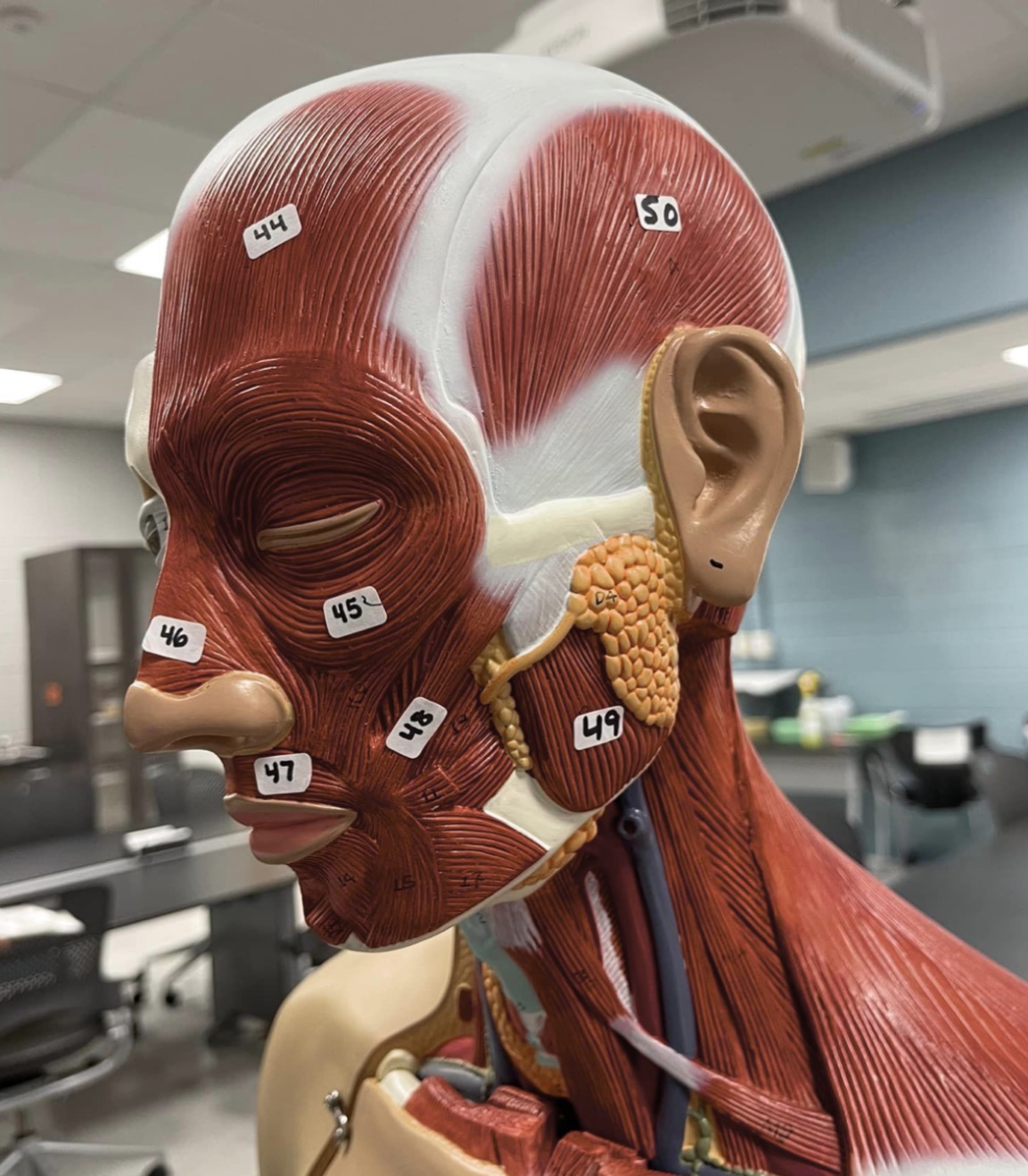
49
Masseter muscle of mastication
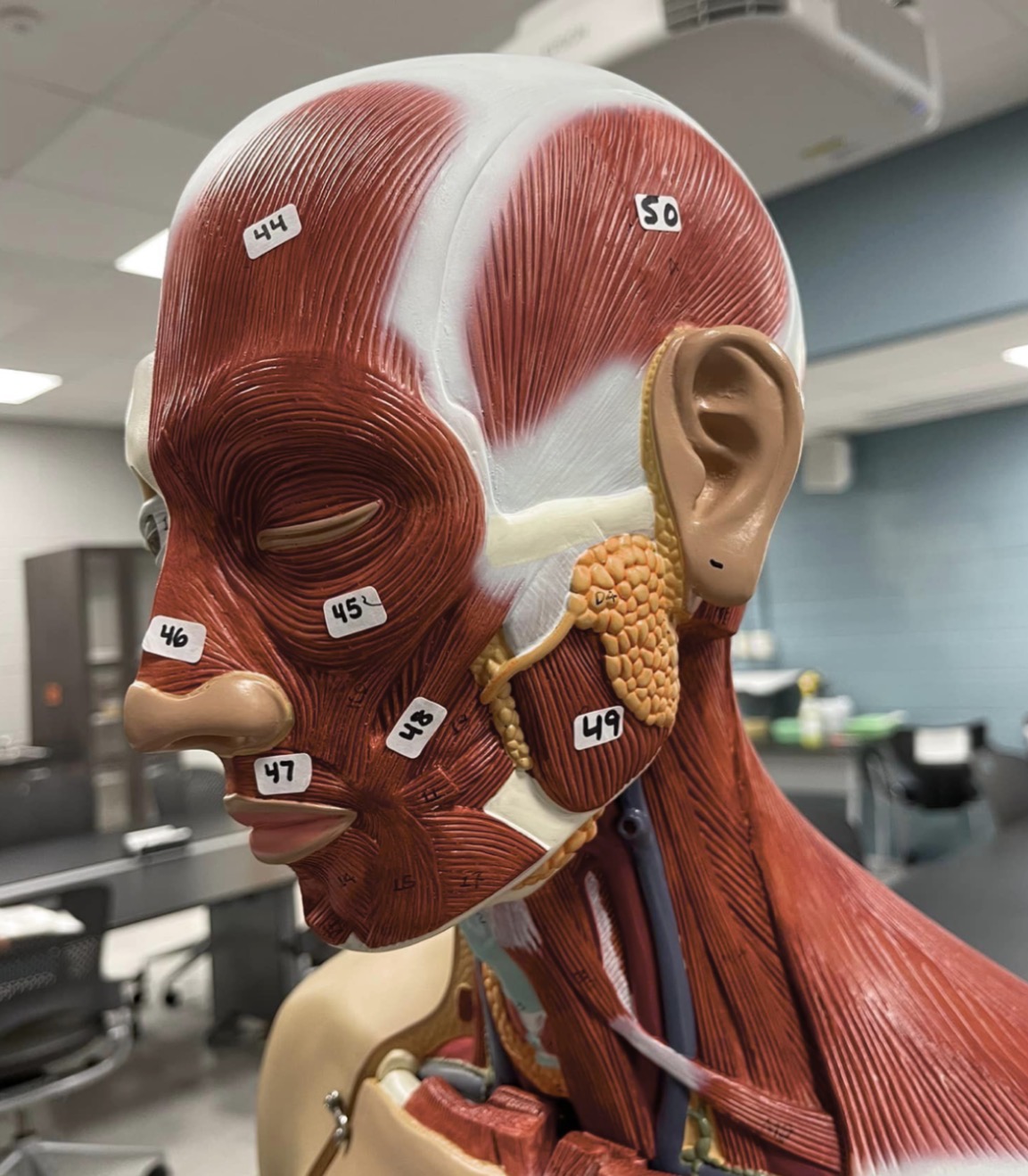
50
Temporalis muscle of mastication
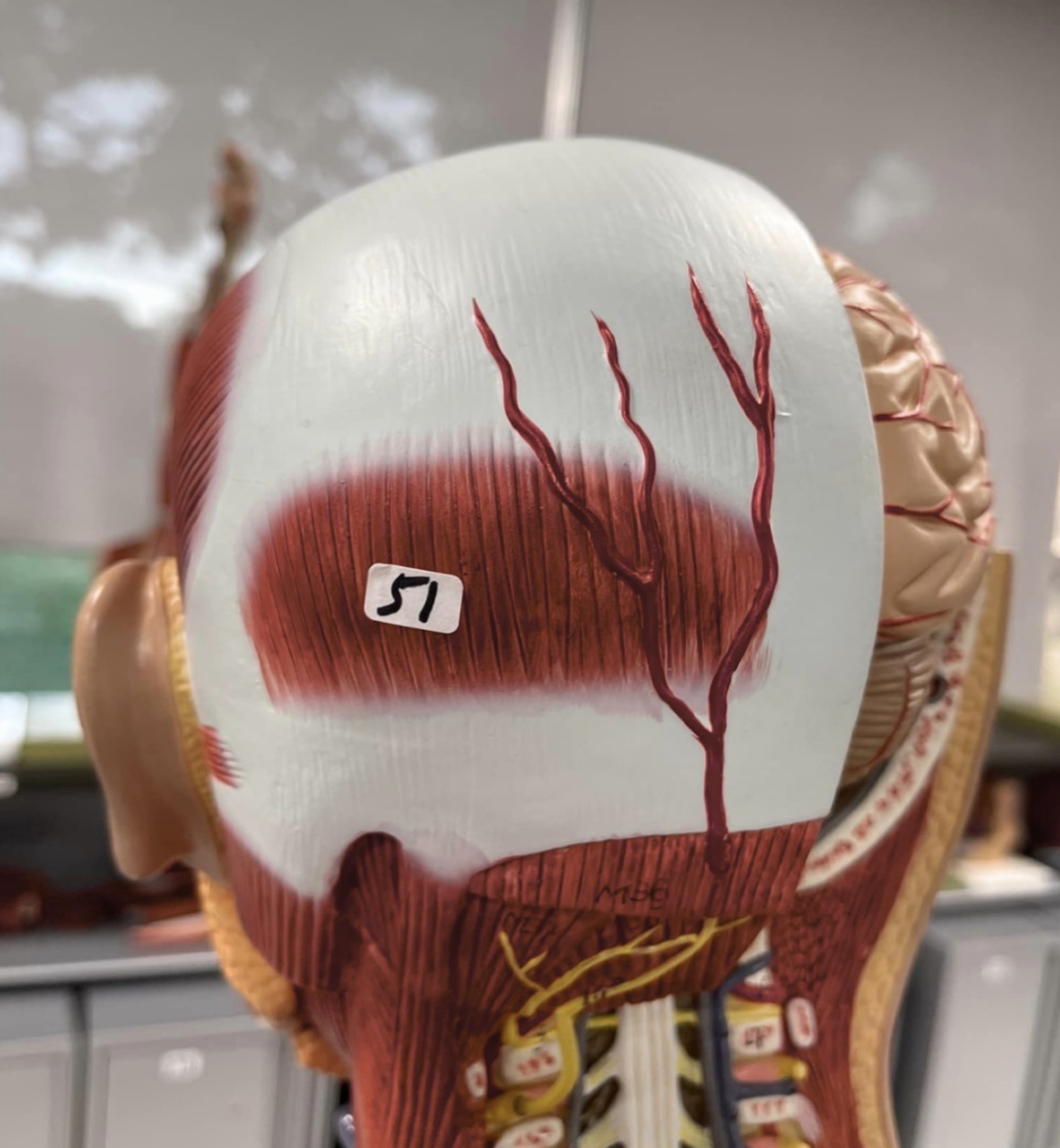

51
Occipitalis muscle of the skull
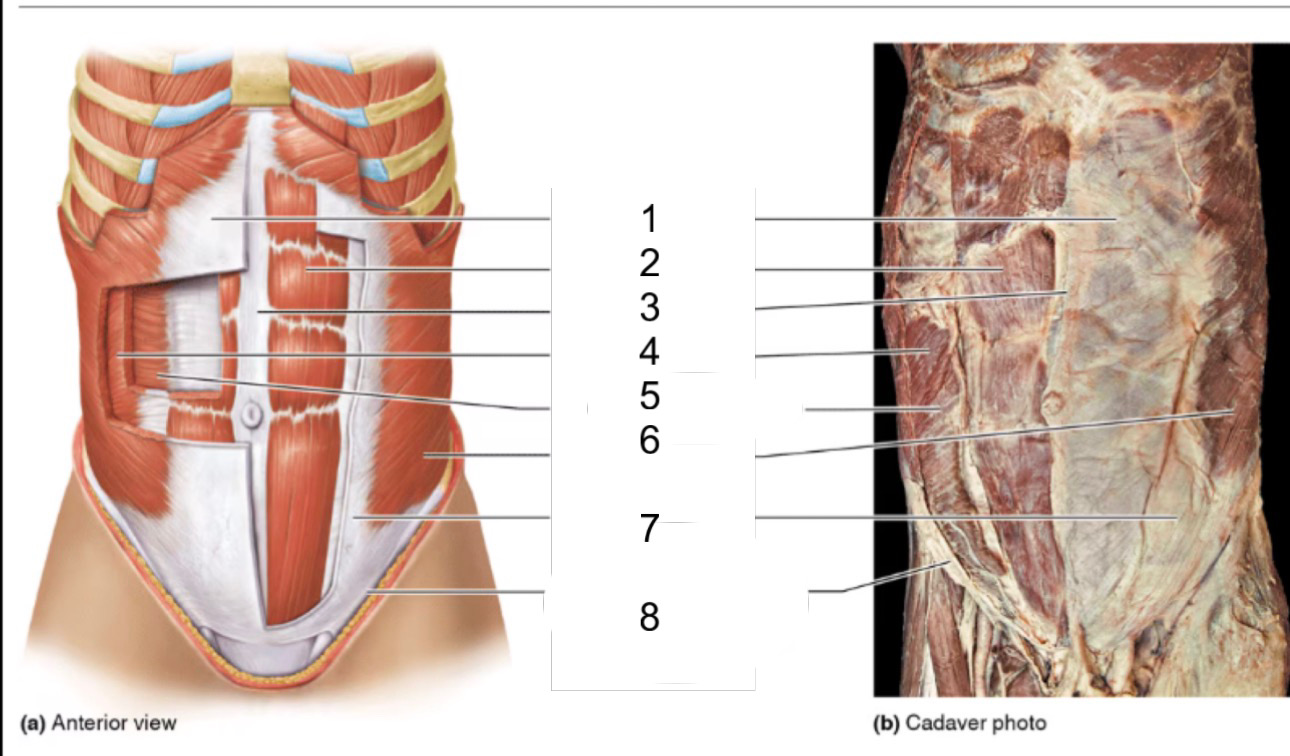
1
rectus sheath
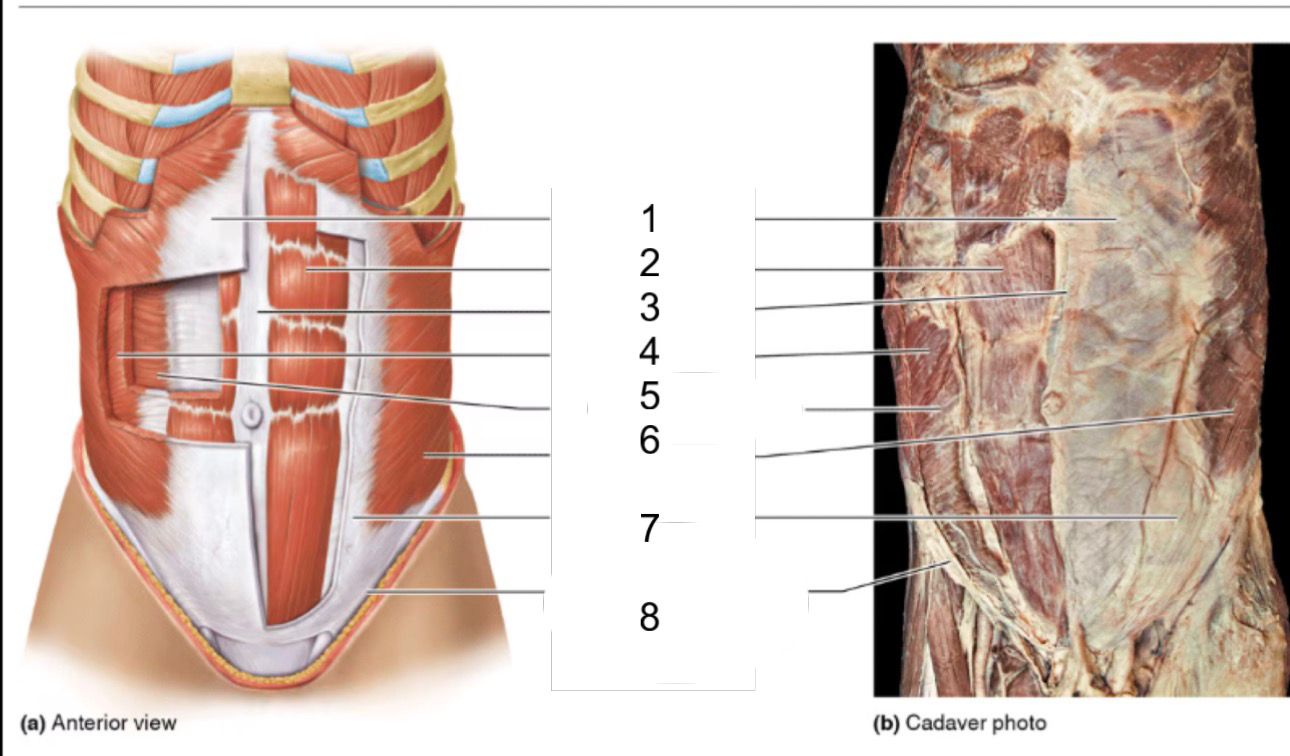
2
rectus abdominis
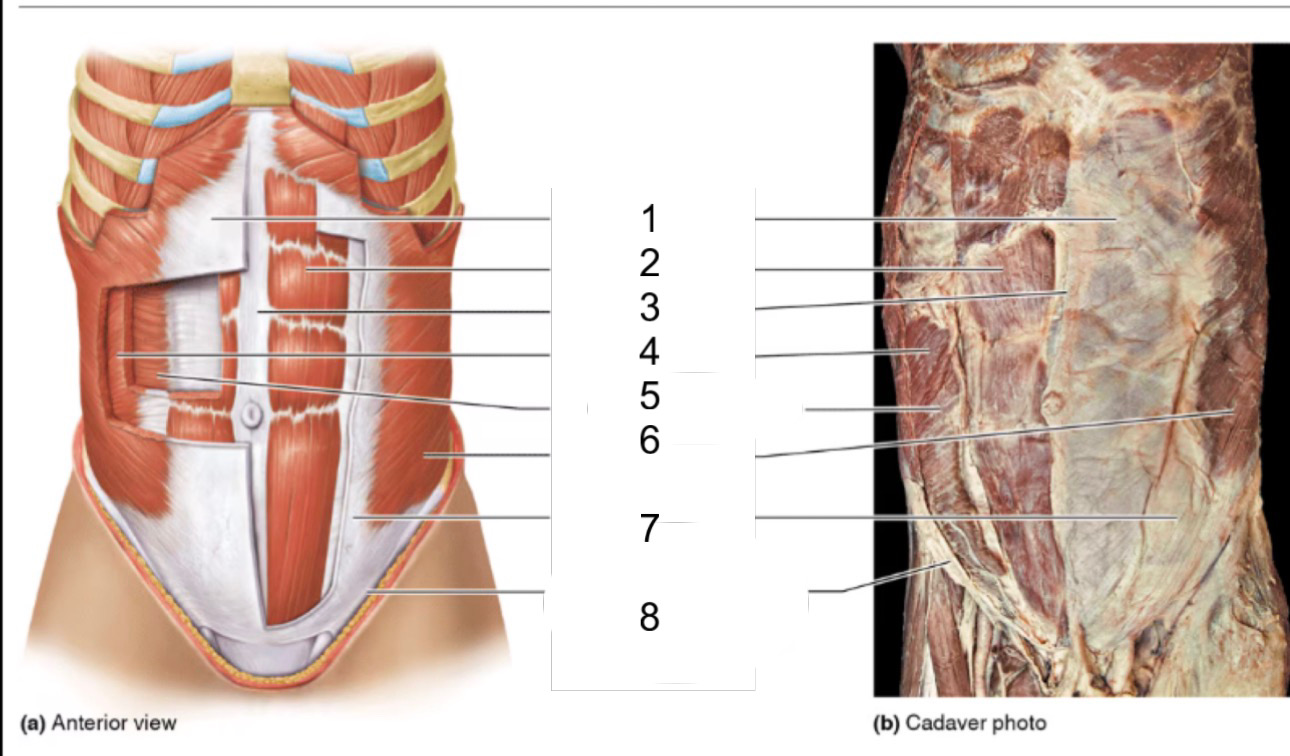
3
linea alba
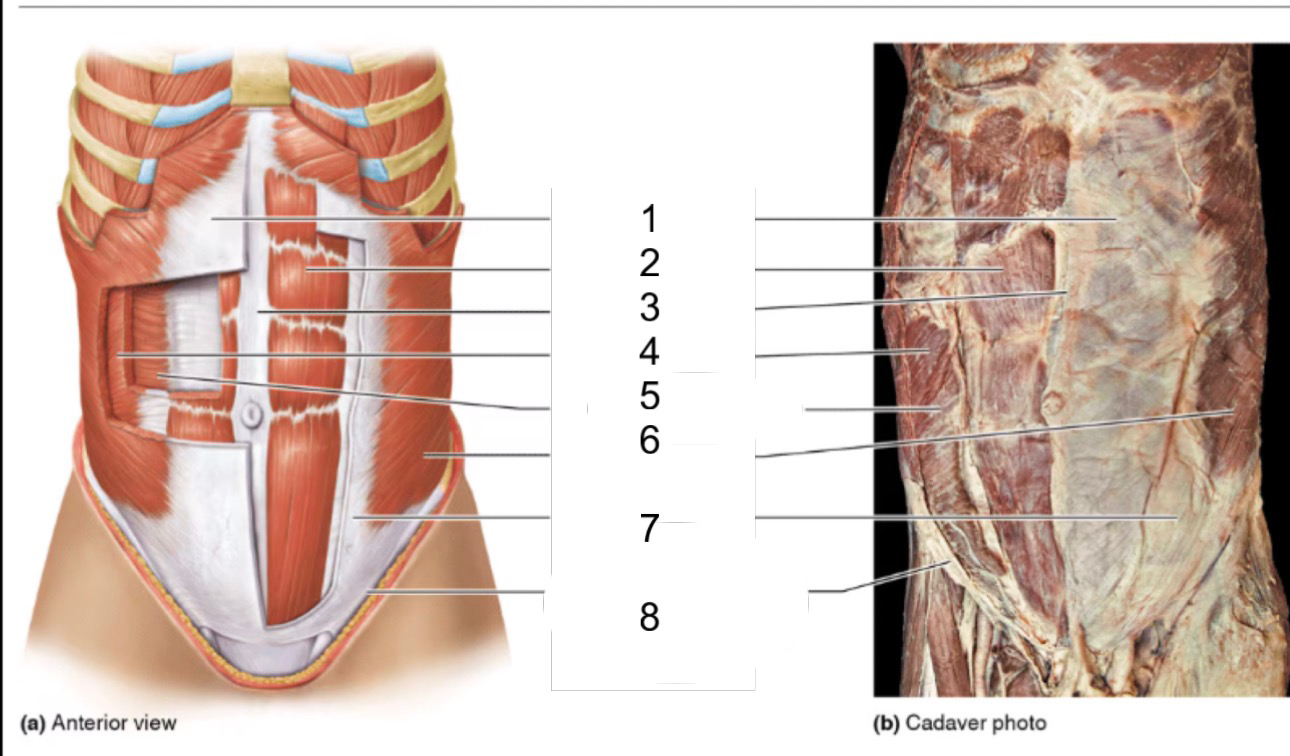
4
internal oblique
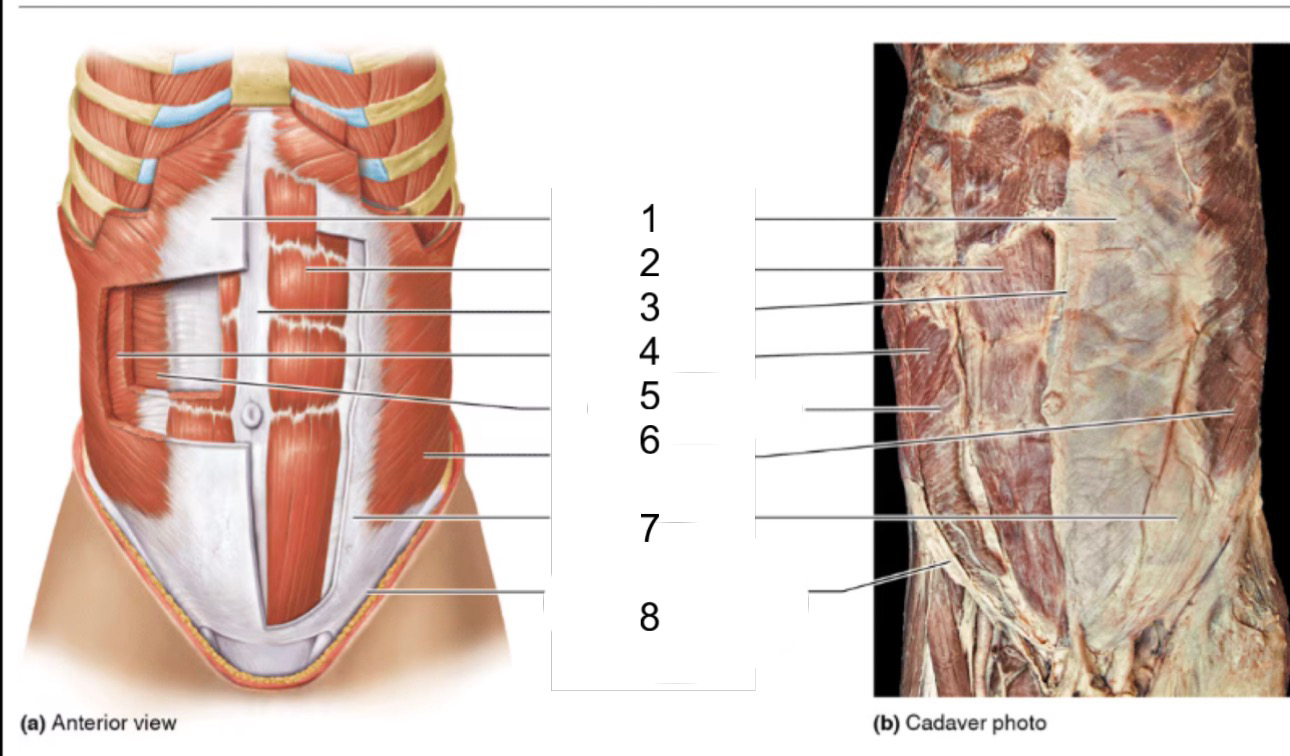
5
transversus abdominis
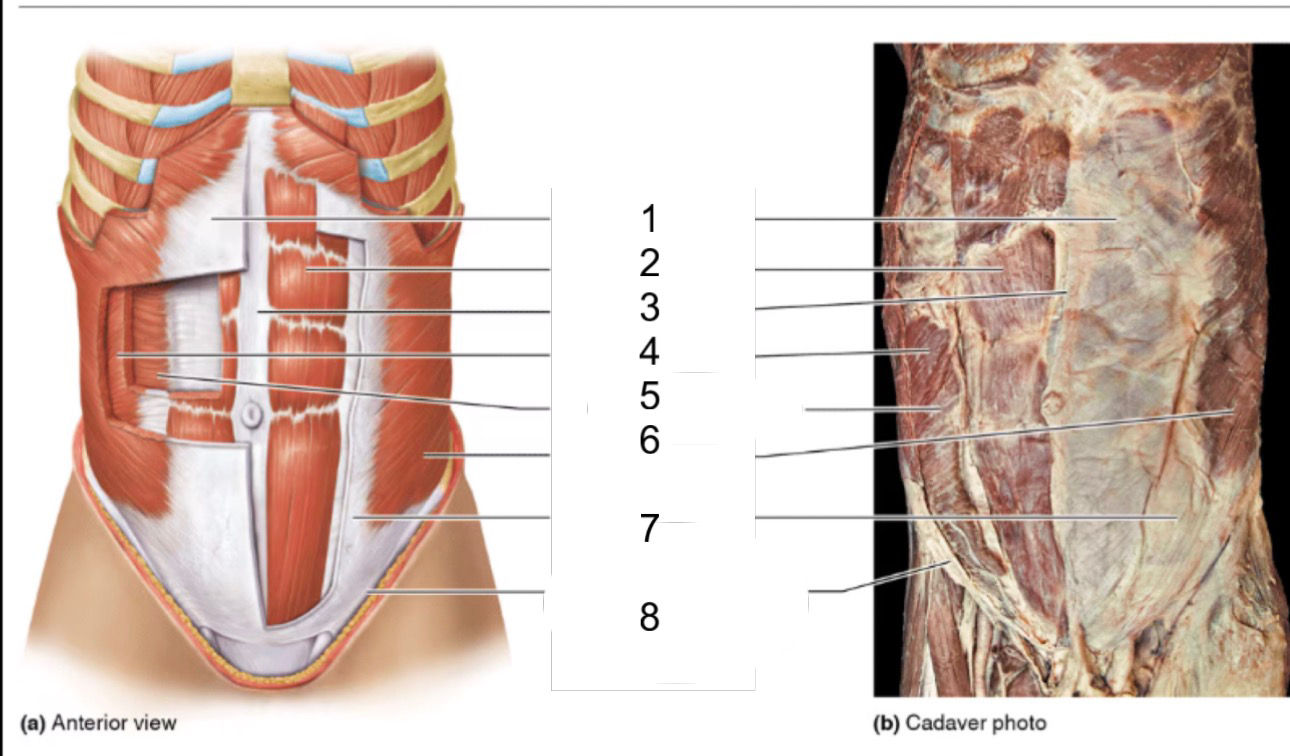
6
external oblique
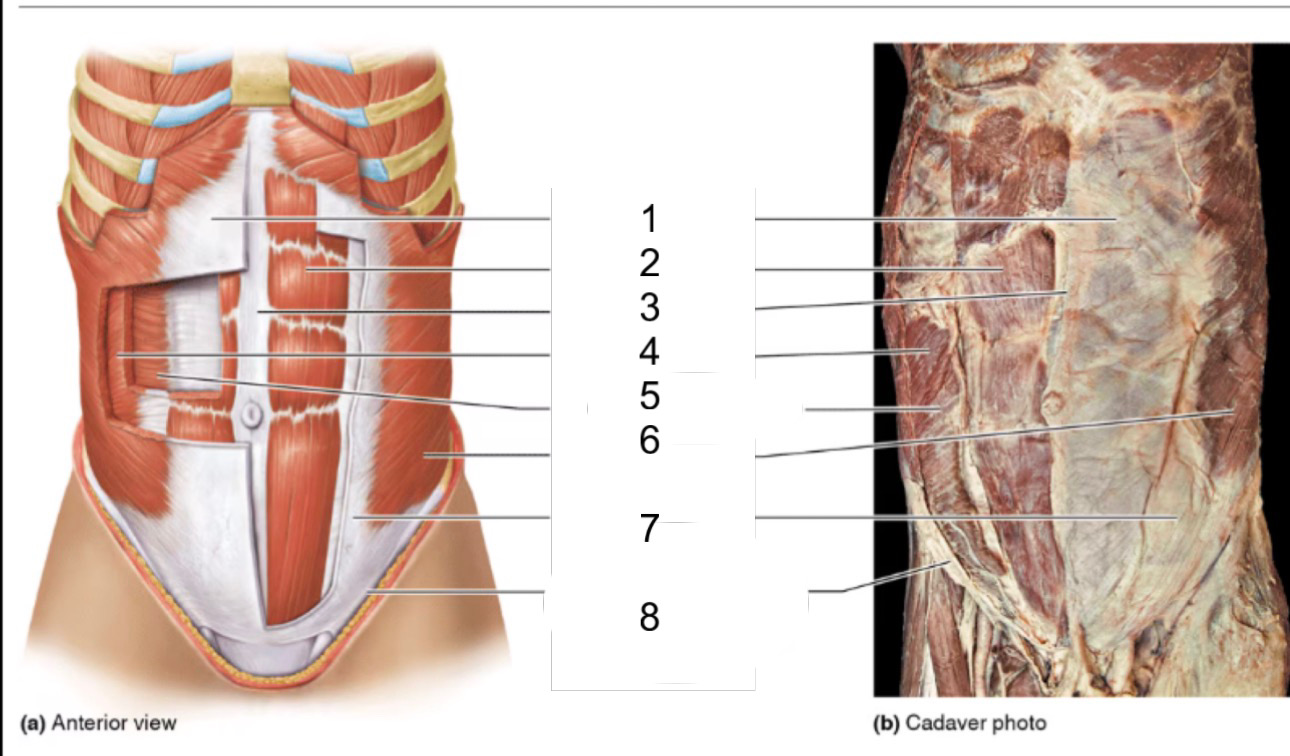
8
inguinal ligament
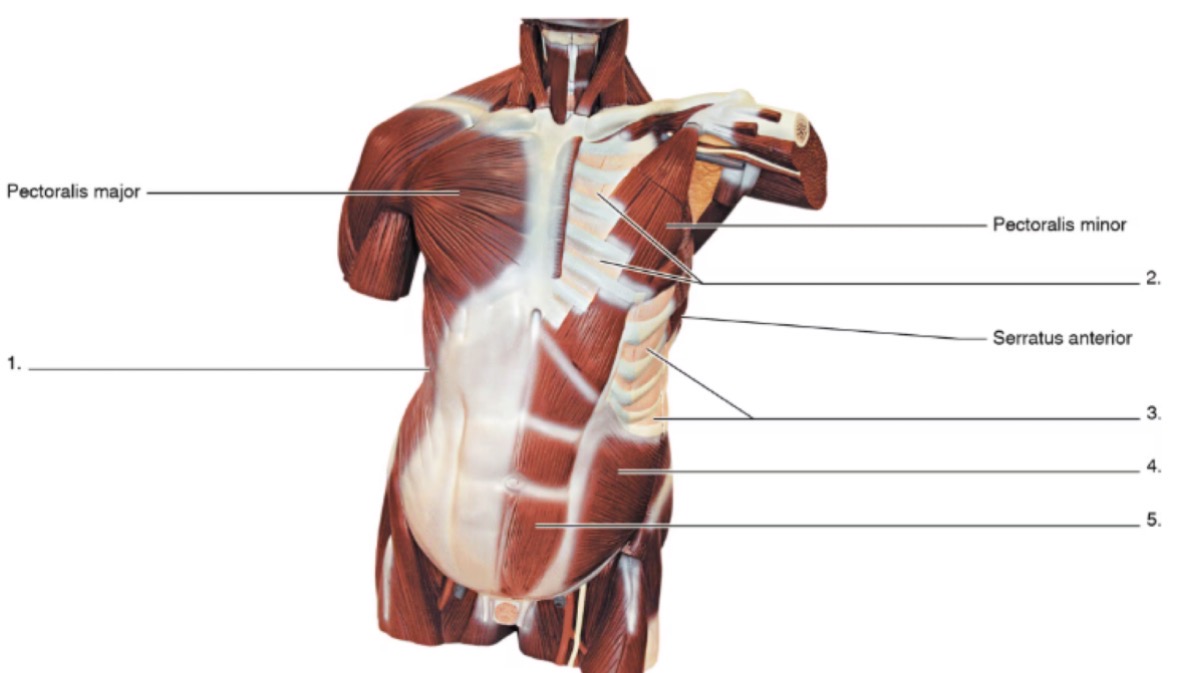
1
external oblique
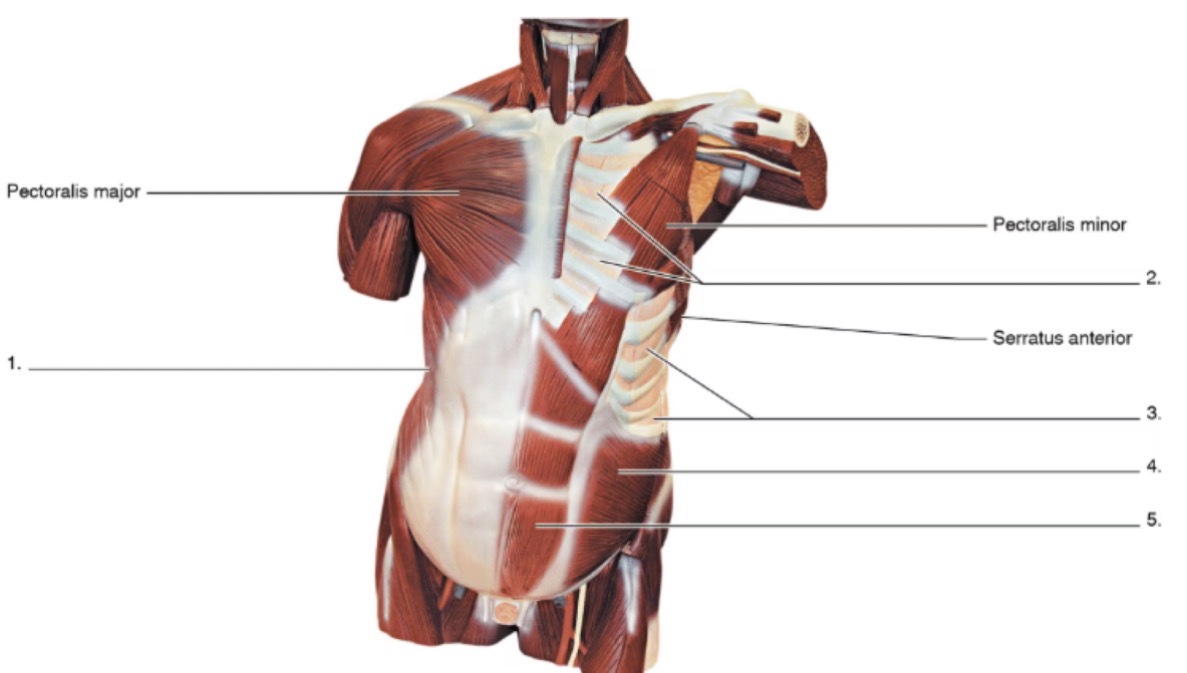
2
internal intercostals
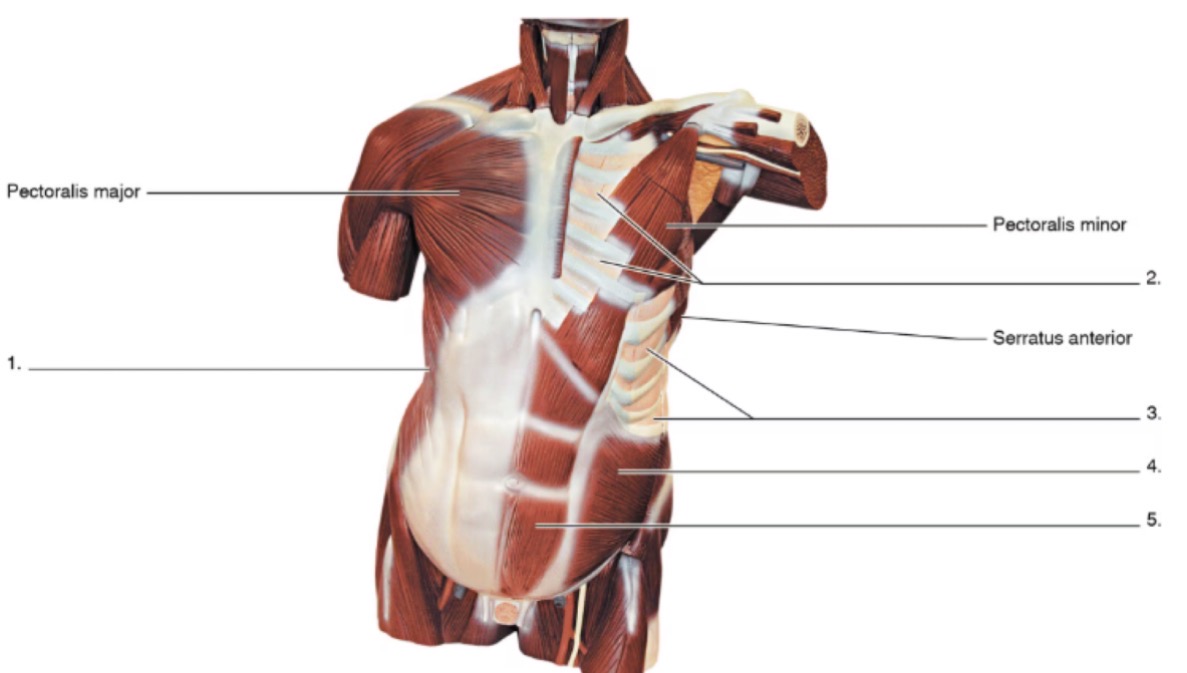
3
external intercostals
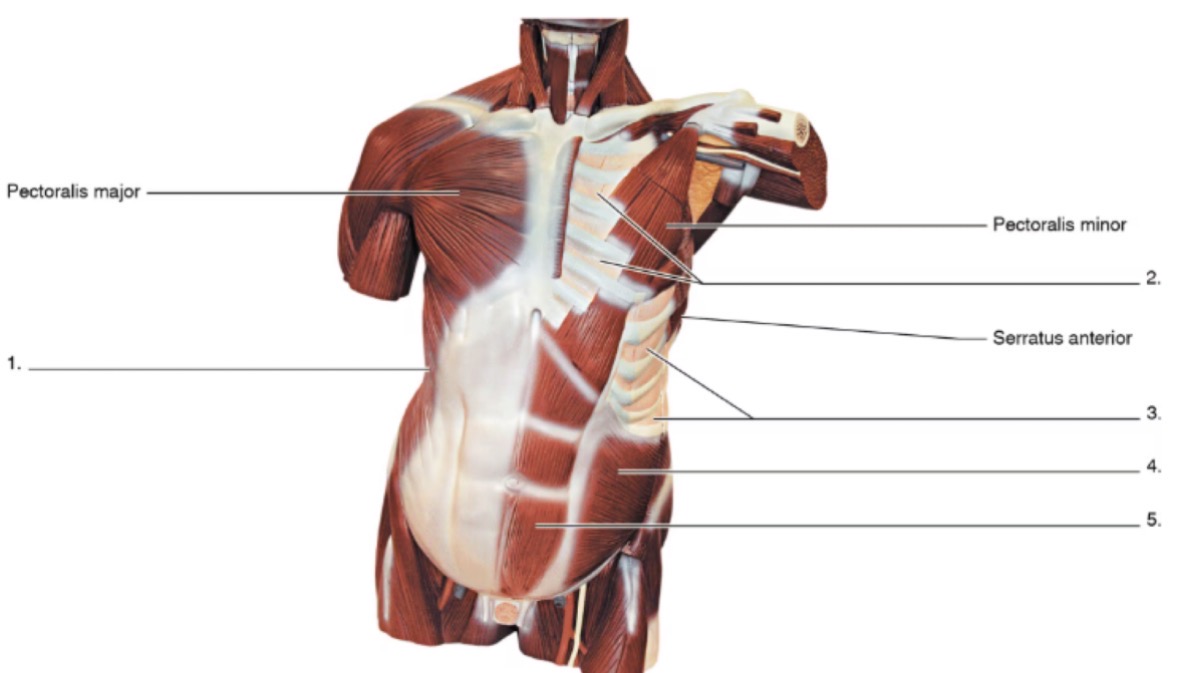
4
internal oblique
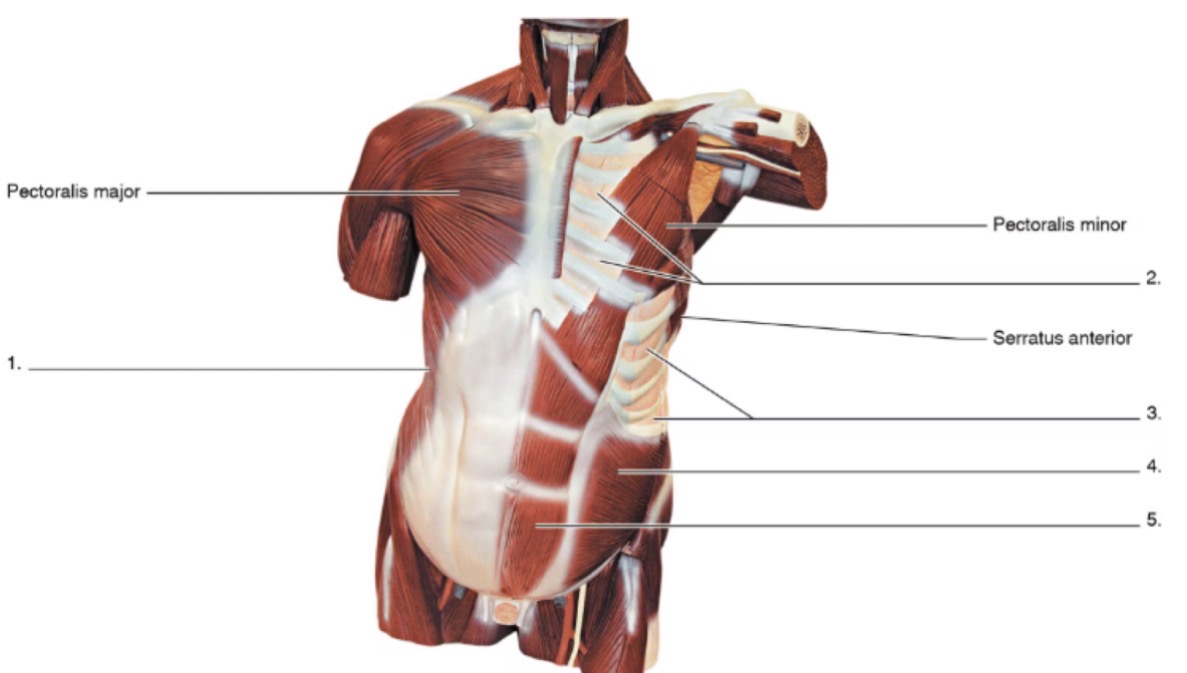
5
rectus abdominis
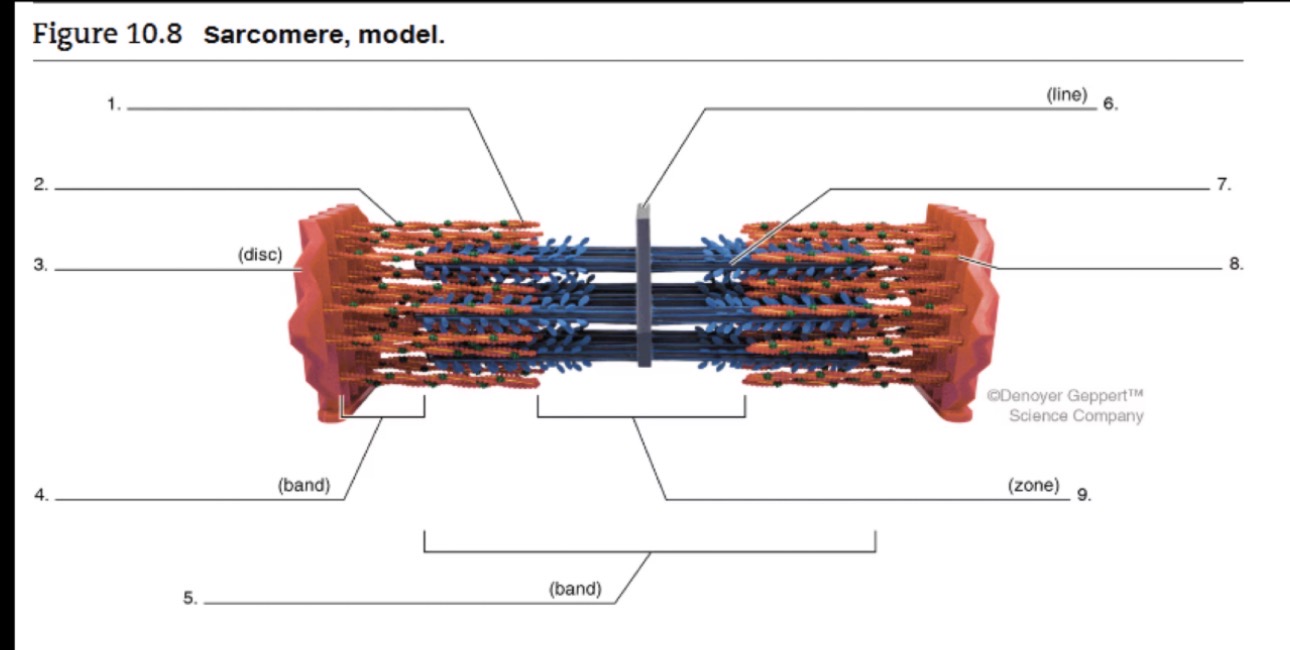
1
actin