8b- Mitosis and Cancer
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
How many chromosome pairs are there in a human?
23 homologous pairs
What is a haploid number?
the number of chromosomes found in a single set
> sperm and egg both have 23 chromosomes in each
What is a diploid number?
the total number of chromosomes in a normal body cell
What happens before cell division of DNA?
the chromosomes replicate and each chromosome becomes 2 threads called chromatids held together at the centromeres
not visible (just referred to as chromatin)
Draw a diagram to show a duplicated chromosome (sister chromatids and centromere)
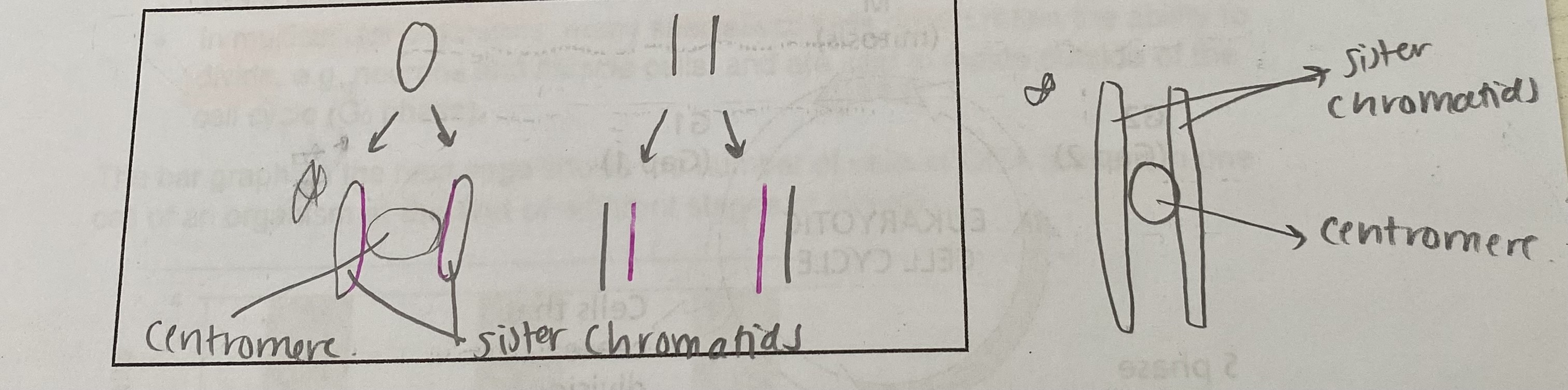
What is a chromosome?
long, linear structures consisting of DNA and histone proteins
What is a homologous chromosome?
a pair of chromosomes containing the same genes in the same positions (loci), each derived originally from a different parent’s gamete at fertilisation
What is a chromatid?
one of the 2 threads of a chromosome, formed after DNA replication
What is a centromere?
holds together 2 identical sister chromatids
What is chromatin?
DNA + proteins together form this substance
What is the cell cycle?
G1= cells prepare for DNA replication - cells grow, respire and new proteins and organelles are produced
S= DNA replication occurs
G2= a relatively short gap before mitosis- cell grows and prepares for mitosis
M= mitosis
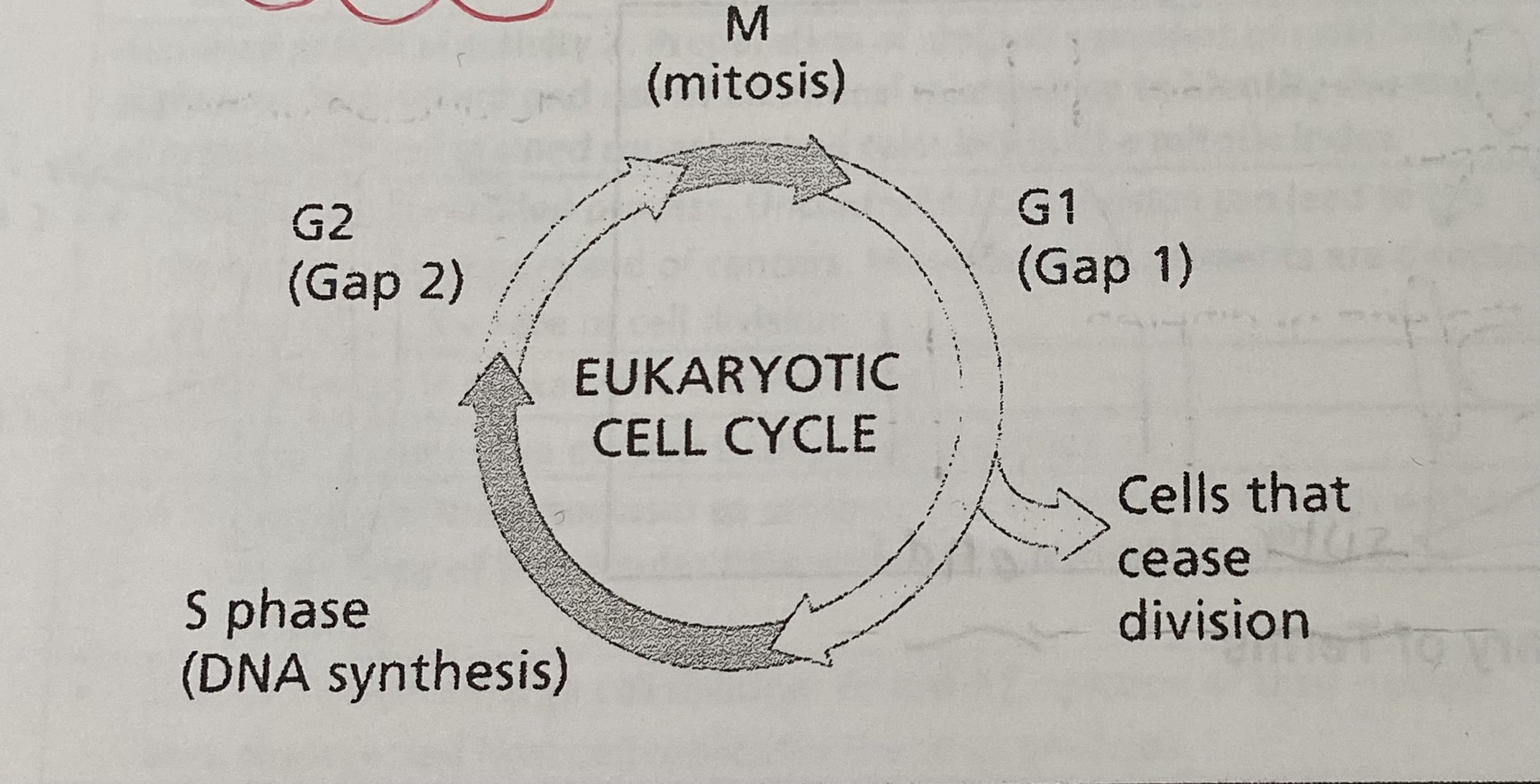
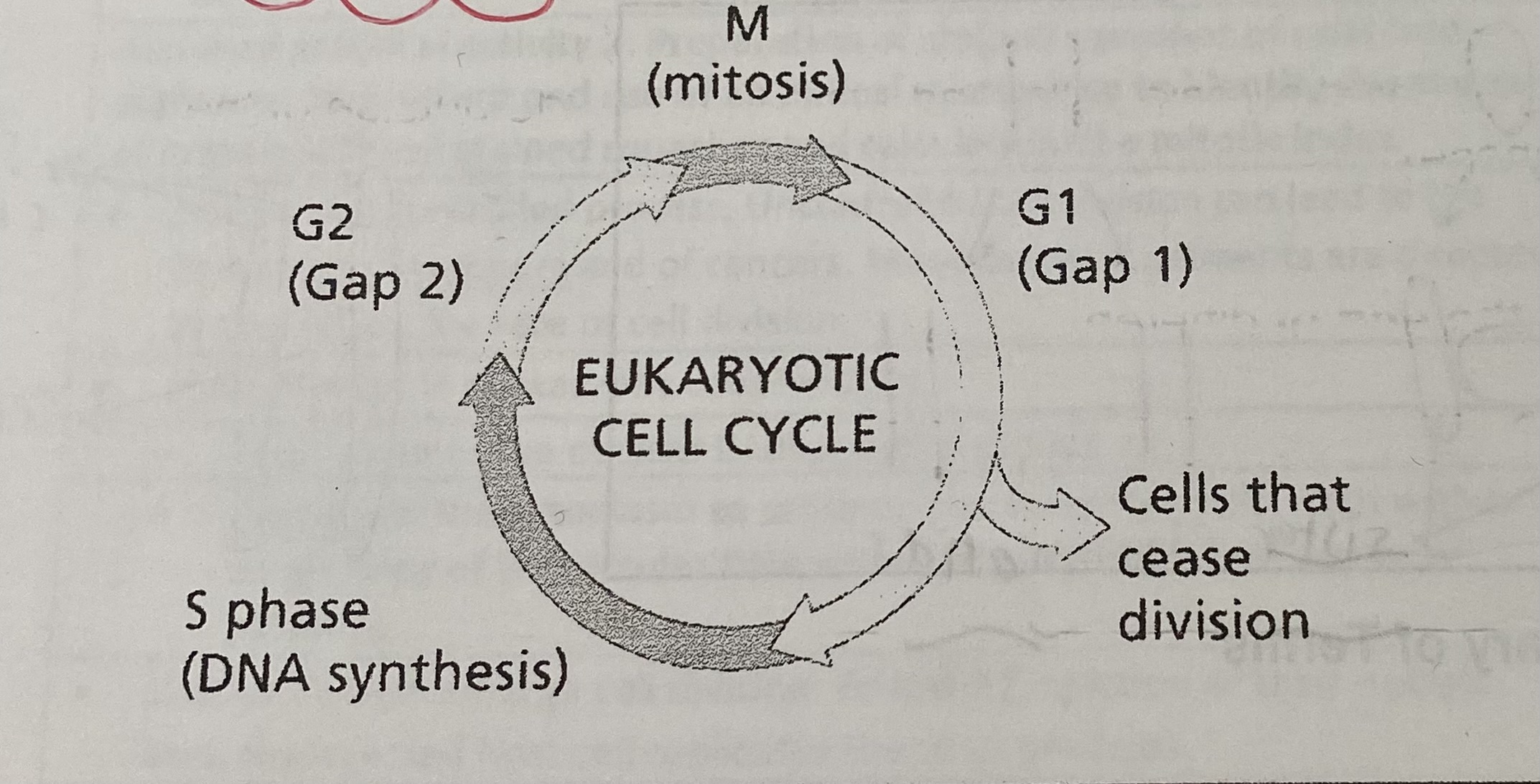
Which phase or phases correspond to interphase?
G1,S + G2
What happens to the DNA during interphase?
semi-conservative replication
What other events occur during interphase?
protein synthesis
increase in number of organelles
ATP production (respiration)
What does it mean if cells have a shorter interphase?
divide more often
What is mitosis?
parent cell divides to produce 2 daughter cells
each daughter cell contains an exact copy of the DNA of the parent (genetically identical)
What is mitosis used for?
growth and replacing tissue during repair (increases number of cells during growth)
allows asexual reproduction
What does mitosis do?
maintains same chromosome number from one generation to the next
What is the only way that variation can arise when a cell divides by mitosis?
a mutation
What is interphase?
the phase where the ell makes preparations for division
What are the phases of mitosis?
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
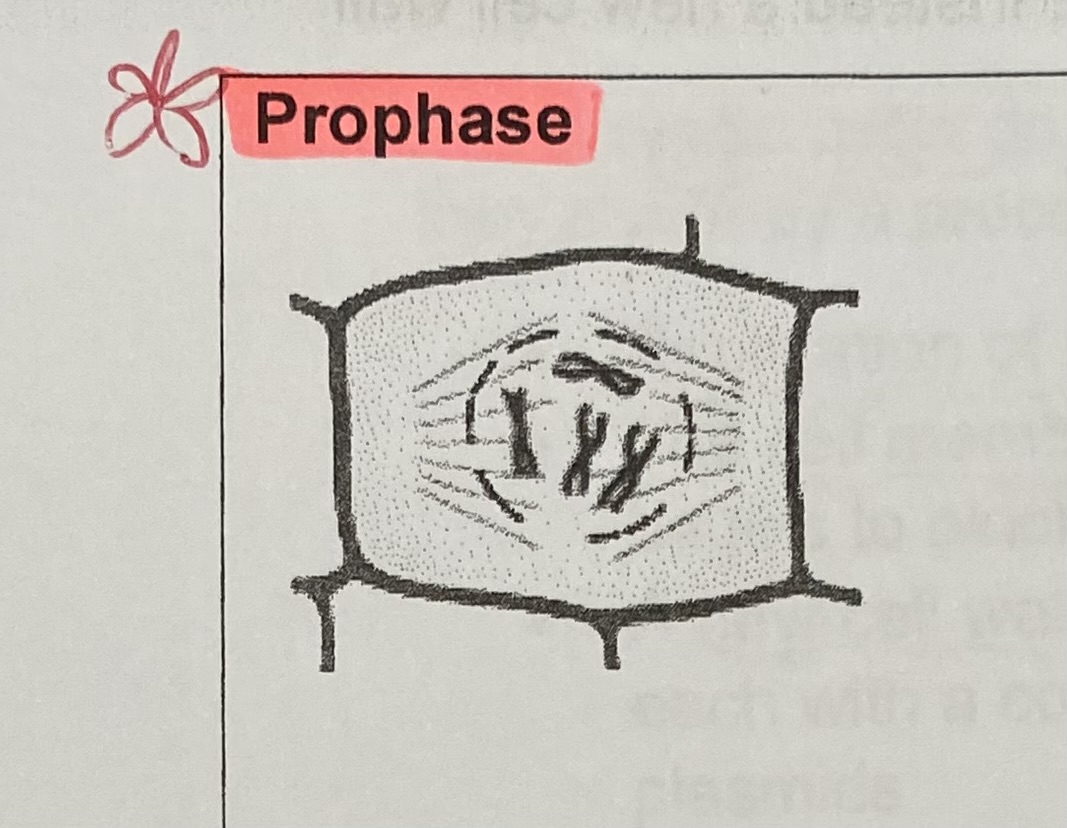
What happens to the chromosomes during prophase?
condense/ shorten due to coiling up of DNA and become visible
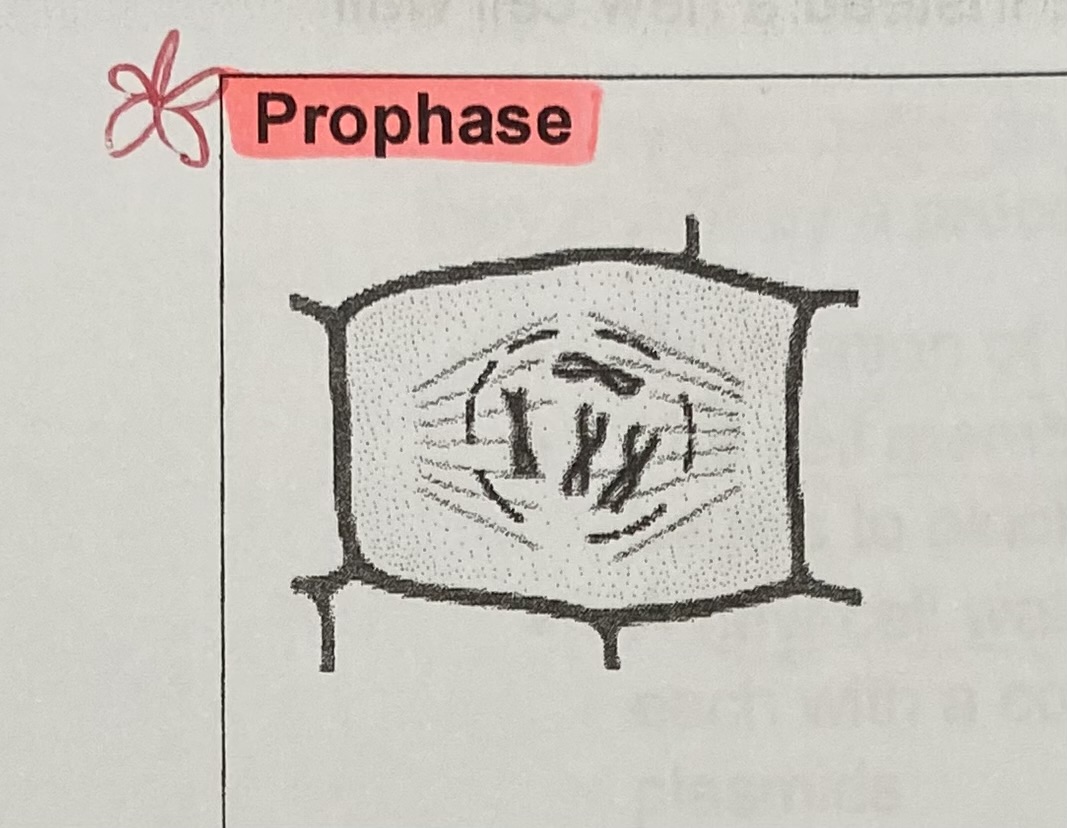
What is the function of the centromere in prophase?
holds 2 sister chromatids together
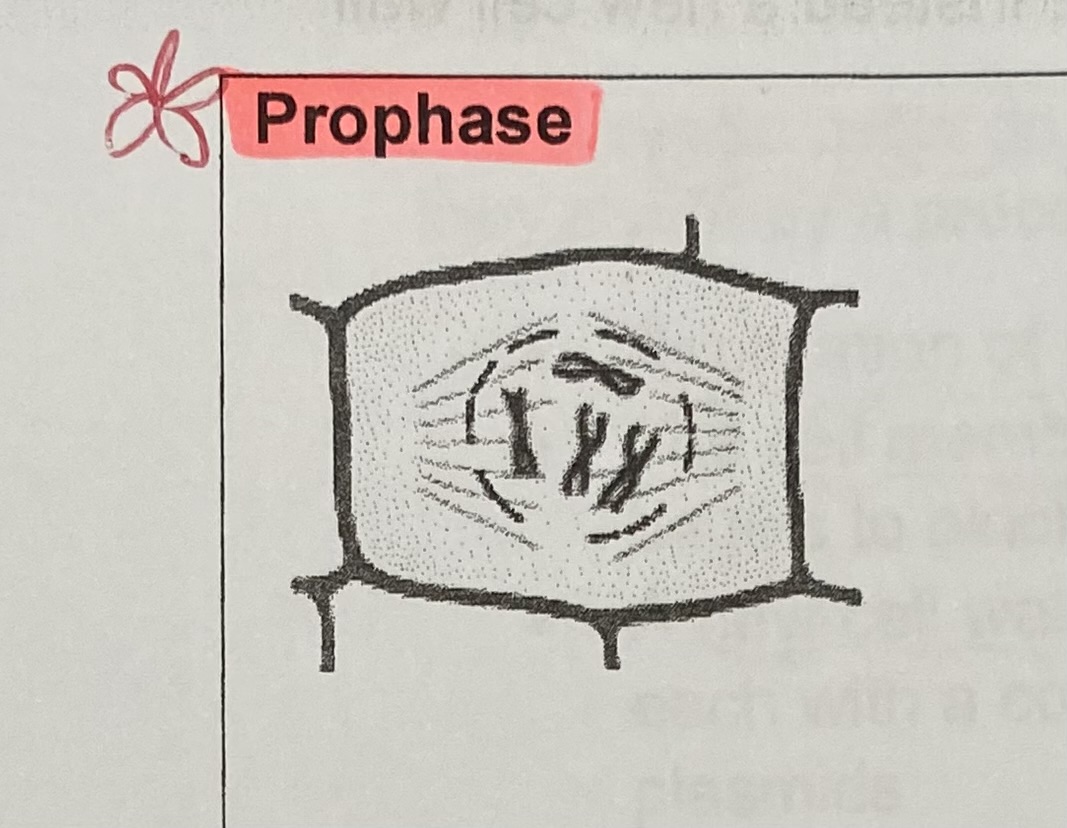
What happens to the nuclear membrane at the end of prophase?
breaks down
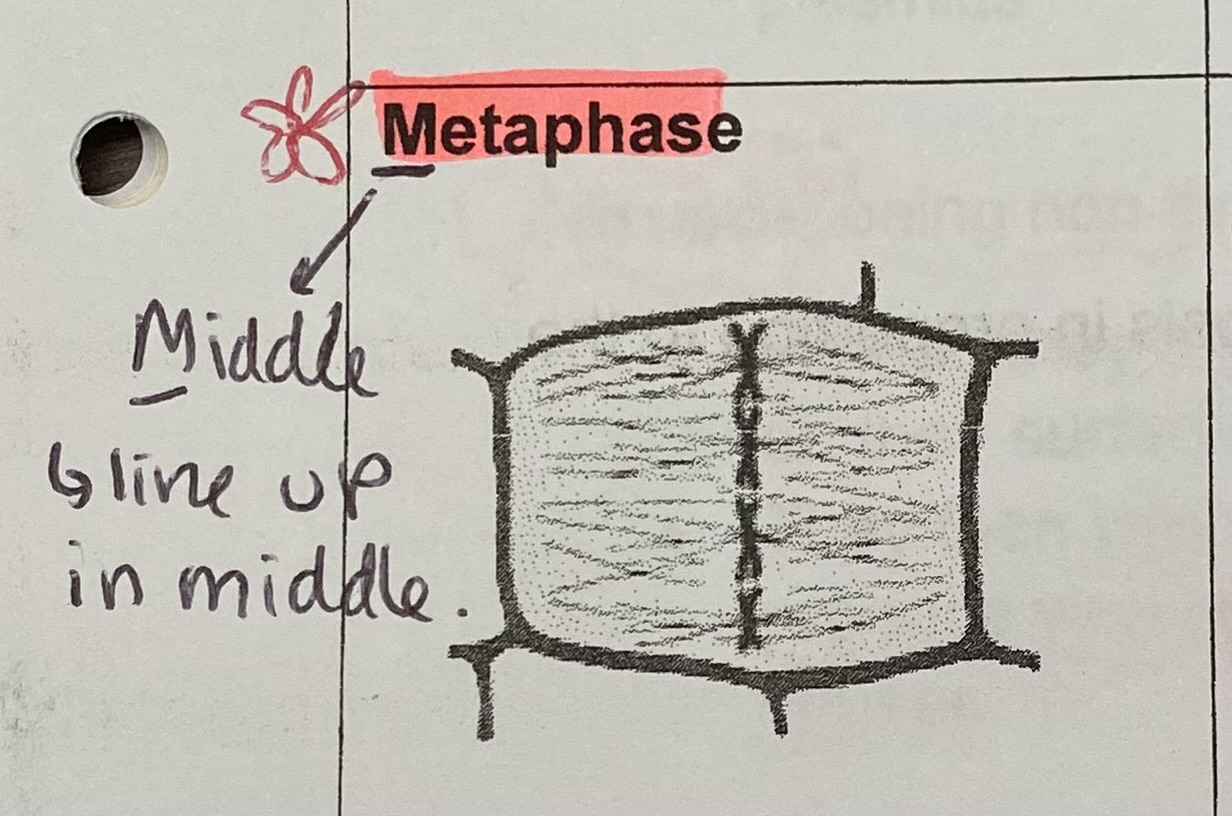
What happens to the chromosomes during metaphase?
line up along the equator of the cell and attach to spindle fibres by their centromeres
centromeres replicate so both sister chromatids have a centromere
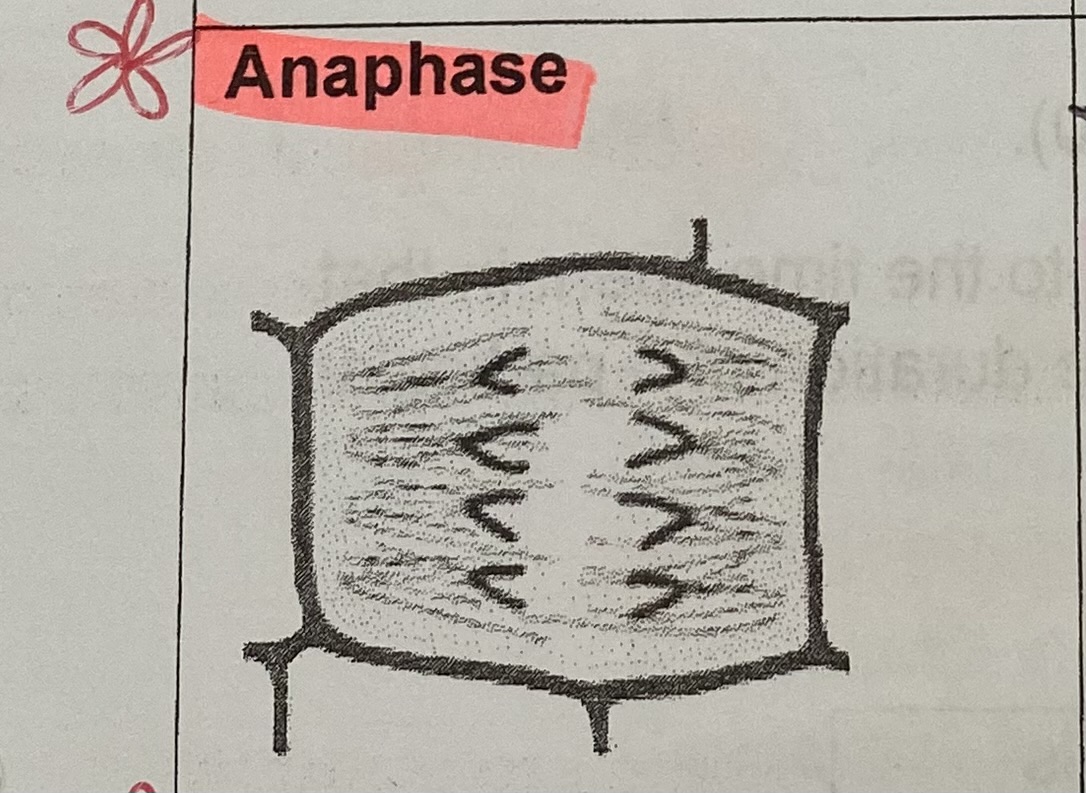
What happens to the chromosomes during anaphase?
centromere divides, spindle fibres contract pulling apart the chromatids of each chromosome
> sister chromatids go to opposite poles
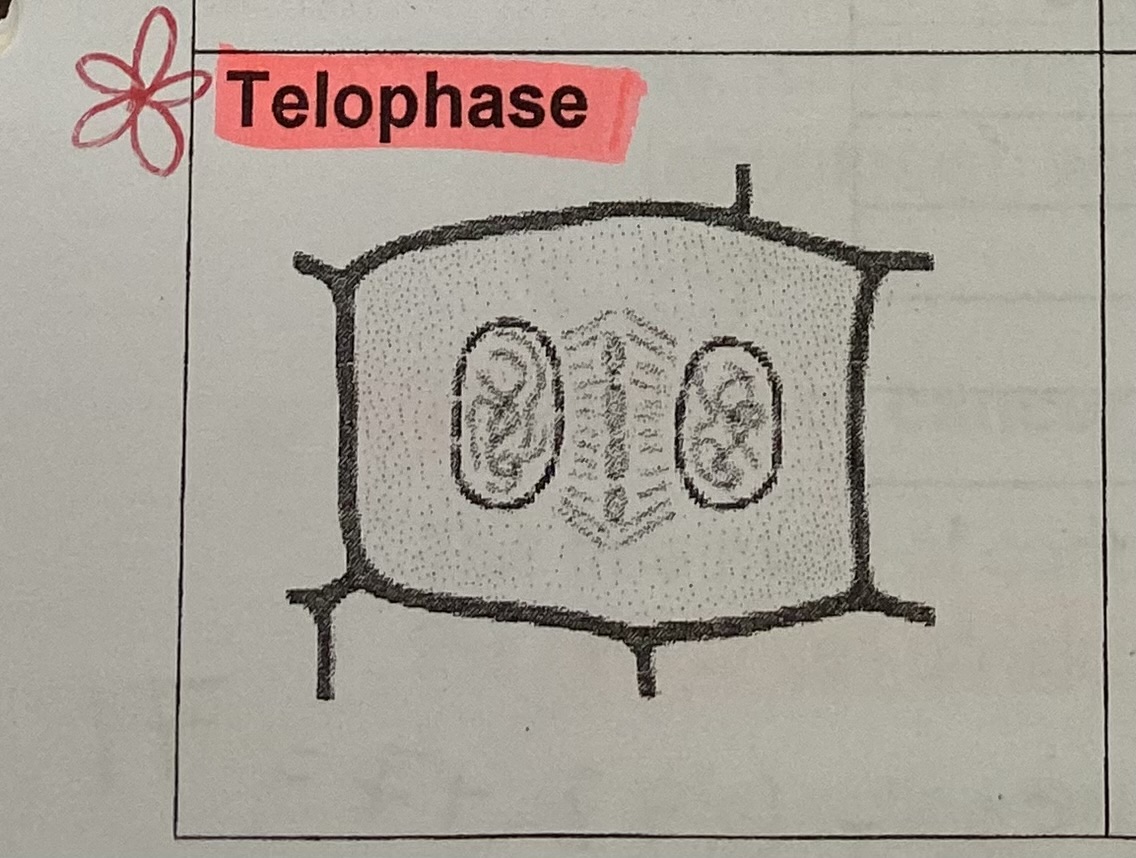
What happens to the chromosomes during telophase?
uncoil and become threadlike again, no longer visible
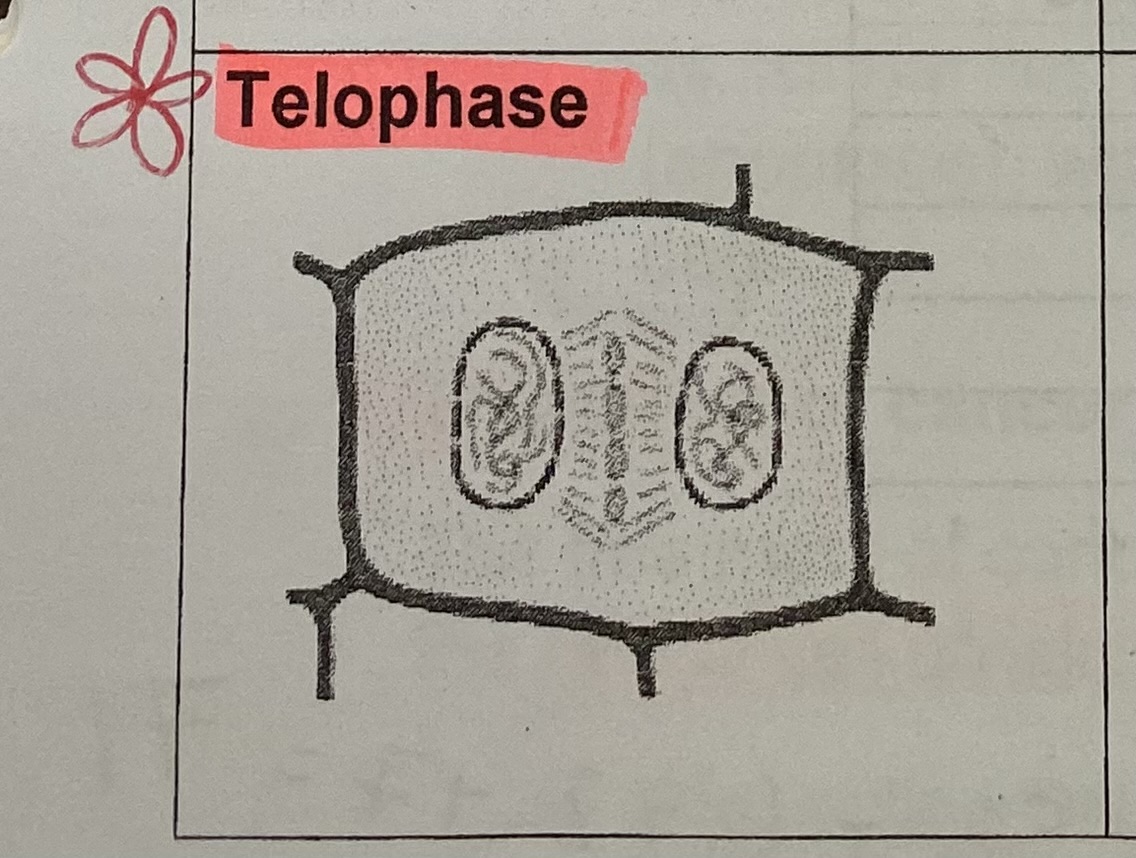
What forms around each set of daughter chromosomes during telophase?
new nuclear envelope
What happens at the end of telophase?
cytokinesis (marks the ends of mitosis)
What is cytokinesis?
division of the cytoplasm
cells without a cell wall pinch themselves into 2 and a membrane forms in the middle of the cell and eventually 2 new daughter cells separate
What is mitotic index?
a ratio showing the number of cells undergoing mitosis in proportion to the total number of cells
What is the calculation for mitotic index?
number of cells undergoing mitosis/
total number of cells
What is cell division like in prokaryotic cells?
Binary fission
replication of the circular DNA
cell membrane begins to grow and begins to pinch inward, dividing the cytoplasm
new cell wall forms, forming 2 daughter cells
What is cell division like in viruses?
they do not undergo cell division as they are non-living
replicate by attaching to a host cell
inject their nucleic acid into host cell and used to produce viral components
then assemble into new viruses
What is cell division like in cancer?
mitosis is a controlled process
cancer results from mutations which causes rapid, uncontrolled growth and division of cells
this results in a mass of abnormal cells (called a tumour)
Describe cancerous tumour cells
do not respond to signals from nerves and hormones
do not undergo programmed cell death
How is cancer treated?
blocking some part of the cell cycle to control rate of division
drugs= prevent DNA from replicating and prevent spindle formation
chemotherapy= drugs/ chemicals (lose hair as hair-producing cells divide rapidly)
radiotherapy
surgery= removal