Archaeplastida/Fungi - UNL Life 121
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Which of these characteristics is shared by algae and seed plants?
A. vascular tissue
B. chloroplasts
C. pollen
D. roots and shoots
Eembryo development within gametangia
B. chloroplasts
Which statement is true for all sexually reproducing plants and animals?
A. The process of meiosis produces haploid cells.
B. The process of mitosis always produces diploid cells.
C. The process of mitosis produces gametes.
D. The process of meiosis produces diploid cells.
E. The process of meiosis produces gametes.
A. The process of meiosis produces haploid cells.
Which structures are haploid? Select all that apply.
A. Zygote
B. Egg
C. Spores
D. Gametophyte
E. Sporophyte
B. Egg
C. Spores
D. Gametophyte
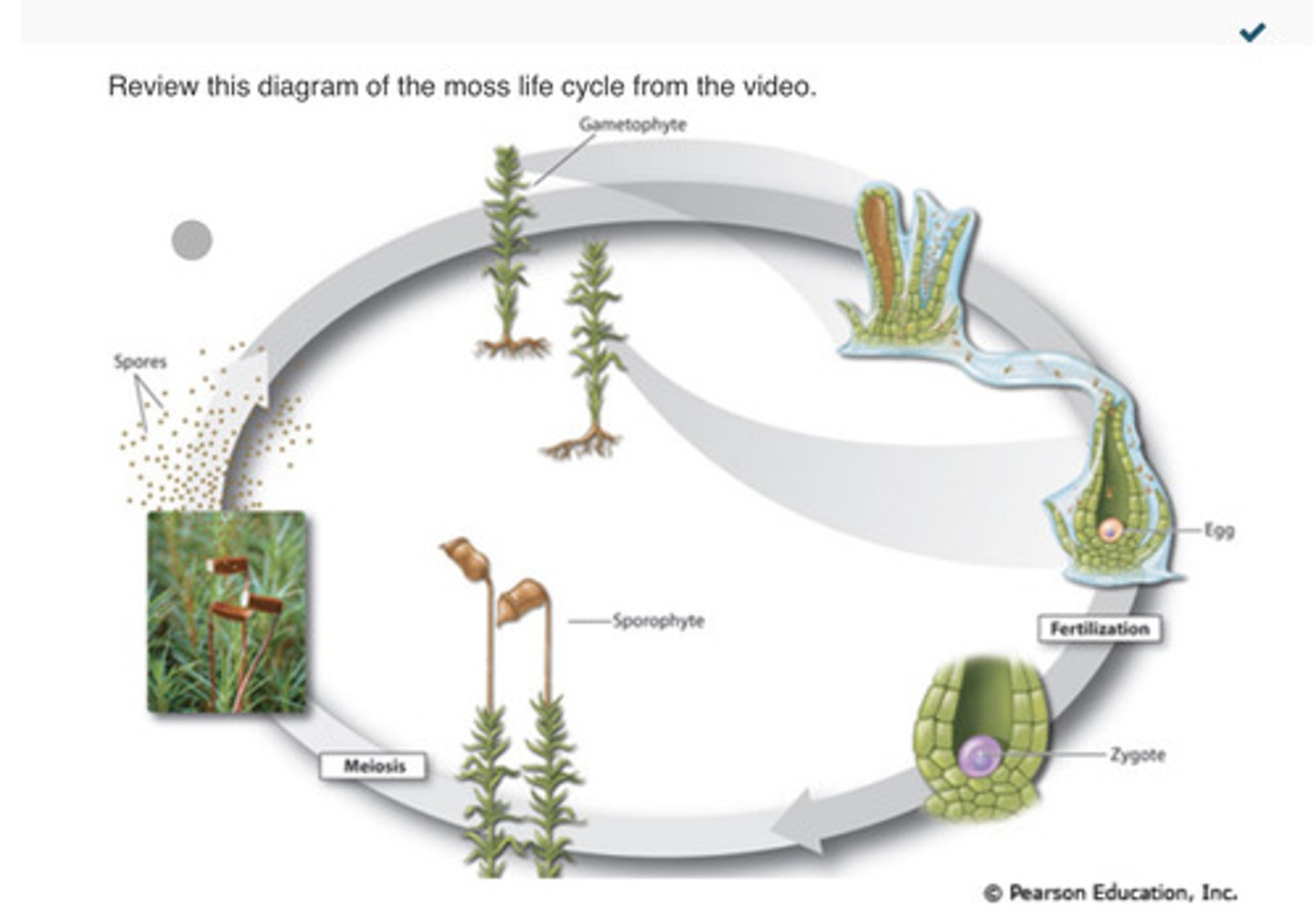
Consider the characteristics of moss and fern life cycles.
Which of the following sets of statements is true?
A. The gametophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle in both mosses and ferns. Mosses require moisture for sperm to reach the egg, but ferns do not.
B. The gametophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle in both mosses and ferns. In both mosses and ferns, moisture is required for sperm to reach the egg.
C. In mosses, the gametophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle; in ferns, the sporophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle. Ferns require moisture for sperm to reach the egg, but mosses do not.
D. In mosses, the sporophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle; in ferns, the gametophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle. In both mosses and ferns, moisture is required for sperm to reach the egg.
E. In mosses, the gametophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle; in ferns, the sporophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle. In both mosses and ferns, moisture is required for sperm to reach the egg.
E. In mosses, the gametophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle; in ferns, the sporophyte is the dominant stage of the life cycle. In both mosses and ferns, moisture is required for sperm to reach the egg.
Which of these facts provides the best support for the hypothesis that plants evolved from green algae?
A. Plants and green algae have chloroplasts.
B. The chloroplasts of plants and green algae all have both chlorophyll a and b.
C. Plants and green algae are photosynthetic.
B. The chloroplasts of plants and green algae all have both chlorophyll a and b.
Which of the following is a difference between plants and fungi?
A. Fungi have cell walls.
B. Fungi are strictly asexual, and plants undergo sexual reproduction.
C. Fungi are heterotrophic, and plants are autotrophic.
D. Plants produce spores.
E. Plants have diploid and haploid phases, and fungi have only haploid stages.
C. Fungi are heterotrophic, and plants are autotrophic.
This diagram shows the structure of a multicellular fungus, with an expanded view of two types of hyphae. Identify the structures and determine which hypha is septate and which is coenocytic. (Note that although this diagram shows the two types of hyphae, a fungus can have either one type or the other, but not both.)
A. Mycelium
B. Pore
C. Septum
D. Spectate hypha
E. coenocytic hypha
The following statements describe something about the body structures or functions of fungi. Identify those statements that are correct.
Select all that apply. ( 4 correct terms )
A. Nutrients can flow through the entire mycelium in fungi with coenocytic hyphae, but not in fungi with septate hyphae.
B. Cellulose gives rigidity and strength to the cell walls of fungi.
C. Some fungi can grow as either filamentous or single-celled forms.
D. All fungi are heterotrophs; some species live as decomposers and others as symbionts.
E. Some fungi secrete digestive enzymes into the environment and then absorb the digested nutrients.
F. Mycelia are made up of small-diameter hyphae that form an interwoven mass, providing more surface area for nutrient absorption.
C. Some fungi can grow as either filamentous or single-celled forms.
D. All fungi are heterotrophs; some species live as decomposers and others as symbionts.
E. Some fungi secrete digestive enzymes into the environment and then absorb the digested nutrients.
F. Mycelia are made up of small-diameter hyphae that form an interwoven mass, providing more surface area for nutrient absorption.
Most fungi are decomposers; they recycle the nutrients from nonliving organic matter. Other fungi are specialized to live in symbiotic relationships with other organisms. Some fungi live as parasites and others as mutualists. Most plants, in fact, could not survive and grow without their fungal partner.
This table lists some examples of different fungal strategies for obtaining nutrients.
Fungus - Septobasidium spp.
Nutrition - Fungal hyphae penetrate a living scale insect's body and absorb its nutrients. The individual insect that serves as the food source is immobilized, but the rest of the insect colony benefits from the shelter the fungus provides.
Fungus - Mycorrhizal fungi on pine tree roots.
Nutrition - Mycorrhizal fungi associate with roots and receive carbohydrates from the pine tree. The tree receives phosphorus, and may die without this association.
Fungus - fungi in the family Lepiotaceae.
Nutrition - Leaf-cutter ants cultivate fungal gardens that consist of fungi in the family Lepiotaceae. The ants feed and care for the fungi,and the fungi serve as a food source for the ants.
Fungus - Cordyceps spp.
Nutrition - Spores from these fungi attach to insects. The mycelium grows into the insect's body and absorbs nutrients from the soft tissues. Eventually the fungus sends up its reproductive structure through the insect's head.
Fungus - Trichophyton spp.
Nutrition - Trichophyton is one genus of fungi responsible for athlete's foot, ringworm, and jock itch. The fungi colonize the outer skin layer and utilize keratin as their food source.
Fungus - coprophilous fungi
Nutrition - These fungi absorb nutrients from animal feces.
Fungus - Cryphonectria parasitica
Nutrition - C. parasitica absorb nutrients after breaking down the cells of living chestnut trees, causing chestnut blight.
Decomposer -
coprophilous fungi
Fungi in association with a fallen log
Fungi in association with a dead rabbit
Mutualist -
Mycorrhizal fungi on pine tree roots
Fungi in the family Lepiotaceae
Parasite -
Septobasidium spp. and an individual scale insect infected by fungal hyphae
Cordyceps spp.
trichophyton spp.
Cryphonectria parasitica
Fungi obtain nutrients through __________.
A. chemosynthesis
B. endocytosis
C. photosynthesis
D. ingestion
E. absorption
E. absorption
The body of most fungi consists of threadlike __________, which form a network called a __________.
A. hyphae ... mycelium
B. mycelia ... hypha
C. hyphae ... chytrid
D. sporangia ... dikaryon
E. mycelia ... dikaryon
A. hyphae ... mycelium
Most fungi are _____.
A. photoautotrophs
B. decomposers
C. herbivores
D. carnivores
E. chemoautotrophs
B. decomposers
Fungi release digestive enzymes into their _____.
A. surroundings
B. gastrovascular cavity
C. stomach
D. hyphae
E. mycelia
A. Surroundings
Basidia produce spores by a process known as _____.
A. decomposition
B. mitosis
C. meiosis
D. hyphae
E. binary fission
C. meiosis
Fungi produce _____ spores.
A. dikaryotic
B. heterokaryotic
C. haploid
D. diploid
E. triploid
C. haploid
Karyogamy produces a _____.
A. diploid zygote
B. haploid zygote
C. spores
D. mycelium
E. hypha
A. diploid zygote
Plasmogamy is indicated by the letter _____.
A fungal life cycle. Each letter marks a definite process of this cycle. Letter A marks the process of spore development. Letter B marks fusion of cytoplasm of two hyphae. Letter C follows process B and marks fusion of nuclei. Letter D follows C and marks a process by which a zygote forms spore-producing structures. Letter E follows D and marks a process by which mycelium is formed from spores. Then the mycelium can either enter process A or go to stage B and continue the cycle.
A
B
C
D
E
B
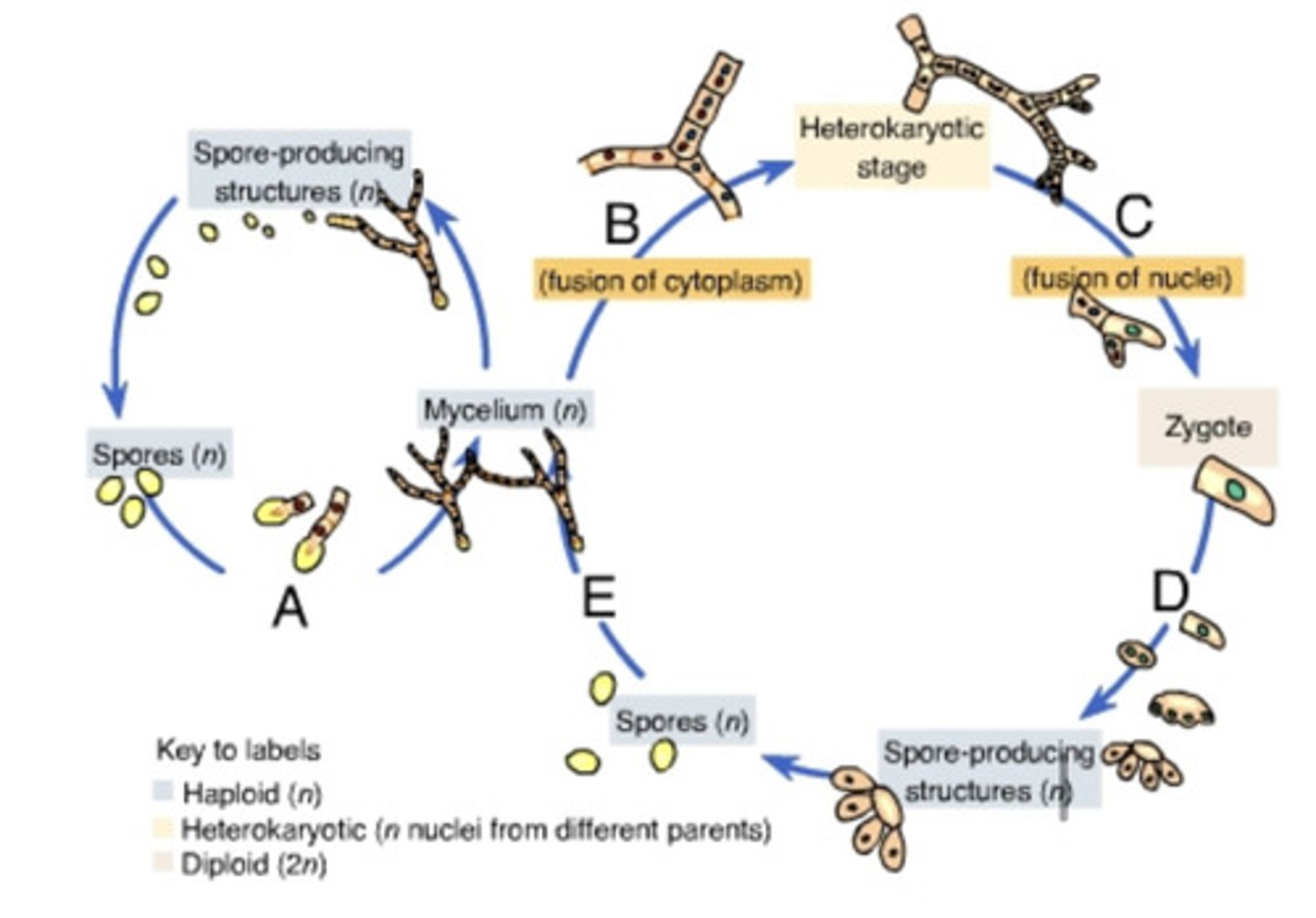
Which of these contains two haploid nuclei?
A. the heterokaryotic stage of the fungal life cycle
B. zygote
C. spore-producing structures
D. mycelium
E. hypha
A. the heterokaryotic stage of the fungal life cycle
The process indicated by the letter _____ produces a diploid structure.
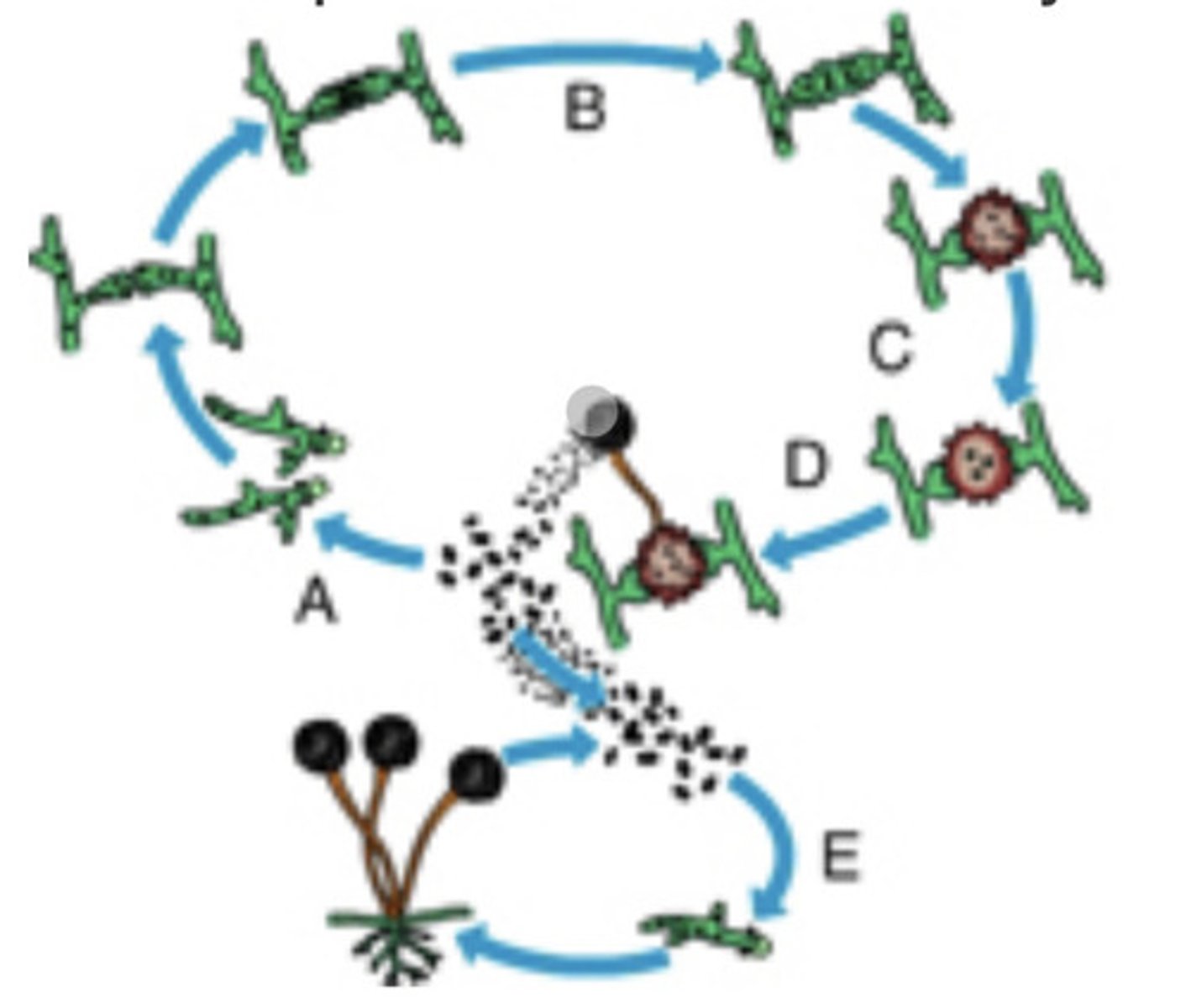
A life cycle of the black bread mold. Each letter marks a definite process of this cycle. Letter A marks a process of spore germination. Letter B marks a process of cytoplasm fusion. Letter C marks fusion of nuclei and formation of a round solid structure. Letter D marks a process by which the round solid structure produces spores. Letter E marks the other cycle, by which mycelium is formed from the spores.
A
B
C
D
E
C
Cup fungi are in the phylum _____.
A. Zygomycota
B. Chytridomycota
C. Ascomycota
D. Chordata
E. Basidiomycota
C. Ascomycota
What sexual processes in fungi generate genetic variation?
A. budding and meiosis
B. karyogamy and meiosis
C. haustoria and karyogamy
D. plasmogamy and meiosis
E. diploidy and the heterokaryotic condition
B. karyogamy and meiosis
Which of the following is likely the most harmful to England's mushroom populations?
A. Foraging for medicinal purposes.
B. Foraging for personal consumption.
C. Foraging for the illegal drug market.
D. Foraging to sell to markets and restaurants.
D. Foraging to sell to markets and restaurants.
You live in Minnesota and decide to take up mushroom hunting. Where would likely be the best place to look?
A. city yards
B. forest
C. abandoned farm field
D. grassland
B. forest
You wish to raise mushrooms on a commercial scale. Which of the following will you need to get started?
A. roots
B. spores
C. seeds
D. eggs
B. spores
Which of the following would likely be best to help the native mushrooms of England?
A. Protect their remaining habitat.
B. Require training and licensing for people interested in harvesting mushrooms.
C. Increase the prices being paid for wild mushrooms.
D. Fine those that harvest mushrooms illegally.
C. Increase the prices being paid for wild mushrooms.
If trends continue, which of the following will occur in England?
A. An increasing interest in wild foods, including mushrooms.
B. A decreasing interest in wild foods, but an increasing interest in mushrooms.
C. A decreasing interest in wild foods, including mushrooms.
D. An increasing interest in wild foods, except for mushrooms.
A. An increasing interest in wild foods, including mushrooms.