B1.1 Carbohydrates
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What are covalent bonds?
When valence electrons are shared between two non-metal elements.
Why are electrons shared between atoms?
To generate strong bonds between compounds
Which four major categories of biological molecules is carbon present in?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic acids
How many electrons does carbon have in its outer shell?
Four
How many covalent bonds can one carbon atom form?
Four
Which two atoms does carbon usually form covalently-bonded compounds with?
Hydrogen and oxygen
What can carbon compounds form?
Chains, branches, rings, double bonds
What are functional groups?
Groups of atoms that are found in organic compounds (contains carbon)
What are examples of functional groups?
Hydroxyl, Carboxyl, Amino, Phosphate groups
What is the role of functional groups?
Add chemical reactivity to the carbon backbone, give organic compounds their individual properties
What are monomers?
Molecules which join to other similar molecules to form polymers
What are polymers?
Molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together in a chain
What is the process of polymerisation?
When monomers join to form polymers
What are macromolecules?
Contain 1000 or more atoms and have a high molecular mass
What are condensation reactions?
When molecules combine together, forming covalent bonds and resulting in polymers or macromolecules. Water is removed
How are polysaccharides formed?
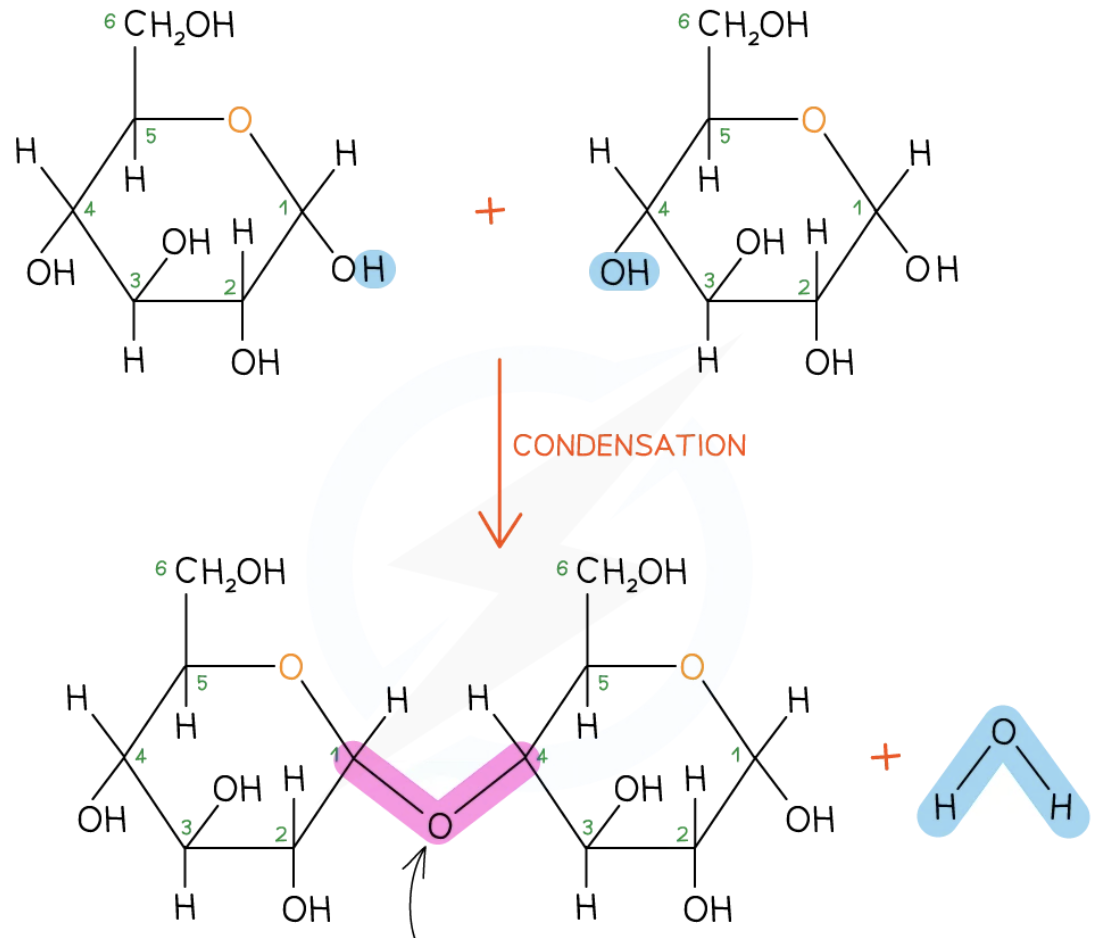
By condensation reactions, when two hydroxyl (OH) groups on different monosaccharides interact to form a strong covalent bond (glycosidic bond)
What is a glycosidic bond?
A strong covalent bond linking a sugar (carbohydrate) molecule to another group
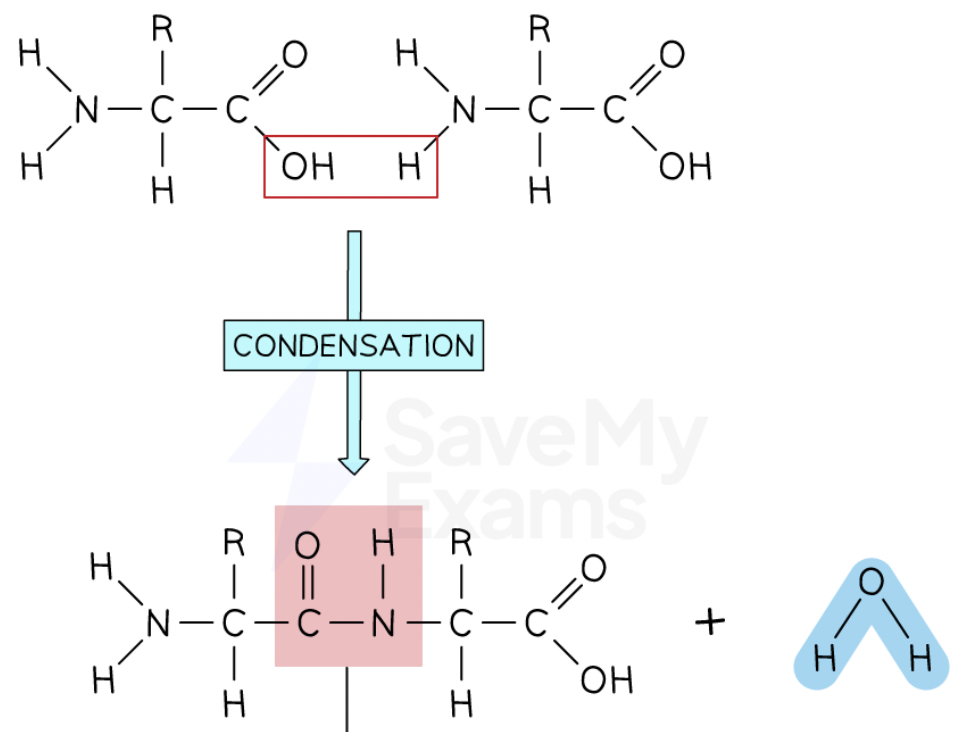
How are polypeptides formed?
By condensation reactions, when two amino acid monomers interact to form a strong covalent bond called a peptide bond
What are peptide bonds?
Strong covalent bonds that links amino acids together
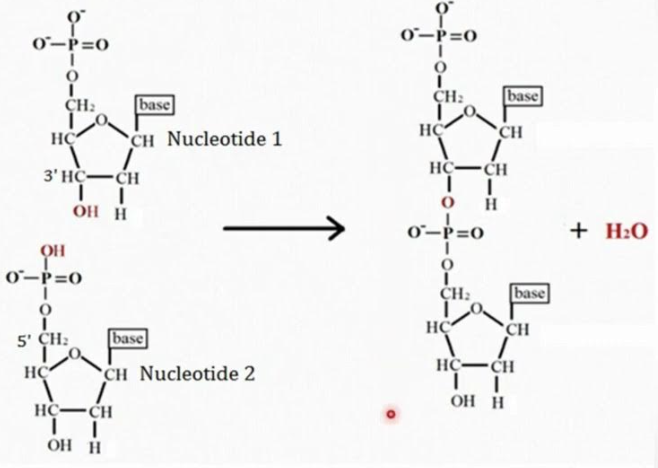
What are phosphodiester bonds?
Strong covalent bonds where a phosphate group connects the 3' carbon of one sugar to the 5' carbon of another sugar. Consist of a phosphate group and two ester bonds
What bond does this image show?
Glycosidic bond
What bond does this image show?
Peptide bond
What bond does this image show?
Phosphodiester bond
What are hydrolysis reactions?
Covalent bonds in polymers are broken into monomers when water is added
What are monosaccharides?
Simple sugars with 3-7 carbons, mostly ring forms
What are some properties of monosaccharides?
Colourless crystalline molecules, soluble in water
What are the isomers of glucose?
Alpha (α) glucose and beta (β) glucose
Which polysaccharides are made from alpha glucose?
Starch and glucose
Which polysaccharides are made from beta glucose?
Cellulose
How does glucose have a stable structure?
The presence of covalent bonds which are strong and hard to break
How is glucose soluble in water?
It is polar
How is glucose easily transportable?
Soluble in water
How is glucose a source of chemical energy?
When its chemical bonds are broken, up to 36 ATP molecules are released
What is the function of carbohydrates?
Energy storage molecules and structural molecules
What are polysaccharides composed of?
Many sugar molecules combined through a series of condensation reactions or removed by hydrolysis reactions.
What is the polysaccharide that serves as a store of energy in plants?
Starch
What is the polysaccharide that serves as a store of energy in animals and fungi?
Glycogen
Why are starch and glycogen effective storage polysaccharides?
They are:
Compact - large quantities can be stored in a small space
Insoluble - soluble molecules will dissolve in cytoplasm, causing water to move inside and the cell to burst
Why is cellulose a structural polysaccharide?
It is:
Strong and durable
Insoluble and slightly elastic
Chemically inert
What 2 polysaccharide molecules is starch composed of?
Amylose and amylopection
What is amylose?
Unbranched helix-shaped chain with 1,4 glycosidic bonds between alpha glucose molecules
What is amylopectin?
Branched molecule with 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds between alpha glucose molecules
What is glycogen?
Branched molecule with 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds between alpha glucose molecules
Why is glycogen more branched than amylopection?
It has more free ends where glucose can be removed by hydrolysis so it can be broken down quickly
What is cellulose?
Straight unbranched polysaccharide with beta glucose molecules
What is the structure of cellulose?
Every alternate molecule of beta glucose is inverted to allow hydrogen bonding to occur between strands
What are microfibrils?
Groups of cellulose molecules held together by hydrogen bonds.
What is the function of cellulose microfibrils?
Maintains structural integrity of plants cell walls due to high tensile strength
What are glycoproteins?
Integral proteins within phospholipid bilayers with a chain of carbohydrates attached that can act as an antigen
How are glycoproteins formed?
When carbohydrates and polypeptides combine via covalent bonds
How do glycoproteins aid cell to cell adhesion?
They interact with glycoproteins on neighbouring cells, allowing the formation of tissues
How do glycoproteins act as receptors for hormones?
When a hormone binds to a specific glycoprotein receptor, it changes metabolism within the cell
How do glycoproteins aid cell to cell communication?
Neurotransmitters bind to glycoproteins.
How do glycoproteins aid immune responses?
Glycoproteins act as markers on cells allowing the immune system to distinguish between self and non-self cells
What are antigens?
Substances which stimulate an immune response and the production of antibodies