AP Psychology Unit 1, Part II: Research Methods (UPDATED)
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
hindsight bias
The tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it-
"I knew it all along"

critical thinking
Is rationally deciding what to believe or what to do. When one rationally decides something, he or she evaluates information to see if it makes sense, whether it's coherent, and whether the argument is well founded on evidence.
validity
the extent to which a test or experiment measures or predicts what it is supposed to do
theory
A hypothesis that has been tested with a significant amount of data
hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory
operational definition
A statement of the procedures used to define research variables that is specific and allows research to be replicated
replication
replicate the original study
case study
An observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles.
population
the whole group that you want to study and describe
random sample
A sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
correlation
A measure of the relationship between two variables
correlation coefficient
A statistical index of the relationship between two things (from -1 to +1)
scatterplot
A graphed cluster of dots, each of which represents the values of two variables.
experiment
A research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process
random assignment
Assigning participants to experimental and control conditions by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between those assigned to the different groups
double-blind study
An experiment in which neither the participant nor the researcher knows whether the participant has received the treatment or the placebo
placebo effect
Experimental results caused by expectations alone; any effect on behavior caused by the administration of an inert substance or condition, which is assumed to be an active agent.
experimental group
A subject or group of subjects in an testing environment that is exposed to the factor or condition being tested.
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
independent variable
The variable that is manipulated in an experiment
confounding variable
in an experiment, a type of type of extraneous variable; interferes directly with the outcome of a study.
dependent variable
the variables that is being measured
mode
Measure of central tendency that uses most frequently occurring score.
mean
Average
median
A measure of center in a set of numerical data.
range
Distance between highest and lowest scores in a set of data.
standard deviation
A computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score.
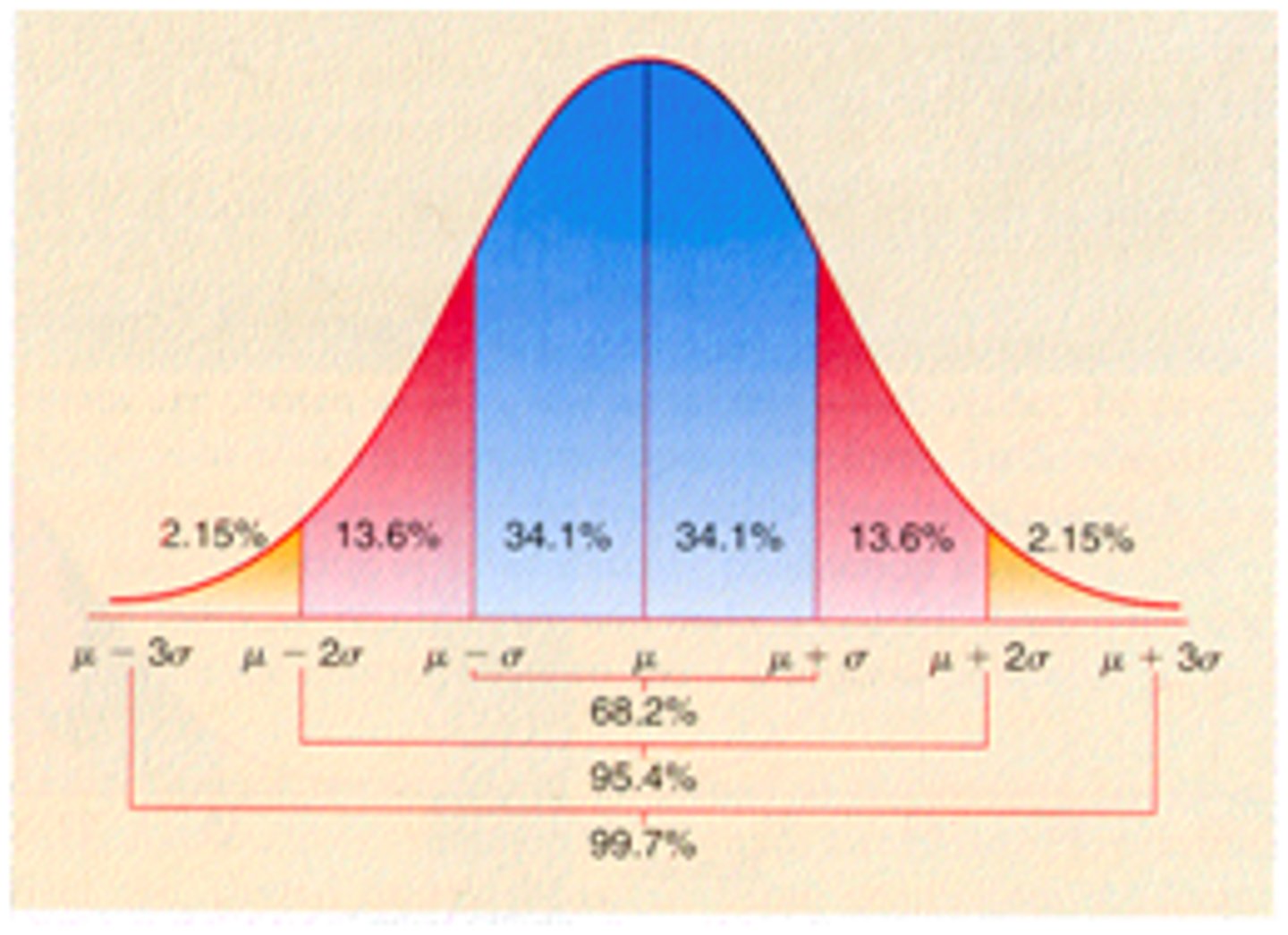
normal curve
the symmetrical bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical and psychological attributes. Most scores fall near the average, and fewer and fewer scores lie near the extremes.
statistical significance
A statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance; p-value
culture
Beliefs, customs, and traditions of a specific group of people.
informed consent
A written agreement to participate in a study made by an adult who has been informed of all the risks that participation may entail.
debriefing
A verbal description of the true nature and purpose of a study
sample
A part of the population you are studying.
overconfidence
We tend to think we will perform better than we do.
hindsight
"knew it all along " phenomena
3 main components of scientific attitude
curiosity
skepticism
humility
disadvantage of a case study
overgeneralization - suggests that the results could be for everyone but they need more research to back it up
a theory is useful if :
- it effectively organizes a range of self-reports / observations and leads to a clear hypothesis that anyone can use to check a theory
- it stimulates research to lead to a revised theory that better organizes and predicts what we know
wording effect of a survey
the way a question or situation is presented affects how people feel about the matter (ex. better wording = more desired results)
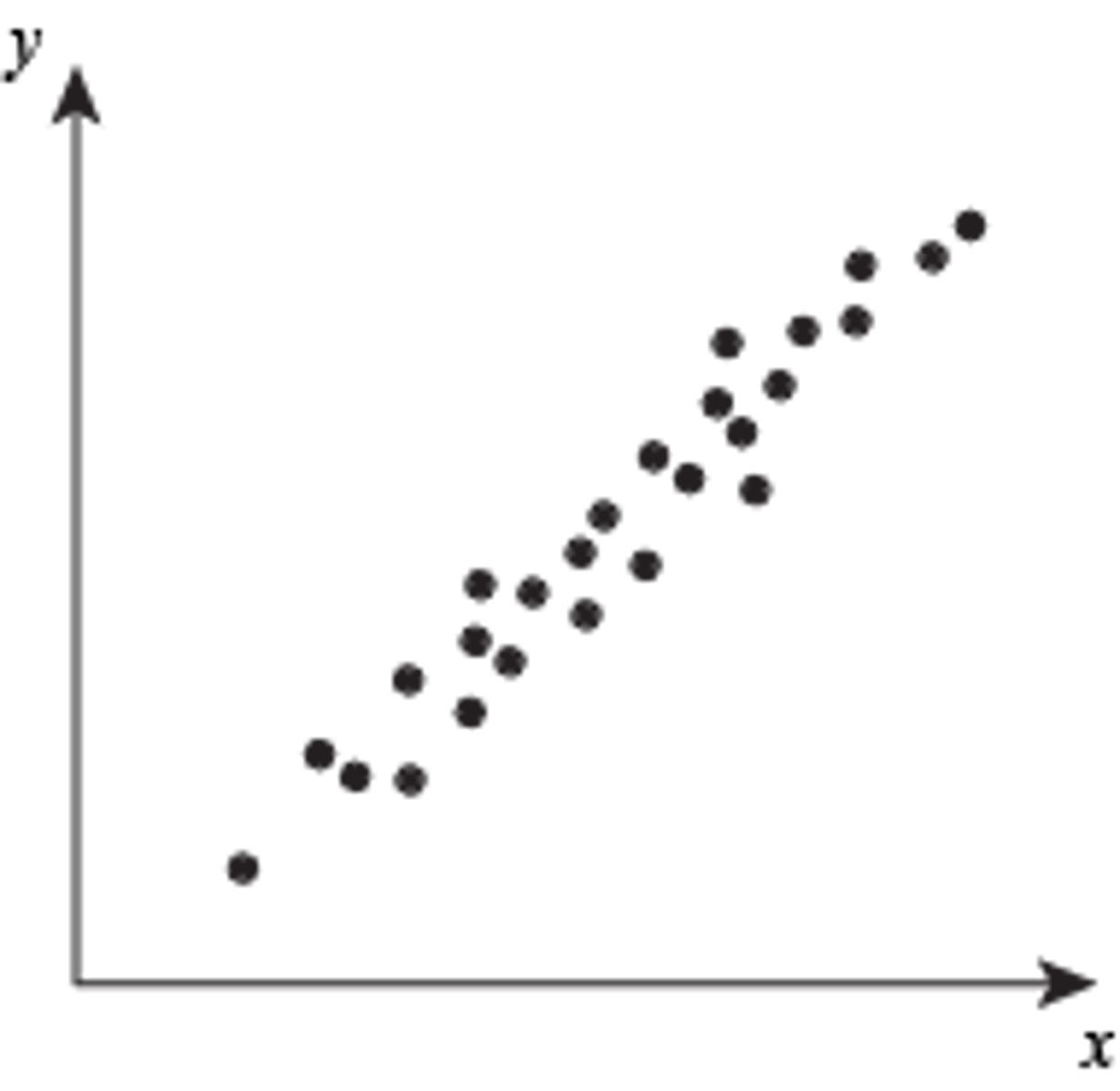
positive correlation
two variable rise and fall together, such as height and weight
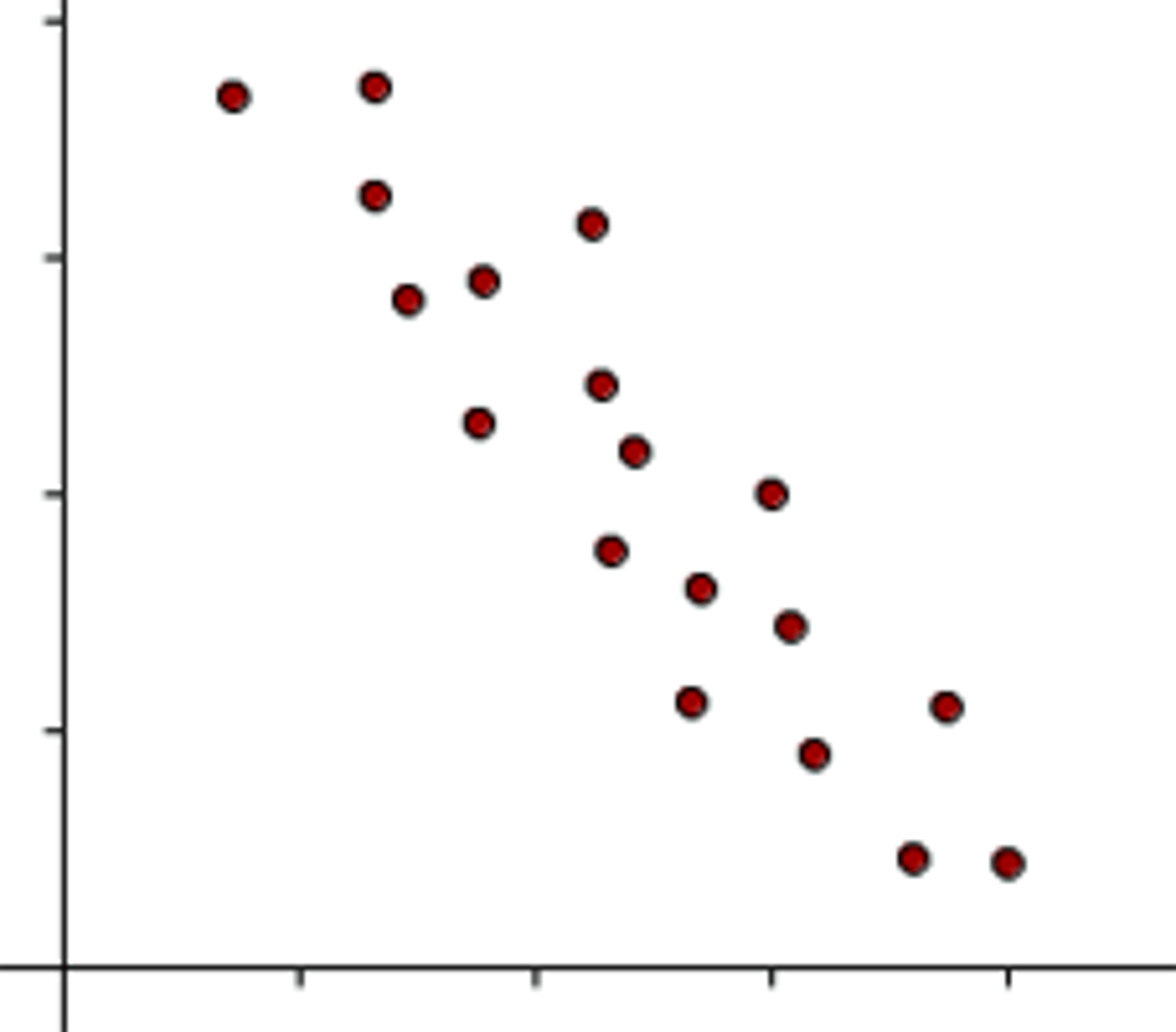
negative correlation
variables are related inversely, one goes up and the other goes down, such as inner speech and psychological distress
1 standard deviation
68%
deception
investigators providing false or incomplete information to participants for the purpose of misleading research subjects
descriptive statistics
numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics of groups, including measures of central tendency and variation
example of a positive correlation
+0.98
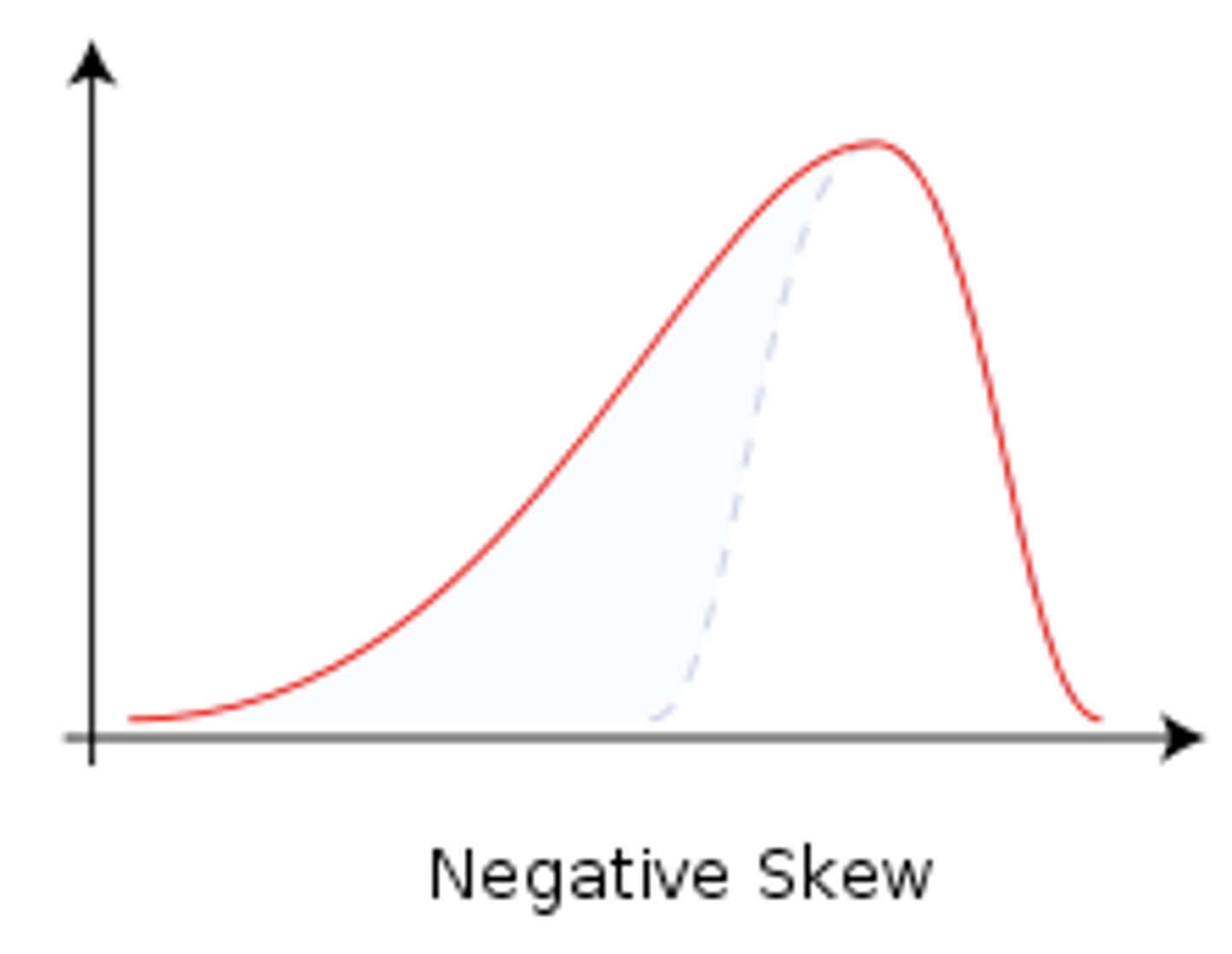
skewed graph
mode, median, and mean are different
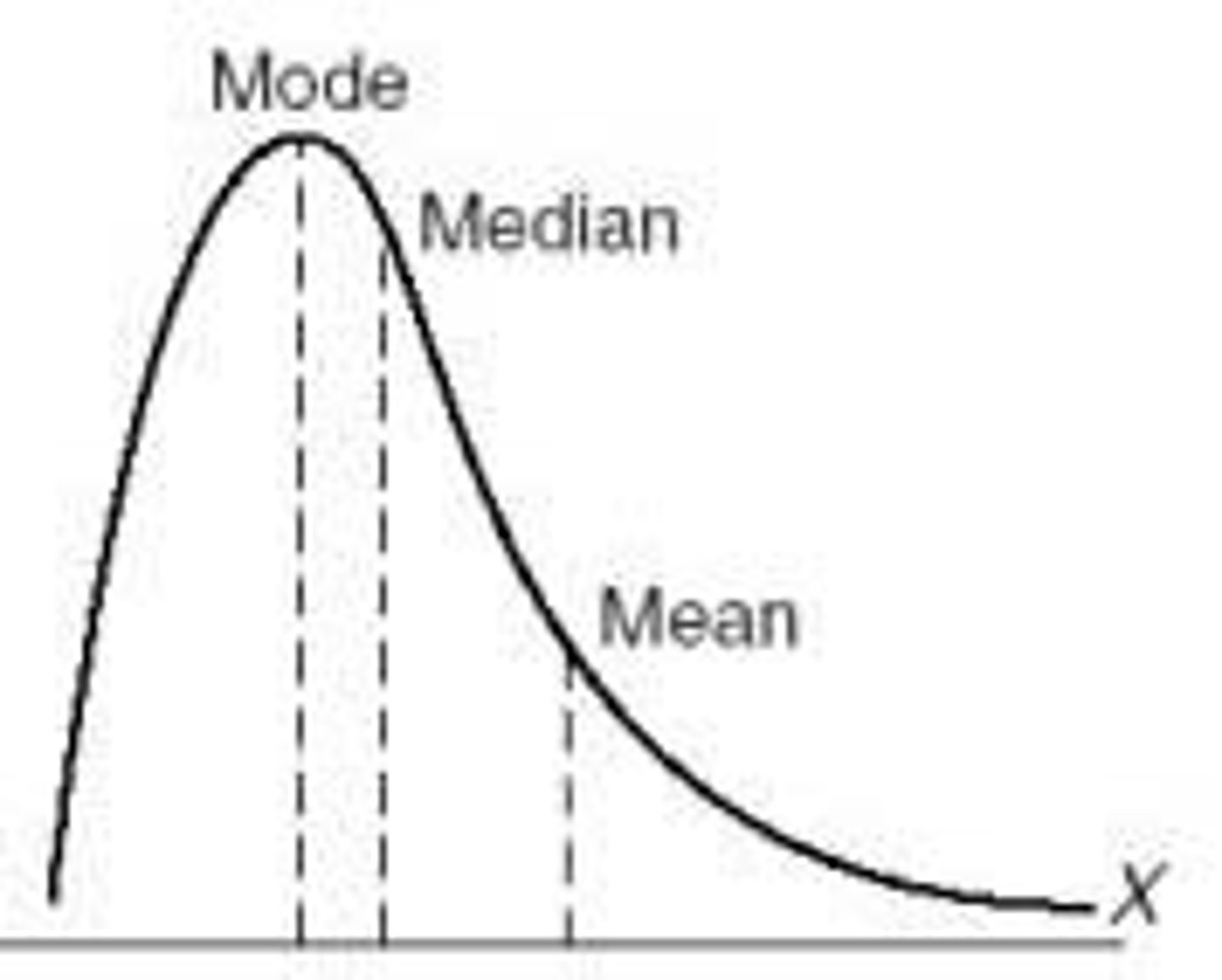
positive skew
high outlier
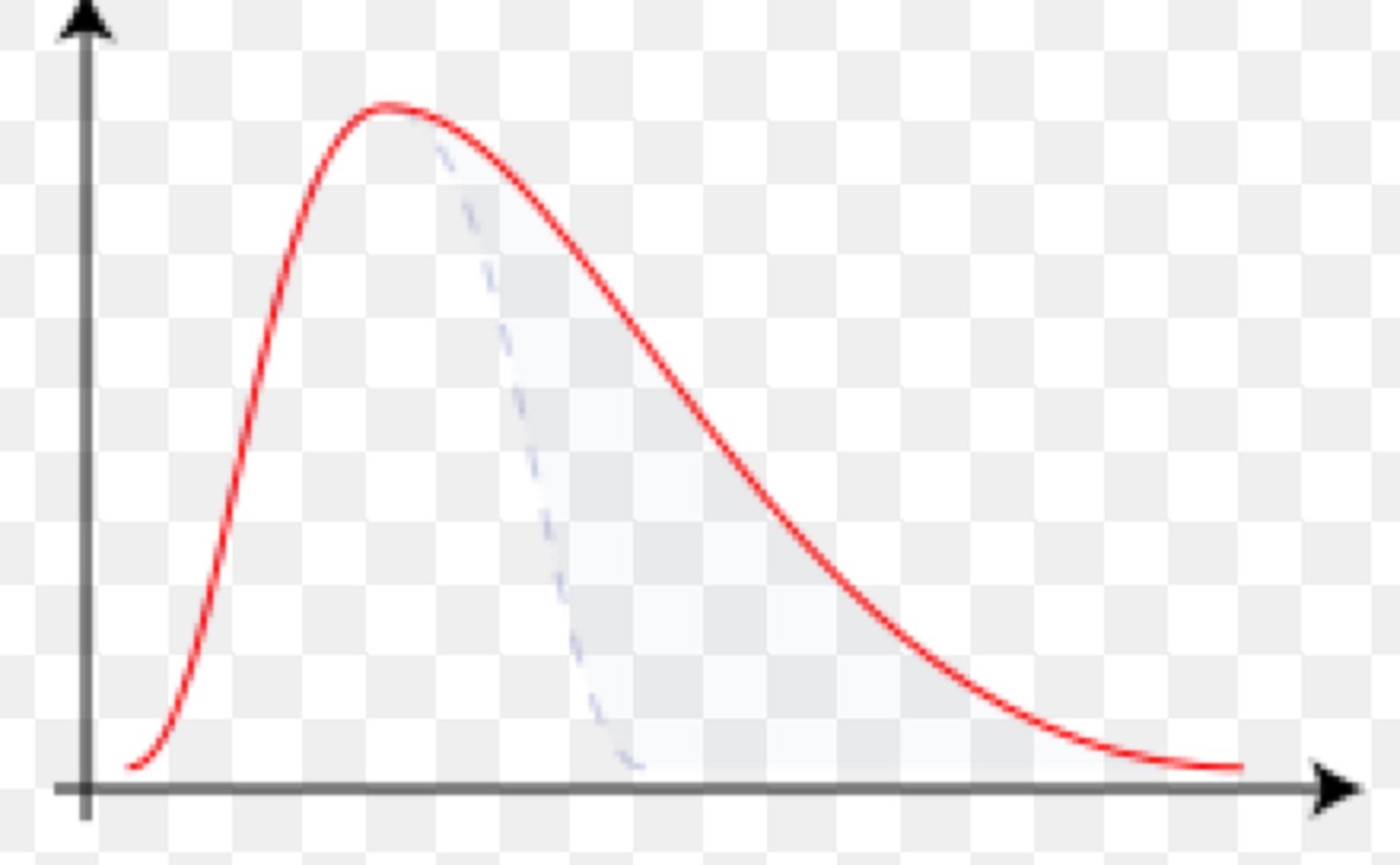
negative skew
low outlier
measures of variability
depict diversity of the distribution (range, standard deviation)
normal curve
mean, median and mode are all equal
3 principles of being reliable
representative samples are better than biased
less variable observations are more reliable than thsoe that are more variable
more cases are better than fewer
descriptive stats vs. inferential stats
d : allows us to summarize info about the sample studied
i : determine whether or not findings can be applied to a larger population from which the sample was selected
culture (behavior)
enduring behaviors ideas, attitudes, and how people perceive different situations, such as body shape, early sex, etc.
ethics in research
informed consent
protection from harm/discomfort
maintain confidentiality
debriefing
convenience sampling
using a sample of people who are readily available to participate
Likert Scales
questionnaires that require individuals to indicate their degree of agreement or disagreement with a set of statements
Social Desirability Bias
A tendency to give socially approved answers to questions about oneself.
Structured Interviews
interview process that asks the same job-relevant questions of all applicants, each of whom is rated on established scales
Directionality Problem
a problem encountered in correlational studies; the researchers find a relationship between two variables, but they cannot determine which variable may have caused changes in the other variable
Informed Assent
a process that allows minors and people who are not legally able to give informed consent to agree to participate in research
Effect Sizes
The most common way of quantifying and comparing outcomes across studies in meta-analytic reviews
Extraneous variable (EV)
any variable other than the IV that can cause a change in the DV