DNA translation
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
3/11/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
what is the purpose of translation? steps of translation?
turning mRNA into protein using tRNA
occurs in ribosome in cytoplasm
initiation, elongation, termination
what is tRNA?
transfer RNA
vital for bringing amino acids in to form a polypeptide chain
clover shape due to intermolecular forces that cause it to fold in on itself
ester bond attaches amino acid on top
anti-codon at bottom that matches to codon
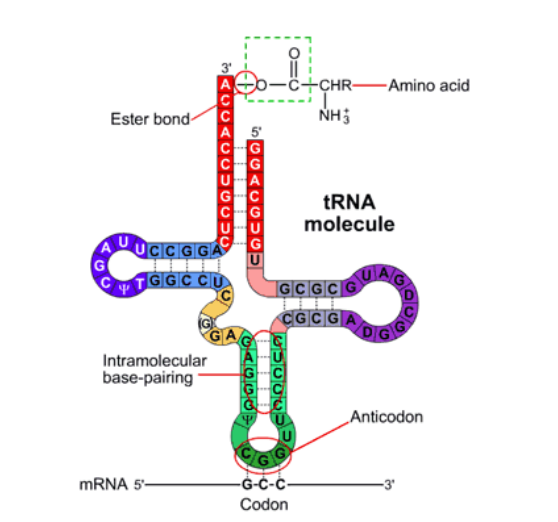
anti codon vs codon
codon: 3 base pairs, read in group of 3
anticodon: opposite bases of codon, matches to codon
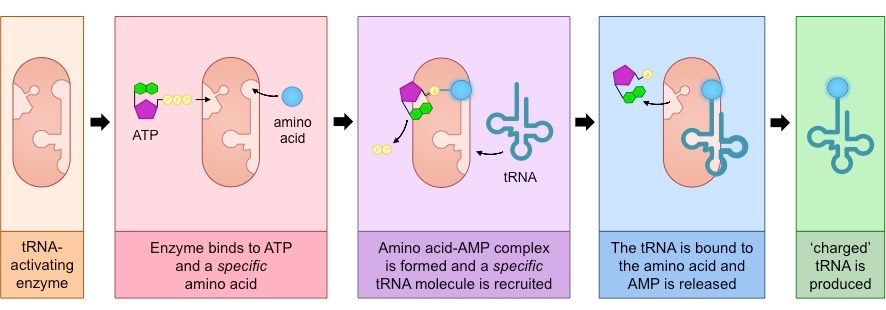
how does amino acid attach to tRNA?
atp and an amino acid are joined in an enzyme
tRNA is joined to the amino acid in the enzyme
forms ‘charged’ tRNA: activated amino acid attached to tRNA through ester bond
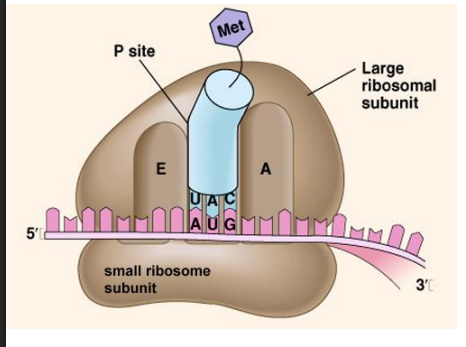
ribosome
site of protein synthesis
made of ribosomal RNA and proteins
consist of small ribosome subunit and large ribosomal subunit
three tRNA sites
A site: acceptor site
P site: peptide site, polypeptides formed here
E site: exit site, tRNA exits ribosome
movement of tRNA through ribosome
tRNA comes to A site
anti codon matches to codon
moves to P site and gives away amino acid to subsequent tRNA
moves to E site and exits
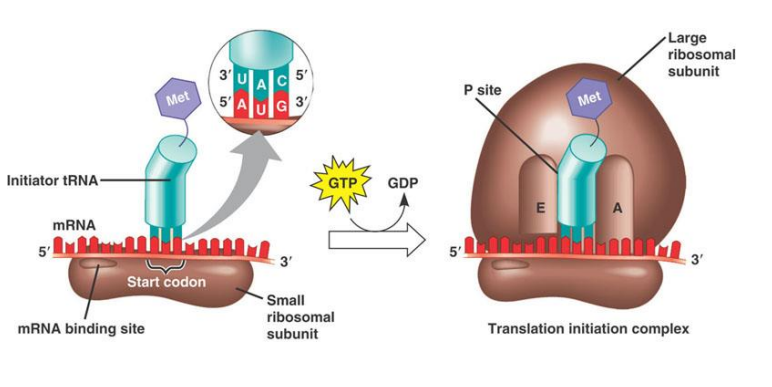
initiation of translation
small subunit recognizes mRNA
binds to 5’ cap upstream (before) starting codon → met: AUG
subunit moves 5’ to 3’ until met codon is found
anticodon UAC recognizes AUG codon
initiator tRNA enters ribosome, binds directly to P site with met amino acid (no a site)
large subunit attaches on top to complete ribosome complex
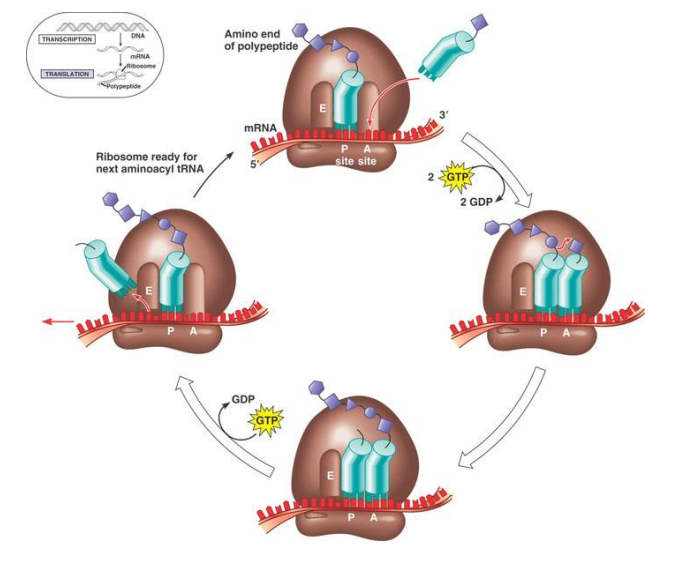
elongation of translation
complex is ready
mRNA is read through
tRNA comes into A site and has matching anticodon
peptide bonds form between P site and A site junction
tRNA moves to p site, gives amino acid to subsequent tRNA
polypeptide chain is being built at the top
tRNA move to E site then leave ribosome
tRNA in A site moves to P site
new tRNA enters A site
continuously moving like factory line
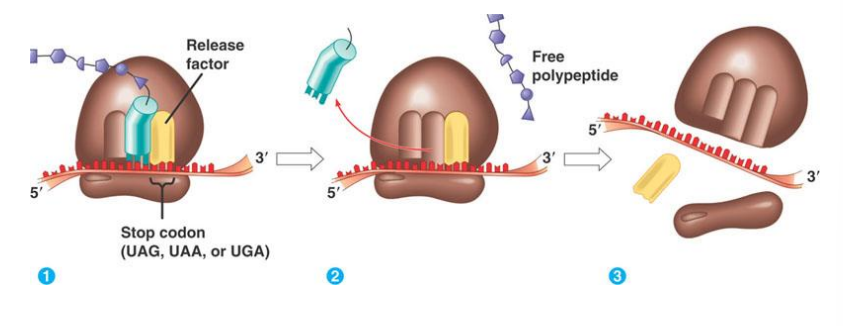
termination of translartion
stop codon enters ribosome
no tRNA with anticodon as they do not need to code for amino acids
release factor binds instead of tRNA and dismantles complex
releases polypeptide, free polypeptide
ribosome breaks apart
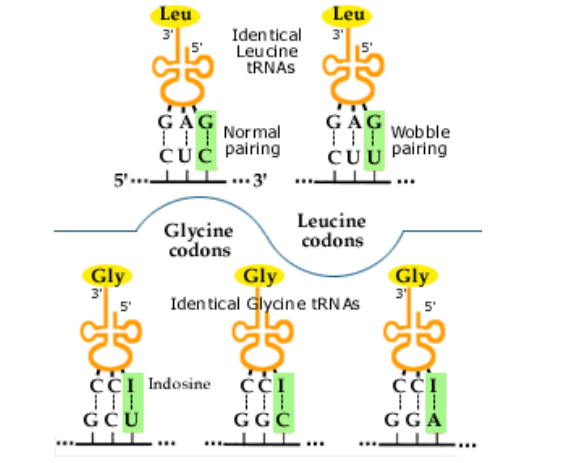
wobble hypothesis
wobble refers to the third spot on the codon
the third base on the codon is less strict in pairing
multiple codons code for the same amino acid

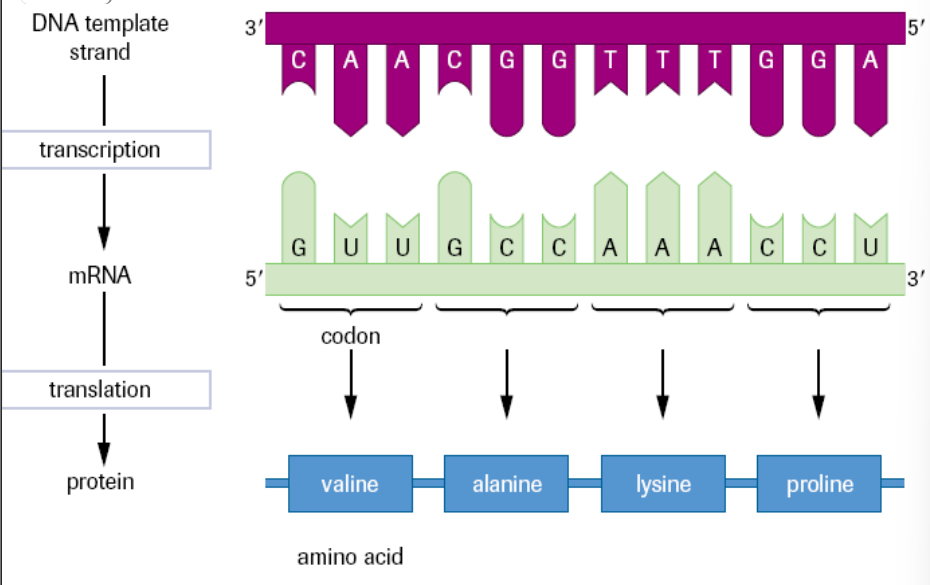
transcribe and translate this template strand of dna and state what is formed after each process
transcription: 5’ - GUUGCCAAACCU - 3’
forms mRNA
translation: Val - Ala - Lys - Pro
forms polypeptide chain, one or more fold to become functioning protein
location of transcription vs translation
transcription occurs inside nucleus
mRNA leaves nucleus and finds ribosome
translation occurs in cytoplasm
builds polypeptide protein
what are ribosomes made up of?
protein and rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
what happens to polypeptide chain after being fully synthesized?
it travels to the golgi body to undergo folding to be able to carry out a specific function