spatial reference systems
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
georeferencing
= the process of describing location, using place names, addresses, directions, or some sort of coordinate system
When combining data sets together, your data must be georeferenced in the same way
two types of positioning
relative positioning = giving location in reference to one thing or another → what we do when we give people directions → basically how we talk about locations and how to get there
absolute position = the use of coordinate systems that superimposes a grid over an area
local grid = grid format can be used universally and what is on the grid depends on where you are (ex: a city map or a world atlas)
global (geographic) grid = tied to the earth, every single point of the earth can be described uniquely and that description world never change → used universally
latitude and longitude = system of uniquely positioning points
UTM gird
longitude and latitude
= a system for uniquely locating points
graticule
= the imaginary network of lines of longitude and latitude that are measured using a sexagesimal system of degrees, minutes, and seconds
sexagesimal system (base 60)
= measures in degrees, minutes, and seconds -> base 60 because there are 60 minutes in a degree and 60 seconds in a minute
latitude
= the parallels: the horizontal lines that go from east to west
the origin is the equator
parallels are labelled north or south of the equator from 0 degrees to 90 degrees north/south
parallels get shorter and shorter toward the poles, until they are at the poles
the north pole is 90 degrees, the equator is 0 degrees, Vancouver is 49 degrees and 13 minutes N latitude
longitude
= the meridians: vertical lines that go north to south
the origin is the prime meridian, which goes through Genrich, England → the origin can be any line of longitude, but the agreed point is the prime meridian
meridians are labelled west or east of the prime meridian from 0 degrees to 180 degrees W/E of the prime meridian
meridians are always the same length and converge at the poles
Vancouver is west of the prime meridian and 123 degrees and 6 minutes W of the prime meridian
decimal degrees (base 10 system)
we convert the base 60 system into base 10 when we use computers and GIS programs
north and east are represented as (+); south and west are represented as (-)
the conversion is basically the degree + the minutes/60 and the (+)/(-) depends on direction
convert 49 degrees 13 minutes north and 123 degrees six minutes west to decimal degrees
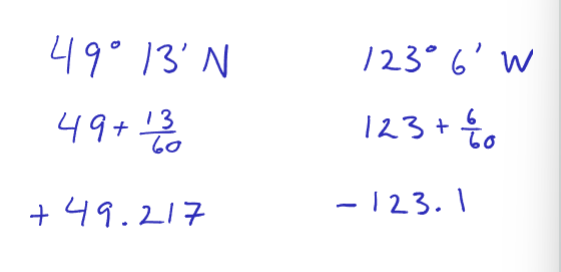
how much space is between each degree of latitude and longitude
latitude = 111km from each degree of latitude
longitude = 111km between any 1 degree of longitude along the equator (as you move away from the equator the longitude lines get small and so does the distance as you move closer to the north/south pole)

ways to measure direction of longitude and latitude lines
Great circle = results from a plain slicing through the center of the earth (ex: the equator is a great circle) -> to be a great circle, it needs to cut through the center of the earth
All meridians and the equator are great circles and there are many more
The arc of the great circle represents the shortest path between two points
Very useful for airline navigation
The shortest distance then is not necessarily a line of constant direction
Rhumb lines = great circle route approximations -> using a series of short lines of constant direction to approximate the great circle route - it is a series of lines of constant direction
What airline navigation does when creating it's routes
Small circles = results from a plain slicing through the earth (doesn't cut through the center of the earth)
The arcs of these circles do not measure the shortest path between two points
UTM (Universal Transverse Mercator) grid
= a geographical global grid commonly used instead of latitude and longitude → used for large scale mapping (ex: reference mapping), topographical maps, and survey maps
divides the earth into 60 6 degree wide vertical strips between 80 N and 8 S latitude
each vertical strip has its own central meridian and you measure out from there → it is measured in meters → vertical strips are called zones numbered 1-60
the zones are divided into horizontal bands → each band is 8 degrees tall from north to south
this creates a grid made of grid zones → each grid zone is subdivided into 100km/100,000m squares called quadrilaterals
a location on earth is referred to by its zone number, band number, and coordinate (made up from an easting and a northering measured in meters)
ex: British Columbia is part of zones 7-11
mapping BC with a UTM uses zone 10 because it covers most of BC
scale and the three ways to express scale
= expresses distance on the map to distance on the earth
Representative fraction = the relationship between map distance and earth distance, represented by a ratio
It is unitless
It is hard to measure distances with representative fractions
You can estimate distances but it is not easy to use
Invalid if a map is reduced or enlarged in size
Good for maps where you can't change it's size - i.e physical maps
Ex: 1:100,000
Verbal scale = added units to represent the distance - tells you what to do when you are using a representative fraction
Ex: 1 cm = 1km
Easier to estimate
Invalid if the map is reduced or enlarged in size
Hard to measure still
Bar scale = adding a bar to represent the distance - its like putting a ruler on the map
Will still be valid if the map changes in size
Easy to estimate
Most preferred use of scale
3 types of north
True north = defined by the axis the earth rotates
Ex: the north pole
Grid north = based on the coordinate system you are using
Will be similar to true north
Magnetic north = the direction a compass takes based on the magnetic pole - the magnetic pole is not at true north and it also changes from north to west at 40km a year
If a map is designed for compass users then you will need to include the multiple expressions of north
Magnetic declination = the difference between true north and magnetic north
do you have to include north every time?
no → depends on context
reference maps need inclusion of north; thematic maps of familiar areas might not need it
don’t need north if using a graticule, but then you need to label the graticule where longitude and latitude is
do you need to include a scale every time?
depends on the map
reference maps need all three scales because they are used for navigation
thematic maps don’t need to have a scale → if the area mapped is recognizable to all map readers and distance is not relevant to the theme you prob don’t need it
when in doubt add a scale