1. Health Promotion & Family Structure
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
health
a state of complete physical, mental, & social well-being
not merely the absence of disease or infirmity
defined by each person regarding their own values and beliefs
as well as family, culture, community, and society
health promotion
The process of allowing people to improve their state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being by increasing their control over the determinants of health
public health is measured by:
morbidity - how frequently a disease occurs
mortality - the number of deaths resulting from a disease
internal variables of health
perception of symptoms
coping skills
locus of control
how well they feel they can control things
external variables of health
visibility of symptoms (e.g. rash, limping)
social groups
cultural backgrounds (e.g. balance, rituals, opinion on meds)
economic variables
HC access
social support
wellness
an active state of being healthy by living a lifestyle promoting physical, mental, and emotional health
disease
medical term, referring to the pathologic changes in the structure or function of the body or mind
illness
the response of a person to a disease
an abnormal process involving changed level of functioning
both acute & chronic illnesses can be life-threatening
acute illness
rapid onset of symptoms that last a short time
e.g. common cold, diarrhea, asthma
tx: usually self-limiting, meds, surgery
chronic illness
broad term encompassing many physical & mental alterations in health
1 or more of the following:
permanent, causes/ed irreversible alterations, special education for rehab, long period of care
can have periods of remission & exacerbations
e.g. COPD, diabetes, arthritis
risk factors for illness and injury
modifiable and nonmodifiable things
age, genes, physiological factors, health habits, lifestyle, environment
stages of illness behavior
experience symptoms - self care, OTC meds
assume the sick role - give up ADLs
assuming a dependent role - seeking HCW, dx, tx
recovery/rehab - begins in hospital, ends at home when resuming ADLs
health equity
attainment of the highest level of health for all people
health disparity
an unavoidable difference in health status between population groups
influenced by race/ethnicity, poverty, sex, age, mental health, educational level, disabilities, sexual orientation, health insurance, & access to HC
social determinants of health
the conditions in which people live, work, learn, and play that influence their health and well-being
factors affecting health & illness
basic human needs
human dimensions
self-concept
risk factors for illness or injury
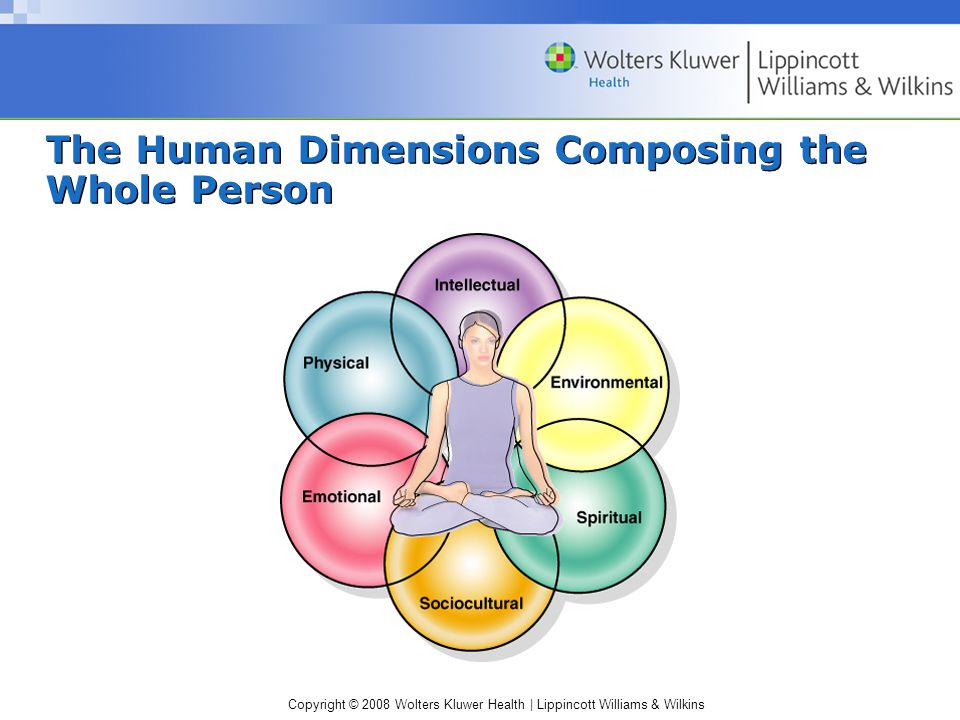
The Human Dimensions Composing the Whole Person
physical dimension - genetics, age, race, gender, developmental level
emotional dimension - how the mind affects body function & responds to body conditions
intellectual dimension - cognitive abilities, educational background, past experiences
environmental dimension - housing, sanitation, climate, pollution
sociocultural dimension - economic level, lifestyle, family, culture
spiritual dimension - spiritual beliefs and values
nurse role in health promotion
information dissemination health risk appraisal
lifestyle/behavior change
environmental control programs
models of health and illness
the health belief model
the health promotion model
stages of change model
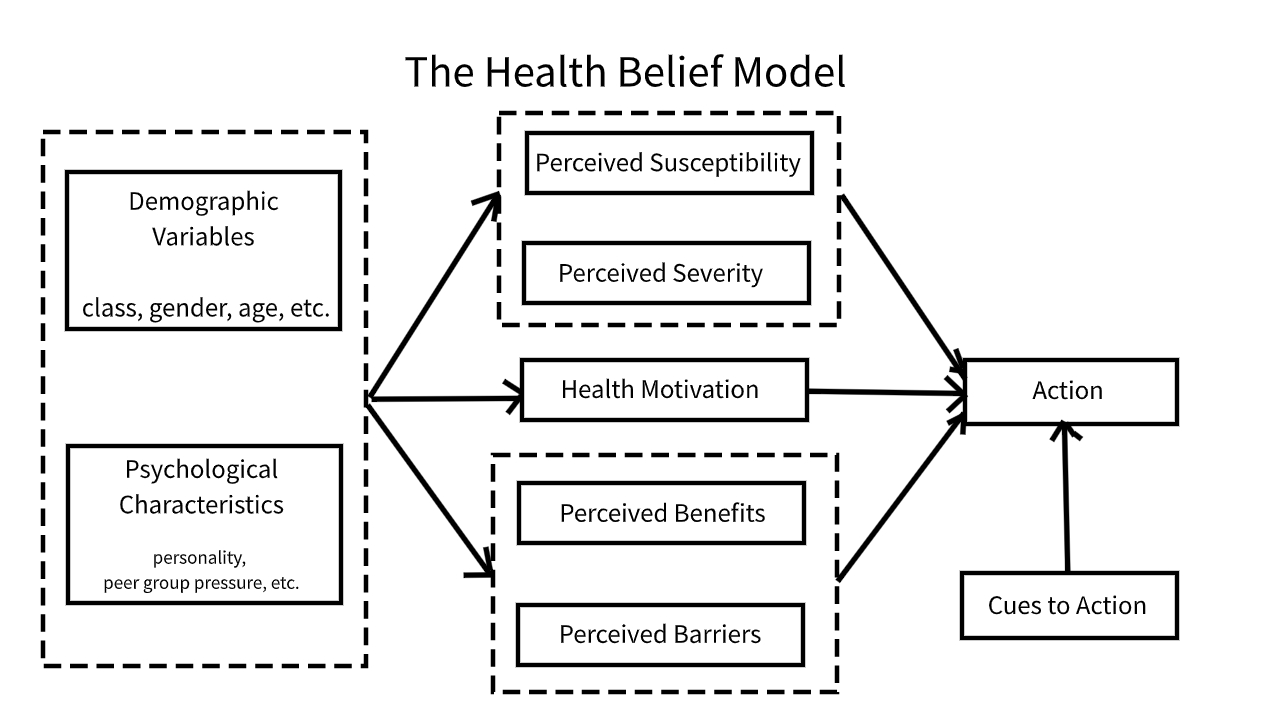
the health belief model (rosenstock)
what people perceive to be true about themselves in relation to their health
modifying factors: demographic & sociopsychological
three components:
perceived susceptibility to a disease
perceived seriousness of a disease
perceived benefits of action
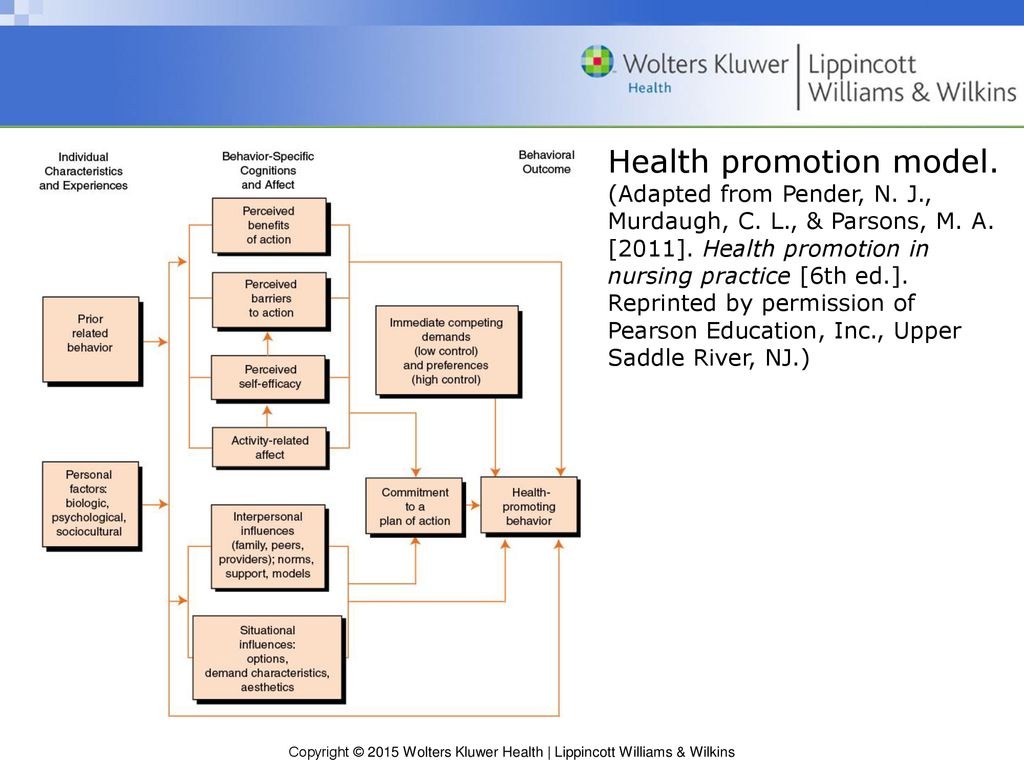
the health promotion model (murdaugh)
developed to illustrate how people interact with their environment as they pursue health
pt characteristics, experiences, & behavior-specific knowledge/believes to motivate health-promoting behavior
variables:
activity-related affect
commitment to a plan of action
immediate competing demands & preferences
stages of change model (prochaska & DiClemente)
used by counselors addressing behavrios including injury prevnetion, addiction, & weight loss
Precontemplation
Person is unaware that change needs to be made
E.g. a smoker who doesn’t think smoking is a problem
Contemplation
Person is aware of problem and are seriously thinking about overcoming it, but have not yet made a commitment to take action
E.g. smoke thinks about quitting but hasn't taken any steps
Determination: commitment to action
Person is getting ready to take action and has some intention to change in the near future
E.g. gathering information, setting goals, taking small steps towards change
Action: implementing the plan
Person is actively changing their behavior by implementing and making changes
E.g. the smoker has quit smoking
Maintenance:
Person is working to prevent relapse
E.g. a former smoker who continues to abstain from smoking and avoids situations that may tempt them to smoke
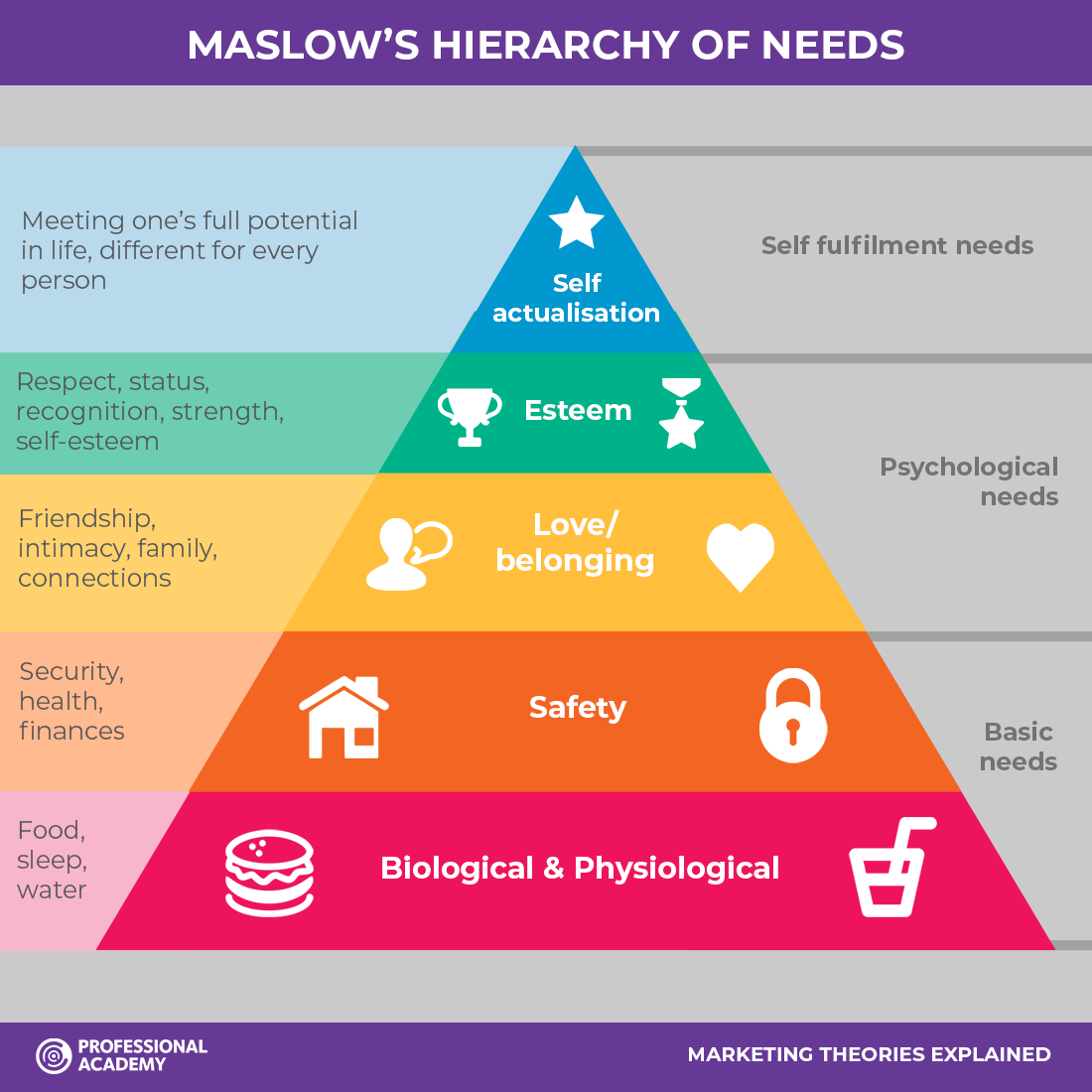
basichuman needs
behaviors, feelings about self and other, values, and priorities
essential for people’s health & survival
some needs are med independently, most require relationships & interactions with other for partial or complete fulfillment
Basic Needs/Maslows Triangle definition
lack of fulfillment can result in illness
fulfillment can help prevent illness
meeting basic needs restores health
fulfillment of basic needs takes priority over other desires and needs when unmet
Basic Needs/Maslows Triangle examples
self-fulfillment needs
self actualization - meeting one’s full potential in life
psychological needs
esteem - respect/status/strength
love & belonging - relationships/family/connections
basic needs - CANT LIVE WITHOUT
safety - security/health/finances
biological & physiological - food/sleep/water
family
any group of people who live together and depend on one another for physical, emotional, and financial support
basic unit of society
nuclear family
traditional family
two parents and their children
extended family
aunts, uncles, and grandparents
blended family
two parents and their unrelated children from previous relationships
single-parent family
may be separated, divorced, widowed, or never marries
echinacea (coneflower) herb
boost immune system; enhance wound healing
may reduce immunosuppressant effectiveness

feverfew herb
prevents migraines, HA, arthritis; stimulates digestion
increases anticoagulant effects

garlic
reduces HPT & cholesterol; antibiotic/antifungal; anticlotting
increases anticoagulant effects

ginger
for digestion/motion sickness/dizziness/nausea
increases anticoagulant effects

ginkgo
improves memory function, relieves stress
increases anticoagulant effects

ginseng
stimulates mental activity & enhances immune system
may interact with caffeine & decrease effects of glaucoma meds

milk thistle
enhances flow in gallbladder, liver, spleen, & stomach
reduces effectiveness of OC

saw palmetto
anti-inflammatory; prostate hypertrophy
may give false low PSA levels delaying dx of prostate cancer

st. john’s wort
antidepressant, anti-inflammatory, antiviral
potentiate antidepressant meds

valerian
sedative/tranquillizer, lowers BP, helps cramps
can increase sedative effects of antianxiety meds

chamomile
GI upset
asthma exacerbation & pregnancy - miscarriage

eucalyptus
anti-inflammatory
asthma & low BP

jasmine
antidepressant
HPT

lavender
insomnia

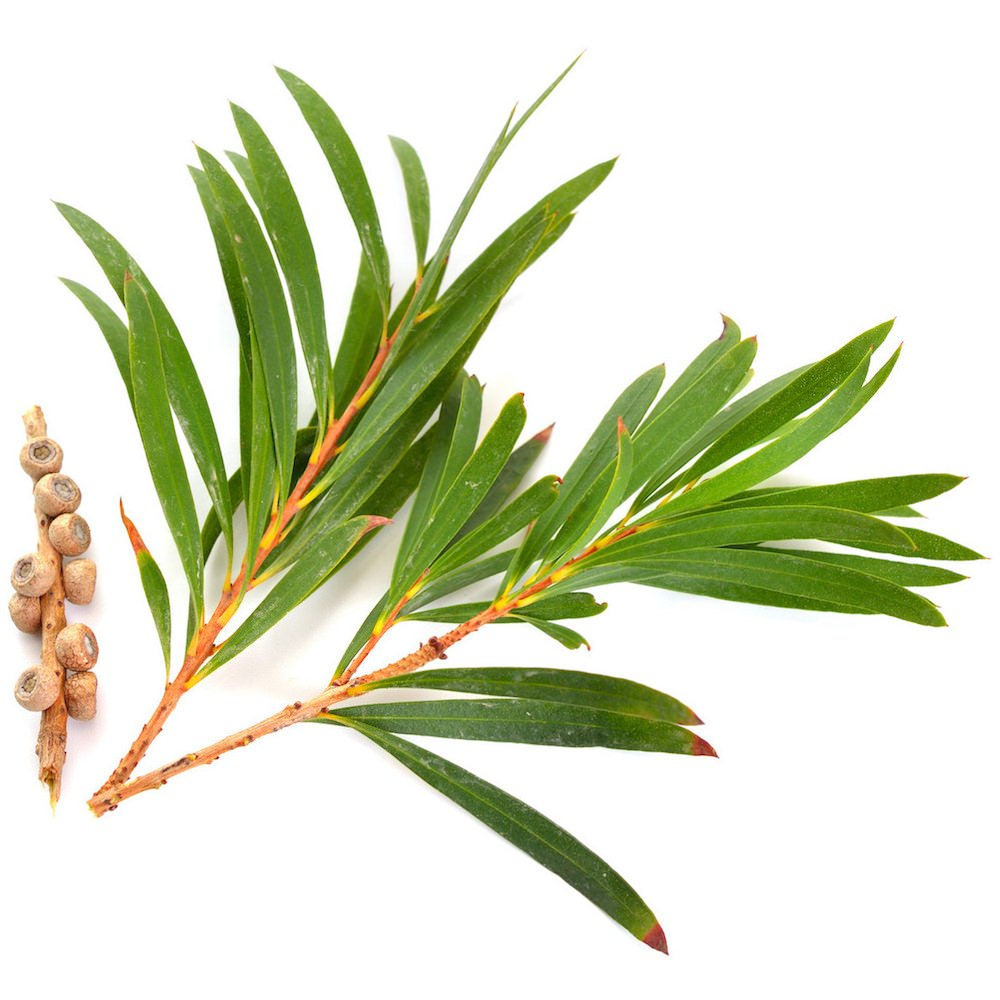
tea tree
antifungal

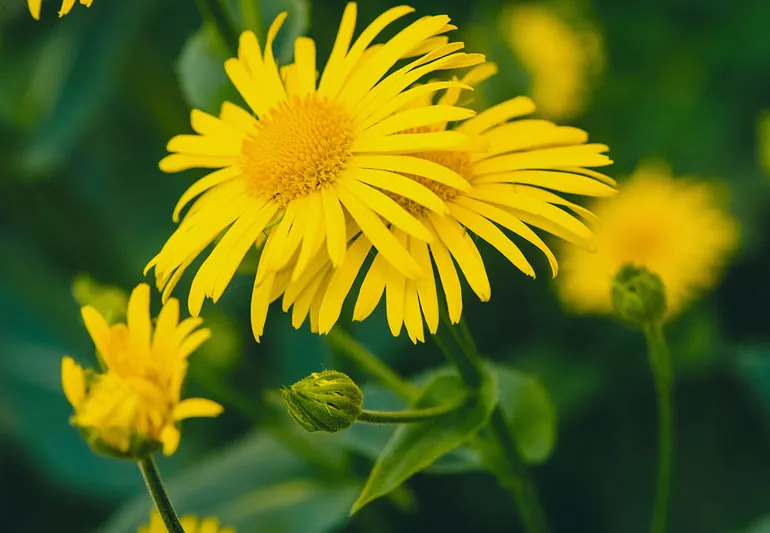
arnica
joint soreness or arthritis
can increase anticoagulation

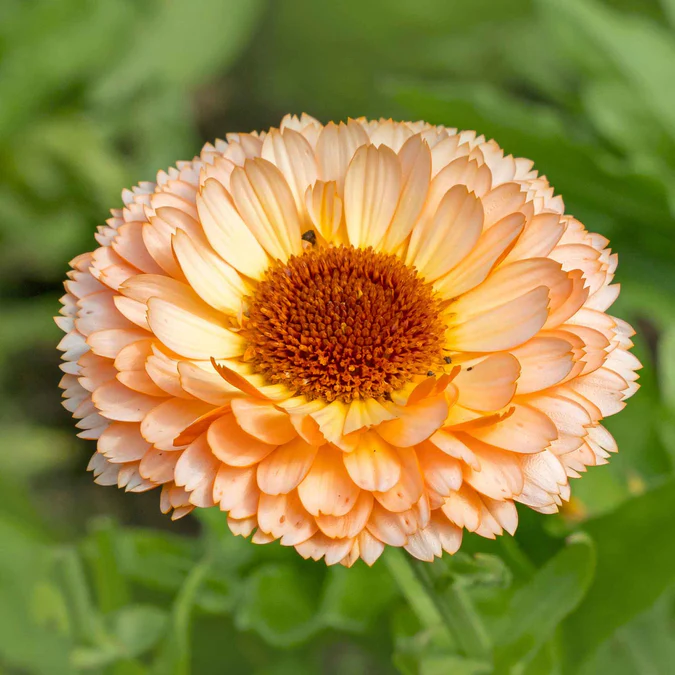
calendula
muscle spasms/menstrual period
pregnant & breastfeeding

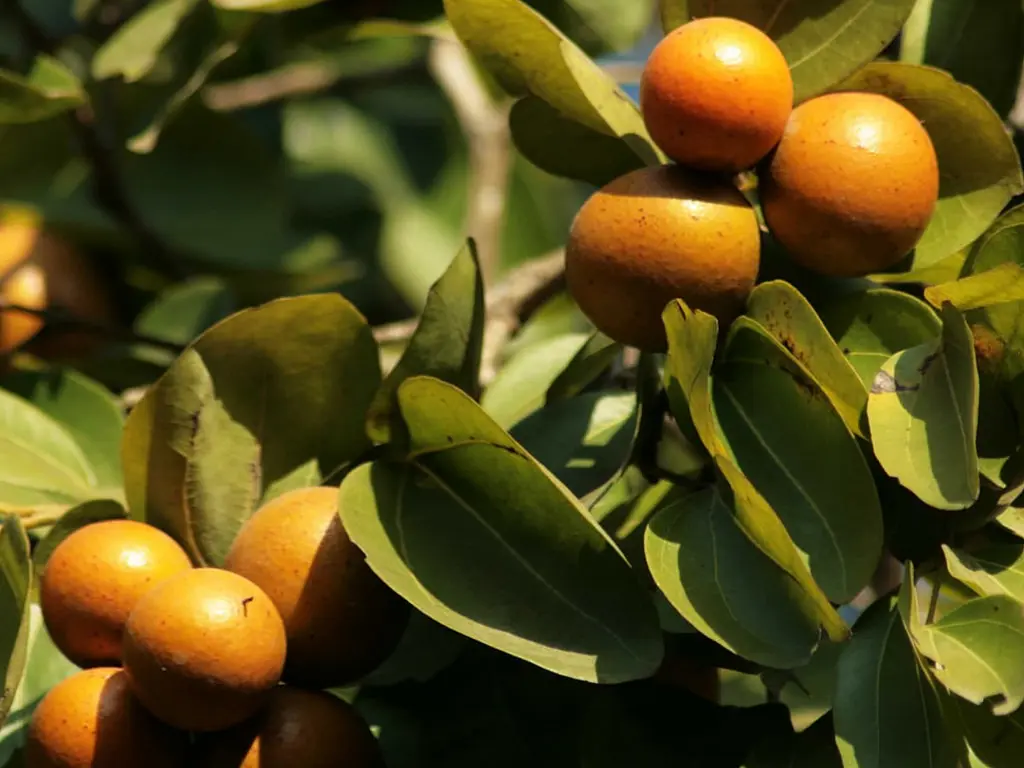
ignatia
anxiety
pregnancy & breast-feeding

peppermint
natural pesticide, N/D
