Neuroanatomy 450 (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/171
Earn XP
Last updated 3:44 AM on 1/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
1
New cards
define neuroscience
study of brain and neurosystem
2
New cards
define neurology
diseases in nervous system, clinicians who do assessments and treatments
3
New cards
define neurosurgery
surgical intervention for treatment of nervous system
4
New cards
define neuroanatomy
study organization of CNS at gross and cellular level- neurons, fiber tracts, glial cells
5
New cards
define neuroradiology
identification of normal and abnormal brain tissue as it is in body- imaging, CT
6
New cards
define neuroembryology
embryonic growth of nervous system
7
New cards
define neuropathology
nature of diseased tissue and pathology, diagnose tissues, do not manage patients
8
New cards
why do CSD professionals need to have basic understanding of neuroscience?
prevent, assess, diagnose, treat disorders of communication and swallowing
share language with interdisciplinary care teams
share language with interdisciplinary care teams
9
New cards
what structures are a part of the CNS?
brain, spinal cord, fasciculus, nucleus, tract
10
New cards
what structures are a part of PNS?
ganglion, nerve
11
New cards
what subsystems are a part of the PNS?
somatic nervous system: cranial nerves, spinal nerves, association nerves
autonomic nervous system: sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
autonomic nervous system: sympathetic nervous system and parasympathetic nervous system
12
New cards
what is the somatic nervous system?
system that is related to voluntary control of skeletal muscle movements
13
New cards
When a signal is created in the brain, it is sent to a _______________, which is connected to general muscle.
cranial nerve
14
New cards
When a signal is created in the brain, it is sent to a _________________, which is connected to muscles of respiration.
spinal nerve
15
New cards
what are association nerves?
smaller sets of nerves that assist in transmission systems
16
New cards
what is the autonomic nervous system?
system related to involuntary (self-governing) control of skeletal muscle movements
regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands
regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands
17
New cards
what is the sympathetic nervous system’s function?
controls body arousal and body’s expenditure of energy when in hypervigilant state
18
New cards
what is the parasympathetic nervous system’s function?
controls functions of relaxation- salivation, gastric motility (movement of digestive system)
restores function when sympathetic excitement messes it up
restores function when sympathetic excitement messes it up
19
New cards
each hemisphere has _ lobes
4
20
New cards
the frontal lobe contains the
prefrontal cortex, primary motor cortex, supplementary motor area, Broca’s area, premotor cortex
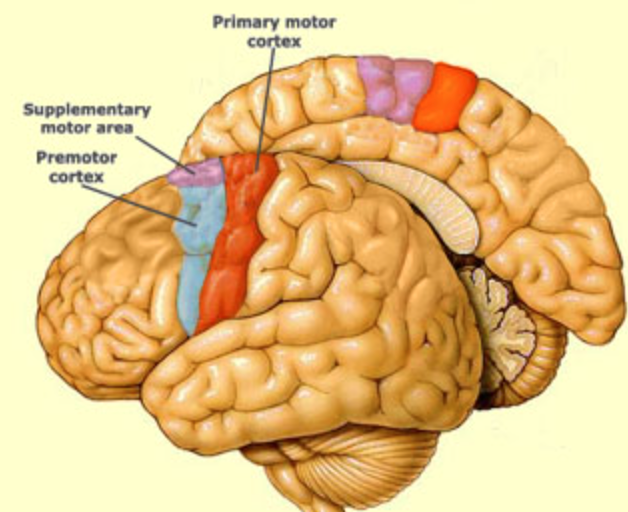
21
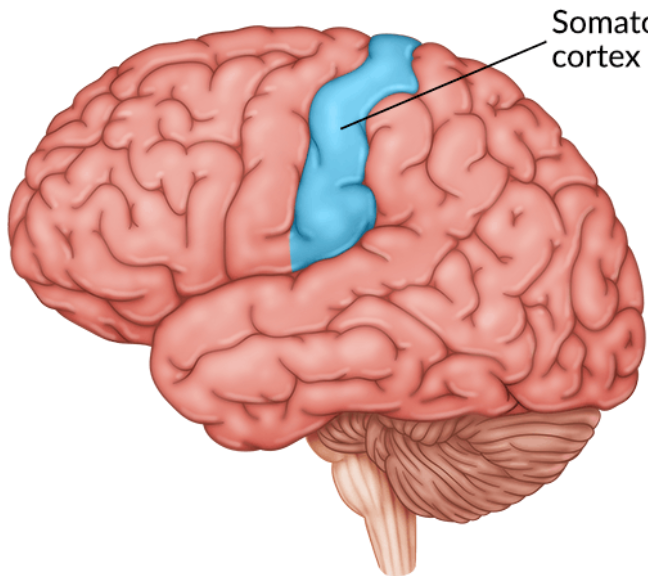
New cards
the parietal lobe contains the
primary sensory cortex
22
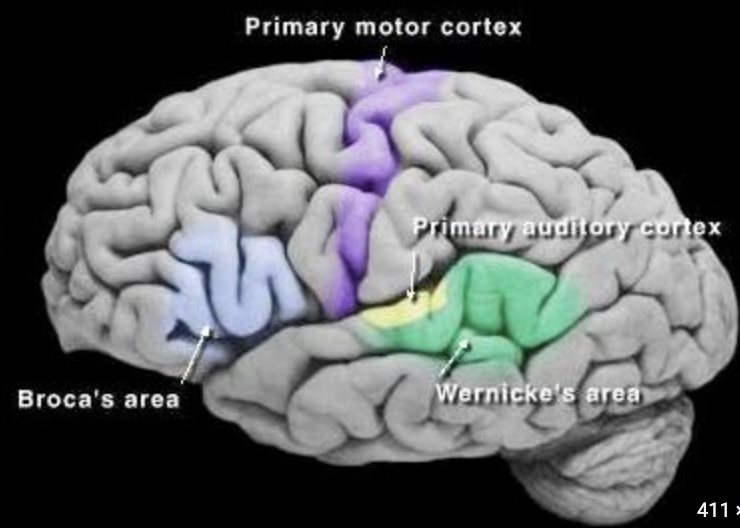
New cards
the temporal lobe contains the
primary auditory cortex, Wernicke’s area
23
New cards
what are gyri?
convolutions/ridges/hills of cerebral cortex
24
New cards
what are sulci?
furrows/valleys of cerebral cortex
25
New cards
what is a fissure?
particularly deep sulcus
26
New cards
where is the sylvian fissure (lateral sulcus)?
separates frontal lobe from temporal lobe
27
New cards
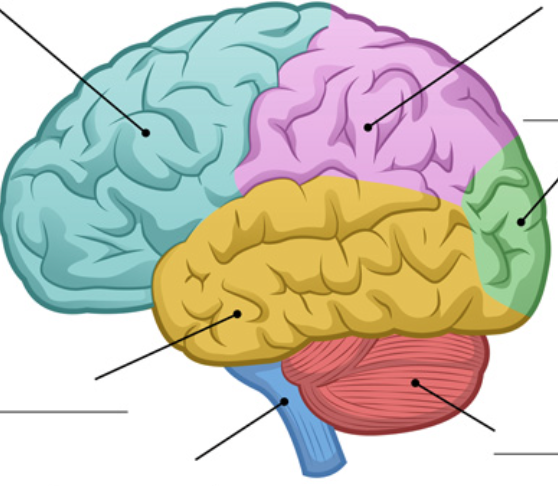
identify the frontal lobe
blue area
anterior to central sulcus
anterior to central sulcus
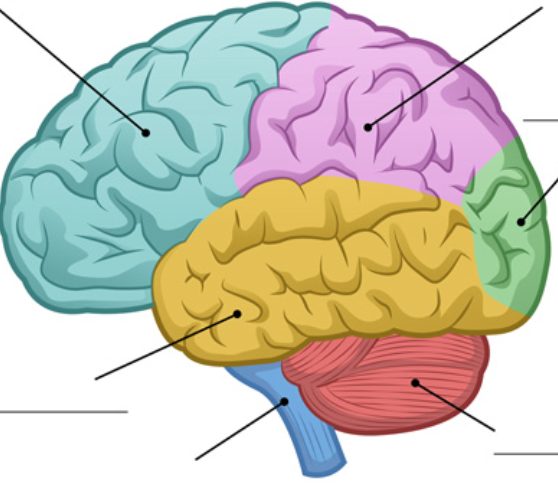
28
New cards
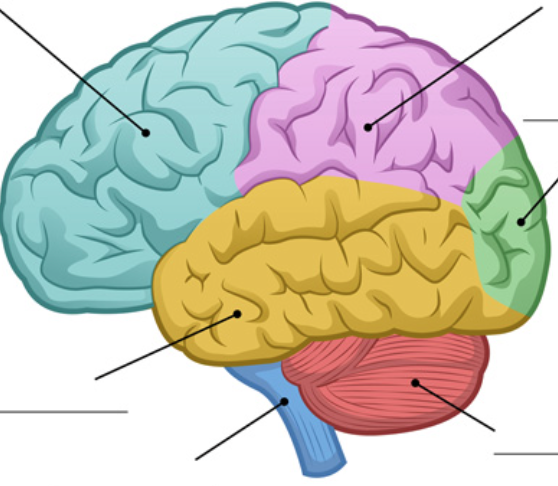
identify the parietal lobe
lavender area
posterior to central sulcus and superior to sylvian fissure
posterior to central sulcus and superior to sylvian fissure
29
New cards
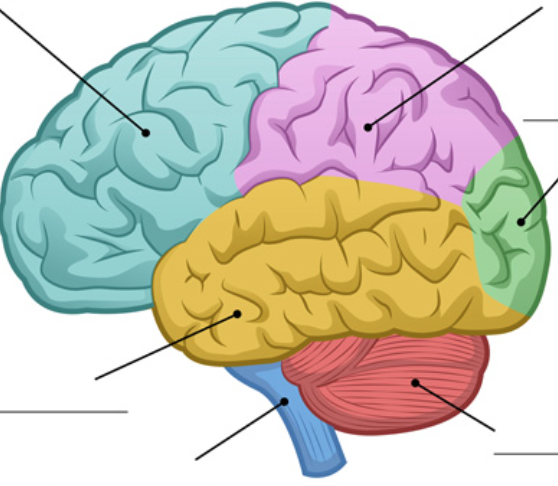
identify the temporal lobe
yellow area
inferior to sylvian fissure, anterior to occipital lobe
inferior to sylvian fissure, anterior to occipital lobe
30
New cards
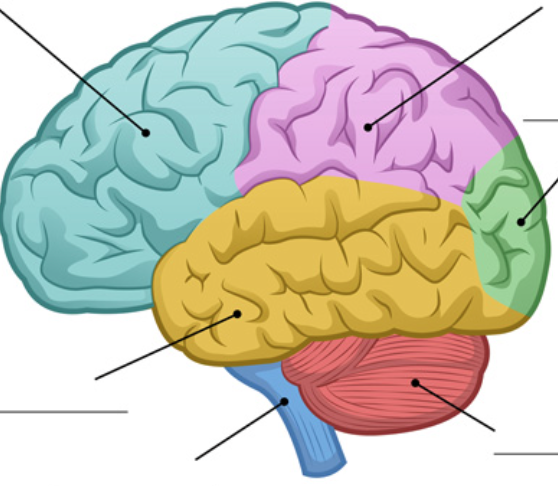
identify the occipital lobe
green area
posterior to parietal and temporal lobes
posterior to parietal and temporal lobes
31
New cards
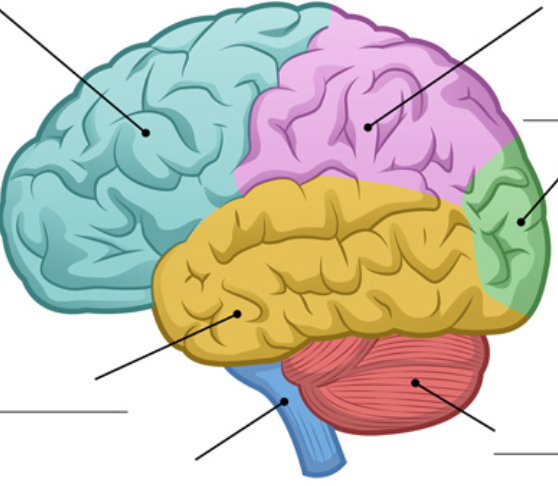
identify the cerebellum
red area
dorsal to pons and medulla
dorsal to pons and medulla
32
New cards
where is the central sulcus?
posterior part of frontal lobe
divides the frontal and parietal lobes
divides the frontal and parietal lobes
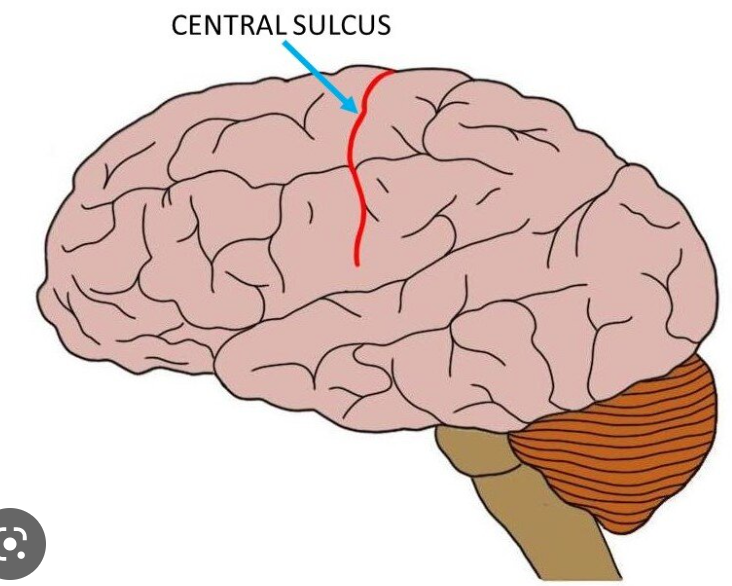
33
New cards
what are white matter tracts?
axons covered in myelin
cell bodies connecting different parts of the brain
cell bodies connecting different parts of the brain
34
New cards
Define tract
bunch of axons bundled together
part of CNS
part of CNS
35
New cards
Define nerve
bunch of axons bundled together
part of PNS
part of PNS
36
New cards
what is the function of the frontal lobe?
executive functioning, decision maker and decider, initiation of motor movement, connections to all other parts of brain
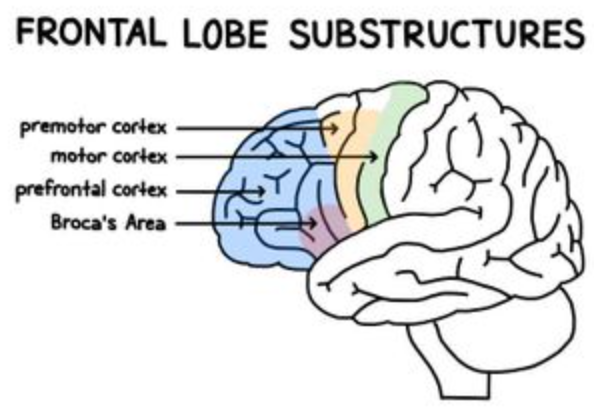
37
New cards
where is the prefrontal area?
most anterior area of frontal lobe
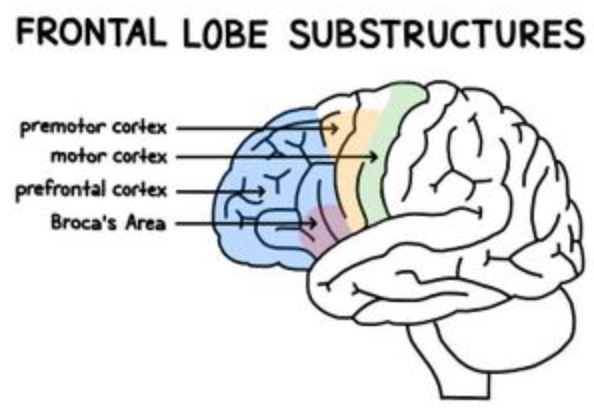
38
New cards
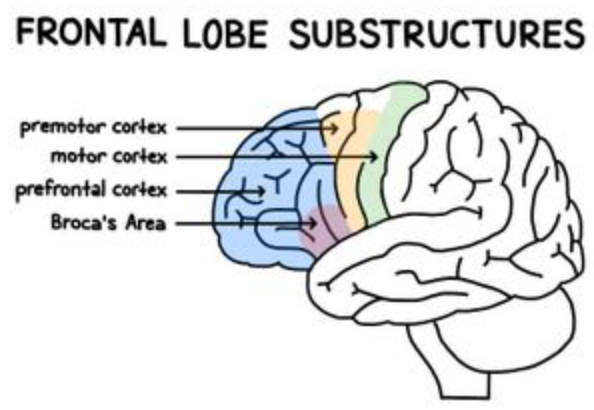
what is the function of the prefrontal cortex?
executive functions and thinking
39
New cards
what does the motor cortex include?
primary motor cortex, premotor cortex, supplemental motor cortex
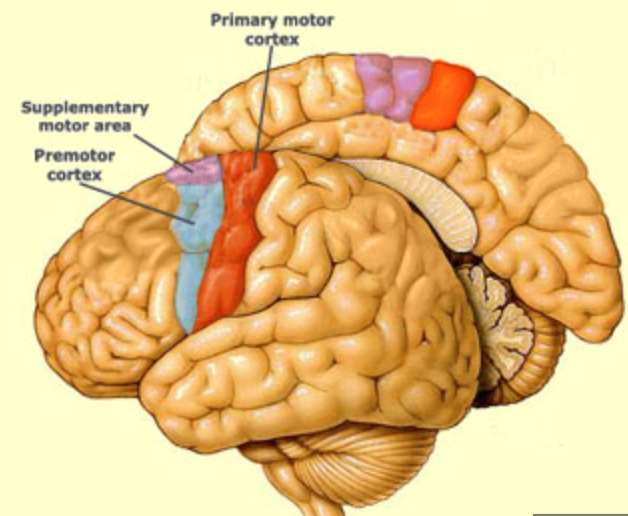
40
New cards
where is the primary motor cortex?
precentral gyrus
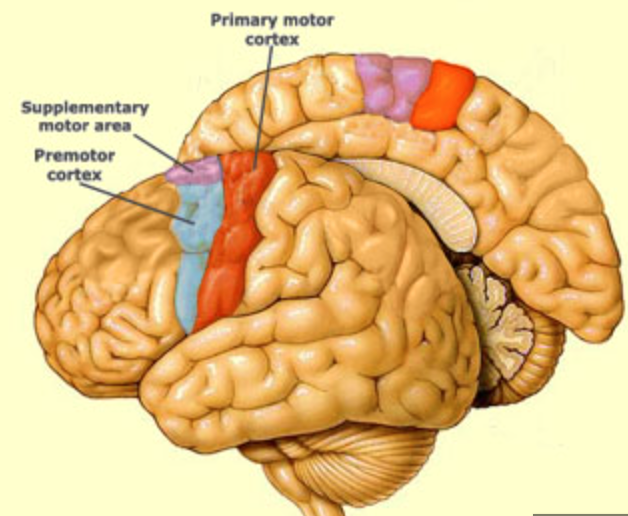
41
New cards
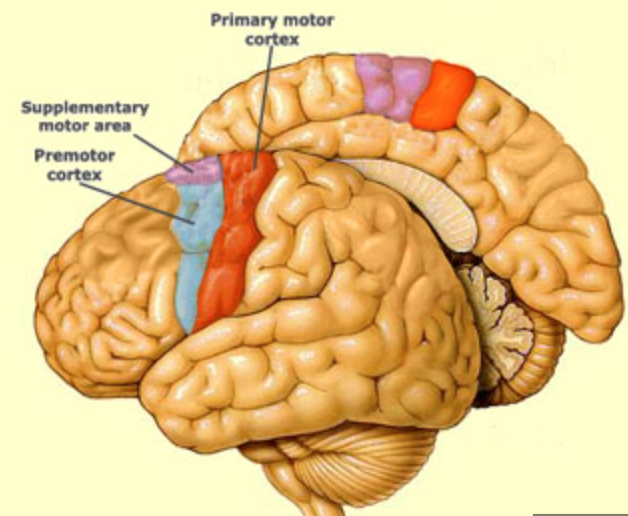
what is the primary motor cortex function?
initiation of motor activity and muscle control
has somtotopic organization
has somtotopic organization
42
New cards
where is the premotor cortex?
inferior to the supplementary motor area, stays lateral
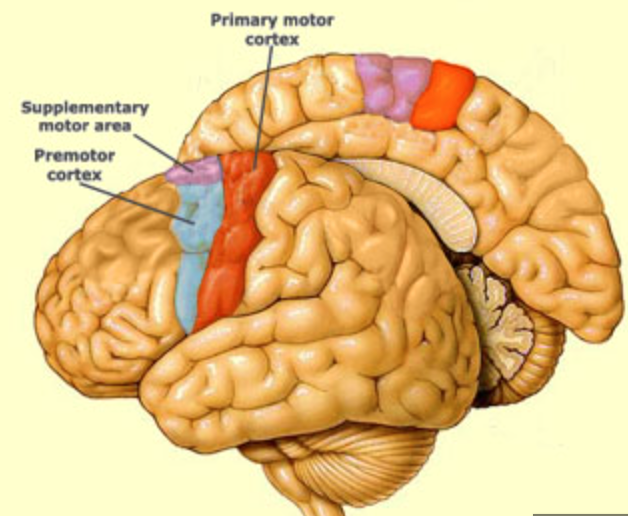
43
New cards
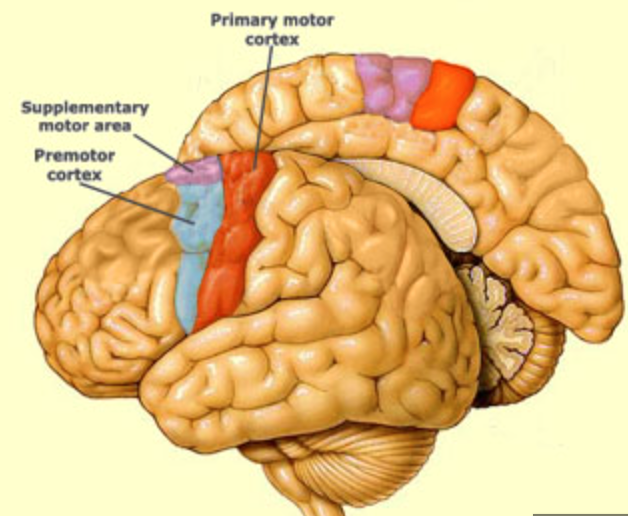
what is the function of the premotor cortex?
helps to acquire new motor sequences that aren’t stored or preplanned
44
New cards
where is the supplementary motor area?
medial surface of frontal lobe, anterior to precentral gyrus
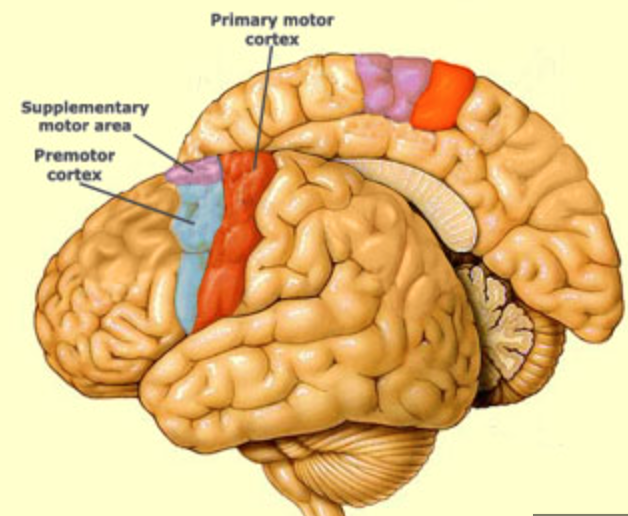
45
New cards
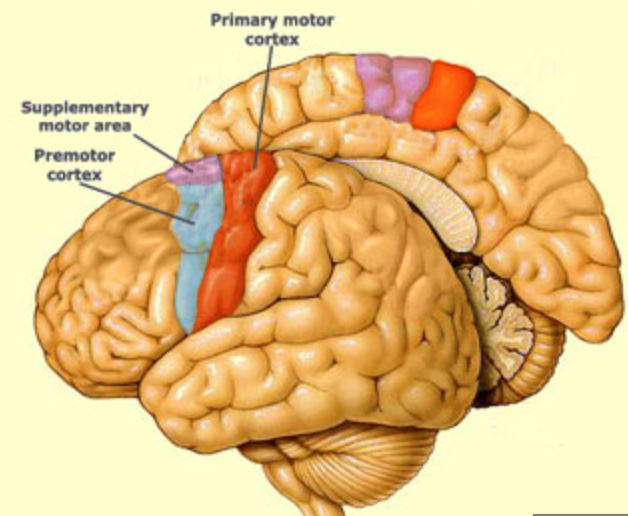
what is the function of the supplementary motor area?
helps to plan and sequence motor actions
support area
support area
46
New cards
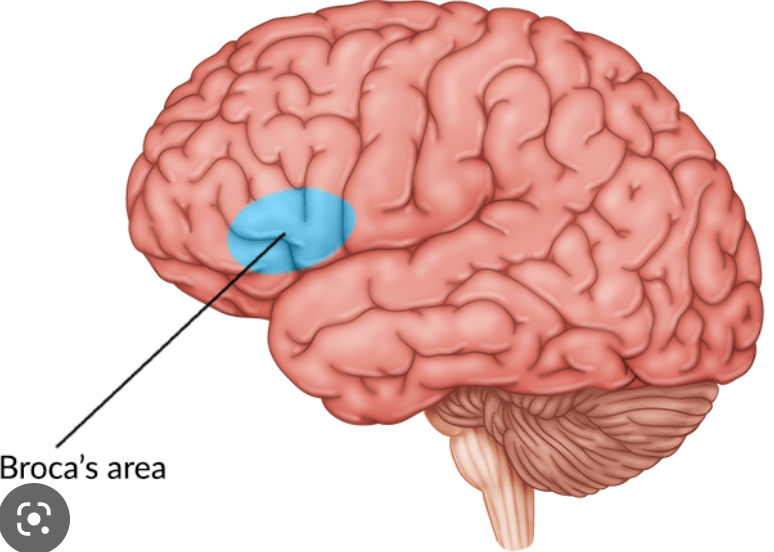
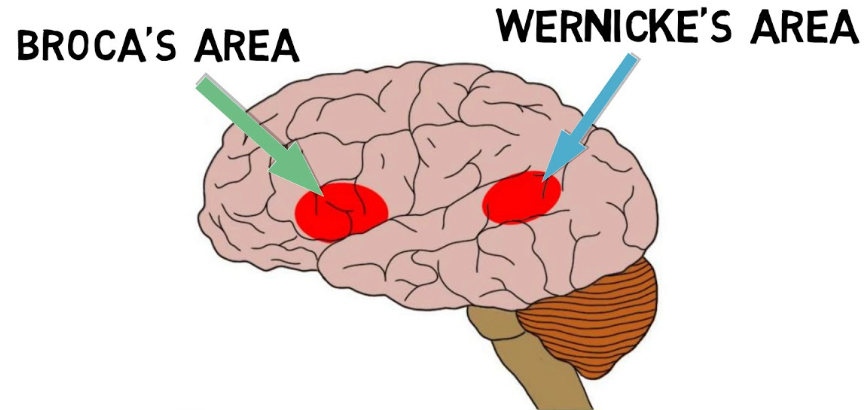
where is Broca’s area?
posterior portion of left inferior frontal gyrus (3rd frontal convolution)
47
New cards
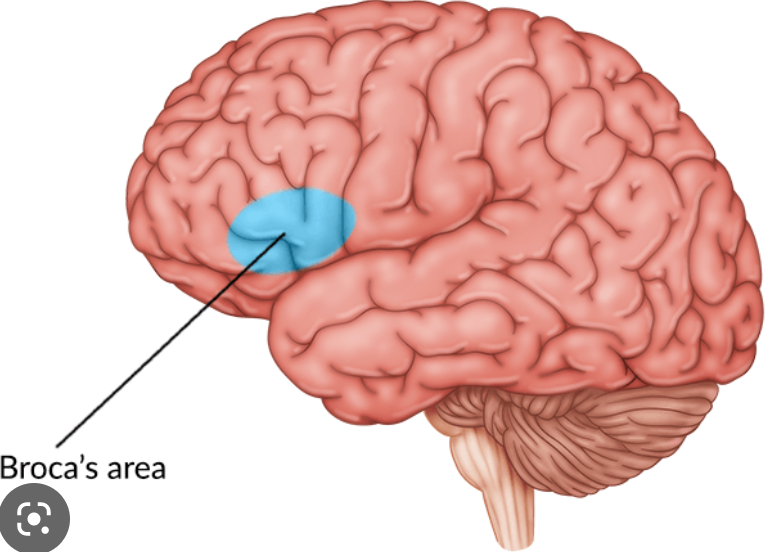
what is the function of Broca’s area?
verbal expressions (syntax, grammar) and programming movements for speech production
48
New cards
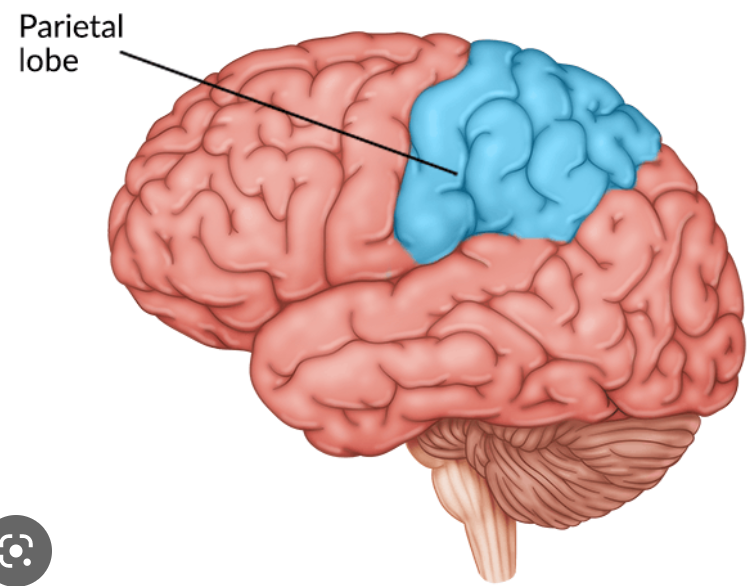
what is the function of the parietal lobe?
supplies sensory feedback to support and adjust motor movement
sensory and sensation information
sensory and sensation information
49
New cards
where is the primary sensory strip?
postcentral gyrus
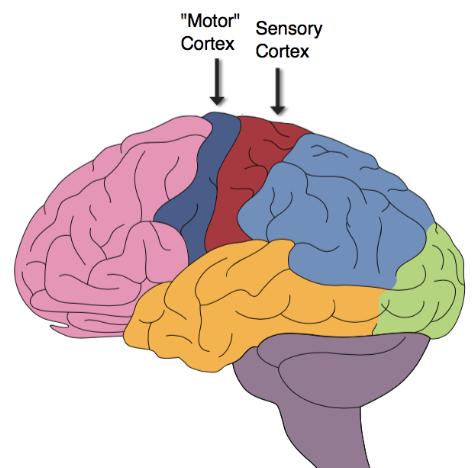
50
New cards
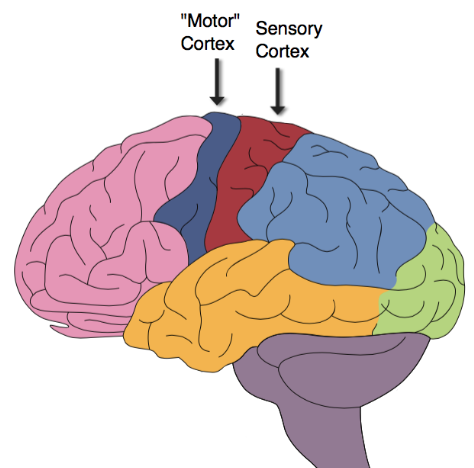
what is the function of the primary sensory strip?
processes incoming sensory information
sensory counterpart to the primary motor strip
sensory counterpart to the primary motor strip
51
New cards
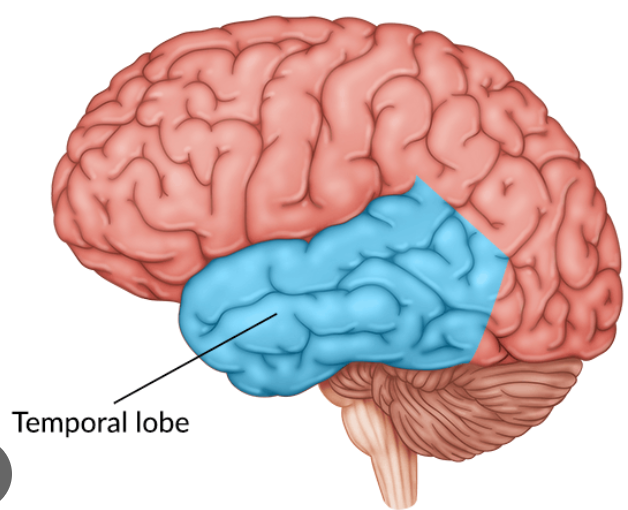
what is the function of the temporal lobe?
auditory processing
52
New cards
where is the primary auditory cortex?
transverse temporal gyrus or Heshl’s gyrus
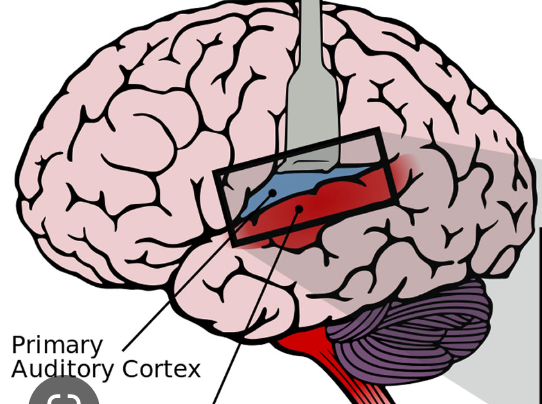
53
New cards
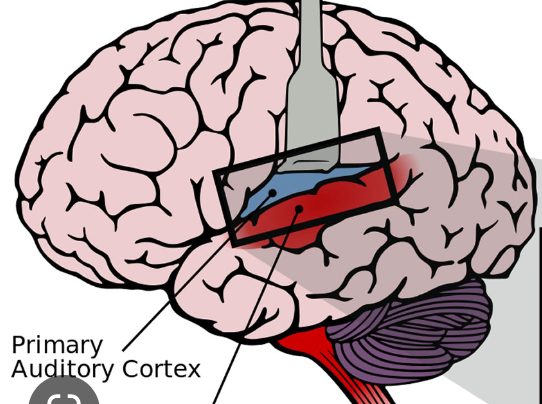
what is the function of the primary auditory cortex?
first cortical structure where auditory info is processed
figures out where to send the info to be processed
figures out where to send the info to be processed
54
New cards
where is Wernicke’s area?
posterior 1/3 portion of the left superior temporal gyrus
55
New cards
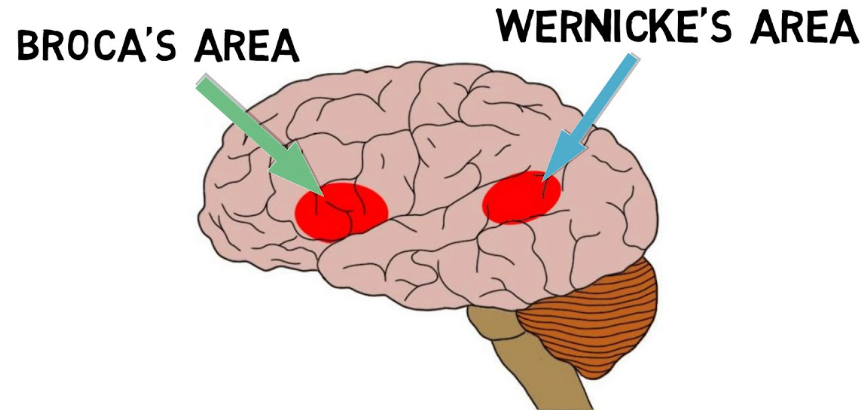
what is the function of Wernicke’s area?
auditory comprehension for language
56
New cards
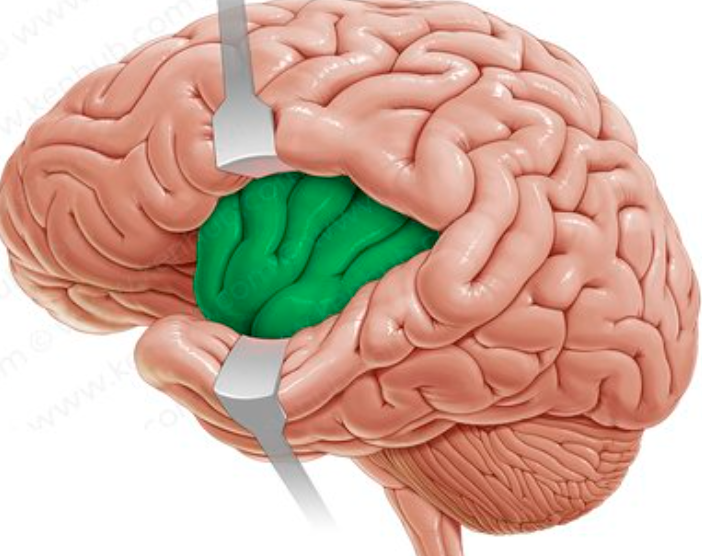
where is the insula?
deep within sylvian fissure
covered by frontal, temporal and parietal lobes
covered by frontal, temporal and parietal lobes
57
New cards
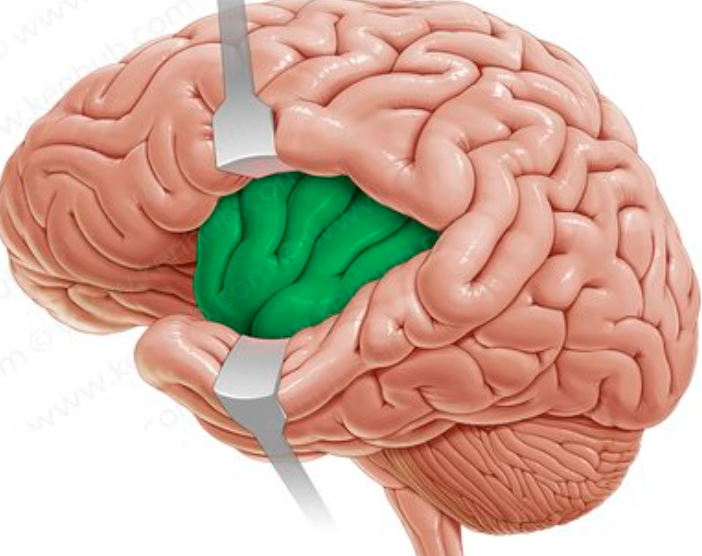
what is the insula’s function?
motor movements and cognitive functioning (self-awareness, interpersonal experience)
58
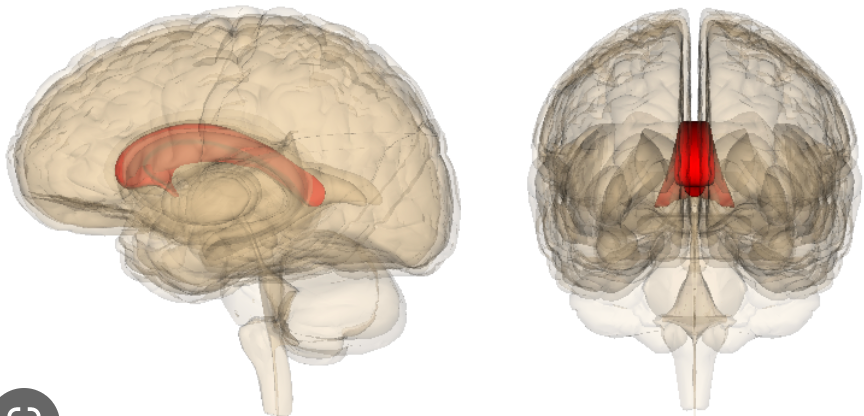
New cards
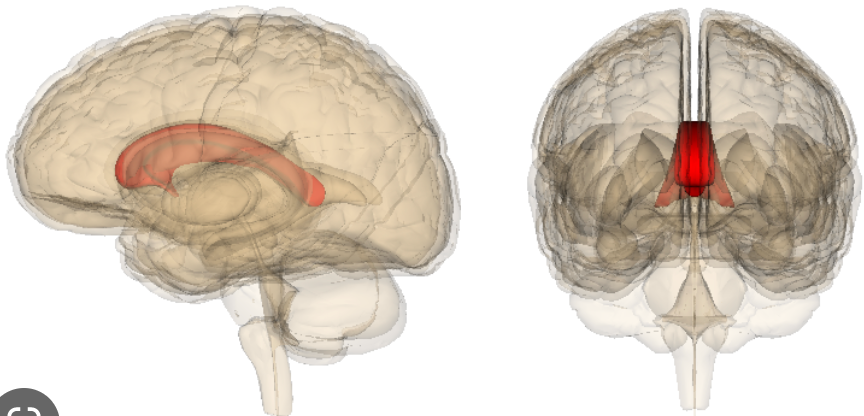
what is the function of the corpus callosum?
major white matter tract that connects the two hemispheres
59
New cards
where is the corpus callosum?
floor of longitudinal fissure and forms roof of ventricular cavities
60
New cards
where is the limbic lobe/system?
forms ring around medial-most margins of frontal, parietal, temporal lobes
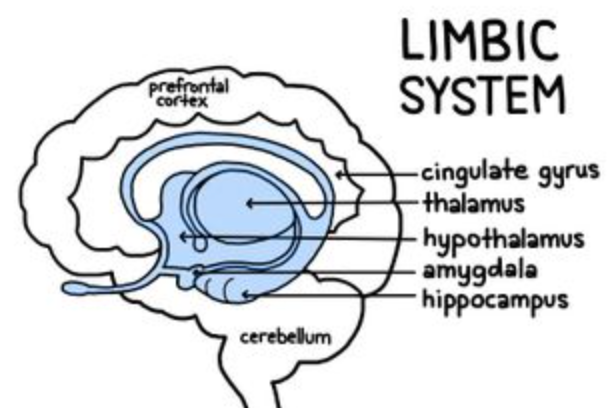
61
New cards
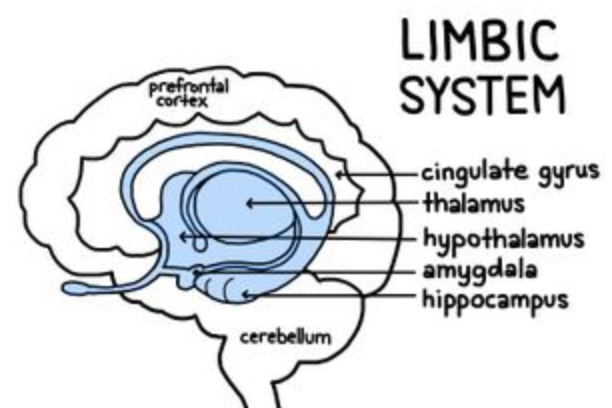
what is the function of the limbic system?
produces instinctual reflexes, emotional drive for vegetative and visceral functions, feeling and reacting
62
New cards
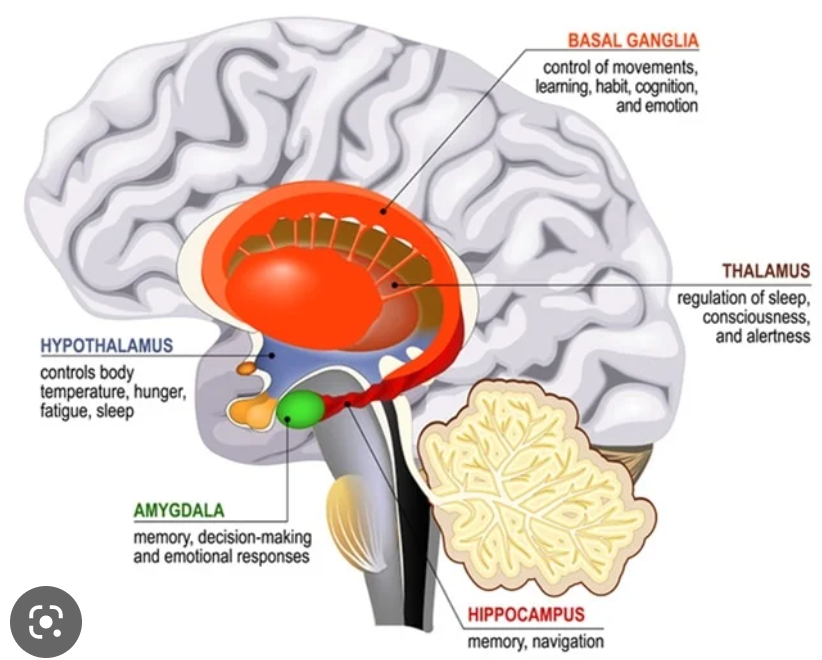
what is the function of the hippocampus?
long term memory
63
New cards
where is the hippocampus?
deep medial structure whose fornix wraps around basal ganglia
cortical structure of the limbic lobe
cortical structure of the limbic lobe
64
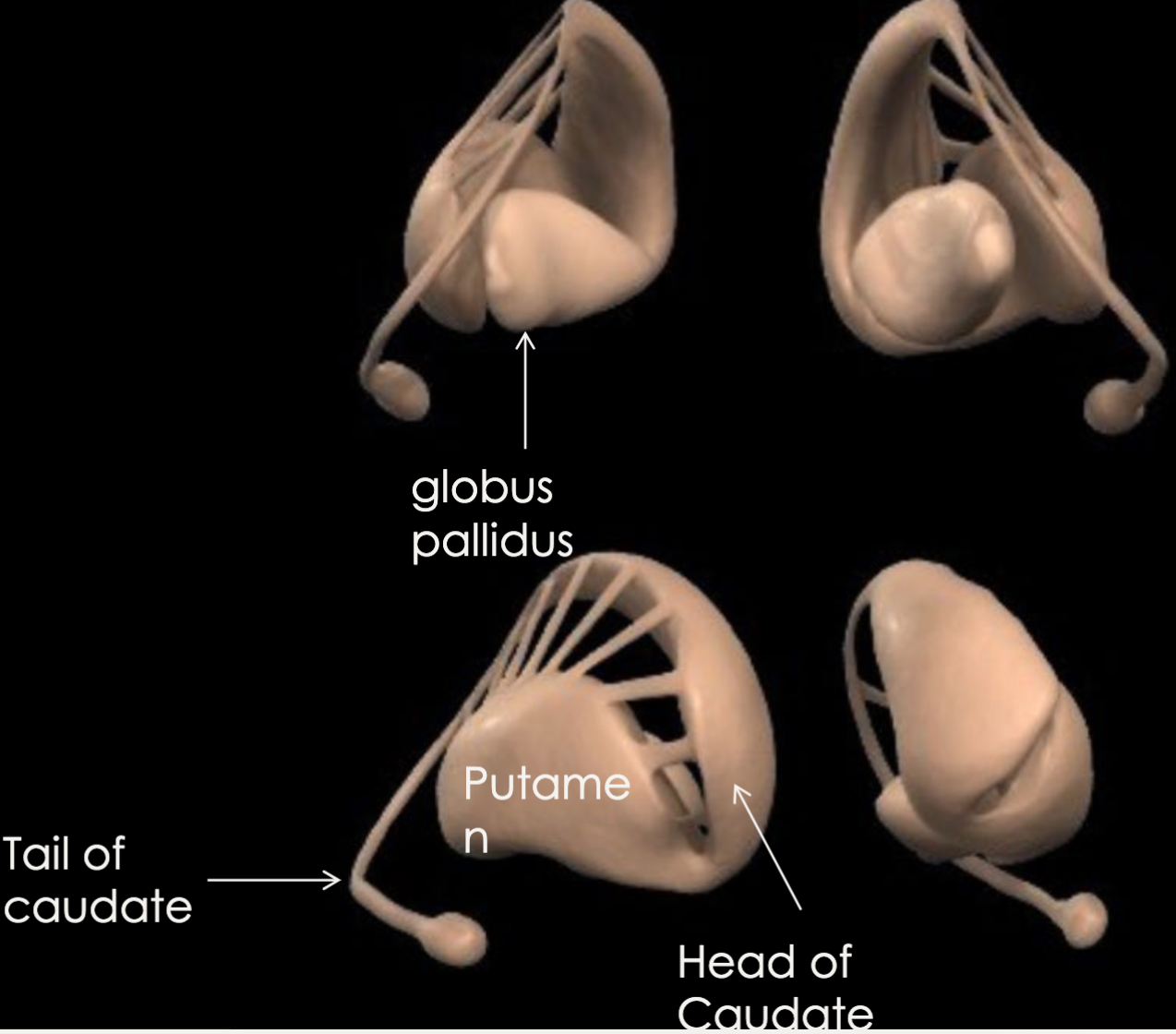
New cards
where is the basal ganglia (nuclei)?
group of structures deep within brain
3 blobs of gray matter
3 blobs of gray matter
65
New cards
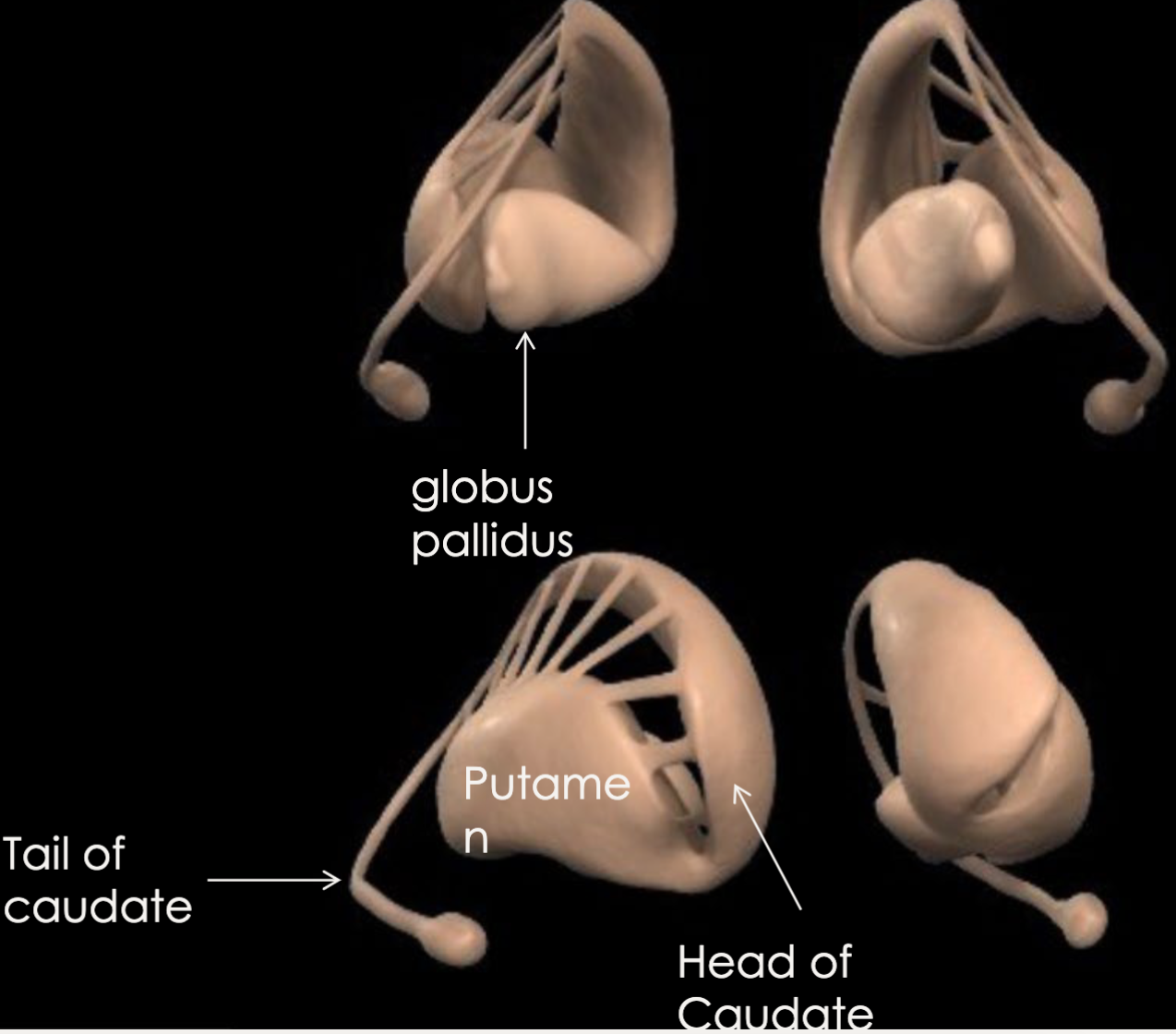
what is the function of the basal ganglia?
regulates movement
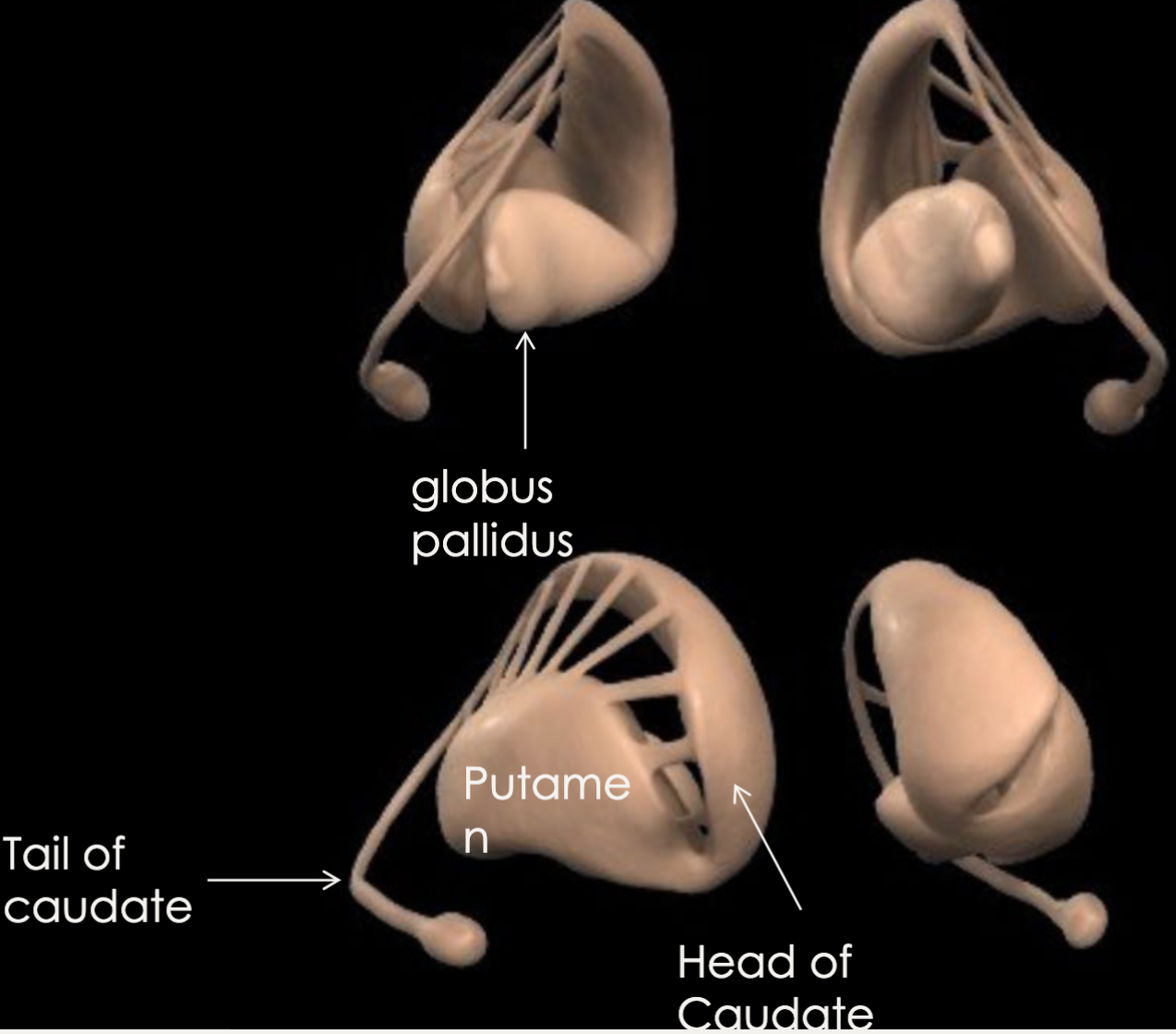
66
New cards
what are the primary structures of the basal ganglia?
caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus
67
New cards
where is the amygdala?
almond shaped deep medial structure near end of tail of caudate
subcortical structure of the limbic lobe
subcortical structure of the limbic lobe
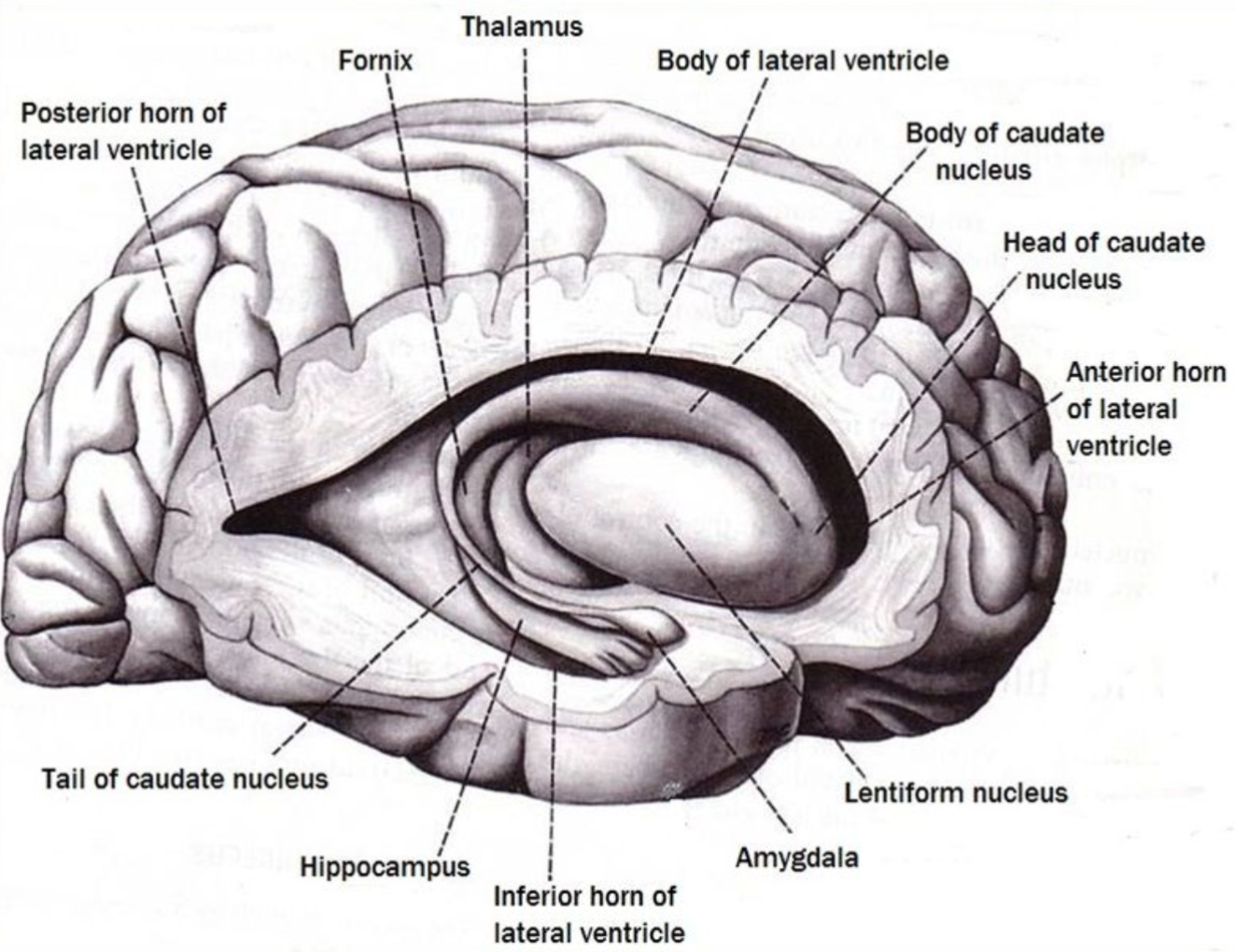
68
New cards
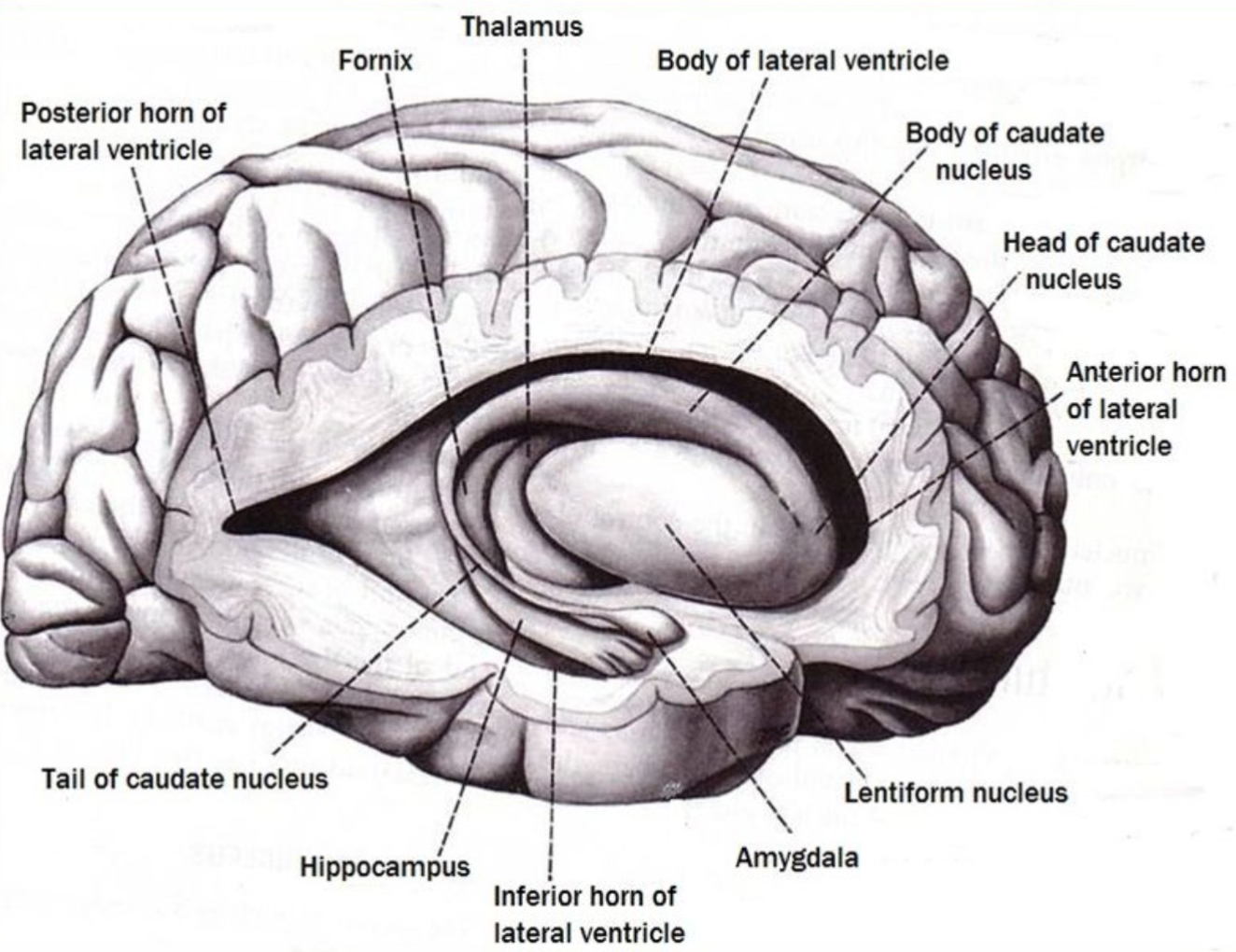
what is the function of the amygdala?
emotion and fear regulation
69
New cards
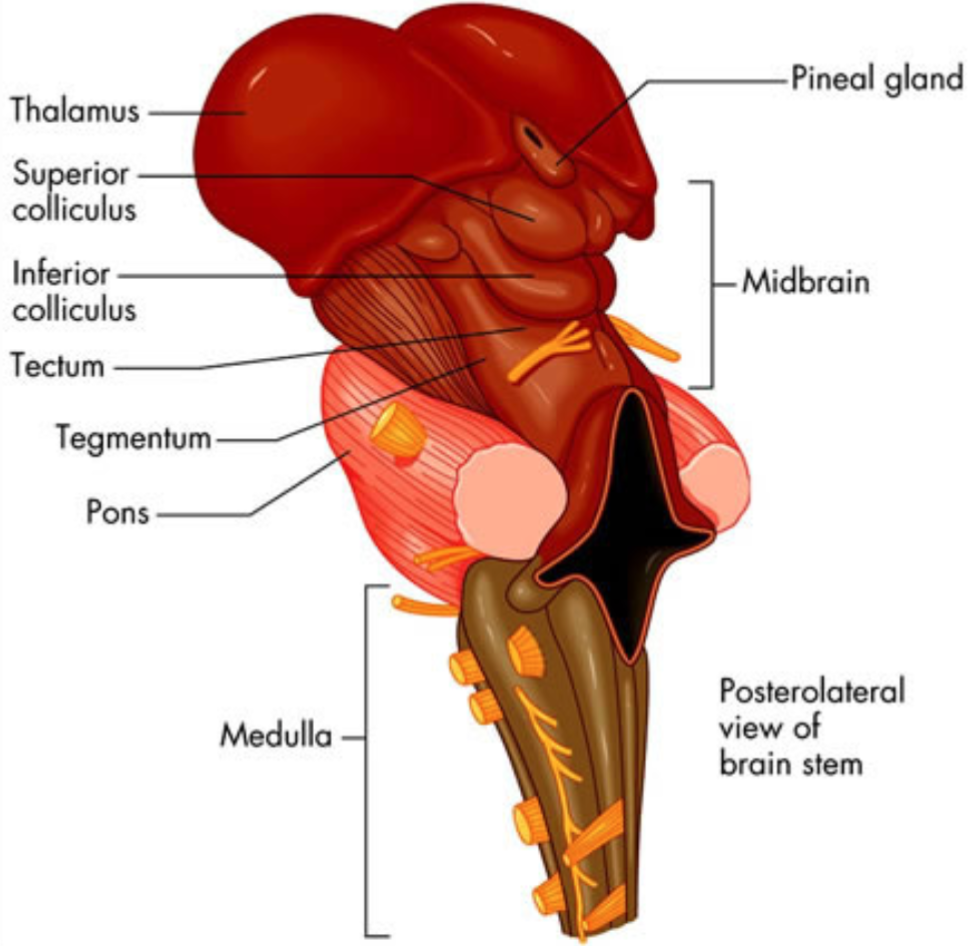
what is the function of the thalamus?
sensory relay station
any sensory info to be processed goes through thalamus first and is sent on to be further processed
any sensory info to be processed goes through thalamus first and is sent on to be further processed
70
New cards
where is the thalamus?
top of midbrain above brainstem, forms lateral wall of third ventricle
divided into several parts is called the thalamic nuclei
separates basal ganglia on each side
divided into several parts is called the thalamic nuclei
separates basal ganglia on each side
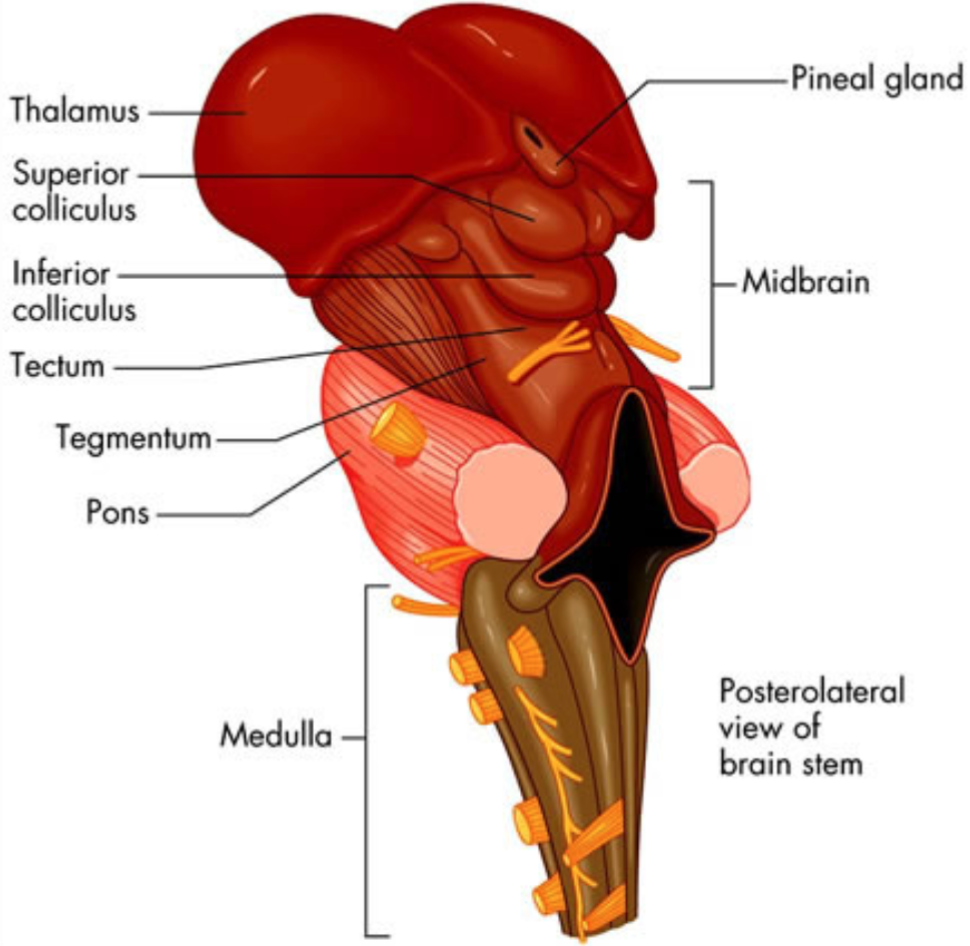
71
New cards
how is information taken into the thalamus?
information comes into and is processed in thalamus in organized way, not just a blob
72
New cards
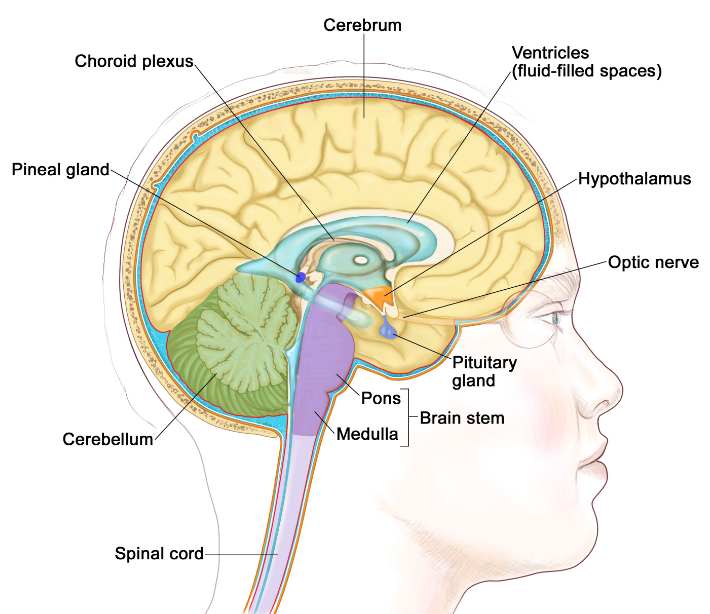
what is the function of the hypothalamus?
autonomic functions: body temp, hunger, attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep
73
New cards
what system does the hypothalamus link the nervous system to?
endocrine system
74
New cards
where is the hypothalamus?
below thalamus and near pituitary gland
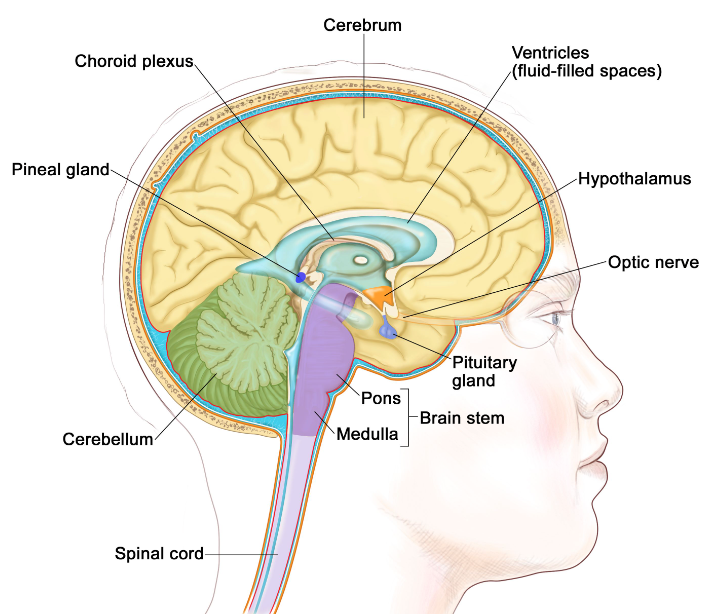
75
New cards
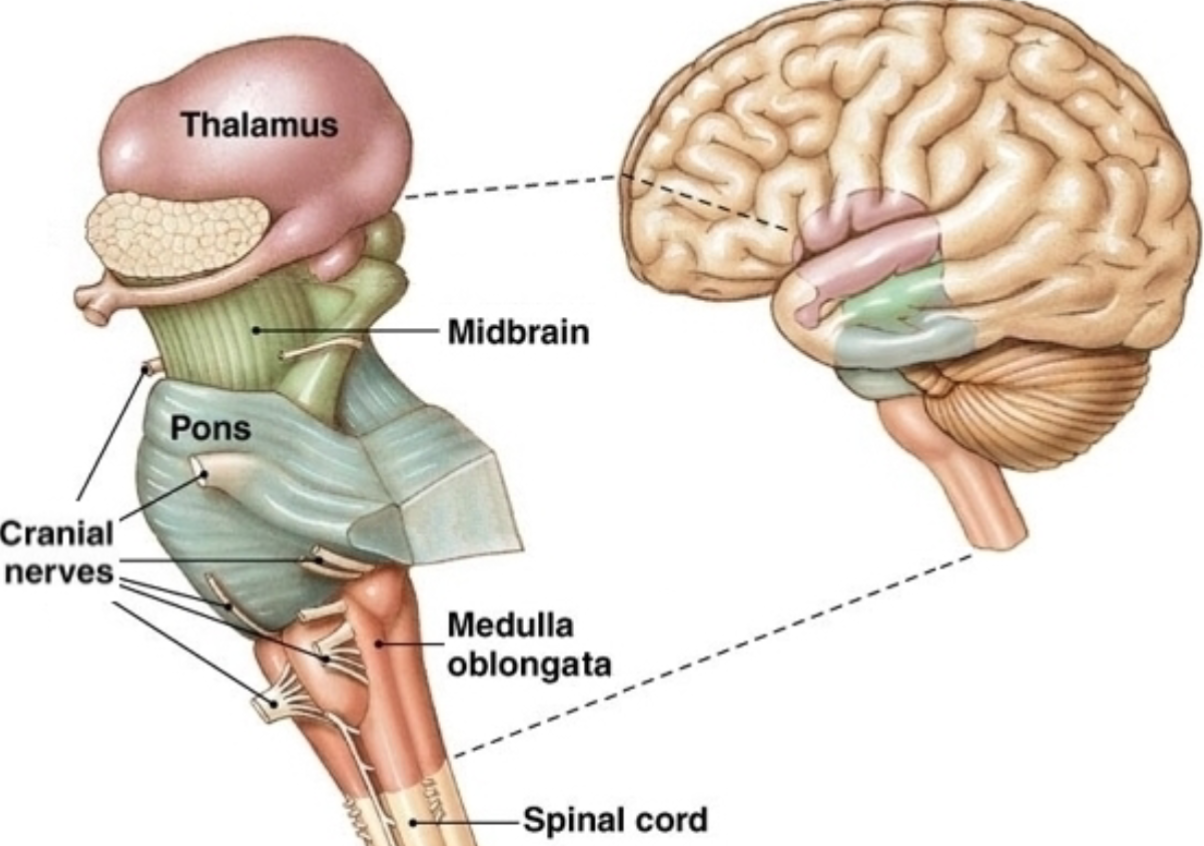
what is the function of the midbrain?
processing and relay system
76
New cards
where is the midbrain?
connects brainstem and thalamus
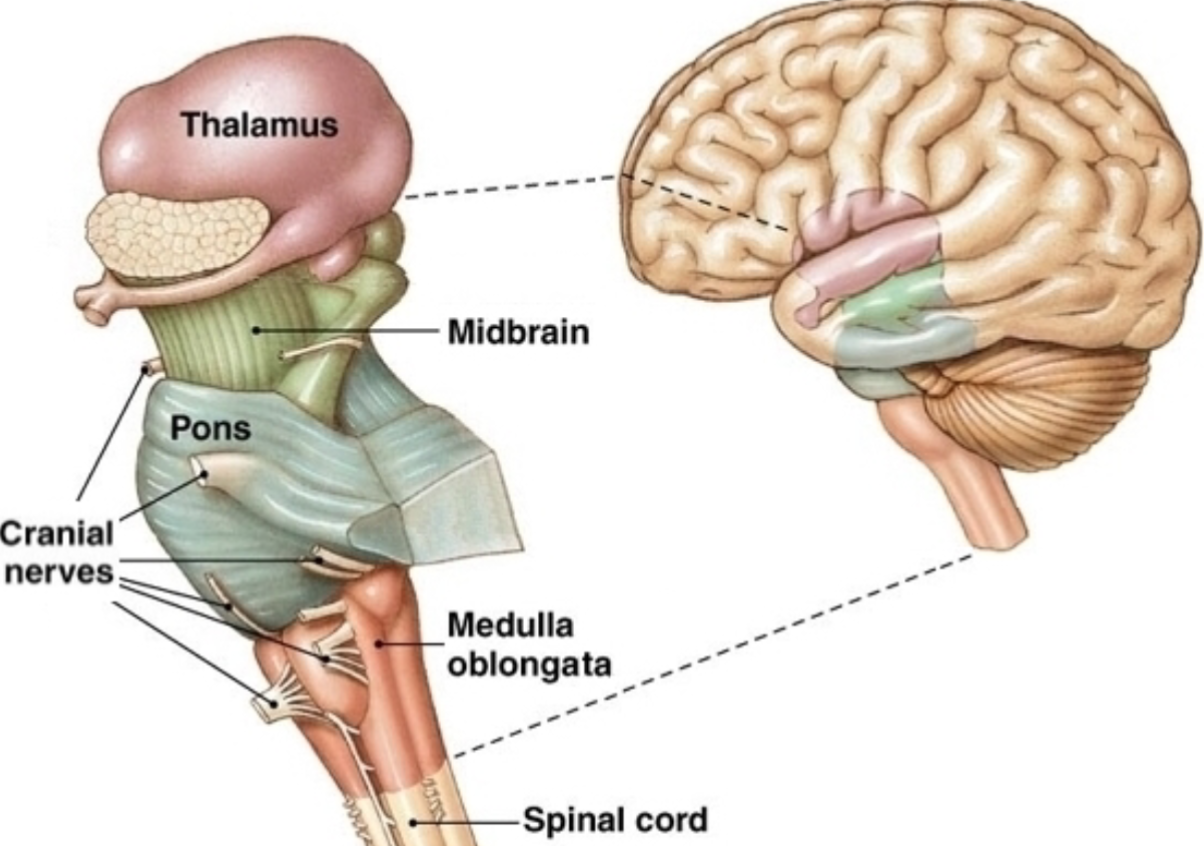
77
New cards
what are the three main structures of the midbrain?
substantia nigra, red nucleus, subthalamic nucleus
78
New cards
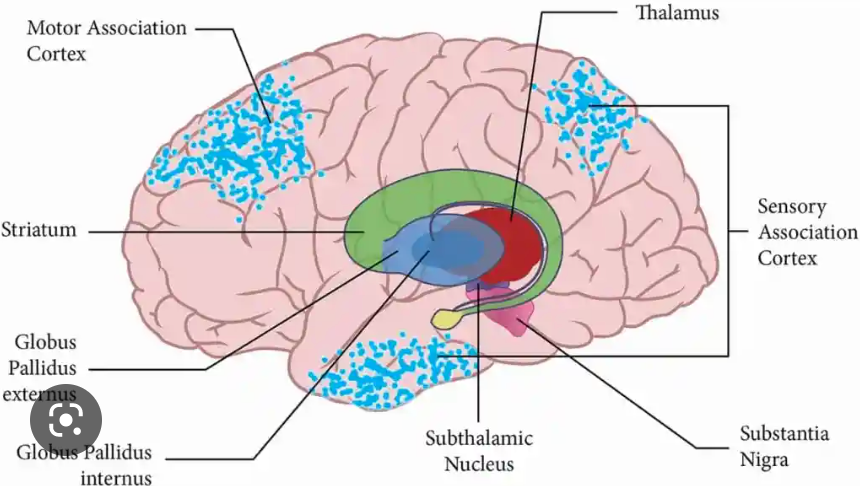
what is the function of the substantia nigra?
supplies dopamine to basal ganglia
79
New cards
where is the substantia nigra?
midbrain
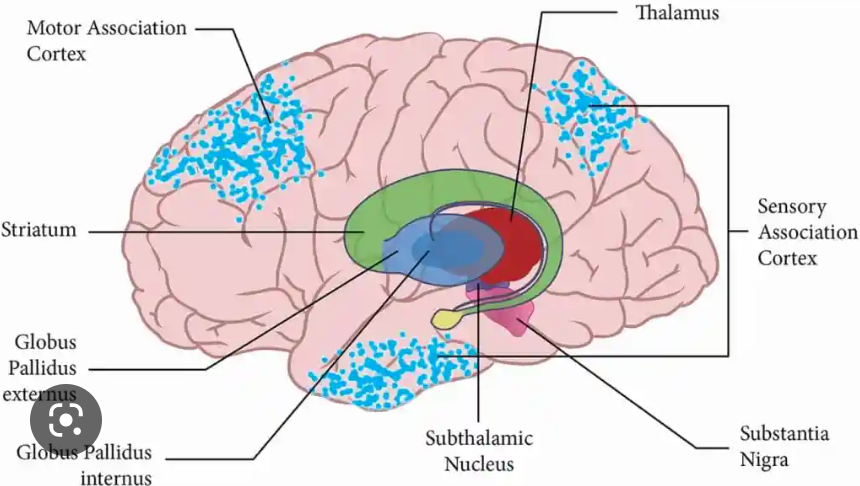
80
New cards
where is the red nucleus?
midbrain
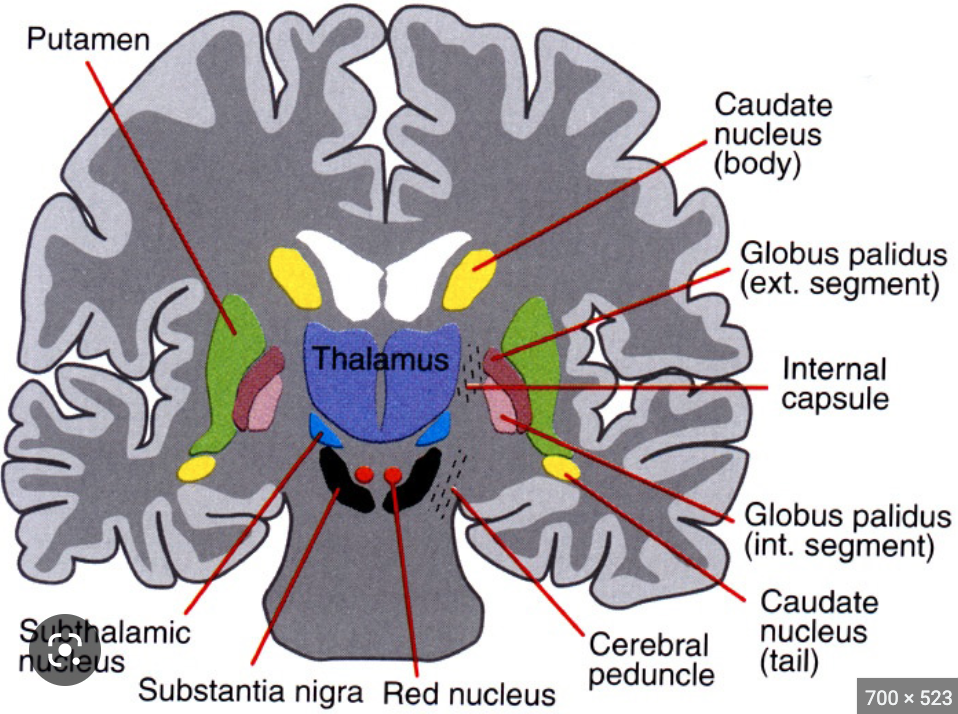
81
New cards
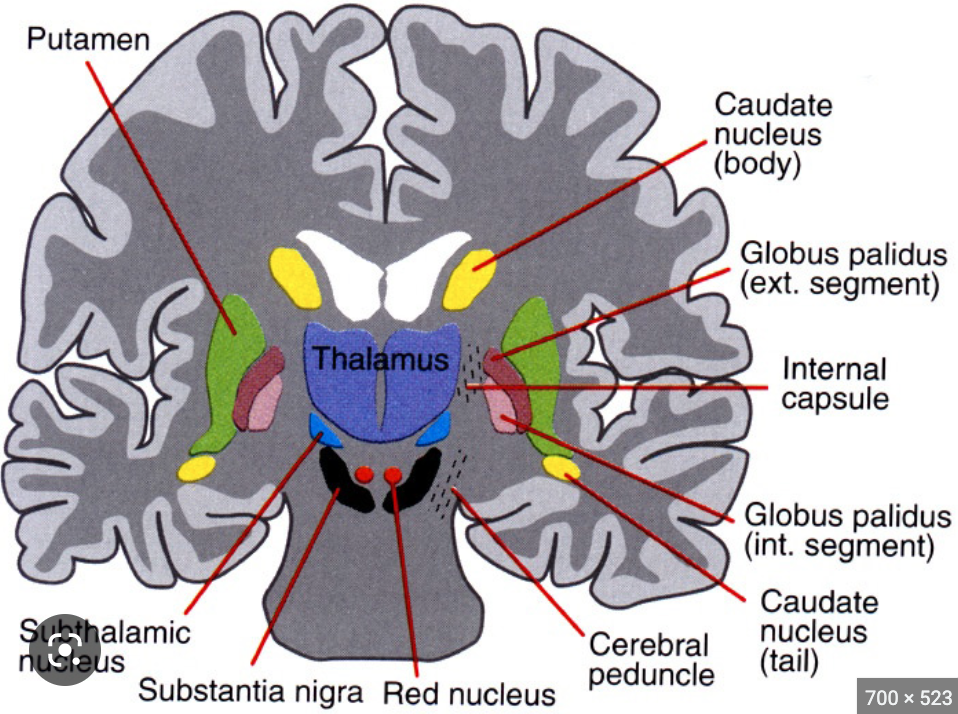
what is the function of the red nucleus?
oval mass of cells that acts as relay station for sensorimotor info
supports basal ganglia
supports basal ganglia
82
New cards
where is the subthalamic nucleus?
midbrain
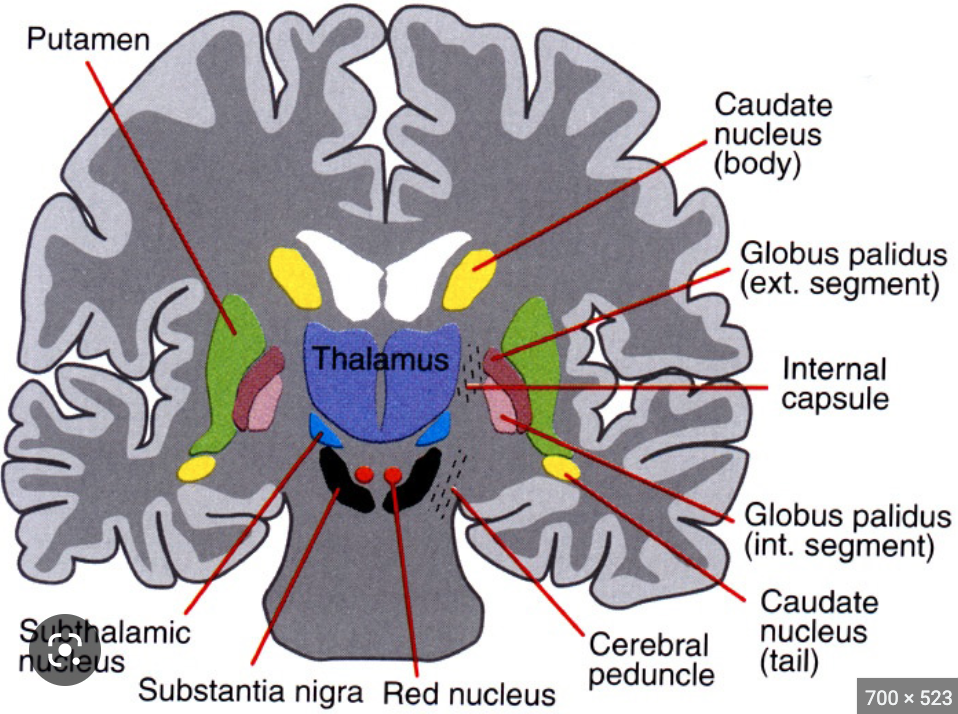
83
New cards
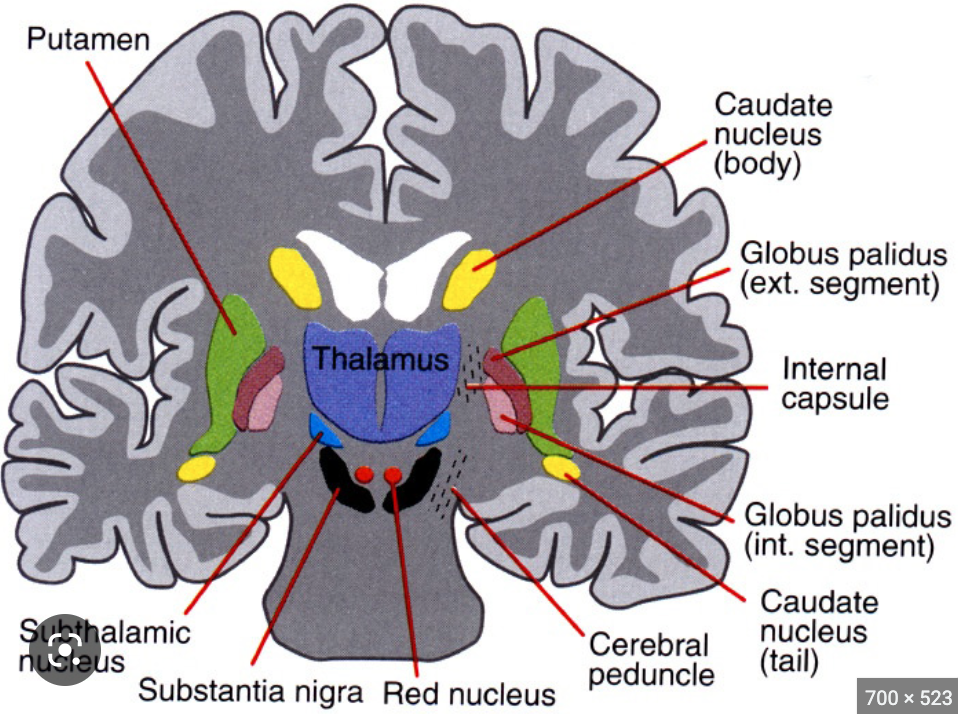
what is the function of the subthalamic nucleus?
supports motor movement and basal ganglia
84
New cards
rostral
toward nose (front of brain)
85
New cards
caudal
toward the tail (back of brain)
86
New cards
dorsal
top of brain
87
New cards
ventral
bottom/lower brain
88
New cards
superior
above
89
New cards
inferior
below
90
New cards
anterior
front
91
New cards
posterior
back
92
New cards
medial
close to midline
93
New cards
lateral
close to side (away from midline)
94
New cards
proximal
near main part of body
95
New cards
distal
away from main part of body
96
New cards
peripheral
further away from center
97
New cards
superficial
near outer surface
98
New cards
deep
further away from surface
99
New cards
sagittal plane
vertical cut that divides brain into left and right portions
100
New cards
midsagittal plane
vertical cut that divides brain into left and right equal halves