bisc 310 laboratory midterm 2025
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
protection
to keep microorganisms away from you and anything you may take out of the lab classroom
prevention
to keep microorganisms from the environment out of your work so that you can maintain the integrity of the culture you are working with
sanitizing
reduces number of microbes on a surface to a level that is considered safe
disinfecting
aims to target all microbes on a surface (viruses and bacteria)
subculturing
transferring bacteria from an old culture to fresh broth or agar
inoculation
to transfer bacteria to fresh media
four-quadrant streak designed for
allowing the isolation of single colonies of bacteria
isolated colonies often desire to provide a sample of cells that is
genetically consistent, sometimes referred to as “clonal colonies”
label plates and tube media with
your name, section number, date, organism name (or number), (and incubation temperature for plates/slants)
nutrient agar (NA)
basic lab culturing medium containing 1.5% agar that allows the medium to solidify (Nutrient Broth (NB) has same composition but w/o addition of agar
amphipathic molecules
molecules with hydrophilic polar head region and hydrophobic non-polar tail region (why soap is effective)
alcohol based sanitizers are _____ towards gram-pos and gram-neg bacteria as well as _______ towards enveloped and non-enveloped viruses, like SARS-CoV
bactericidal, viricidal
tryptic soy agar (TSA)
nutrient rich medium designed to facilitate growth of a wide range of organisms (glucose is energy source and soybean/casein provide amino acids)
fastidious
microbes with complex nutritional needs
other types of media used
sheep blood agar (SBA)
stage
platform of microscope where slide is held
mechanical stage
grip on stage where slide is held
condenser
series of lenses combined to function together below the stage
height of condenser adjusted by the
substage adjustment knob
diaphragm
controls amount of light that reaches condenser
objectives
just above the stage, attached to a rotating nosepiece, two lens systems in the microscope that are responsible for magnifying the specimen
shortest objective is aka
the low power objective (4x magnification)
longest objective is aka
the oil immersion objective (100X magnification)
40x objective is aka the
high-dry objective since it produces highest mag w/o oil
ocular or eyepiece
other lens system that provides magnification, specifically by enlarging the image that is transmitted by the objective (10x in this lab)
resolution
minimum distance between two objects which still allows them to be seen as separate (power to see two objects as separate, not same as magnification)

magnification
deals w the size of the image, extent to which an object appears bigger than true size
focus
deals with sharpness of image
numerical aperture
inherent property of the objective lense that has a fancy formula (R=λ/2NA)
never use what for microscope cleaning?
kimwipes
total magnification of the image is product of
individual magnifications provided by the objective and the ocular lenses (for example, 100x objective times 10x = 1000x magnification)
parfocal
means that once specimen is found under 10x objective, it will be in correct focal plane for other objectives as well
how to adjust ocular lenses
adjust interpupillary distance and diopter ring
calibration
process for assigning distance to the ocular micrometer
differential stains
four procedures used in prepared slides
-gram stain
-flagella stain
-capsule stain
-endospore stain
monotrichous
single flagellum
amphitrichous
has flagella at both ends
lophotrichous
tuft of flagella at one or both ends
peritrichous
has flagella surrounding the cell
capsule stains
complex stains because uses 2 stains, first positively stain with pink dye, then negatively stain with a dye that does not penetrate the capsule (physical process and not a chemical one in which a dye binds to a cellular material)
endospore stains
gram stain procedure used for these stains
flagella
specialized structure that many bacteria use for movement
motility test medium (MTM)
semi solid medium prepared as an agar deep (aka agar butt) made w or w/o indicator triphenyl tetrazolium chloride (TTC)
-as bacteria grow, ttc is reduced forming a red precipitate, allows to see if bacteria are motile (move) or not
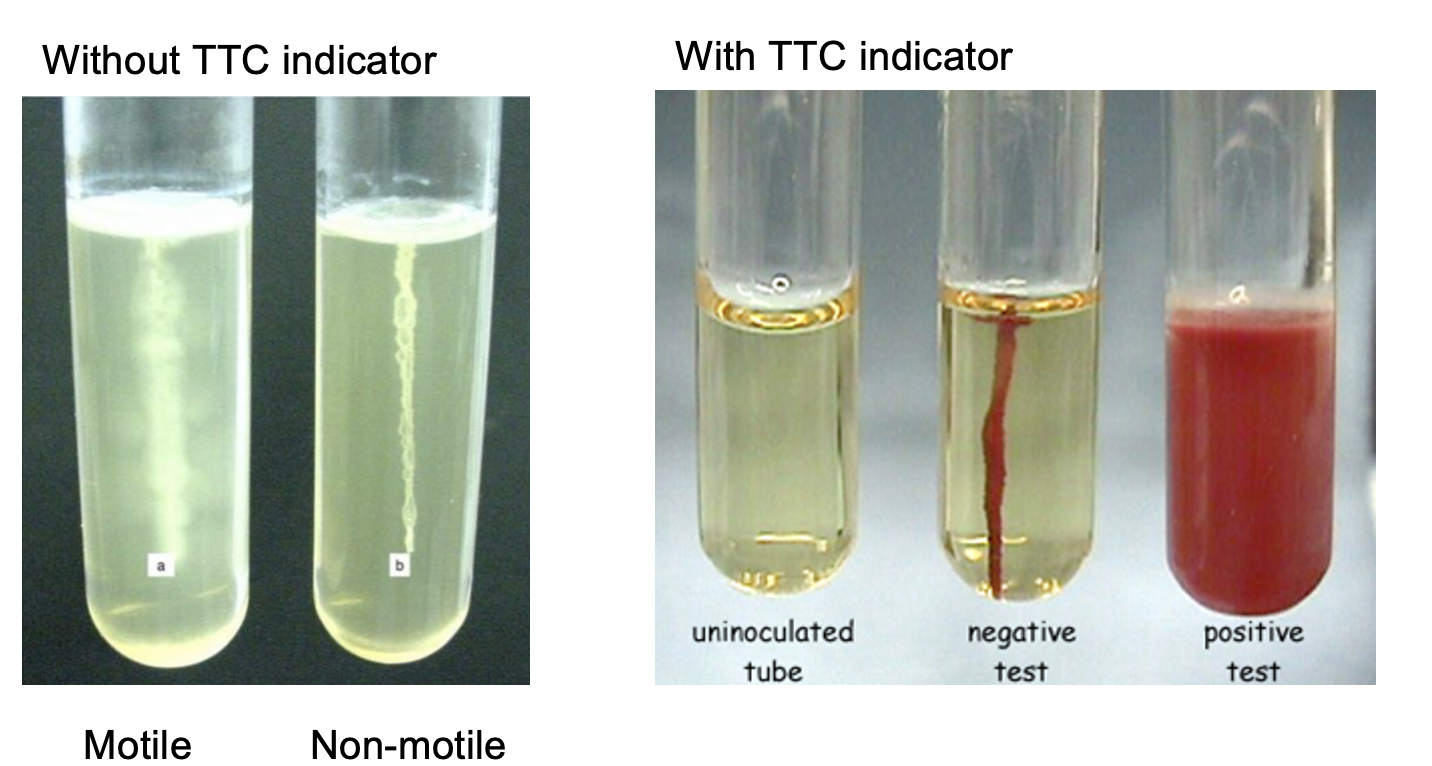
gram+ and gram- are what kind of stain?
differential stains, also a complex stain (involves multiple reagents, unlike a simple stain)
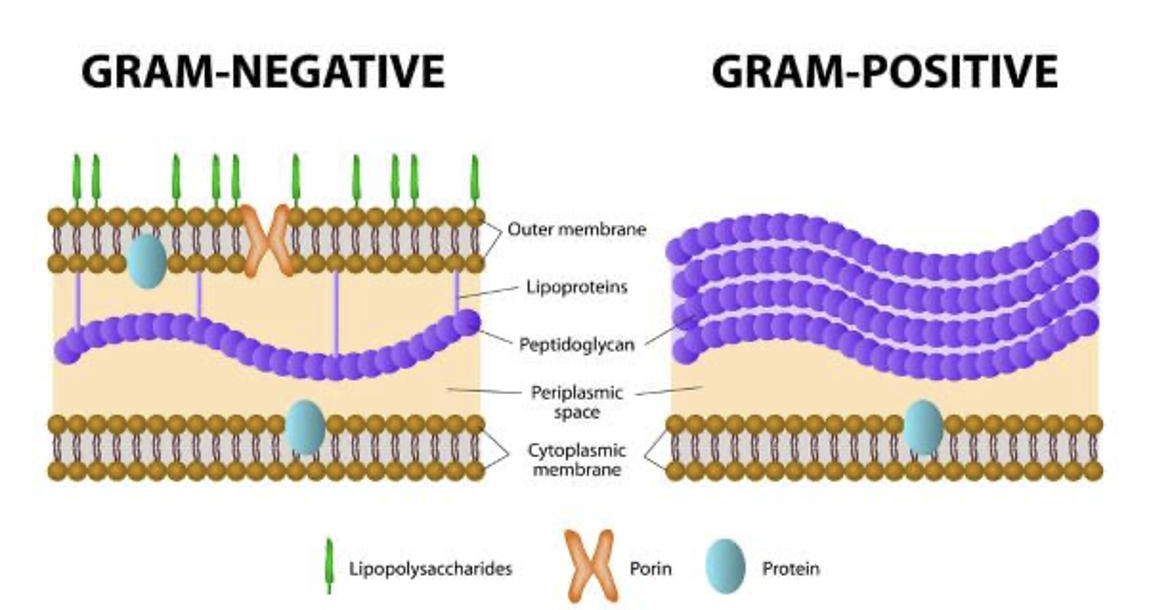
gram+ purple
thick layer of peptidoglycan that accounts for 90% of cell wall
primary stain of gram stain
crystal violet (penetrates through both gram+ and gram- walls and binds w negatively charged bacterial components)
mordant (iodine)
2nd step of gram staining, binds to crystal violet ions to form violet-iodine clumps in the cell
ethanol
3rd gram staining step, decolorizer, removes outer membrane of gram- cells (thinner peptidoglycan becomes disrupted and crystal violet washes away)
counterstain (safranin)
4th gram staining step, no effect on gram+ bacteria but still stain decolorized gram- cells pinik
gram stain not used on ___ or ____ because they have no ______
eukaryotes, archaea, peptidoglycan
heat-fixing
adheres cells more firmly to the slide
bacterial smear aka
slide smear (start of every staining process)
shapes of bacteria in this class
coccus, rod/bacillus, spirillum, (& vibrium or corkscrews)
arrangements of bacteria in this class
diplo (2), strepto (chain), staphylo (clump)
arrangements
patterns bacterial shapes are found in
mesophiles
organisms that grow best at moderate temperatures (between 20-45 degC)
psychrophiles
aka cryophiles, grow in extreme cold (-20 to 20degC)
thermophiles
grow only at elevated temps (41 to 122degC)
optical density (OD)
aka biomass, number of bacterial cells present
(OD of 0.8 has higher bacterial density than an OD of 0.5)
canthaxanthin
red-orange pigment, part of the carotenoid pigment family
violacein
purple pigment known as violacein from chromobacterium violaceum
pyoverdine or fluorescein
yellow-green pigment, fluorescent
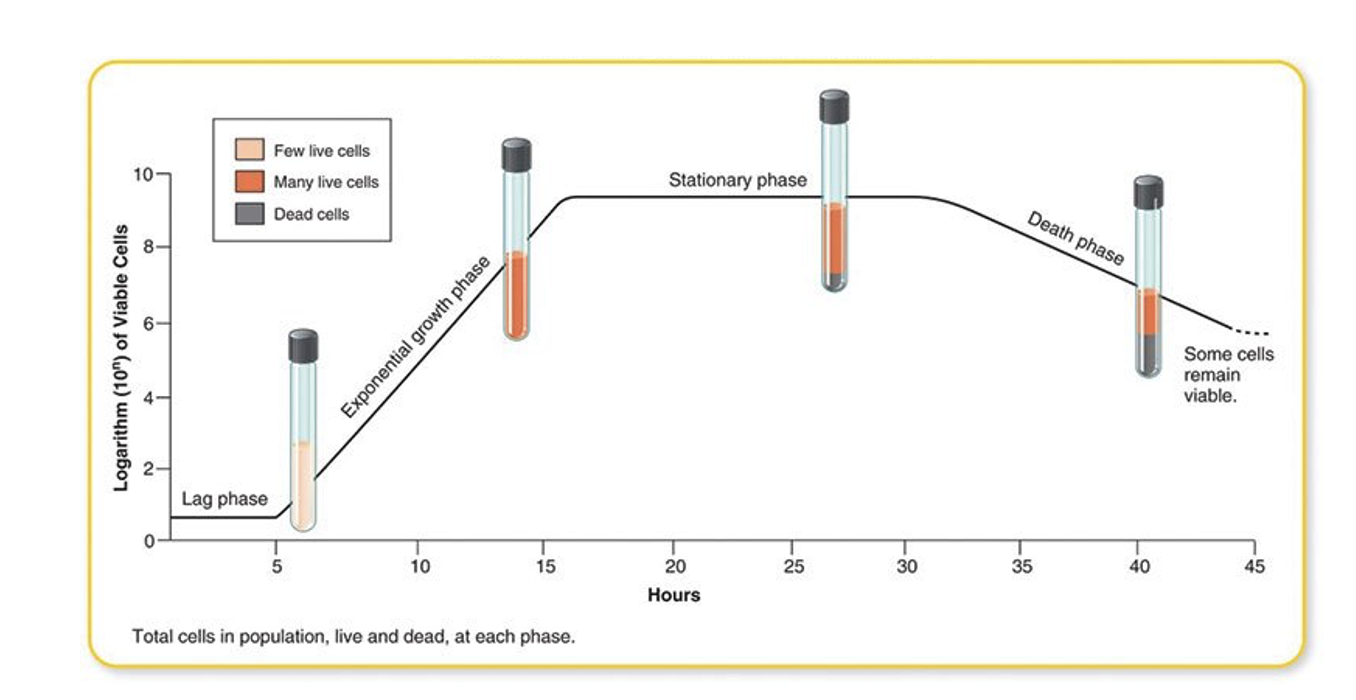
lag phase
first phase, organisms not dividing, adjusting to new conditions, synthesizing components needed to begin active reproduction (enzymes, cofactors, ribosomes)

exponential or log phase
rapid growth after cell division begins

generation time or doubling time
fixed characteristic for diff types of bacteria, time it takes for a bacterial culture to double i think?
stationary phase
flat line on bacterial growth curve, balanced by bacterial death
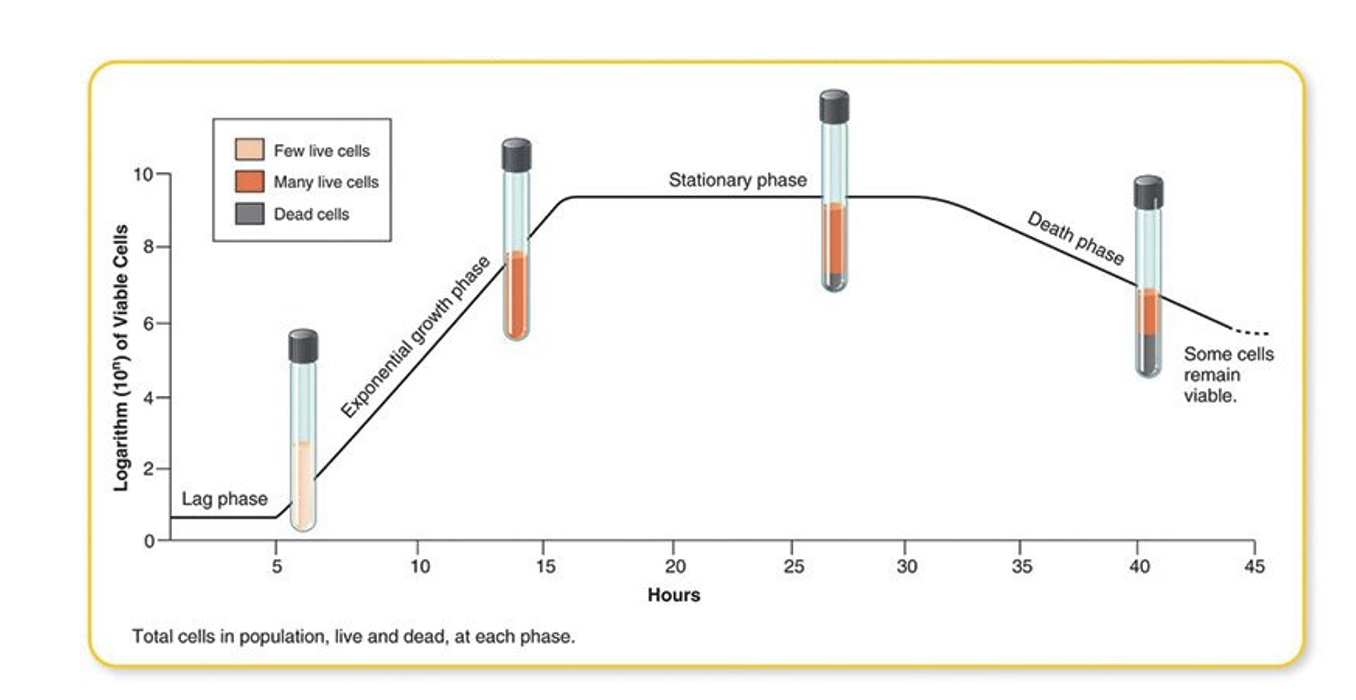
death phase
numbers of viable bacteria decrease rapidly
standard curve for bacteria
allows to estimate concentration of new OD readings
growth curve
can use standard curve to construct, shows increase and decrease in bacterial numbers over time
bacteria replicate through
binary fission (each cell splits into two)
bacterial colony shape options
punctiform, circular, rhizoid, filamentous, or irregular
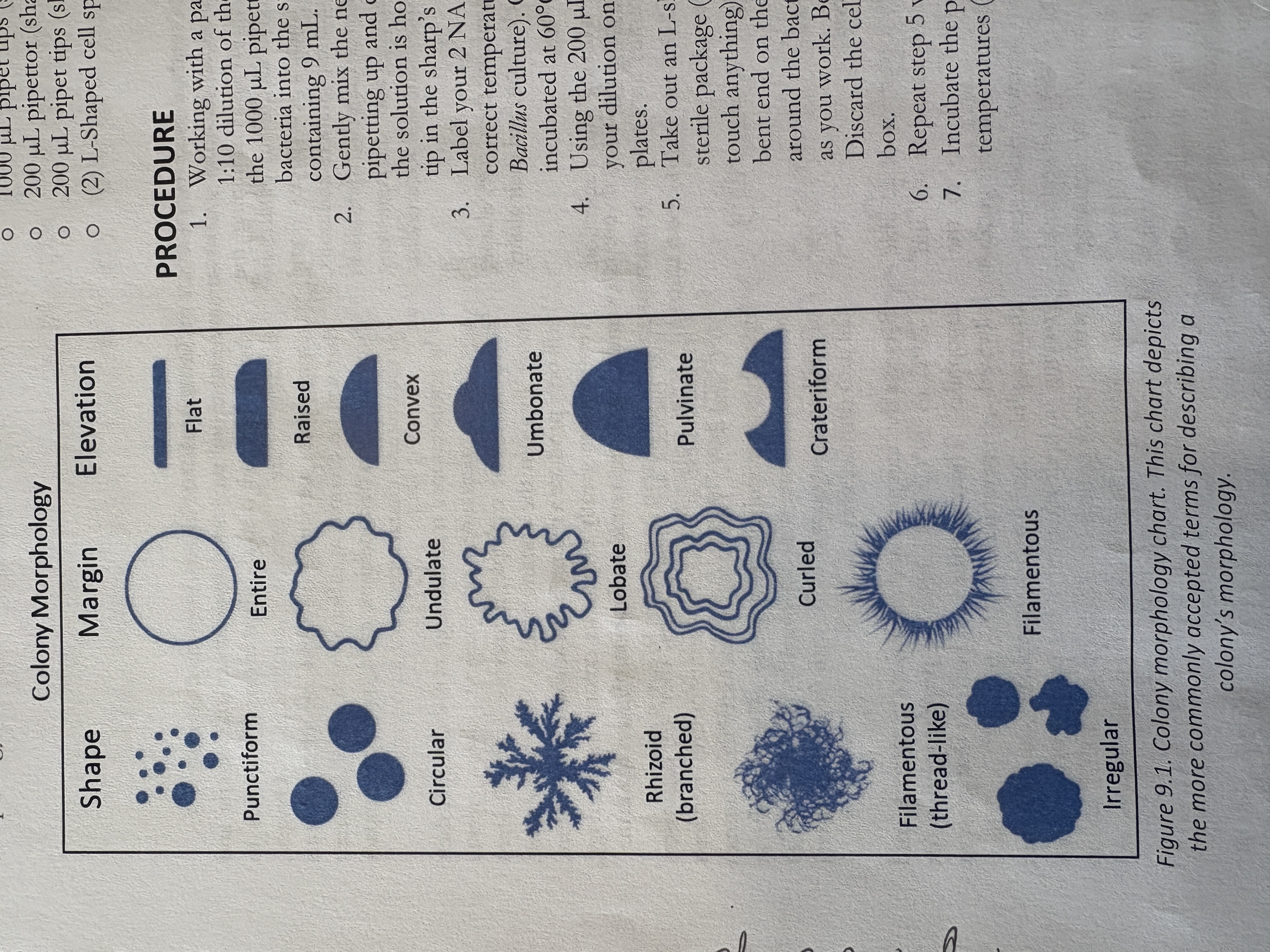
bacterial colony margin options
entire, undulate, lobate, curled, filamentous
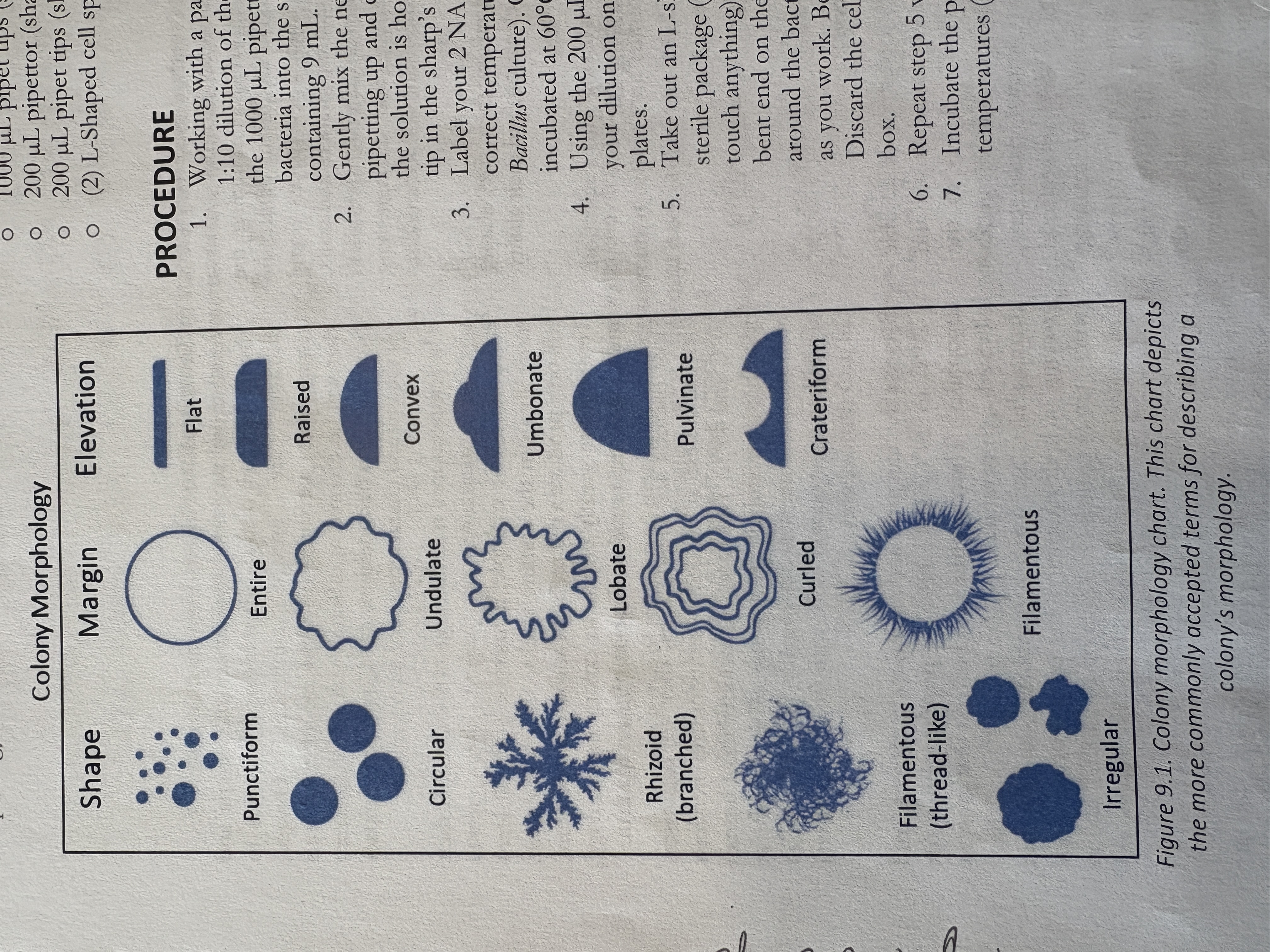
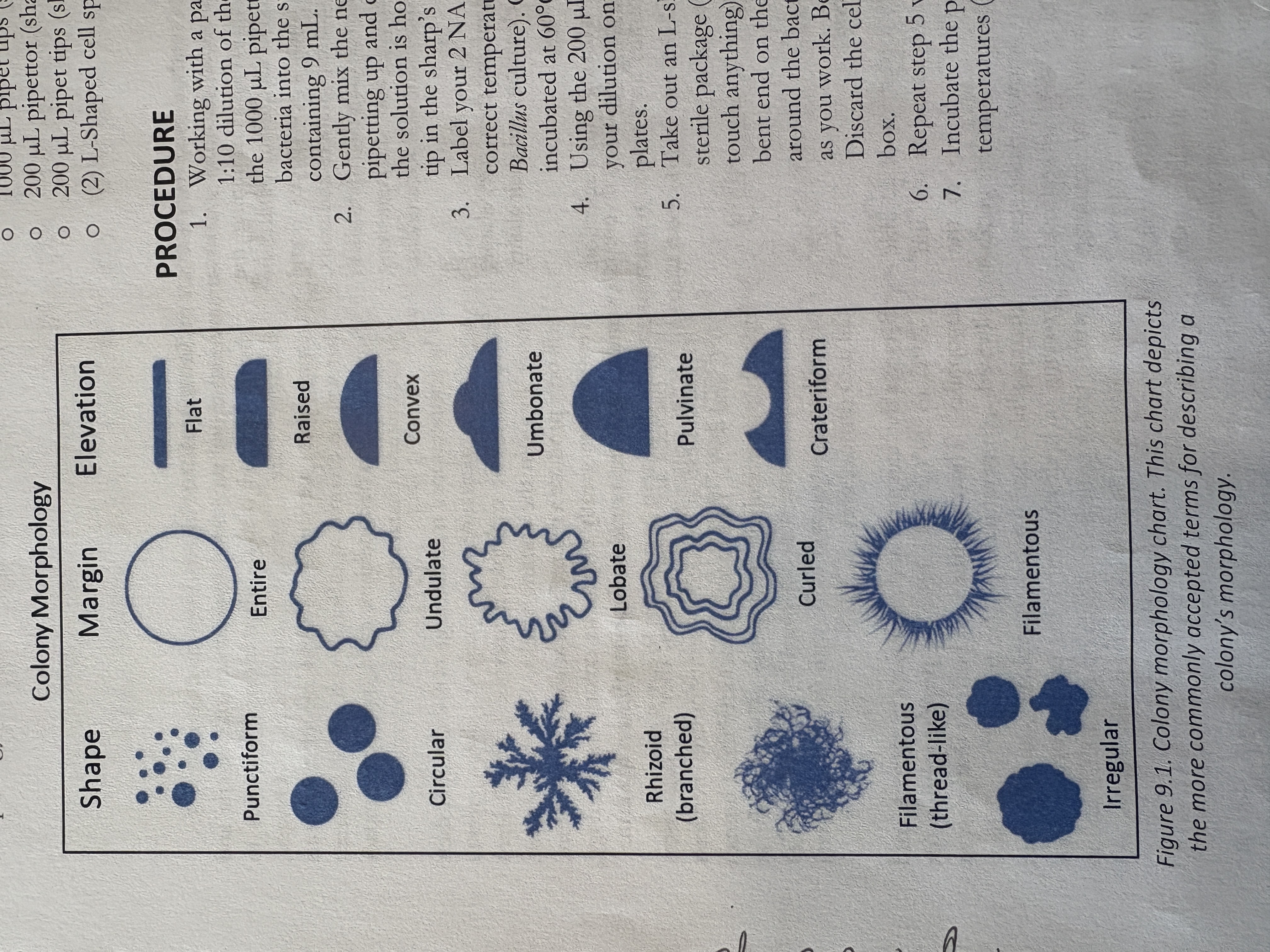
bacterial colony elevation options
flat, raised, convex, umbonate, pulvinate, crateriform
direct count of bacteria
visually count bacterial cells, time-consuming/hard
(OD) optical density
measuring absorbance of liquid culture, cannot differentiate between alive vs dead cells
viable count
measures how many live bacteria are in your culture
-make dilutions
-plate aliquots from each
-count number of colonies (countable = 30-300)
viable count is the: No. of colonies x Plating factor x Final dilution factor
serial dilution is better than simple dilution why?
-more efficient
-uses less media/broth so there is less waste
CFU/ml
(No. of colonies x final dilution factor) / Volume of culture plated (ml)
prodigiosin
pigment, produced by Serratia marcescens only at RT/ 30℃ (water insoluble- soluble in organic solvents)
pyocyanin
pigment, produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa (water soluble)