radiopaque jaw lesions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
radiographic presentation of root remnants
has a thin RL rim or PDL space (sometimes, this is when it harder to distinguish it between DBI)
long oval shape
pulp canal sometimes visible
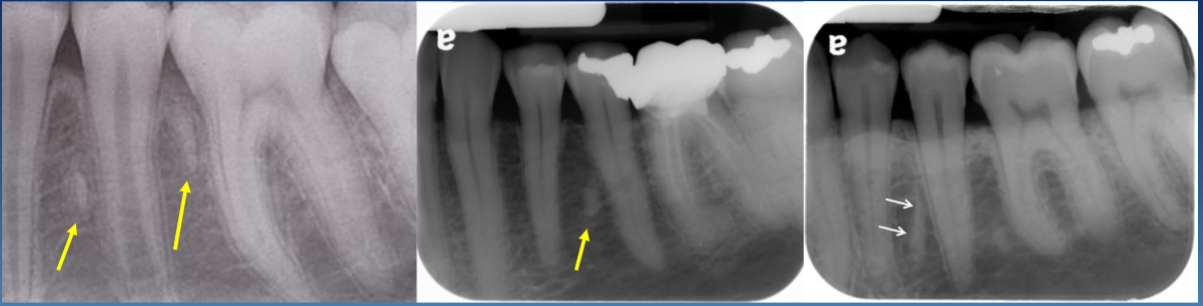
common location for root remnants
M or D of premolars, mand > max
post ext sites
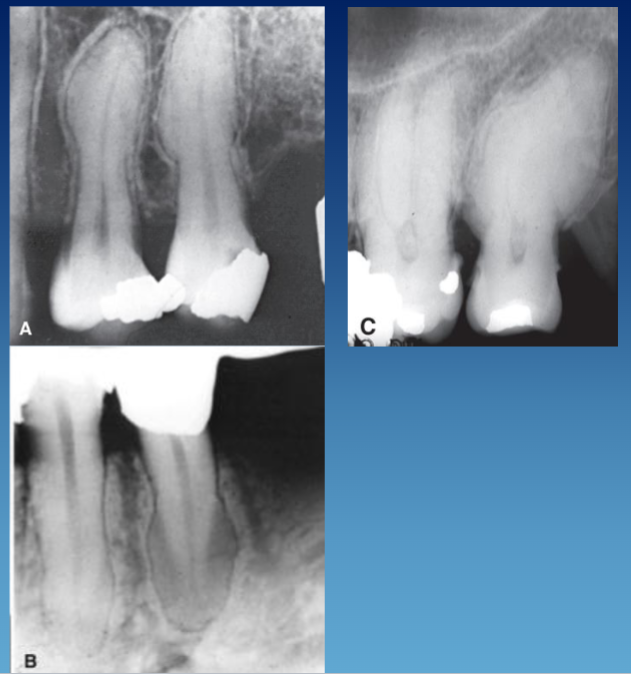
radiographic presentation of hypercementosis
within PDL space
bulbous root
lamina dura and PDL in tact
well defined
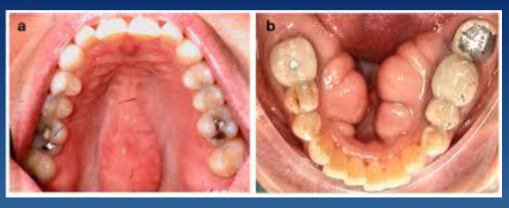
what is hyperostosis/exostosis/tori
bony masses arising from cortical (or cancellous) bone; is non-neoplastic
where hyperostosis/exostosis/tori would arise in the maxilla
exostoses: most commonly along B or palatal alveolar bone
tori: palatal midline
where hyperostosis/exostosis/tori would arise in the mandible
exostosis: can be B alveolar bone
tori: lingual
what is the most common hyperostosis
tori: hard palate midline or lingual mandible
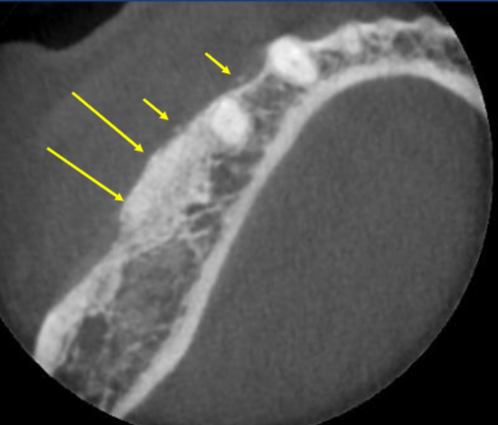
radiographic presentation of foreign body/bone graft
granular, RO material
edentulous site
within sockets, along alveolar ridge
sinus floors
loose fragments within soft tissue
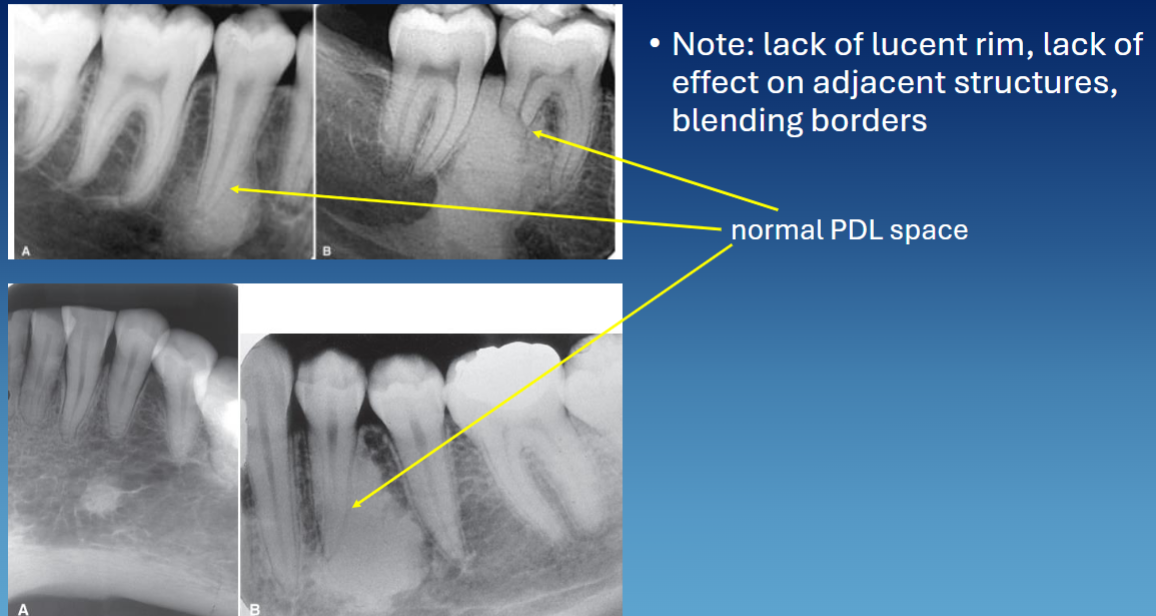
dense bone island is also called
idiopathic osteosclerosis
radiographic presentation of dense bone island
well defined
no RL rim, can blend w bone or lamina dura
PDL in tact
vital teeth but can induce resorption
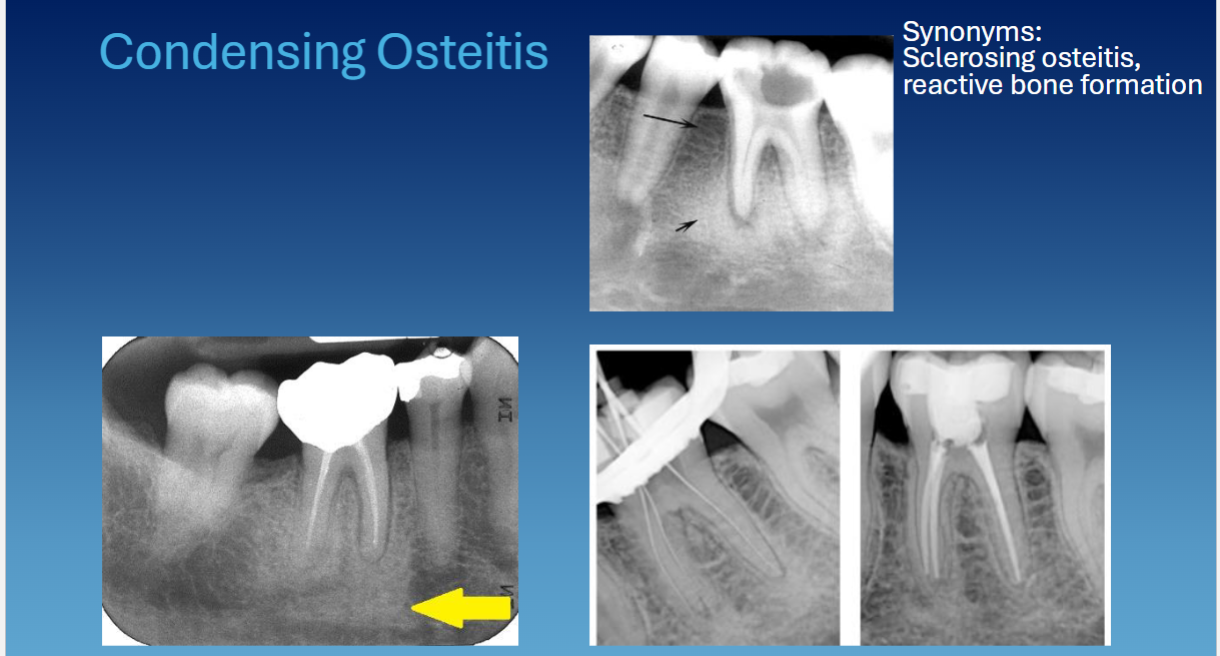
condensing osteitis is also called
sclerosing osteitis, reactive bone formation
condensing osteitis clinical presentation
associated w teeth due to inflamed or infected tooth → tooth is non-vital
radiographic presentation of condensing osteitis
periapical to tooth
no RL rim
widened PDL space
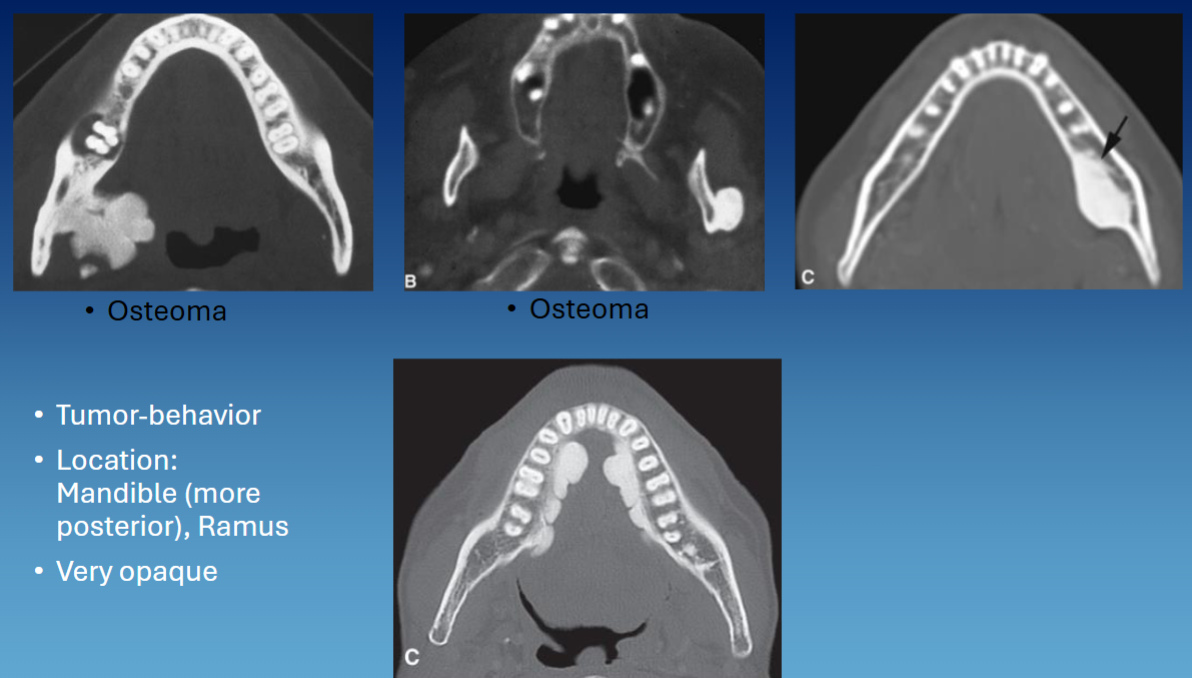
what is an osteoma
benign slow growing bone tumor from periosteum that can occur on a bone surface or within paranasal sinuses; non-neoplastic
common location associated w osteoma
sinuses, ramus, inferior border of mandible, condyle/coronoid, max/mand
radiographic presentation of osteoma
well defined
convex/lobulated
RO mass
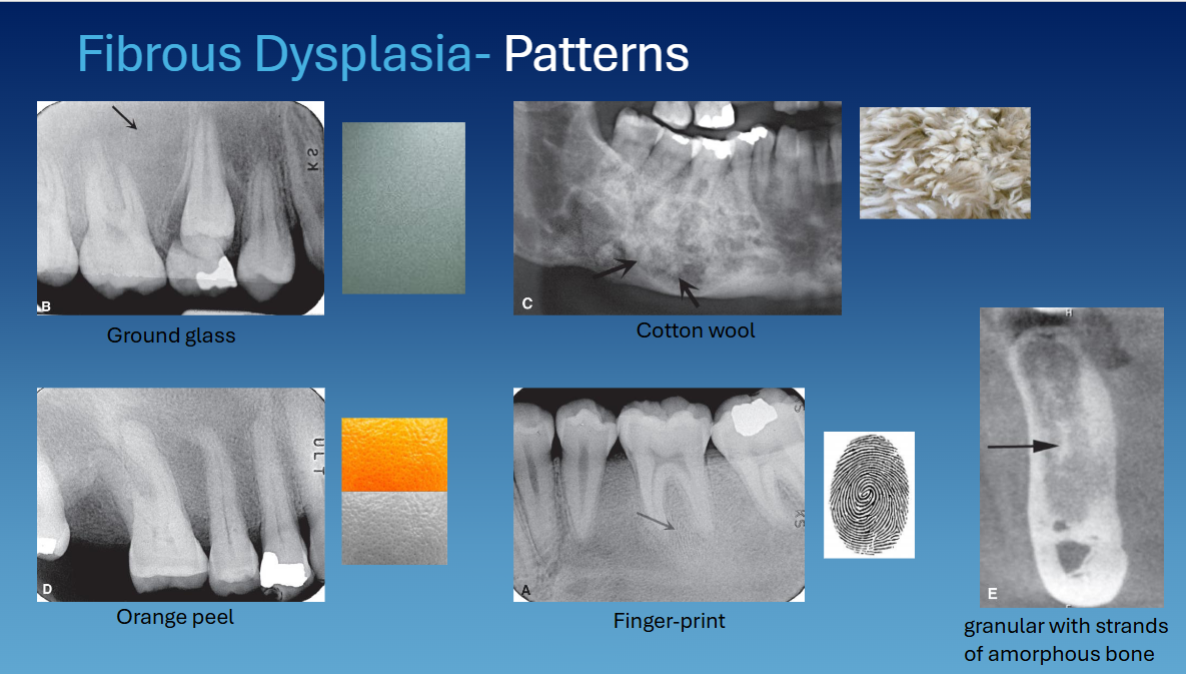
what are common patterns to describe fibrous dysplasia radiographically
ground glass
orange peel
cotton wool
finger print
fibrous dysplasia effect on adjacent structures
no effect on teeth
can cause lateral wall of maxilla to expands into maxillary sinus
cortical bone thin out but no perforation
superior displacement of IAC
what are the 3 types of cemento-osseous dysplasia
periapical
focal
florid
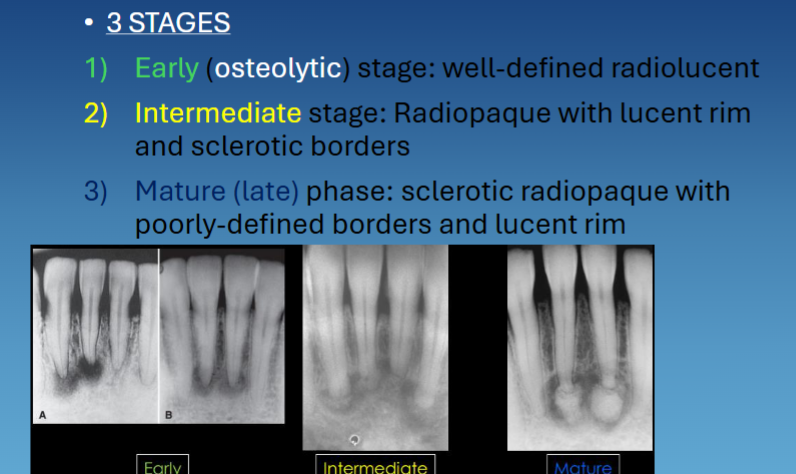
3 stages of periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
early → RL
intermediate → RO w RL rim and sclerotic borders
mature/late phase → sclerotic RO w RL rim
location associated w periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
anterior mandible
location associated w focal cemento-osseous dysplasia
posterior mandible
location associated w florid cemento-osseous dysplasia
multi quadrant
radiographic presentation of cemento-osseous dysplasia
RO lesion w RL rim
surrounded by sclerotic bone
continuous w PDL
loss of lamina dura
cemento-osseous dysplasia effects on surrounding structures
no root resorption → teeth are vital
can displace cortical bone and IAC
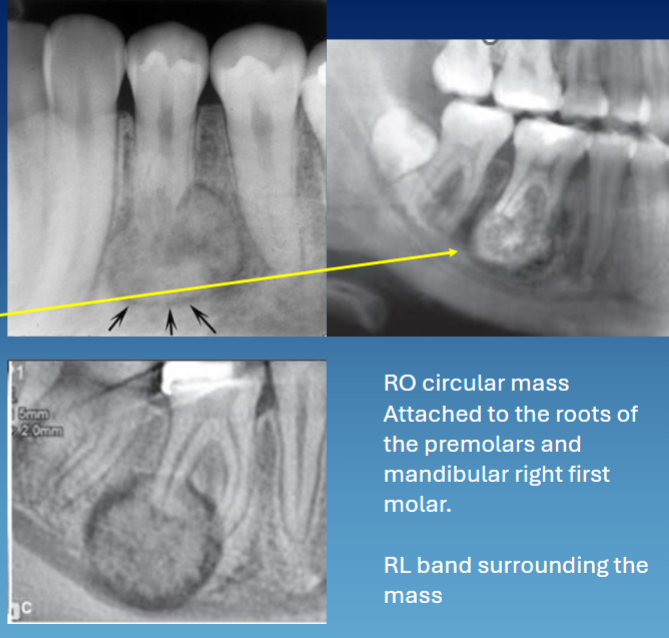
location associated w cementoblastoma
root/apices of mandibular dentition → premolars and molars
radiographic presentation of cementoblastoma
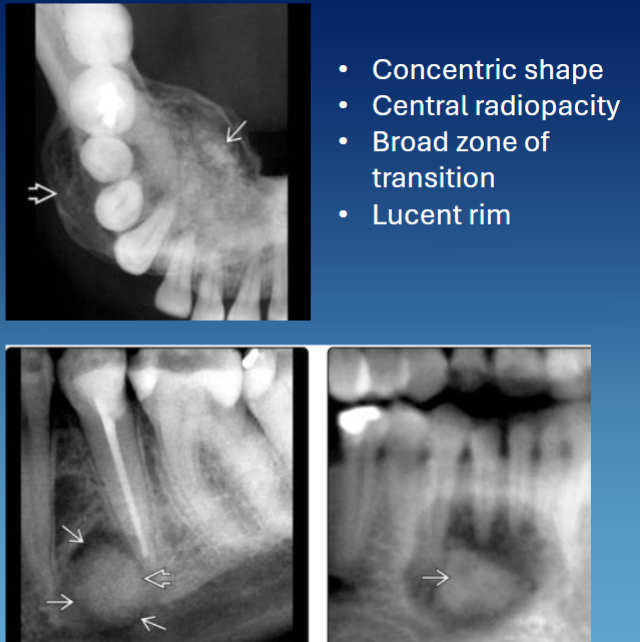
concentric
RL rim
attached to the root w resorption → tooth vital but can be associated w pain
PDL not visible
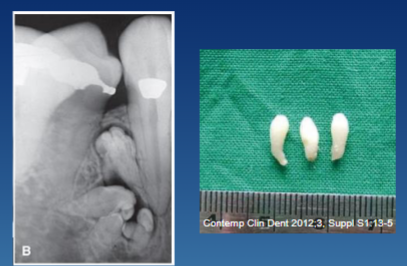
what are the 3 types of odontoma
compound → more common
complex
dilated
radiographic presentation of compound odontoma
cluster of teeth, common in anterior maxilla
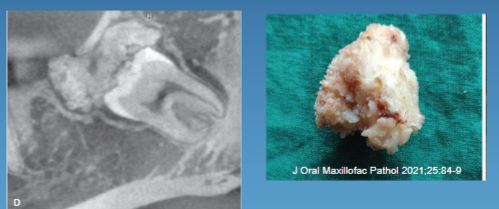
radiographic presentation of complex odontoma
irregular mass of RO, common in posterior mandible
dilated odontoma
des e dente
location associated w ossifying fibroma
mandible > max
radiographic presentation of ossifying fibroma
concentric, multilocular
wide zone of transition or thin cortication
RL rim
wispy, granular or solid
ossifying fibroma effects on adjacent structures
root resorption
displace teeth
cortical expansion