Week 4 - Thin Lenses
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
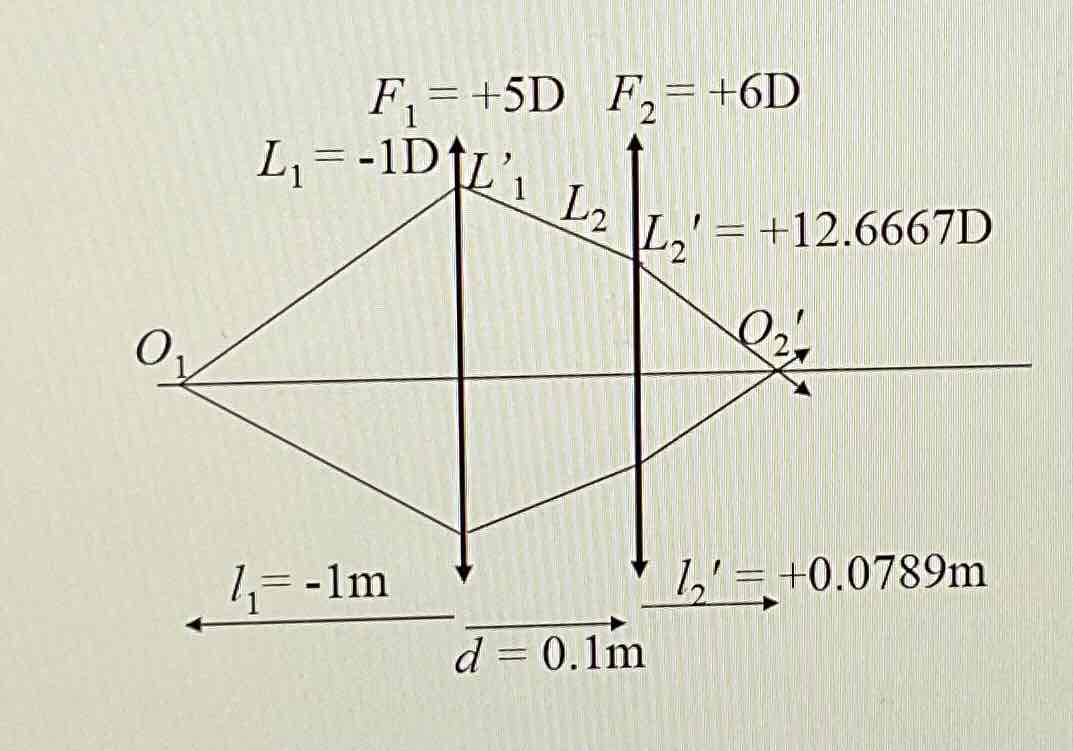
How do you do the step along method to calculate the image distance when the thin lenses are seperated?
Calculate L1
Calculate L’1
Calculate L2 ( L’1/1-dL1’)
Calculate L’2 ( L’2 = L2 + F2)
Calculate l’2
Draw a diagram to show the passage of light through a thin lens system (2 lenses) using the step along calculations in the diagram
How do you calculate magnification for thin lens systems?
m = L1 x L2/L’1 x L’2
m = h’2/h1 = L1 x L2/L’1 x L’2
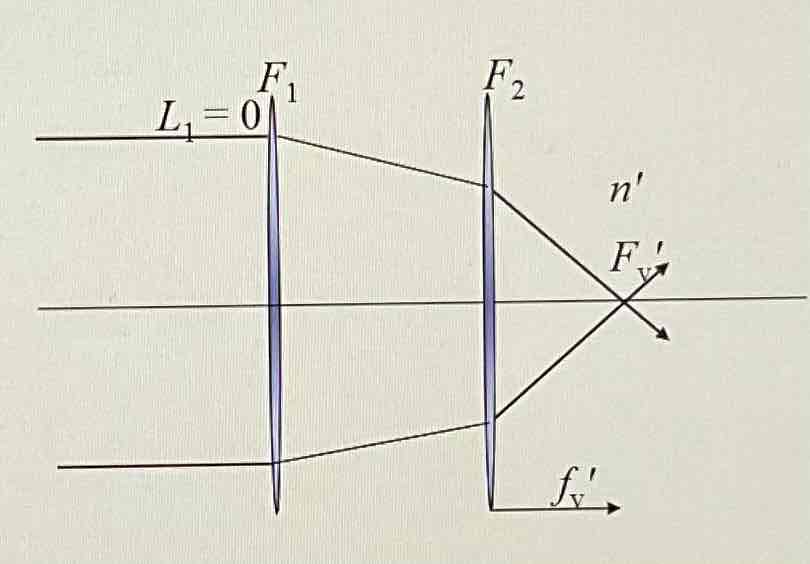
What happens when an object is placed at infinity (placed at the first focal point) in a thin lens system? Also draw a diagram.
L1 = 0
Image lies at back vertex focus (
Nf’v (back vertex focal length) - distance from second surface to F’v
F’v (back vertex power - Vergence leaving last lens) = n’/f’v
In air: 1/f’v
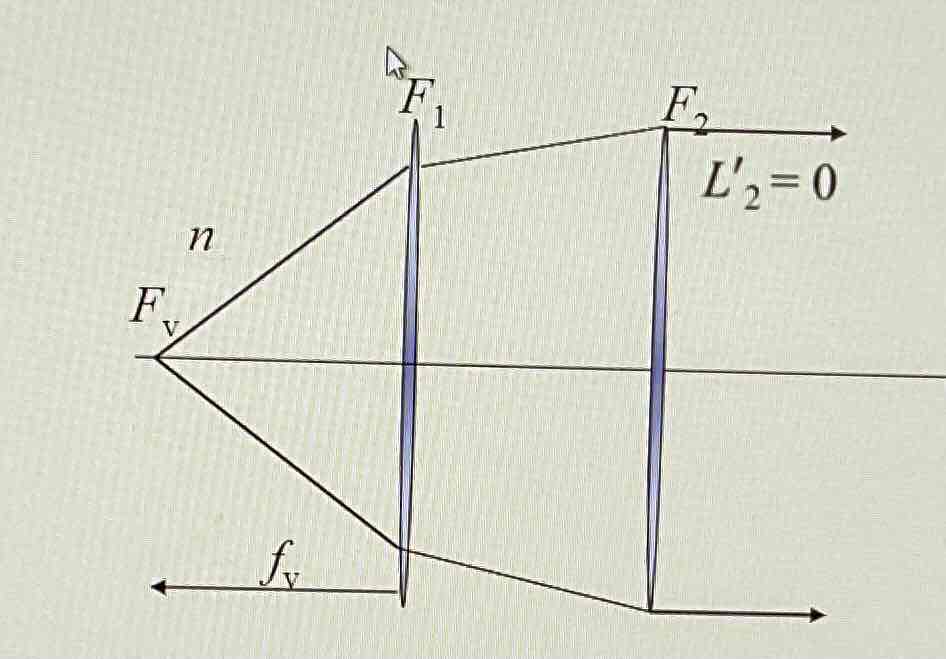
What happens when the image is at infinity (at the second focal point) in a thin lens system? Also draw a diagram.
L’2 = 0
Object lies at the front vertex focus
Front vertex focal length = fv
Fv = - n/fv
In air = - 1/fv
What is the back vertex power equation?
F’v = F1/1-dF1 + F2
What is the front vertex equation?
Fv = F2/1-dF2 + F1

Do this calculation
Mag = -0.23 (minified, inverted and real)
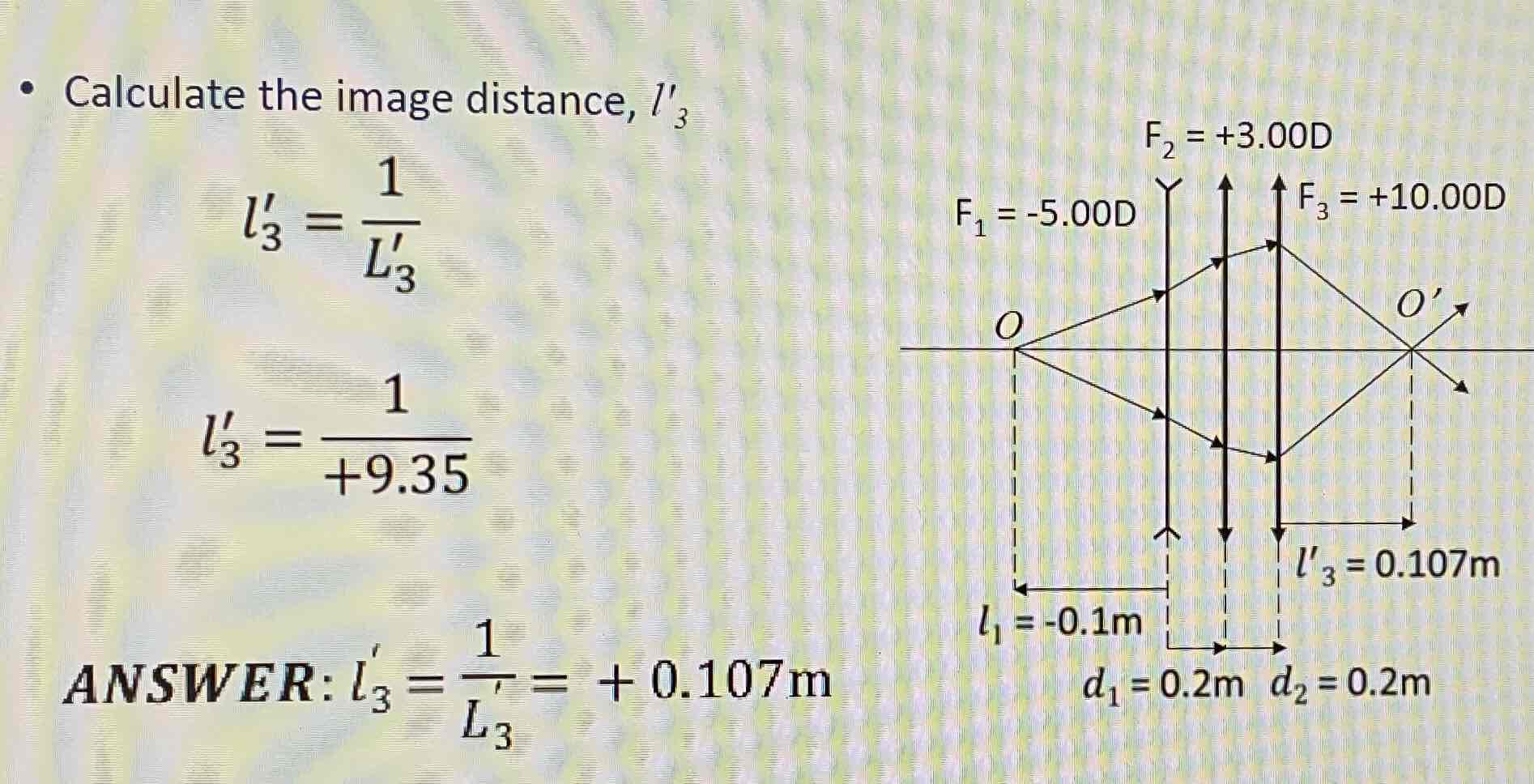
What circumstance is the retinal image clear?
When patient is emmetropic
What circumstance is the retinal image blurry?
Ametropia
What is the retinal image?
the size of the image formed in the uncorrected eye
Ignoring the effects of blur circles
How do you calculate uncorrected retinal image size (h’)?
h’ = -k’(mm)/ne x tan w (Angle)
h’ is given in mm
what is a blur circle diameter?
ametropia: a point on an object represented by a blur circle/disc on retina
In uncorrected ametropia, what is the retinal image going to look like?
A series of overlapping blur ellipses
May be on disc of least confusion (astigmatism)
How do you calculate blur circles in myopia?
y = p(-K/K’)
p = pupil size in mm
How do you calculate blur diameter in hypermetroia?
y = p(K/K’)
How does pupil size effect blur circle diameter?
the smaller the pupil the smaller the blur circle diameter
How does ametropia effect blur circle diameter?
As ametropia increases blur circle diameter increases
If too big it gets hard to recognise letters