Tuberculosis infections (Latent) (Fouty)
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Additional material (lecture)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Gibbus spine POTS infection in vertebral column compression fractures
TB
Robert Koch developed tuberculin
severe skin reaction when injected into the skin of patients with active TB
Some people without TB also reacted to tuberculin
People without disease but who lived with people who had TB
Tuberculin testing was used to control _____ tuberculosis first
bovine
____ testing of cows and pasteurization of milk eliminated bovine transmission of TB
Tuberculin
precipitated protein fraction from a single strain of human tubercle bacillus
purified and potent
non-sensitizing
dose could be standardized and delivered SQ
PPD
Standard PPD __ TU= 0.001 mg
5
High strength PPD increases ______ rates
false positives
Tools required for chemoprophylaxis available by late 1940’s
Standardized skin test to reliably detect infection.
chest radiographs.
drugs for chemotherapy
- streptomycin, PAS (1944)
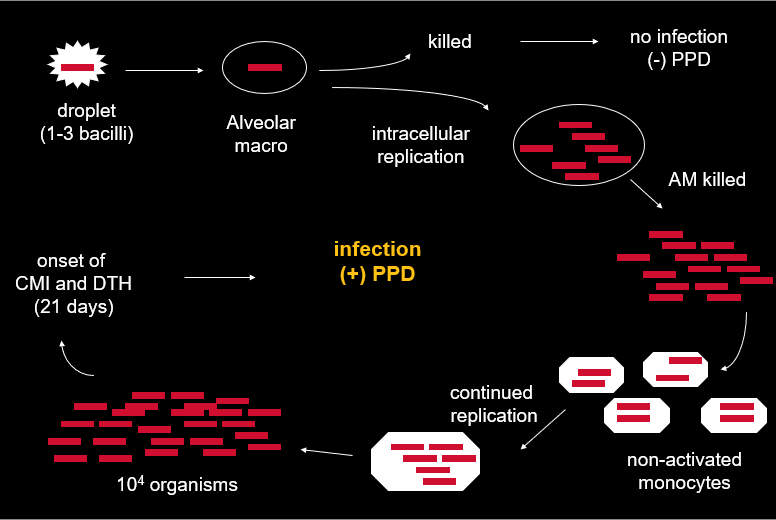
Fork in the road image
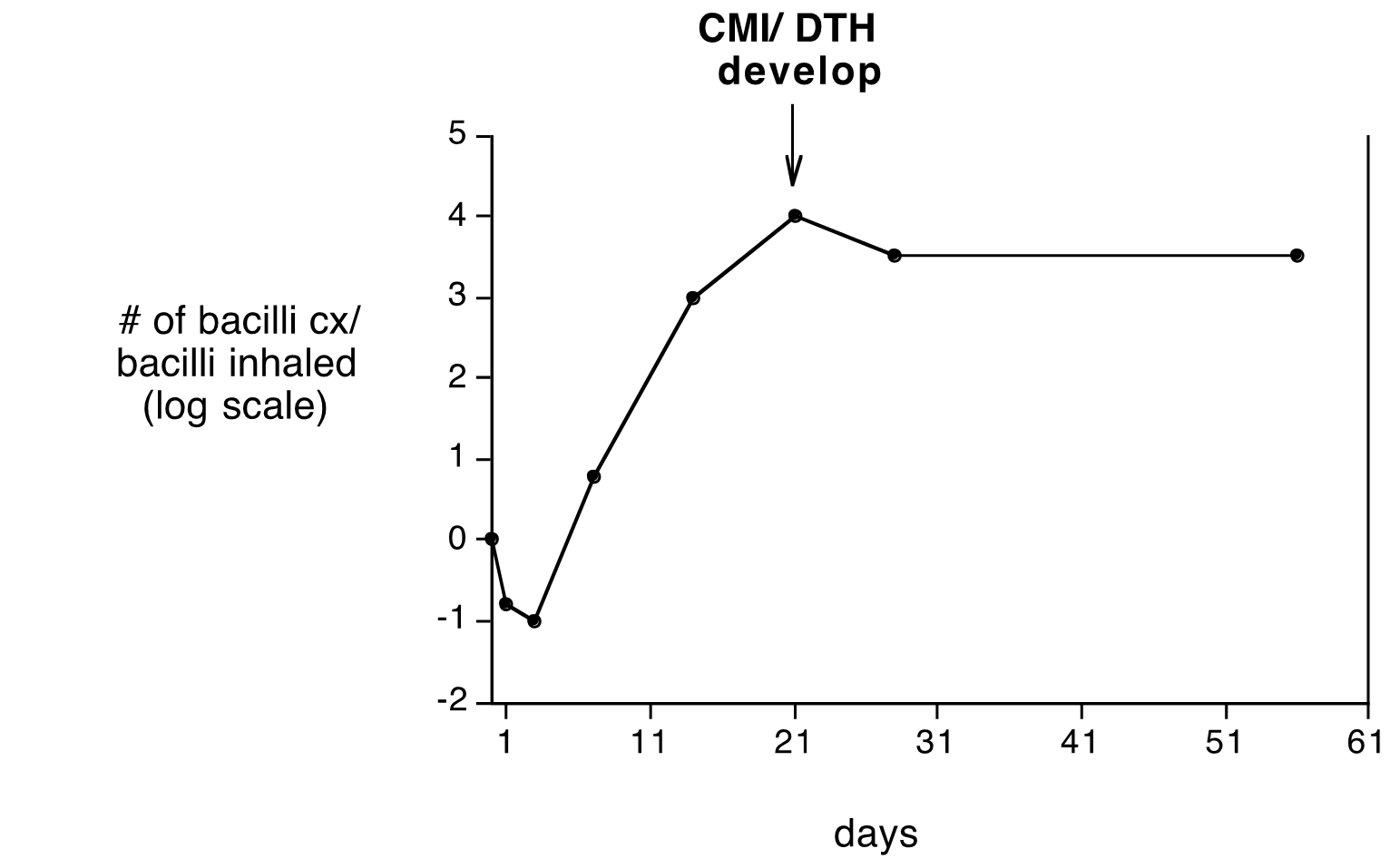
Logmarithmic growth from 5-21 days
then CMI and DTH cell mediated immunity start to work to try to kill and control
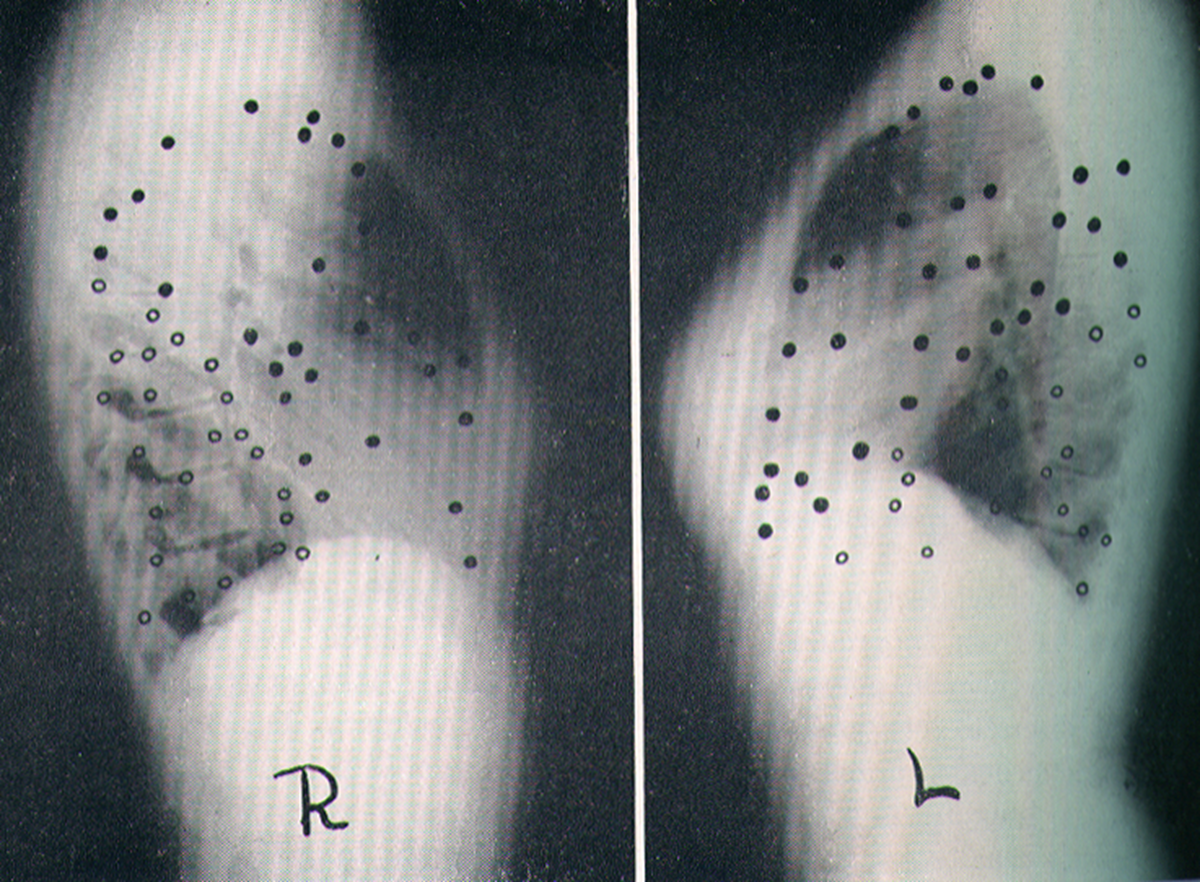
Location Of Primary Calcified Foci
primarily in lower lobes
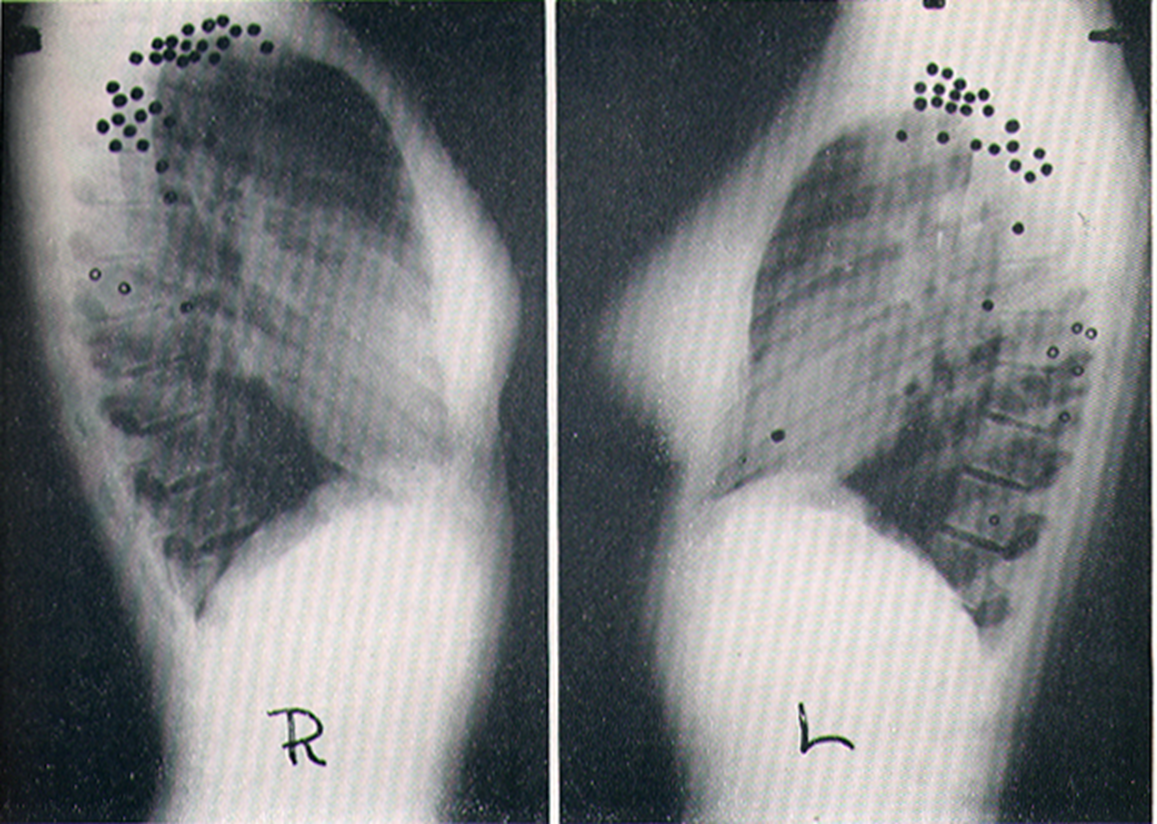
Location Of Re-Infection Tuberculosis
cluster in upper lobes
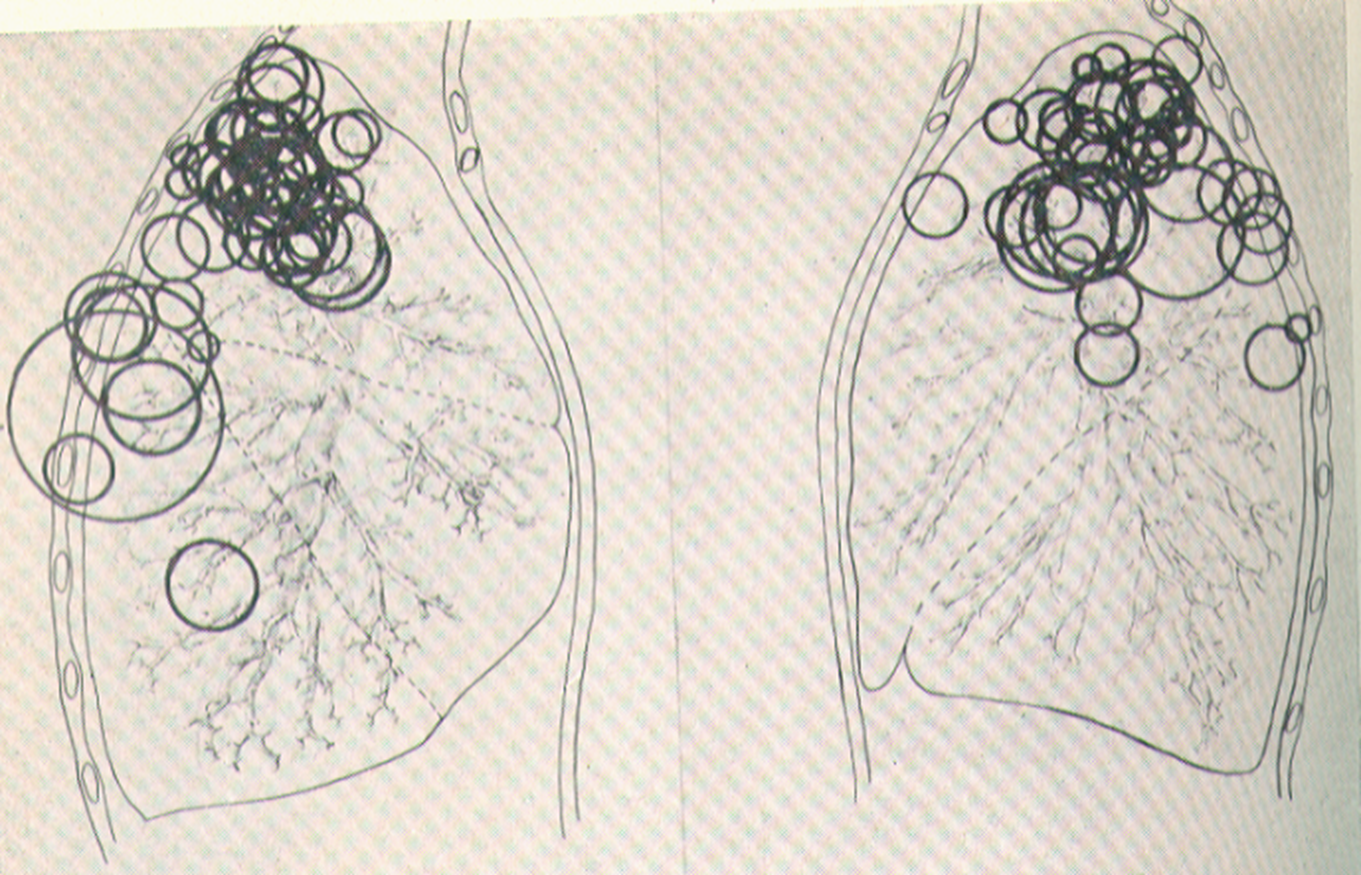
Location Of Single Tuberculosis Cavities
RML interestingly spared
There is ________While CMI/DTH Controls Initial Infection
dissemination
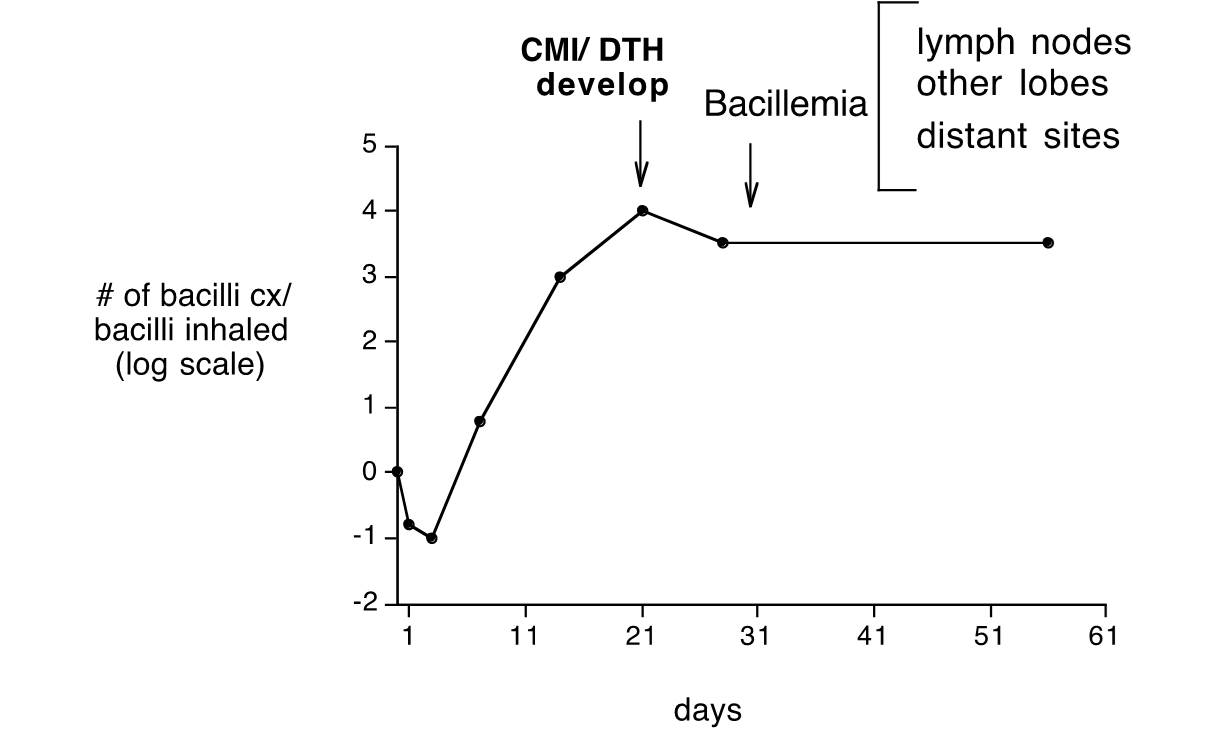
dissemination
access through alveolar macrophages
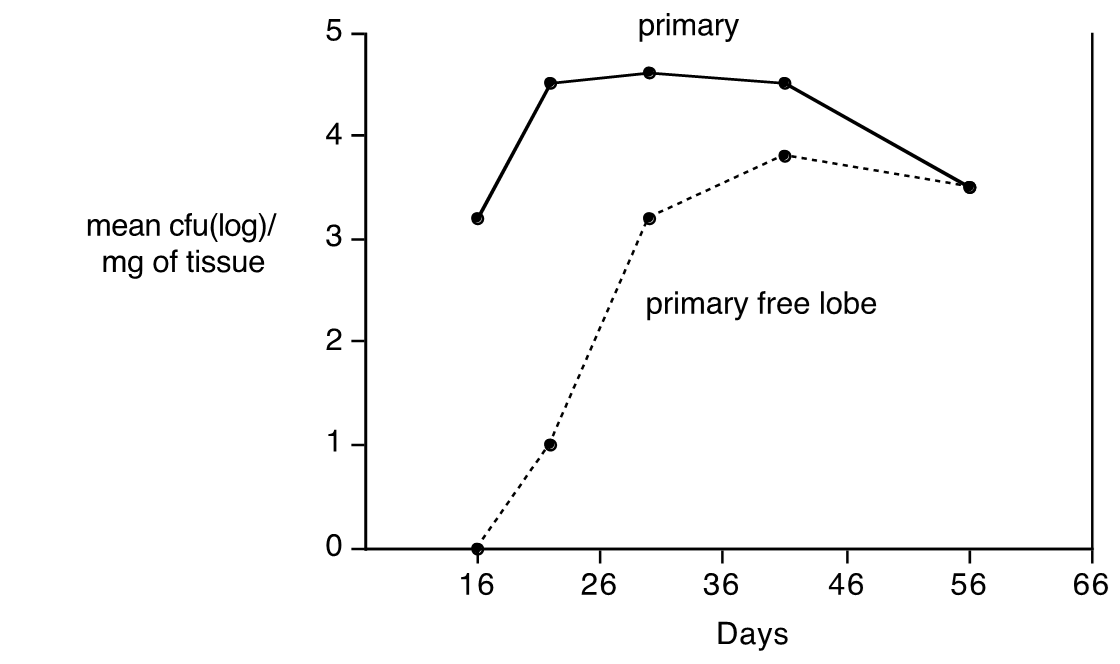
Secondary lesions not completely eradicated
Distal Disease Progresses While Primary Focus Is Controlled
TB life graph
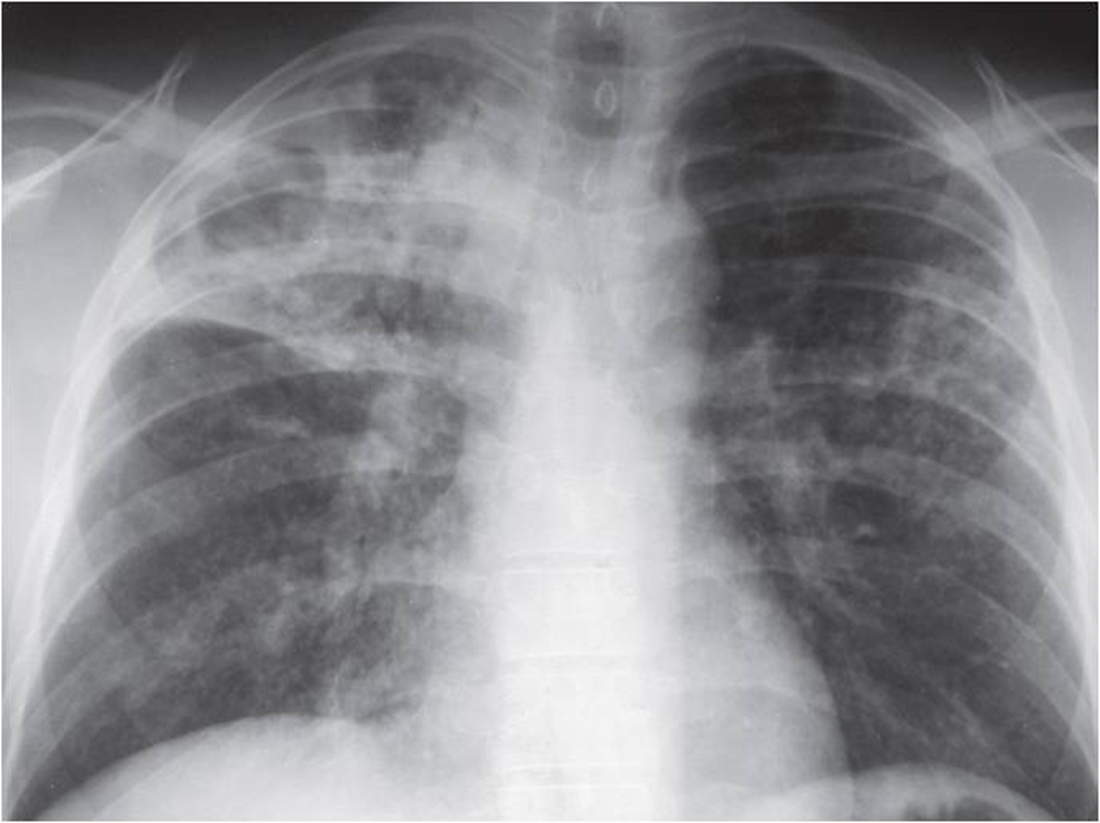
Classic TB radiograph
White in upper lobe and cavities
Reactivation
TB reactivation is more common in ____ ____ lobe
Right upper
Does the skin test represent a true Tuberculosis Infection?
Infected without clinical symptoms and with negative cultures (latent disease)
What is the risk of progressing to Tuberculosis Disease?
Infected with clinical symptoms with positive cultures (active disease)
Question to ask yourself
Greater than 5 mm
HIV infected or at risk
close contacts of newly diagnosed tuberculosis
fibrotic lesions on CXR c/w old healed TB
Greater than 10 mm
IVDU known to be HIV (-)
foreign born from high prevalence countries (Mexico, Vietnam, Phill, Korea)
Medical conditions increasing risk of TB
Medically underserved low income
High-risk racial groups (Hispanics, Blacks, Native Americans)
Recent converters (> 10 mm increase within 2 years)
Greater than 15 mm
Low risk groups
18 y/o white male who lives in Beverly Hills has 12 mm of induration on his PPD during a screen to obtain a food handler’s card. He has no known exposures to TB and has lived his entire life next to the Kardashians. He is asymptomatic with a normal chest radiograph.
No treatment
Does the skin test represent a true Tuberculosis Infection? NO
size of induration
risk of exposure
Value Of Skin Testing Is Related To ______ Of Disease
prevalence
99 false positives in low prevalence groups. Only 8 percent actually have it.
Medical Conditions That Increase The Likelihood That Tuberculosis Infection Will Become Tuberculosis Disease
Silicosis (sandblaster)
diabetes (mainly insulin dependent)
chronic renal failure
gastrectomy
malnutrition
jejunoileal bypass
diseases requiring immunosuppressive drugs
TNF-alpha blockers, steroids, cyclophosphamide (RA, Chrons, UC)
malignancies (esp. hematologic)
A 52 y/o woman whose husband has smear-positive Mycobacterium tuberculosis has a PPD of 8 mm induration. She does not remember the results of her old skin test 20 years prior. She is asymptomatic with a normal chest radiograph.
Treatment
45 y/o nurse who after years of non-reactive skin tests develops a 12 mm induration on her annual screen after years of no induration. She works at a county hospital which treats patients with tuberculosis. She is ASX and has a normal CXR. She has no other medical problems.
Treatment
Risk of developing TB disease after infection with M TB lifetime risk:
10%
Risk of developing TB disease after infection with M TB lifetime risk in first 18-24 months after infection
5-7%
Increased risk of developing TB disease immediately following ___ conversion
PPD
_____ prophylaxis decreases incidence of progression form TB infection to TB disease
Isoniazid
45 y/o man immigrating from Vietnam has 14 mm of induration on his initial skin test. He has not had a prior skin test, but his father died of tuberculosis 30 years prior. He has no symptoms and his CXR is normal. He has no other medical problems.
Treatment
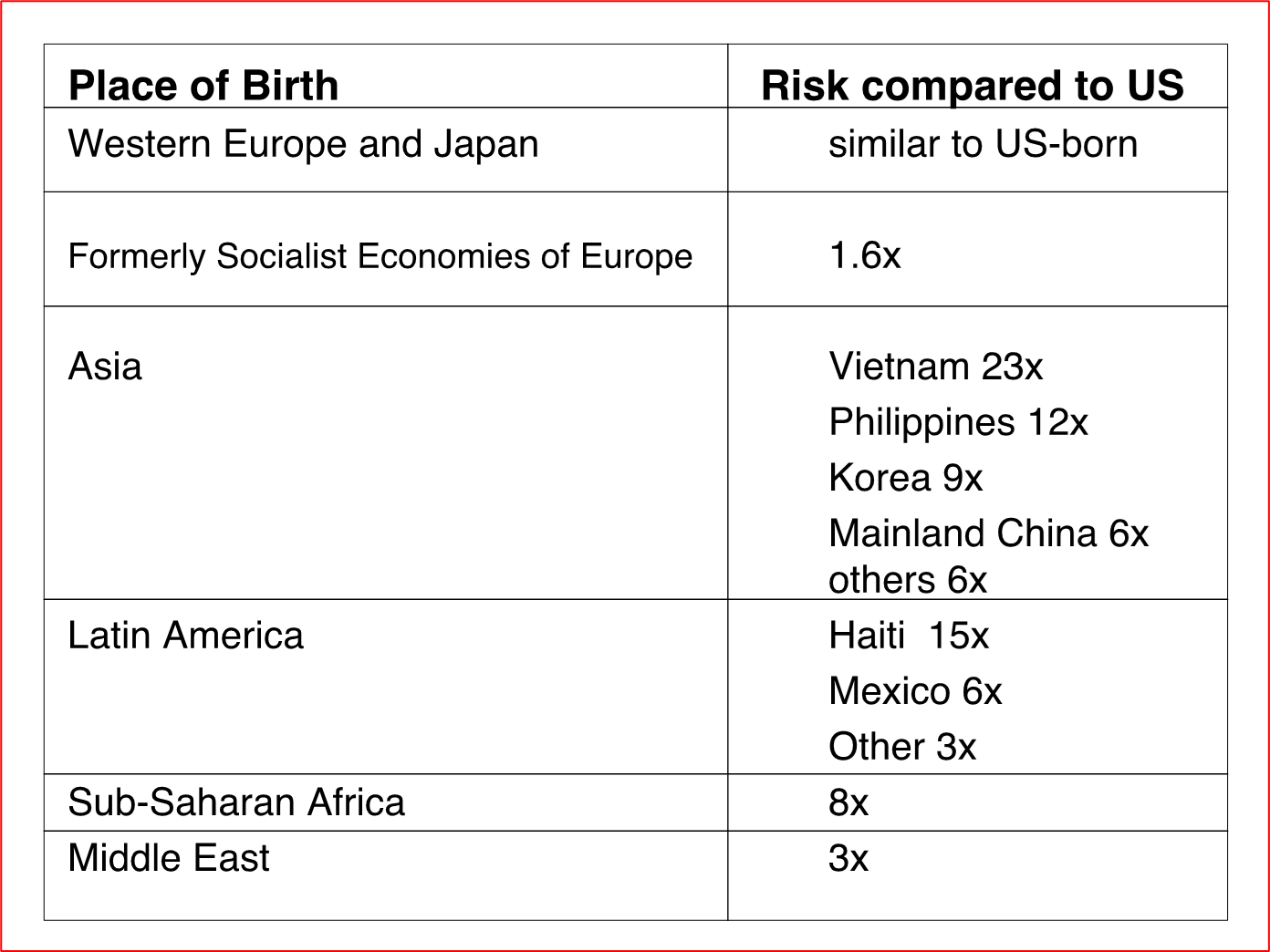
TB risk compared to the US
Immigrants Have The Same Rate Of Progression To TB Disease As That Of Their Native Country For First ____ Years
5
High-risk immigrants treated with chemoprophylaxis if in US less than __ years.
5
The Vietnamese man described previously goes to live with his 55-year-old brother who immigrated to the US 35 years prior. His brother did not have a skin test at that time. His brother’s PPD now is 18 mm. He is asx with a normal chest radiograph and no medical problems.
How do you manage the brother?
No treatment
TB infection is present by test
low rate of progression to TB disease because he has been in the US for 35 years.
Do not treat because of risk of isoniazid (INH) induced hepatitis with low risk of reactivation
Isoniazid induced hepatitis is ____ related
age
•AST (SGOT) > 5 times normal (about 250)
•increases with age
- 1.0 - 1.8% incidence overall
•resolves with discontinuation (usually)
•incidence of fatal hepatitis in over 35 age group with regularly monitored LFT’s (1983- 1992): 0.002%
INH-Induced Hepatitis
Risk Of Hepatitis from isoniazid Increases With _____ Therapy
longer
Immigrants from high-risk countries in US greater than _ years are only treated if another risk is present.
5
Same 55 y/o Vietnamese who has lived in US for 30 years, but he has the following CXR.
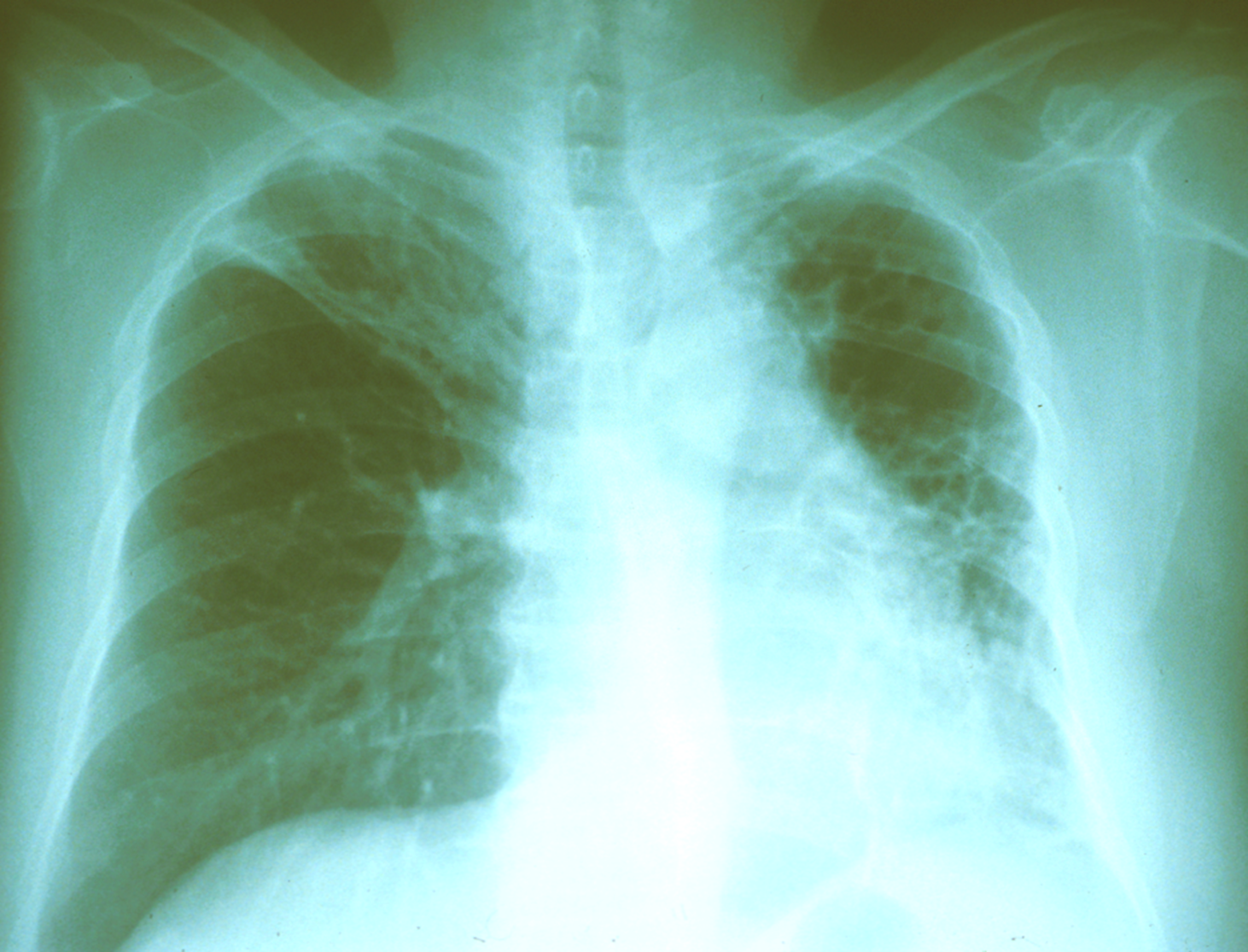
How do you manage him?
Treat
high risk of progressing to TB disease
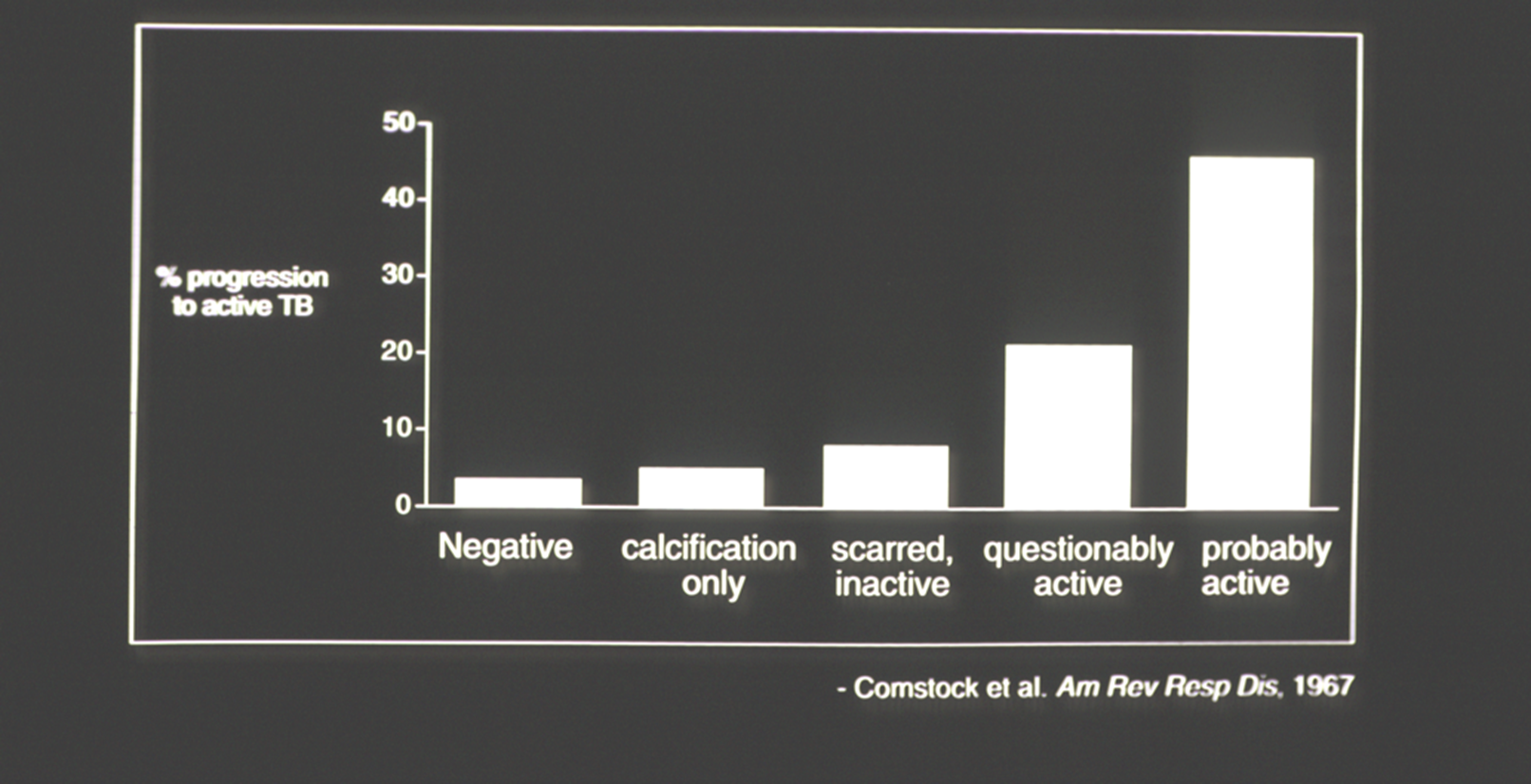
TB Disease Case Rate By CXR Classification In Alaskan Natives
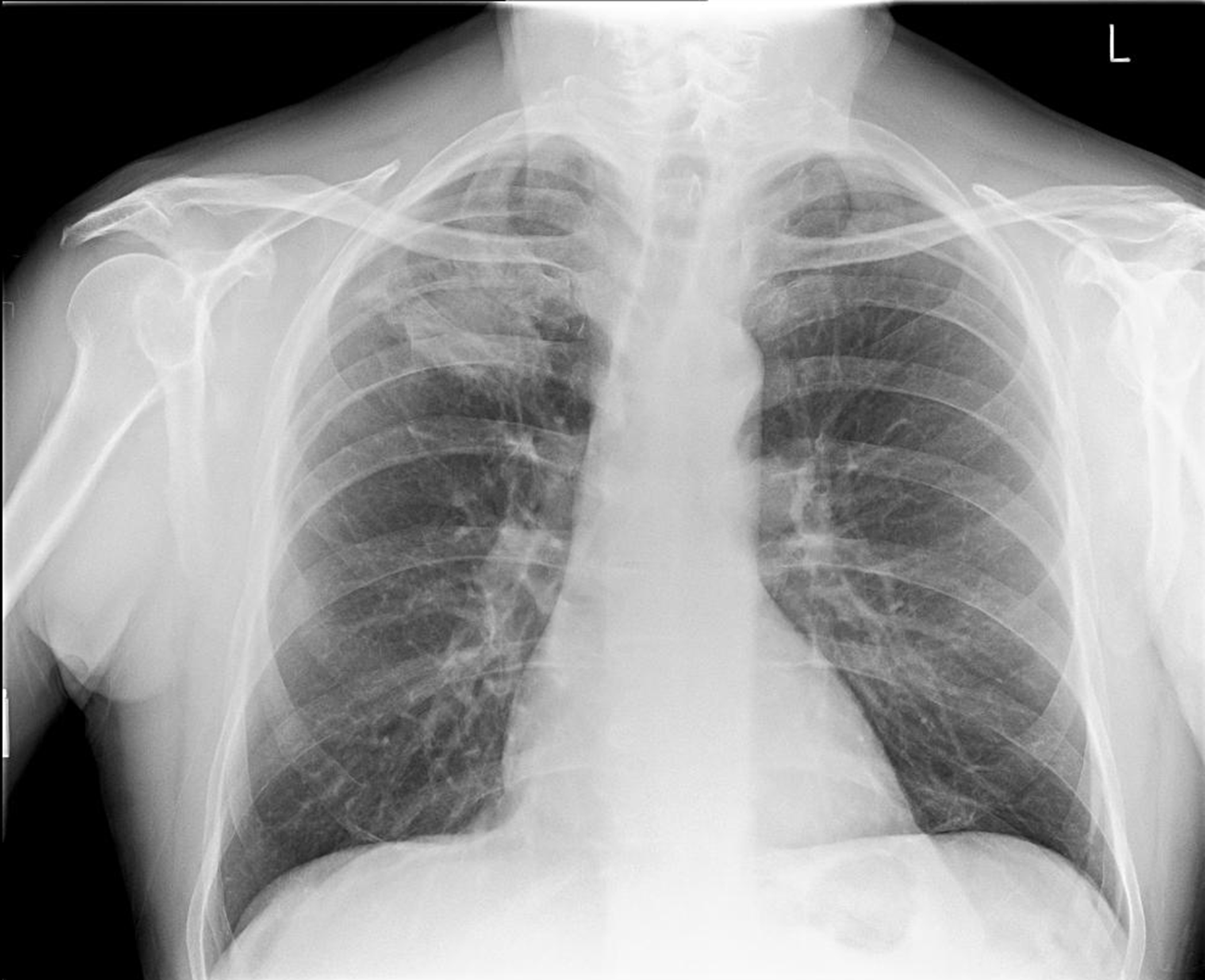
RUL some trouble
Infiltrate
Increase risk of disease progression
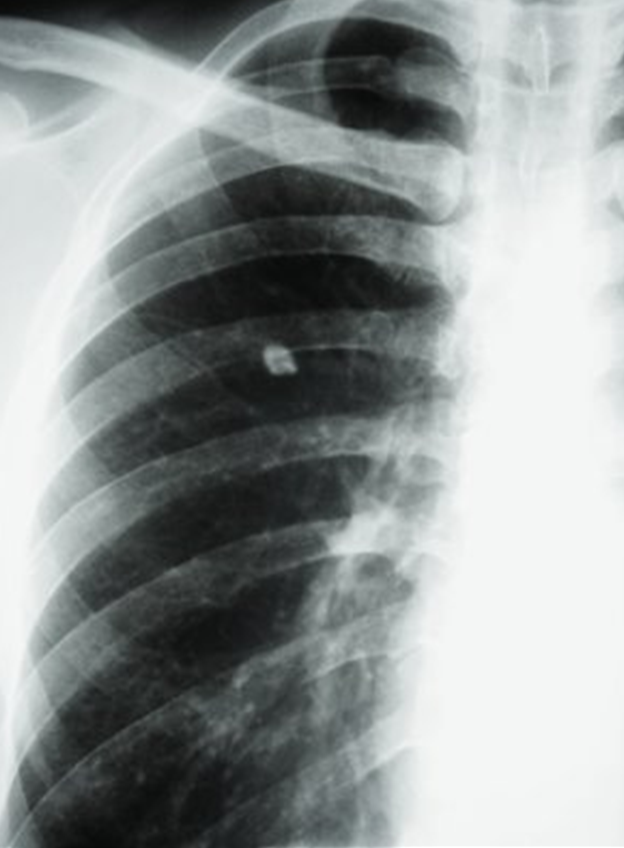
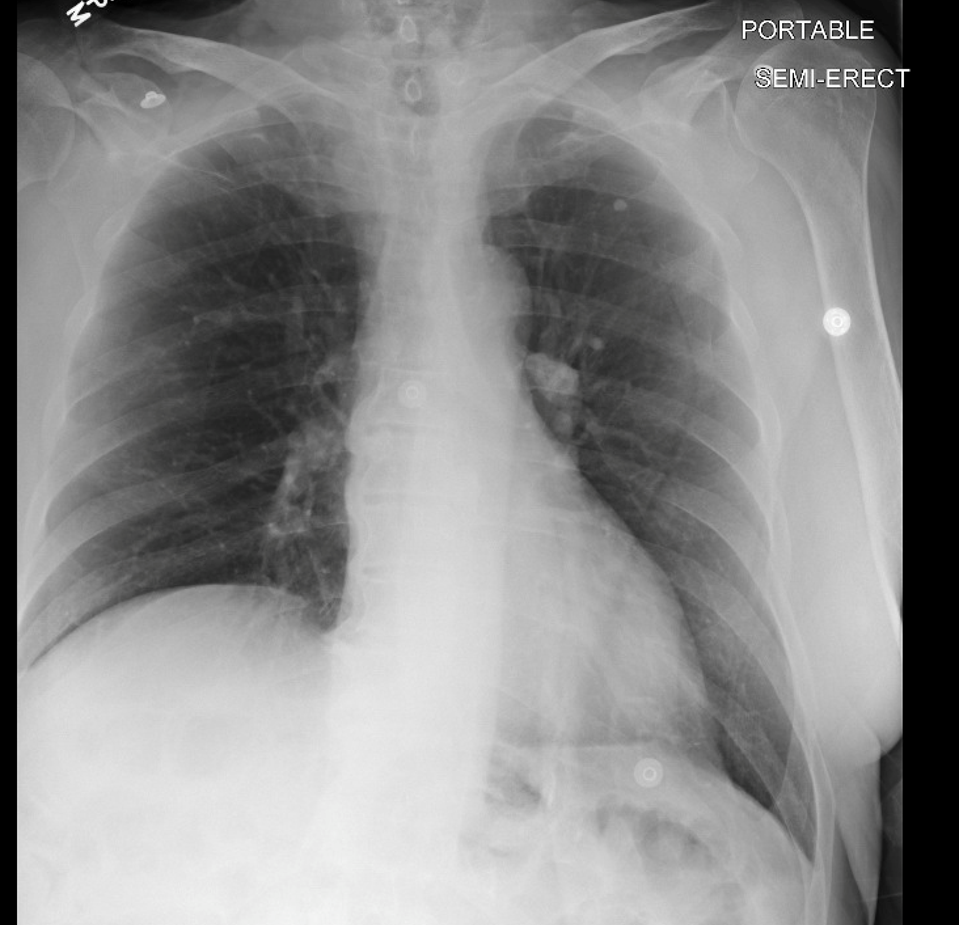
No increased risk of disease progression

Cavity in LUL
Even if culture negative is concerning
still concerning
Longer prophylaxis _____ progression to tuberculosis disease in patients with fibrotic lesions
decreases
A patient admitted to a nursing home one week prior is found to have smear positive TB. Three 45 y/o workers are exposed and tested immediately:
- Worker 1: initial S.T. (-), repeat S.T. (-) @ 3 mos.
- Worker 2: initial S.T. (-), repeat S.T.: 12 mm
- Worker 3: initial S.T.: 18 mm (no previous Tx)
All are ASX with normal CXR’s.
For each worker:
Worker 1: No treatment
Worker 2: Treat
Worker 3: No treatment because the initial was done 1 week after not enough time to build a response this means he already was infected with TB
TB infection appears to protect against progression to TB disease after
re-infection
In children always ____ pending repeat PPD
always
28 y/o woman from Mexico has a 12 mm induration on immigration screen. She had received BCG vaccination at age 2. She denied any known exposure to TB. She is well with a normal CXR.
Treatment
•attenuated (but live) strain of M.Bovis (1924)
•used to prevent tuberculosis disease in developing (and some developed) countries.
•not used in U.S.
•results regarding efficacy are equivocal
- probably effective at preventing disseminated tuberculosis disease (esp. meningitis) in children
BCG vaccine
Bacille-calmette-querin vaccine
Most Non-infected People Vaccinated With BCG Are PPD ______
Negative
Prior BCG Vaccination Is ____ A Factor In Considering Need For Chemoprophylaxis even though BCG vaccination does change skin test
not
people from high-risk countries are considered TB infected if PPD > 10 mm regardless of ___ status.
BCG
people from low-risk countries still using BCG are considered TB infected if PPD > __ mm.
15
Measures interferon gamma release from sensitized T cells in patients blood
IFN gamma release assays
QuantiFERON gold
ESAT-6
CFP-10
TB7.7
TB antigens
Inexpensive
Does not require blood draw or lab
Relatively easy to perform
Long history
Tuberculin skin test (PPD)
Does not require return patient visit
Results within 24 hours
Is not affected by prior BCG vaccination
Interferon gamma release assay
Both tests can lose ______ in immunosuppressed individuals
sensitivity
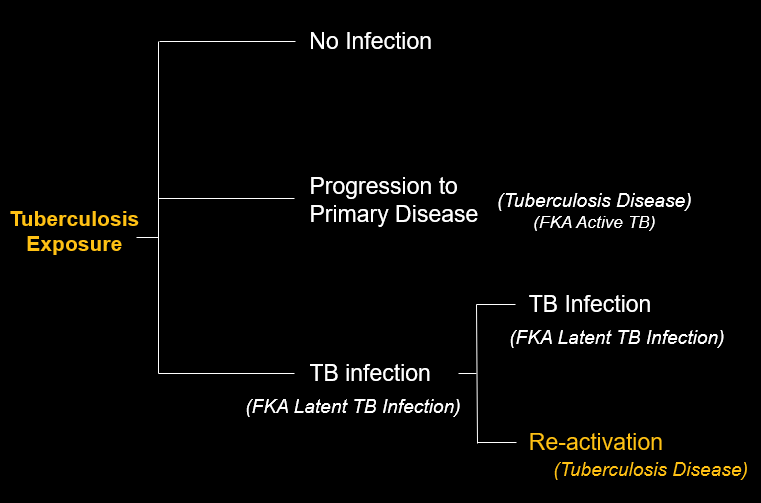
TB pathways
The worst thing you can do it treat a patient for TB ____ if they have TB _____
Infection
Disease
Who Gets Treated for a Tuberculosis Infection?
•Under 35 years of age
Or
•Any age who is a/has a:
–Recent converter
–Medical condition/medications that increase risk
–Abnormal CXR deemed high risk
Approved Treatment Regimens For TB Infections
(PPD/IFRA (+) Without Symptoms Or Positive Culture):
Isoniazid + Rifapentin weekly for 12 weeks
Rifampin daily for 4 months
Isoniazid + Rifampin daily for 3 months
Isoniazid daily for 6-9 months
Things Many People Do, But Shouldn’t:
Repeat a skin test on a person with known TB infection
Check routine yearly CXRs on asymptomatic people with TB infections
should check CXR only for symptoms