Urinary system
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anatomy and physiology 12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Excretion
The process that rids body of metabolic wastes, performed by kidneys, liver, lungs, and skin
Kidneys
Excrete nitrogenous wastes, including ammonia, uria, uric acid, creatinine. Excretes HCO3- (bicarbonate ions) and H+. Excrete urine, regulate blood volume, pH. Reddish-brown organs about 4 inches long, 2 inches wide, 1 inch thick, anchored against the dorsal body wall by connective tissue.
Defecation
The process which rids the body of undigested, unabsorbed food remains, plus bacteria
Ammonia
NH3. A nitrogenous waste that is made from deamination of amino groups. Very toxic to tissue, converted to urea in liver from land animals.
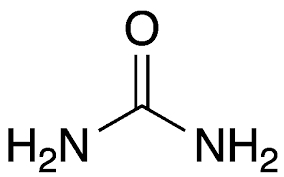
Urea
Waste product formed in the liver when the body breaks down proteins, made from ammonia.
Creatinine
A nitrogenous waste. Comes from phosphocreatine in muscle metabolism.
Bile pigments
Made from breakdown of red blood cells
Carbon dioxide
A substance excreted through the lungs
Ions
Includes salts K+, Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Fe+. Needed for biochemical processes and needed at various concentrations, excreted to maintain balance.
Water
Metabolic end product, maintains blood pressure, consumed with food.
Urine
Mostly composed of urea (3%), salts (2%), H2O (95%)
Glands
Excrete perspiration/sweat (which consists of H2O, salt, and small amounts of urea). Excretion made mostly for cooling.
Liver
Excrete bile, which contains pigments that are breakdown products of RBC metabolism. Bile is sent to small intestine. Also produces urochrome.
Urochrome
Breakdown of heme and gives urine yellow colour.
Lungs
Excrete CO2, some H2O.
Intestine
Excretes some iron and calcium salts, whcih are secreted into here and excreted into feces.
Renal vein
Part of the urinary system. Carries blood from kidneys back to heart.
Renal artery
Part of the urinary system. Carries blood to kidneys.
Ureter
Muscular tubes, moves urine from kidneys to bladder via peristalsis.
Bladder
Holds up to 600 ml to 1000 ml urine, can expand/contract. Has stretch receptors that indicate when it is full, notifies the brain.
Urethra
Tube connecting bladder to outside. For man is 6 inches long, but women is 1 inch.
3 divisions of kidneys
Cortex (outer layer), medulla (middle, striated), pelvis (inner cavity)
Kidney stones
Formed in pelvis, consists of calcium salts and uric acid. Can pass naturally or be treated with surgery, or destroyed with sound waves of laser light. Primary cause is too much protein.
Nephrons
The functional units of the kidney. Filter wastes from the blood and retain water and other needed materials. About 1 million per kidney, urine formation occurs here. Where urine formation occurs.
Bowman’s capsule
Cup-like end of nephron where wastes are forced out of the blood and into the nephron.
Glomerulus
A network of small blood vessels (capillaries) known as a tuft, located at the beginning of a nephron in the kidney. Where water, salts, nutrient molecules, and waste products move inside.
Afferent arteriole
Carries blood to glomerulus
Efferent arteriole
Carries blood from glomerulus
Proximal convoluted tubule
The first segment of the renal tubule, located in the kidney's cortex
Loop of henle
A U-shaped tube in the kidney that forms part of a nephron, the functional unit of the kidney. Surrounded by peritubular capillary network. Used for reabsorption of water.
Peritubular capillary network
A specialized network of blood vessels in the kidney that plays a crucial role in reabsorbing essential substances from the filtrate back into the bloodstream. Molecules are exchanged between blood vessels and nephrons here.
Distal convoluted tubule
A short segment of the kidney nephron located between the macula densa and the connecting tubule. Occurs after loop of henle.
Collecting duct
Acts as a final pathway for urine, collecting it from multiple nephrons and transporting it to the renal pelvis and ultimately, the ureter
Pressure filtration
Occurs inside bowman’s capsule as SMALL molecuels (H2), nitrogenous wastes, nutrients, ions) are forced through the glomerus due to high blood pressure. Large molecules unable to pass (platelets, RBC, proteins), remain in blood and leave via efferent arteriole).
Filtrate
Small, filterable molecules that are forced into Bowman’s capsule
Juxtaglomerular apparatus
Causes high blood pressure, a special region of afferent arteriole, will releave renin to increase blood pressure if necessary.
Renin
An enzyme produced by the kidneys that plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure. Made from juxtaglomerular apparatus.
Kidney disease
High blood pressure due to juxtaglomerular apparatus is constantly releasing renin
Selective reabsorption
Reabsorb molecules from the filtrate that are needed by the body (water, nutrients, some salts0. Move from proximal convoluted tubule to peritubular capillary network.
Reabsorbed
Most H2O, nutrients, some salts (Na+, Cl-)
Not reabsorbed
Some H2O, wastes, excess salts. Continues through the loop of henle.
Active transport
Needed for absorption. Requires ATP and carrier molecule (glucose, Na+)
Passive
Needed for absorption but no ATP. Includes Cl- and water.
Tubular excretion
Active process by which other non-filterable wastes can be added to the tubular fluid so that it can be excreted in the urine. Occurs in the distal convoluted tubule, include chemicals (penicillin, histamine), H+ ions, NH3.
Cortex
Outer layer of kidney. Fluid in duct is isotonic to the surrounding cells, therefore no net movement of water.
Medulla
Inner layer of kidney. Fluid is hypotonic to cells therefore H2O passively diffuses out of collecting duct
Urine
Tubular fluid. Passes from duct into pelvis of kidney, and enters ureter for transport to bladder.