6 - Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle (Kreb Cycle)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:32 PM on 4/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
1
New cards
where does pyruvate oxidation and citric acid cycle occur?
matrix of mitochondria
2
New cards
what are different ways that acetyl-CoA is formed?
1. pyruvate from glycolysis
2. B-oxidation of FA
3. amino acid catabolism produce pyruvate or acetyl-CoA
3
New cards
what enzyme is used for the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA?
pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
4
New cards
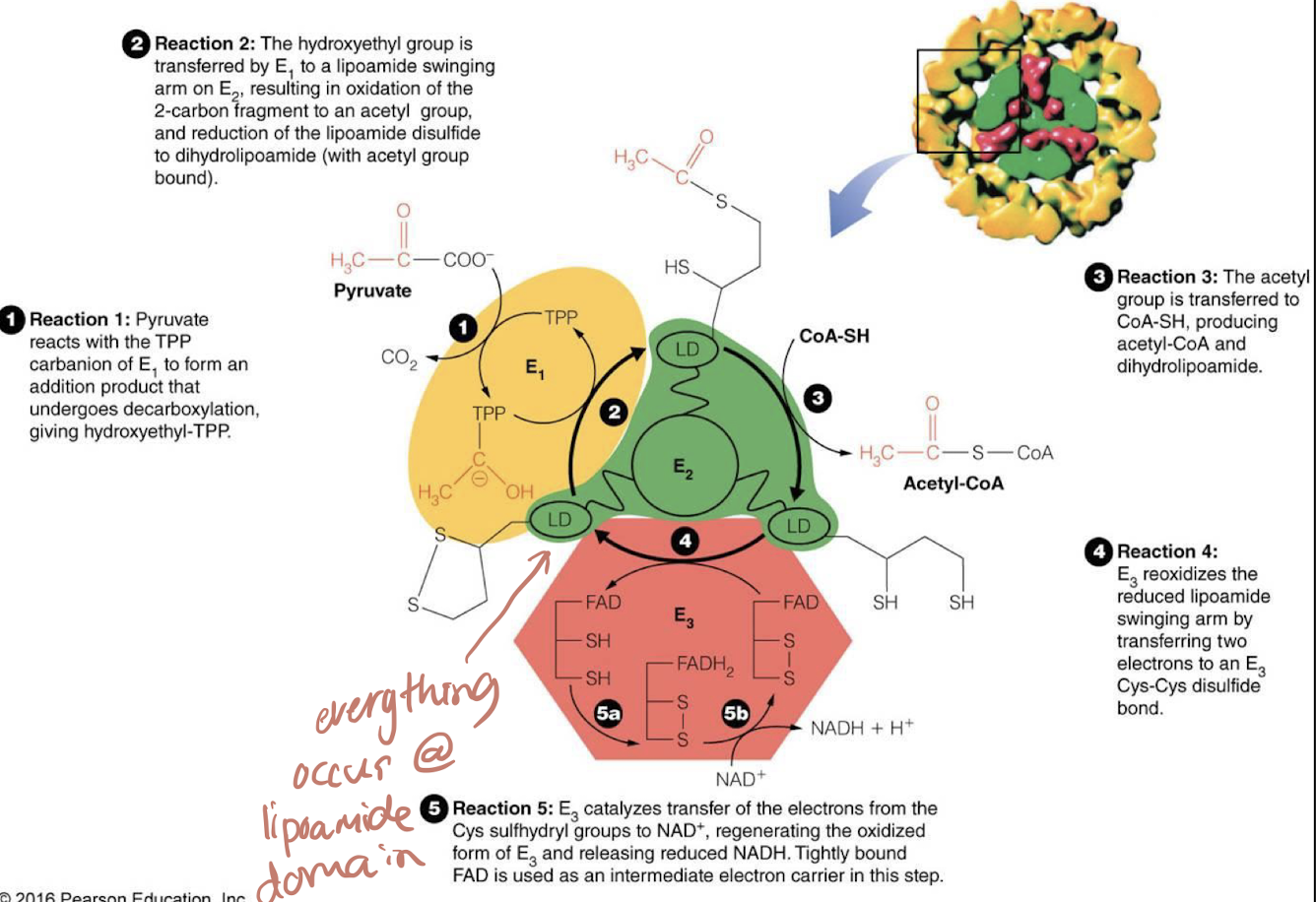
what are each subunit of pyruvate dehydrogenase ? and what are the cofactors?
E1 = pyruvate dehydrogenase → TPP
E2 = dihydroliposmide transacetylase → lipoic acid, Coenzyme A
E3 = dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase → flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
E2 = dihydroliposmide transacetylase → lipoic acid, Coenzyme A
E3 = dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase → flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD), Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
5
New cards
what is the purpose of riboflavin ?
phosphorylation of riboflavin forms flavin mononucleotide (FMN) which is then used as a electron acceptor on the E3 of pyruvate dehydrogenase
6
New cards
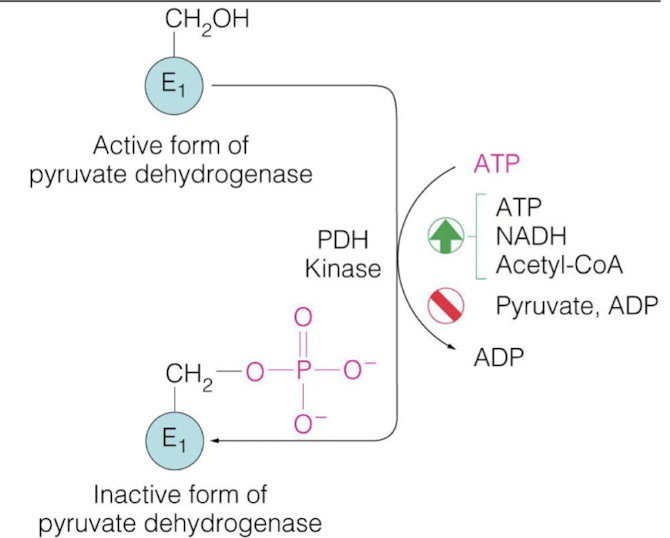
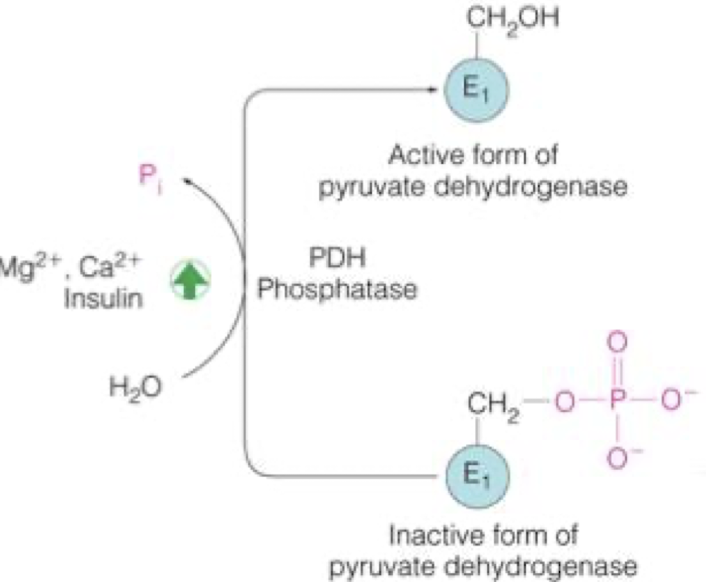
how is the E1 subunit regulated ?
activated = PDH phosphatase (dephosphorylation)
inhibited = PDH kinase (phosphorylation)
inhibited = PDH kinase (phosphorylation)
7
New cards
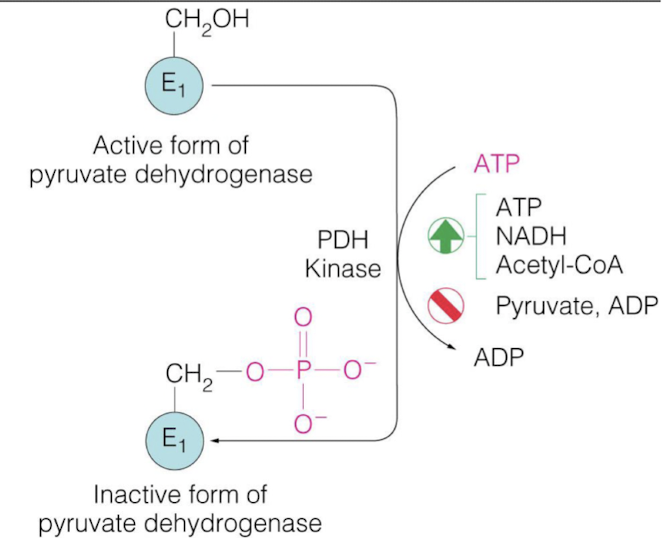
how is the E1 pyruvate dehydrogenase regulated?
activated = PDH phosphatase
inhibited = PDH kinase
inhibited = PDH kinase
8
New cards
how is PDH kinase regulated?
activate = ATP, NADH, Acetyl-CoA
inhibit = Pyruvate, ADP
inhibit = Pyruvate, ADP
9
New cards
how is PDH phosphatase regulated ?
activate = Mg2+, Ca2+, and insulin
10
New cards
what are the general reactions in the TCA cycle?
1. condensation
2. done to citrate → isocitrate
1. dehydration
2. hydration
3. oxidative decarboxylation
4. oxidative decarboxylation
5. substrate-level phosphorylation
6. dehydrogenation
7. hydration
8. dehydrogenation
11
New cards
what is produced for each acetyl-CoA?
1 GTP (S5)
3 NADH (S3, S4, S8)
1 FADH2 (S6)
2 CO2
3 NADH (S3, S4, S8)
1 FADH2 (S6)
2 CO2
12
New cards
what are the irreversible steps of the TCA cycle?
S1: condensation (acetyl-CoA + oxaloacetate → citrate)
S3: decarboxylation (isocitrate → a-ketoglutarate)
S4: oxidative decarboxylation (a-ketoglutarate → succinyl-CoA)
S3: decarboxylation (isocitrate → a-ketoglutarate)
S4: oxidative decarboxylation (a-ketoglutarate → succinyl-CoA)
13
New cards
what is an important characteristic of succinate dehydrogenase ?
located in inner mitochondrial membrane
belongs to complex II of respiratory chain
belongs to complex II of respiratory chain
14
New cards
why is step 8 of the TCA cycle despite have a negative free energy?
low concentration of reactants
* more oxaloacetate is converted back to L-malate
* to be used in gluconeogenesis
* more oxaloacetate is converted back to L-malate
* to be used in gluconeogenesis
15
New cards
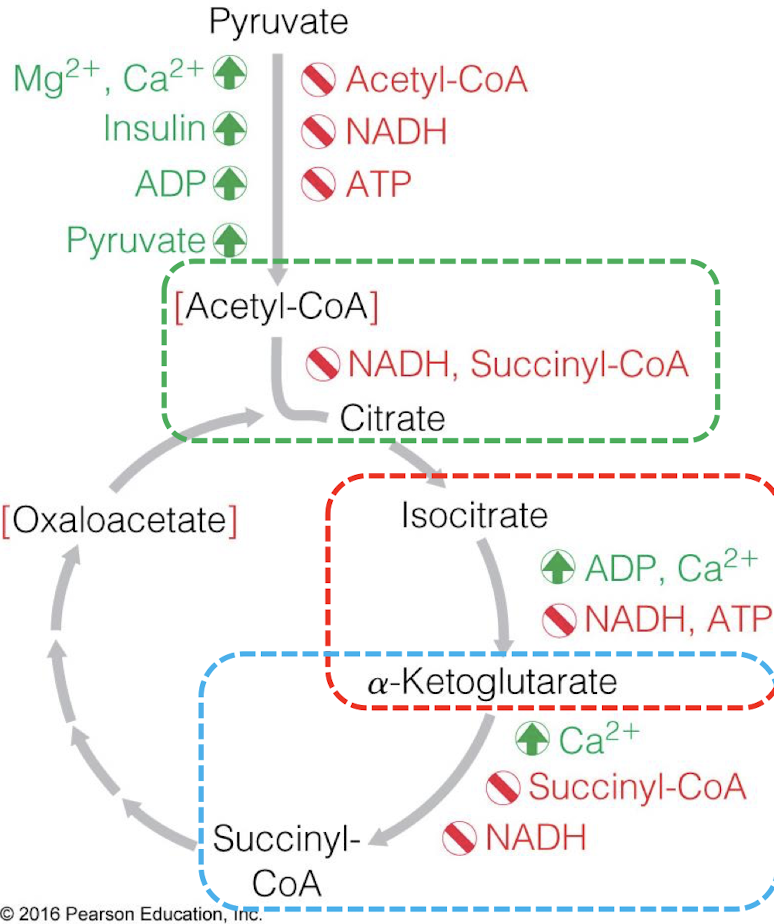
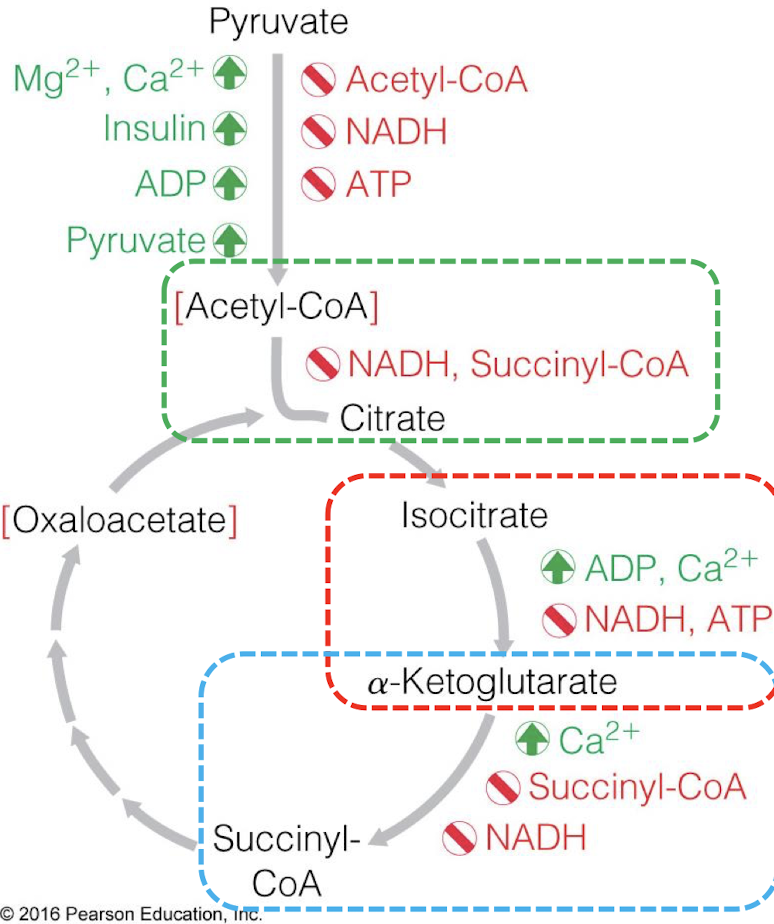
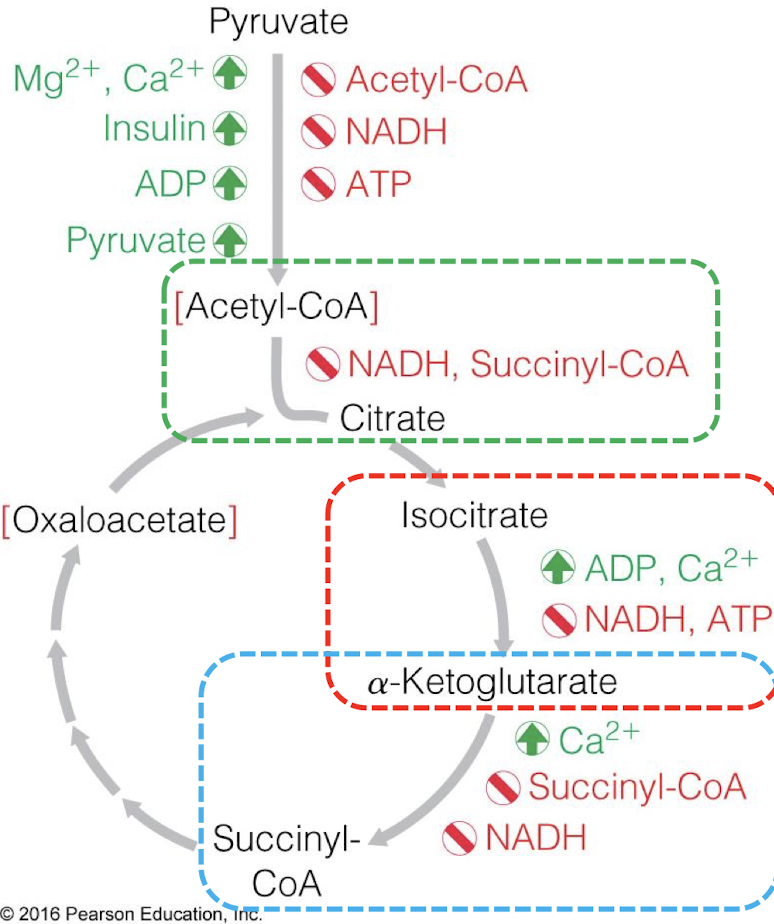
how is citrate synthase regulated?
inhibited = NADH, succinyl-CoA
16
New cards
how is isocitrate dehydrogenase regulated?
activated = ADP, Ca2+
inhibited = NADH, ATP
inhibited = NADH, ATP
17
New cards
how is a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase regulated?
activated = Ca2+
inhibited = NADH, succinyl-CoA
inhibited = NADH, succinyl-CoA
18
New cards
citrate is a allosteric inhibitor of what? why?
PFK
* high conc increase inhibitory effect of ATP
* high conc increase inhibitory effect of ATP
19
New cards
what are anaplerotic and cataplerotic reactions ?
anaplerotic = rxn replenish intermediates of TCA cycle
cataplerotic = rxn that use TCA intermediates to make others
cataplerotic = rxn that use TCA intermediates to make others
20
New cards
how many ATP is produced as a result of NADH and FADH2
NADH = 2.5ATP
FADH2 = 1.5 ATP
FADH2 = 1.5 ATP
21
New cards
how many ATP is produced in each step up till the electron transfer phosphorylation?
glycolysis = 2 ATP
TCA cycle = 2 ATP
electron transfer phosphorylation = 28 ATP
TCA cycle = 2 ATP
electron transfer phosphorylation = 28 ATP
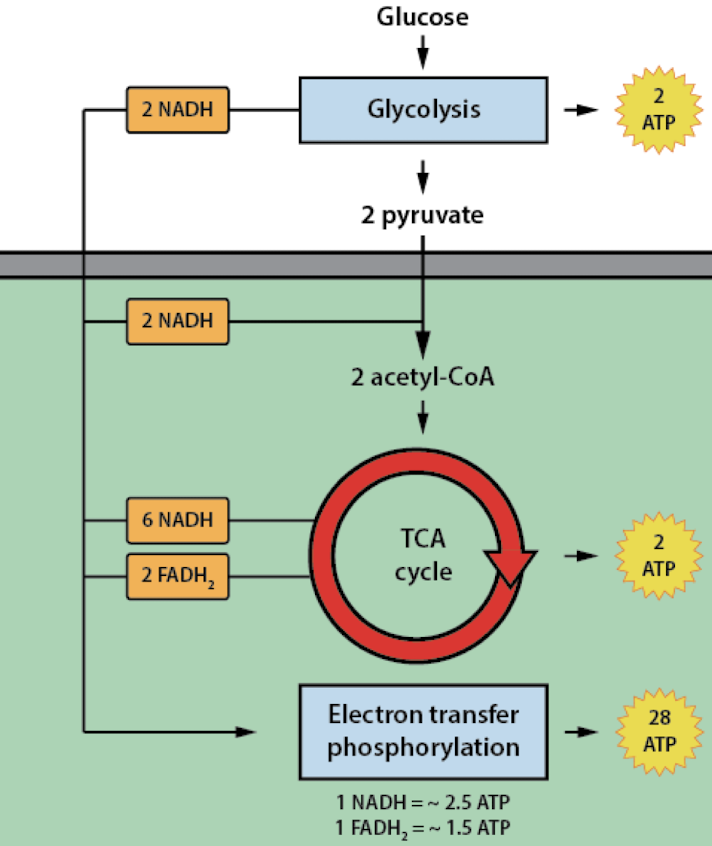
22
New cards
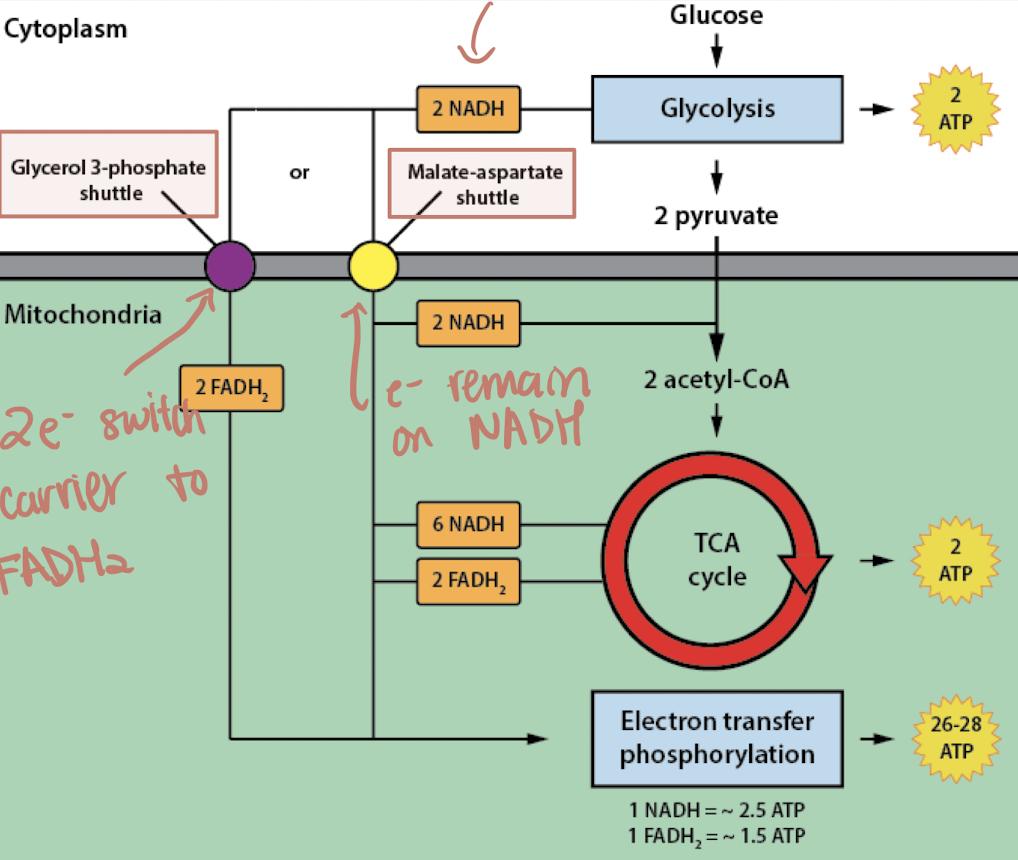
how many reducing power is converted using the glycerol-3-phosphate pathway or the malate-asparate shuttle?
G3P shuttle → 2 NADH = 2 NADH
malate-aspartate shuttle → 2 NADH = 2 FADH2
malate-aspartate shuttle → 2 NADH = 2 FADH2