Understanding Amnesia: Types, Causes, and Memory Effects
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Anterograde Amnesia
Inability to form new memories post-event.
Retrograde Amnesia
Loss of memories from before an event.
Episodic Memory
Memory of personal experiences and events.
Semantic Memory
Memory of facts and general knowledge.
Cognitive Perspective
Focus on cognitive deficits in amnesia.
Biological Localization
Identifying brain areas related to memory.
Alzheimer's Disease
Common cause of amnesia with dementia symptoms.
Korsakoff Syndrome
Amnesia from chronic alcoholism, memory impairment.
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis
Rare virus causing severe amnesia.
Temporal Lobe Surgery
Surgical procedure leading to memory loss.
H.M. (Henry Molaison)
Patient with profound memory problems post-surgery.
Hippocampus
Brain region crucial for memory formation.
Short-term Memory
Temporary storage of information for immediate use.
Procedural Memory
Memory for skills and tasks, like drawing.
Implicit Memory
Influence of past experiences without awareness.
Free Recall
Retrieving information without cues or prompts.
Recognition Task
Identifying previously learned information from options.
Recollection
Active retrieval of specific details from memory.
Familiarity
Sense of knowing without specific details.
Claparède's Handshake
Example of implicit memory in amnesia.
Degraded Pictures/Words
Improved recognition of previously seen stimuli.
Graf et al. (1984) Study
Demonstrated explicit vs implicit memory performance.
Doors and People Test
Memory test assessing recollection and familiarity.
Developmental Amnesia
Memory impairment from early life, often due to anoxia.
Anoxia
Lack of oxygen affecting brain function, especially hippocampus.
Hippocampus
Brain region crucial for memory formation and recall.
Recollection
Recall of specific details from past experiences.
Familiarity
Sense of knowing without recalling specific details.
Remember/Know Paradigm
Distinction between recollection and familiarity in memory.
ERP Study
Event-related potential study measuring brain response to stimuli.
Hypoxia
Condition of insufficient oxygen supply to tissues.
Hippocampal Atrophy
Shrinkage of hippocampus, often linked to memory deficits.
Dual-Process Model
Theory distinguishing between recollection and familiarity processes.
Retrograde Amnesia
Loss of memories formed before onset of amnesia.
Probe Method
Technique for recalling memories by prompting with cues.
Autobiographical Memory Interview (AMI)
Assessment tool for recalling personal memories over time.
Ribot's Law
Older memories are easier to recall than recent ones.
Temporal Gradient
Variation in memory recall ability based on time of event.
Standard Consolidation Model
Theory explaining memory transfer between brain regions.
Perirhinal Cortex
Brain area associated with familiarity in memory processing.
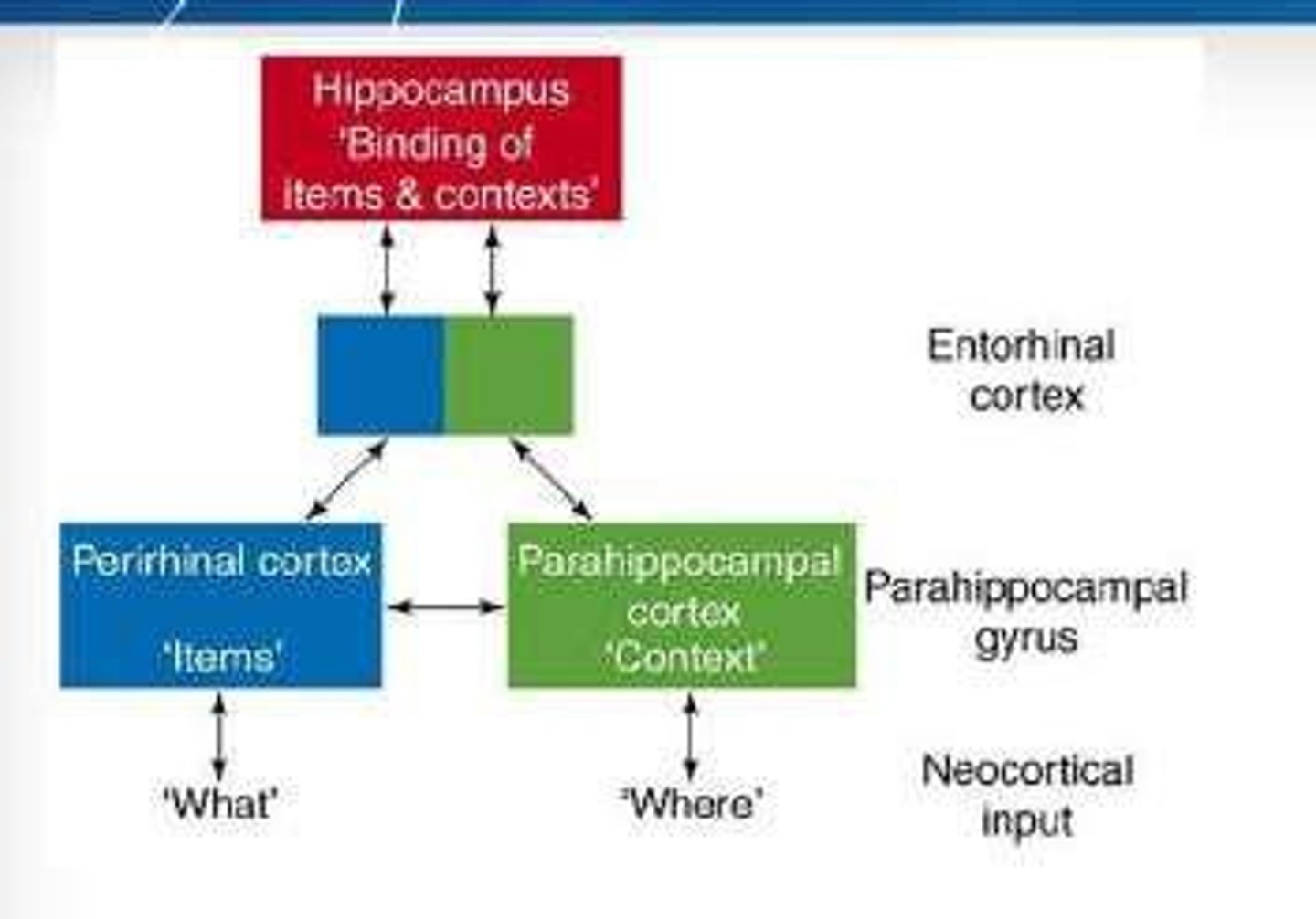
Parahippocampal Cortex
Region involved in context and spatial memory.
Neocortical Input
Information processed by the neocortex, influencing memory.
Memory Strength Criterion
Judgment based on how strong a memory feels.
Memory Encoding
Process of transforming information into a memory trace.
Memory Retrieval 1
Accessing stored information from memory.
Ribot's Law
Early memories don't require hippocampus for retrieval.
Reactivation
Hippocampus replays neural activity for memory consolidation.
Cortical Connections
Connections between cortical areas strengthen over time.
Multiple Trace Hypothesis
Detailed episodic memory requires hippocampal-neocortical trace.
Semantic Memory
Knowledge of facts and vocabulary independent of episodic memory.
Episodic Memory 2
Memory of personal experiences and specific events.
Trace Transformation Theory
Memory traces evolve from hippocampal to neocortical connections.
Neocortex
Brain region involved in storing long-term memories.
Hippocampus
Brain structure critical for forming new memories.
Memory Retrieval 2
Process of recalling stored information from memory.
Semanticization
Older memories become more factual and less personal.
Developmental Amnesia
Preserved semantic knowledge with impaired episodic memory.
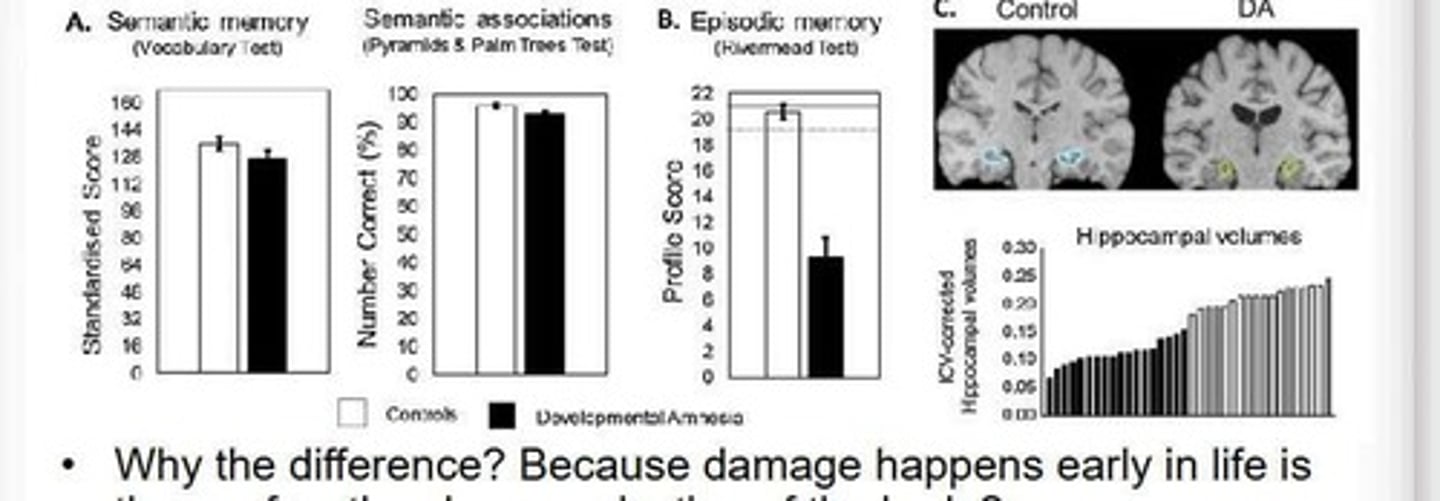
MTL Damage
Damage to medial temporal lobe affects memory acquisition.
Lexical Knowledge
Knowledge of words and their meanings.
Amnesic Patients
Individuals with memory deficits due to brain damage.
Cognitive Impairments
Other mental deficits complicating memory assessment.
Procedural Memory 2
Memory for skills and tasks performed automatically.
Implicit Memory
Unconscious memory influencing behavior without awareness.
Standardized Score
Metric used to compare performance across individuals.
Acquisition of New Knowledge
Learning new information after memory impairment.
Repetition in Learning
Need for repeated exposure to retain new information.
H.M. Case Study
Famous amnesic patient illustrating memory theories.
Neural Activity Replay
Hippocampus reactivates patterns for memory consolidation.