Chapter 2: Chemical Principles (made by Natalie)
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Made by Natalie Cartee!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Atomic mass
Number of protons and neutrons
Isotopes
Atoms with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
Atomic number
number of protons
Hydrogen's mass?
1
Carbon atomic # and mass?
6 & 12
Nitrogen atomic # and mass?
7 & 14
Oxygen atomic # and mass?
8 & 16
Valence electrons
electrons in the outermost shell
Chemical bonds
the attractive forces that hold atoms together
A compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
Cations
lose electrons and have a positive charge
Anions
gain electrons and have a negative charge
Ionic bonds
Formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another
Covalent bonds
Bonds created by sharing electrons with other atoms.
Molecular mass
The sum of the masses of all the atoms in a molecule
Water properties
inorganic, polar molecule, a solvent, hydrogen bonds absorb heat
Hydrogen bonds
Very weak bonds; occurs when a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to an O or N
Chemical reactions
the making and breaking of chemical bonds
Chemical energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds
endergonic
absorb energy
exergonic
release energy
Anabolism
synthesis of molecules in a cell
Catabolism
decomposition reactions in cell
Most organisms grow between what pH?
6.5-8.5
Acids
compounds that form hydrogen ions when dissolved in water (H+)
Bases
substances that dissociate into one or more hydroxide ions (-OH)
Salts
substances that dissociate into cations and anions
inorganic compounds
Compounds that do not contain carbon; small and simple
organic compounds
Compounds that contain carbon attached to a H, N, O
Carbon skeleton
the chain of carbon atoms in an organic molecule
Functional groups
chemical groups attached to carbon skeletons that give compounds their functionality
Macromolecules
polymers consisting of many small repeating molecules called monomers
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules covalently bond to each other with the removal of a water molecule.
Carbohydrates
cell structure and cellular energy, include sugar and starches, consist of C, H, O
Many carbohydrates are what?
Isomers
What are isomers?
Molecules with the same chemical formula, different structure.
Monosaccharides
simple sugars with 3 to 7 carbons
What are 2 examples of monosaccharides?
glucose and deoxyribose
Disaccharides
formed when two monosaccharides are joined in a dehydration synthesis
Disaccharides can be broken down by what?
Hydrolysis
Polysaccharides
consist of tens or hundreds of monosaccharides joined through dehydration synthesis
Examples of polysaccharides
starch, glycogen, dextran, and cellulose
Simple lipids
Fats or triglycerides, contain glycerol and fatty acids
How are simple lipids formed?
Dehydration synthesis
Saturated fat
NO double bonds in a fatty acid
Unsaturated fat
one or more double in a fatty acid
cis
H atoms on the same side of a double bond
trans
H atoms on opposite sides of a double bond
Complex lipids
Contain C, H, and O + P, N, or S
Membranes are made of phospholipids
What does a phospholipid contain?
Glycerol, two fatty acids, and a phosphate group
TRUE OR FALSE: Phospholipids have nonpolar and polar areas.
TRUE
Steroids
four carbon rings with an -OH group attached to one ring
Proteins
Made of C, H, O, N, and sometimes S, essential in cell structure and function
Enzymes
speed up chemical reactions
Transporter proteins
move chemicals across membranes
What do flagella & pilli do?
aid in movement
Amino Acids
subunits in proteins
What is an alpha carbon attached to?
carboxyl group (-COOH), amino group (-NH2), side group
What are the 2 stereoisomers of an amino acid called?
L and D
What form is mostly found in nature?
L
How many amino acids are there?
20 amino acids
Glycine
Gly, G

Alanine
Ala, A
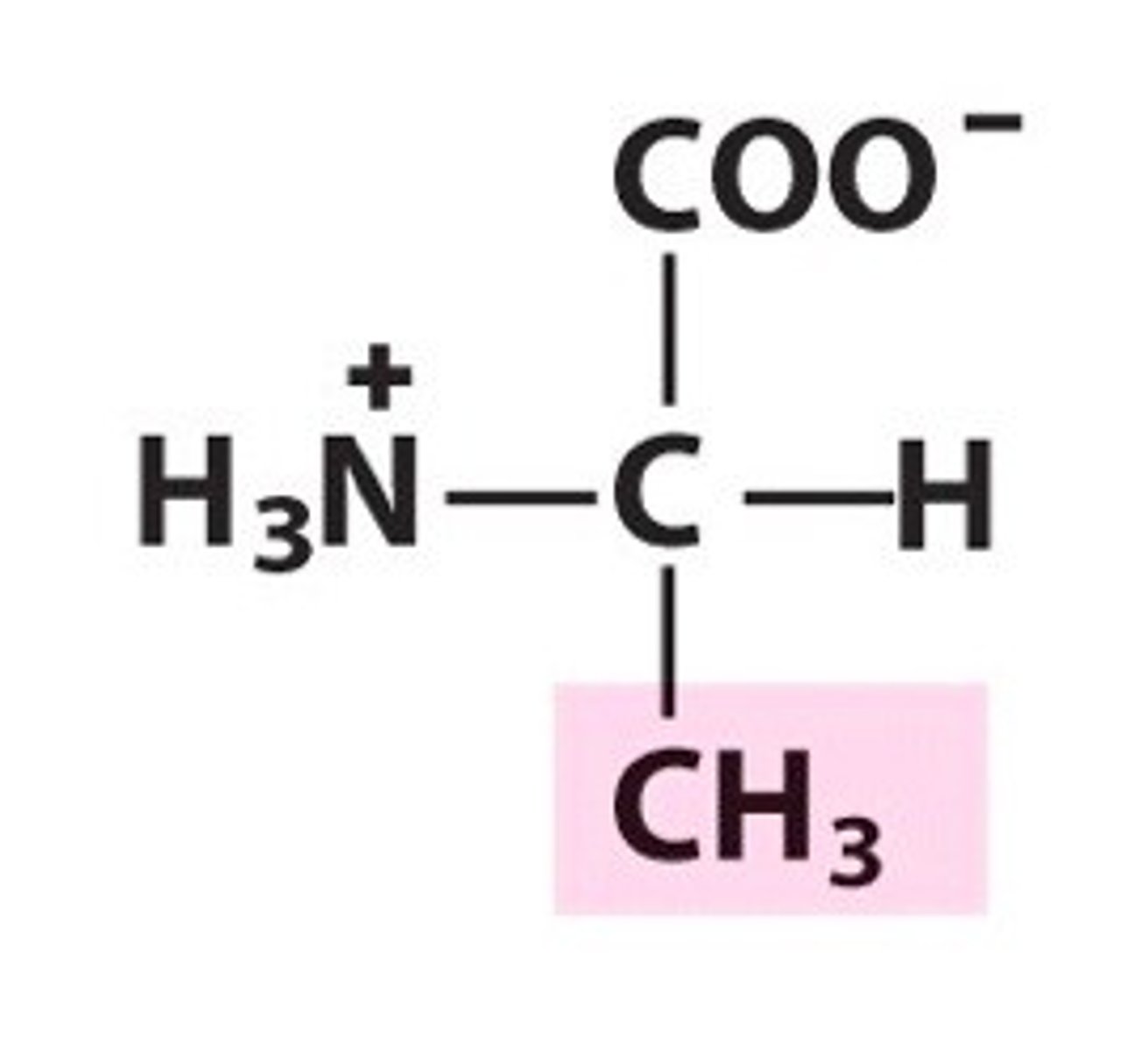
Valine
Val, V
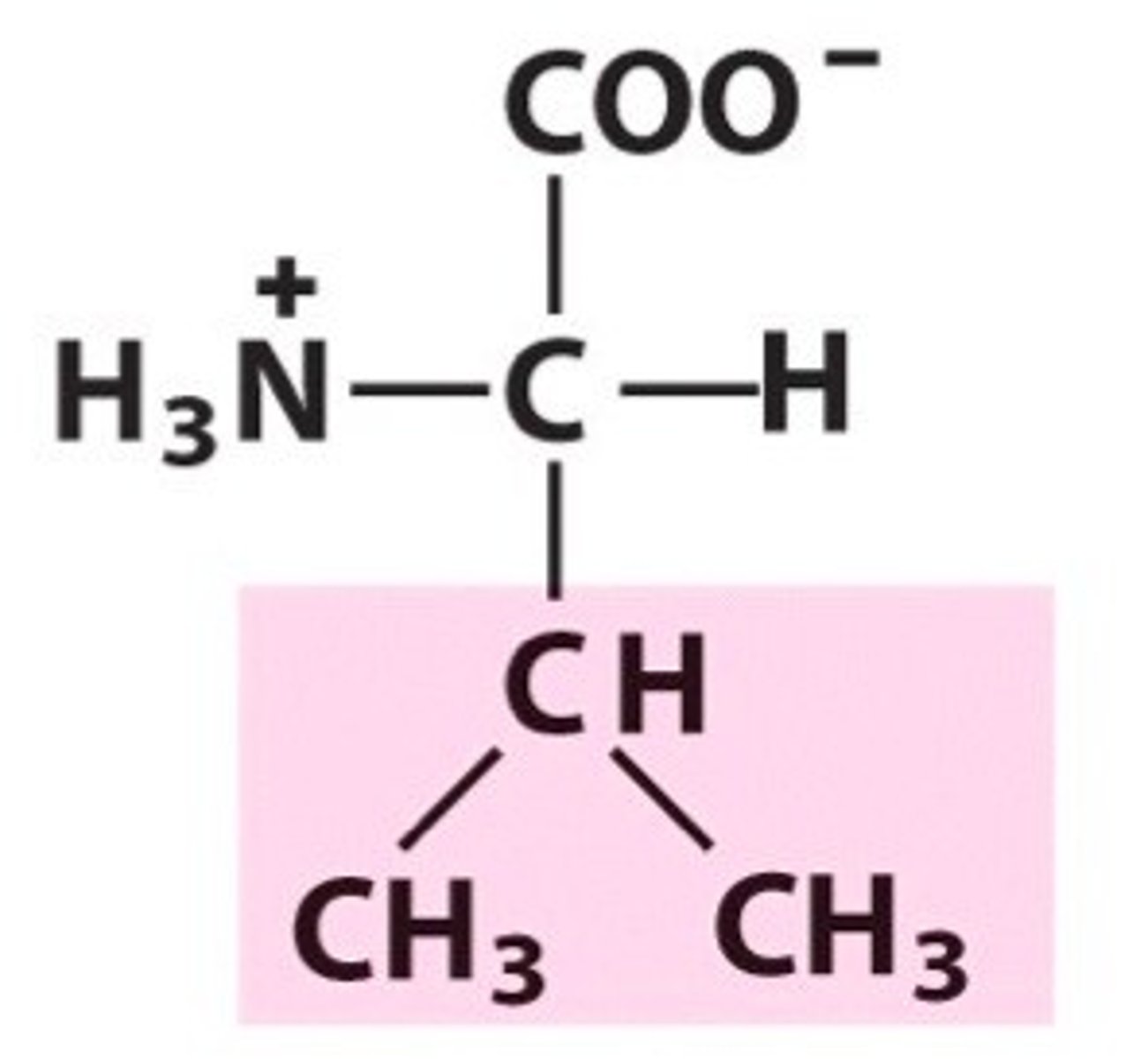
Leucine
Leu, L
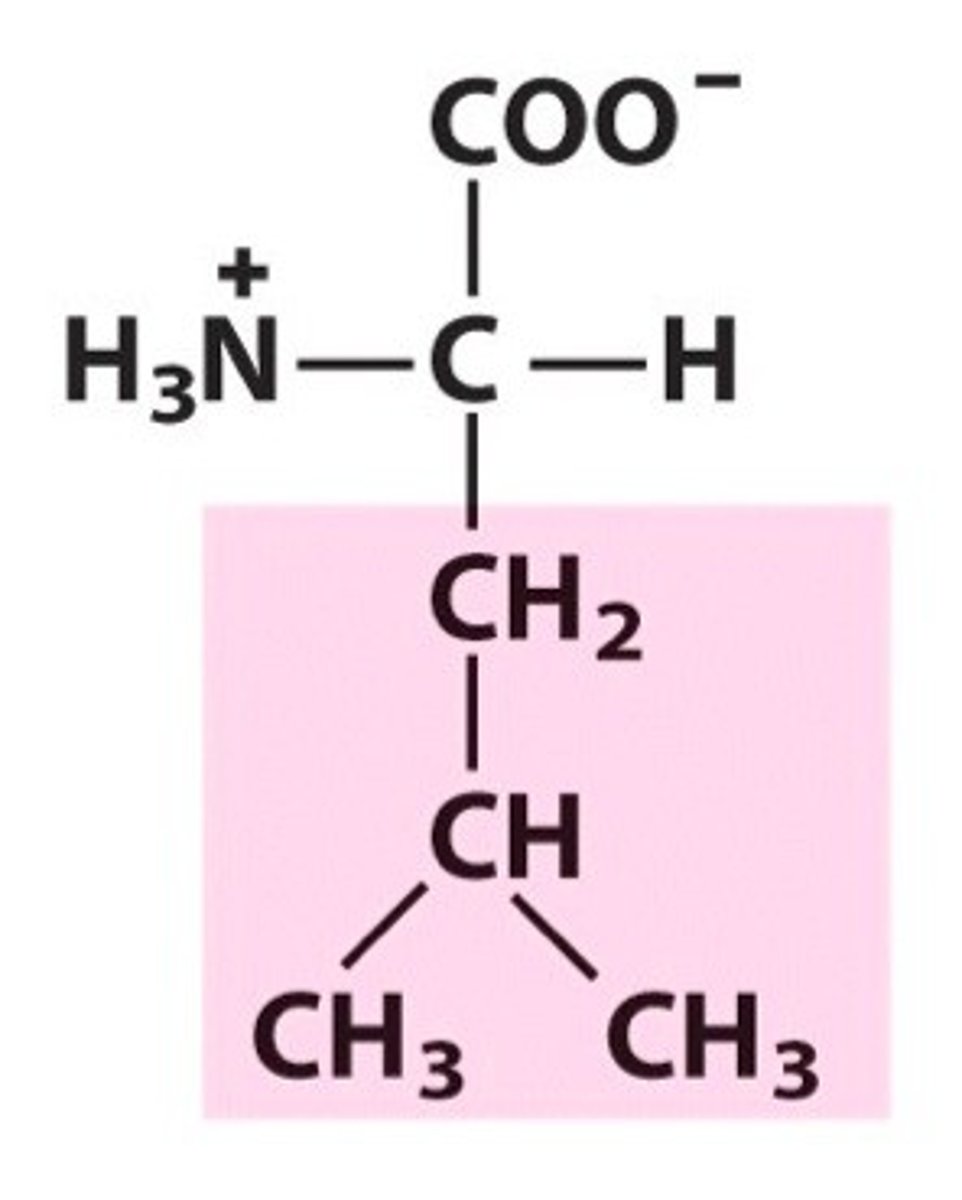
Isoleucine
Ile, I
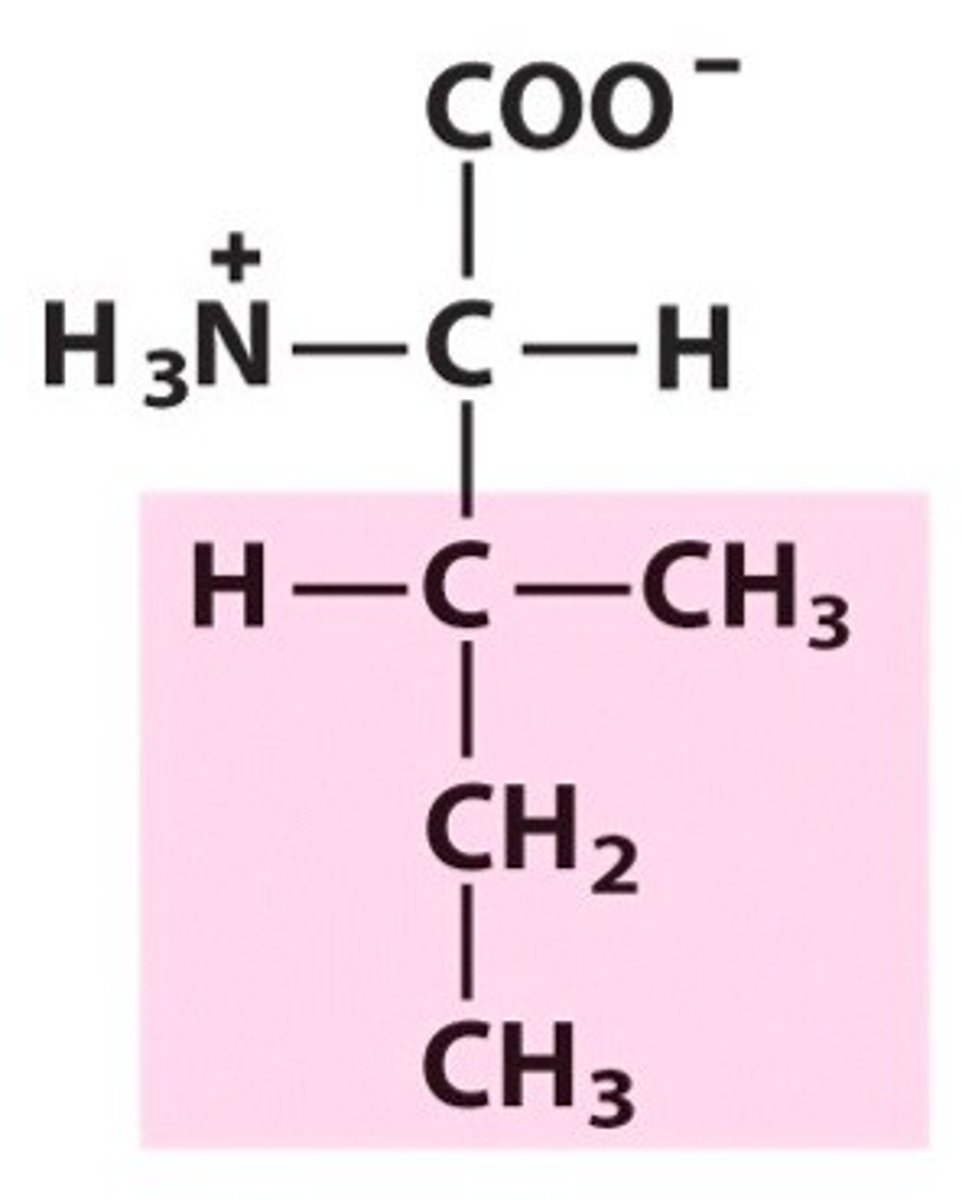
Serine
Ser, S
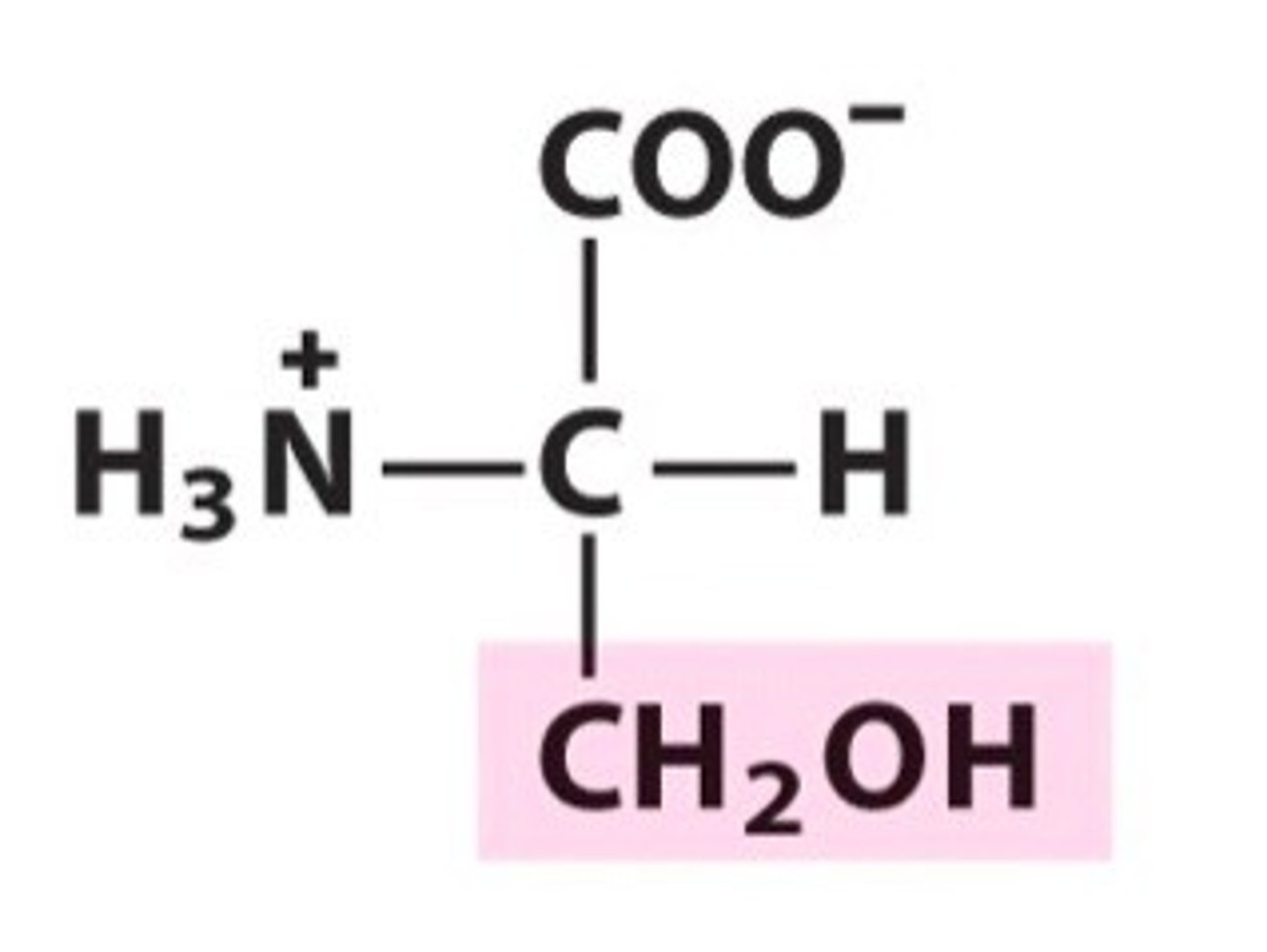
Threonine
Thr, T
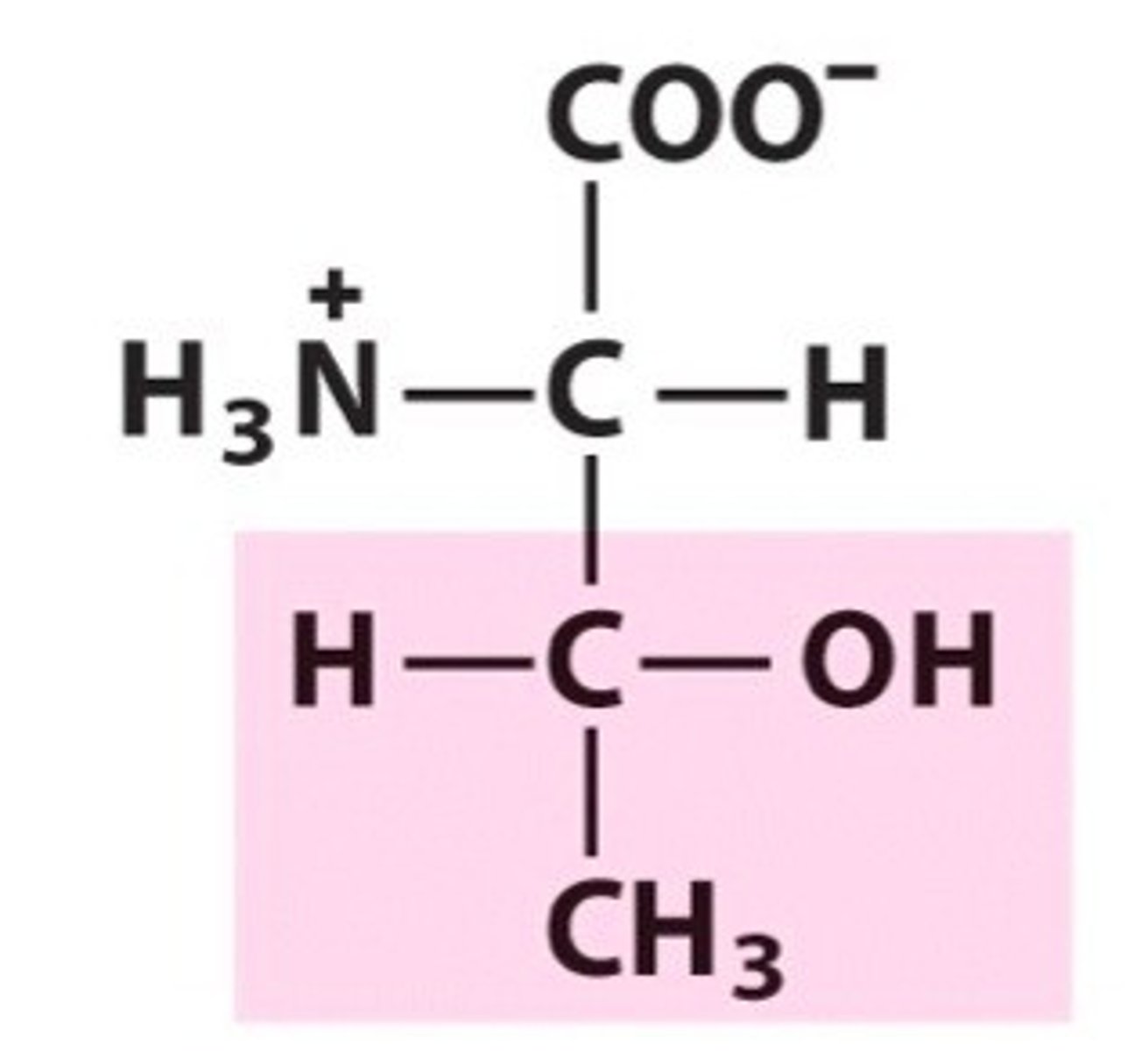
Cysteine
Cys, C
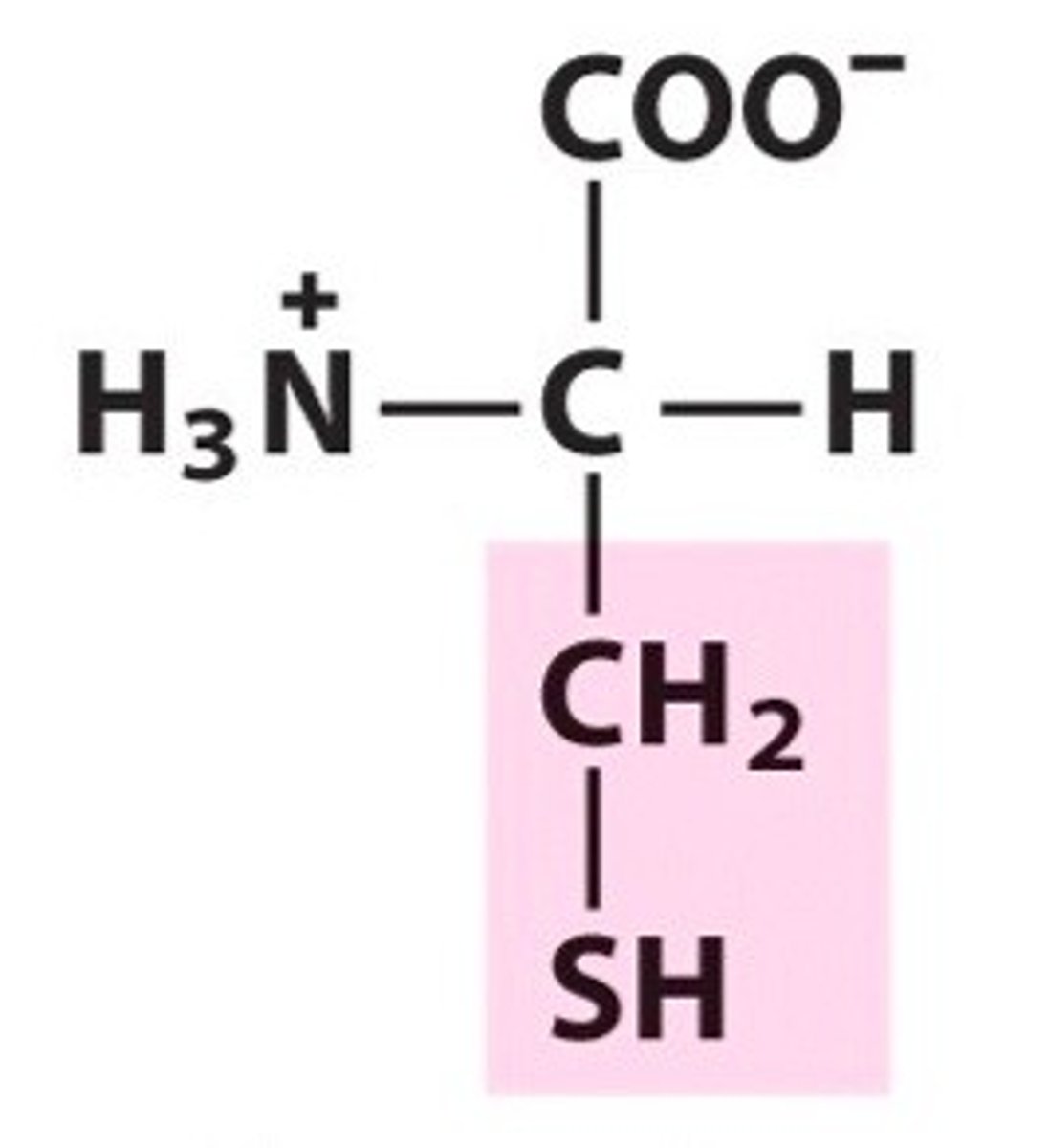
Methionine
Met, M
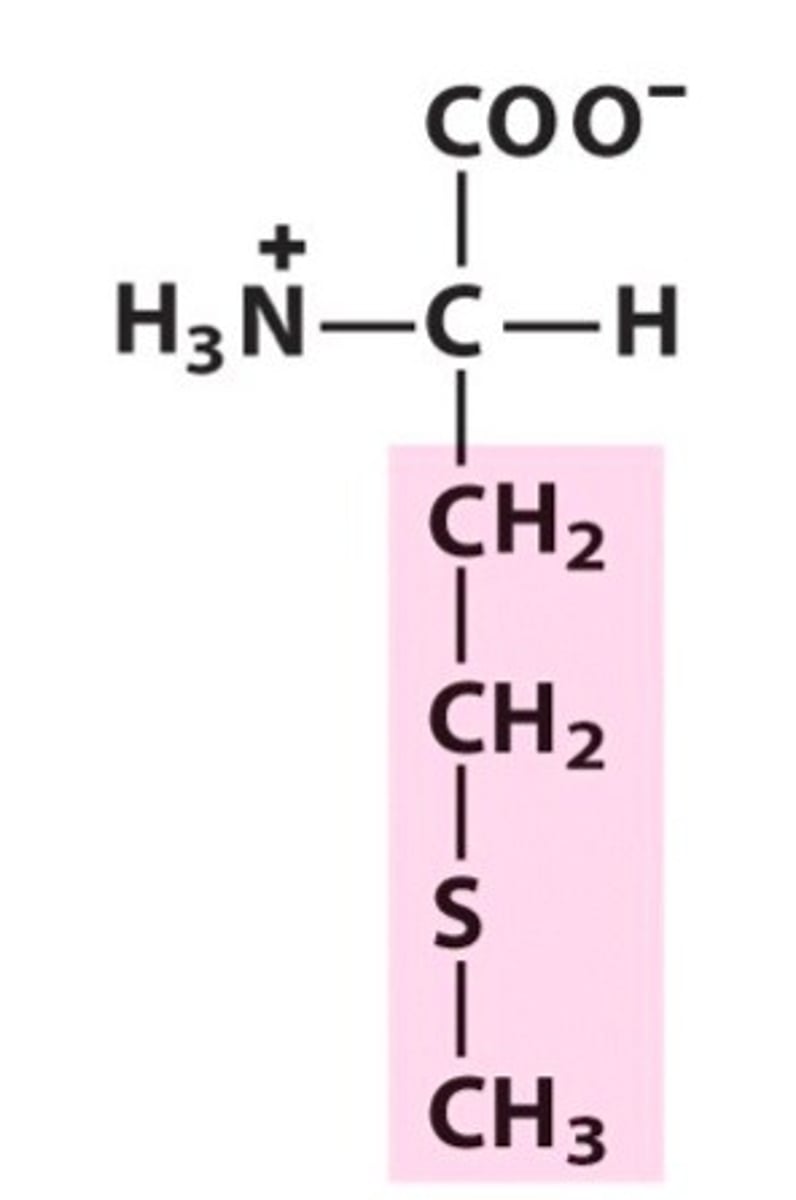
Glutamic acid
Glu, E
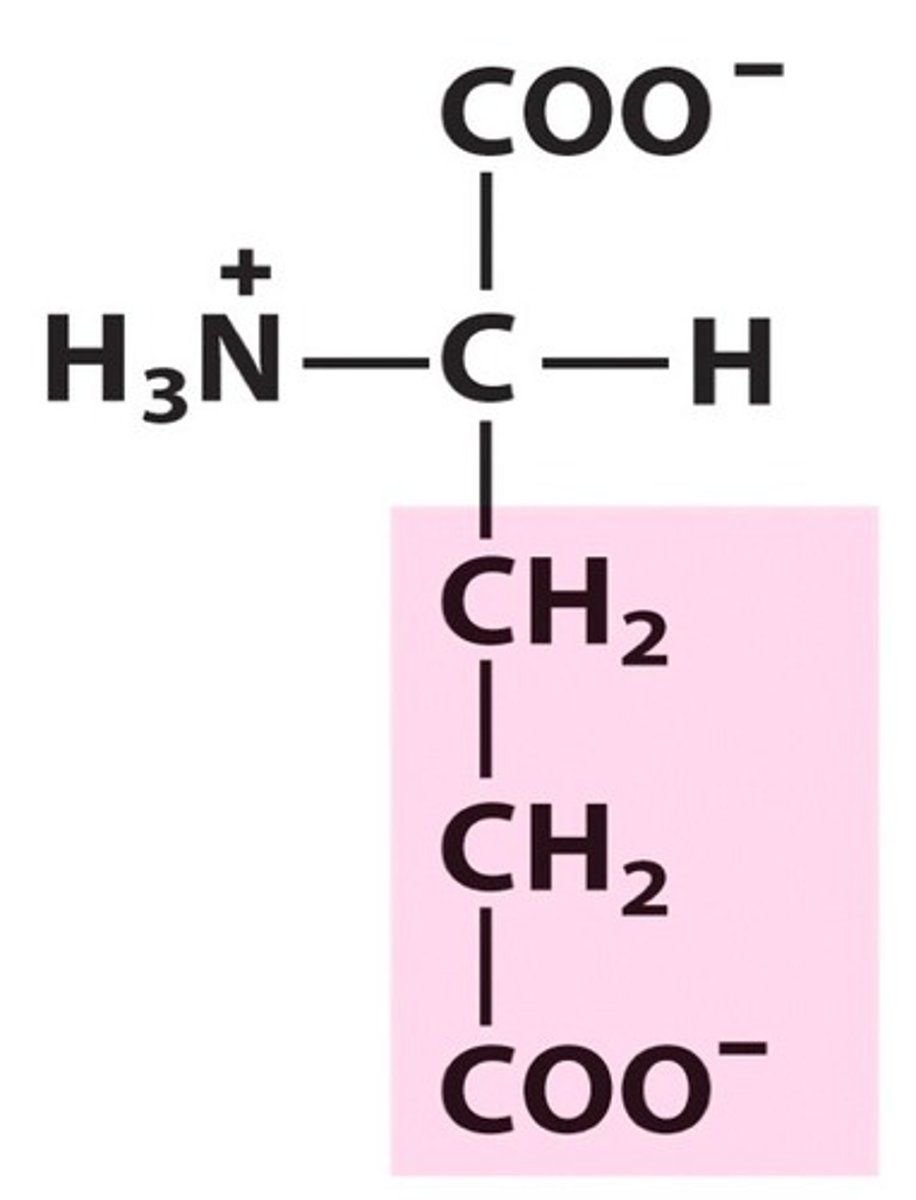
Asparatic Acid
Asp, D
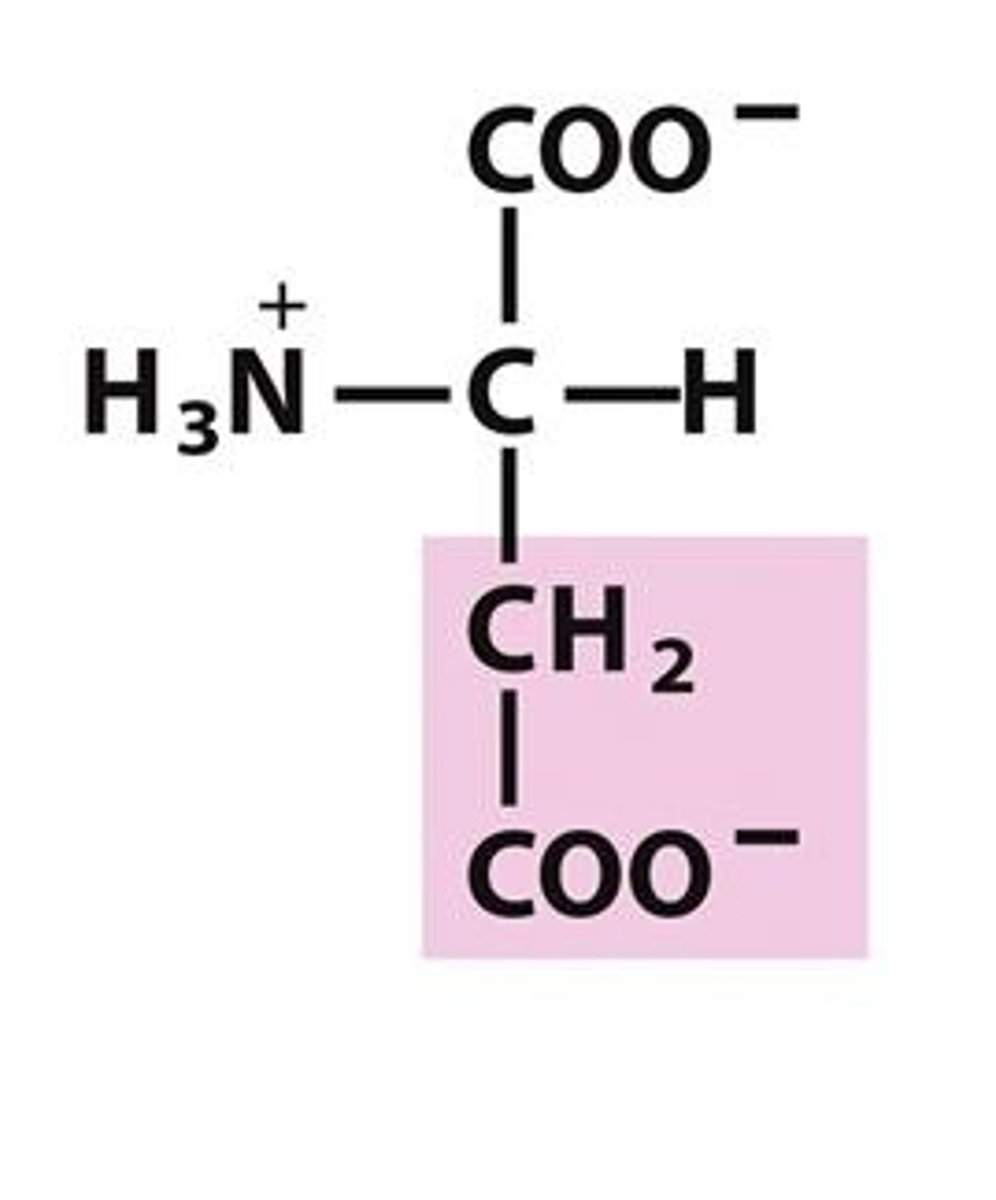
Lysine
Lys, K
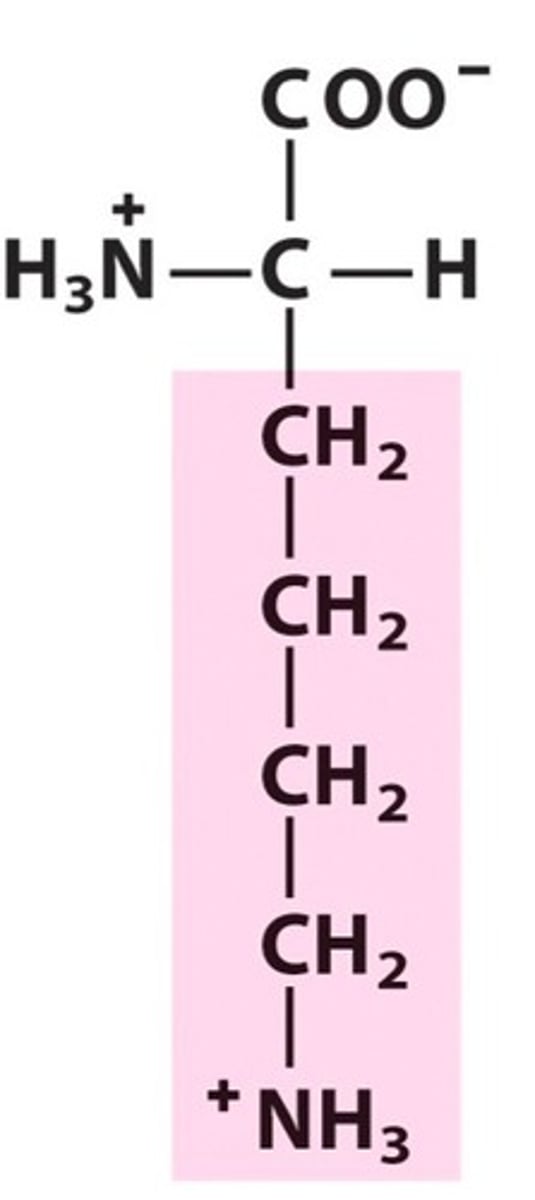
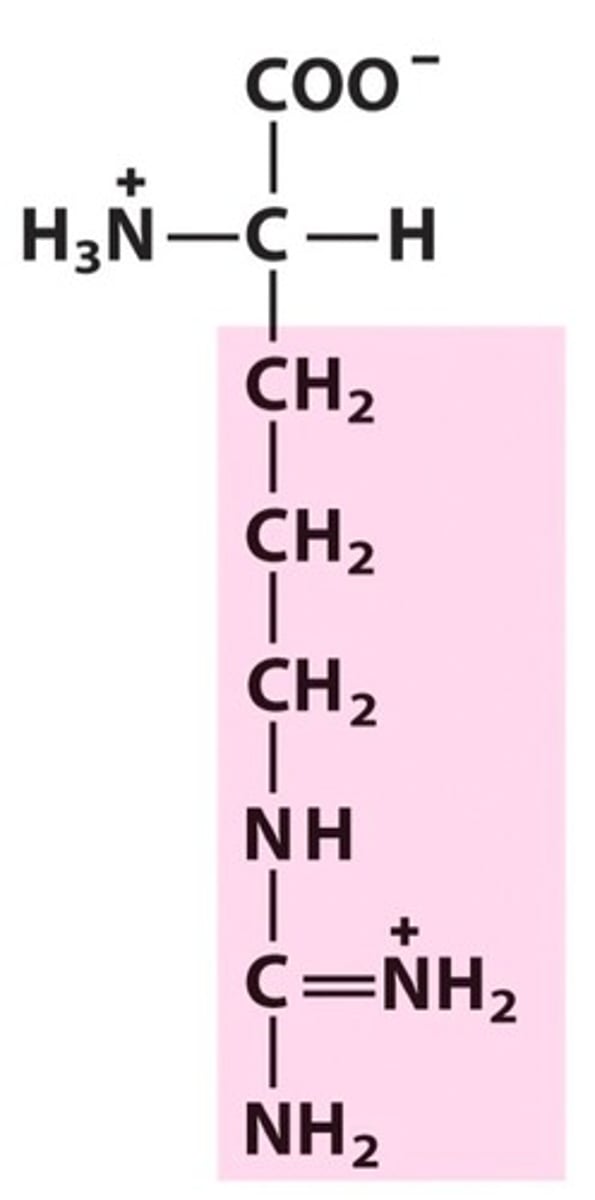
Arginine
Arg, R
Asparagine
Asn, N

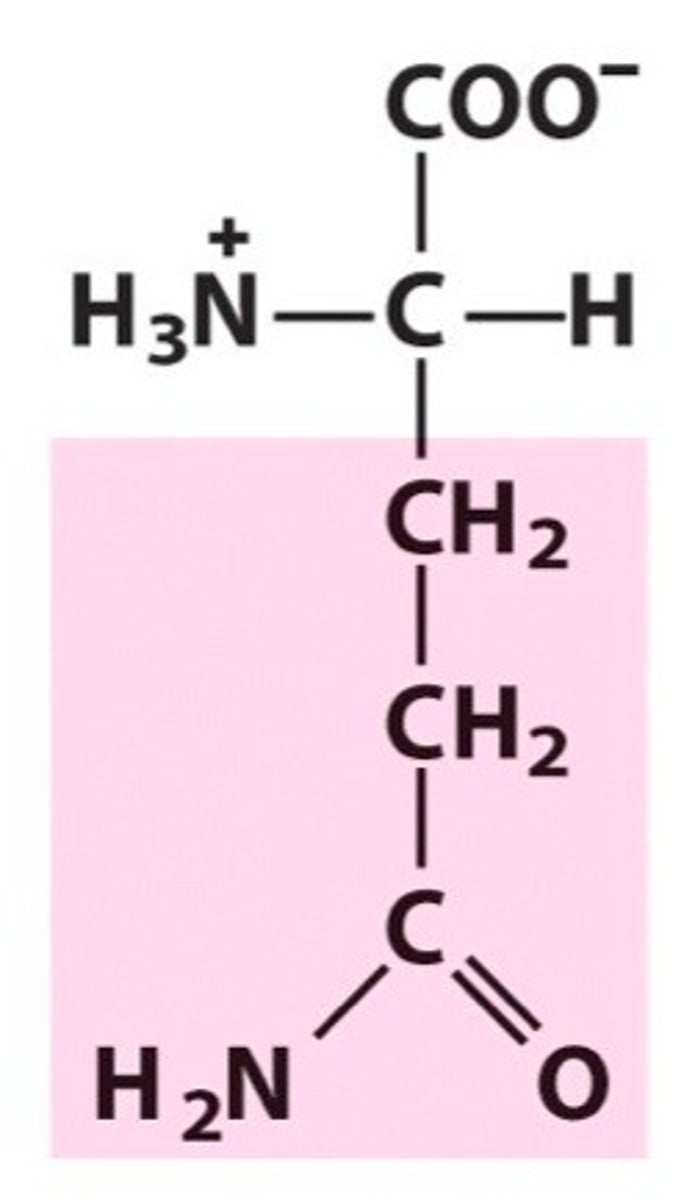
Glutamine
Gln, Q
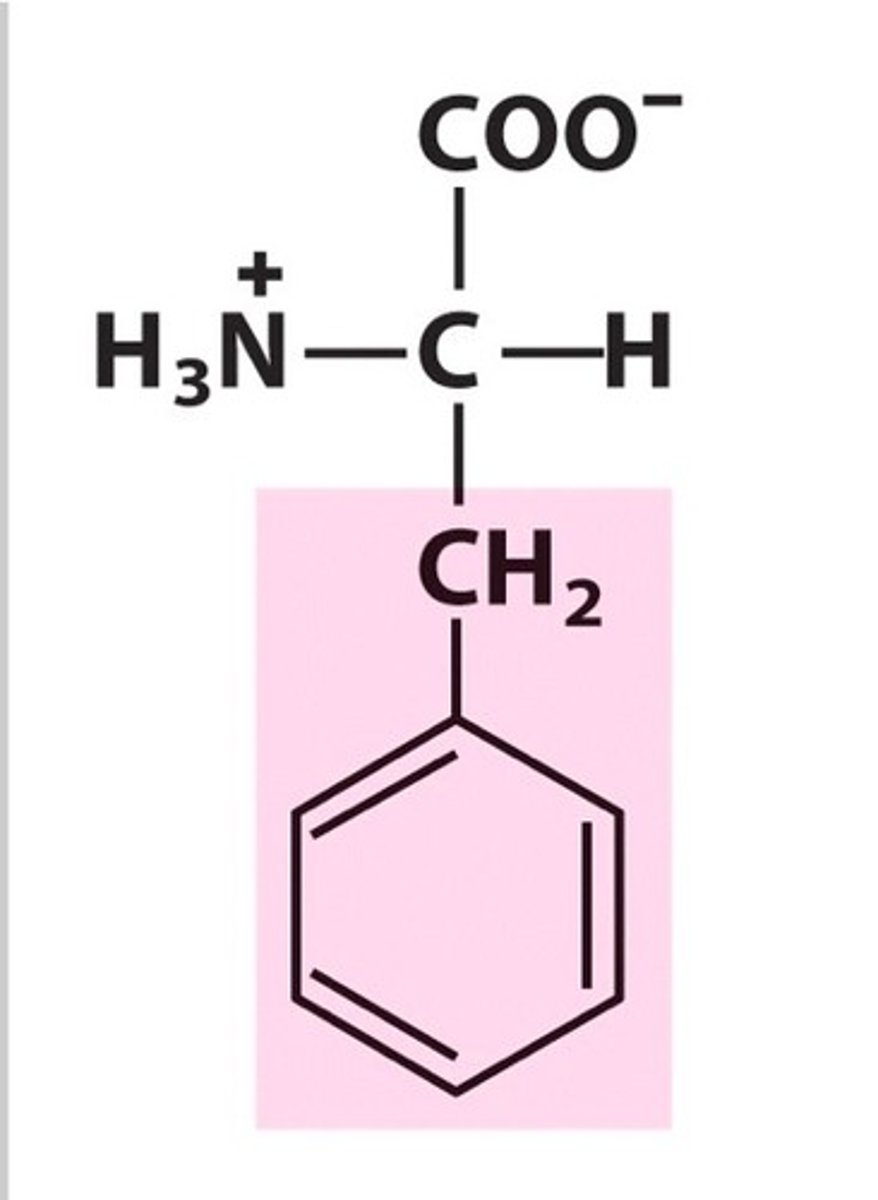
Phenylalanine
Phe, F
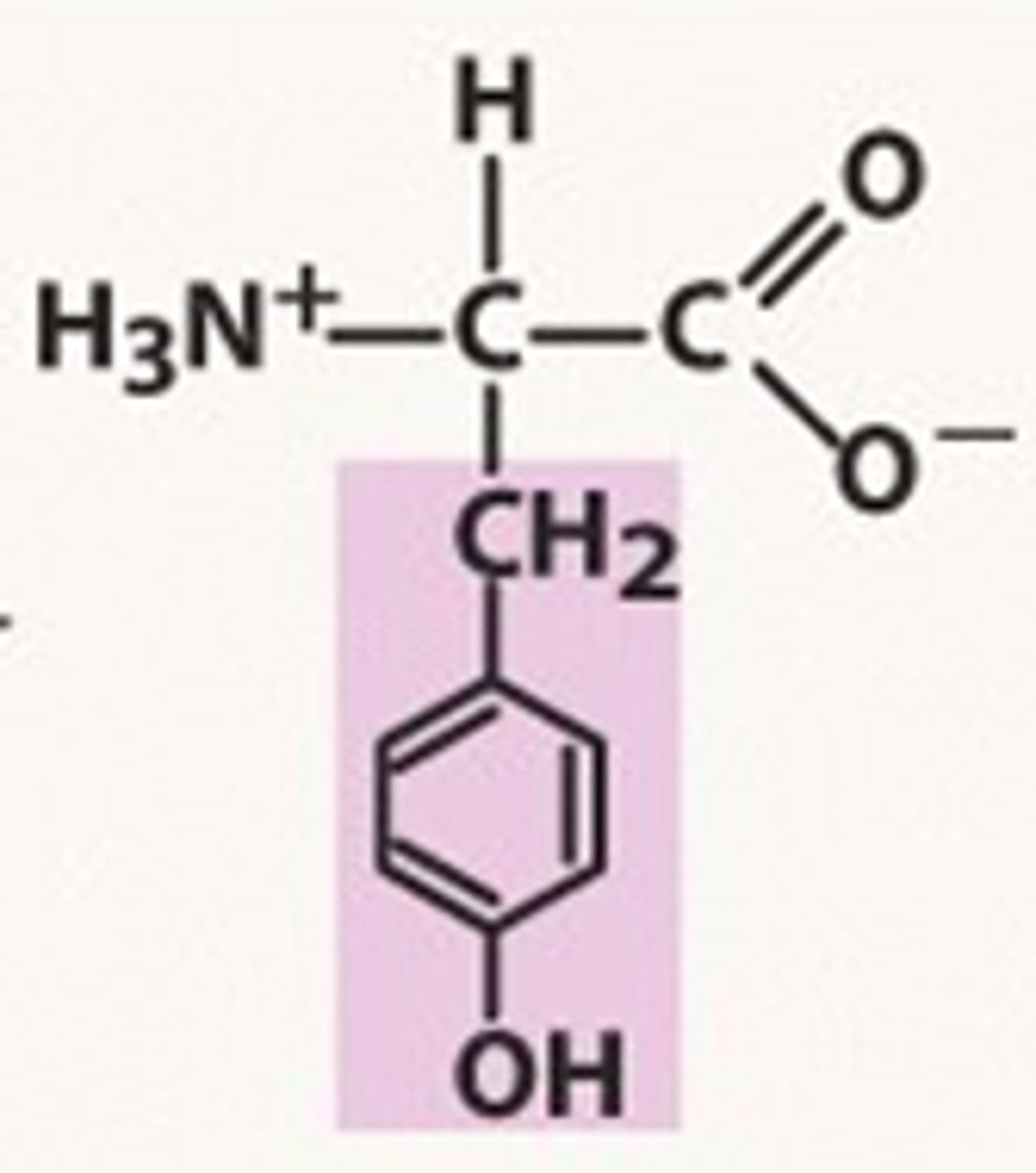
Tyrosine
Tyr, Y
Histidine
His, H
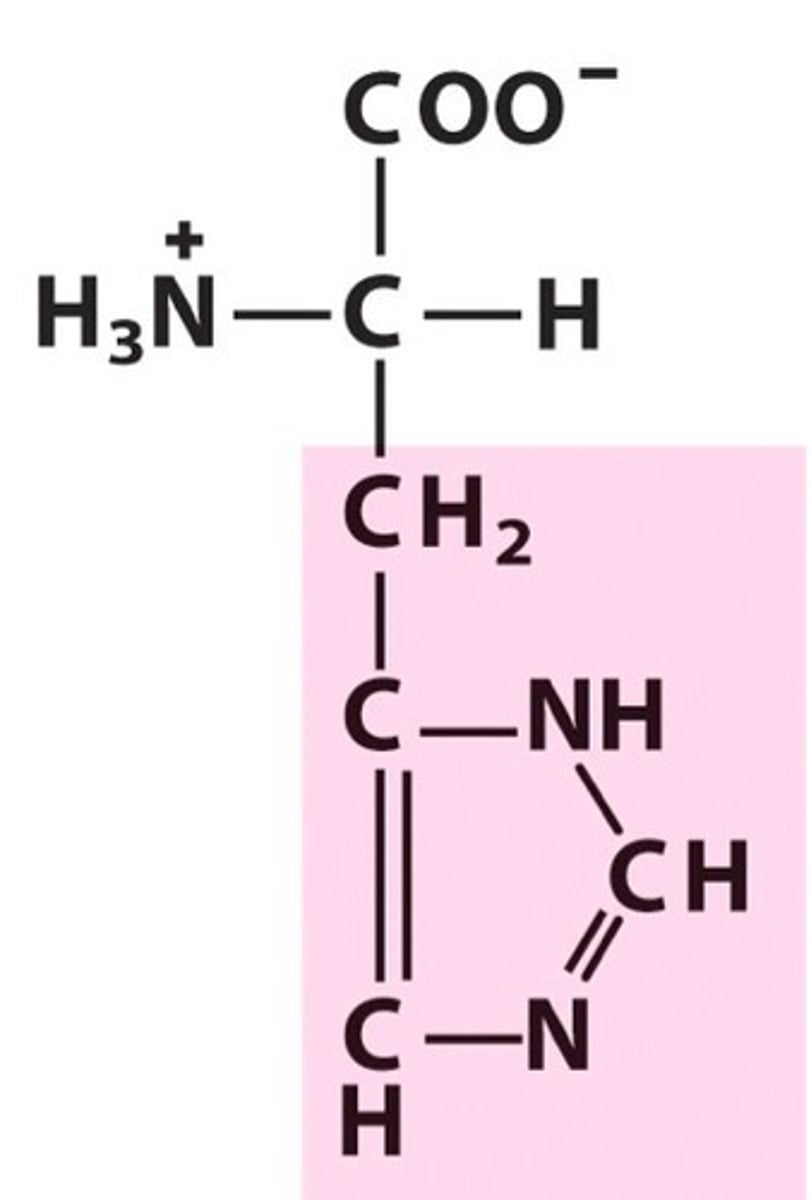
Tryptophan
Trp, W
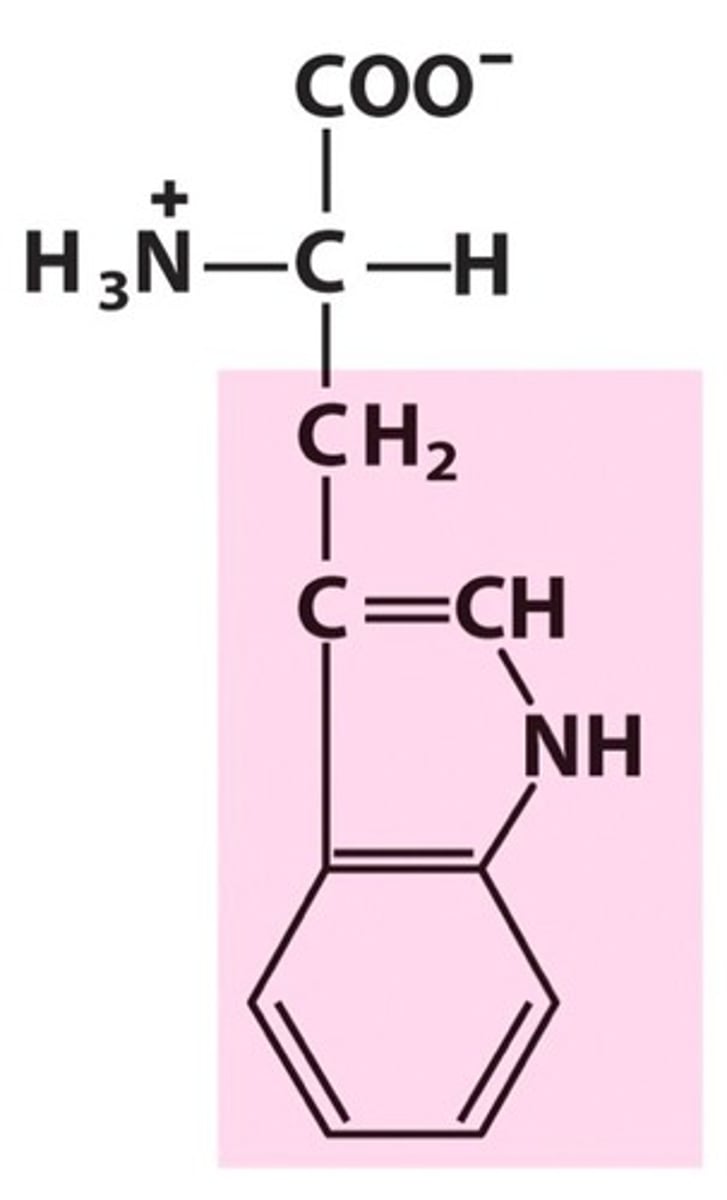
Proline
Pro, P
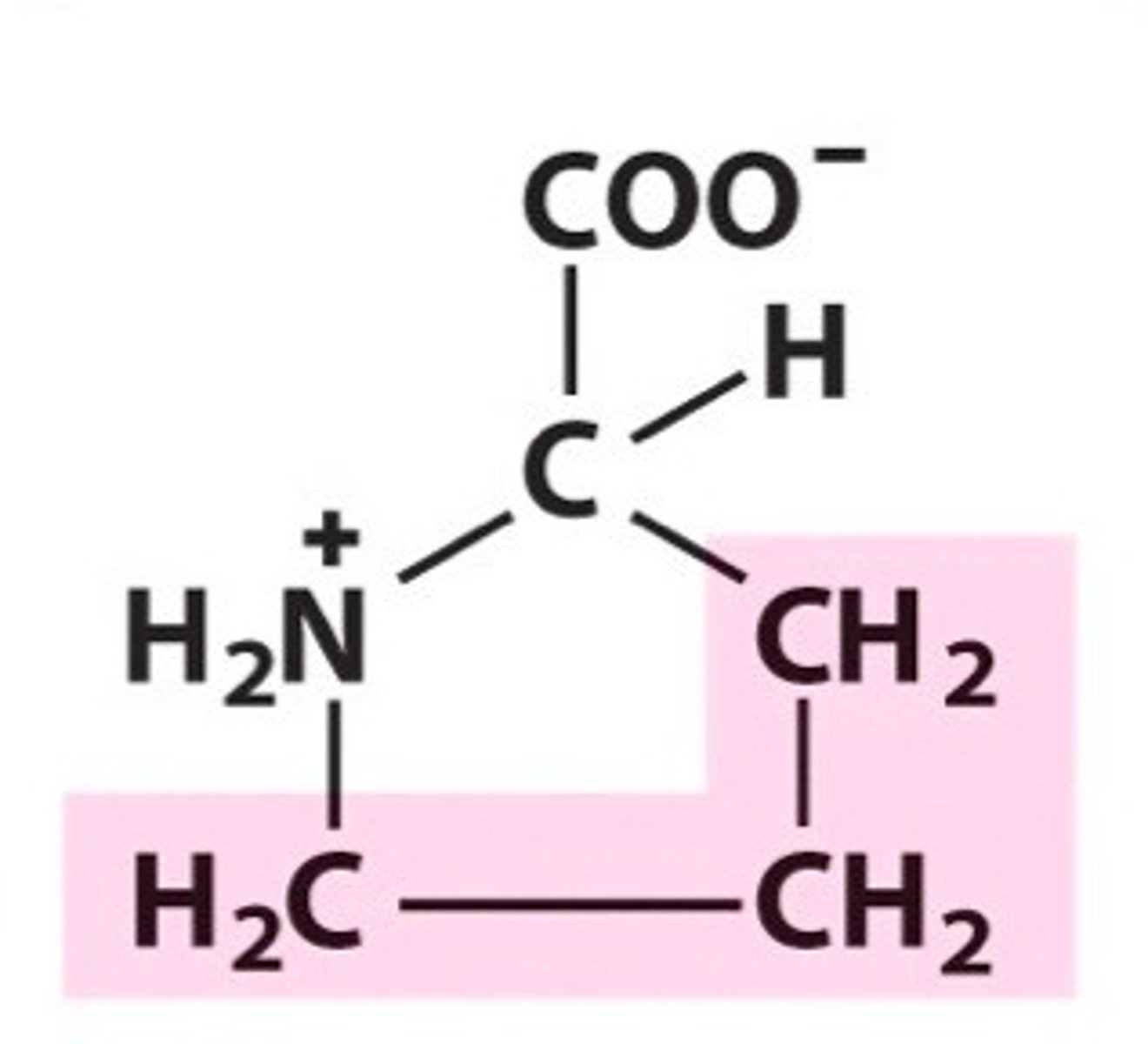
Peptide bond
covalent bonds between amino acids, formed by dehydration synthesis
Primary structure of protein
polypeptide chain
secondary structure of protein
a-helix and B-sheets
tertiary structure
The third level of protein structure; the overall, three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide due to interactions of the R groups of the amino acids making up the chain.
Denaturation
A process in which a protein unravels, losing its specific structure and function; can be caused by changes in pH or high temperature.
Nucleic acids contain what?
nucleotides
nucleotides are made of what?
5 C sugar, phosphate, nitrogen base
nucleosides are made of what?
pentose & nitrogen base
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
deoxyribose, double helixes, contains Adenine, Thymine, Cysteine, Guanine
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
ribose, single helix, Adenine, Uracil, Cysteine, Guanine
What is ATP made of?
adenine, ribose, 3 phosphate groups
ATP
Stores the chemical energy released by some chemical reactions, formed by ATPase complex
ether
R-O-R

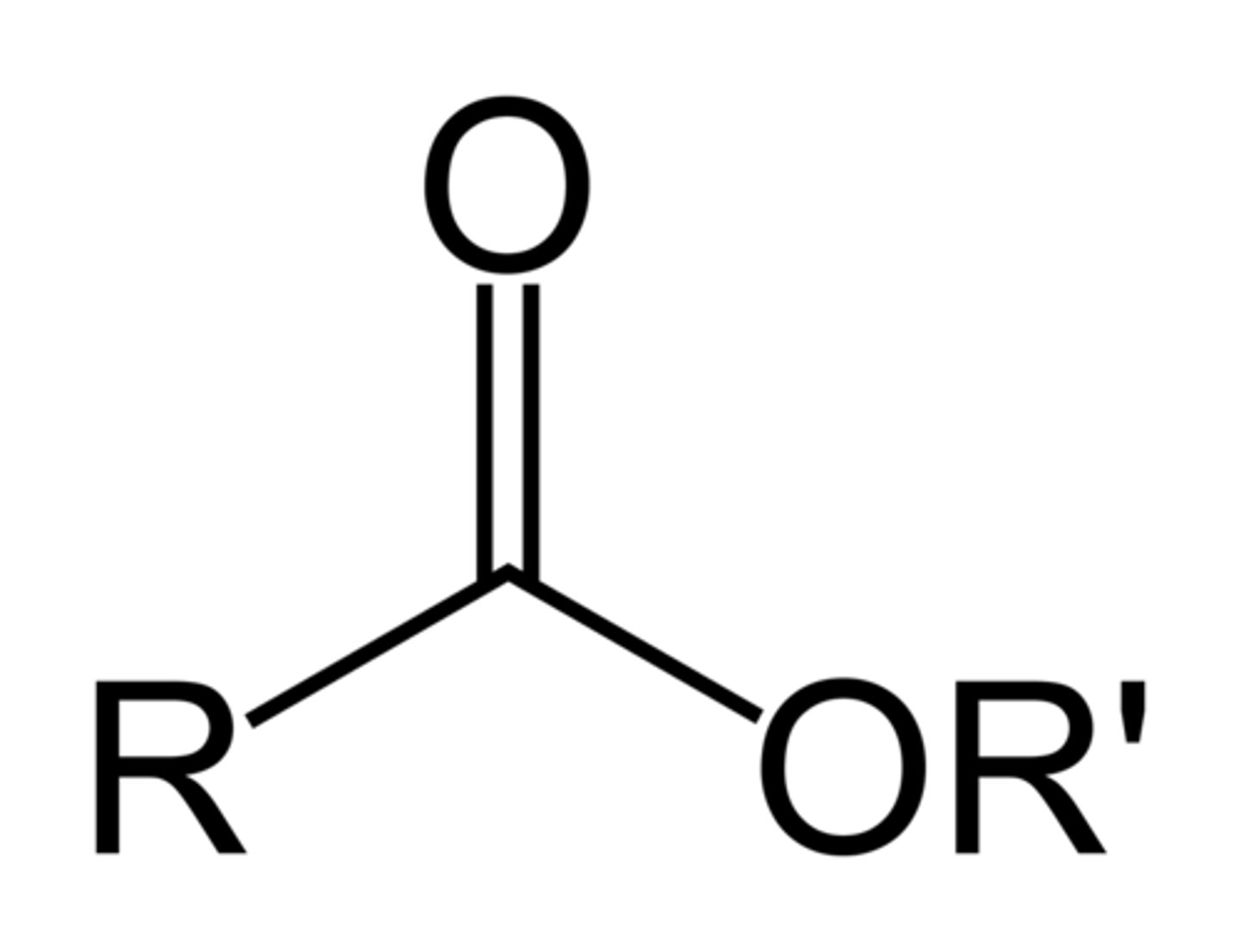
ester
RCOOR
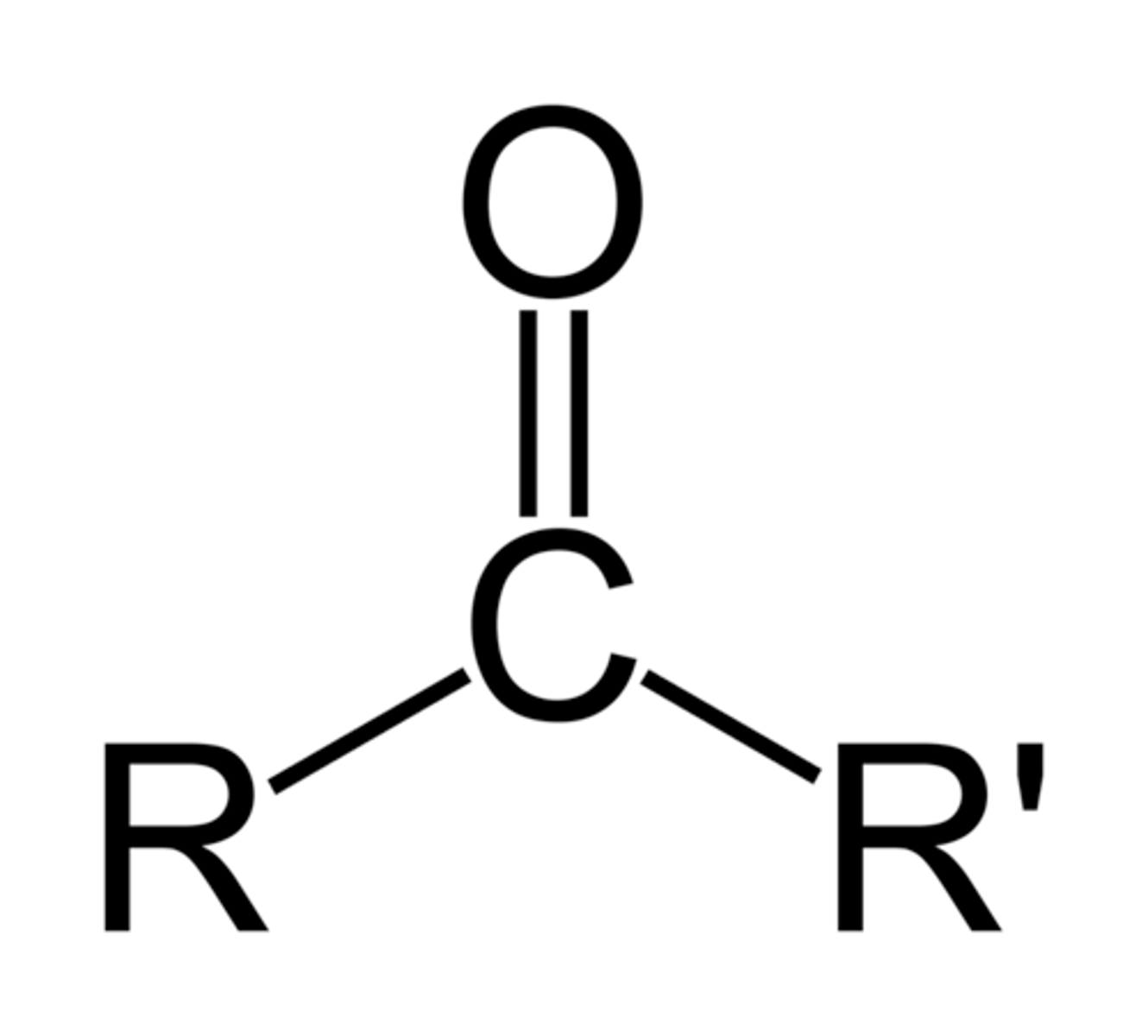
ketone
R-C=O-R
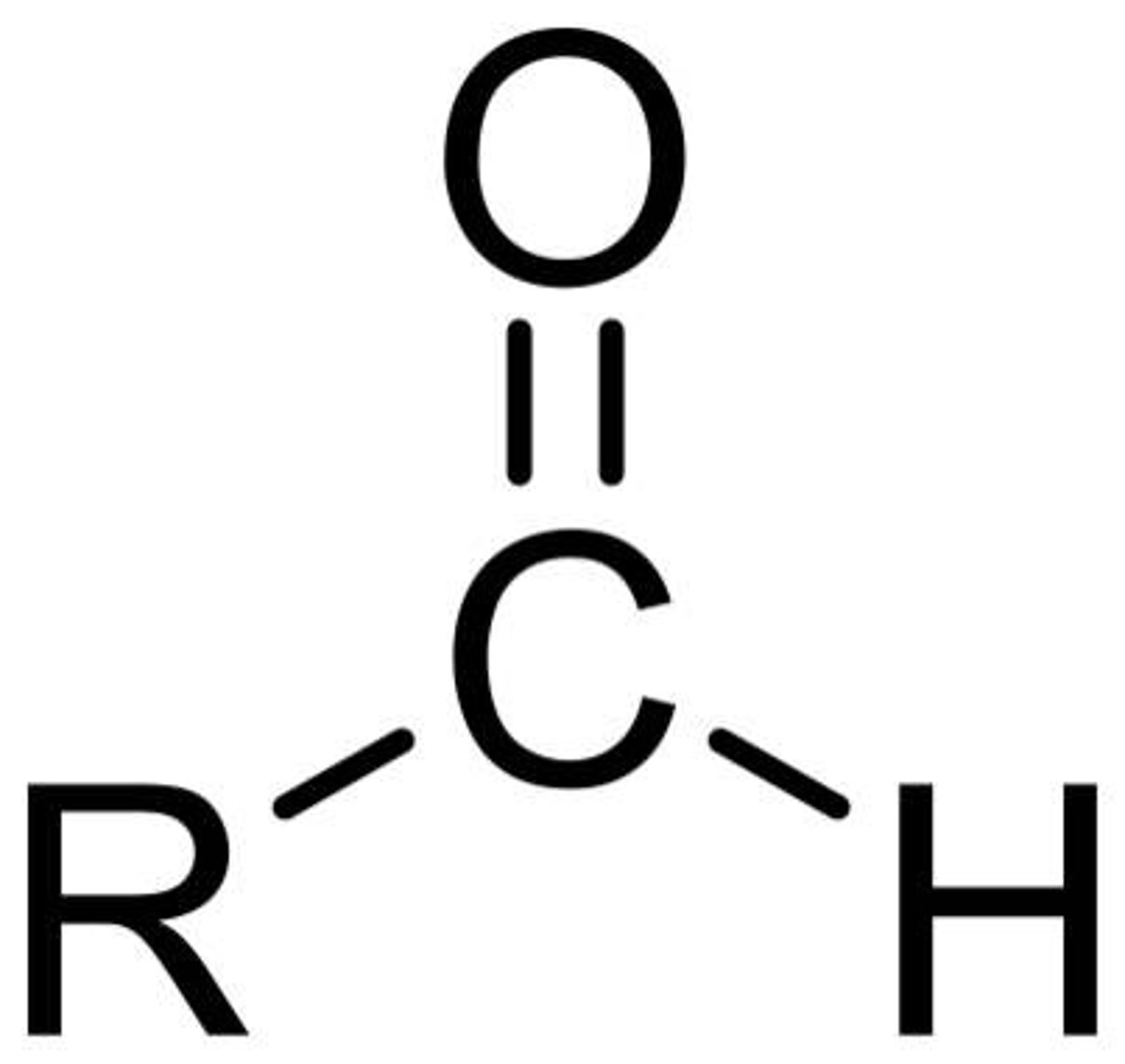
aldehyde
CHO
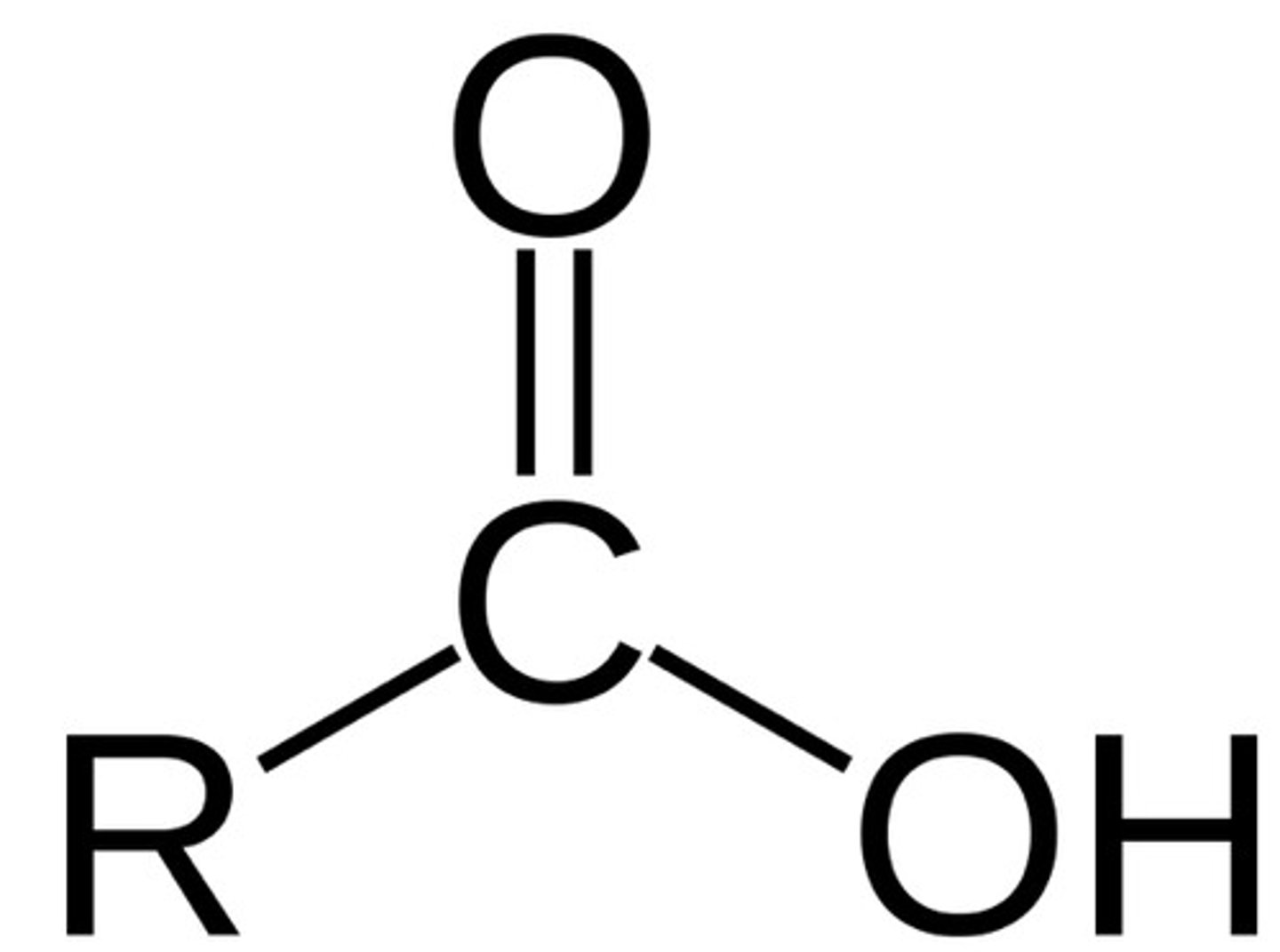
carboxylic acid
COOH
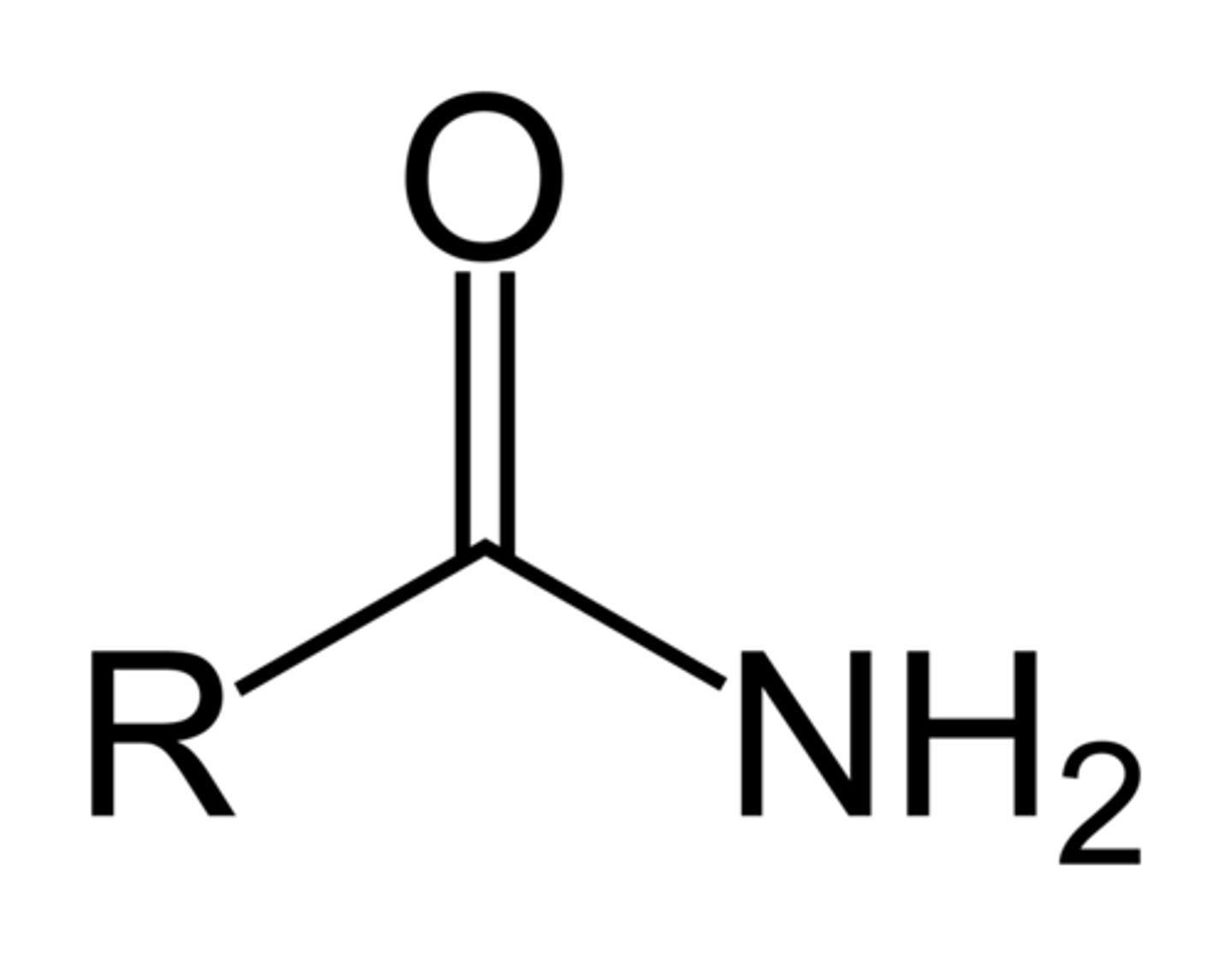
amide
NH2
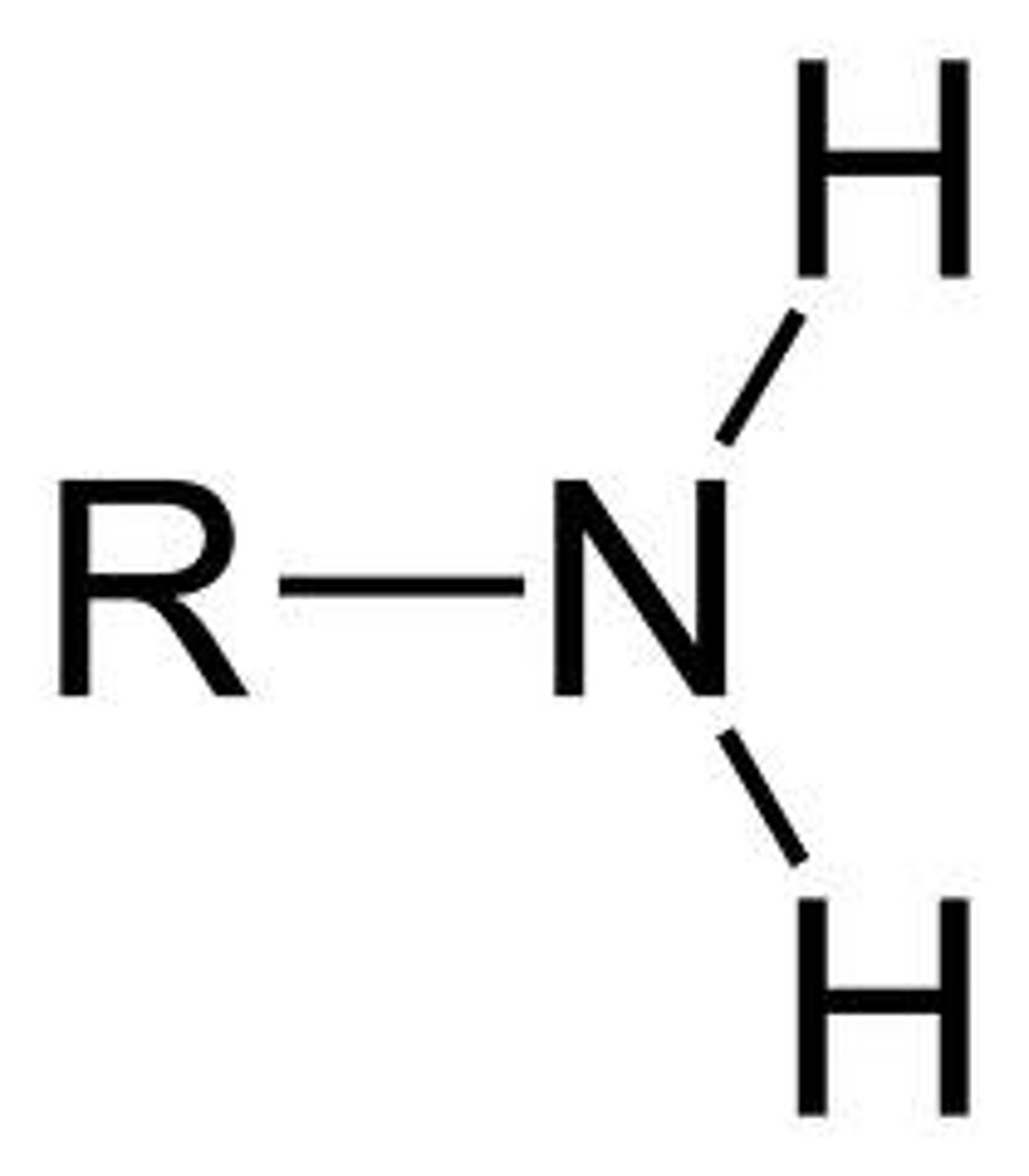
amine
NH2