Nuclear Physics
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
How Joseph John Thomson Discovered the Electron
studies light rays in vacuum tubes- and rays traveled from anode to cathode
studied light rays in vacuum tubes- and rays traveled from cathode to anode
studied cathode rays in vacuum tubes- rays traveled from anode to cathode
studied cathode rays in vacuum tubes- rays traveled from cathode to anode
studied cathode rays in vacuum tubes- rays traveled from cathode to anode
What did Joseph John Thomson observe?
observed that rays were reflected by electric and magnetic fields
observed that lights were reflected by electric and magnetic fields
observed that rays were deflected by electric and magnetic fields
observed that lights were deflected by electric and magnetic fields
observed that rays were deflected by electric and magnetic fields
What was the conclusion of Jospeh John Thomson ?
concluded that light carried negative charge, electrons
concluded that light carried positive charge, protons
concluded that rays carried negative charge, electrons
concluded that rays carried positive charge, protons
concluded that rays carried negative charge, electrons
Ernest Rutherfords discovery of the nucleus, was found from what experiment and led to what conclusion?
the experiment was aiming a beam of beta particles at a thin silver foil. Led to the conclusion that atoms have a non-heavy nucleus that occupies a very tiny volume within the whole atom
the experiment was aiming a beam of beta particles at a thin gold foil. Led to the conclusion that atoms have a heavy nucleus that occupies a very tiny volume within the whole atom
the experiment was aiming a beam of alpha particles at a thin silver foil. Led to the conclusion that atoms have a non-heavy nucleus that occupies a very tiny volume within the whole atom
the experiment was aiming a beam of alpha particles at a thin gold foil. Led to the conclusion that atoms have a heavy nucleus that occupies a very tiny volume within the whole atom
the experiment was aiming a beam of alpha particles at a thin gold foil. Led to the conclusion that atoms have a heavy nucleus that occupies a very tiny volume within the whole atom
Chadwicks Discovery of what ?
proton
neutron
electron
particles
neutron
What was the experiment conducted by James Chadwick and what was the conclusion?
the experiment was in 1932, James Chadwick bombared beryllium with beta particles, since the radiation couldnt be explained by gamma rays due to its mass and momentum, he concluded it was neutrons
the experiment was in 1932, James Chadwick bombared beryllium with alpha particles, since the radiation couldnt be explained by gamma rays due to its mass and momentum, he concluded it was neutrons
the experiment was in 1932, James Chadwick bombared beryllium with beta particles, since the radiation couldnt be explained by gamma rays due to its mass and momentum, he concluded it was electrons
the experiment was in 1932, James Chadwick bombared beryllium with alpha particles, since the radiation couldnt be explained by gamma rays due to its mass and momentum, he concluded it was electrons
The cross sectional area of nuclei can be determined from particle scattering experiments
true
false
true
What is (in)stability in nuclear physics?
For subatomic particles, stability often relates to the particle’s tendency to decay into other particles. Particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons are considered stable because they have extremely long lifetimes, with no evidence of decay under normal conditions.
For atomic particles, stability often relates to the particle’s tendency to decay into other particles. Particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons are considered stable because they have extremely long lifetimes, with no evidence of decay under normal conditions.
For subatomic particles, stability often relates to the particle’s tendency to decay into other particles. Particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons are considered less stable because they have extremely long lifetimes, with no evidence of decay under normal conditions.
For atomic particles, stability often relates to the particle’s tendency to decay into other particles. Particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons are considered less stable because they have extremely long lifetimes, with no evidence of decay under normal conditions.
For subatomic particles, stability often relates to the particle’s tendency to decay into other particles. Particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons are considered stable because they have extremely long lifetimes, with no evidence of decay under normal conditions.
Isotopes, in the neutral state have:
equal number of protons, equal number of electrons
different number of protons, different number of electrons
equal number of protons, equal number of electrons
Isotopes, not in the neutral state have:
equal number of protons, equal number of electrons
different number of protons, different number of electrons
equal number of protons, equal number of electrons
what is the method used to determine the age of organic materials using carbon radioactive
radiocarbon dating
carbon-14-dating
carbon dating
old dating machine
more than one are correct
more than one are correct
radiocarbon dating
carbon-14-dating
How does radiocarbon dating work ?
By measuring the amount of carbon-14 remaining in the sample and comparing it to the amount of carbon-14 present in the atmosphere at the time the organism died one can calculate the approximate age of the sample.
By measuring the amount of carbon-16 remaining in the sample and comparing it to the amount of carbon-14 present in the atmosphere at the time the organism died one can calculate the approximate age of the sample.
By measuring the amount of carbon-16 remaining in the sample and comparing it to the amount of carbon-16 present in the atmosphere at the time the organism died one can calculate the approximate age of the sample.
By measuring the amount of carbon-20 remaining in the sample and comparing it to the amount of carbon-20 present in the atmosphere at the time the organism died one can calculate the approximate age of the sample.
By measuring the amount of carbon-14 remaining in the sample and comparing it to the amount of carbon-14 present in the atmosphere at the time the organism died one can calculate the approximate age of the sample.
two neutrons and one proton, which elements of the nuclei belong to?
tritium
helium
water
air
tritium
two protons and one neutron, which elements of these nuclei belong to?
tritium
helium
water
air
helium
Fewer than ___ of the known nuclei are stable (not radioactive)
20%
5%
50%
10%
10%
Stable nuclei cluster __ to the curve called the line of stability
higher
lower
very close
very far
very close
there are no stable nuclei with Z…?
Z>82
Z<82
Z>80
Z<80
Z>82
The force that holds the nucleons together is called the strong force.
it is an ___ force between any two nucleons
repulsive
attractive
attractive
The force that holds the nucleons together is called the strong force.
it does not on __________
protons
electrons
neutrons
electrons
The force that holds the nucleons together is called the strong force.
it is a _____ range force, acting only over nuclear distances
long
short
medium
constant
short
The force that holds the nucleons together is called the strong force.
Over the range where it acts, it is ____ than the electrostatic force that tries to push two protons apart.
stronger
weaker
neutral
stronger
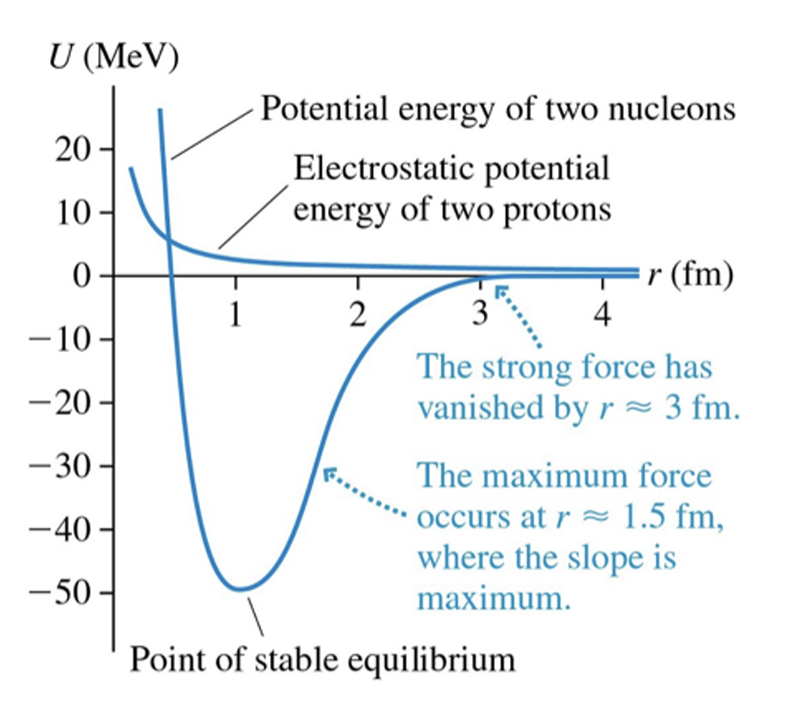
What the difference in potential energy of two nucleons versus. electrostatic potential energy of two protons
the strong force has vanished by r~ 3fm
the maximum force occurs at r ~ 1.5 fm where the slope is the maximum
the maximum force have vanished by 2fm
more than one are correct
the strong force has vanished by r~ 3fm
the maximum force have vanished by 2fm
what balances the repulsive coulomb force?
attractive “strong interaction”
weak “interactions”
attractive “ energy interactions”
weak “energy interactions”
attractive “strong interaction”
strong interactions only work where?
long range
short range
“surface” of the nuclei
“center” of the nuclei
“center” of the nuclei
In large nuclei which interaction wins
coulomb interaction
strong interaction
weak interaction
“surface” interaction
coulomb interaction
The mass of the nucleus is the same as the sum of the mass of its nucleons
true
false
true
LESS
A nucleus is a bound system. Energy is required to disperse the nucleons by breaking the nuclear bonds between them
binding energy
healthy energy
collapsing energy
strong energy
binding energy
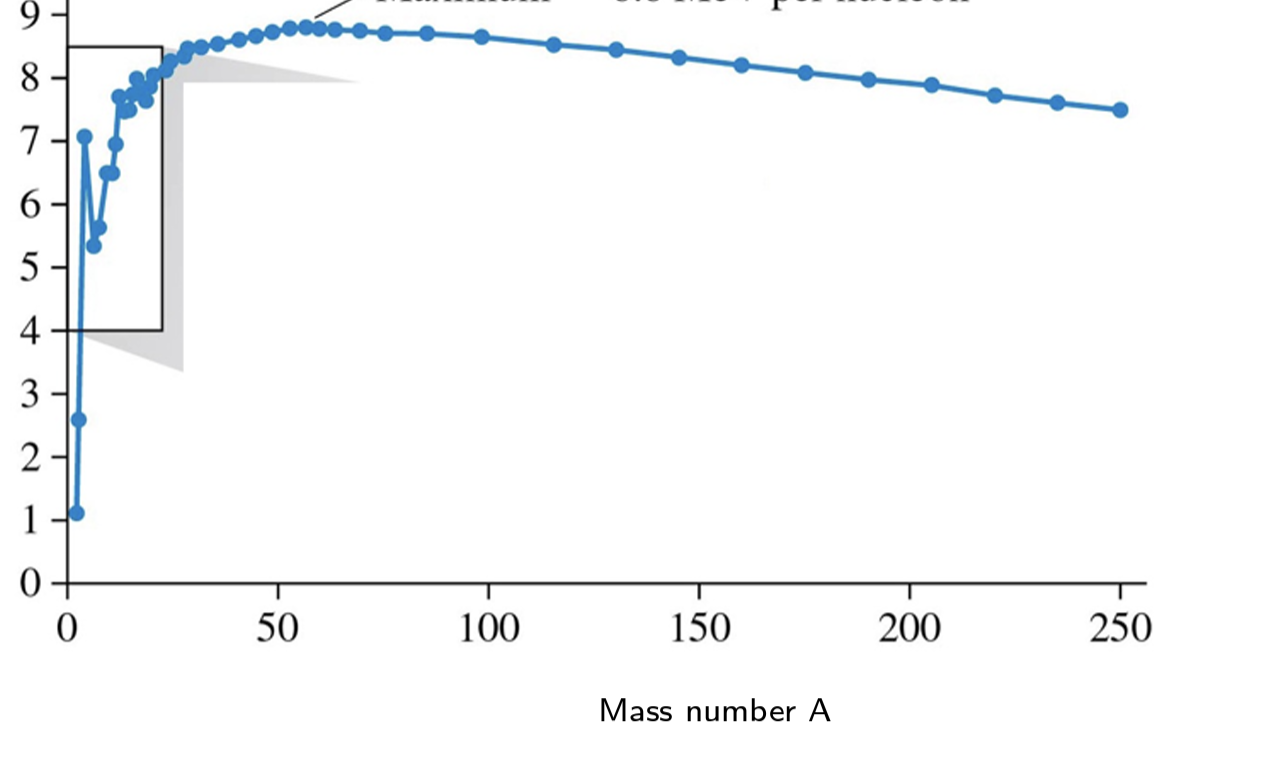
the most stable elments of the universe are at the ____ energy part of the graph
lowest
highest
medium
center
highest
As heavy elements decay into lighter ones, they approach a highly stable state, resulting in a massive release of energy, this is
fussion
explosions
fission
collapse
fission
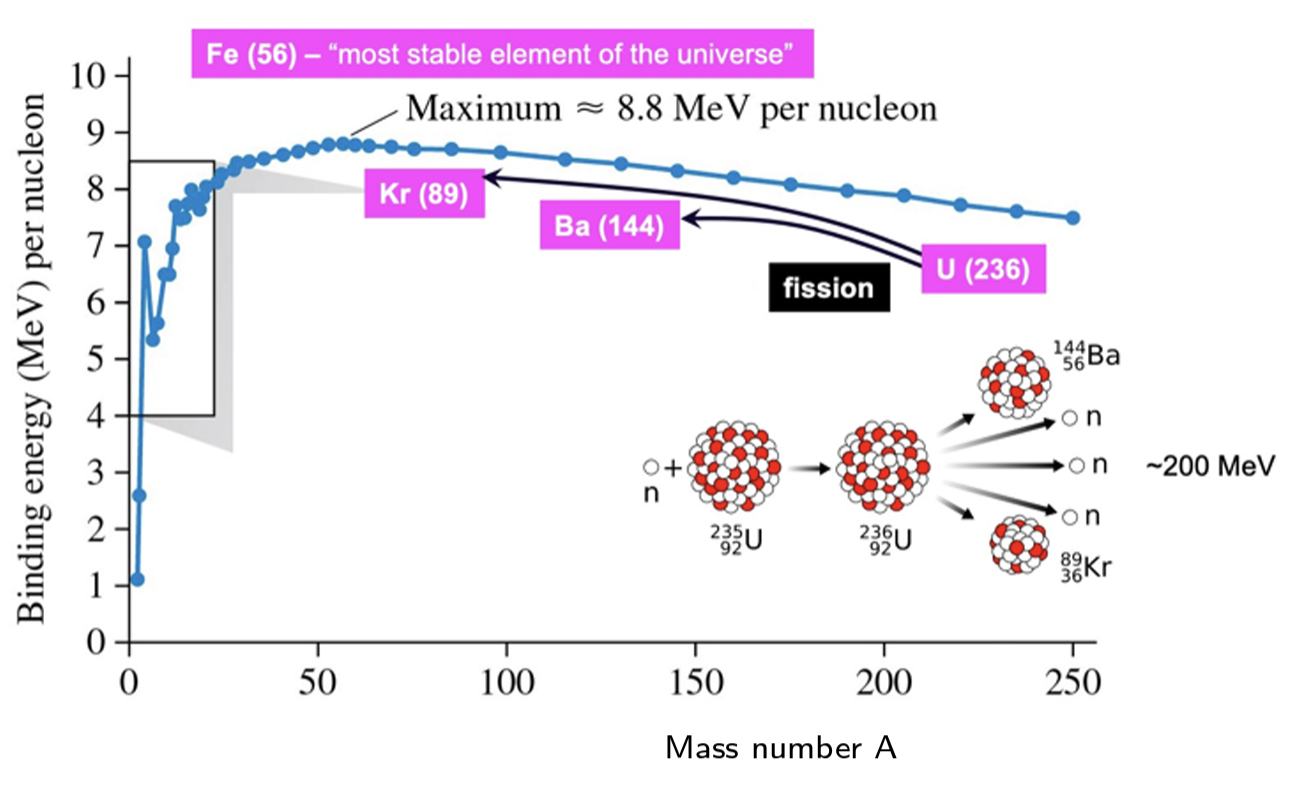
As light nuclei merge, they form heavier ones, also approaching a highly stable state, resulting in a massive energy release, called
thermonuclear fusion
fission
vision
nothing
thermonuclear fusion
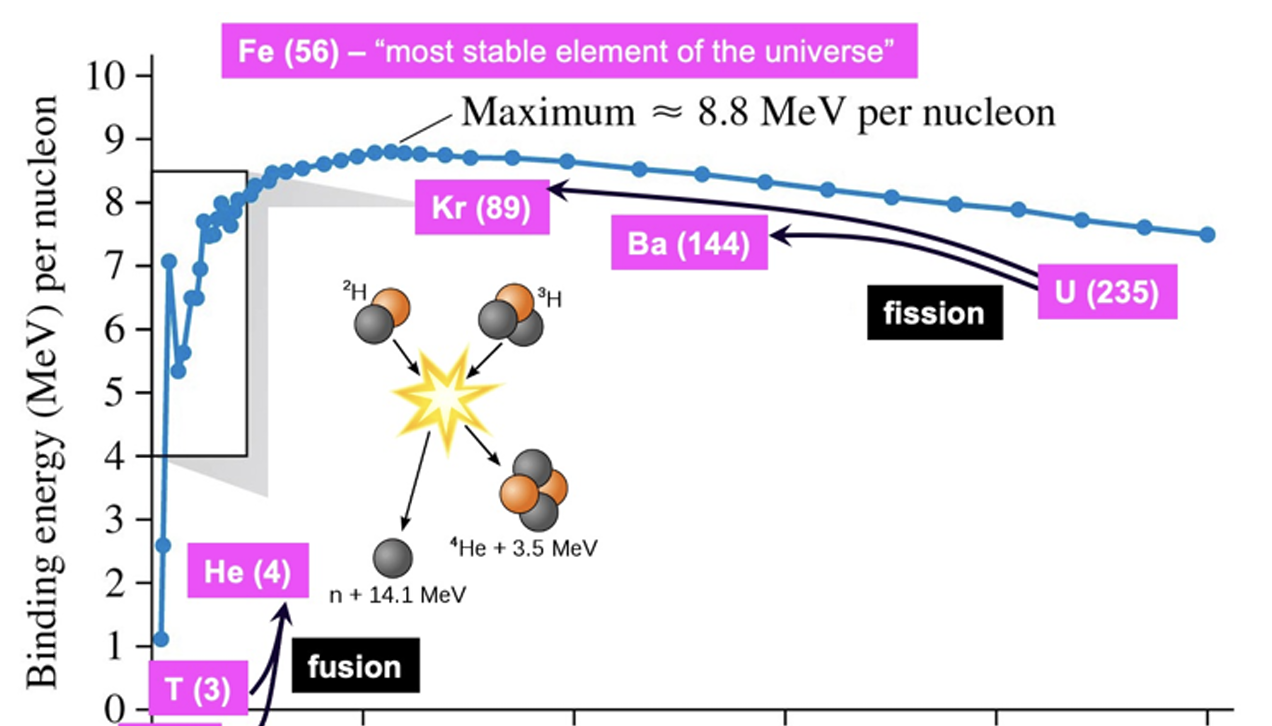
What is the most stable element of the universe
Fe(56)
He(4)
Kr(89)
Ba(144)
Fe(56)
The product of the uncertainty in the position and the uncertainty in the momentum of a particle is greater than or equal to a constant value.
energy time uncertainty principle
angular momentum uncertainty principle
position momentum uncertainty principle
position momentum uncertainty principle
Relates the uncertainty in the energy of a system to the uncertainty in the time over which the energy is measured.
energy time uncertainty principle
angular momentum uncertainty principle
position momentum uncertainty principle
energy time uncertainty principle
For a particle with angular momentum L about a particular axis, the product of the uncertainty in angular momentum and the uncertainty in the angular position is greater than or equal to a constant.
energy time uncertainty principle
angular momentum uncertainty principle
position momentum uncertainty principle
angular momentum uncertainty principl
quantum tunneling allows particles to pass through barriers that are not allowed in
classical physics
normal physics
microscopic physics
macroscopic physics
classical physics
Quantum tunneling follows both from the ___ and from ___
uncertainty principle, Schrondingers equation
classical principle, Schrondingers equation
uncertainty principle, Einsteins equation
classical principle, Einsteins equation
uncertainty principle, Schrondingers equation
Quantum tunneling has reduced probability but NOT
reduced energy
increased energy
partical energy
wave energy
reduced energy
In classical physics can particle be in the middle barrier
yes, it can be on the right side, left and middle barrier
no, only in the left or right barrier
no, only in the left or right barrier
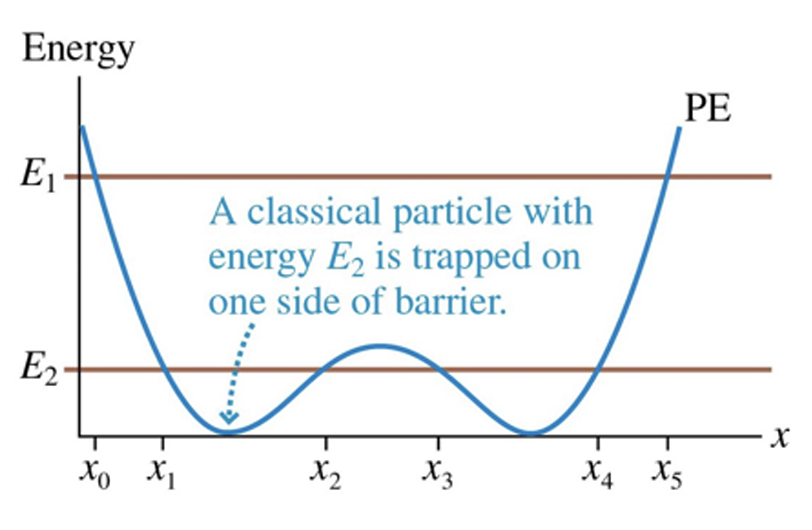
In quantum physics can the particle be in the middle barrier?
yes, through a process called tunneling
no, because classical physics doesnt allow it
yes, though a process called fussion
no, because it is impossible
yes, through a process called tunneling
Some example of qauntum tunneling include:
alpha decay
STM( scanning tunnleing microscopy
quantum dots
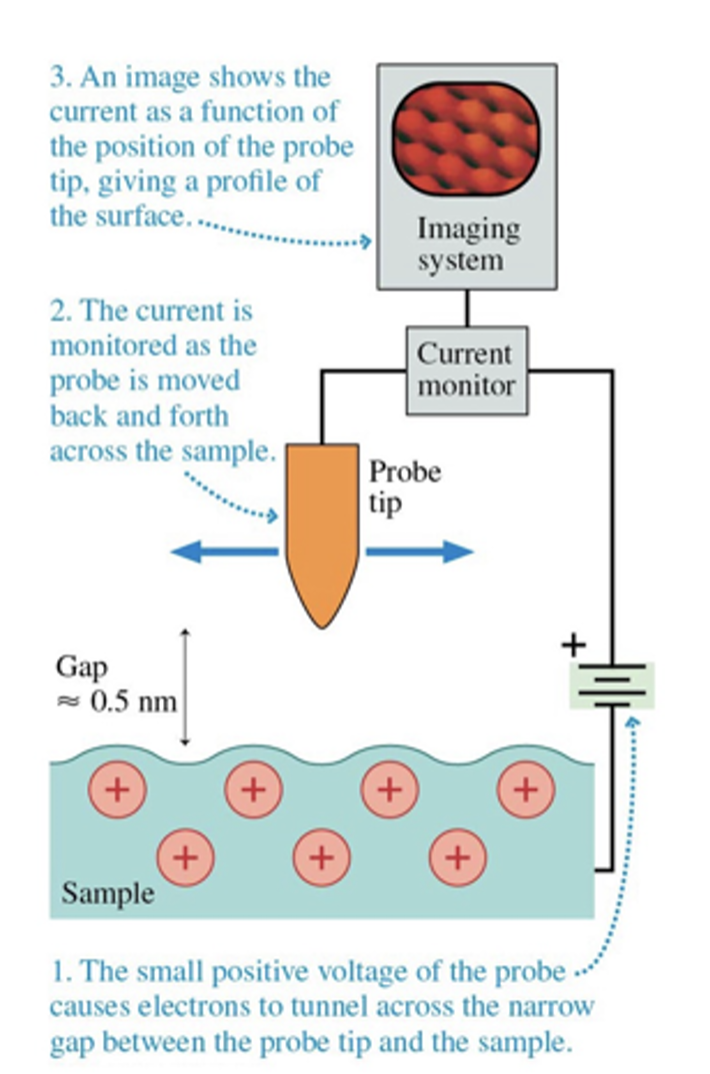
The three steps of scanning tunneling microscope include:
small positive voltage of the probe causes electrons to tunnel across the narrow gap between the probe tip and the sample
the current is monitored as the probe is moved back and forth across the sample
an image shows the current as a function of the position of the probe tip, giving a profile of the surface
Using uranium crystals, physicists Thomson and Rutherford discovered three types of _____- the spontaneous emission of particles or high-energy photons from unstable nuclei as they decay from higher-energy to lower-energy states.
radioactive decay
electron decay
energy decay
multiactive decay
radioactive decay
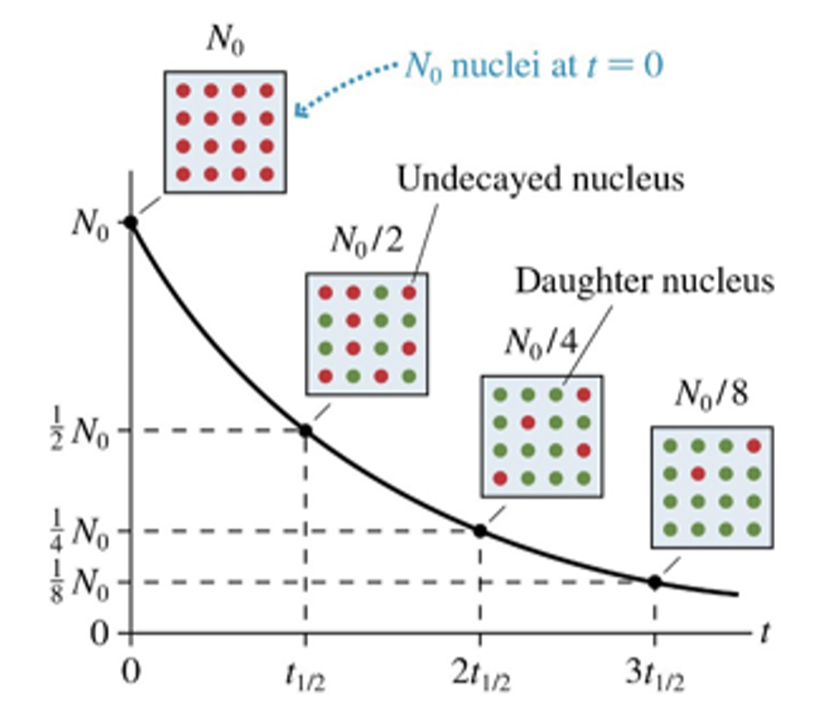
A radioactive sample’s half-life is defined as the time interval in which ___ of a sample of radioactive atoms decays.
half
¼
doubles
1/3
half
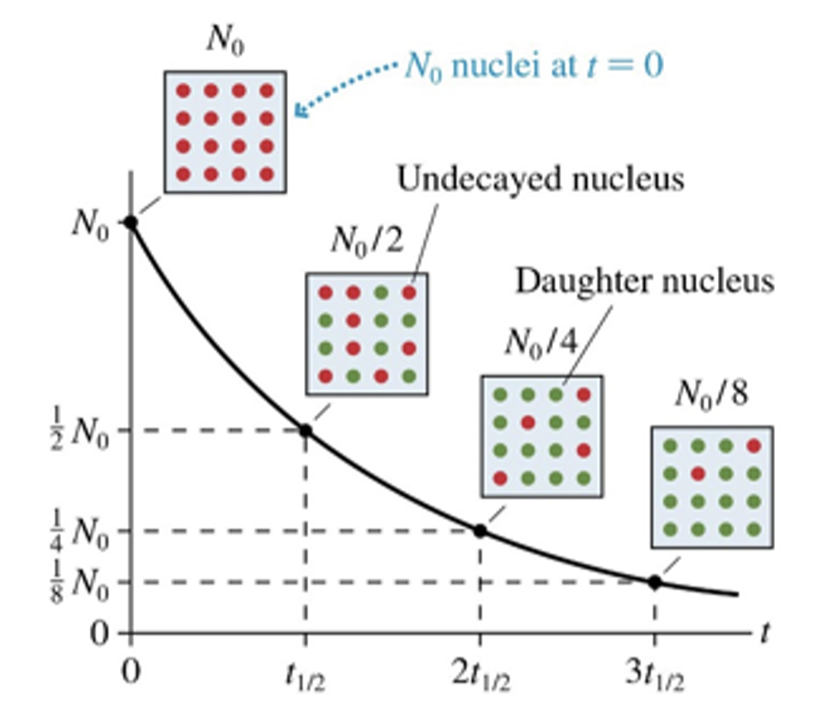
Nuclei don’t vanish when they decay. The decayed nuclei have become some other kind of nuclei, called the
decay nuclei
half nuclei
daughter nuclei
middle nuclei
daughter nuclei
The decay rate is a property of the ___
electron
repulsive forces
decay force
nucleus
nucleus
Sum of nuclear potenital and coulumb potenital
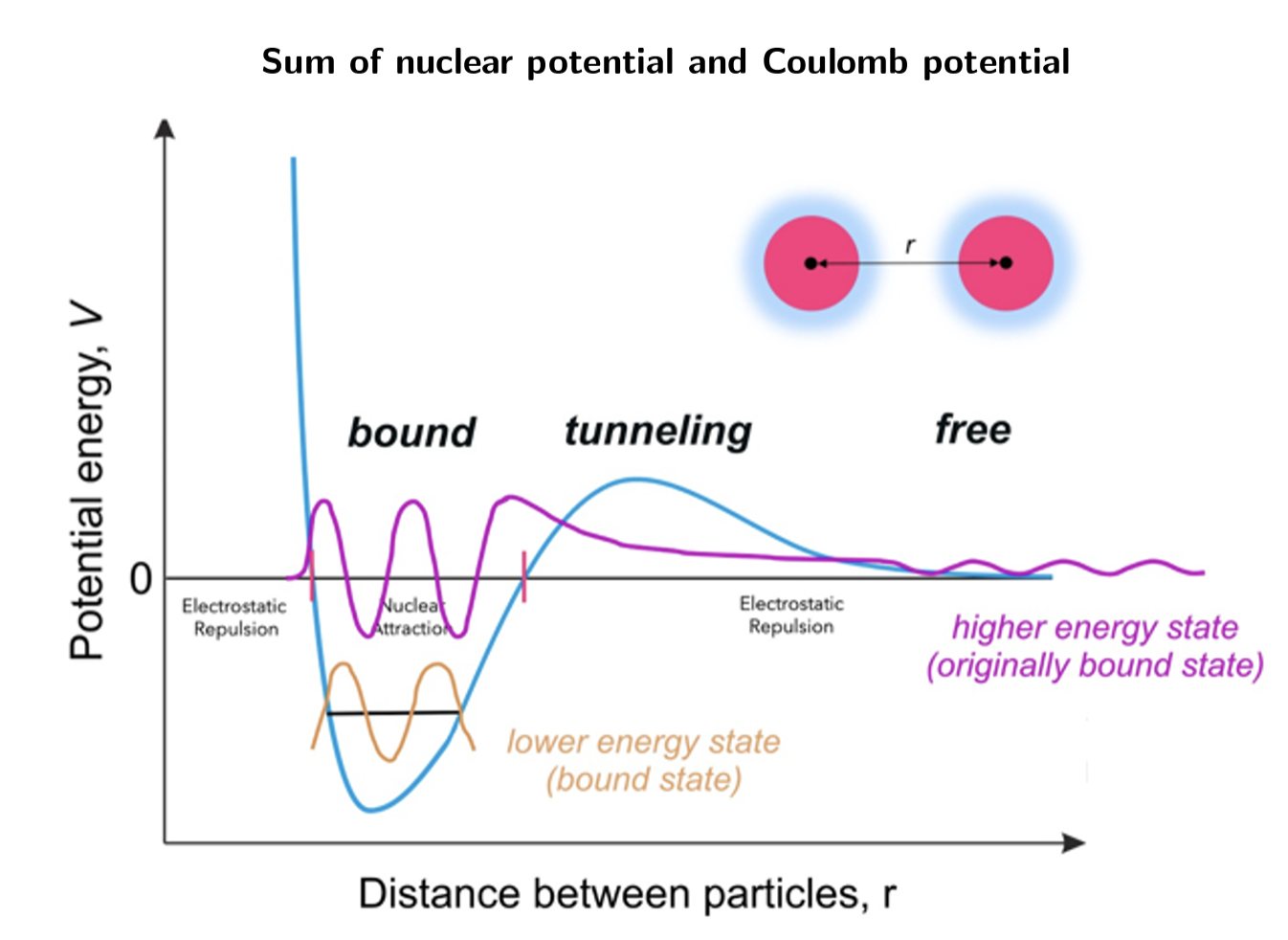
The original nucleus X is called the ____ nucleus and the decay-product nucleus Y is the daughter nucleus.
mother
parent
original
first
parent
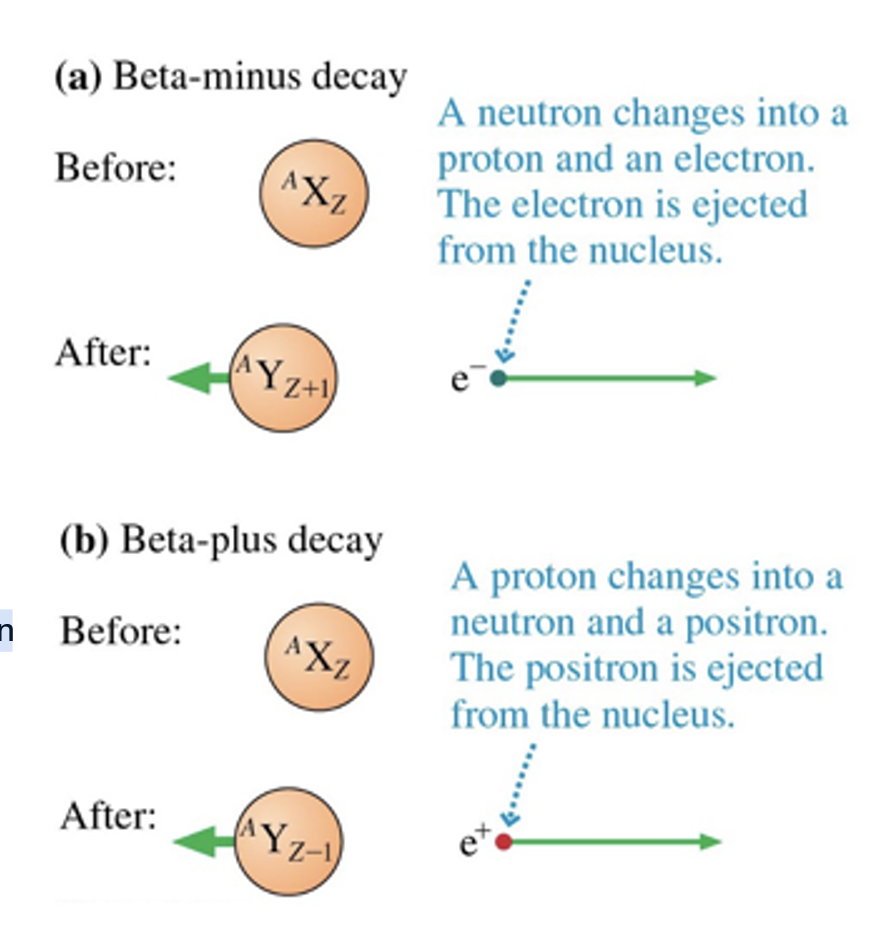
Beta decay is the emission of an electron (____) or a positron (____):
beta-minus decay, beta-plus decay
beta-plus decay, beta minus decay
-
beta-minus decay, beta-plus decay
A third form of beta decay occurs when a proton changes into a neutron by ”capturing” an electron from the innermost shell of orbiting electrons. This is called electron ___:
capture
decay
release
inhibition
capture
Previously unknown fundamental force, the ____, is responsible for beta decay. 2 The beta decay process emits a particle called a neutrino
weak interaction
strong interaction
vague interaction
medium interaction
weak interaction
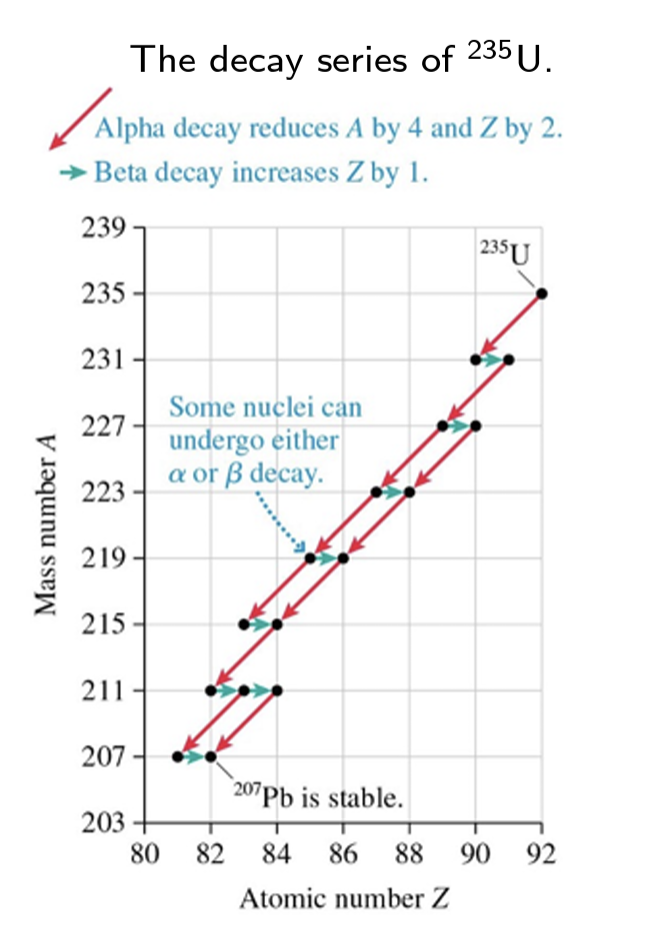
Nuclei move toward the line of stability by undergoing ___ decay.
beta
alpha
gamma
neutral
beta
A proton or a neutron in an excited nuclear state can undergo a quantum jump to a lower-energy state by emitting a high-energy photon. This is the ___-decay process.
decrease
increase
gamma
alpha
gamma
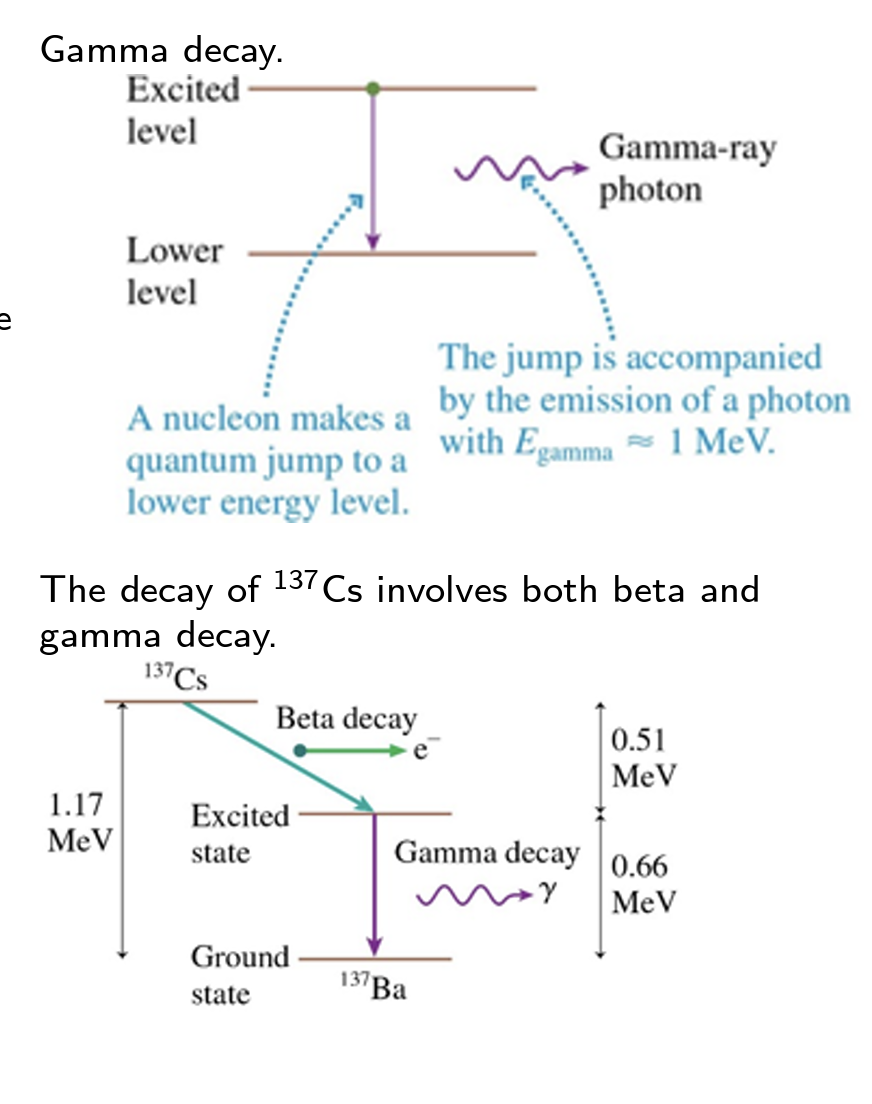
The sequence of isotopes, starting with the original unstable isotope and ending with the stable isotope, is called a ___ series.
lowering
decrease
decay
gamma
decay
Nuclear imaging, unlike x-ray images, uses internal source radiation from decaying isotopes inside the body.Also, nuclear imaging creates an image of the biological activity of tissues in the body.
A ___ camera, for example, is a device that can measure and produce an image from gamma rays within the body. Its operation is shown below.
display
alpha/beta
gamma
operation
gamma
Protons and neutrons must also obey the Pauli exclusion principle. Nuclear shells:
also follows the same simple rules as electron shells
don’t follow the same simple rules as electron shells.
don’t follow the same simple rules as electron shells.
____of the nucleus is based on the shell model of atoms that explains the periodic table of elements.
The best model
The decay model
The gamma model
The shell model
The shell model

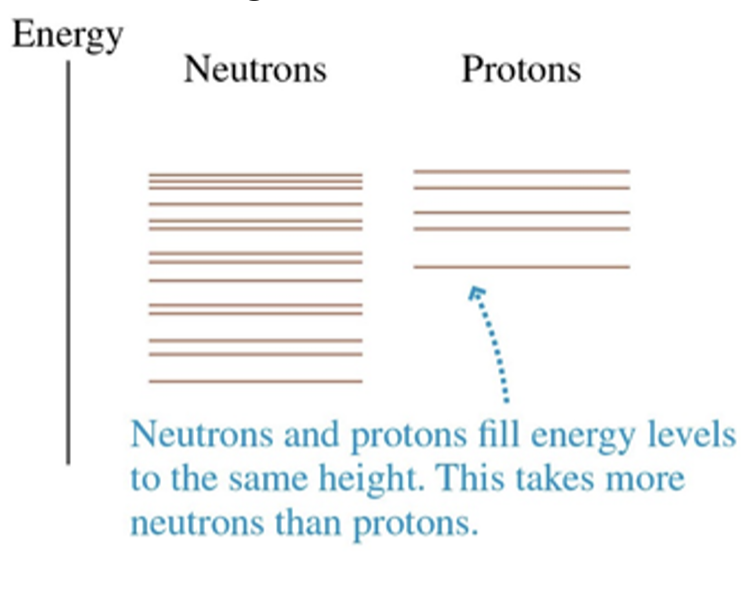
Proton energy levels are displaced upward in a high- Z nucleus
The net result of beta decay is to keep the levels on both sides filled to just about the same energy.