Pharmacology Adams Ch 25
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
The nurse practitioner conducts education for home-health nurses who care for geriatric patients. Many of the patients abuse laxatives, so the nurse practitioner focuses the education on problems that can be caused by chronic laxative use. The nurse practitioner evaluates that learning has occurred when the nurses make which statements?
Select all that apply.
1. "The kidneys and GI tract keep electrolytes in narrow balance, where they must be."
2. "Electrolytes carry electricity in the body and must stay in balance."
3. "The electrolytes can be replaced by eating the right foods."
4. "The most important electrolytes are sodium, potassium, and magnesium."
5. "Laxatives can lower the level of potassium, necessary for proper heart function."
1, 2, 3, 5
The patient is receiving sodium bicarbonate intravenously (IV) for correction of acidosis secondary to diabetic coma. The nurse assesses cyanosis, slow respirations, and irregular pulse. What is the nurse's priority action?
1. Increase the rate of the infusion and continue to assess the patient for symptoms of acidosis.
2. Decrease the rate of the infusion and continue to assess the patient for symptoms of alkalosis.
3. Continue the infusion; the patient is still in acidosis.
4. Stop the infusion and notify the physician; the patient is in alkalosis.
4
The nurse cares for a patient in the emergency department who was just severely burned. The wife of the patient asks the nurse, "Why does he need those intravenous infusions (IVs)?" What are the best responses by the nurse that indicates the primary reasons for intravenous infusions (IVs) with a burned patient?
Select all that apply.
1. "So we have an open line for resuscitation in case his heart stops."
2. "So he can receive his antibiotics."
3. "So we can keep his blood pressure stable."
4. "So we can be sure he keeps enough blood volume."
5. "So we can rapidly administer his pain medications."
3, 4
The physician orders a hypertonic crystalloid solution for the patient in critical care who has cerebral edema. The nurse hangs a bag of a hypotonic solution. What will the priority assessment by the nurse include?
1. Headache, irritability, and decreasing level of consciousness
2. Nausea, projectile vomiting, and pinpoint pupils
3. Confusion, hallucinations, and agitation
4. Hypertension, headache, and nausea
1
The patient is dehydrated but has a normal blood pressure. The new medical intern orders normal serum albumin intravenously (IV) for this patient. What is the best evaluation by the nurse regarding this order?
1. It is a correct and valid order.
2. The intern should have ordered 5% dextrose in normal saline.
3. The intern should have ordered 0.45% NaCl.
4. The intern should have ordered 0.9% NaCl.
3
The patient has been running in a long-distance marathon on a very warm day. The patient complains of dizziness and nausea and is taken to the hospital where she becomes lethargic. The serum sodium level is 125 mEq/L. What will be the best plan of the nurse?
1. Prepare to encourage the patient to drink fluids.
2. Prepare to administer normal saline intravenous (IV).
3. Prepare to administer 0.45% NaCl.
4. Prepare to provide a diet high in NaCl.
2
The patient has a potassium level of 5.9 mEq/L. The nurse is administering glucose and insulin. The patient's wife says, "He doesn't have diabetes, why is he getting insulin?" What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "Insulin will cause his extra potassium to go into his cells and lower the blood level."
2. "Insulin lowers his blood sugar levels and this is how the extra potassium is excreted."
3. "Insulin is safer than giving laxatives such as Kayexalate."
4. "Insulin will help his kidneys excrete the extra potassium."
1
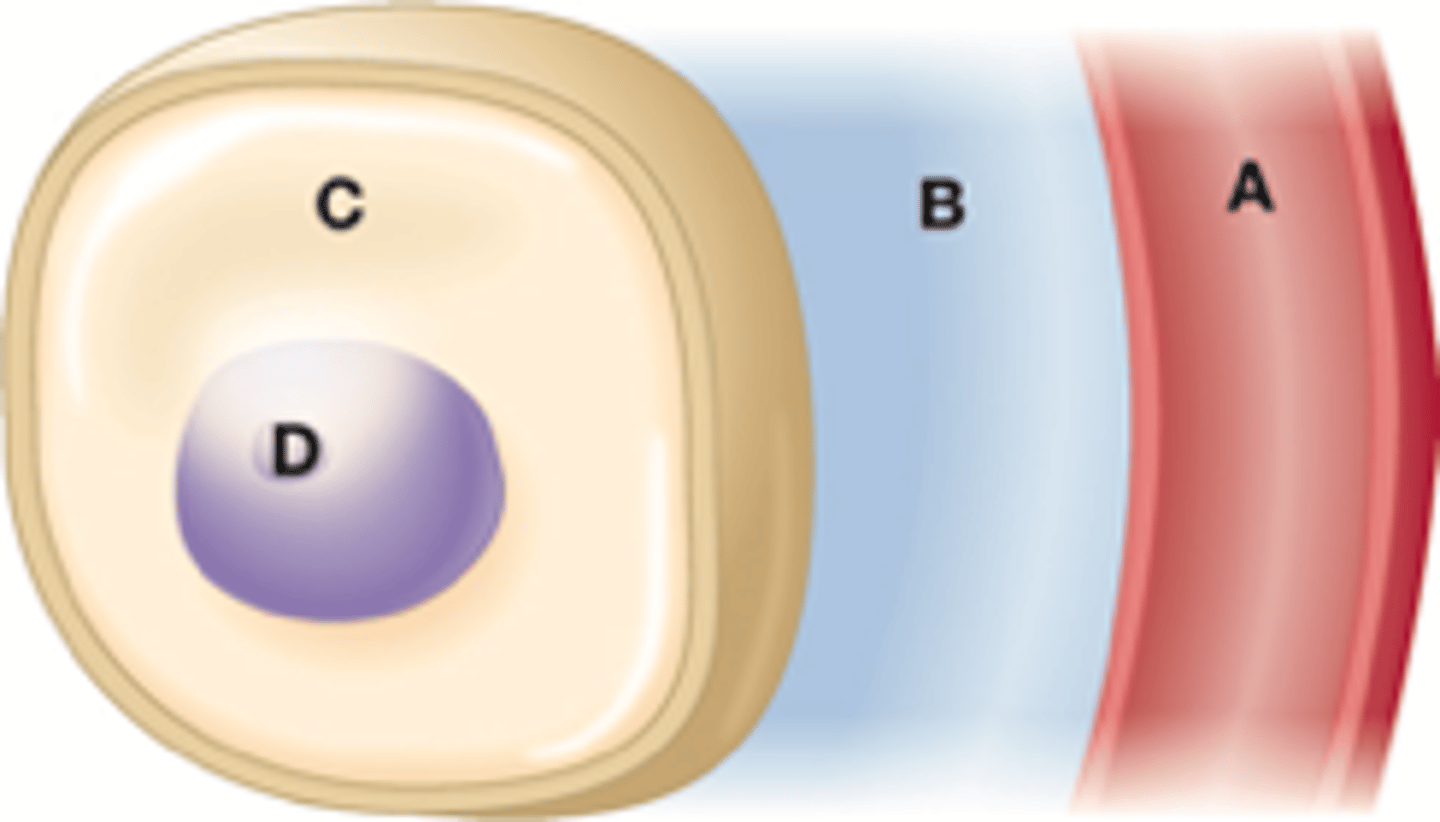
In order to explain the importance of hydration, the nurse shows this diagram to a group of high school athletes. The nurse would indicate that which fluid component holds fluid composing 40% of total body weight?
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
3
The patient receives dextran 40 (Gentran 40). The patient experiences tachycardia, dyspnea, and a cough. What is the best evaluation by the nurse?
1. The drug caused an interaction with another drug the patient receives.
2. The patient experienced impending kidney failure.
3. The patient is allergic to the drug.
4. The drug was infused too rapidly.
4
The physician orders potassium chloride (KCl) intravenous (IV) for the patient. The nurse administers this drug intravenous (IV) push. What will be the most likely outcome for this patient?
1. The patient will most likely experience cardiac arrest.
2. The patient will not experience adverse effects if the push was given slowly.
3. The patient will most likely experience tissue necrosis at the injection site.
4. The patient will most likely experience renal failure.
1
The physician orders potassium chloride (KCl) for the patient who has a nasogastric (NG) tube. What will the nurse plan to do prior to the administration of this drug?
1. Dilute the drug prior to administration through the nasogastric (NG) tube.
2. Flush the nasogastric (NG) tube with Coca-Cola before and after administration.
3. Flush the nasogastric (NG) tube with normal saline before and after administration.
4. There is no particular preparation prior to administration.
1
The patient has overdosed on aspirin. In the emergency department, the physician orders sodium bicarbonate. A family member says to the nurse, "I thought that was for stomach ulcers." What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "It will prevent excessive bleeding from the stomach."
2. "It will change the pH of the blood to neutralize the aspirin."
3. "It will change the urine so the kidneys can get rid of the aspirin quickly."
4. "It will help the liver break down the aspirin more quickly."
3
The patient receives normal serum albumin. What are the priority assessments by the nurse?
1. Blood pressure and urinary output
2. Urinary output and pupil response
3. Blood pressure and level of pain
4. Urinary output and nausea or vomiting
1
What is a priority outcome when a patient receives dextran 40 (Gentran 40)?
1. The patient will immediately report any ototoxicity.
2. The patient will immediately report any diarrhea.
3. The patient will immediately report any hiccoughs.
4. The patient will immediately report any itching or flushing.
4
The nurse provides group education to active adolescents about sodium replacement after exercising outdoors. What is the best information to include?
1. Have extra salt with your breakfast on days you exercise outdoors.
2. It is best to avoid exercising outdoors in the summer.
3. You should take one salt tablet for every 2 hours spent outside.
4. Water is the best fluid replacement after exercising.
4
Intravenous therapy would be indicated if
1. hypertension were present.
2. fluid intake were greater than 2500 mL/day.
3. intake and output were deregulated.
4. constipation were present.
3
A patient who is hyperkalemic reports being constipated. Which advice should the nurse provide?
Select all that apply.
1. “Drinking more water may help.”
2. “Prune juice is an effective laxative.”
3. “You should add fruits and vegetables to your diet.”
4. “Walking may stimulate your bowel function.”
5. “Use salt substitutes to reduce your sodium level.”
1, 4
Dextran 40 (Gentran 40) has been prescribed for nonemergency infusion. The nurse should plan to take which actions? Select all that apply.
1. Start the infusion no faster than 240 mg/min.
2. Monitor the patient’s vital signs continuously during administration.
3. Monitor for signs of anaphylaxis.
4. Teach the patient to avoid use of any over-the-counter herbal products.
5. Discard any portion of the infusion that is not used.
1, 2, 3, 5
Hyponatremia is marked by a serum sodium level less than
1. 137 mEq/mL.
2. 140 mEq/mL.
3. 133 mEq/mL.
4. 145 mEq/mL.
3
Which condition is a sign of hypokalemia?
1. Constipation
2. Hypertension
3. Muscle weakness
4. Weight gain
3
Buffers are chemicals that help maintain normal body pH. The two primary buffers in the body are
1. sodium and calcium ions.
2. sodium and bicarbonate ions.
3. bicarbonate and phosphate ions.
4. potassium and phosphate ions.
3
Potential causes for respiratory alkalosis include
1. hypotension.
2. hypertension.
3. hypoventilation.
4. hyperventilation.
4
The nurse is caring for a group of patients on a medical-surgical unit. For which patients would the nurse anticipate the need for intravenous fluid therapy to correct fluid depletion? Select all that apply.
1. A patient suffering from constipation
2. A patient exhibiting nausea and vomiting following a surgical procedure
3. A patient with a severe burn
4. A patient with congestive heart failure with edema to the lower extremities and rales
5. A patient with uncontrolled diabetic ketoacidosis
2, 3, 5
A nurse is caring for a patient receiving intravenous fluid therapy for dehydration. The nurse knows that the osmolarity or tonicity of a fluid causes water to move to a different compartment. The nurse is caring for a patient who weighs 40 kg. The osmolality of the body fluids for this patient is between 11,000 and _____ milliosmoles.
11,800
The nurse is reviewing the tonicity of the different intravenous fluids on the medical-surgical unit in preparation for an educational presentation. Which fluids are considered to be isotonic and appropriate in the treatment of fluid loss due to a surgical procedure?
Select all that apply.
1. 5% dextrose in lactated Ringer’s
2. 0.9% sodium chloride (NS)
3. 0.45% sodium chloride
4. Lactated Ringer’s
5. 5% dextrose in water
2, 4 5
The nurse is caring for a patient with severe electrolyte imbalances that have occurred as a result of kidney failure. The nurse knows that this patient is at risk for what disorders as a result of this electrolyte imbalance? Select all that apply.
1. Fluid retention
2. Muscle spasms
3. Fractures
4. High cholesterol
5. Depression
1, 2, 3
The nurse is caring for a patient with a pH of 7.32. Which medications would be appropriate to administer to a patient with this condition?
Select all that apply.
1. Oral bicarbonate
2. Sodium chloride
3. Sodium citrate
4. Potassium chloride
5. Ammonium chloride
1, 3
A patient has been prescribed potassium chloride (KCl). The patient states, “This is sure a big pill.” What nursing actions are indicated?
Select all that apply.
1. Have the patient sit straight up to attempt to swallow the pill.
2. Crush the tablet and put it in a soft food for the patient to swallow.
3. Have the patient chew the tablet.
4. Consult with the prescriber about an alternative drug form.
5. Have the patient take the pill at the beginning of a meal.
1, 4, 5
A nurse providing medication education about loop diuretics advises patients to avoid eating licorice. What is the nurse’s rationale for this statement? Select all that apply.
1. Licorice causes acid-base imbalances.
2. Licorice can cause potassium loss.
3. Licorice can cause sodium retention.
4. Licorice can cause gastric irritation.
5. Licorice causes renal absorption of calcium.
2, 3
A patient who has a potassium level of 5.9 mEq/L will be given oral polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate). What nursing actions are necessary?
Select all that apply.
1. Monitor for onset of action of this drug in an hour.
2. Administer sorbitol concurrently.
3. Repeat the dose in 4 hours if needed.
4. Mix the dose with a high sugar liquid.
5. Follow the dose with an enema.
1, 2, 3