Bio 181 Module 2
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
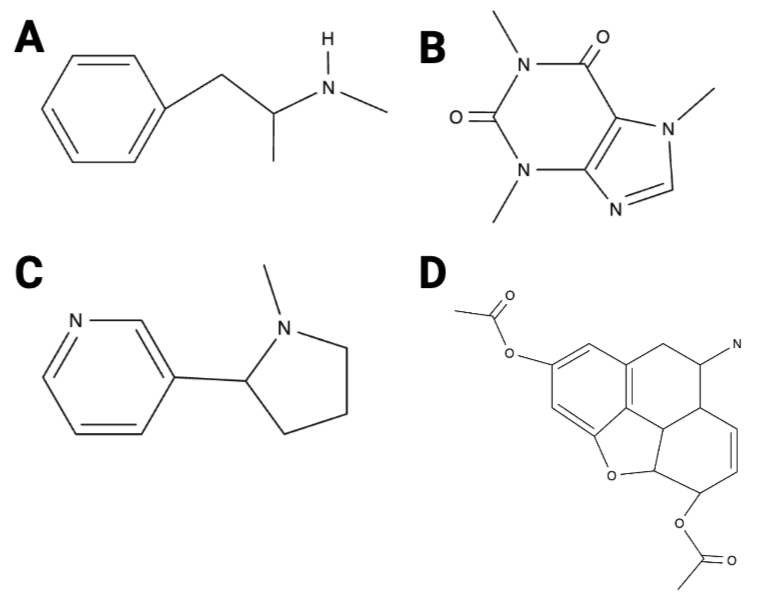
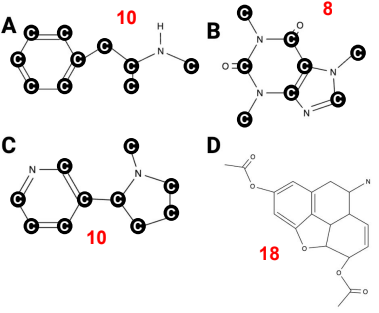
True or False? Image B has 10 hydrogen atoms.
True
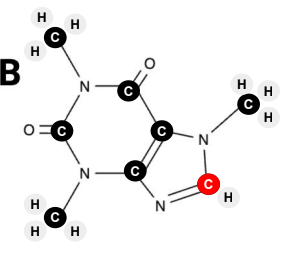
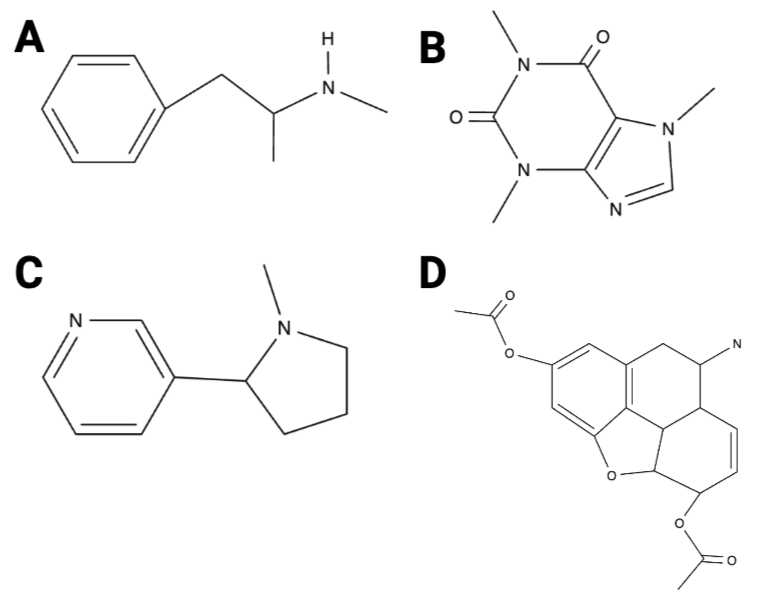
True or False? Image D has five oxygen atoms.
True
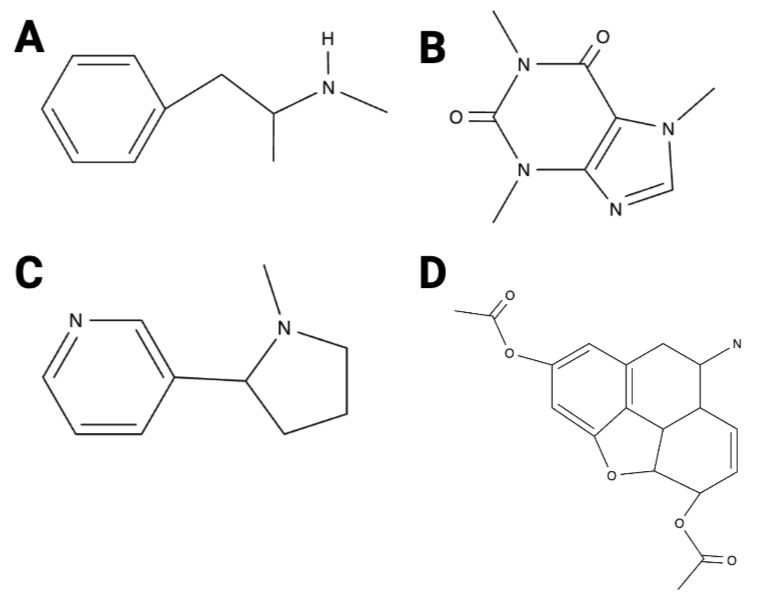
True or False? Of the four images, image A has the fewest carbon atoms.
False
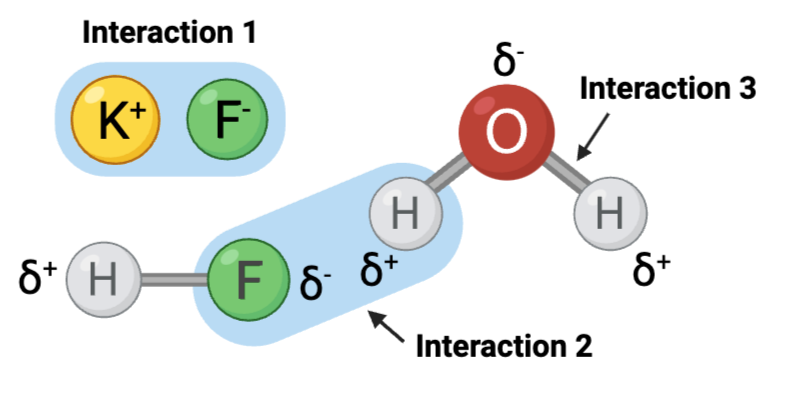
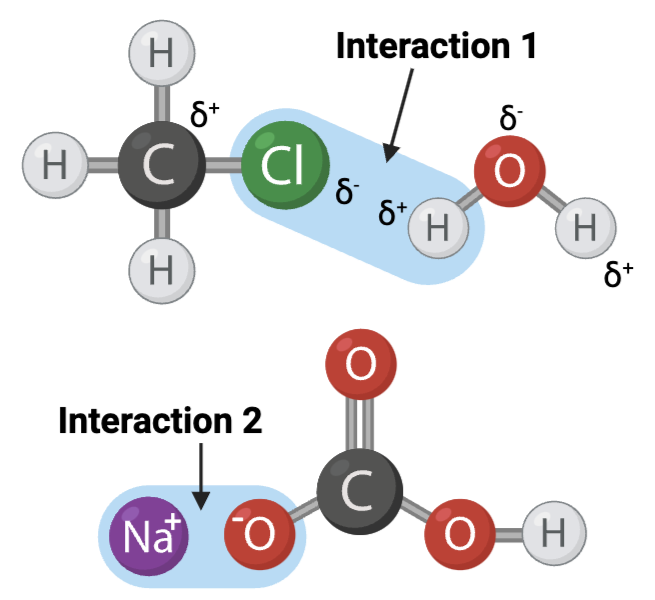
Interaction 1 is ____.
a. a covalent bond
Should not have been checked.
b. a hydrogen bond
Should not have been checked.
c. an ionic bond
c. an ionic bond
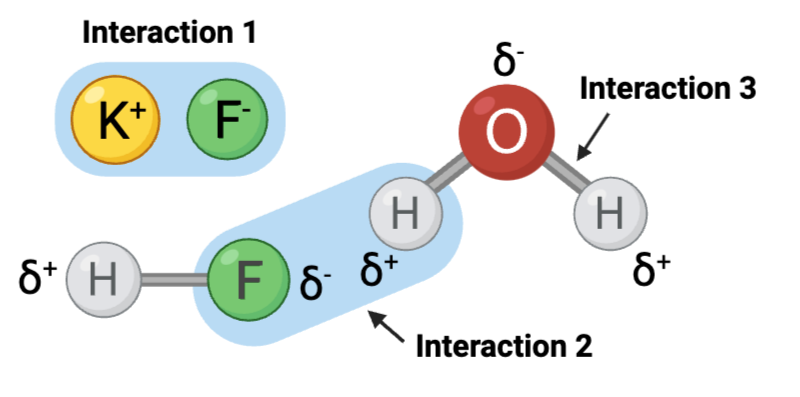
Interaction 2 is ____.
a. a covalent bond
b. a hydrogen bond
c. an ionic bond
b. a hydrogen bond
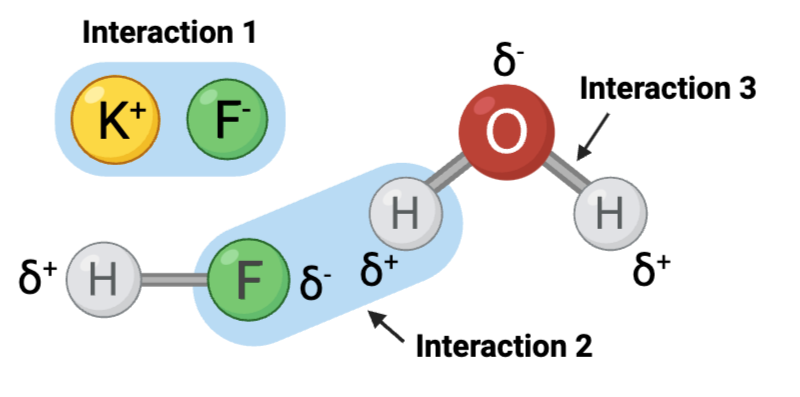
Interaction 3 is ____.
a. a covalent bond
b. a hydrogen bond
c. an ionic bond
a. a covalent bond
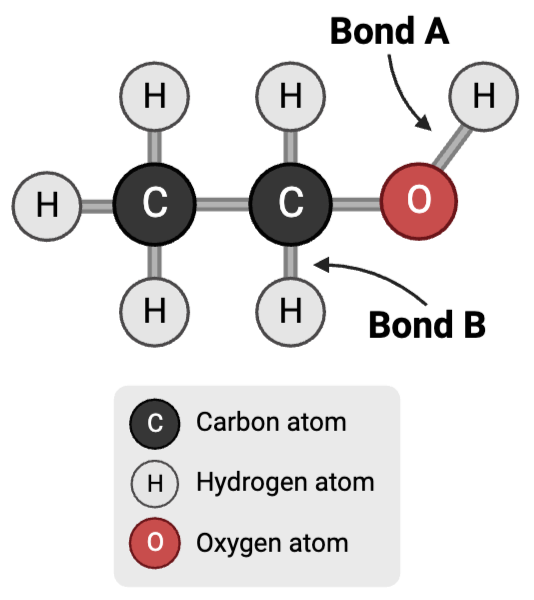
Bond A is a ____.
a. polar covalent bond
b. nonpolar covalent bond
a. polar covalent bond
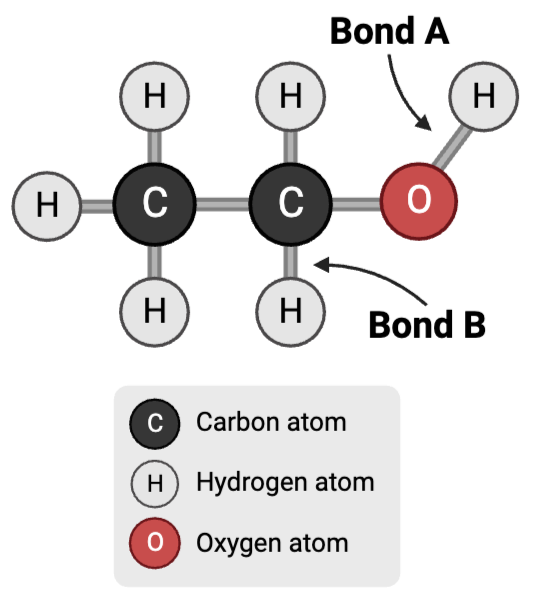
Bond B is a ____.
a. polar covalent bond
b. nonpolar covalent bond
b. nonpolar covalent bond
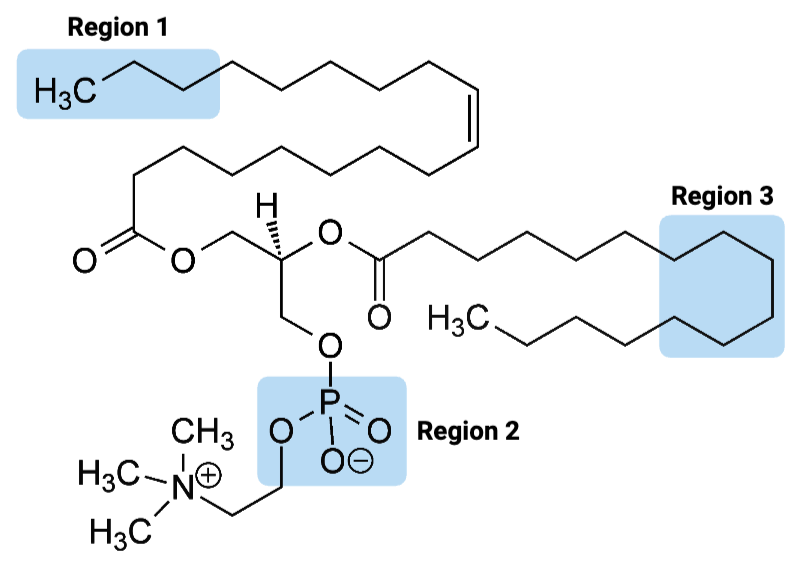
Region 1 of the molecule is considered ____.
a. amphiphilic
b. hydrophilic
c. hydrophobic
c. hydrophobic
Region 2 of the molecule is considered ____.
a. amphiphilic
b. hydrophilic
c. hydrophobic
b. hydrophilic
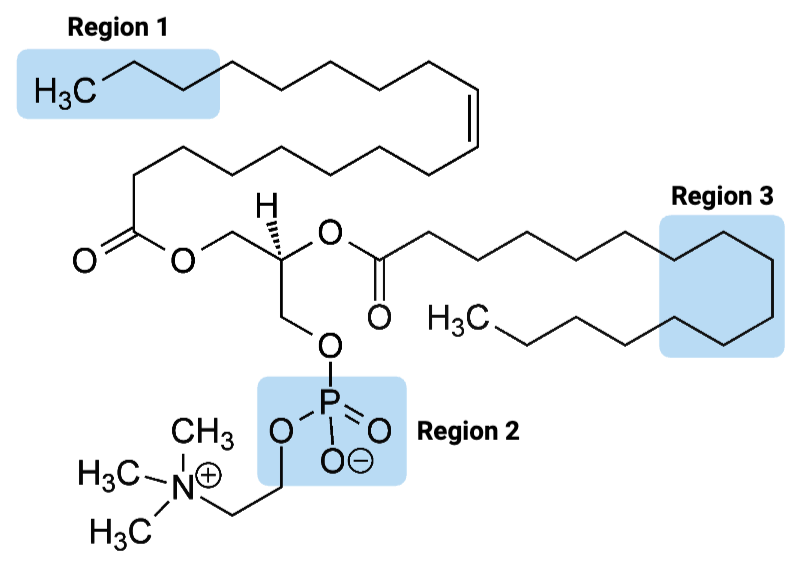
Region 3 of the molecule is considered ____.
a. amphiphilic
b. hydrophilic
c. hydrophobic
c. hydrophobic
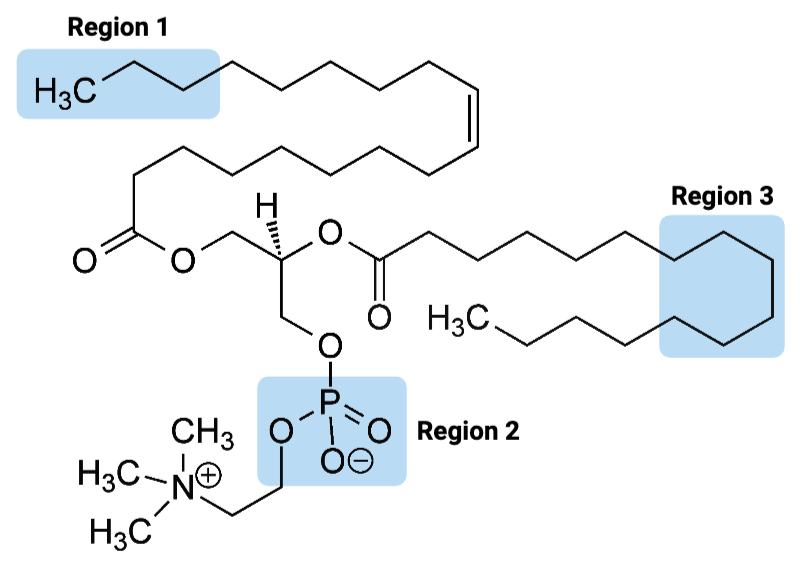
The entire molecule is best classified as ____.
a. amphiphilic
b. hydrophilic
c. hydrophobic
a. amphiphilic
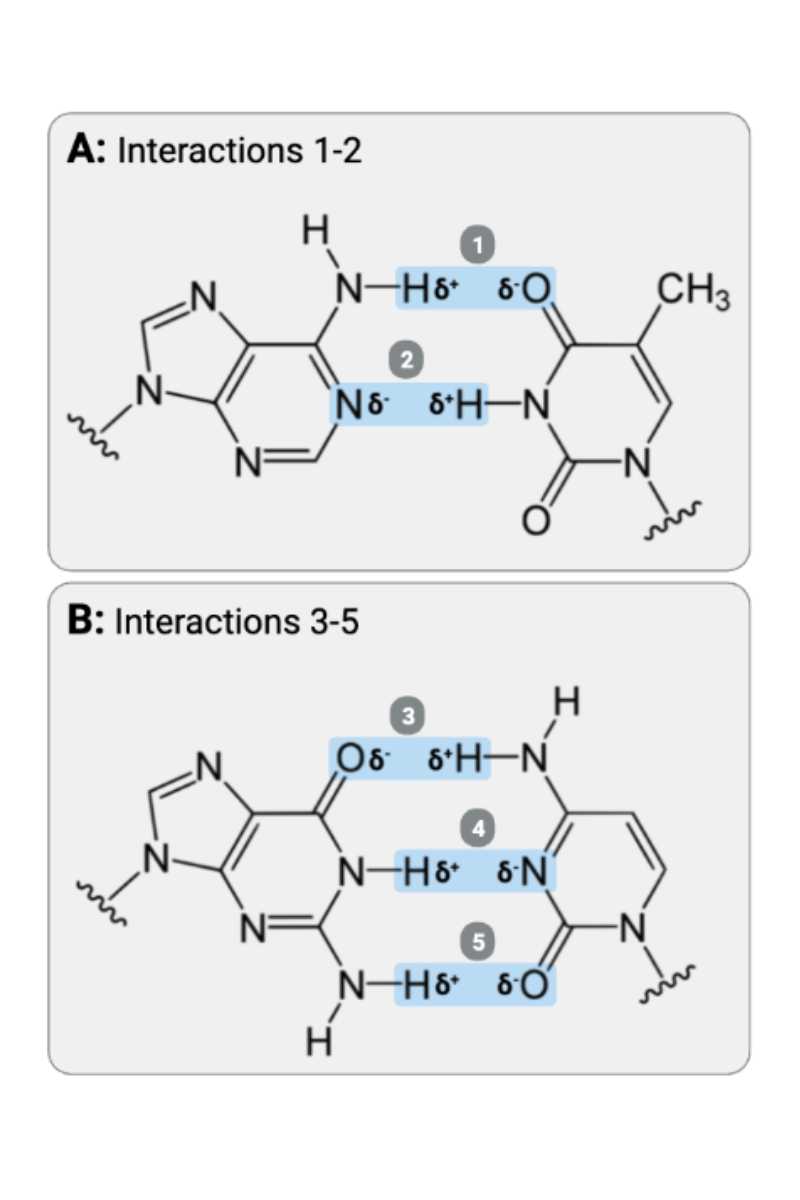
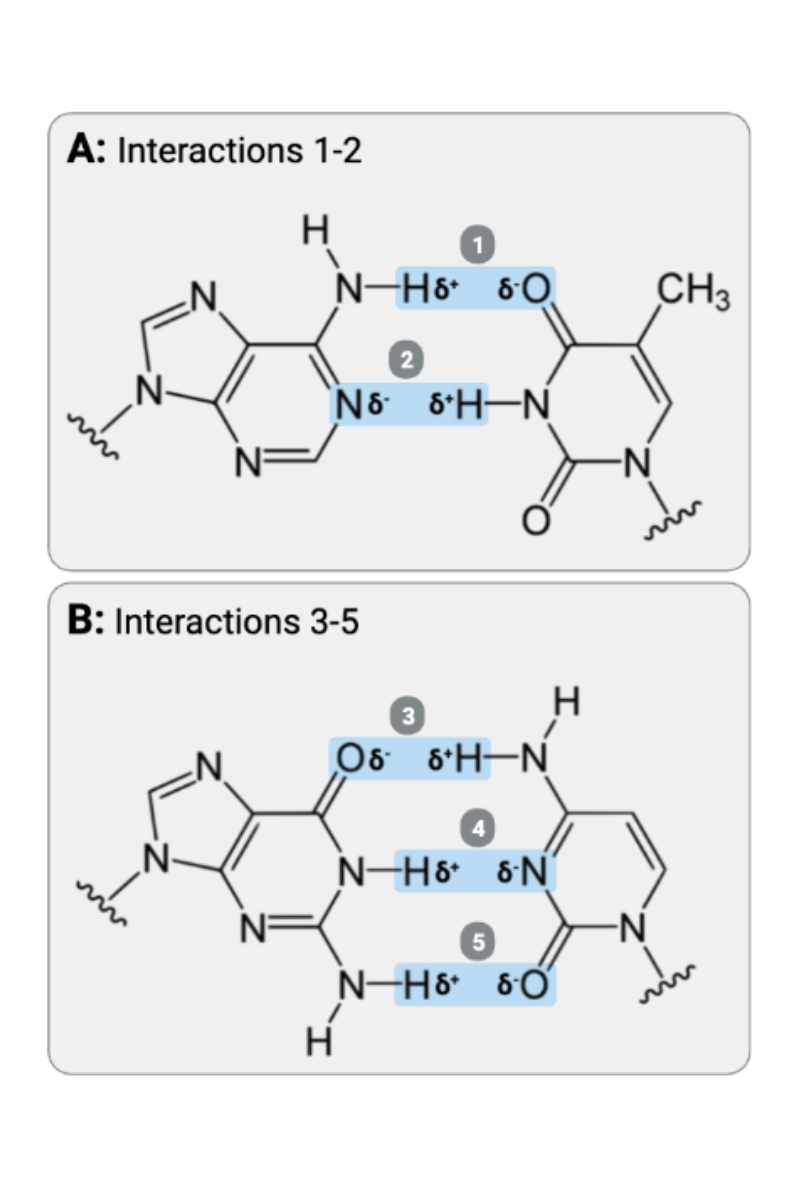
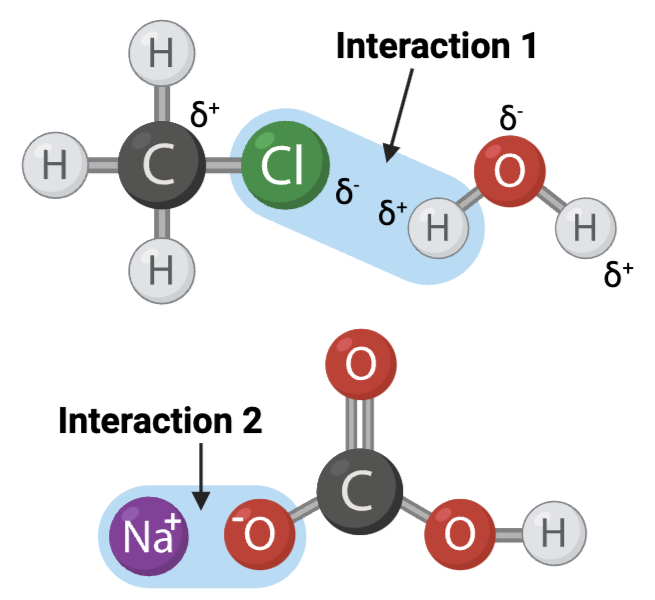
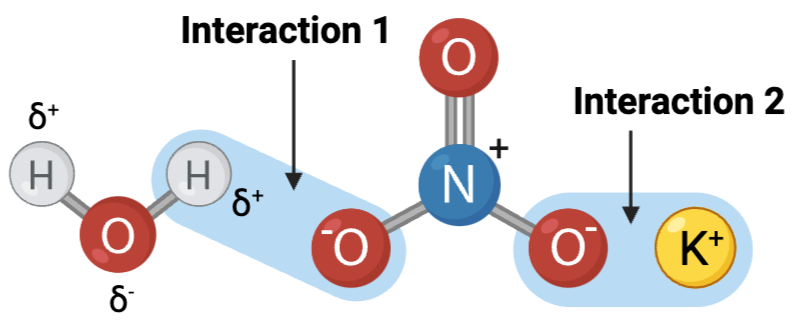
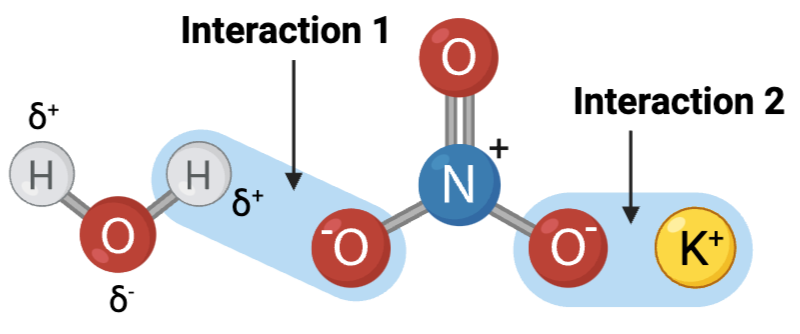
Interactions 1 and 2 are ____?
a. covalent bonds
b. hydrogen bonds
c. ionic bonds
b. hydrogen bonds
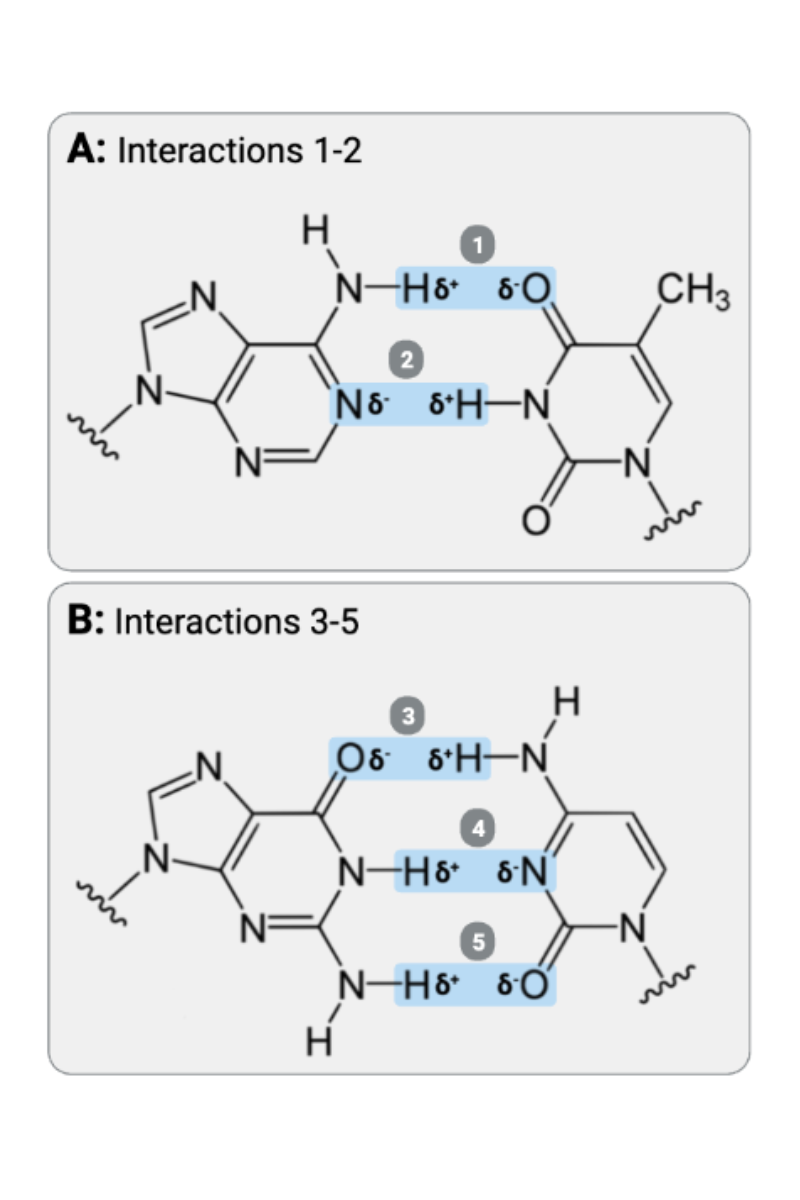
Interactions 3, 4, and 5 are ____?
a. covalent bonds
b. hydrogen bonds
c. ionic bonds
b. hydrogen bonds
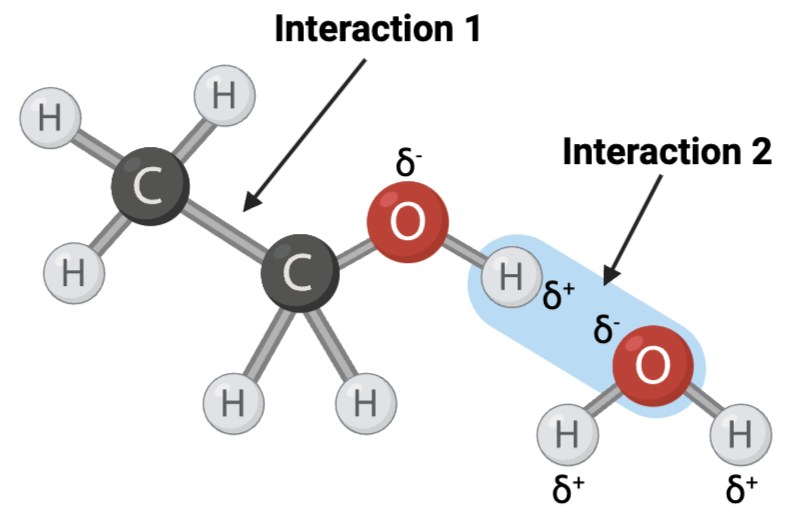
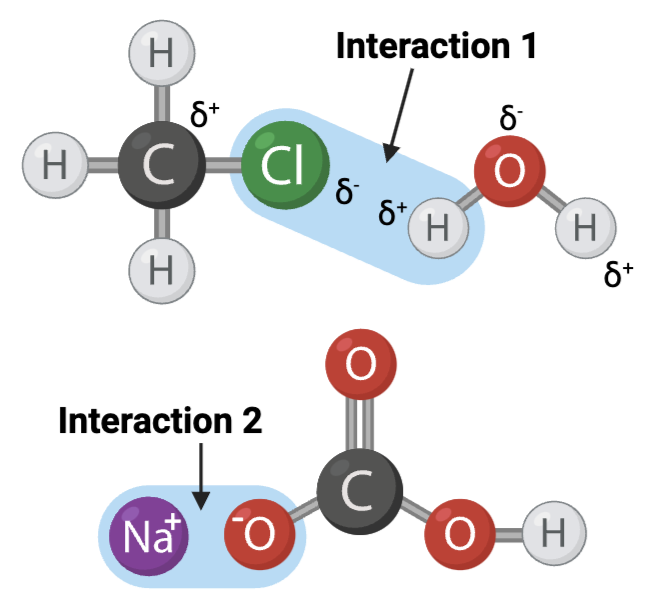
Which set of interactions is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature, the interactions between molecules shown in Set A or the interactions between molecules shown in Set B?
Set A
Interaction 1 is ____?
a covalent bond
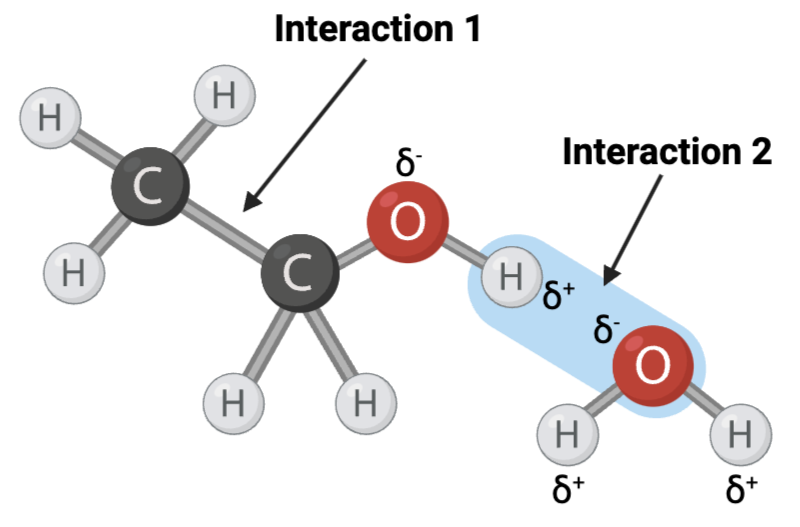
Interaction 2 is ____?
a hydrogen bond
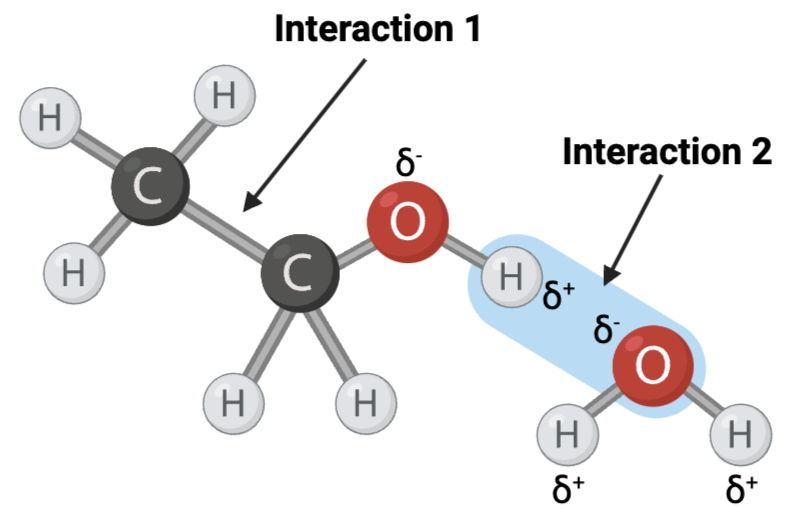
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
interaction 2
The figure shows two interactions within or between molecules. An arrow points to each interaction.
Interaction 1 is ____?
a hydrogen bond
Interaction 2 is ____?
an ionic bond
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
interaction 1
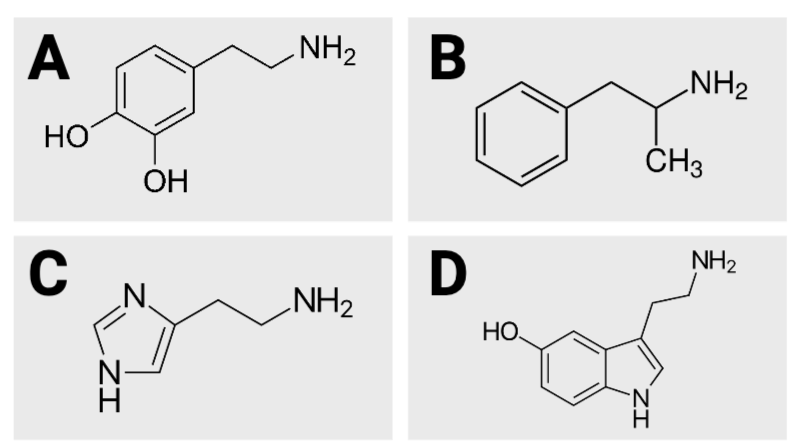
True or False? Of the four images, image A has the most carbon atoms.
False
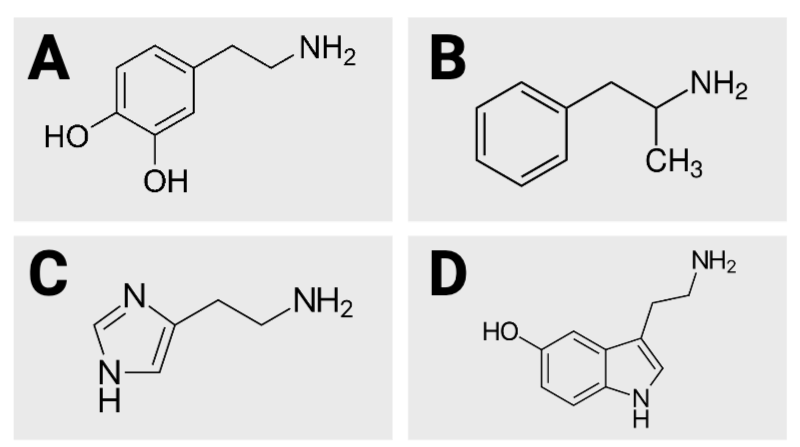
True or False? Image C has three nitrogen atoms.
True
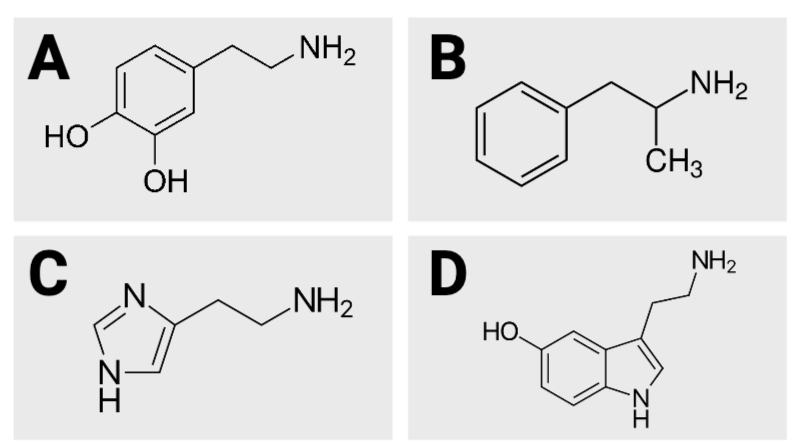
True or False? Image D has 12 hydrogen atoms.
True
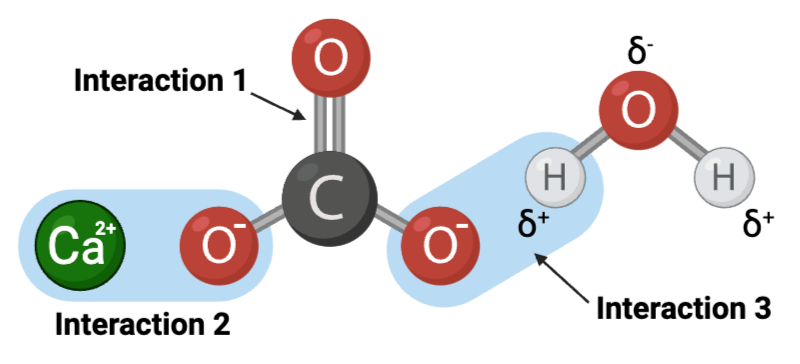
Interaction 1 is ____.
a covalent bond
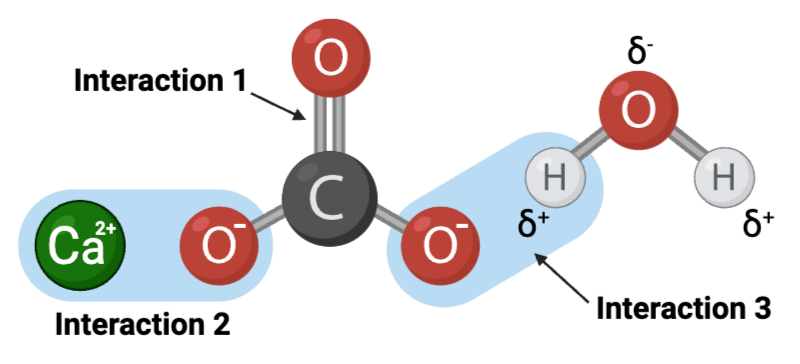
Interaction 2 is ____.
an ionic bond
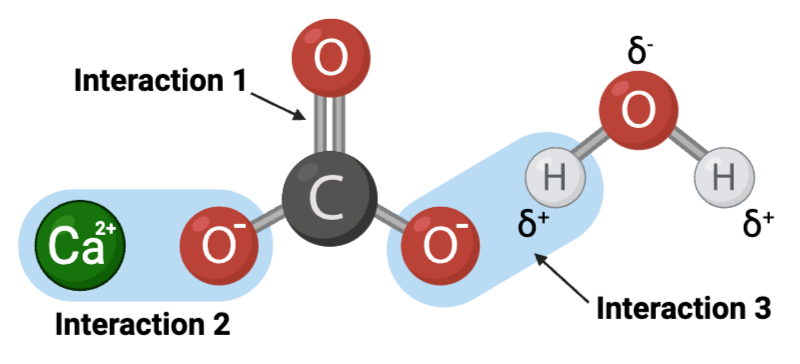
Interaction 3 is ____.
a hydrogen bond
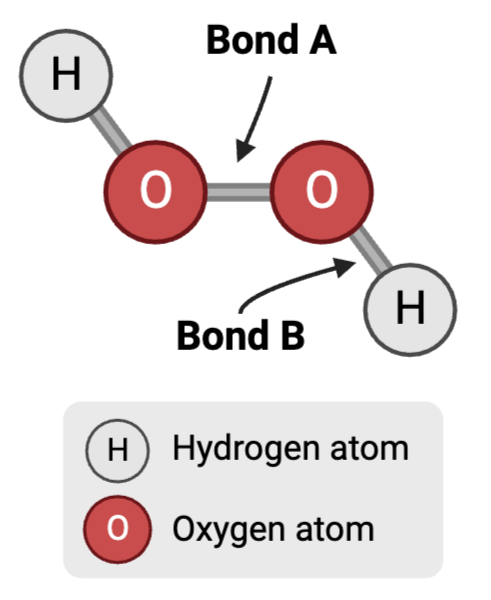
Bond A is a ____.
nonpolar covalent bond
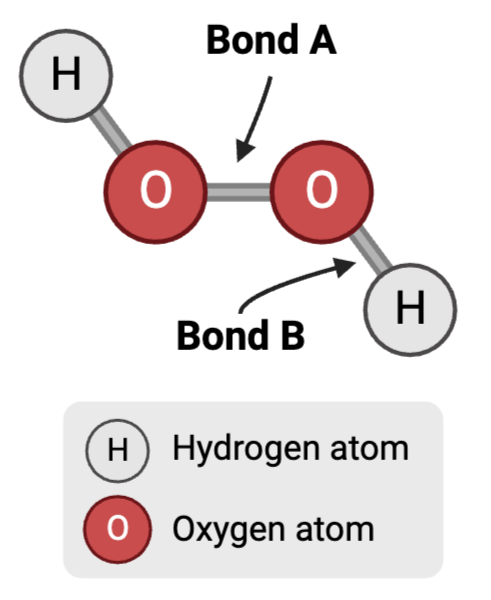
Bond B is a ____
polar covalent bond
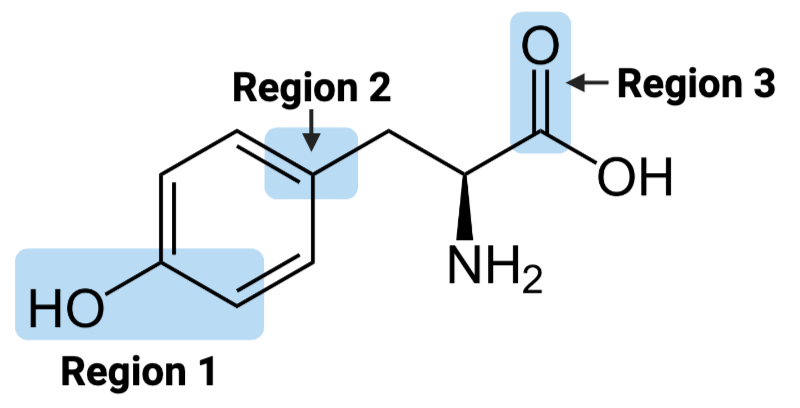
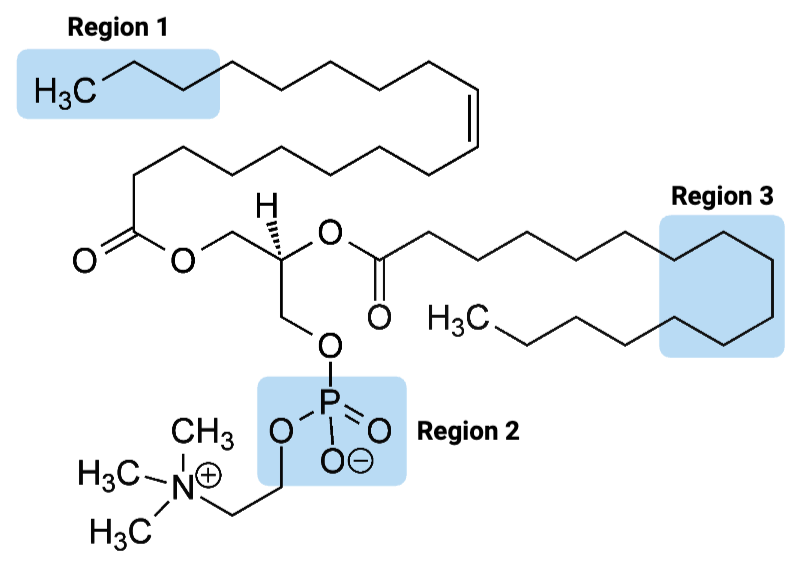
Region 1 of the molecule is considered __
amphiphilic
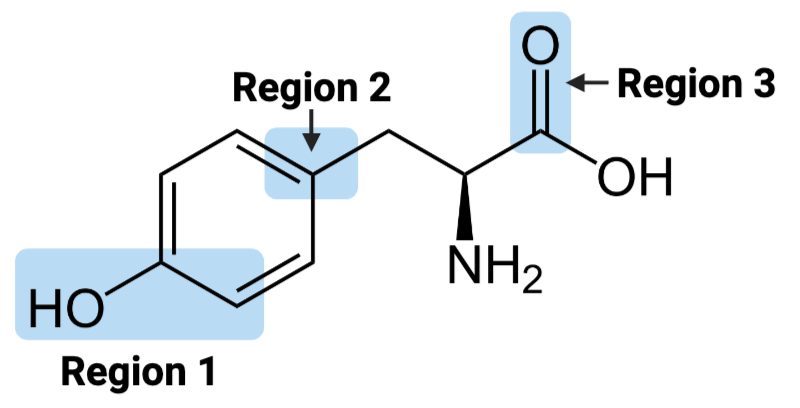
Region 2 of the molecule is considered ____.
hydrophobic
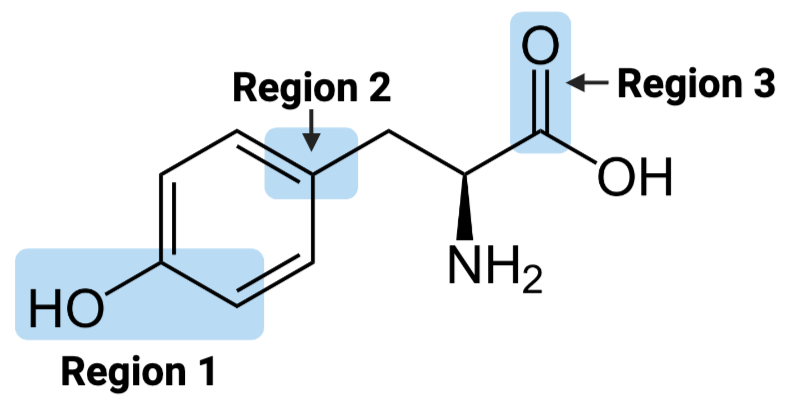
Region 3 of the molecule is considered ____.
hydrophilic
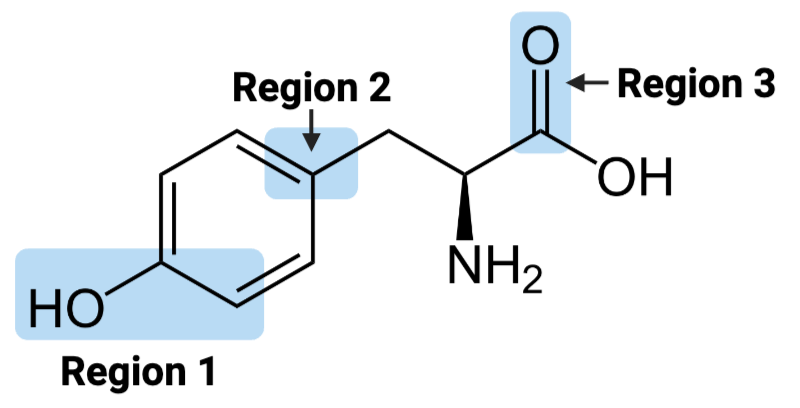
The entire molecule is best classified as ____.
amphiphilic
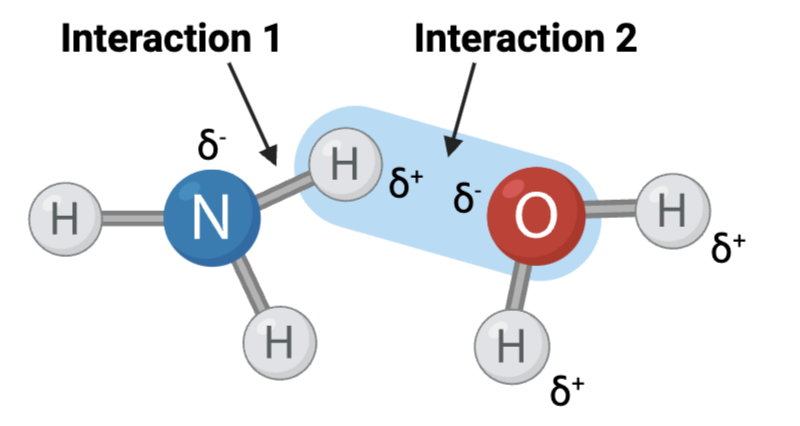
Interaction 1 is ____?
a covalent bond
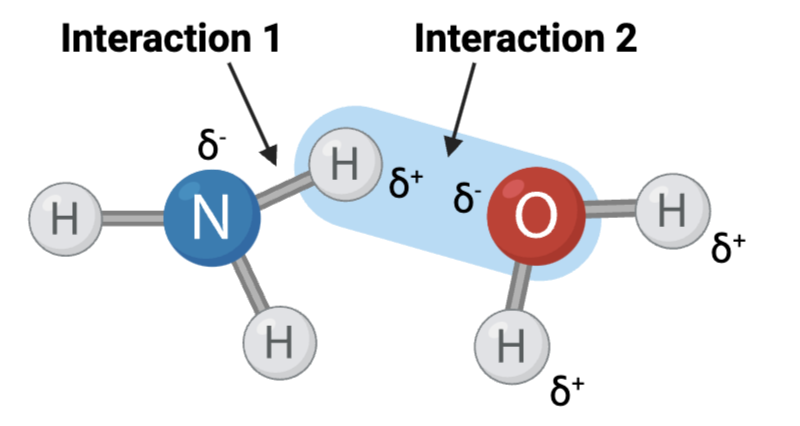
Interaction 2 is ____?
a hydrogen bond
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
interaction 2
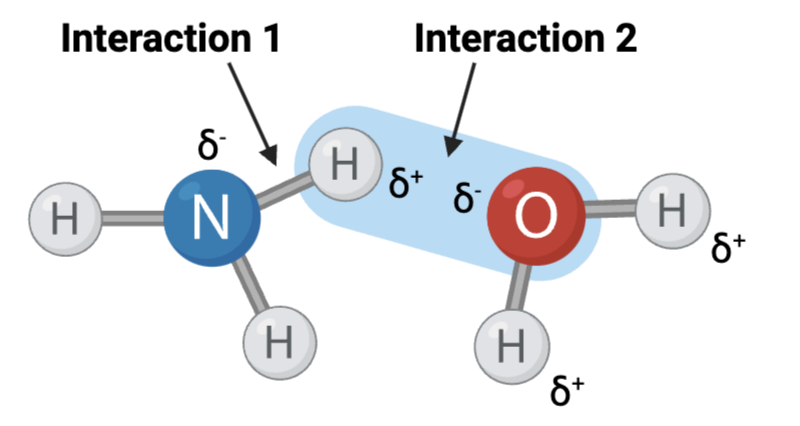
Interaction 1 is ____?
a hydrogen bond
Interaction 2 is ____?
an ionic bond
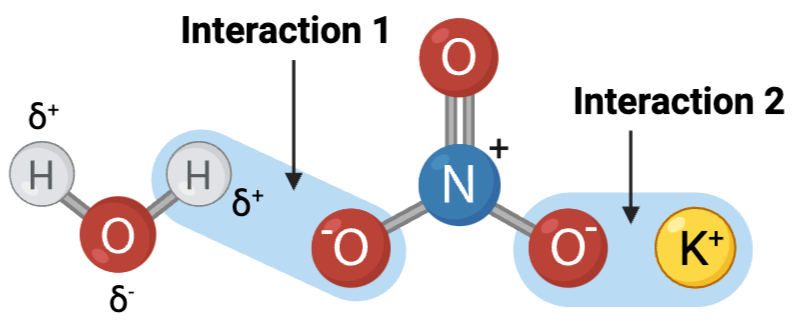
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
interaction 1
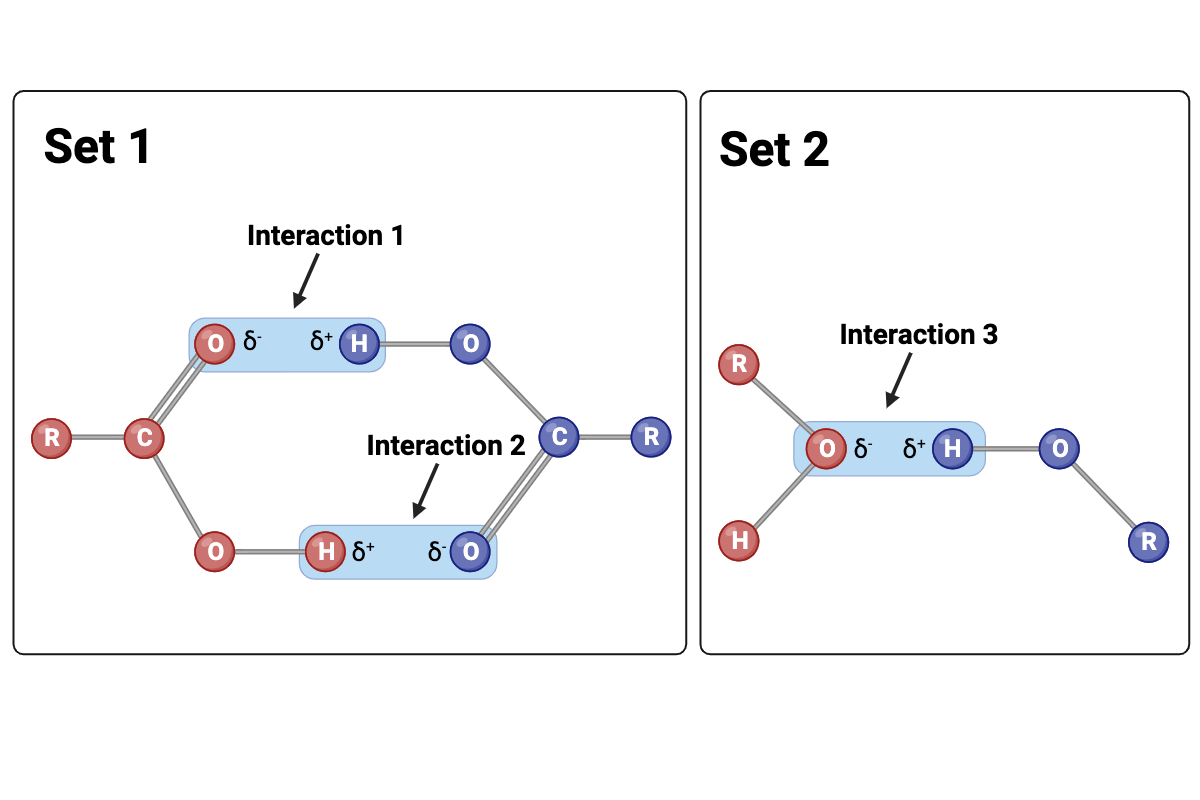
Interactions 1 and 2 are ____?
hydrogen bonds
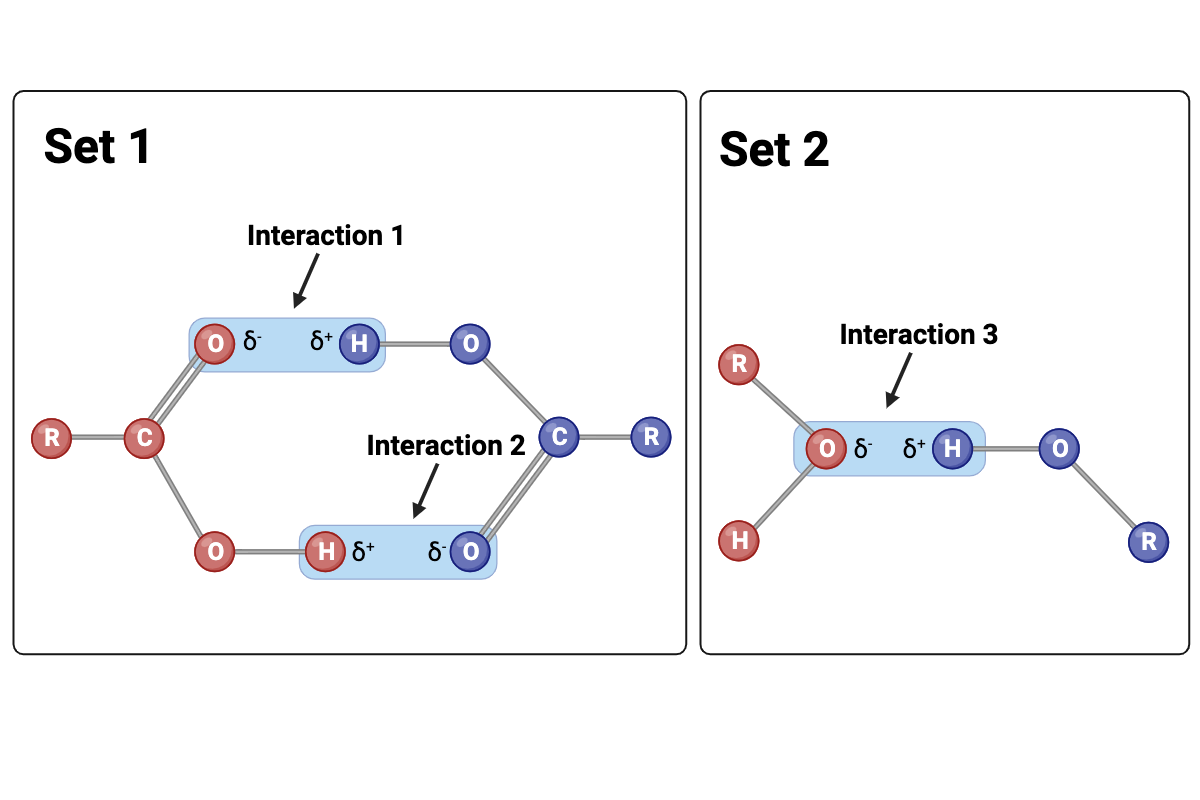
Interaction 3 is ____?
hydrogen bonds
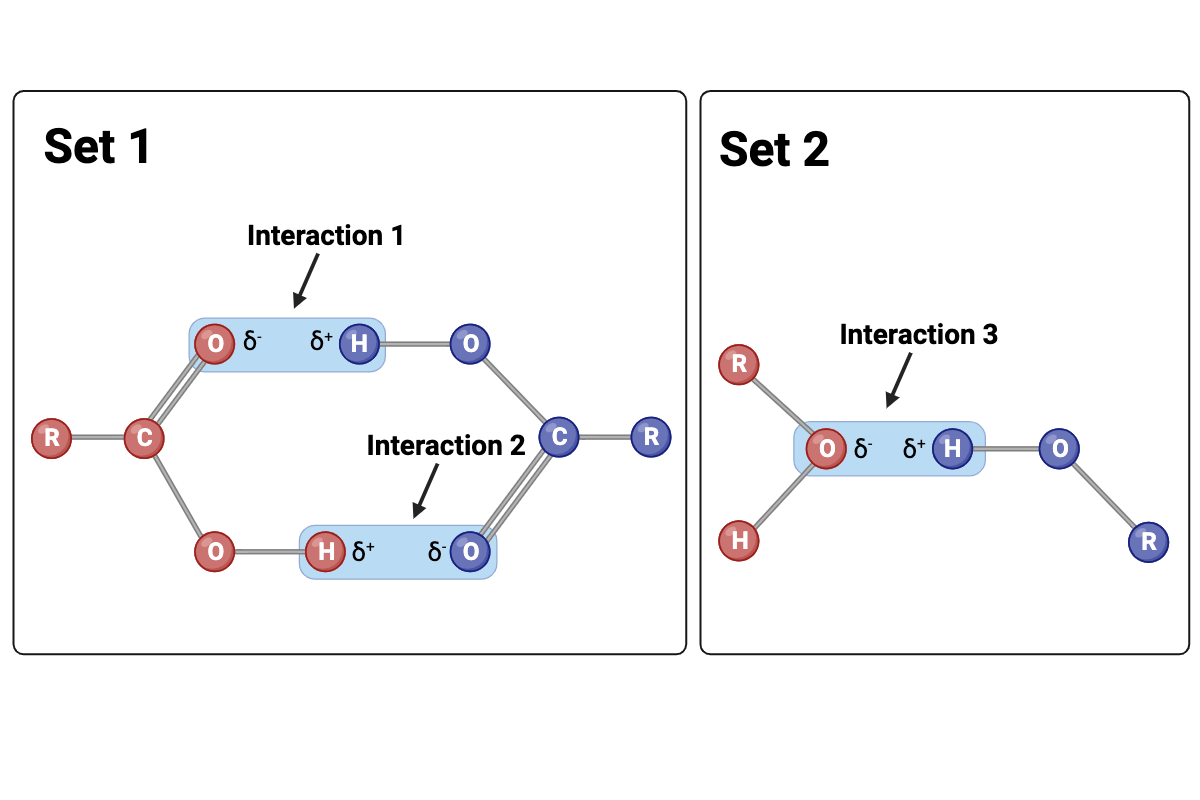
Which set of interactions is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature? The interactions between molecules shown in Set 1 or the interactions between molecules shown in Set 2?
Set 2
A(n) ___ is a large molecule made up of one or more chains of amino acids.
a. monomer
b. polymer
c. amino acid
d. peptide bond
e. protein
e. protein
A(n) ___ is made up of a central carbon atom attached to an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and an R group. These molecules bond together to form proteins.
a. monomer
b. polymer
c. amino acid
d. peptide
e. peptide bond
c. amino acid
A(n) ___ is a molecule made up of two or more amino acids bonded to each other in a single chain.
a. monomer
b. polymer
c. amino acid
d. peptide
e. peptide bond
d. peptide
A(n) ___ is the general term for a small molecule that can bond with other similar molecules to form a polymer.
a. monomer
b. polymer
c. amino acid
d. peptide
e. peptide bond
f. protein
a. monomer
A(n) ___ is the general term for a large molecule made up of 2 or more smaller, similar molecules bonded together.
a. monomer
b. polymer
c. amino acid
d. peptide
e. peptide bond
f. protein
b. polymer
A(n) ___ is the name for a covalent bond that connects two amino acids together.
a. monomer
b. polymer
c. amino acid
d. peptide
e. peptide bond
f. protein
e. peptide bond
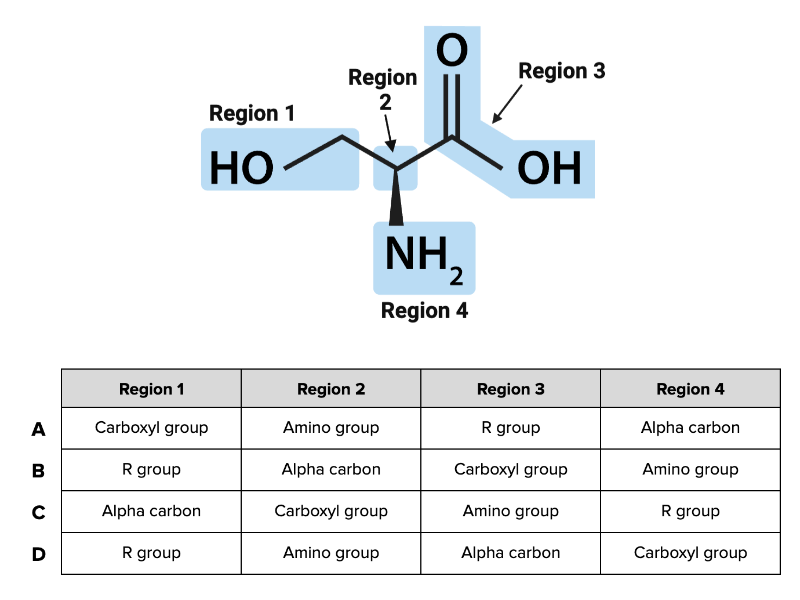
Which combination of terms (A, B, C, or D) in the table accurately describes each region of the amino acid shown in the figure?
a. Combination A
b. Combination B
c. Combination C
d. Combination D
b. Combination B
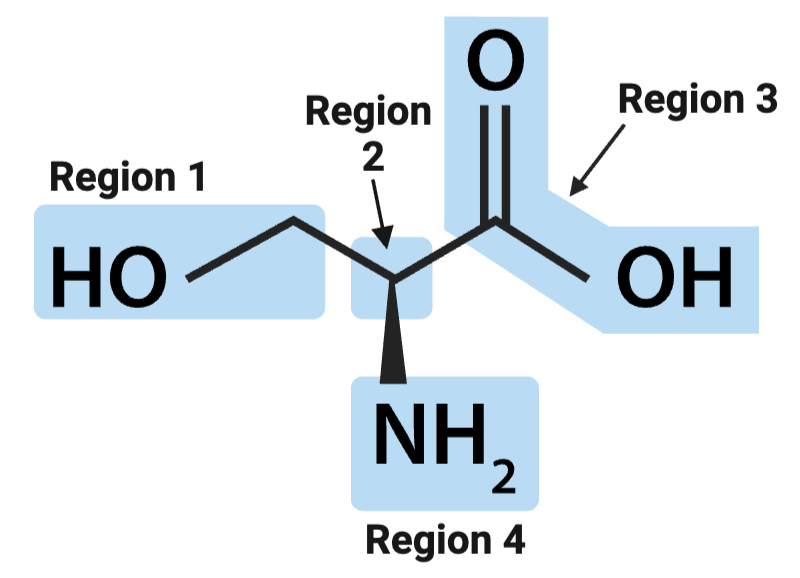
True or False? The alpha carbon is the carbon atom bound to both the amino and carboxyl groups.
True
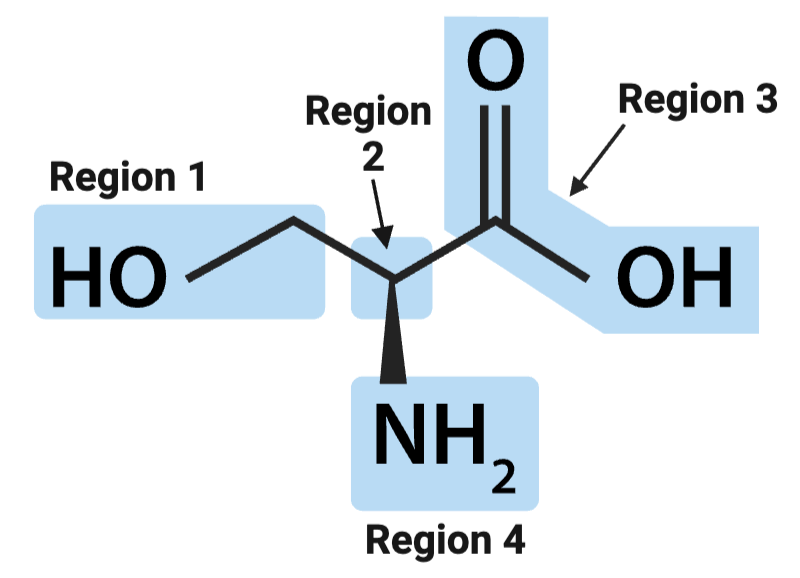
True or False? The amino group is best identified by the presence of a carbon atom double bonded to an oxygen atom.
False
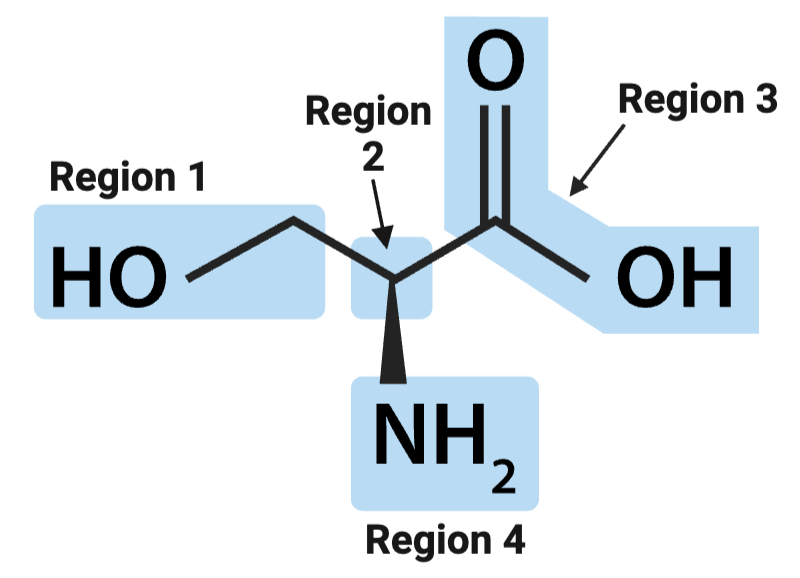
True or False? The position of the alpha carbon changes from amino acid to amino acid.
False
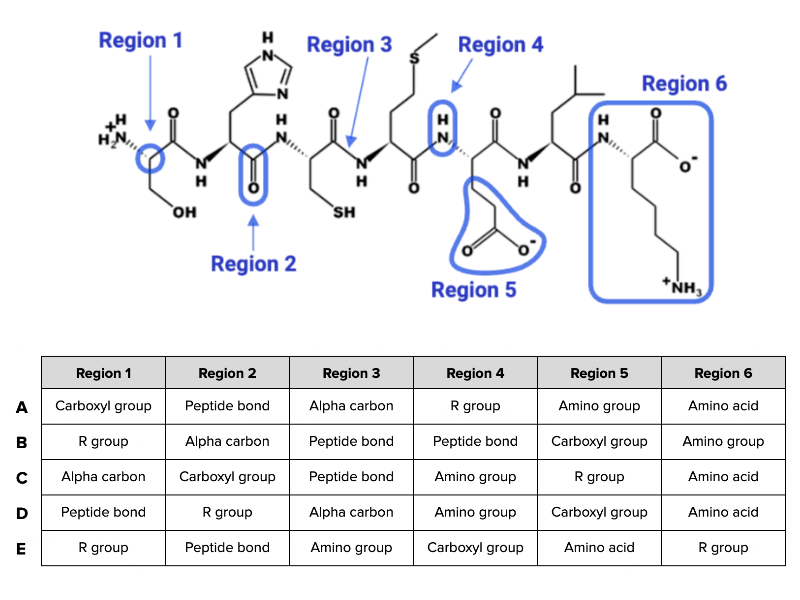
Which combination of terms (A, B, C, D, or E) shown in the table accurately describes each region of the peptide in the figure?
Combination C
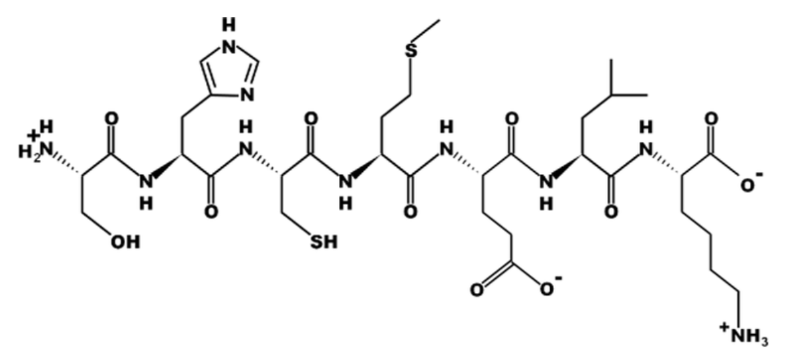
How many unique amino acids are in this peptide?
a. One
b. Three
c. Five
d. Seven
d. Seven
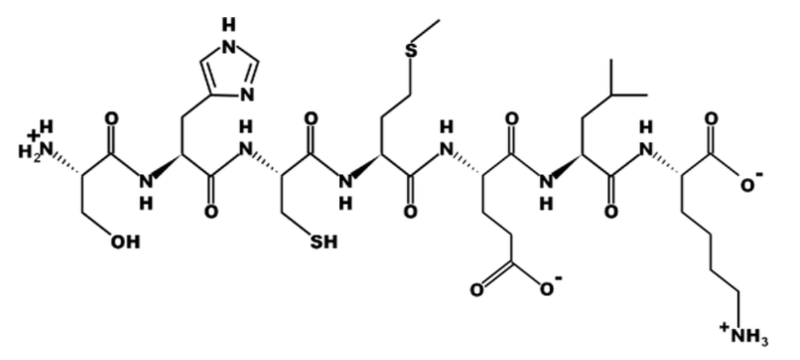
True or False? All amino acids in this peptide have a carboxyl group.
True
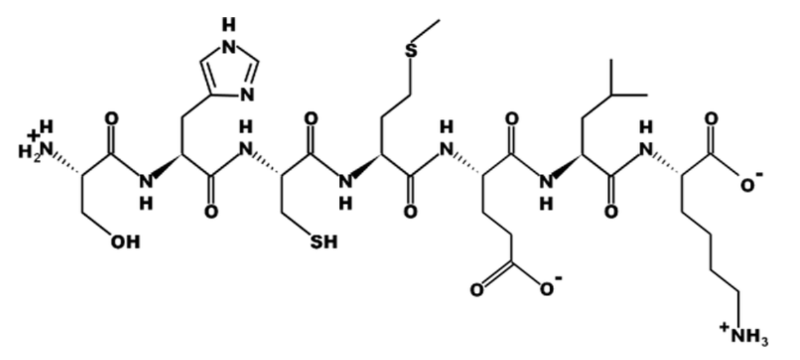
True or False? All of the amino acids in this peptide have the same R group.
False
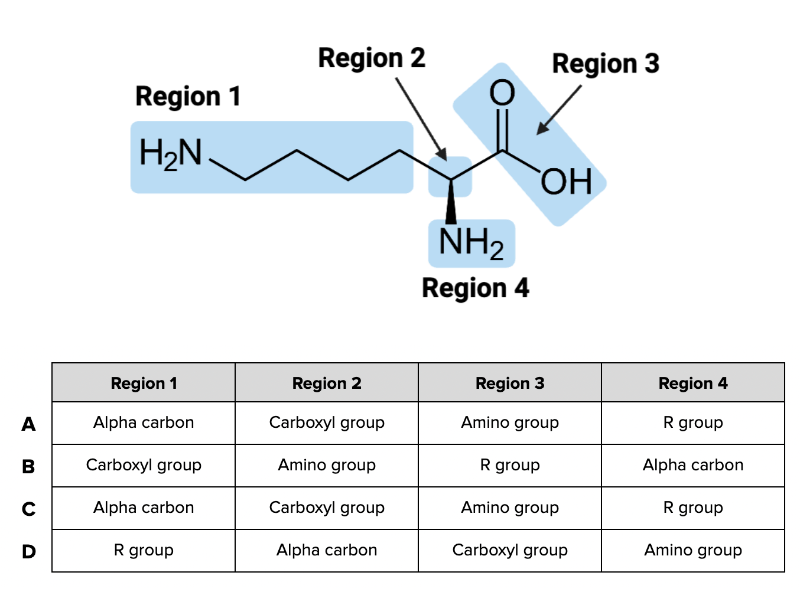
Which combination of terms (A, B, C, or D) in the table accurately describes each region of the amino acid in the figure?
Combination D
True or False? The alpha carbon is the carbon atom found within the carboxyl group.
False
True or False? The R group is best identified as the unique side chain on each amino acid.
True
True or False? The position of the amino group changes from amino acid to amino acid.
False
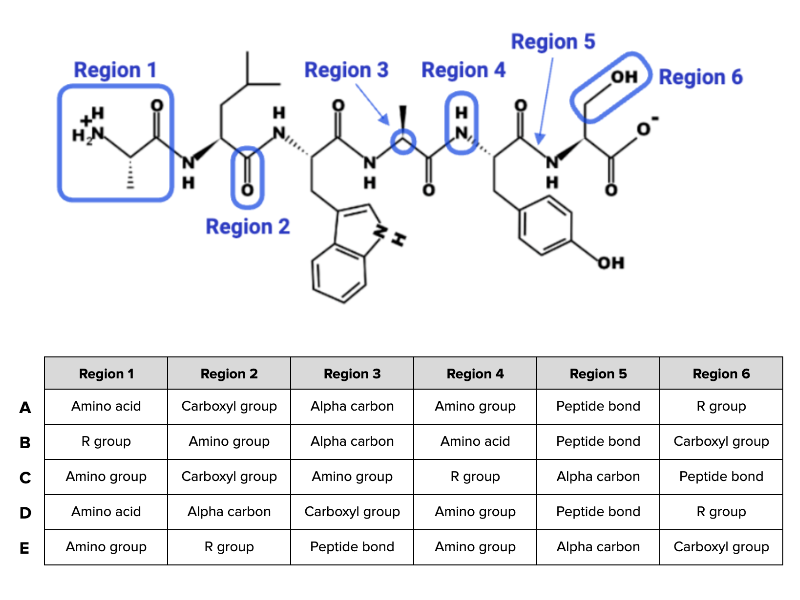
Which combination of terms (A, B, C, D, or E) shown in the table accurately describes each region of the peptide in the figure?
combinaton A
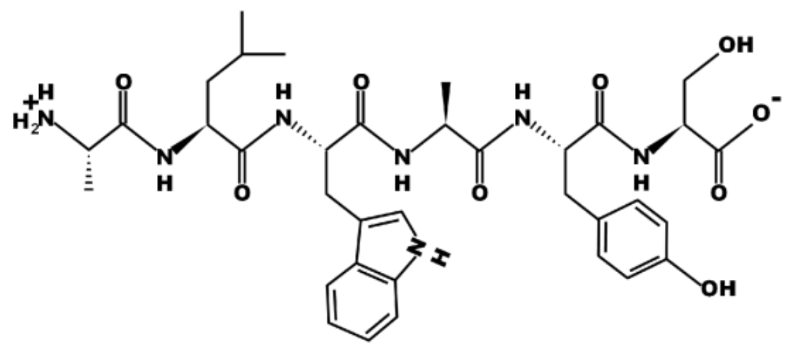
How many unique amino acids are in this peptide?
Six
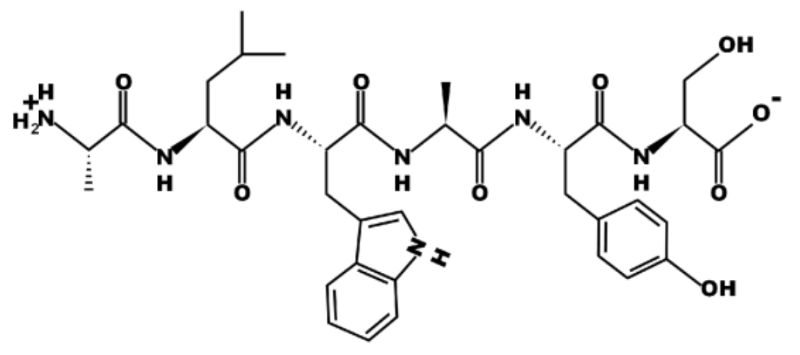
True or False? All amino acids in this peptide have an amino group.
True
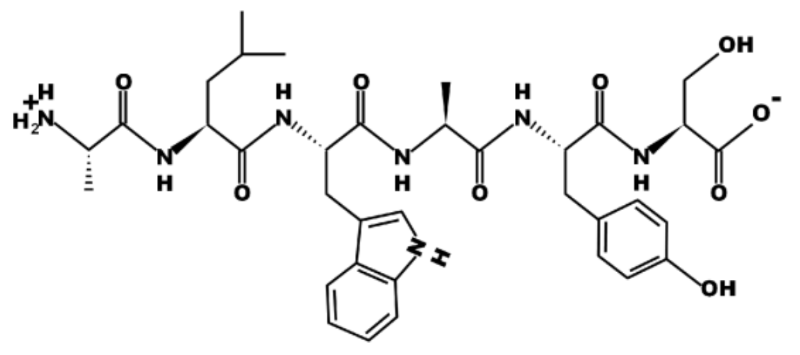
True or False? The first and third amino acids in this peptide have the same R group. Note that the first amino acid is on the far left of the image, the last amino acid is on the far right of the image.
False
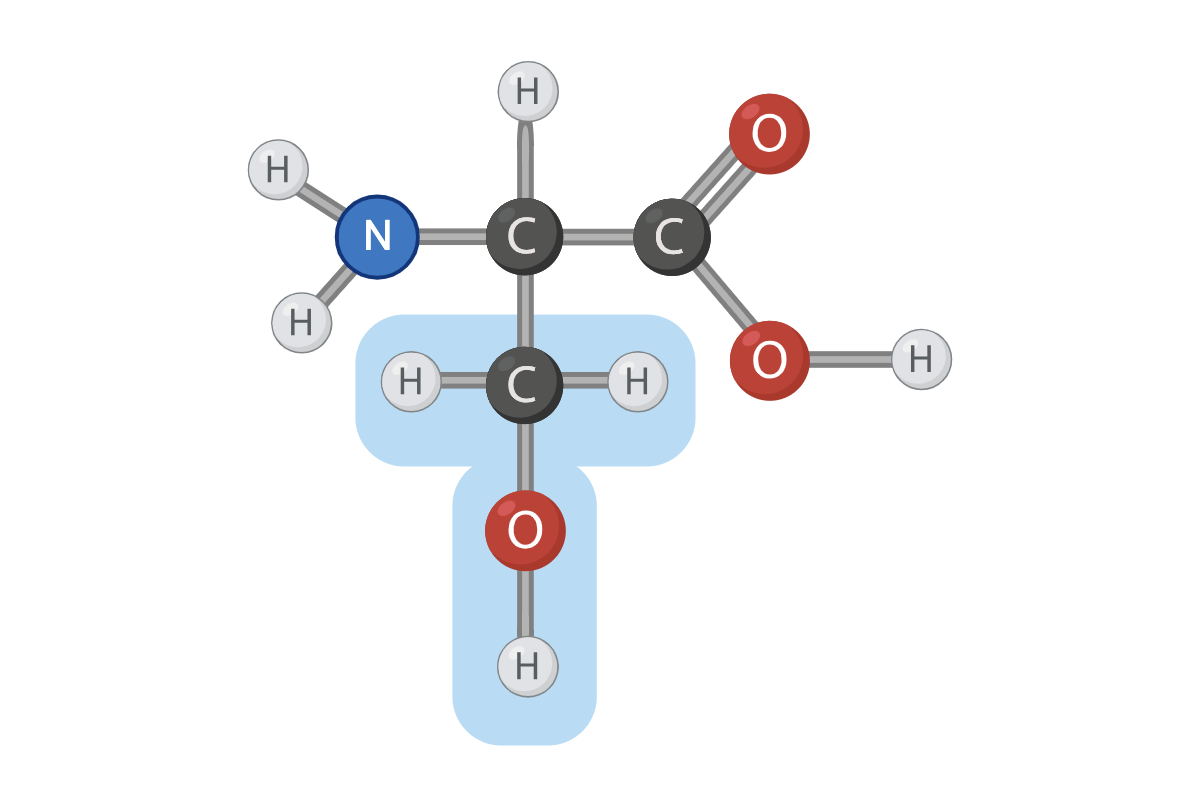
True or False? The R group of this amino acid can form hydrogen bonds
True
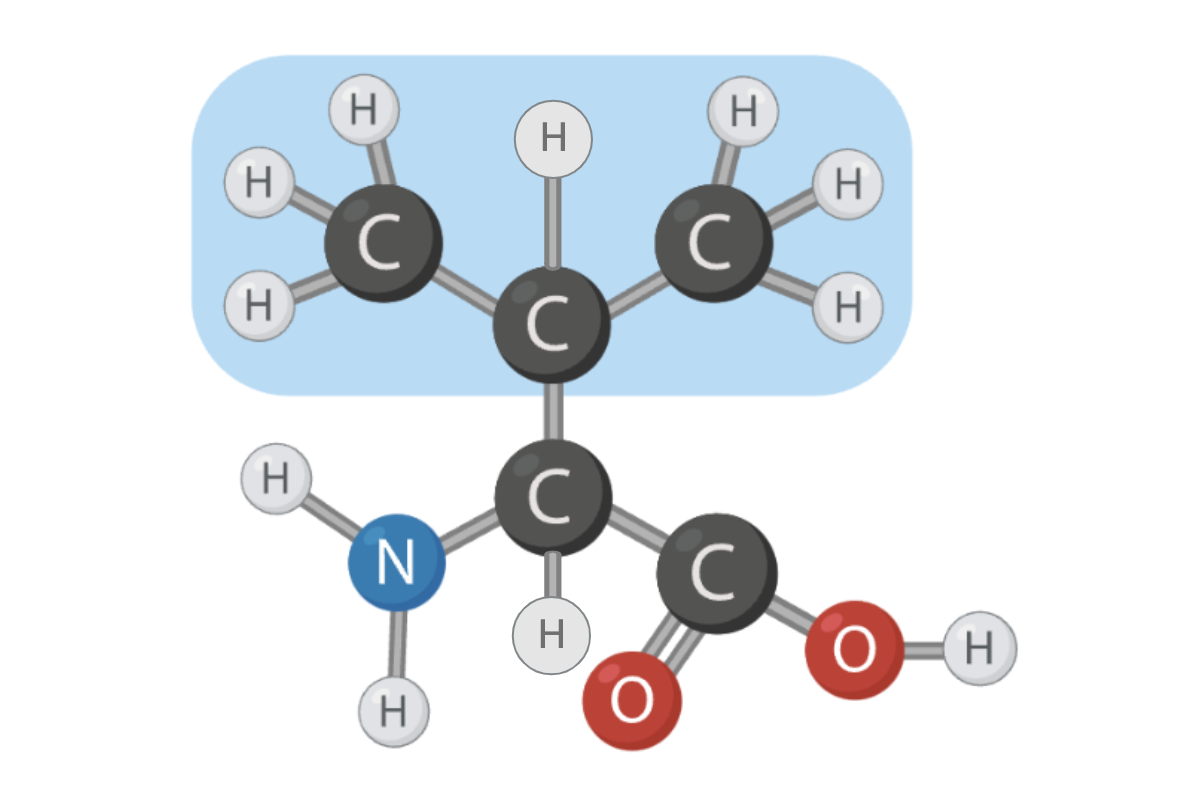
True or False? The R group of this amino acid can form hydrogen bonds.
False
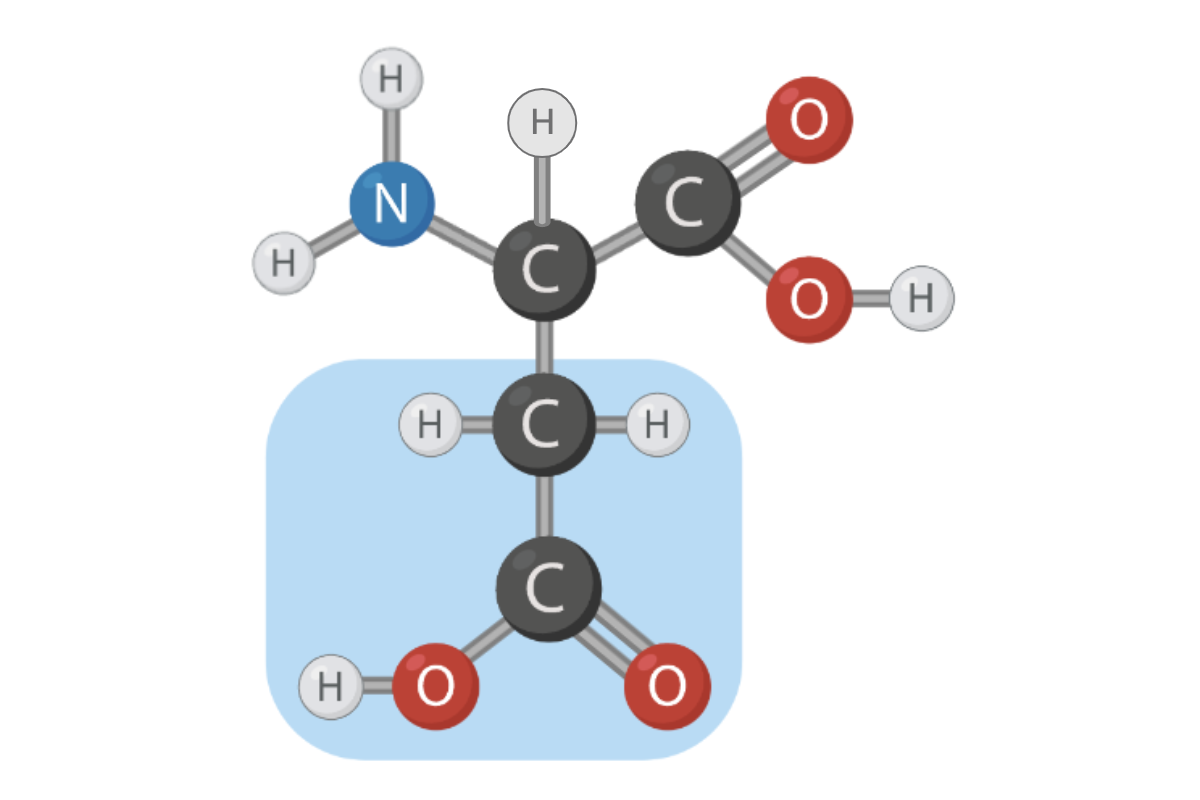
True or False? The R group of this amino acid can form hydrogen bonds.
True
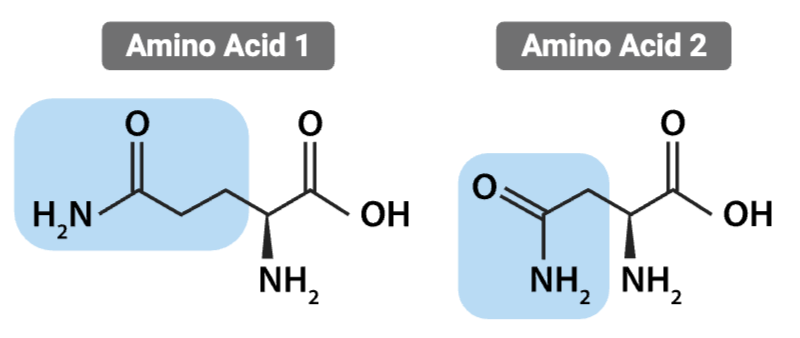
What is the most likely interaction between the R groups of these amino acids?
Hydrogen bond
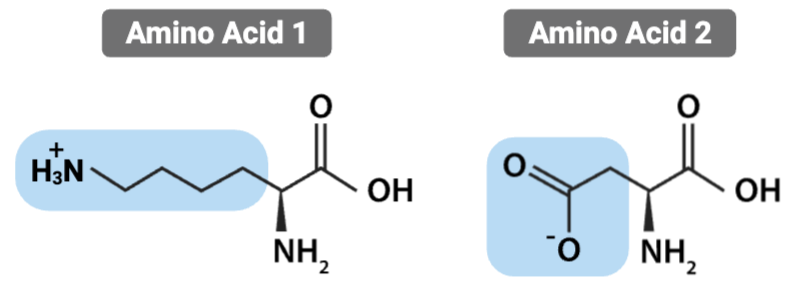
What is the most likely interaction between the R groups of these amino acids?
Ionic bond
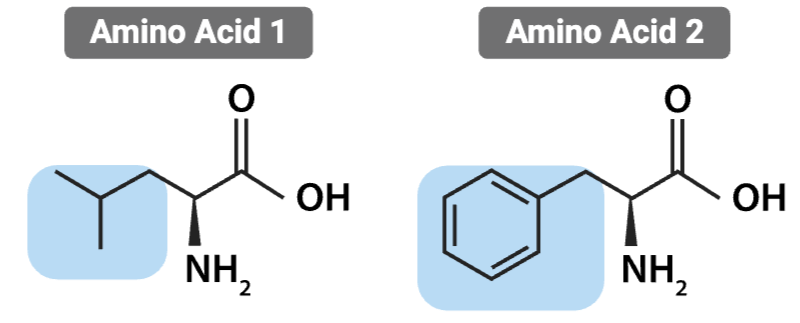
What is the most likely interaction between the R groups of these amino acids?
Hydrophobic interaction
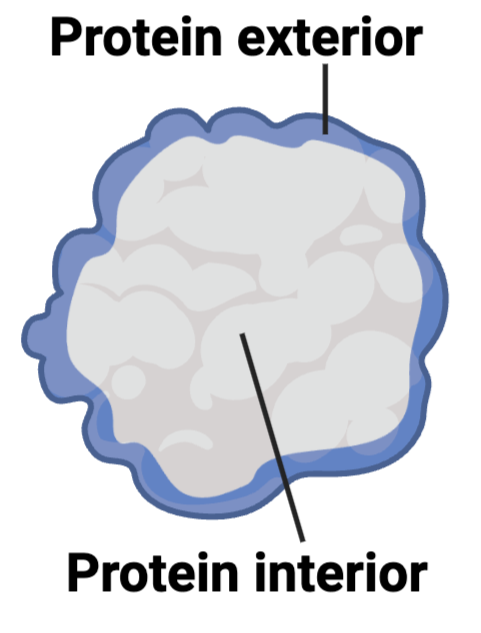
What are the most likely chemical properties of the amino acids at the interior and the amino acids on the exterior of the protein?
a. interior = hydrophilic; exterior = hydrophobic
b. interior = hydrophobic; exterior = hydrophobic
c. interior = hydrophilic; exterior = hydrophilic
d. interior = hydrophobic; exterior = hydrophilic
d. interior = hydrophobic; exterior = hydrophilic
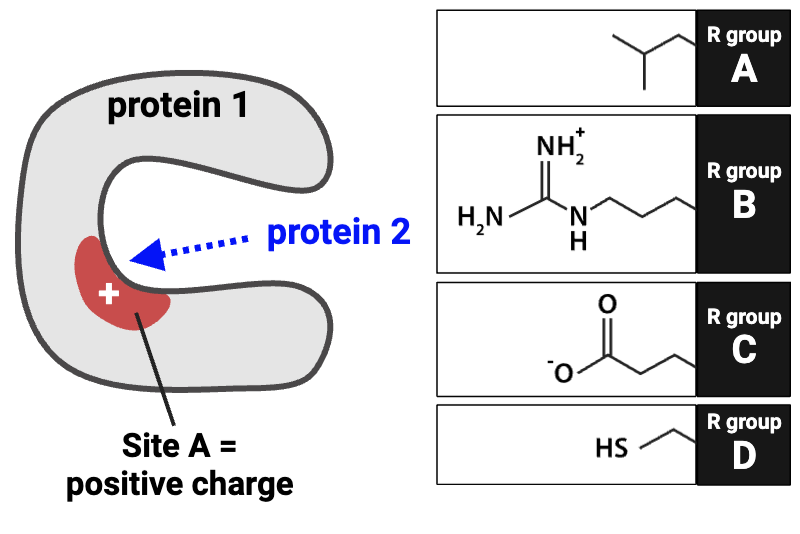
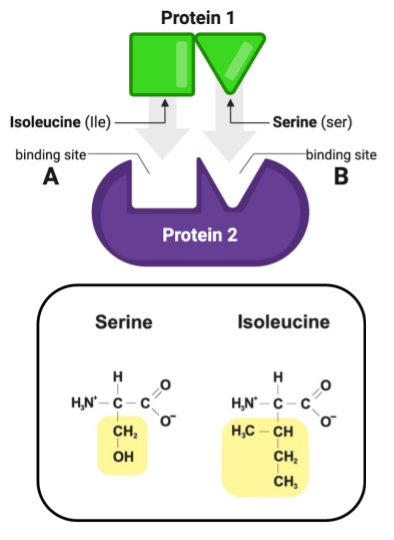
Which R group on protein 2 (A-D) would cause it to bind to Site A with the greatest affinity?
R group C
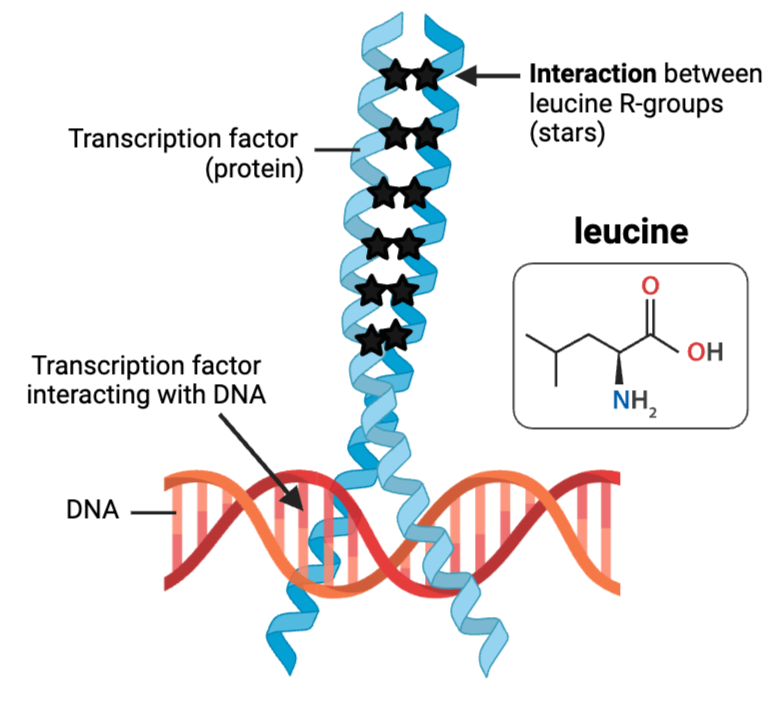
What kind of interactions enable these leucine molecules to contribute to the structure of this protein?
a. hydrogen bond
b. hydrophobic interaction
c. ionic bond
d. nonpolar covalent bond
e. polar covalent bond
b. hydrophobic interaction
The amino acids at a binding site of a protein have polar R groups. Researchers designed a drug that could bind to this site.
Which of the following chemical properties could describe a drug that interacts with the binding site of the protein? Select all that apply.
a. negatively charged
b. nonpolar
c. polar
d. positively charged
a. negatively charged
c. polar
d. positively charged
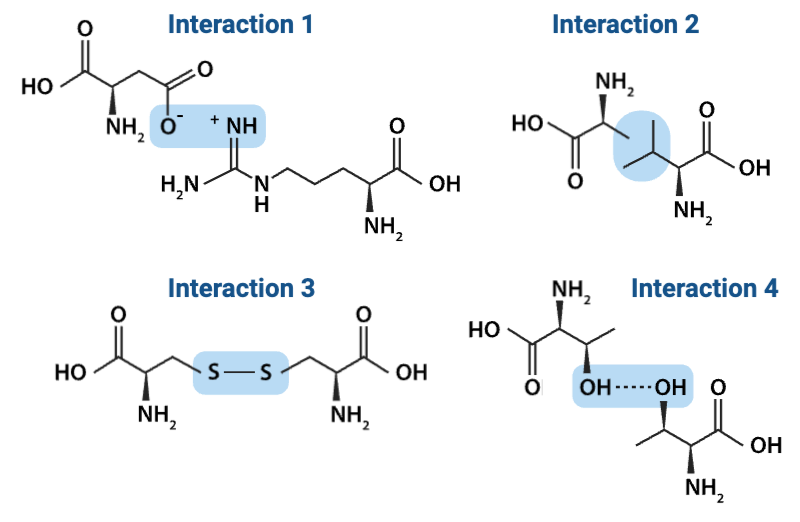
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
a. Interaction 1
b. Interaction 2
b. Interaction 2
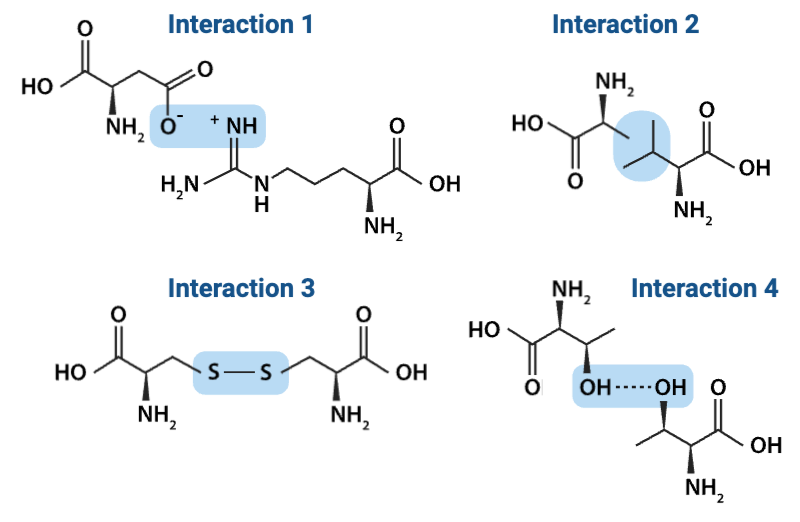
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
a. Interaction 1
b. Interaction 4
b. Interaction 4
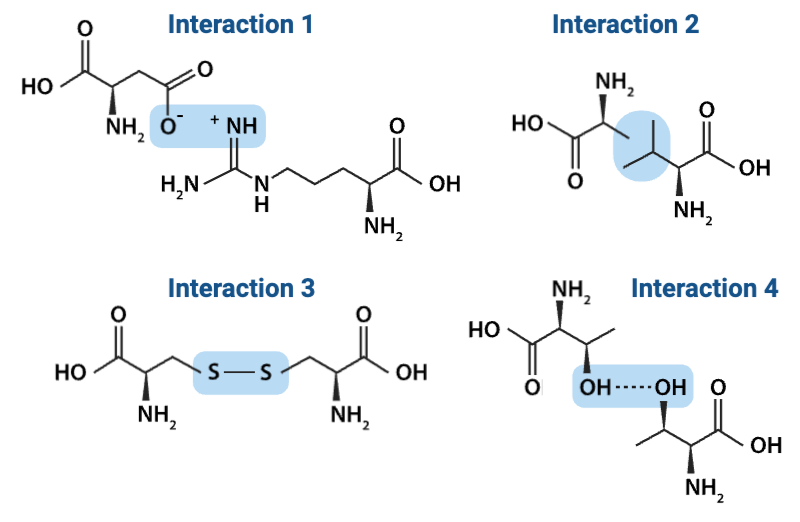
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
a. Interaction 2
b. Interaction 3
a. Interaction 2
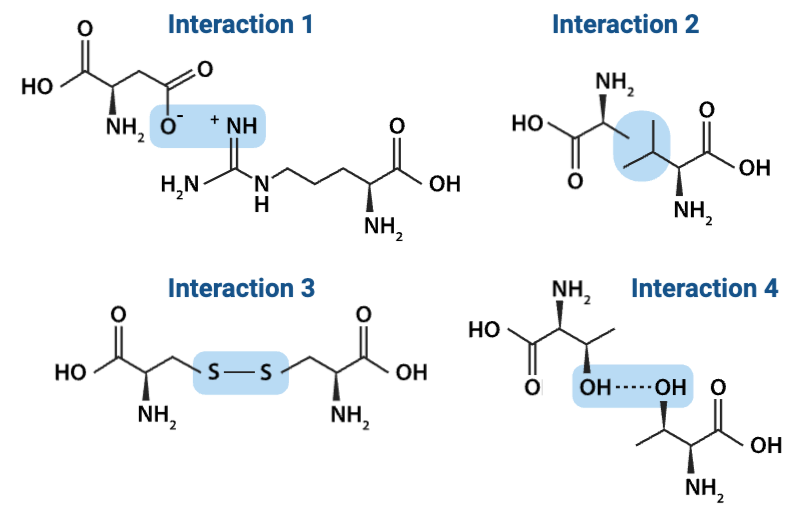
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
a. Interaction 2
b. Interaction 4
a. Interaction 2
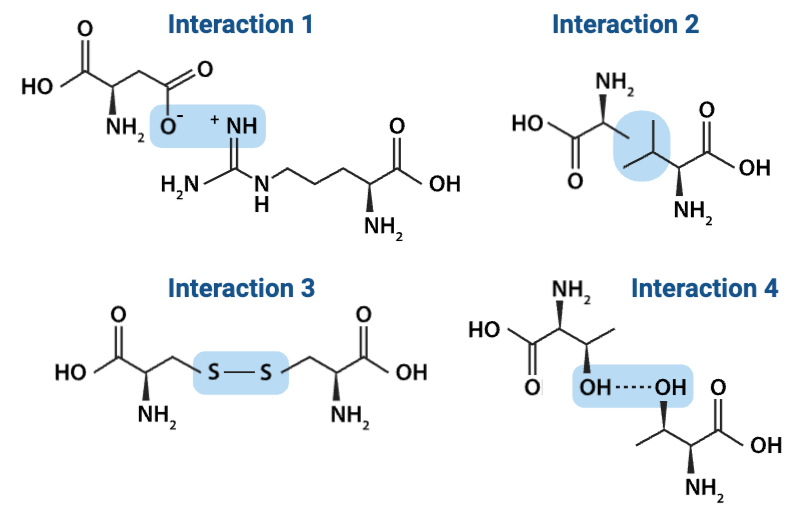
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
a. Interaction 3
b. Interaction 4
b. Interaction 4
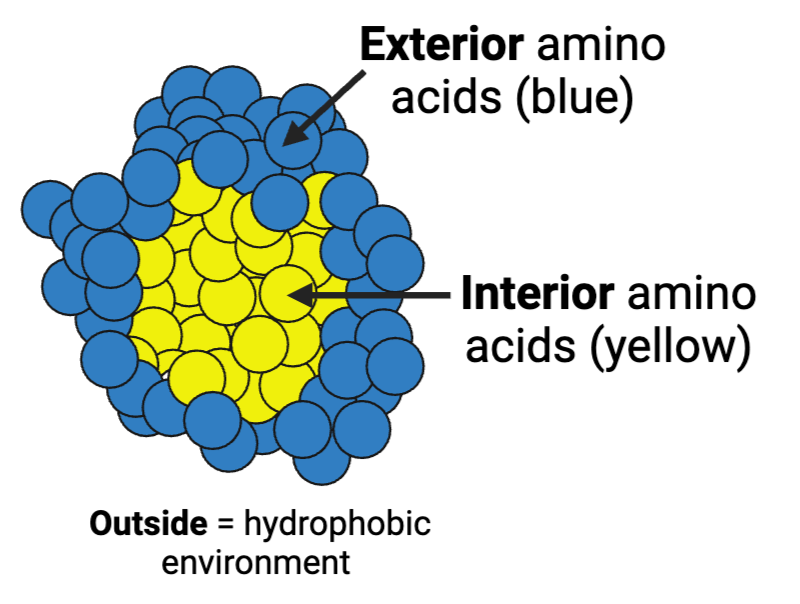
What are the most likely chemical properties of the amino acids at the interior and the amino acids on the exterior of the enzyme?
a. interior = hydrophilic; exterior = hydrophobic
b. interior = hydrophobic; exterior = hydrophilic
c. interior = hydrophobic; exterior = hydrophobic
d. interior = hydrophilic; exterior = hydrophilic
a. interior = hydrophilic; exterior = hydrophobic
a. Site A = nonpolar, Site B = nonpolar
b. Site A = polar, Site B = polar
c. Site A = nonpolar, Site B = polar
d. Site A = polar, Site B = nonpolar
c. Site A = nonpolar, Site B = polar
The amino acids on the exterior of a protein have positively charged R groups. Researchers need to design a drug that will bind to this protein.
Which chemical property would enable the drug to bind most strongly to the exterior of the protein?
a. negatively charged
b. nonpolar
c. polar
d. positively charged
a. negatively charged
The amino acids at the binding site of a protein have y hydrophobic R groups. Researchers need to design a drug that can interact with the binding site of the protein.
Which chemical property would enable the drug to interact most strongly with the binding site?
a. negatively charged
b. nonpolar
c. polar
d. positively charged
b. nonpolar
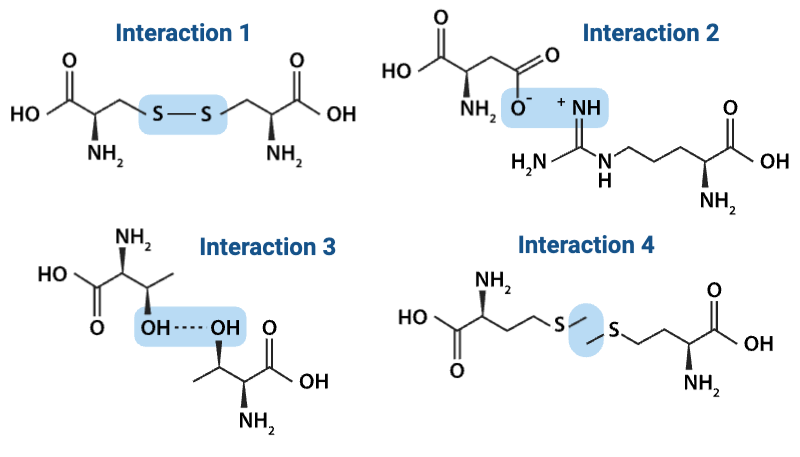
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
a. Interaction 1
b. Interaction 3
b. Interaction 3
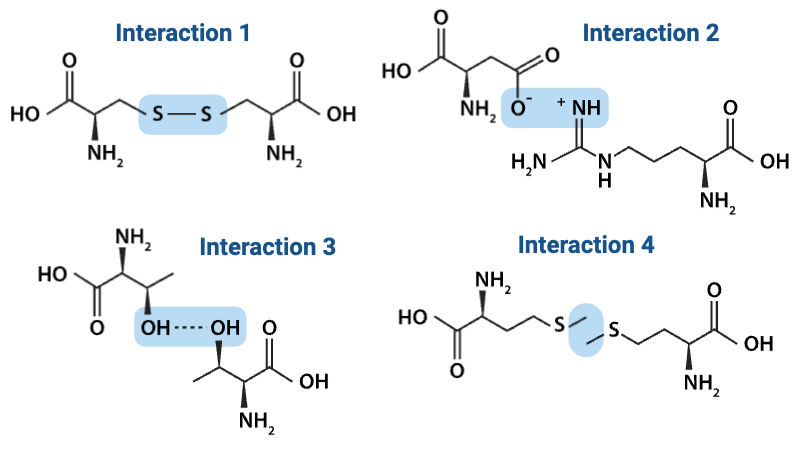
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
a. Interaction 1
b. Interaction 4
b. Interaction 4
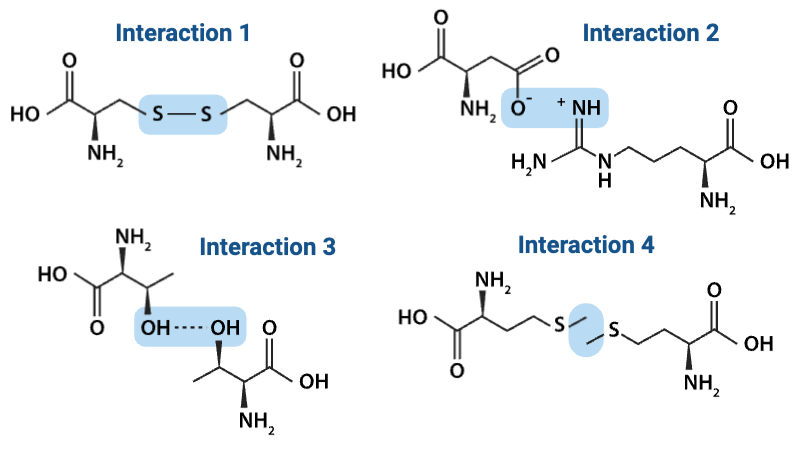
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
a. Interaction 2
b. Interaction 3
b. Interaction 3
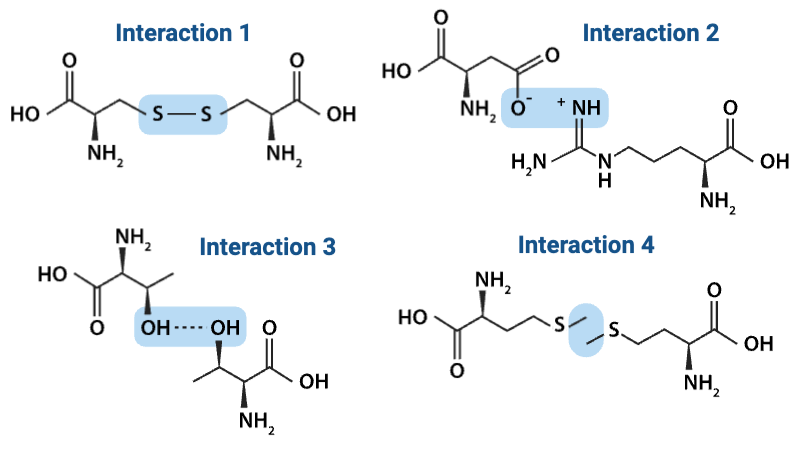
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
a. Interaction 2
b. Interaction 4
b. Interaction 4
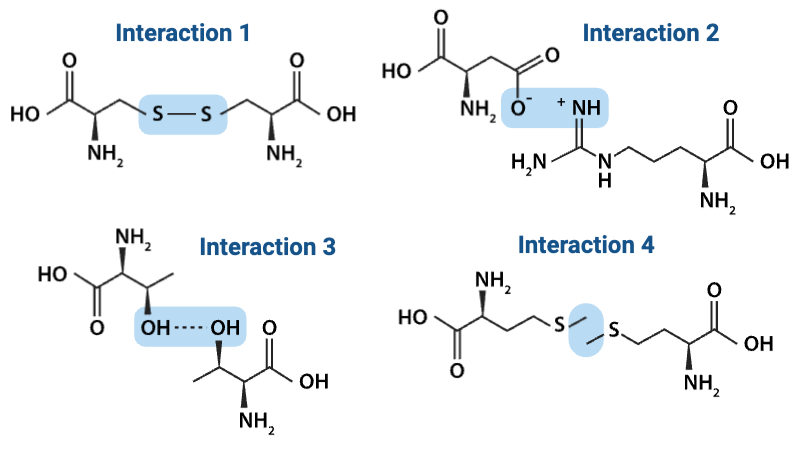
Which interaction is more likely to be disrupted by an increase in temperature?
a. Interaction 3
b. Interaction 4
b. Interaction 4
Which term best describes a molecule that participates in a chemical reaction catalyzed by a protein?
a. active site
b. enzyme
c. affinity
d. product
e. specificity
f. substrate
f. substrate
Which term best describes a molecule created when a protein catalyzes a reaction?
a. active site
b. enzyme
c. affinity
d. product
e. specificity
f. substrate
d. product
Which term best describes a protein that speeds the rate of a chemical reaction by lowering the energy required.
a. active site
b. enzyme
c. affinity
d. product
e. specificity
f. substrate
b. enzyme
Which term best describes a site on a protein where a substrate can bind?
a. active site
b. enzyme
c. affinity
d. product
e. specificity
a. active site
Which term best describes the ability of a protein to bind a specific type of molecules?
a. active site
b. enzyme
c. affinity
d. product
e. specificity
f. substrate
e. specificity
Which term best describes the likelihood that two molecules will interact?
a. active site
b. enzyme
c. affinity
d. product
e. specificity
f. substrate
c. affinity
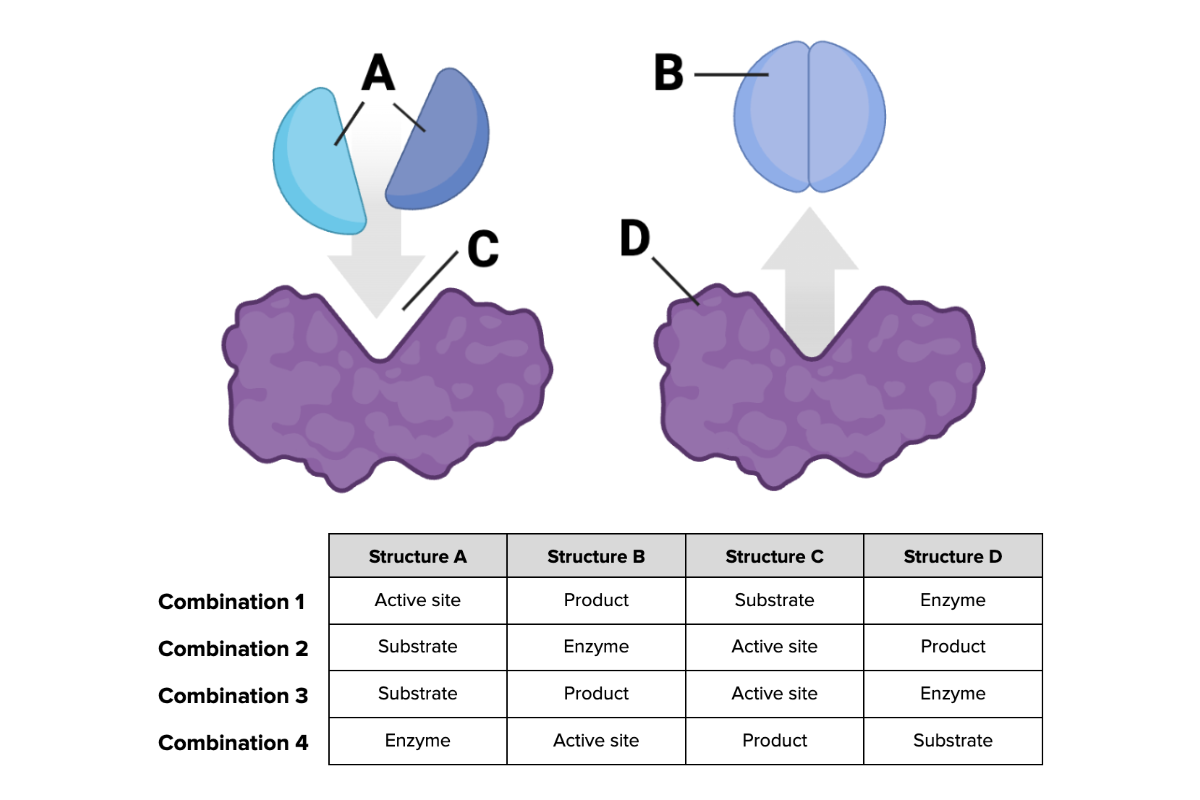
Which combination of terms (1 through 4) in the table provided accurately describes each structure shown in the figure? The terms are as follows: active site, enzyme, product, and substrate.
Combination 3
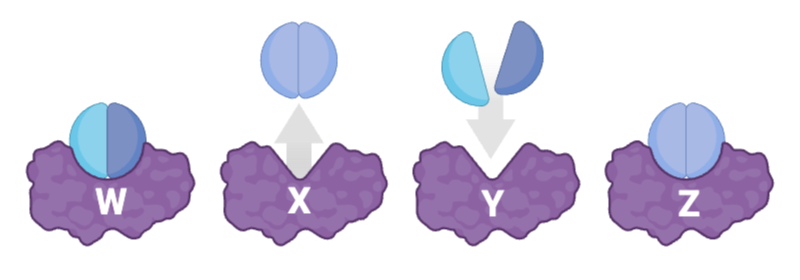
Which sequence correctly orders these stages, from the initial step of catalysis to the final step?
Y, W, Z, X
The four statements below describe steps of an enzyme catalyzing a reaction. What is the correct order of the statements, from the initial step to the final step, in catalysis?
Statement 1: The enzyme changes its conformation, enabling the product to leave the active site.
Statement 2: One or more substrates bind to an active site of the enzyme.
Statement 3: The enzyme changes its conformation, creating an environment that favors a reaction involving the substrate(s).
Statement 4: The enzyme catalyzes a reaction, converting the substrate(s) to the product(s).
2, 3, 4, 1
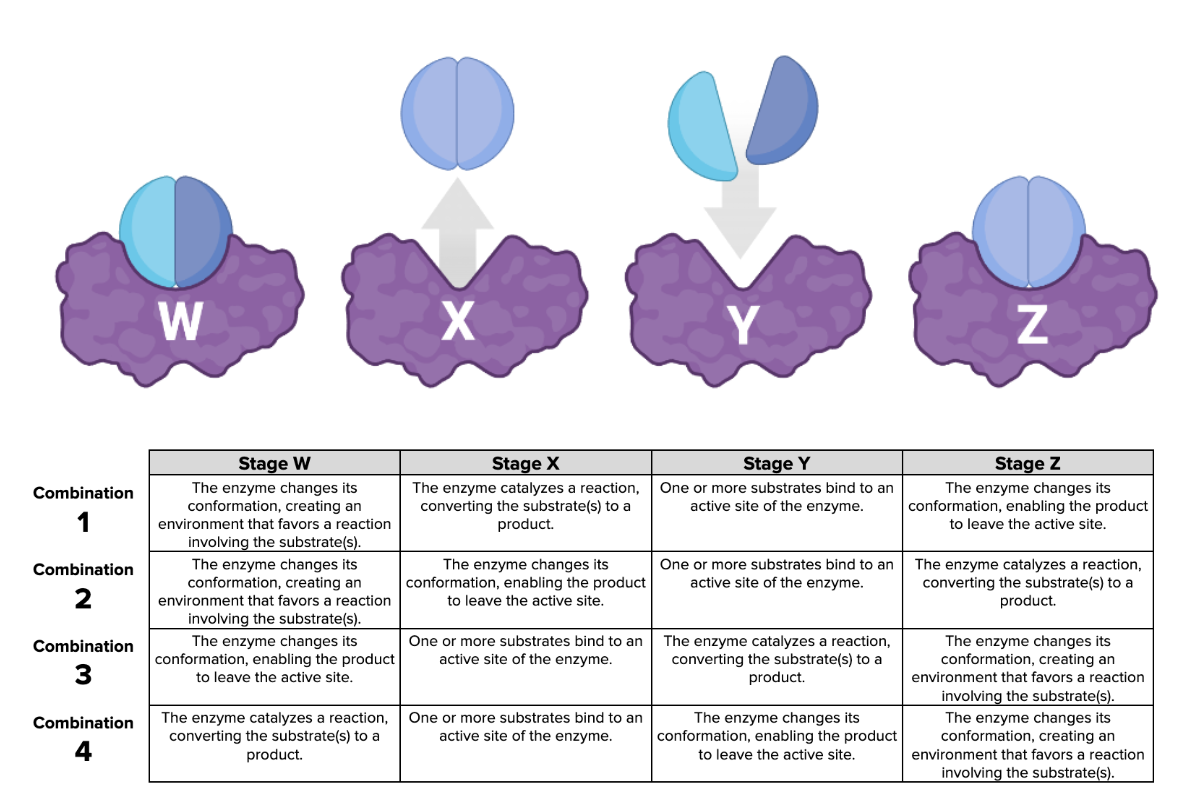
Which combination of descriptions (1, 2, 3, or 4) in the table accurately describes each stage in the figure?
Combination 2
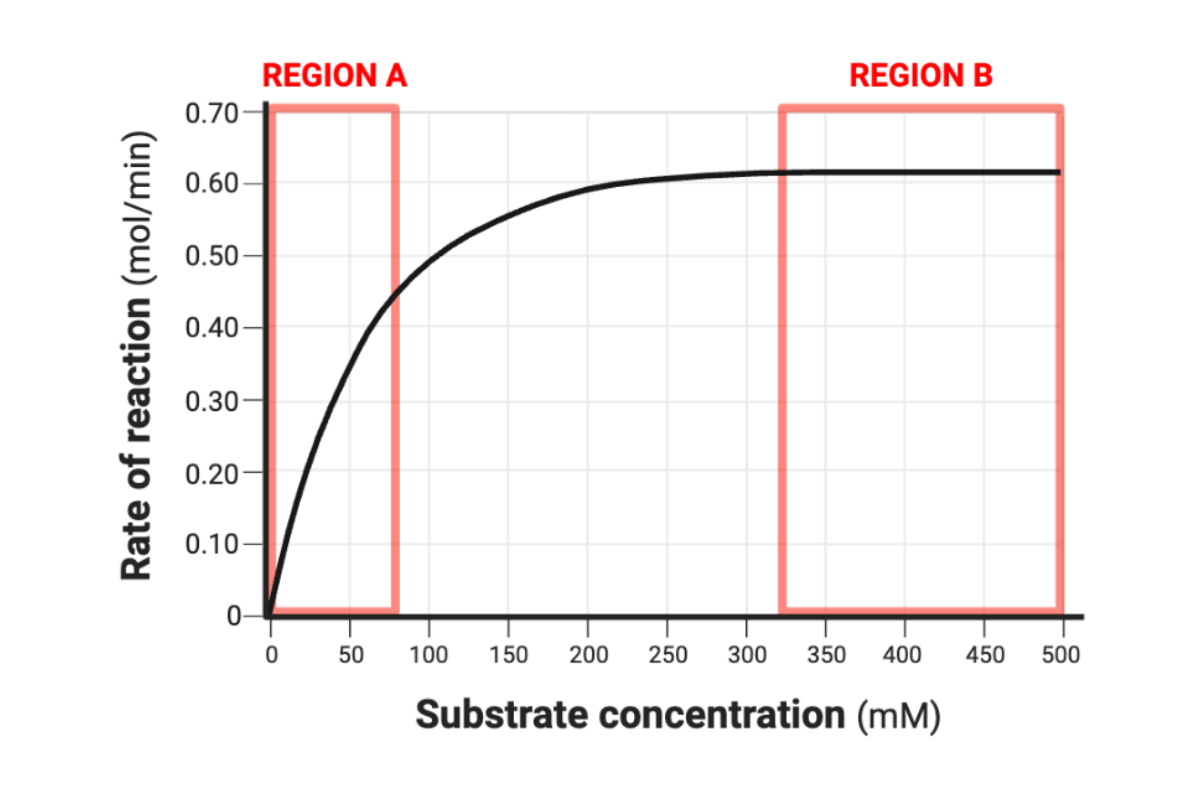
Complete the following sentence. The rate of reaction can be predicted between substrate concentrations of __________.
0 mM and 500 mM
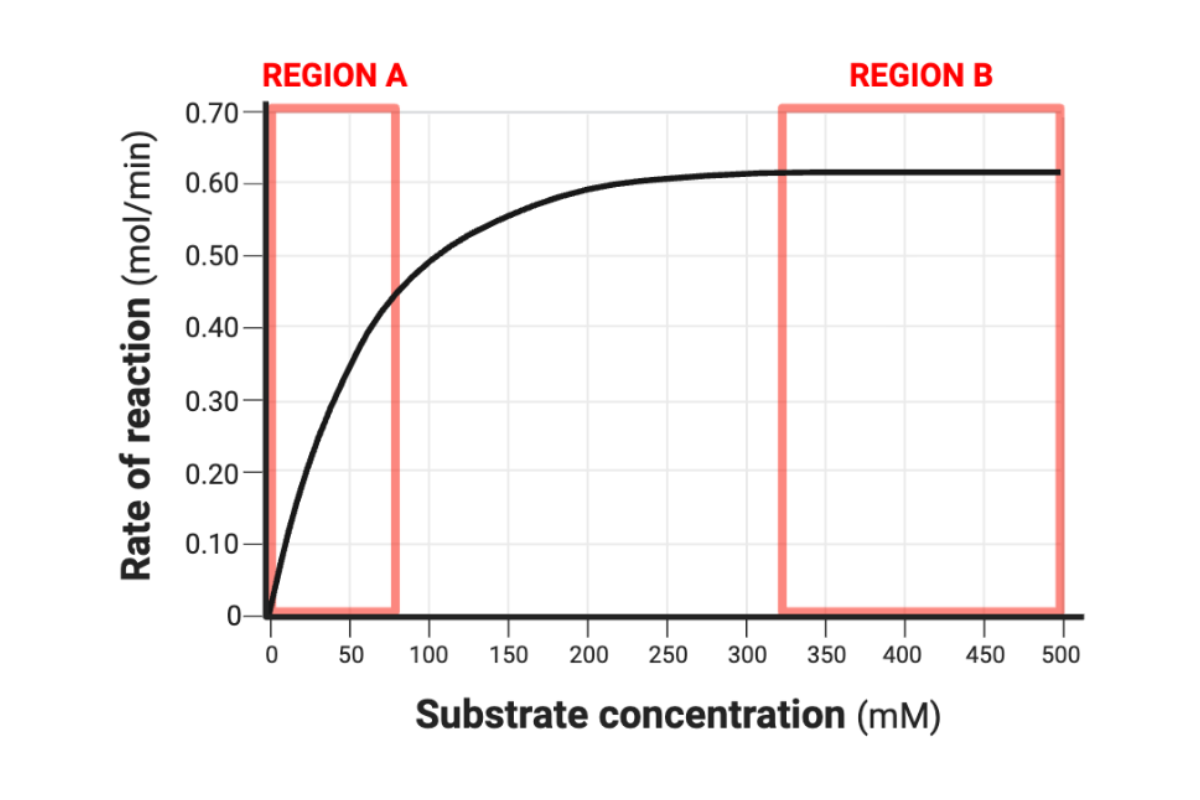
Complete the following sentence. In Region A, an increase in the substrate concentration would ______ the rate of reaction.
increase