Biology EOY Exam
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
What are ciliated cells?
cells that have hairs (cilia) that move mucus up and away from the lungs in the trachea and bronch
What are root hair cells?
Cells that have long projections that give a larger surface area for absorption of water
What are xylem vessels?
long cells with walls strengthened with a substance called lignin for transporting water
What are Palisade mesophyll cells?
plant cells in the upper layer of leaves that have large numbers of chloroplasts that help carry out photosynthesis
What are nerve cells?
elongated cells that have a fibre that can conduct electrical impulses
What are red blood cells?
disc-shaped, biconcave, large surface area and haemoglobin for transporting oxygen
What is the simple structure for the organization of living things?
Cells, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
What are tissues?
A group of similar cells that carry out a function
What is an organ?
a structure composed of a number of tissues that work together to carry out one or more functions.
What is an organ system?
a number of organs working together to carry out one or more functions.
What does permeable mean?
a membrane that allows all substances to pass in and out
What does impermeable mean?
a membrane that does not allow any substances to pass in and out
What does selectively permeable mean?
a membrane that allows some substances to pass freely in and out but controls the movement of other substances
What is diffusion?
The net movement of particles from a region of their higher concentration to a region of their lower concentration down a concentration gradient.
Where does the energy for diffusion come from?
The energy for diffusion comes from the random movement of molecules and ions.
What are some factors that affect diffusion?
Surface area, Short distance, Temperature, and Concentration gradient
What is a solvent?
a liquid that dissolves other substances
What is a solute?
a substance that has been dissolved
What is osmosis?
the movement of water particles through a partially permeable membrane from a high water potential(dilute) to a low water potential (more concentrated) solution.
What is active transport?
the movement of particles through a cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration using energy in the form of ATP i.e. against the gradient
What is an organism?
A complete living thing
What is metabolism?
The chemical reactions that take place in living organisms
What is a species?
A group of organisms that can reproduce fertile offspring
What is a genus?
A group of species that are related to one another
What are cells?
The smallest units from which all organisms are made
What are carbohydrates?
Substances that include sugars, starch, and cellulose, they contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What are sugars?
Carbohydrates that have relatively small molecules they are soluble in water
What is glucose?
A carbohydrate that is used as an energy store in animal cells
What is glycogen?
A carbohydrate that is used as an energy store in animal cells
What is starch?
A carbohydrate that is used as an energy store in plant cells
What is the formula for carbohydrates?
6 carbon atoms, 12 Hydrogen atoms, and 6 oxygen atoms.
What elements are in carbohydrates and fats/lipids?
Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
Name and explain the test for starch/carbohydrates?
The iodine test. It involves adding a few drops of iodine solution to the sample. If starch is present, the iodine changes from yellow-brown to a blue-black color, indicating the presence of starch/carbohydrates.
Name and explain the test for reducing sugars
The benedict’s test. It involves adding Benedict’s reagent to the sample and heating it. If reducing sugars are present, the solution changes from blue to green, yellow, orange, or red, depending on the sugar concentration
Name and explain the test for fats
The emulsion test. it involves adding ethanol to the sample, shaking it, and then adding water. If fats are present, a milky-white emulsion forms, indicating the presence of lipids.
Name and explain the tests for proteins
The biuret test. It involves adding Biuret reagent (a solution of copper sulfate and sodium hydroxide) to the sample. If proteins are present, the solution changes from blue to purple.
What is a catalyst?
A substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction and is not changed by the reaction
What are enzymes?
Proteins that are involved in all metabolic reactions, where they function as biological catalysts
What is the alimentary canal?
The part of the digestive system through which food passes as it moves from the mouth to the anus
What is amylase?
An enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of starch to maltose it is produced in the salivary glands and pancreas
What is protease?
An enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of protein to amino acids it is produced in your stomach, pancreas, and small intestine
What is catalase?
An enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of Hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen
What are carbohydrases?
Enzymes that break down carbohydrates they are produced in the pancreas, salivary glands, and small intestines
What are lipases?
Enzymes that break down lipids and are produced in the pancreas mouth and stomach
What is maltase?
An enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of maltose to glucose and is produced by the cells of the mucous membrane lining the intestinal wall.
What is the formula for magnification using lenses?
eye piece lens x objective lens
Why do humans needs fats and oils?
Energy source, cells structure and function, absorption of vitamins, and hormone production and regulation
Why do humans need proteins?
Muscle growth and repair, enzyme and hormone production, tissue repair and regeneration, and immune system function
Why do humans need water?
Temperature regulation, joint lubrication, digestive health, and hydration and bodily function
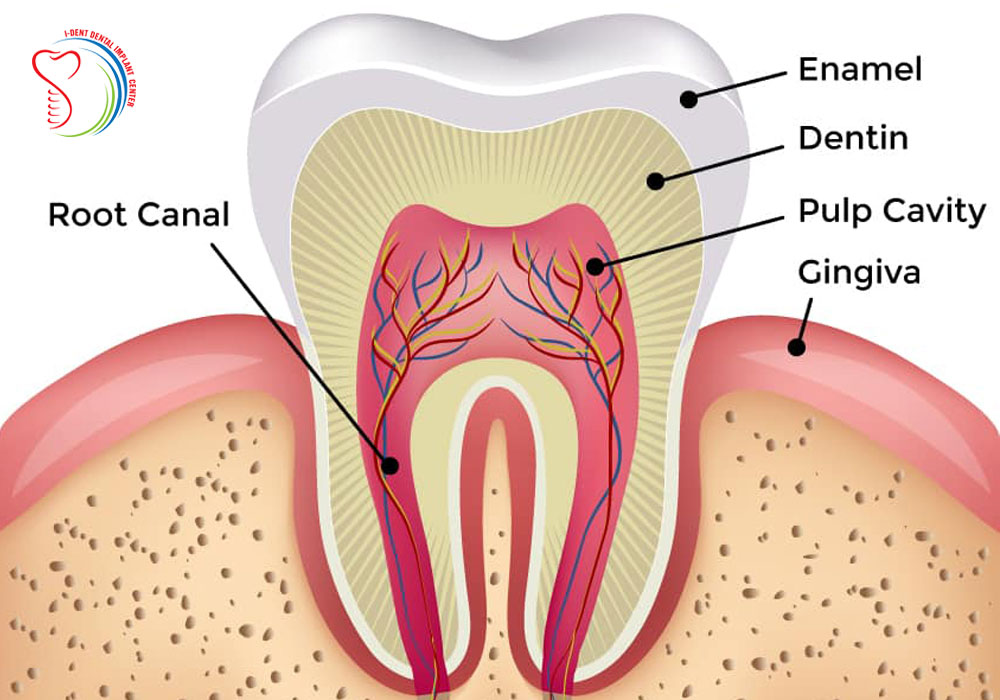
What is enamel?
The very strong material that covers the surface of a tooth, it is the hardest substance made by animals.
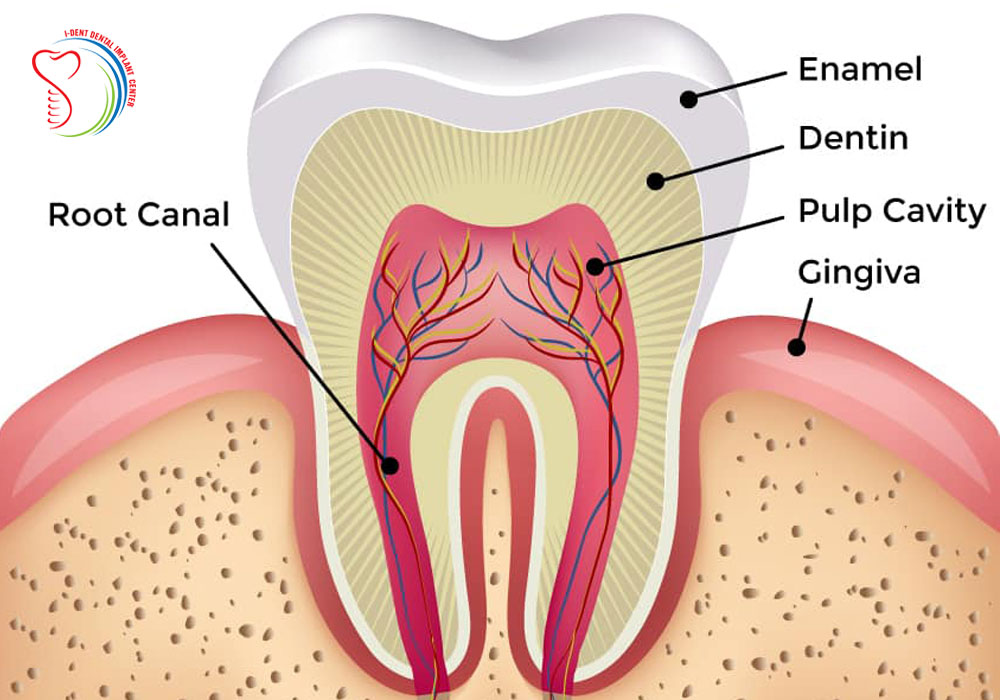
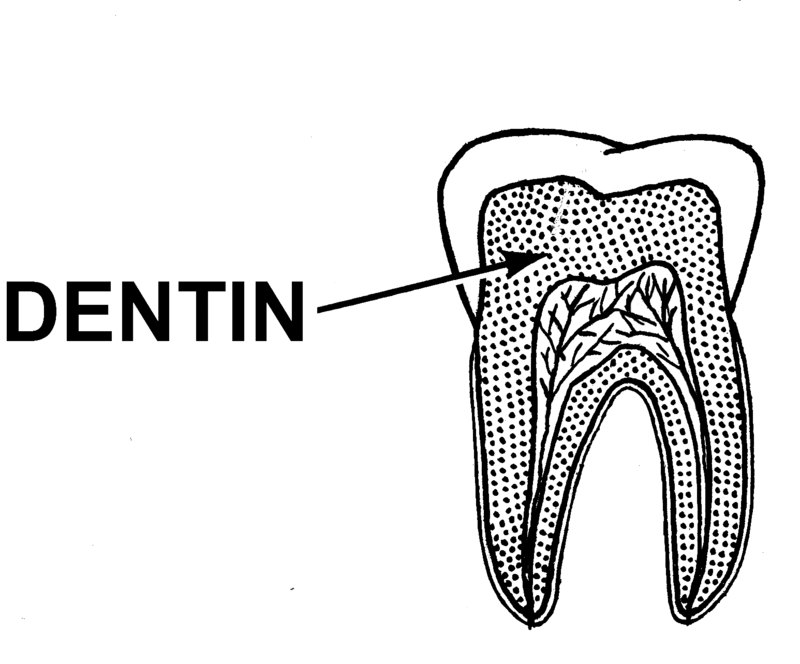
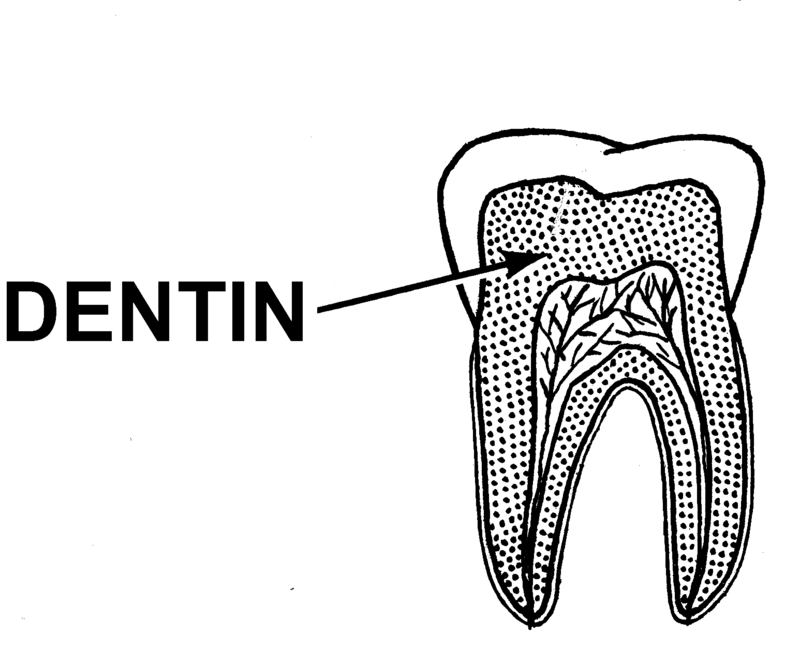
What is dentine?
A living tissue that lies just beneath the enamel of a tooth it supports the enamel, provides strength to the tooth, and protects the inner pulp.
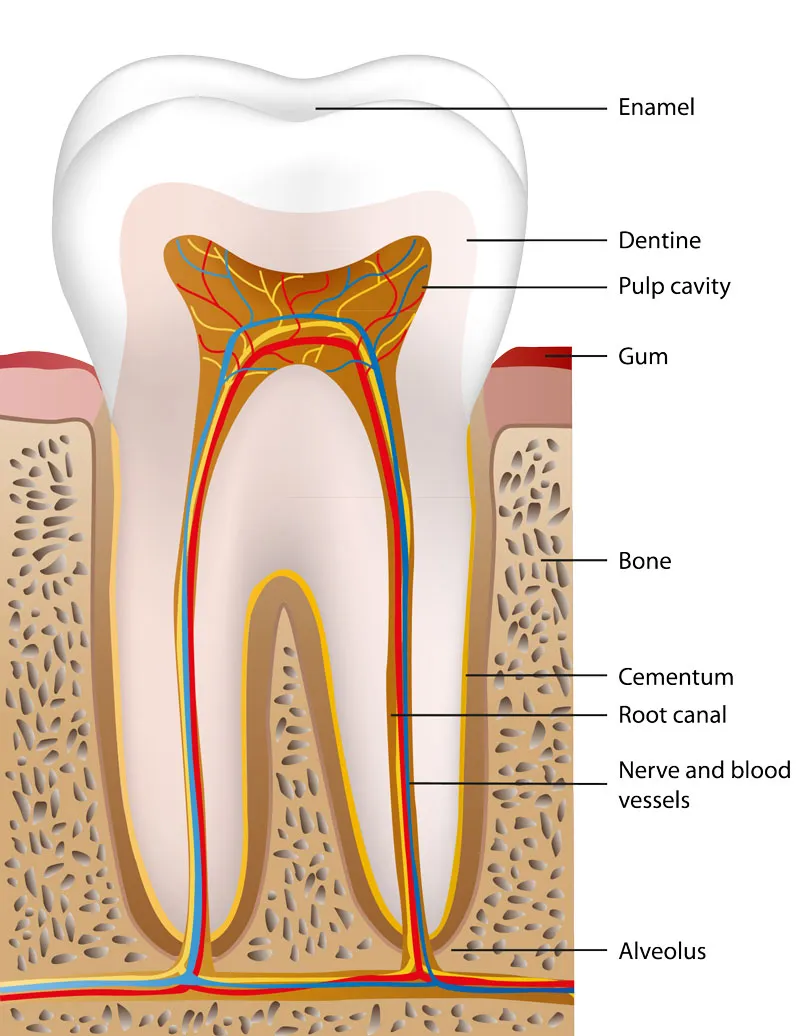
What is cement?
The material that holds a tooth in the gums.
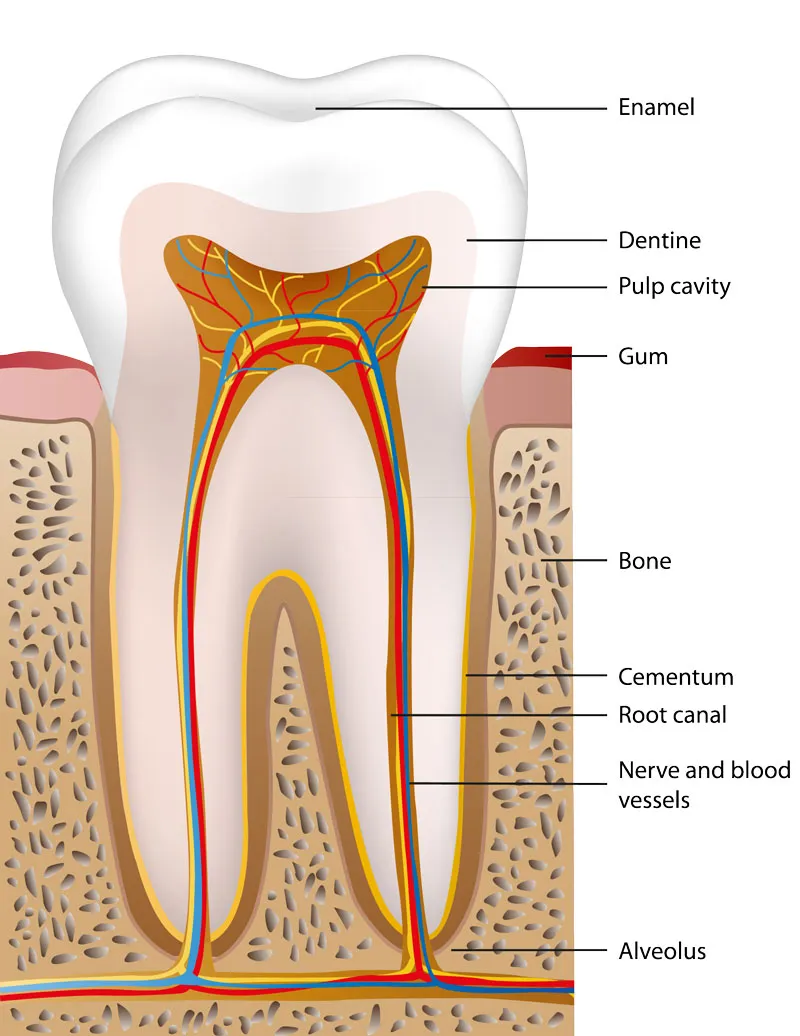
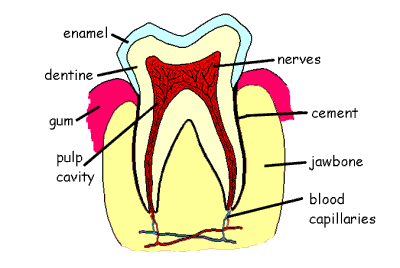
Describe the structure of a tooth
A tooth has three main layers: the enamel (hard outer layer), dentin (beneath enamel, softer and supports the tooth), and pulp (inner part, containing nerves and blood vessels). The root anchors the tooth in the jaw.
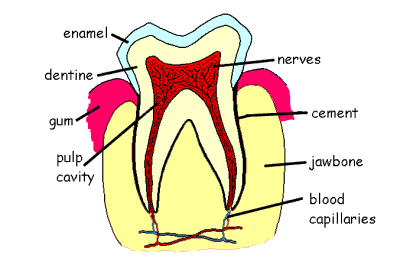
How does tooth decay happen?
when bacteria in the mouth break down sugars and produce acid that erodes tooth enamel
What are the two stages of digestion?
Chemical Digestion and Physical digestion
Describe the process of physical digestion
First, large pieces of food are broken down into smaller pieces mostly done by the teeth with help from churning movements of the stomach. This does not change the chemical components of the food.
Describe the process of chemical digestion?
After physical digestion, large molecules in the food are broken down into smaller molecules, this involves chemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes. The smaller molecules are soluble in water which makes it easy to be absorbed into cells.
What happens to the large molecules of starch, protein, and fats during digestion?
starch is broken down by amylase and is turned into simple reducing sugars, protein is broken down by protease and turned into amino acids, and fat is broken down by lipase and is turned into fatty acids and glycerol.
Why don’t the molecules of vitamins, water, and mineral ions need to be chemical digested?
Because they are small enough to be absorbed.
What are incisors?
Chisel-shaped teeth at the front of the mouth used for biting off pieces of food.
What are canines?
Pointed, sharp teeth used for tearing food, located next to incisors.
What are premolars?
Flat-topped teeth for crushing and grinding food, located between canines and molars.
What are molars?
Large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth used for grinding and crushing food
What are the characteristics of life?
Movement, Respiration, Sensitivity, Growth, Reproduction, Excretion, Nutrition
What is movement?
action by an organism or part of an organism causing a change of position or place
What is respiration?
the chemical reactions in cells that break down nutrient molecules and release energy for metabolism
What is sensitivity?
the ability to detect and respond to changes in the internal or external environment
What is growth?
permanent increase in size and dry mass
What is reproduction?
the processes that make more of the same kind of organism
What is Excretion?
the removal of the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements from the body
What is nutrition?
the taking in of materials for energy, growth and development
Why are viruses not living?
Do not have their own metabolism and
they cannot reproduce on their own, they require the resources of their host’s cells
What two things do all viruses have?
Protein coat (capsid) and a single strand of DNA or RNA
Describe the binomial naming system
The first word is the genus (starting with capital letter) of that organism and the second word is the species (starting with lower case letter)
What are the five kingdoms of life?
Monera (bacteria), protoctista, fungi, plants, and animals
Give me characteristics of bacteria
Prokaryotic, reproduced asexually, important because as they decompose dead organisms and return substances minerals to the environment.
Prokaryotic meaning:
organisms (like bacteria) whose cells lack a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles
Eukaryotic meaning:
organisms whose cells possess a membrane bound nucleus and other membrane bound organelles.
Charactersitics of protoctista:
single-celled eukaryotes, some photosynthesize, others consume. They live in water, vary widely, and include algae, amoebas, and slime molds.
Charactersitics of fungi
Unicellular and multicelluar eukaryotes, cannot make their own food, decomposers, can reproduced sexually and asexually, mushrooms, truffles, and yeast
Charactersitics of plants
Eukaryotic multicellular organisms that can make their own food and reproduce sexually and asexually
Heterotrophic meaning:
An organism that cannot make its own food
Autotrophic meaning:
An organism that can make its own food
Characteristics of animals:
Eukaryotic, heterotrophic, multicellular organisms
Name all the parts of an animal cell:
Cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, nucleus, ribosomes, vesicles and nucleolus
Name all the parts of a plant cell:
Cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, large vacuole, mitochondria, chloroplast, and ribosomes
Nucleus
Contains DNA in the form of chromosomes and controls the activities of the cell
Cell membrane
selectively-permeable membrane that surrounds the cell and controls what enters and leaves
Cytoplasm
the liquid and organelles of the cell
Nucleolus
part of the nucleus that makes ribosomes
Vesicles
small packages of substances in the cell that move proteins around
Ribosomes
structures that make proteins using instructions from the DNA
Mitochondria
Location of aerobic respiration (where energy is released)
Cell wall
Gives the cell structure and support
Large vacuole
stores water and gives the cell structure
Chloroplasts
Site of photosynthesis
Magnification formula:
Magnification = Size of image/Actual Size
Actual Size formula:
Actual Size = Image Size/Magnification
Image Size formula:
Image Size = Actual Size x Magnification
Where are RBCs produced?
bone marrow in ribs and bones of arms and legs and vertebrae