Human nutrition & Excretion
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
anabolic reaction
a metabolic process that involves synthesis of 2 substrates that form 1 larger molecule
Reabsorption
useful molecules are recovered from filtrate after filtration of blood ( water, salt, amino acids )
Absorption
the movement of nutrients from the intestines to the blood
what
what is the role of the small intestine during digestion
Absorption - food is moving from the alimentary canal into the blood (water is also absorbed)
Nutrients are absorbed
Catabolic reaction
1 substrate that forms 2 smaller molecules
what is the role of chemical digestion
breaking down insoluble molecules into soluble molecules using enzymes so that the products can be absorbed
ingestion
the consumption of food happens in the mouth
egestion
the removal of undigested food from the body as feces- passed through anus
why is the villi important
they increase the surface area for food absorption and adding digestive secretions
what happens when an enzyme denatures
shape of the active site changes so it can no longer fit in the substrate, the function, the enzyme can’t act as a biological catalyst anymore
describe chemical digestion
the breakdown of large insoluble molecules into small soluble molecules happens in the stomach
balanced diet
a diet containing the right food and minerals and minerals and the right amounts
amylase breaks down what? and where is it found
found in the mouth and ileum, breaks down starch into maltose
lipase breaks down what and where is it found
found in the stomach, breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol
maltase breaks down what and where is it found
found in the ileum breaks down maltose into glucose
what factors impact enzyme activity
temperature
pH
concentration of substrate (substance on which enzyme acts)
physical digestion
increases the surface area of food ( by chewing ) for the action of enzymes in chemical digestion
Where are the villi found
in the duodenum in the small intestine
causes of:
1) scurvy
2) rickets
1) lack of vitamin C
2) lack of vitamin D
parts of the digestive system
mouth
esophagous
stomach
small intestine
pancreas
liver
gallbladder
large intestine
rectum
anus
function of stomach in physical digestion
the stomach has muscular contractions which mix the ingested food with gastric juices and producing chyme. The stomach contains HCl, amylase, pancreatic juice, bile
What do goblet cells do in the villi
produce mucus to protect the villi from any acids in chyme
principal dietary sources
carbohydrates
fats and oils
proteins
vitamins
mineral ions
fibre
water
what is urea
a waste product formed by the breakdown of protein in the liver, the kidney filters urea out of the blood and into the urine
what s the role of bile
bile is produced in the liver and breaks down fats and lipids
Fats fatty acids and glycerol - emulsification
Bile is stored in the gall bladder
what is physical digestion
the breakdown of food into smaller pieces without chemical change to the food molecules
protease breaks down what and where is it found
proteins into amino acids found in the intestines
pepsin breaks down what and where is it found
breaks down proteins into peptides found in the stomach
what is assimilation
the uptake and use of nutrients by cells used for energy growth and repair
describe denimation
in the liver an excess group of amino acids is turned into ammonia which is toxic so it is turned into urea which is filtered in the kidney and excreted as urine
what does the lacteal in the villi absorb
digested lipids ( fatty acids and glycerol )
what is bile
bile is an alkaline mixture that neutralises the acidic mixture of food and gastric juices entering the duodenum from the stomach to provide a suitable pH for enzymes
why is emulsification important
because it increases the surface area so that enzymes can break down the fats ( lipase) ensuring fats can be digested and absorbed efficiently
what do the capillaries of the villi absorb during digestion
they absorb glucose and amino acids
what do micro villi do
increase surface area
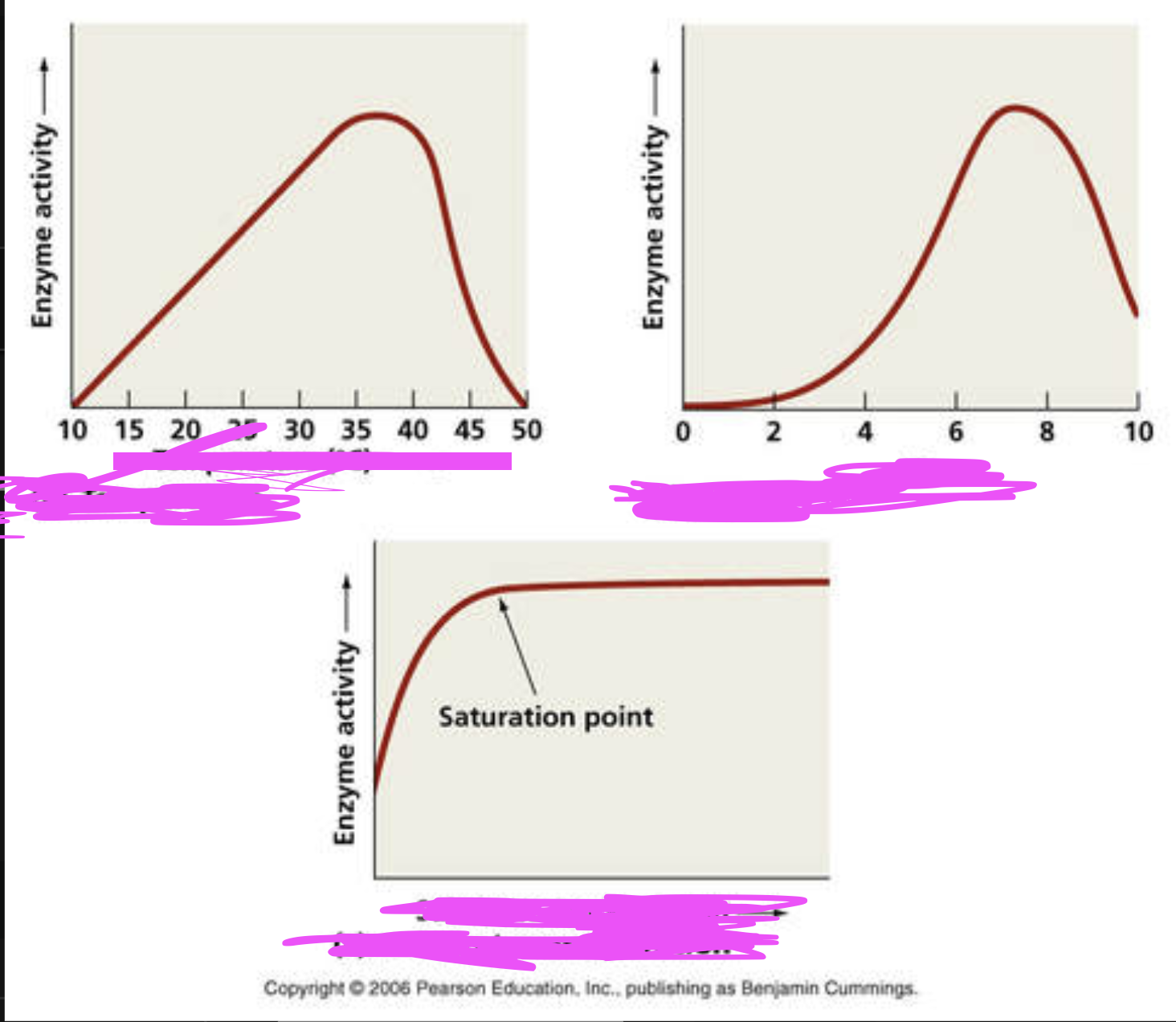
1) temp
2) pH
3) substrate conc
what are the parts of the teeth
enamel ( the top )
dentine ( hardest layer )
pulp cavity ( the inside )
nerves ( inside pulp cavity )
blood vessels ( bottom )
cement ( outer layer )
what are the 4 types of teeth
premolar
molar
incisor
canine
function of molar and premolar
to grind the food
function of incisor and canine
to cut the food
enamel
dentine
pulp cavity
nerves
cement
blood capillaries
jaw bone
gums
function of vitamin A
vision, skin, growth
function of vitamin C
tissue growth, wound healing, immune system
what is the fuction of vitamin D
bone health, nerves, muscles
vitaminnE function
immune system, antioxidant
active transport
the movement of molecules across a cell membrane from a low to high concentration
passive transport
the movement of substances accross a cell membrane from high concentration to low concentration
what are the parts of the kidney
nephron
glomerulus
bowman’s capsule
medulla
renal cortex
renal pyramids
urethra
renal arteries and veins
what are 2 roles of the nephrons in the kidney
1) filtration
2) reabsorption
DCT & role
distilled convoluted tubule - reabsorption of nutrients
PCT & role in nephron & transport
proximal convoluted tubule - reabsorption of glucose amino acids, water and salt ( passive and active transport )
glomerulus role in nephron & function
filters blood - passive transport
henles loop role in nephron & transport
reabsorption of water and salt - passive and active transport
collecting duct role in nephron & transport
reabsorption of water - controlled by adh
bowmans capsule role in nephron and transport
filters blood from glomerulus - passive transport
explain cholera bacteria in the digestive system
cholera bacteria produce a toxin ; toxin causes secretion of chloride ions ; into small intestine ; lowering water potential ; movement of water into the gut ; by osmosis ; results in diarrhoea ;
what is cholera caused by
drinking contaminated water with faeces or the bacteria which infects the intestines