MP2024-ImmuneSystem2.pptx
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
4 functions of Adaptive immune (specific defense) systems
1. Protects against infectious agents & abnormal body cells
2. AMplifies inflammatory response
3. Activates complement
4. Must be primed by initial exposure to specific foreign substances (priming takes time)Know the 4 functions of Adaptive immune (specific defense) systems.
4 functions of Adaptive immune (specific defense) systems. are
1) specific, 2) systemic, and 3) have “memory”
Humoral Immunity: antibodies, produced by
lymphocytes, circulating freely in body fluids
Humoral Immunity, Bind temporarily to target cell
○ Temporarily inactive
○ Mark for destruction by phagocytes or complement
Cellular Immunity: Lymphocytes act against
target cell
Cellular Immunity: Lymphocytes act against target cell
● Directly – by
killing infected cells
Cellular Immunity: Lymphocytes act against target cell
Indirectly – by
releasing chemicals that enhance inflammatory response; or activating other lymphocytes or macrophages
what are Antigenic determinants (epitopes)
specific regions within an antigen to which antibodies or T-cell receptors can bind
Antigenic determinants are Composed of a unique sequence of amino acids or sugar moieties that
elicit an immune response and stimulate the production of antibodies or cellular immunity
Antigenic determinants (epitopes) are Essential in the body's defense against
pathogens and foreign substances, allowing the immune system to recognize and neutralize harmful agents
Only certain parts (antigenic determinants) of entire antigen are
immunogenic
Antibodies and lymphocyte receptors bind to them (Antigenic determinants) as
enzyme binds substrate
Most naturally occurring antigens have numerous antigenic determinants that Mobilize
several different lymphocyte populations
Most naturally occurring antigens have numerous antigenic determinants that Form different kinds of
antibodies against it
Antigenic determinants (epitopes), Large, chemically simple molecules (e.g. plastics) have
little or no immunogenicity
three types of cells in the adaptive immune system
B, T and APCs
Seeding Secondary Lymphoid Organs and Circulation, Immunocompetent B and T cells not yet exposed to antigen called
naive
Seeding Secondary Lymphoid Organs and Circulation are Exported from primary lymphoid organs (bone marrow and thymus) to "seed"
secondary lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, etc.)
– Increases chance of encounter with antigen
B lymphocytes (B-cells) have what kind of immunity
humoral immunity
B cells mature in
B cells mature in red bone marrow
B cells are Positively selected if successfully
make antigen receptors
B-cells that are self-reactive are
Eliminated by apoptosis (clonal deletion)
B cells Do not activate
naive T cells
B cells Present antigens to
helper T cell to assist own activation
T lymphocytes (T-cells) what kind of immunity
cell-mediated immunity
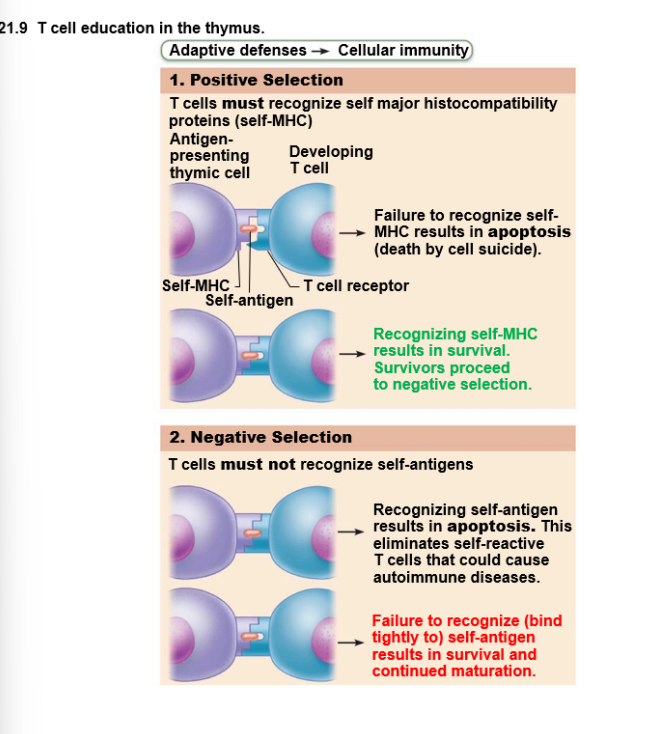
T lymphocytes (T-cells) mature in thymus under
negative and positive selection pressures ("tests")
T lymphocytes (T-cells), A very small fraction of cells
survive this process
Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) do not respond to
specific antigens & play essential auxiliary roles in immunity
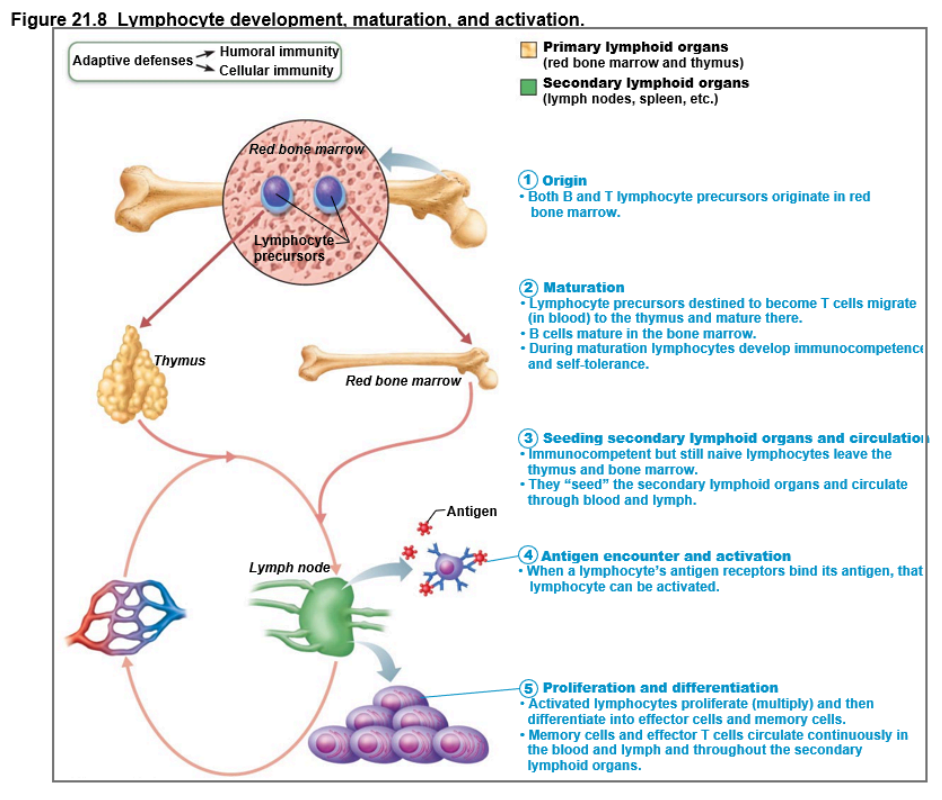
5 steps for Lymphocyte Development, Maturation, and Activation
1. Origin (all originate in red bone marrow)
2. Maturation
3. Seeding secondary lymphoid organs and circulation
4. Antigen encounter and activation
5. Proliferation and differentiation
"Educated" as mature: "Educated" as mature:
B cells in bone marrow & T cells in thymus
"Educated" as mature: Immunocompetence
– lymphocyte can recognize one specific antigen by binding to it
Immunocompetence, B or T cells display unique receptor on surface when
achieve maturity – bind only one antigen
"Educated" as mature, Self-tolerance Lymphocytes unresponsive to
own antigens
positive and negative selection-a very small fraction of cells
survive this process
lymphocyte development, maturation, and activation
T cell education in the thymus diagram
Dendritic cells phagocytize pathogens &
enter lymphatics to present antigens to T cells in lymph node
Dendritic cells Found in various tissues throughout the body, including
the skin (Langerhans cells), mucosal surfaces, lymph nodes, and spleen
Dendritic cells are the Most effective
antigen presenter known
Dendritic cells are the Key link between
innate and adaptive immunity
Dendritic cells Can activate
naive T cells
Dendritic cells Present antigens to T cells to activate themselves into
voracious phagocytes that secrete bactericidal chemicals
Clonal selection of a B cell diagram
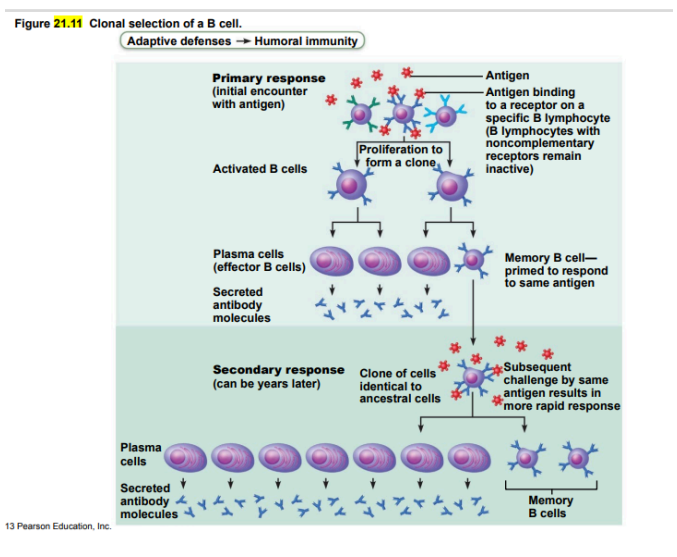
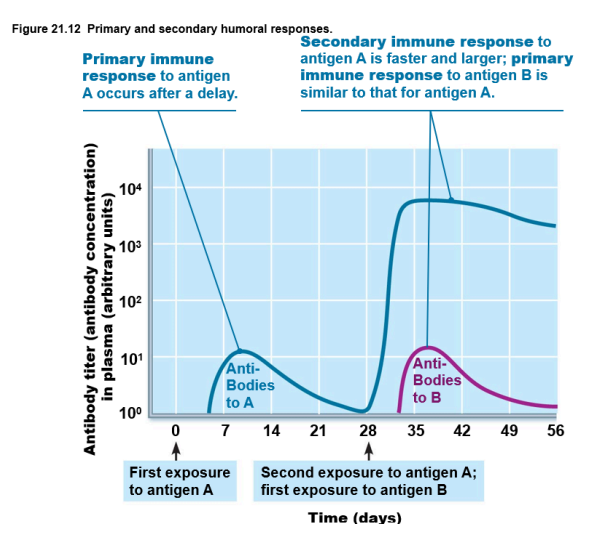
primary and secondary humoral responses
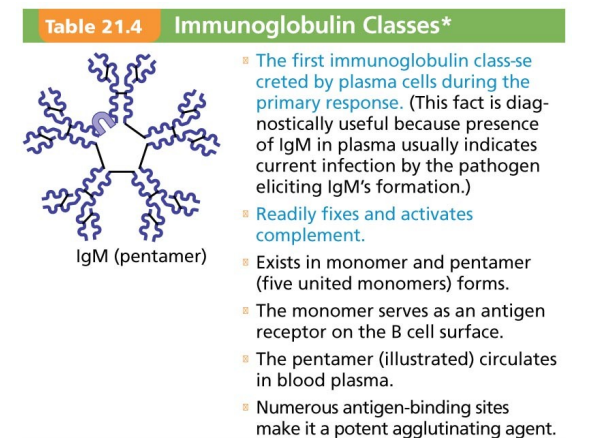
IgM, Pentamer
Pentamer (larger than others), first antibody released
IgM, Potent
Potent agglutinating agent
IgM, Readily fixes and activates
complement
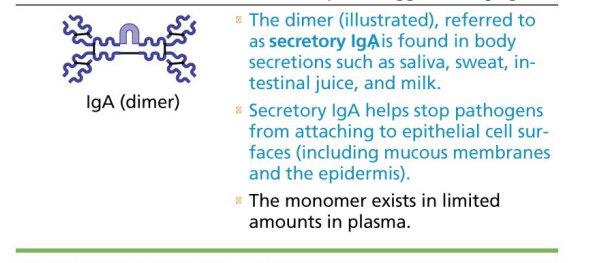
IgA (secretory IgA), Monomer or
dimer, in mucus and other secretions
IgA (secretory IgA), Helps prevent entry
of pathogens
IgD, Monomer attached to
surface of B cells
IgD Functions as
B cell receptor
IgG, Monomer; 75–85% of antibodies
plasma
IgG, From secondary and
late primary responses
IgG, Crosses
placental barrier
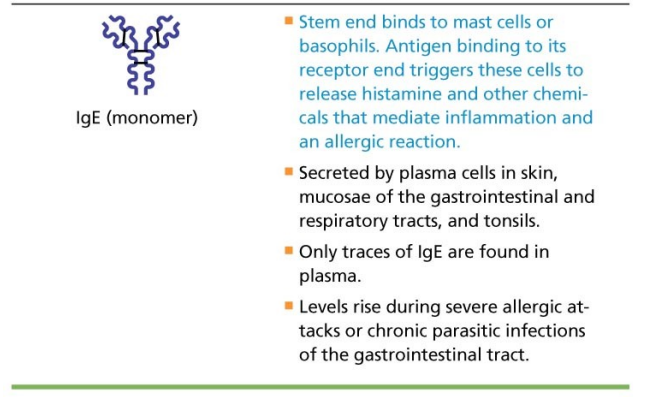
IgE, Monomer active in some allergies and
parasitic infections
IgE, Causes mast cells and basophils to
release histamine
IgE, B cells can switch antibody classes but
retain antigen specificity
IgM at first, then IgG
Almost all secondary responses are IgG
IgM pentamer table 21.4
IgA (dimer) table 21.4
IgD (monomer) table 21.4

IgG (monomer) table 21.4

IgE (monomer) table 21.4