chemistry u3 aos1 (redox reactions and cell chemistry)
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
short hand convention
[O.A./ R.A.]
conjugate redox pair
[reactant/ product]
each overall redox equation will have 2 pairs;
whereas half-equation will only have 1 pair
how does redox reactions occur
both oxidation and reduction reactions occur simultaneously; involve transfer of electrons
oxidation state/ number
= numbers used to represent how oxidised/ reduced particles of a specific element are
oxidation state of O in F2O
+2
oxidation state of H in metal hydrides, list the examples
-1;
NaH, LiH, CaH2
oxidation state of O in H2O2
-1
is combustion reaction a redox reaction?
yes;
O.A.: oxygen
R.A.: any fuel
when do we separate/ not separate the species when we write OA/ RA?
(to separate)
ionic aqueous → separate the ions
e.g. HCl (aq)
(not to separate)
ionic solid
e.g. Ag2O (s)
molecular
oxidation state of H in CaH2
-2
oxidation of N in NH4NO3
for NH4+ → -3
for NO3- → +5
is displacement reaction exo or endo?
(almost) all displacement reactions are exothermic
this is because the bonds in the products are always more stable in those in reactants (lower chemical potential energy; higher kinetic thermal energy); therefore all single displacement reactions are exo
energy conversion in galvanic cell
chemical to electrical energy
general structure of a galvanic cell
composed of 2 half-cells
an electrode (can be reactive/ inert/ within a test tube → for gas reactants)
→ allows delocalised electrons to move through it
→ OR transfer electrons
an electrolyte (solution/ liquid)
→ conducts electricity, due to presence of ions
purpose of voltmeter
to measure the voltage through the wire/ to show the flow of electron (NOT CURRENT!!)
why are electrodes often metals?
good conductor of electricity
purpose of external circuit
allows electrons to flow through this wire from one electrode (anode) to another (cathode)
what is the internal circuit, purpose?
salt bridge
to complete the circuit and balance the charge
what is a salt bridge made up of, give example of the electrolyte
salt bridge contains electrolyte with spectator ions that do not participate in the half-cell reactions
possible solution for salt bridge: NaNO3, KNO3
what are the criteria for the electrolyte for salt bridge?
do not participate in the half-cell reactions
do not react to form precipitate
needs to be soluble in water to produce free moving electrons
types of half cells
** beware of the hydrogen half cell
→ you need a test tube and a Pt electrode
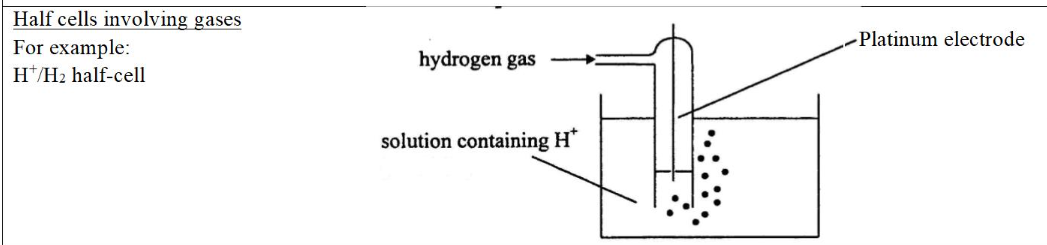
standard lab conditions SLC
298K
100kPa
1M concentration
how do you explain why there is a spontaneous reaction occurring?
when the OA is stronger the the conjugate OA of the RA (or vice versa)
how do we determine the polarity of electrodes when calculating the voltage of a galvanic cell?
note which terminal is each electrode connected to when a positive reading on voltmeter is obtained
how to calculate emf/ cell potential difference?
**emf for a spontaneous reaction will always be POSITIVE

what does a E0 imply?
it DOES NOT indicate the rate of reaction
it DOES indicate whether a spontaneous reaction occur
→ the greater the difference in emf, more likely the spontaneous reaction will occur
→ the smaller the difference, the slower the reaction
why is aluminium sometimes unreactive?
it reacts on exposure to air to form aluminium oxide, which prevent them from reacting
for a Daniel cell, it does not have salt bridge, what is the purpose of having a porous pot separating the electrodes?
to allow migration of ions (cations and anions) to maintain neutrality
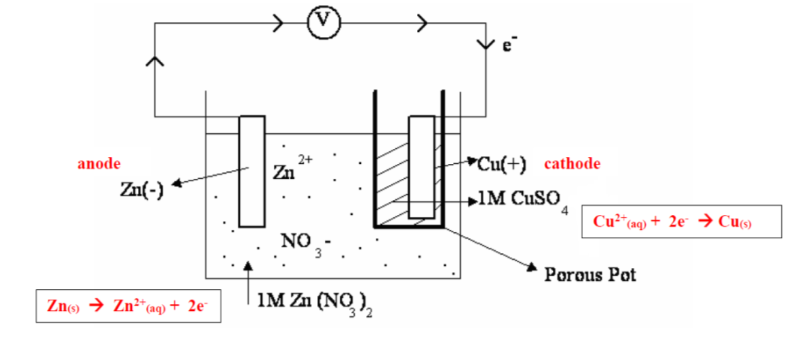
what ions will not be passing through the porous container, why?
Cu2+ , or else there will be a direct reaction between this ion and Zn, no current will then produce
do we need to replace salt bridge? why?
yes, a new salt bridge is needed every time a cell is constructed, because the ions are used up as they migrate into cells
what are the types of galvanic cell?
primary cell
→ alkaline cell
→ button cell
fuel cell
properties for primary cell
non-rechargeable
go flat when reaction reaches equilibrium
must be discarded
products migrate away from electrodes and consumed by side reactions in cell
(unlike secondary that remains around electrodes)
products remain in cell
reactants are solid/ liquid
store energy
properties of fuel cell
reactants are not stored but supplied continuously
constant production of energy
continuous removal of products
combustion reaction
(heat energy is converted directly to electrical energy)
high efficiency
gaseous reactants
electrodes are catalyst
porous electrodes allow reactants to diffuse through to react with ions in electrolyte
do not store energy
compare fuel cell and primary cell
fuel cell
do not store energy
constant supply of reactants
continuous production of electrical energy
constant removal of products
gaseous products
electrodes are catalyst
porous electrodes to allow electrons to pass through to react with electrolyte
primary cell
store energy
solid/ liquid reactants
products remain in cell
similarities
both are galvanic cell
both involve spontaneous redox reaction
both convert chemical energy to electrical energy
hydrogen fuel cell
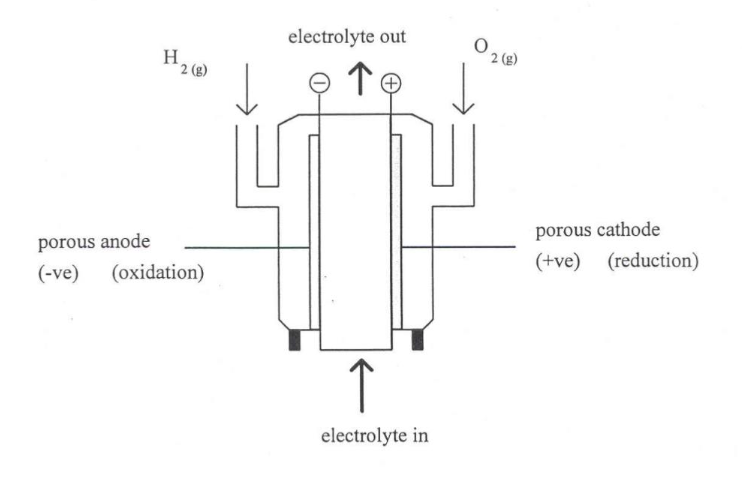
purpose of porous electrode
keep the reactants apart
allows the reactants to diffuse through, react with the ions in electrolyte
why is catalyst incorporated into electrodes in fuel cell?
increase the rate of oxidation and reduction half reactions
do electrodes get consume in fuel cell (think abt how catalyst is incorporated)
no
what would be a possible electrolyte in both an acidic/ alkaline fuel cell?
(acidic) phosphoric acid
(alkaline) potassium hydroxide
what is the state of a methanol as a fuel in combustion reaction?
liquid
why does electrolyte flow continuously throughout the fuel cell?
allows the ions to move
to balance the charge (similar to salt bridge; e.g. anions move towards anode, vice versa)
advantage of fuel cell
high energy efficiency
(due to direct conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy)
continuous electricity production
water is the only product (in hydrogen fuel cell), no CO2 emitted
a variety of fuels can be used
quiet
does not need to be recharged as long as fuel is supplied
does not need to be connected to the electricity grid
disadvantages of fuel cell
continuous supply of fuel is needed
expensive electrodes (catalyst) and electrolyte
some electrodes and electrolytes are harmful
fuel must be very pure or else catalyst will be poisoned
hydrogen is a dangerous gas
hydrogen is mostly sourced from fossil fuels, which its production involves greenhouse gas and requires significant input of energy
few refuelling stations
inverter is required for alternating current
green chemistry principles for designing fuel cell
reducing waste
→ utilise the maximum amount of reactants into desired products
→ utilise energy efficient process
using renewable feedstocks
→ maximise the use of biofuels (e.g. Hydrogen production)
minimising hazardous effects on human health and environment
→ design safer materials/ reduce the use and production of harmful substances
→ chemicals are designed to eventually degrade into harmless products that don’t build up in environment
circular VS linear economy
(circular)
→ optimal use of resources and reuse them
(linear)
→ products are discarded
two ways of producing hydrogen sustainably
electrolysis of water powered by solar/ wind energy/ energy generated from biofuels
steam reforming (methane in biogas sourced from landfill, reacts with steam, in presence of Ni catalyst, forming H2 and CO)
properties of hydrogen
highly flammable
potential explosive
storage of hydrogen
compressed into a high-pressured gaseous form/ liquid hydrogen
does hydrogen powered vehicles contribute to greenhouse gas levels?
yes, water vapour produced is a greenhouse gas
same as fuel cell, as heat as produced during electricity production, which would turn the water into water vapour
compare the amount of hydrogen required by a hydrogen fuel cell and a hydrogen-powered combustion engine to generate the same amount of energy
hydrogen fuel cell would use less hydrogen as it is more efficient (high energy efficiency) than a combustion engine