RBC vocab (clin path)
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
what is the difference between plasma and serum?
plasma: liquid from anti-coagulated whole blood
serum: liquid from coagulated and centrifuged whole blood
mean cell volume (MCV)
average size (volume) of RBCs
units: femtoliters (fL)
mean cell hemoglobin (MCH)
average amount of hemoglobin/RBC
units: picograms (pg)
mean cell hemoglobin concentration (MCHC)
average concentration of hemoglobin/RBC
Hb divided by RBC volume
units: g/dL
more diagnostically useful index than MCH
anisocytosis
variation in RBC size that is abnormal for the species
macrocytosis
↑ RBCs with ↑ diameters (correlates with increased MCV)
what is a common cause of macrocytosis?
regenerative anemia (bone marrow releases reticulocytes, which are larger than mature RBCs)
microcytosis
↑ RBCs with ↓ diameters (correlates with decreased MCV)
what are common causes of microcytosis?
iron deficiency anemia
porto-vascular anomalies in young dogs (ex. portosystemic shunt)
crenation
RBC morphology characterized by evenly spaced, blunt projections around the entire surface
artifact of delayed drying of blood smear on the slide; rarely pathogenic process
poikilocyte
general term meaning abnormally shaped mature RBC
includes abnormal shape of central pallor & RBC shape that is not biconcave disc
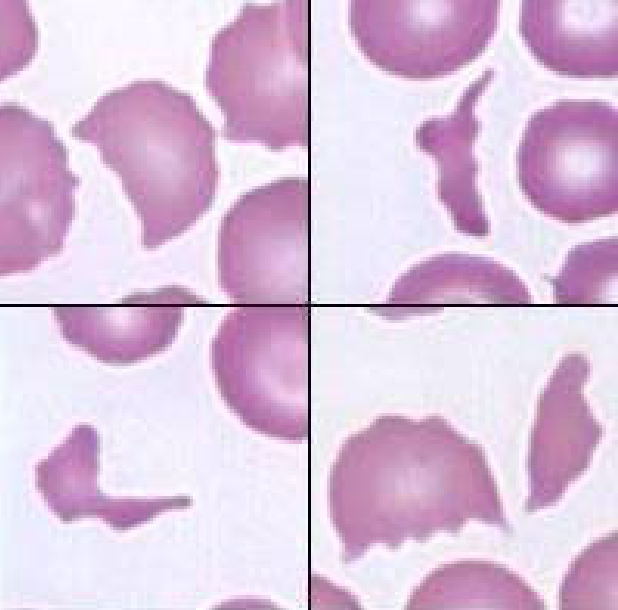
schistocyte
fragmented RBC usually resulting from shearing injury by RBCs traversing intravascular fibrin deposition or abnormal vessels
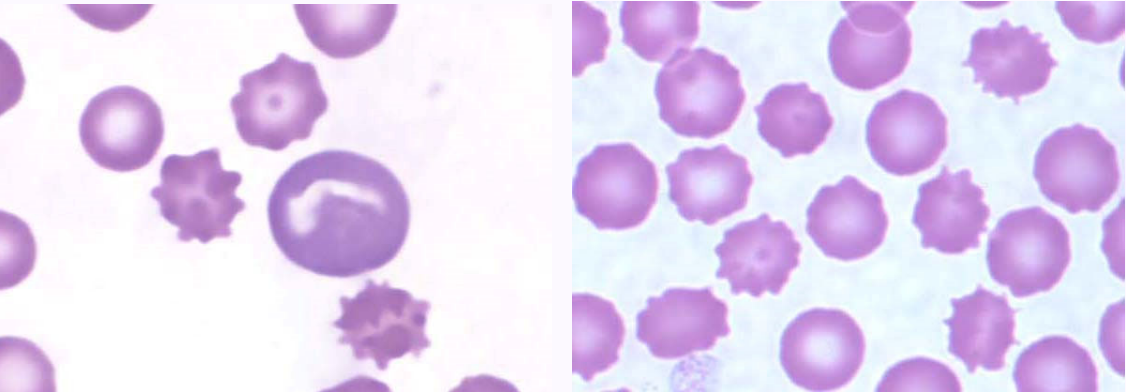
acanthocyte
RBC with projections of irregular number, size, and location
what types of disorders are associated with acanthocytes?
disorders that cause RBC fragmentation
splenic and hepatic disorders
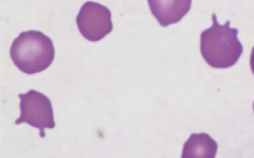
spherocyte
spherical RBCs that appear smaller, denser, and lack central pallor (in dogs)
only reliably detected on canine blood smears; RBCs in other species have little or no visible central pallor
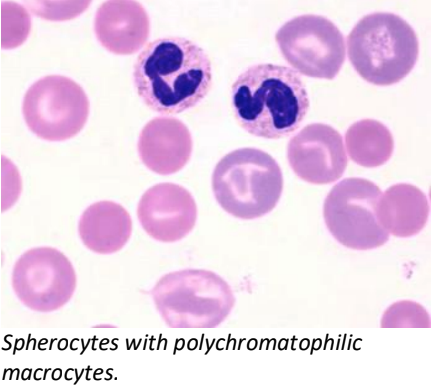
what disorder is associated with spherocytes?
extravascular immune-mediated hemolytic anemia
(IgG) Ab-coated RBC travels to spleen → splenic macrophage removes Ab and small portion of RBC membrane → RBC reassembles into sphere
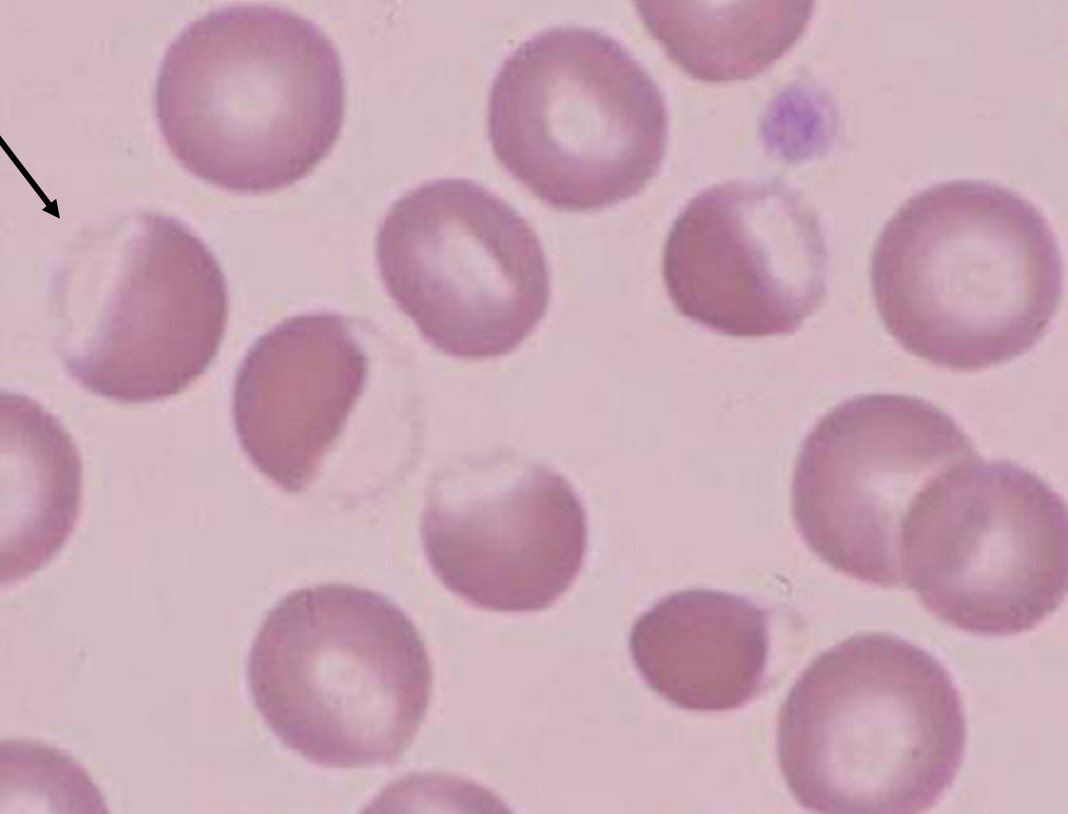
eccentrocyte
RBCs with hemoglobin shifted to one side of the cell
on the other side, there is a clear area and a thin membrane
indicates oxidative membrane damage
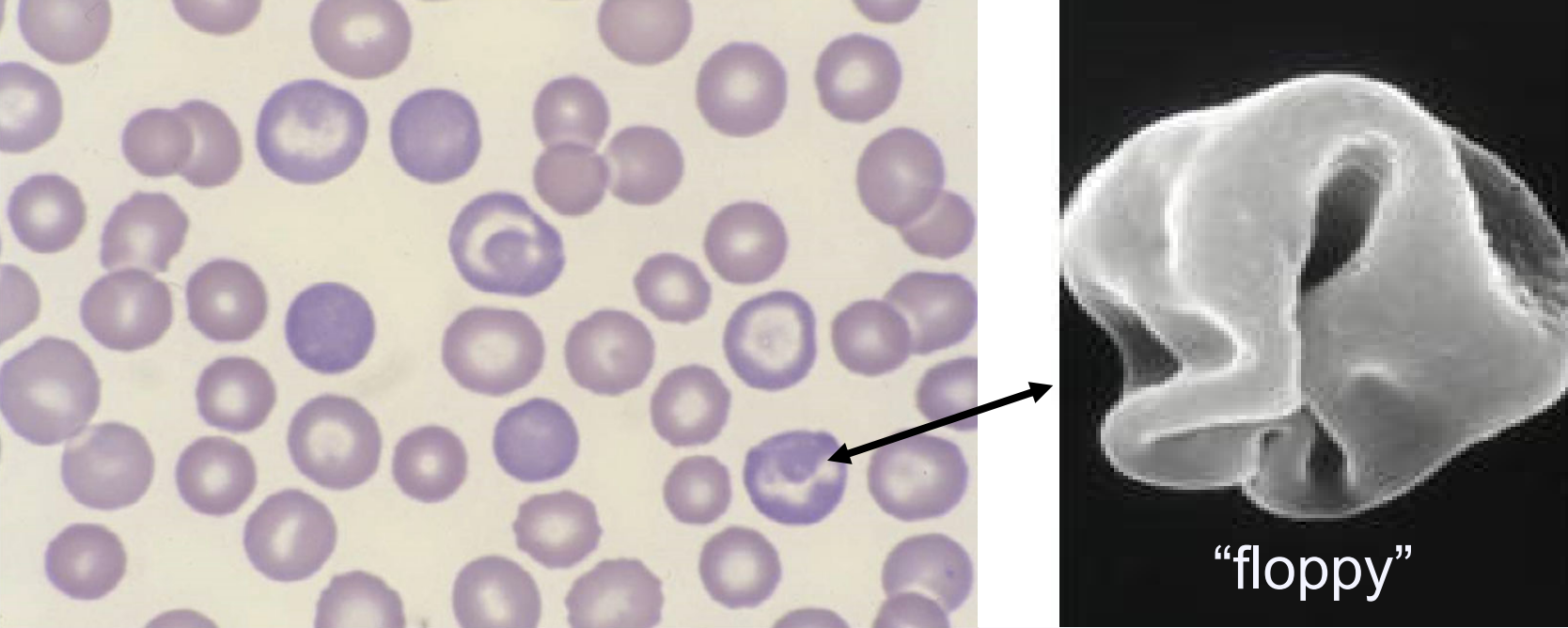
polychromasia/polychromatophilic RBCs
describes blue-purple color of reticulocytes on a blood smear stained with Wright’s stain or Diff-quick
lack nucleus but retain ribosomes that stain blue & blend with salmon color of hemoglobin
variable central pallor size/shape or absent
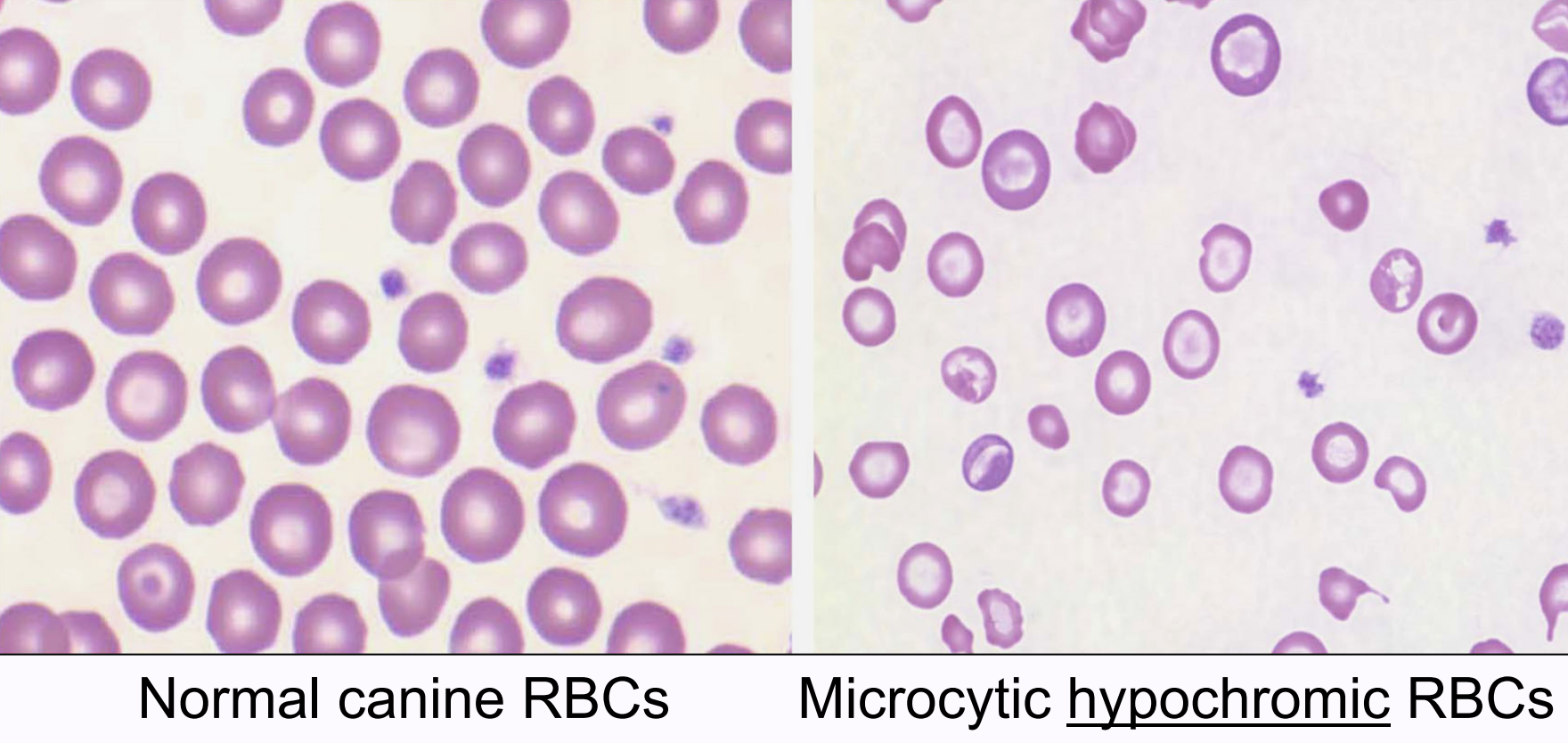
hypochromasia/hypochromia
microcytic RBCs that are pale with increased central pallor (>1/3 RBC diameter)
impaired hemoglobin synthesis due to iron deficiency
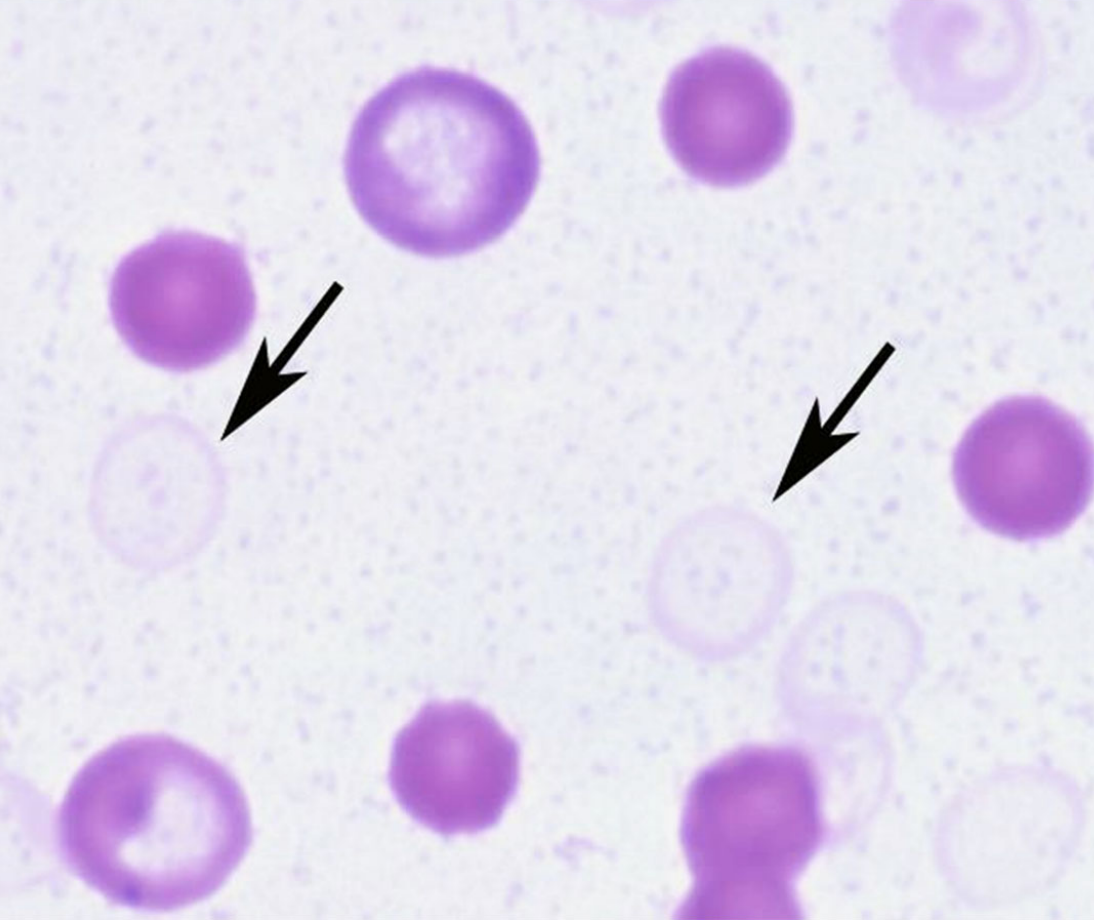
ghost cells
RBC membranes with little to no hemoglobin
primarily associated with intravascular IMHA
RBC releases Hb into plasma
nucleated RBCs (nRBC)
metarubricytes/rubricytes
normal feature of immature RBCs but usually not in circulation
(avian/reptile RBCs are nucleated)
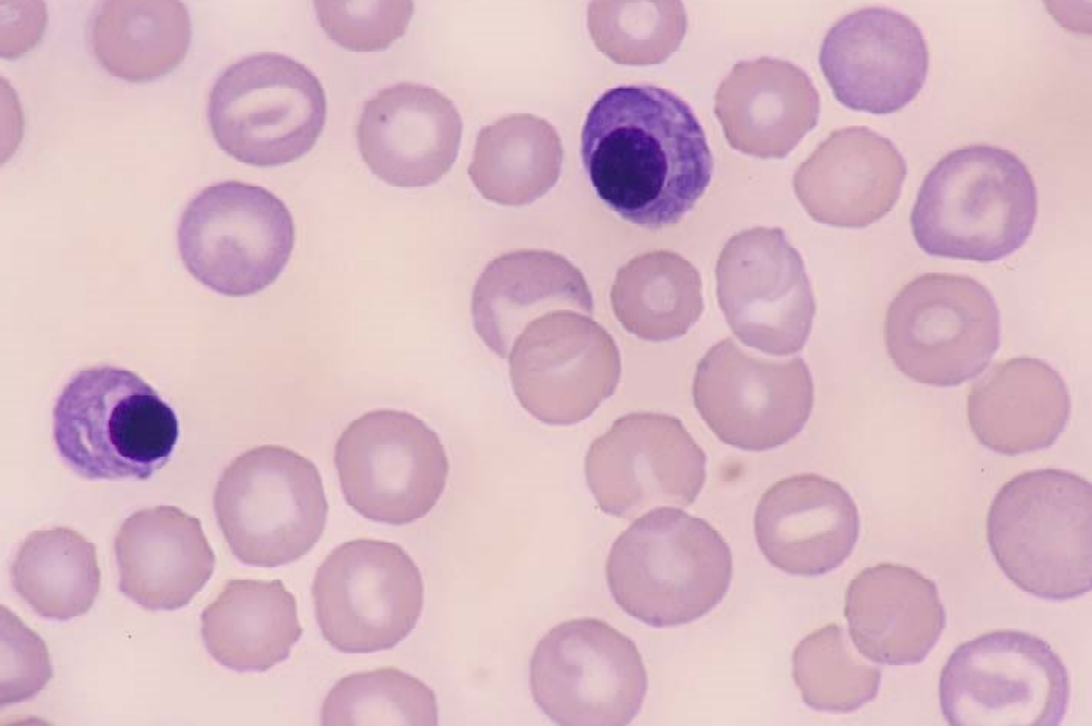
appropriate vs. inappropriate metarubricytosis
appropriate: nRBCs commonly seen in regenerative anemias → not considered pathologic
inappropriate: nRBCs in the absence of regeneration
may be seen with diseases of the spleen and bone marrow & with lead toxicity
howell jolly bodies
small, round, dark inclusion → nuclear remnant
eventually removed by spleen (pitting function)
more frequent in healthy cats due to poor splenic pitting function
frequently seen in regenerative anemia
in the absence of regeneration, may be seen with diseases or absence of the spleen (post-splenectomy)
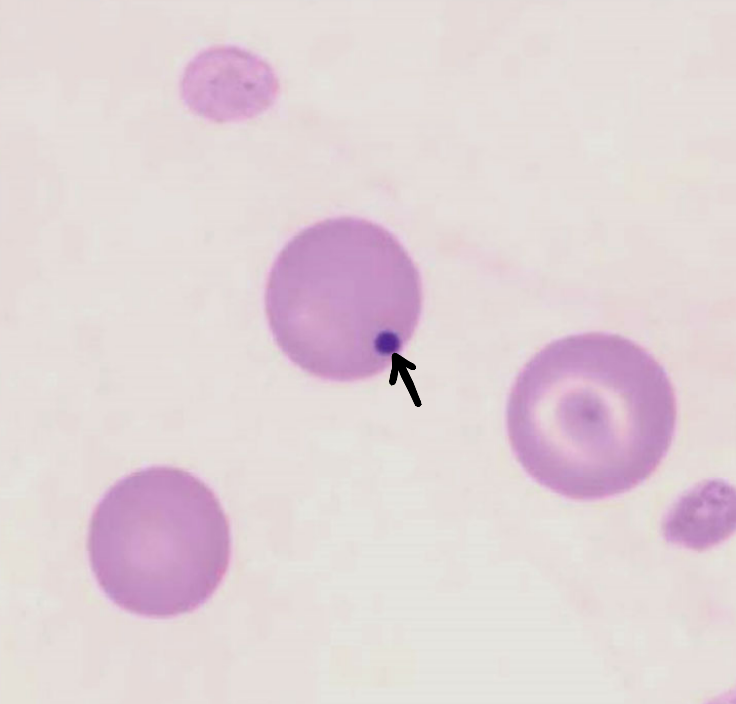
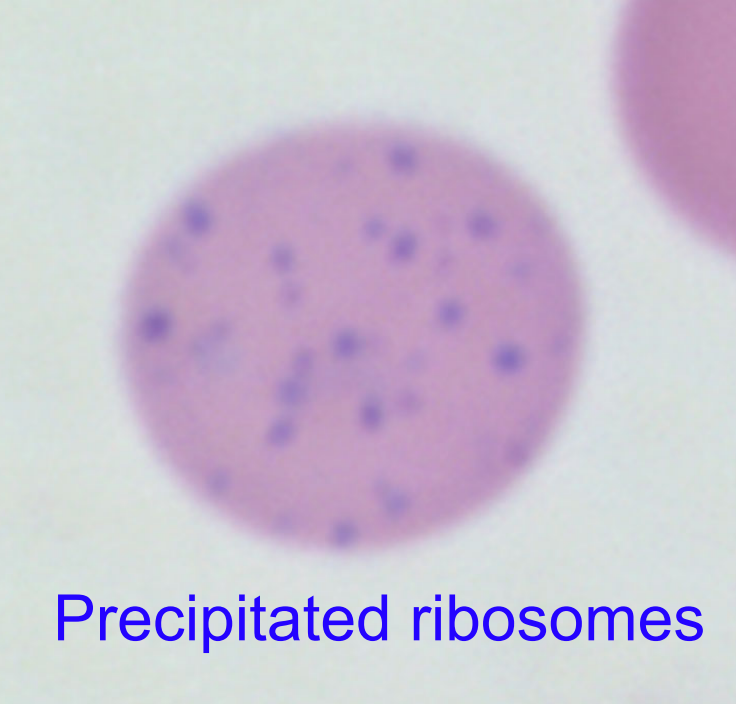
basophilic stippling
precipitated ribosomes in immature RBCs (reticulocyte or polychromatophil)
normal feature of ruminant reticulocytes
may be seen with regenerative anemia in ruminants; severe regen. anemia in dogs, cats
pathologically seen with lead toxicity
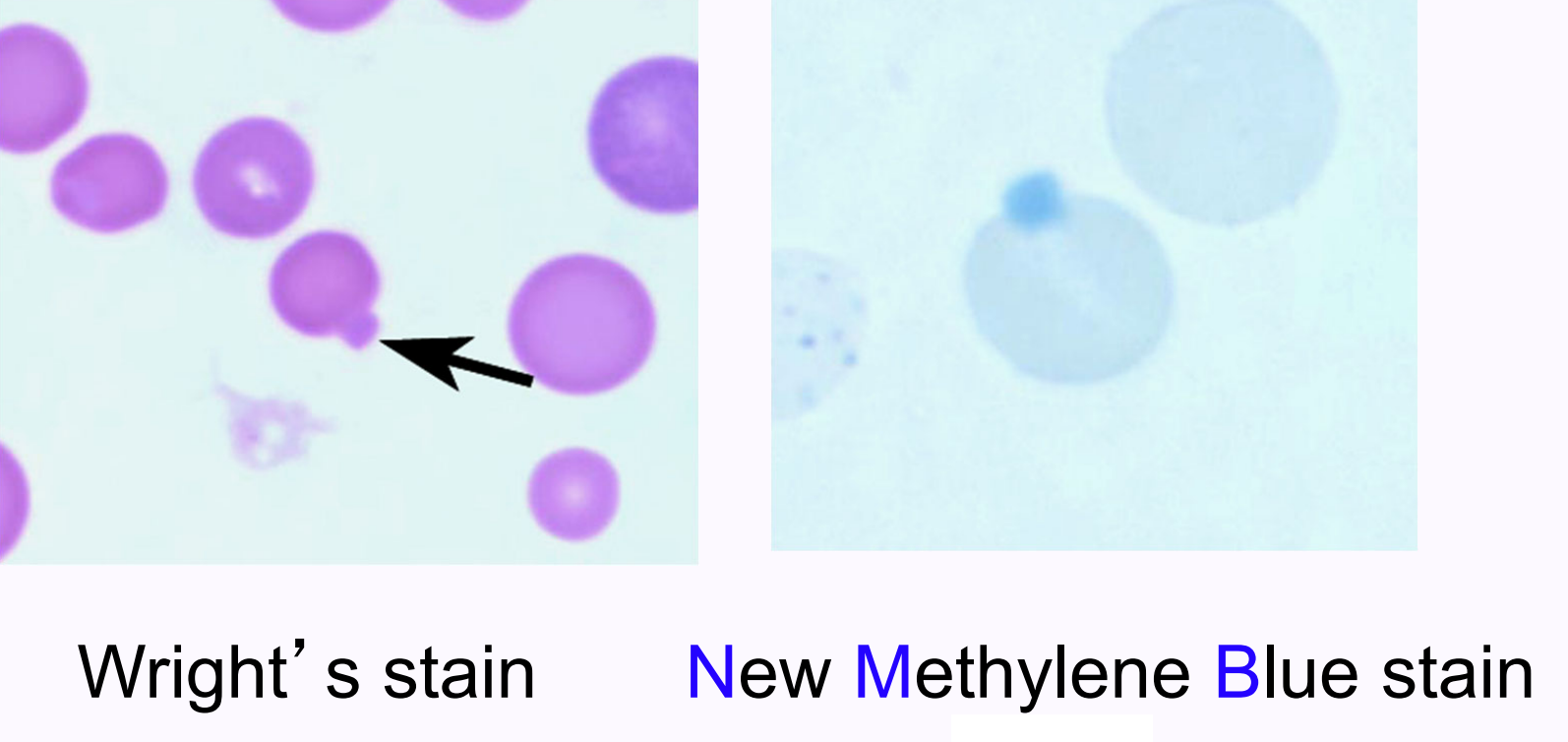
heinz bodies
precipitated, denatured “blob” of globin resulting from oxidation of hemoglobin (oxidative damage)
difficult to see on Wright’s-stained smears; easier to visualize with New Methylene Blue stain
how do domestic species vary in the amounts of reticulocytes released in healthy patients?
dogs: release some
cats: release few
cattle: no reticulocytes in health
horses: do NOT release reticulocytes in healthy OR anemic states
what are submechanisms of regenerative anemia?
hemorrhage
hemolysis
what are submechanisms of nonregenerative anemia?
intra- or extra-marrow disease
ferroportin
iron transporter used to move iron from inside to outside of cells
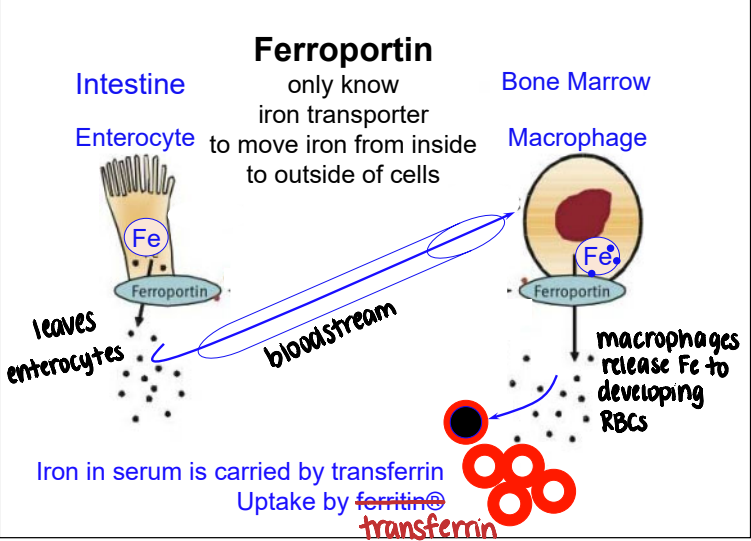
hepcidin
acute phase protein that blocks ferroportin → iron accumulates in macrophages → inhibits erythropoiesis during inflammation
prevent bacteria from stealing and using iron
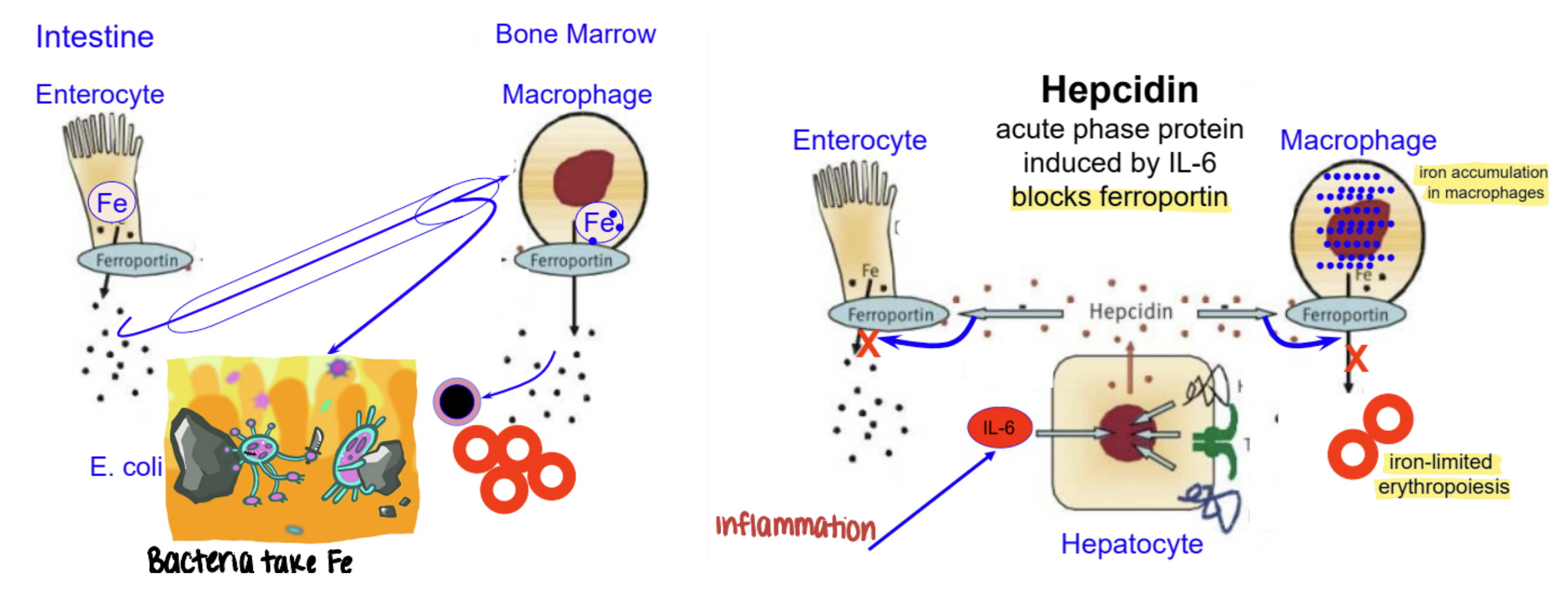
anemia of inflammatory disease
infectious & non-infectious inflammation
hepcidin released
usually normocytic, normochromic
non-regenerative
low serum iron → negative acute phase reactant
due to sequestration of iron
how does chronic kidney disease cause anemia?
↓ production of EPO from renal interstitial fibrosis
other contributing factors:
↓ response of RBC precursors to EPO
↓ RBC lifespan from circulating wastes
mild hemorrhage from gastric mucosal ulcers
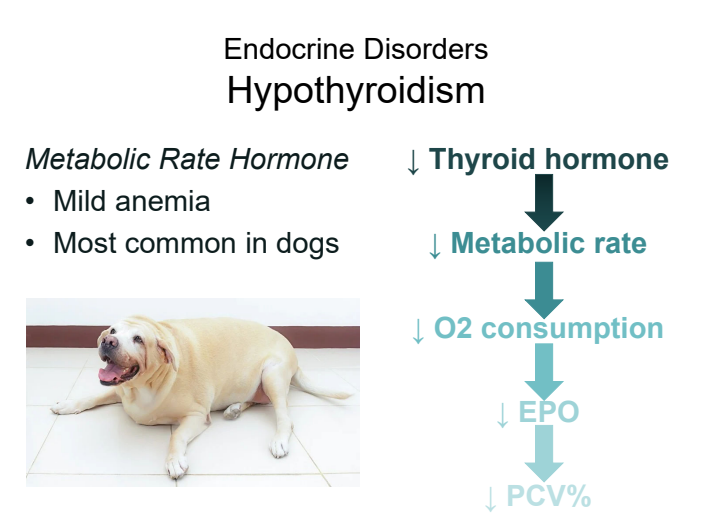
how does hypothyroidism cause anemia?
↓ thyroid hormone → ↓ metabolic rate → ↓ O2 consumption → ↓ EPO → ↓ PCV%
CBC results consistent with intramarrow disease
unexplained non-regenerative anemia +
multiple lineages affected
thrombocytopenia
leukopenia (neutropenia)
lymphocytopenia
inappropriate rubricytosis
howell-jolly bodies
atypical cells
EXTRA-marrow ruled out
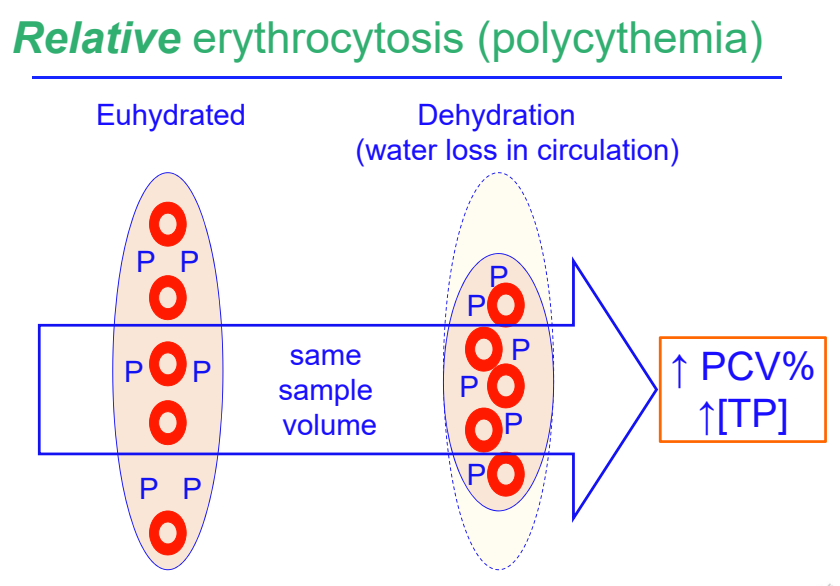
relative erythrocytosis due to dehydration
most frequent cause of relative erythrocytosis
no absolute increase in RBC mass
no increase in EPO
increase relative to plasma H2O
relative erythrocytosis due to splenic contraction
physiologic erythrocytosis mediated by epinephrine — fight or flight response
horses — large spleen, muscular coat
increased PCV, no change in [TP]
transient redistribution of RBCs
appropriate vs. inappropriate secondary absolute erythrocytosis (↑ EPO)
appropriate: ↓ pO2
↑ EPO in response to hypoxemia
inappropriate: normal pO2
EPO-secreting tumor
EPO secretion from focal hypoxic renal tissue
rare
primary (absolute) erythrocytosis or polycythemia vera
bone marrow neoplasm of mature RBCs
↑ RBC mass independent of EPO
primary erythrocytosis: only RBCs increased
polycythemia vera: other cell lines may also be increased (neutrophils, platelets)
rare