1 Lec 15 (Exam 3): Salivary Gland Pathology
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Mucocele
What is the most common reactive salivary gland lesion?
Mucocele
patient presents with a dome-shaped fluctuant vesicle that looks bluish in color on the lower lip. Patient admits to biting lip sometimes. Patient also said that "sometimes the bump gets big and then shrinks again", What is the diagnosis
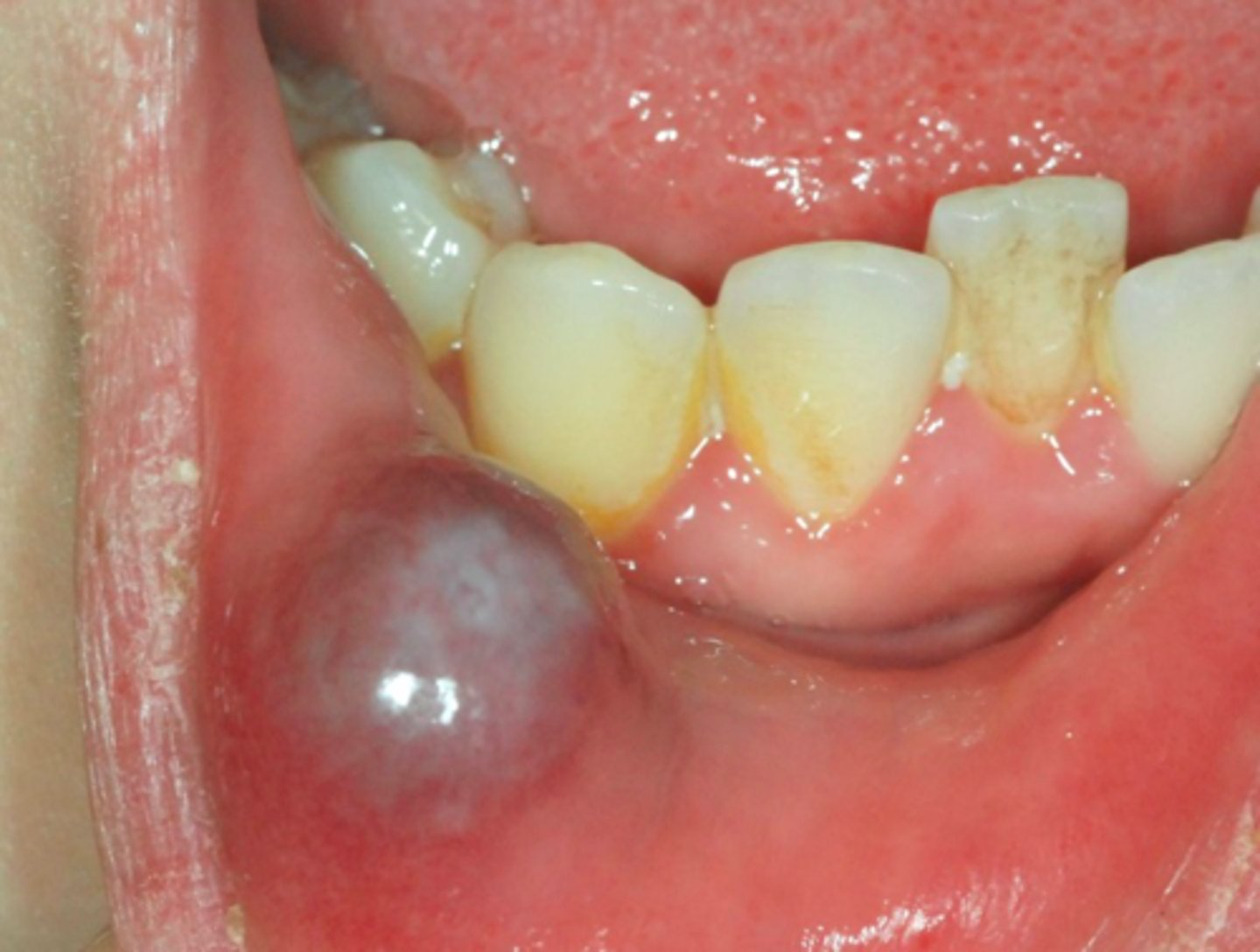
Mucocele
-Common reactive salivary gland lesion
-Traumatized duct spills mucus into adjacent tissues
-Characteristic history of increasing and decreasing in size
lower lip
what is the most common location for mucocele to present?
Mucocele
ID the pathology:
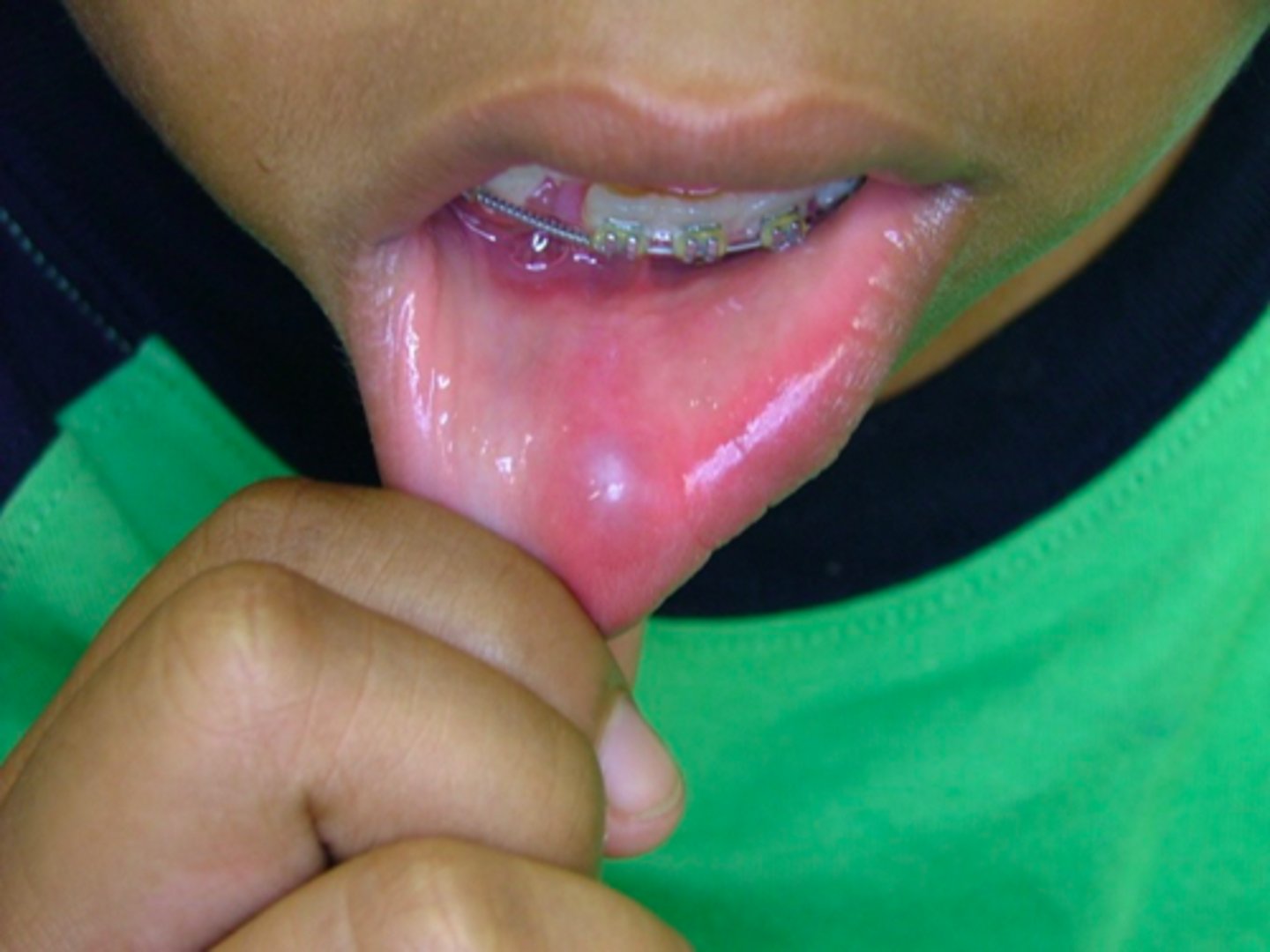
Mucocele
ID the pathology:
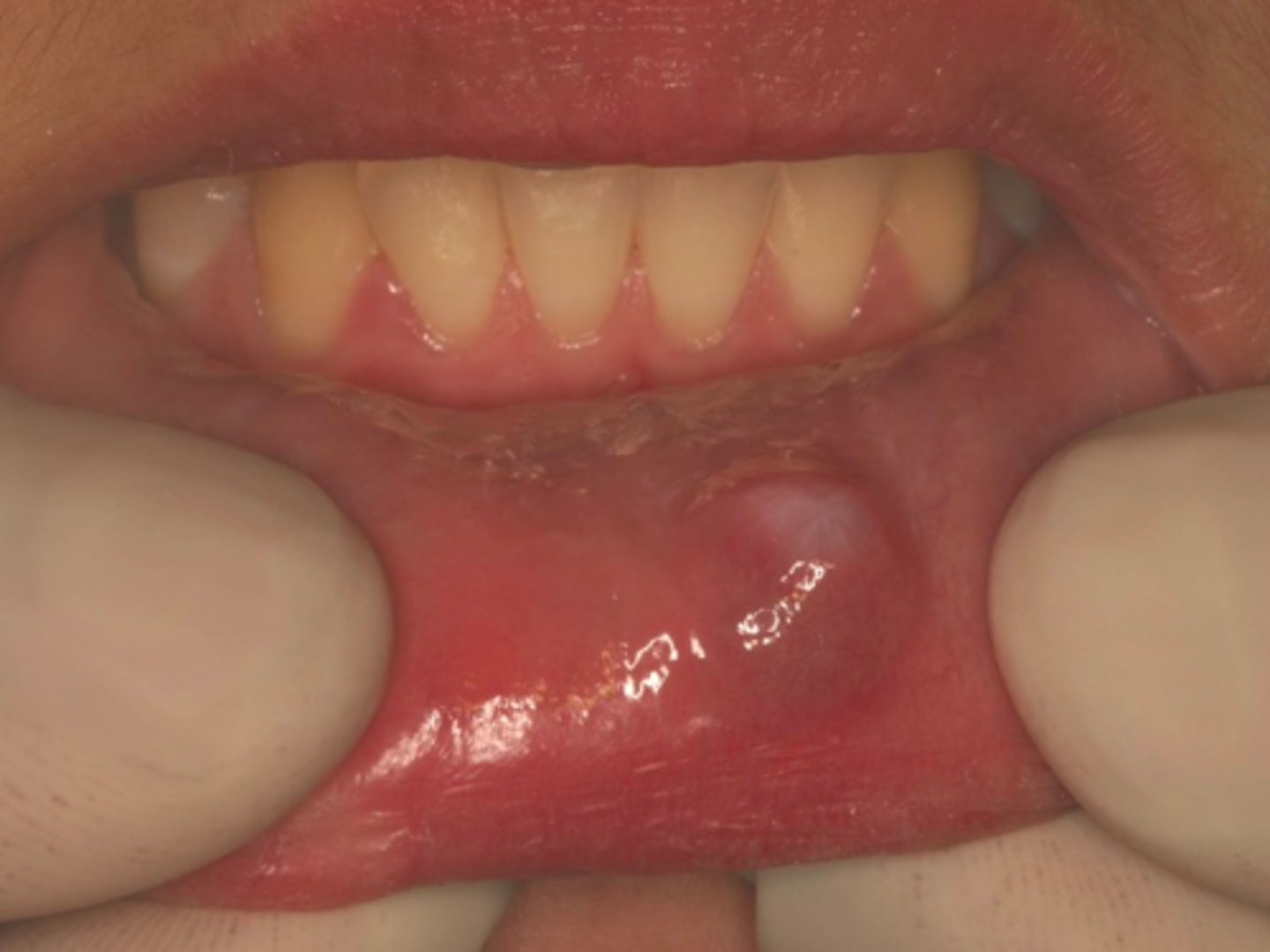
Mucocele
ID the pathology based on the histology findings:
-Spilled mucin surrounded by granulation tissue
-Numerous neutrophils and foamy histiocytes/muciphages
-No epithelial lining
Ranula
A Mucocele on floor of mouth is called a ______
sublingual gland
A Ranula is usually associated with what gland?
mylohyoid
A Plunging ranula variant dissects through the _______ muscle into neck
Ranula
patient presents with a dome-shaped fluctuant vesicle that looks bluish in color on the floor of the mouth. What is the diagnosis?
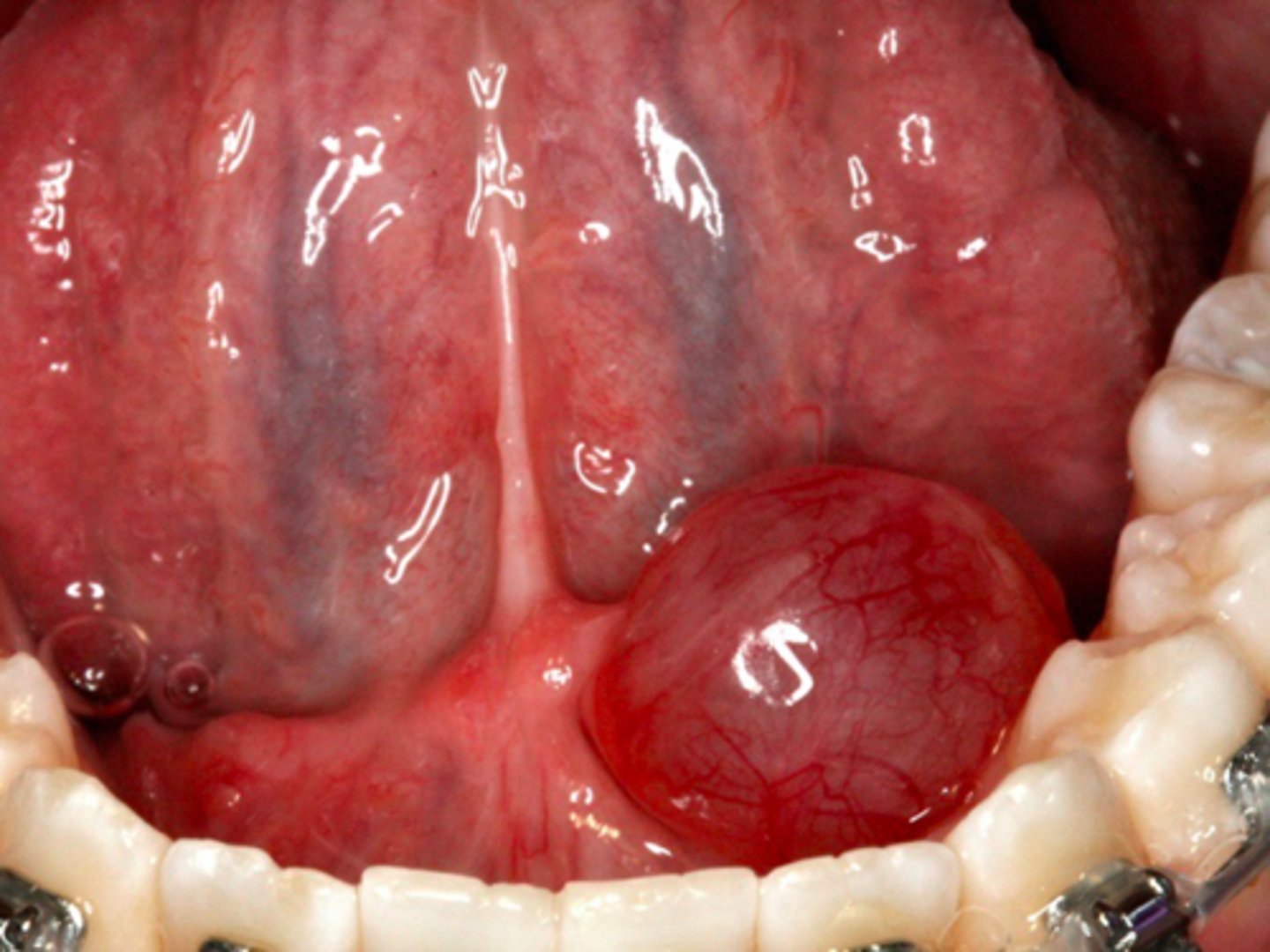
floor of mouth
what is the most common location for a Ranula to present?
Ranula
ID the pathology:
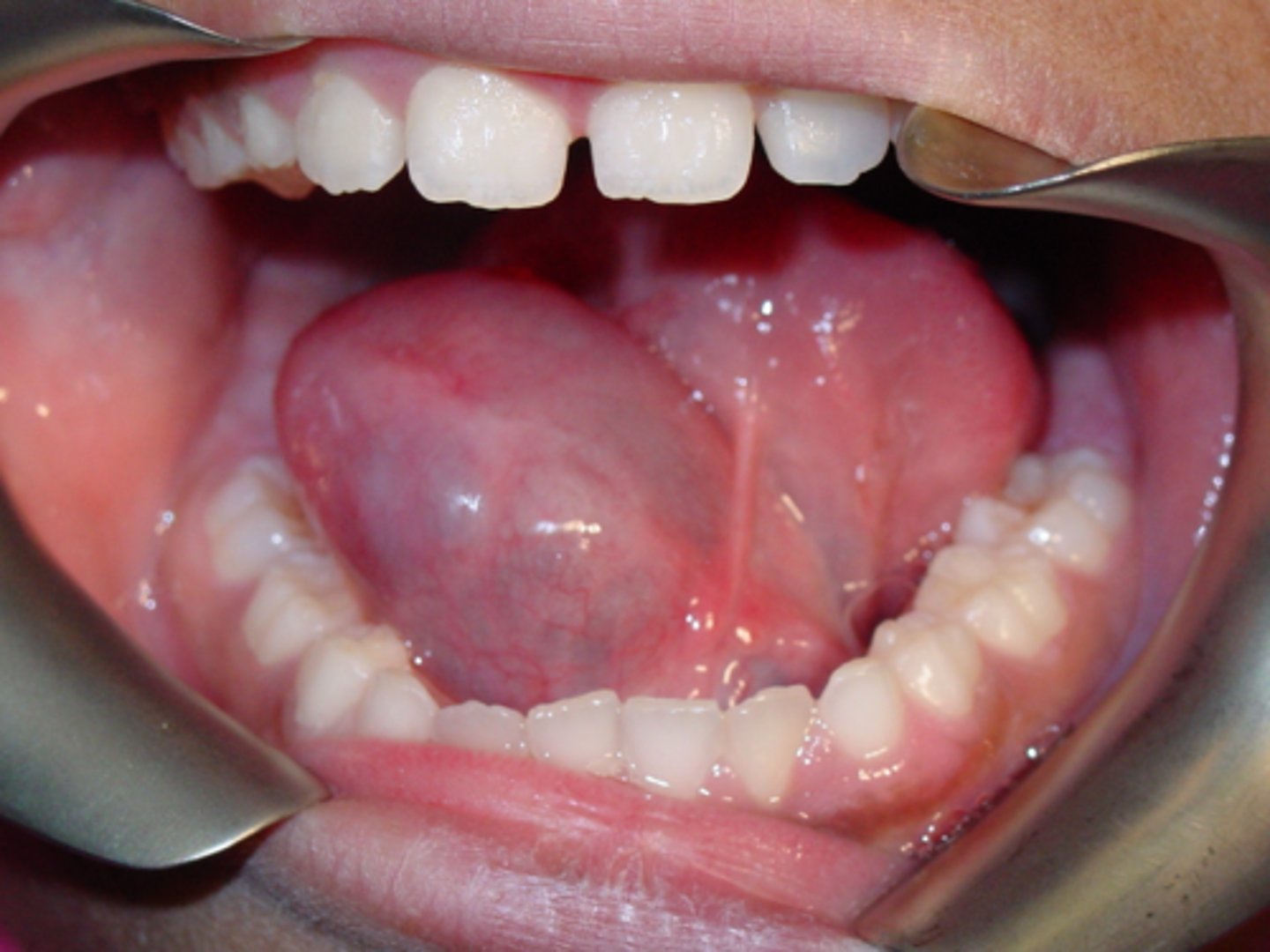
Ranula
Salivary duct cyst
Dermoid cyst
Patient presents with a large nodule on the floor of the mouth lateral to the midline. What is in your differential diagnosis?
Salivary duct cyst (sialocyst)
ID the pathology:
•Acquire dilatation of salivary duct (due to obstruction)
•Usually seen in adults
•Clinically resembles mucocele
parotid gland
Salivary duct cyst (sialocyst) are MOST common originating from what gland?
Sialolithiasis
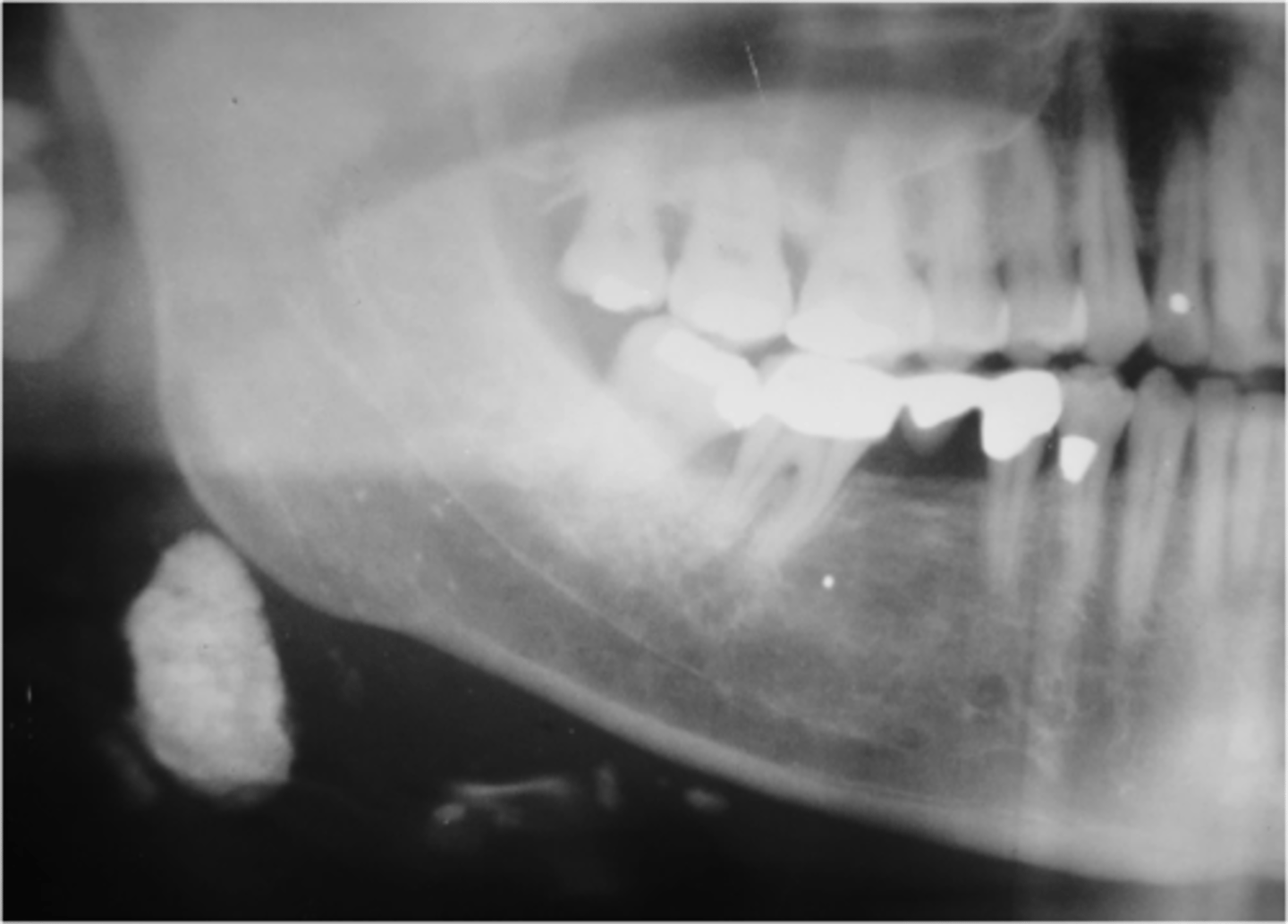
Patient present to your office complaining of pain when he sees food and while eating. A small firm , non-fluctuant mass is visible on the floor of the mouth lateral to the midline. Radiograph shows a radiopaque mass in the location of interest. What is the diagnosis?
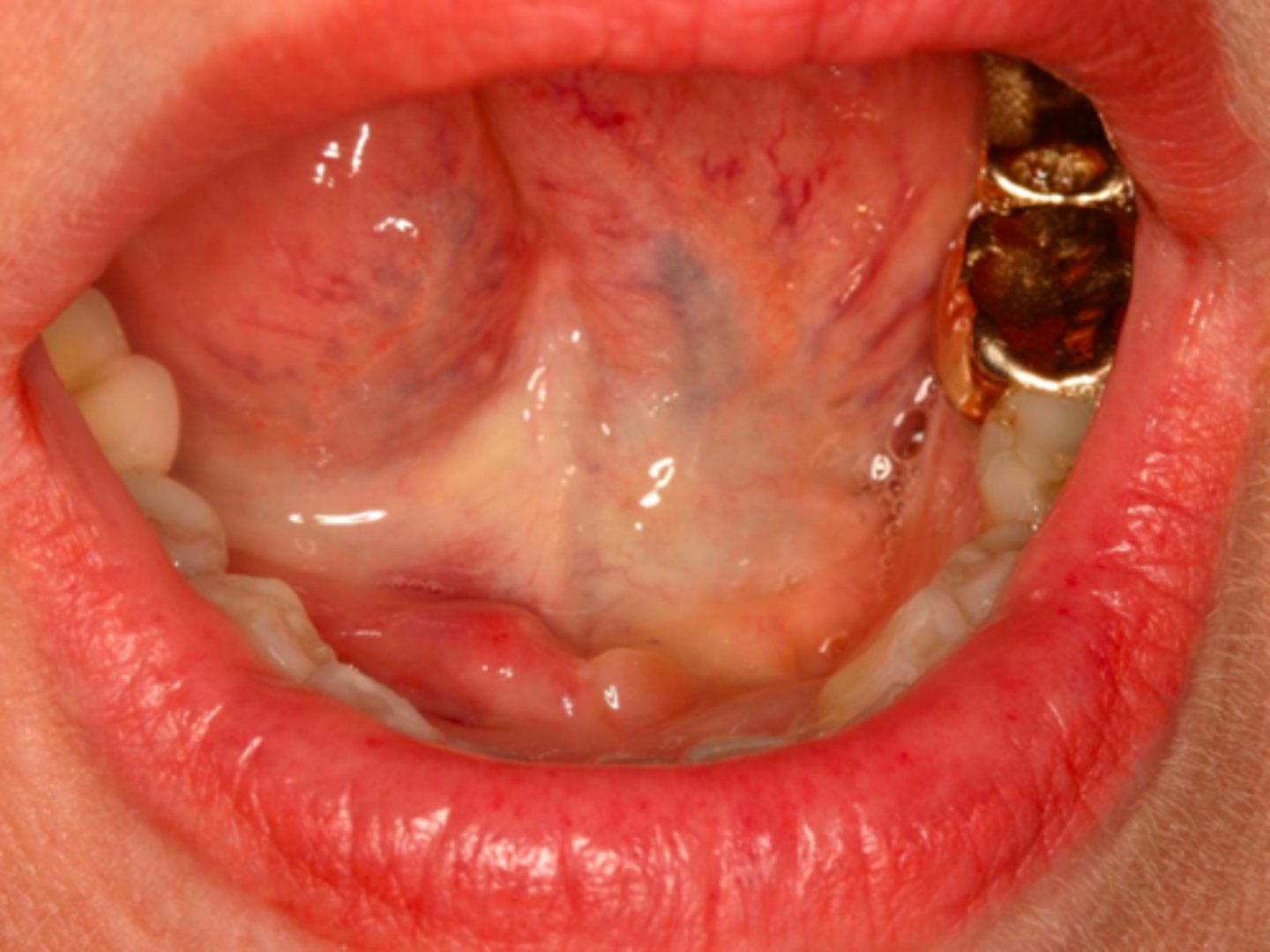
Sialolithiasis
this pathology is associated with pain upon salivation:
submandibular gland
80% of Sialolithiasis are associated with what gland?
Sialolithiasis
ID the pathology:
Sialolithiasis
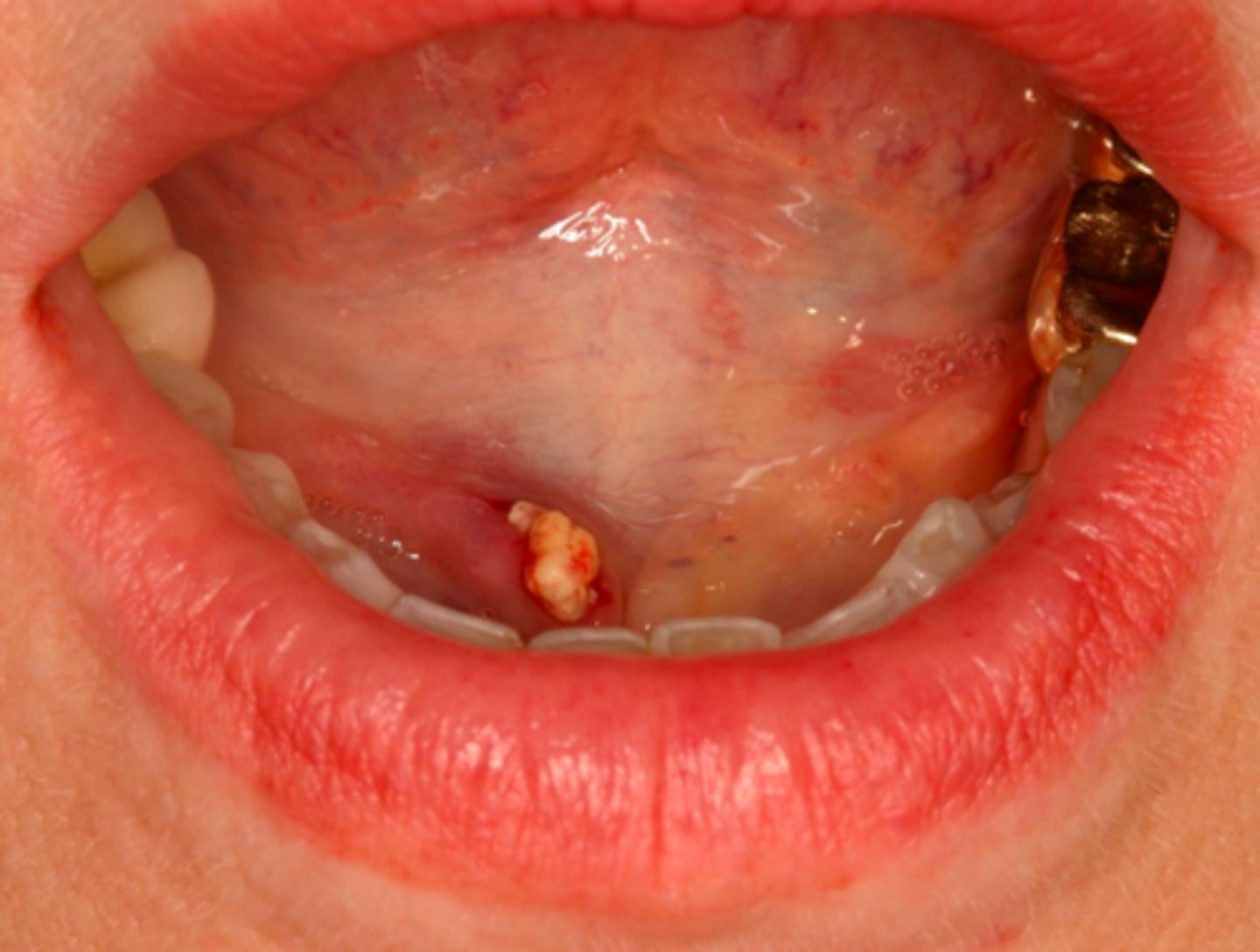
ID the pathology:
-Milking stone toward duct orifice
-Sialologues
-Surgical removal
What is the treatment for Sialolithiasis?
Sialadenitis
Inflammation of the salivary glands:
Acute Sialadenitis
Parotid swelling and tenderness and Low-grade fever are clinical features of what type of Sialadenitis?
Chronic Sialadenitis
Periodic pain and swelling, ductal dilatation are clinical features of what type of Sialadenitis?
Chronic sclerosing Sialadenitis
Persistent swelling in submandibular gland is a clinical features of what type of Sialadenitis?
-Antibiotics
-Rehydration
-Surgical drainage if necessary
what is the treatment for Acute Sialadenitis?
Remove obstruction or surgical gland removal, if advanced
what is the treatment for Chronic Sialadenitis?
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
Patient presents with single ulceration on the hard palatal mucosa. Patient claims it "use to be red and swollen, now it's like a crater". Histo path report reveals Acinar necrosis with preservation of lobular architecture, squamous metaplasia and Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. What is the diagnosis?
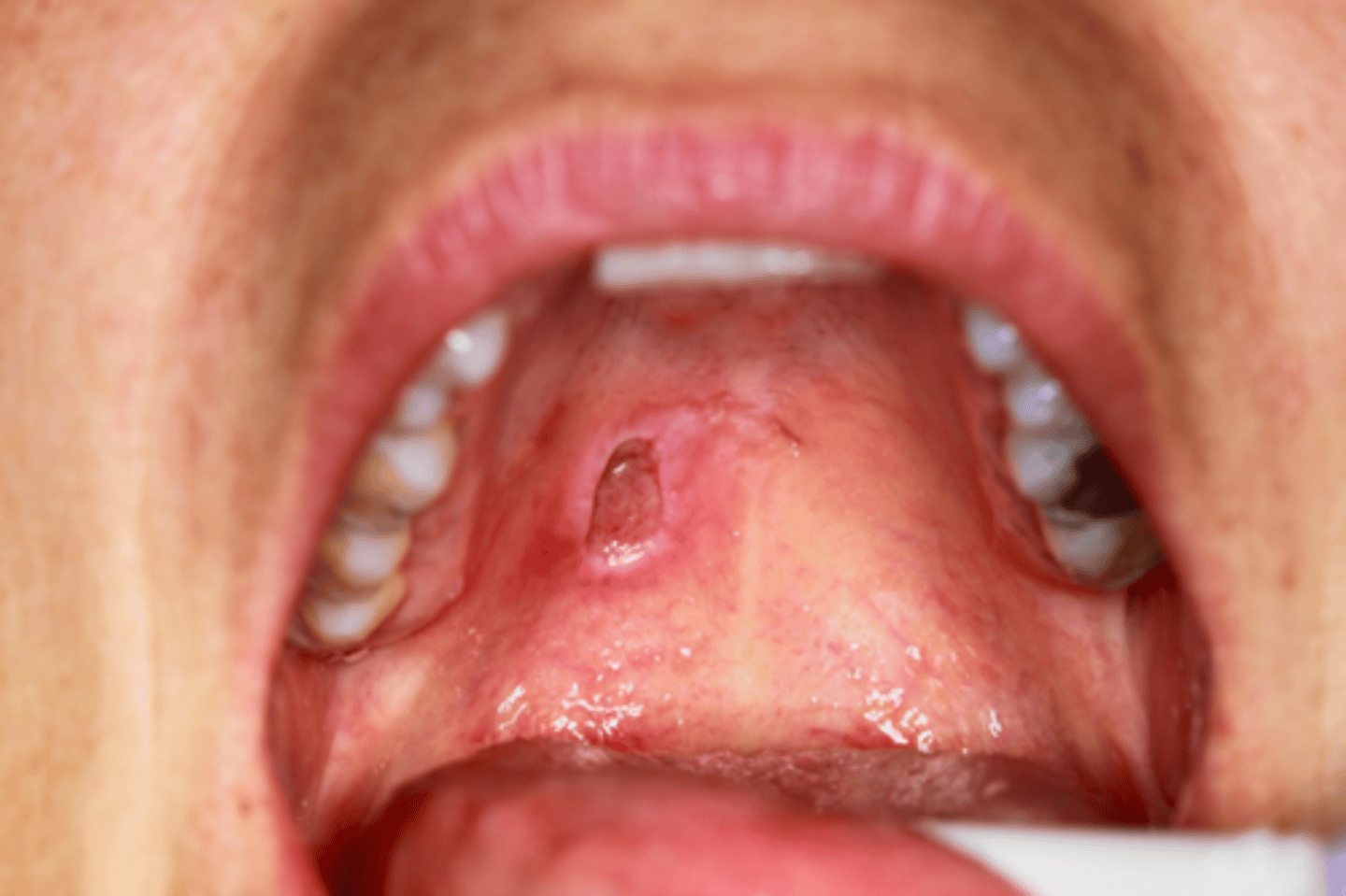
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
ID the pathology:
-Rare inflammatory, destructive condition of salivary glands
Mimics malignancy clinically AND microscopically
-Early swelling and erythema
-Later ulceration
-75% on hard palatal mucosa
-Initial swelling, then craterlike ulcer develops
-Rare destruction of palatal bone
hard palatal mucosa
the most common location for Necrotizing Sialometaplasia to present is the ______
Necrotizing Sialometaplasia
ID the pathology:
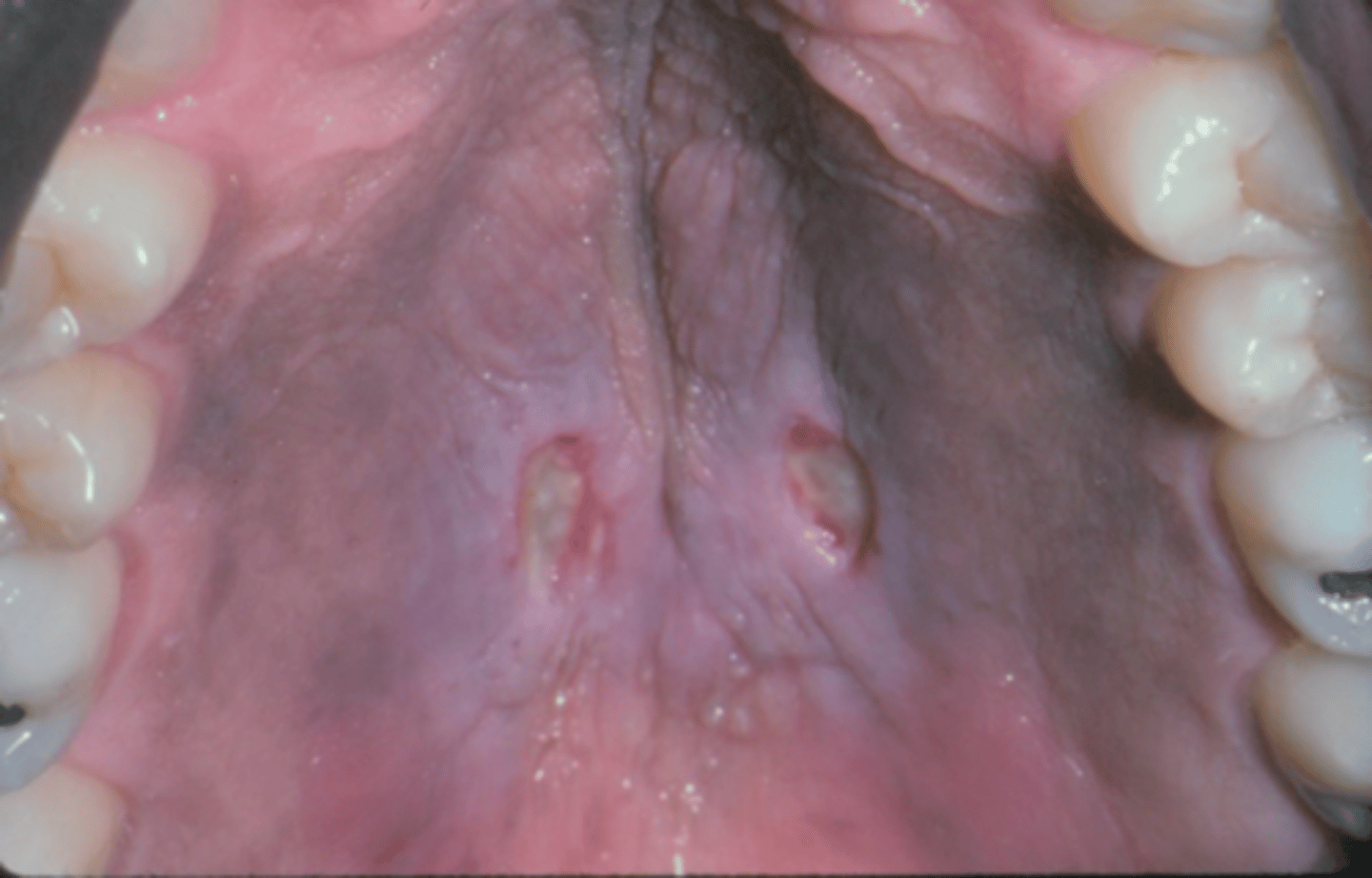
Sjögren Syndrome
ID the pathology:
-Chronic, systemic, autoimmune disorder
•Affects salivary glands and lacrimal glands
Sjögren Syndrome
Patient presents you your office complaining of xerostomia and dysphagia. Patient admits that they also experience dry eyes. Patient also has numerous cervical caries fissured tongue with atrophy of papillae, and a minor case of secondary candidiasis. Upon physical examination, you notice bilateral swelling of the parotid glands. Lab work up shows elevated IgG, positive rheumatoid factor (RF) and Antinuclear antibodies (ANA). What is the diagnosis?
parotid gland
Sjögren Syndrome is associated with bilateral swelling of which gland?
Sjögren Syndrome
this pathology is associated with elevated IgG
Positive rheumatoid factor (RF) and Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) (Anti SS-A (anti-Ro) and anti SS-B (anti-La)):
female
Sjögren Syndrome has a 9:1 _____ gender predilection
lymphoma
patients with Sjögren Syndrome have a 20-fold increased risk of developing ______
Primary Sjögren (Sicca) syndrome
this form of the autoimmune disorder only causes dry eyes and dry mouth:
Secondary Sjögren syndrome
this form of the autoimmune disorder causes dry eyes dry mouth, causes Rheumatoid arthritis and Systemic lupus erythematosus:
Rheumatoid arthritis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
along with dry eyes and dry mouth, Secondary Sjögren syndrome is associated with what other conditions?
Labial salivary gland biopsy (>50/4mm)
this test is used to diagnose Sjögren Syndrome:
true
t/f: for salivary gland tumors, malignancies mimic benign tumors both clinically and histologically
palate
upper lip
buccal mucosa
what oral cavity locations are most common sites for minor gland tumors?
false
t/f: Malignancies are more likely in minor salivary glands than major
parotid gland
About 64-80% of salivary tumors are in the ______, but only about 15-32% are malignant
submandibular gland
About 10% of salivary tumors are in the ______, and about 45% are malignant
sublingual gland
About 1% of salivary tumors are in the ______, and about 90% of them are malignant
minor glands
About 9-23% of salivary tumors are in the ______, and about 50% of them are malignant
Asymptomatic swelling
What is the most common presentation of salivary gland tumors?
false
t/f: for Salivary Gland Tumors, pain is indicative of malignancy
true
t/f: for Salivary Gland Tumors, paresthesia is indicative of malignancy
paresthesia
what clinical presentation of salivary gland tumors suggests poor prognosis/malignancy?
Pleomorphic Adenoma
What is the most common salivary gland tumor?
Pleomorphic Adenoma
Patient presents with firm swelling on the palatal mucosa. Patient is asymptomatic. Patient says they noticed the growth, but didn't realize it had gotten so big because it took a while to grow. Histopath report shows well-circumscribed/encapsulated, Double-layered ducts and Plasmacytoid cells. What is the diagnosis?
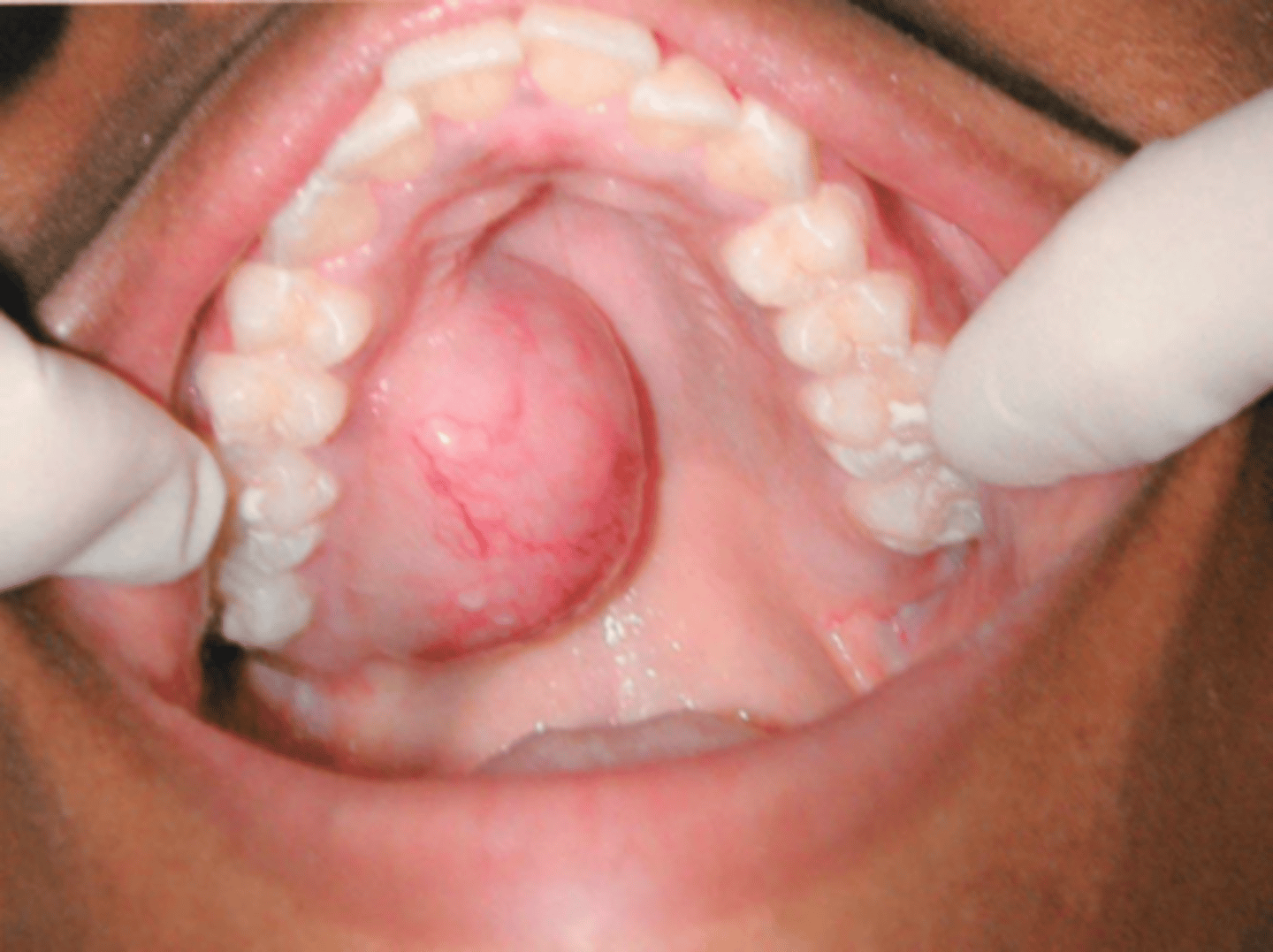
Pleomorphic Adenoma
this common salivary gland tumor is at risk of undergoing malignant transformation:
upper lip
What is the most common location for a Canalicular Adenoma to present?
parotid gland
What is the most common location for a Basal Cell Adenoma to present?
female
Basal Cell Adenomas have a ______ gender predilection
Warthin Tumor
this salivary tumor is associated with cigaret smoking:
male
Warthin Tumors have a ______ gender predilection
bilateral parotid gland
What is the most common location for Warthin Tumors to present?
Warthin Tumor
What is the most likely salivary gland tumor to be bilateral
Warthin Tumor
Male patient presents with bilateral swelling of the parotid glands. Patient has a long history of cigaret smoking. Biopsy was performed and histo path report shows papillary formations, cystic, with lymphoid stroma in walls. What is the diagnosis?
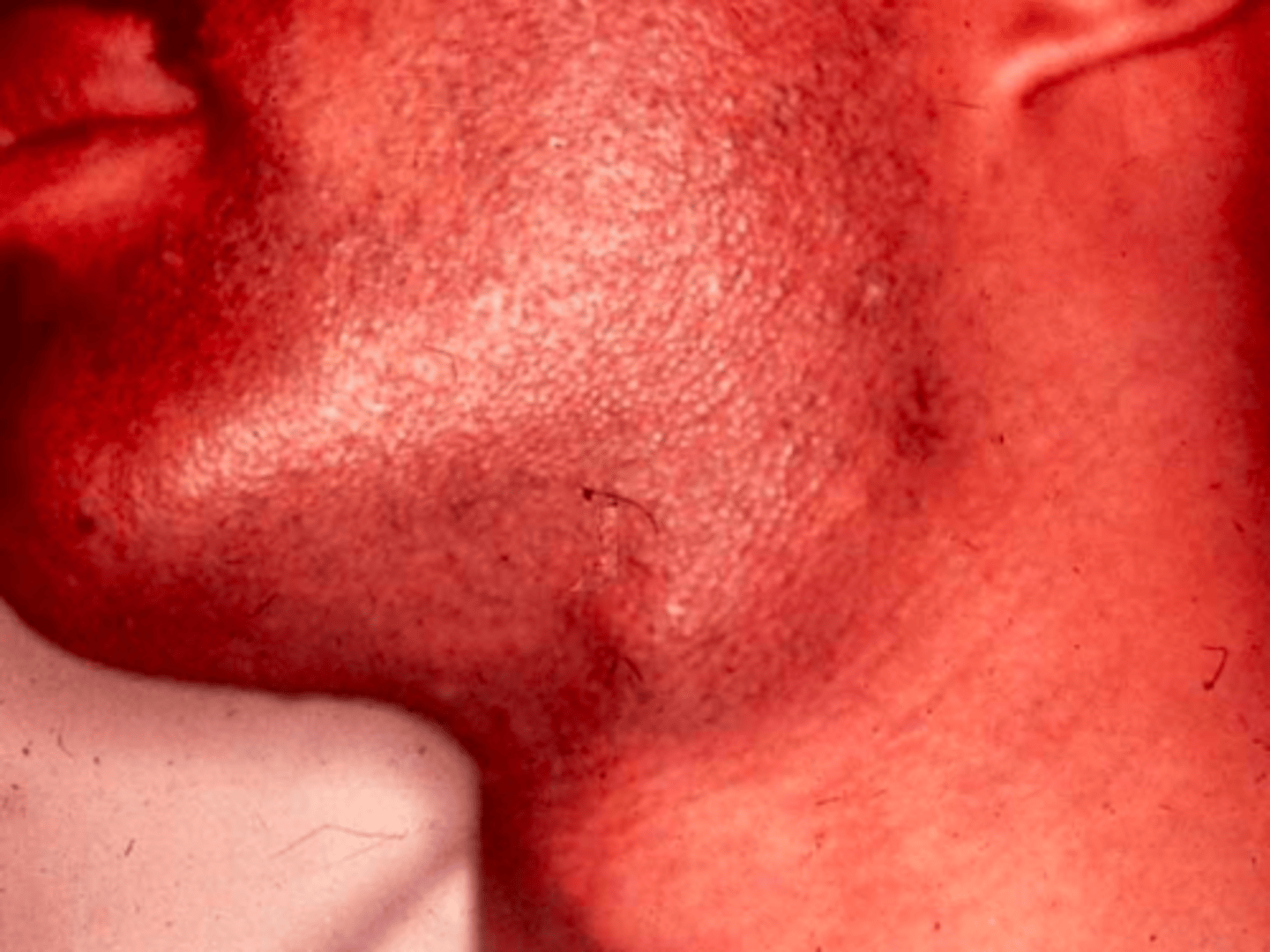
parotid gland
What is the most common location for an Oncocytoma to present?
true
t/f: Most minor salivary gland tumors are malignant
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
What is the most common salivary gland malignancy?
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
What is the most common childhood salivary gland malignancy?
parotid gland or palate
What is the most common location for a Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma to present?
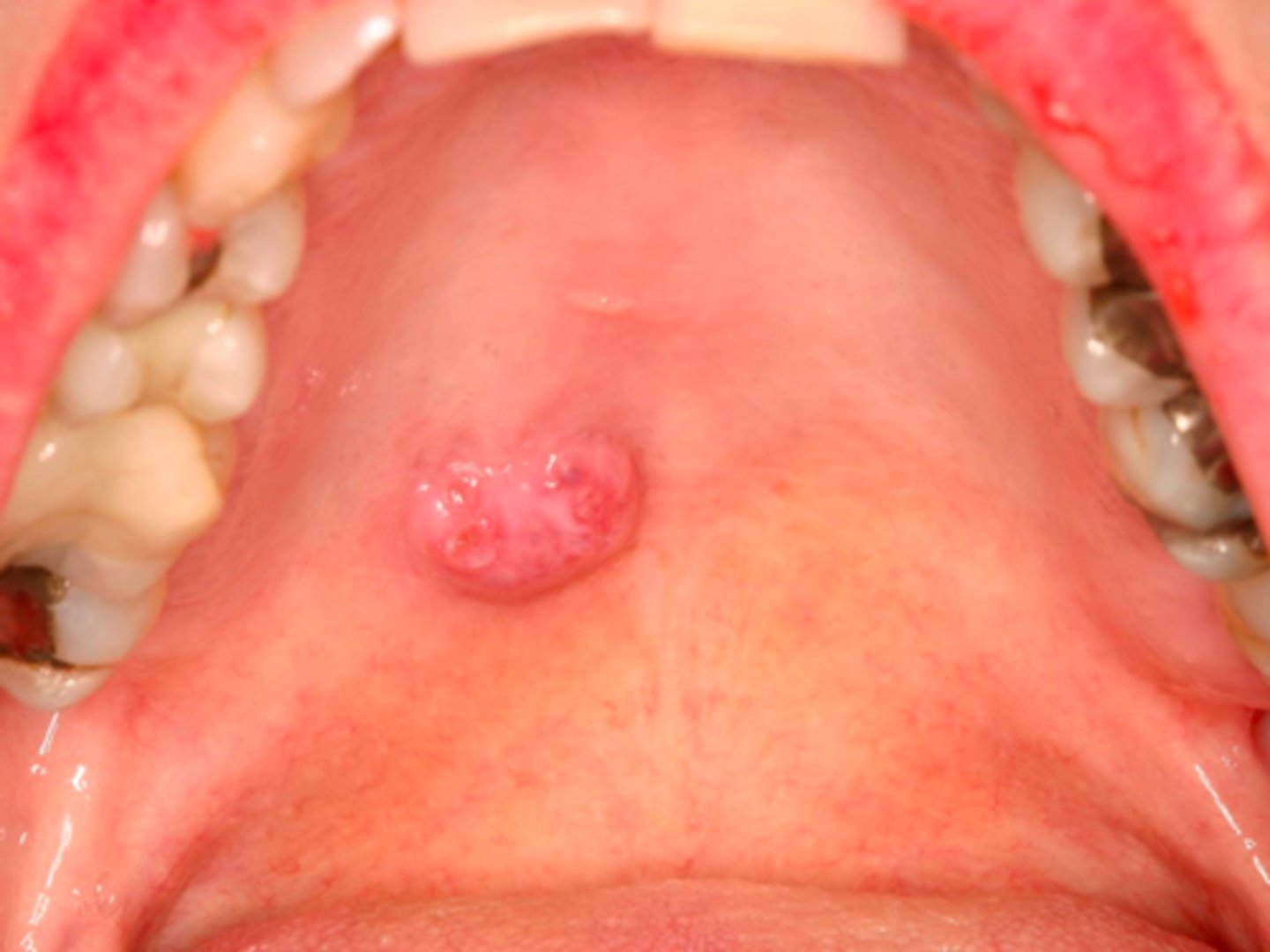
Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma
20 y/o female presents with ulcerated nodule on the palatal mucosa. Histopath report shows mucous cells
and epidermoid cells. What is the diagnosis?
submandibular gland
Although Mucoepidermoid Carcinomas most commonly present in the parotid gland or palate, tumors located on the ________ associated with worse prognoses
hard palatal mucosa
What is the most common location for an Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma to present?
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
65 y/o female presents with a large firm nodule on the hard palatal mucosa. Patient reports pain as well as some unilateral paresthesia in the face. Histopathology shows perineural infiltration with a cribriform
(swiss cheese) appearance. What is the diagnosis?
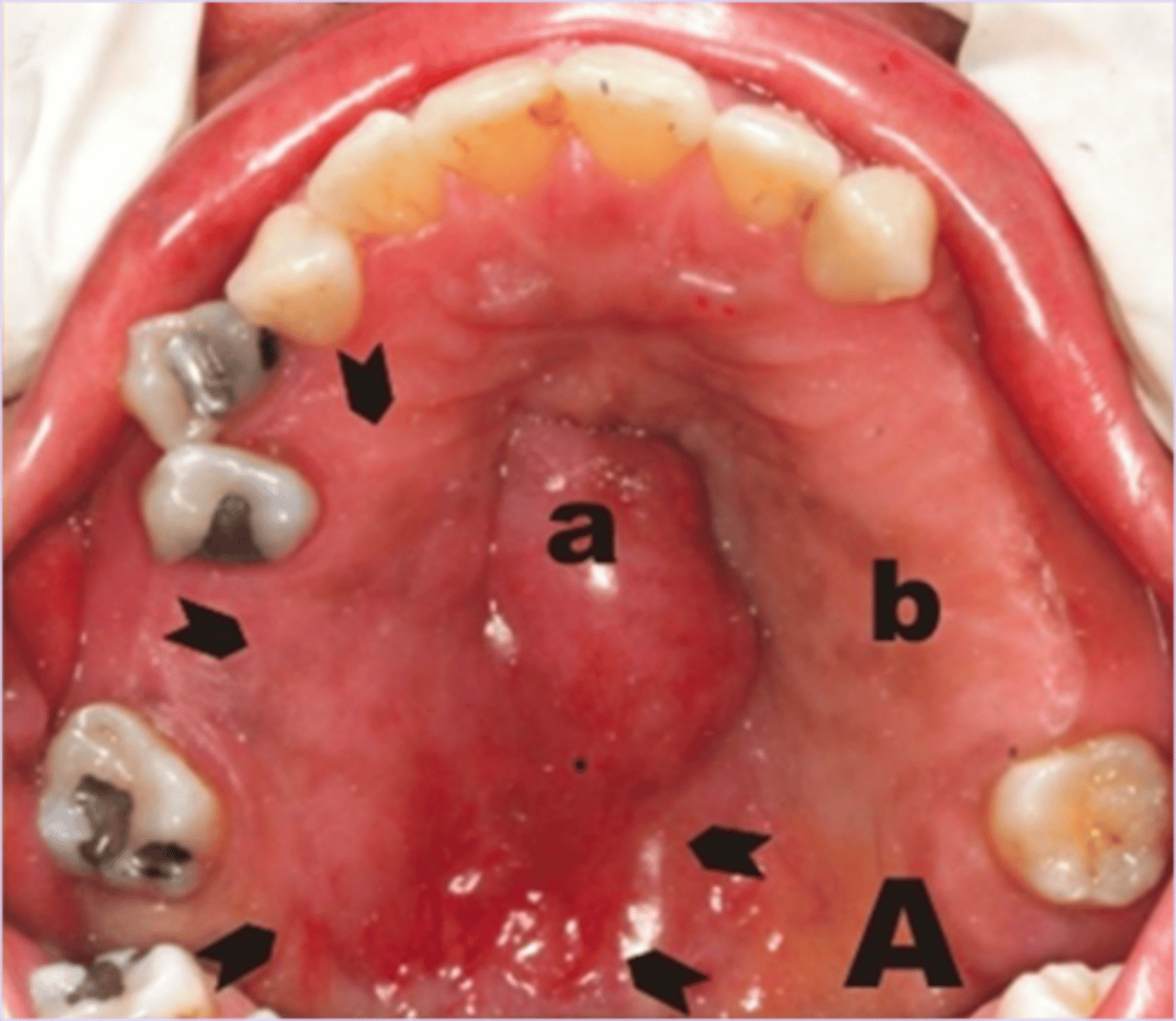
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
this pathology is associated with perineural infiltration with a cribriform (swiss cheese) appearance:
lung and bone
in patients with Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, what is the most common site for metastasis?
recurrence
in patients with Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, what presentation would suggest that it is incurable?
Parotid > submandibular > minor glands
between the Parotid, submandibular and minor glands, order them from best to worst prognosis for a case of Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma:
Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
this pathology is associated with a good short term but poor long term survival:
minor salivary glands
Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma is limited to what type of salivary glands?
conservative complete excision
what is the treatment for Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma ?
Polymorphous Adenocarcinoma
this pathology is associated with a VERY good prognosis of a 98% 10 year survival rate if detected and excised:
Adenocarcinoma
ID the pathology:
•Diagnosis of exclusion
•5th-8th decades
•65% in major glands (mostly parotid)
35% in minor glands
prognosis: High grade - 40% 5-year survival
-Minor gland tumors have improved survival over those of major glands