Understanding Proteins and Their Structures
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
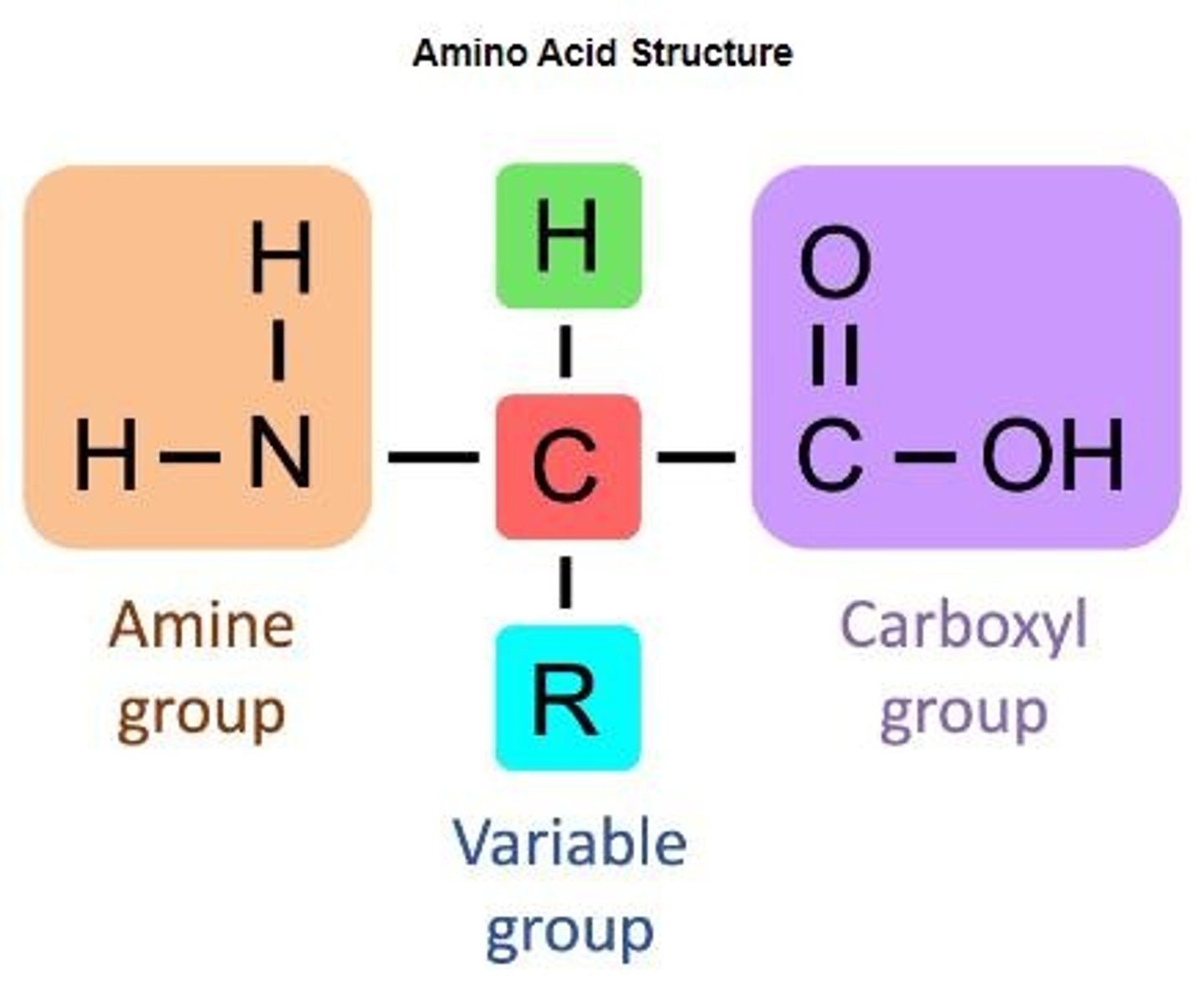
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins with variable side chains.
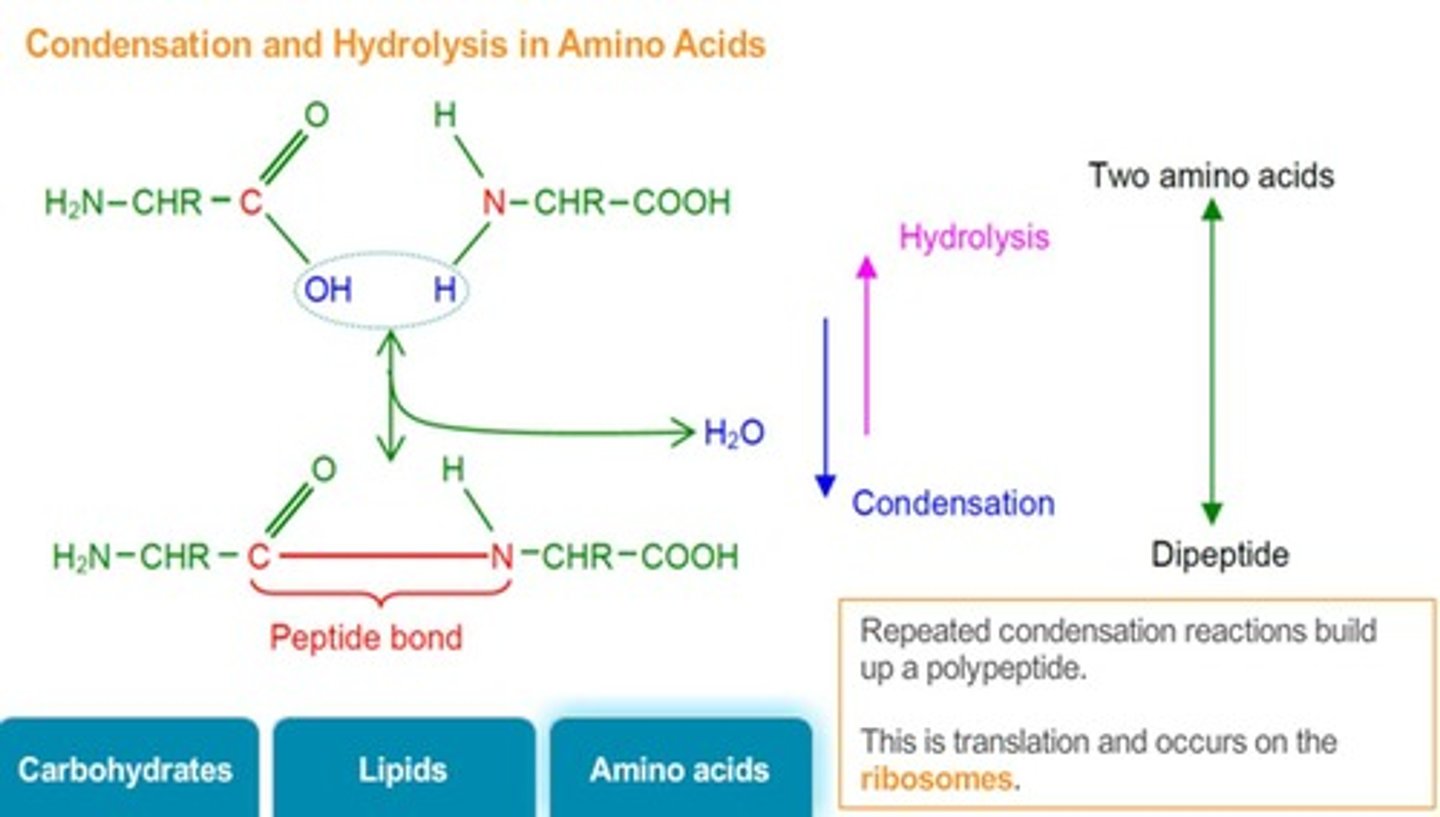
Peptide Bond
Covalent bond between amino acids in proteins.
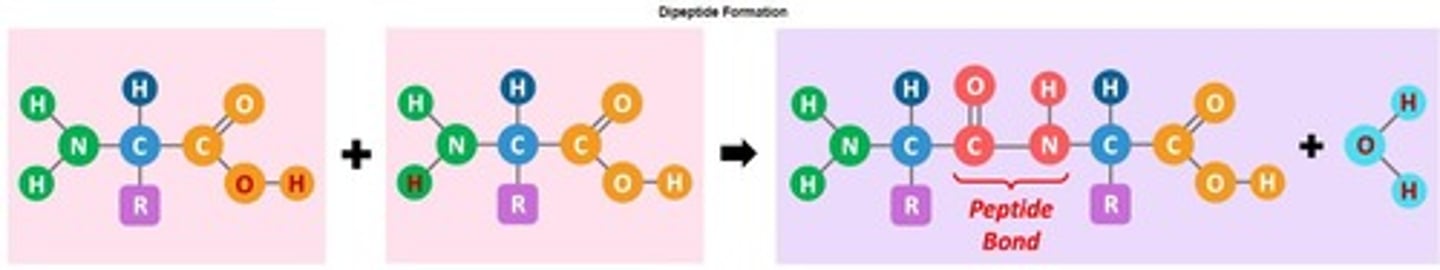
Polypeptides
Chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Protein Folding
Process determining protein's 3D structure and function.
Primary Structure
Sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
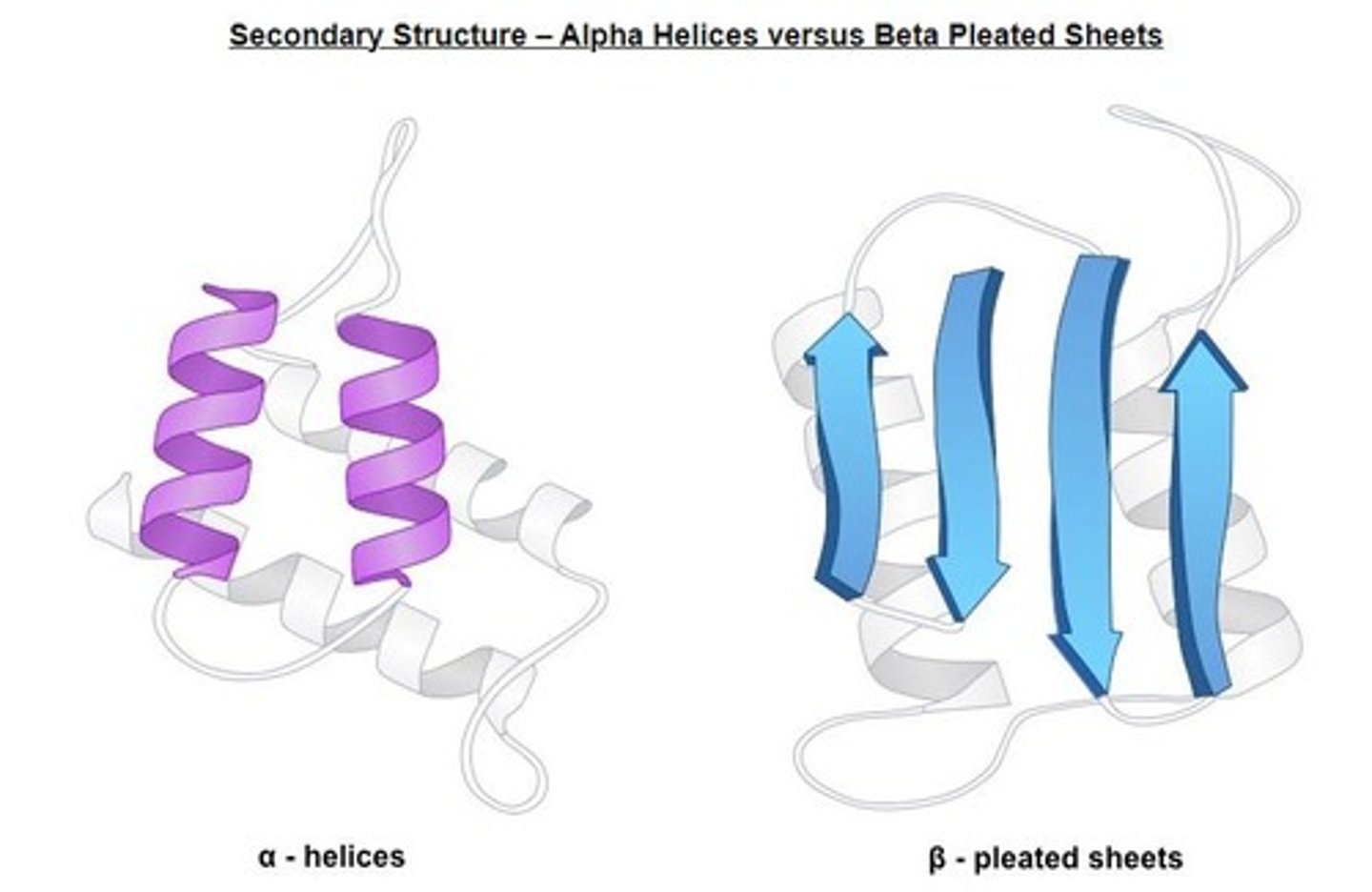
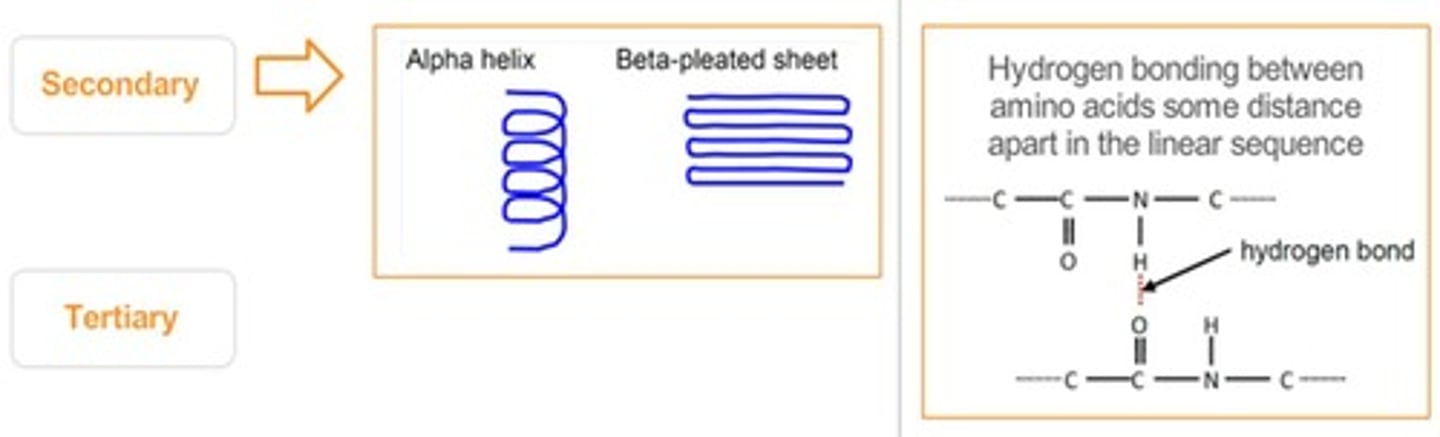
Secondary Structure
Stable configurations like alpha helices and beta sheets.
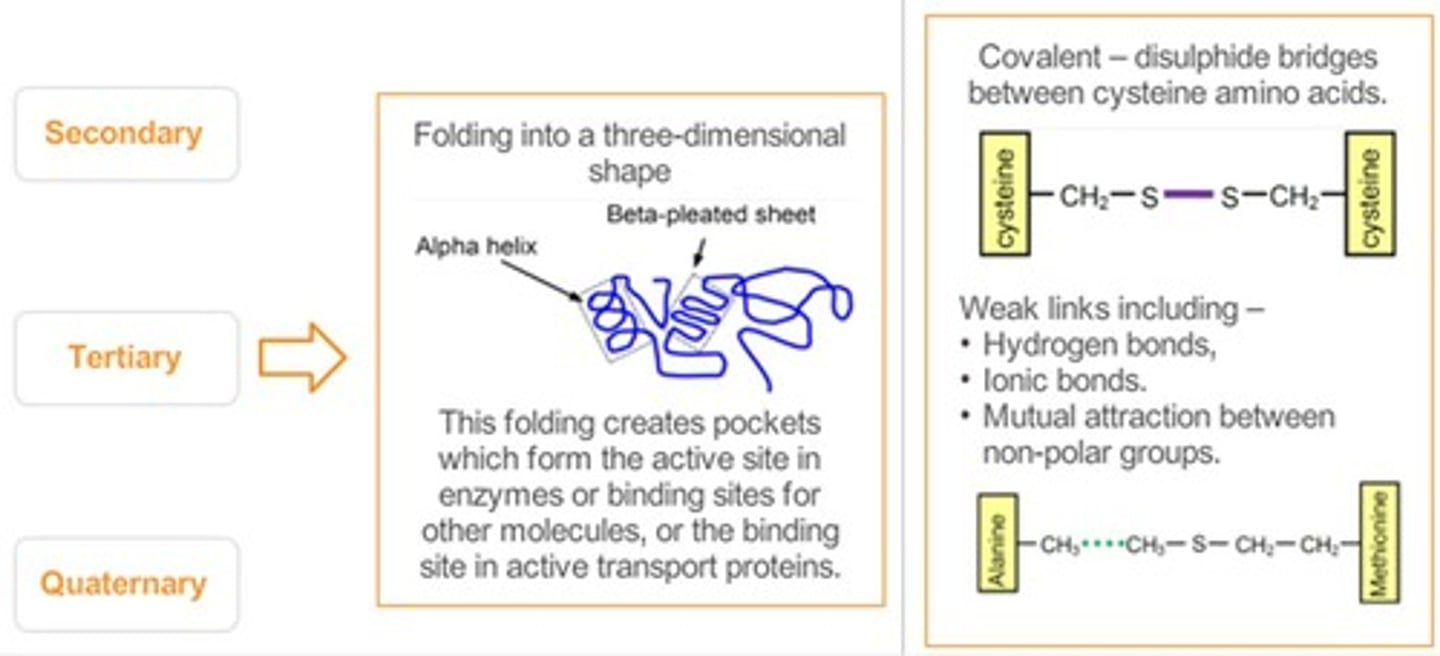
Tertiary Structure
Overall 3D shape of a protein from side chain interactions.
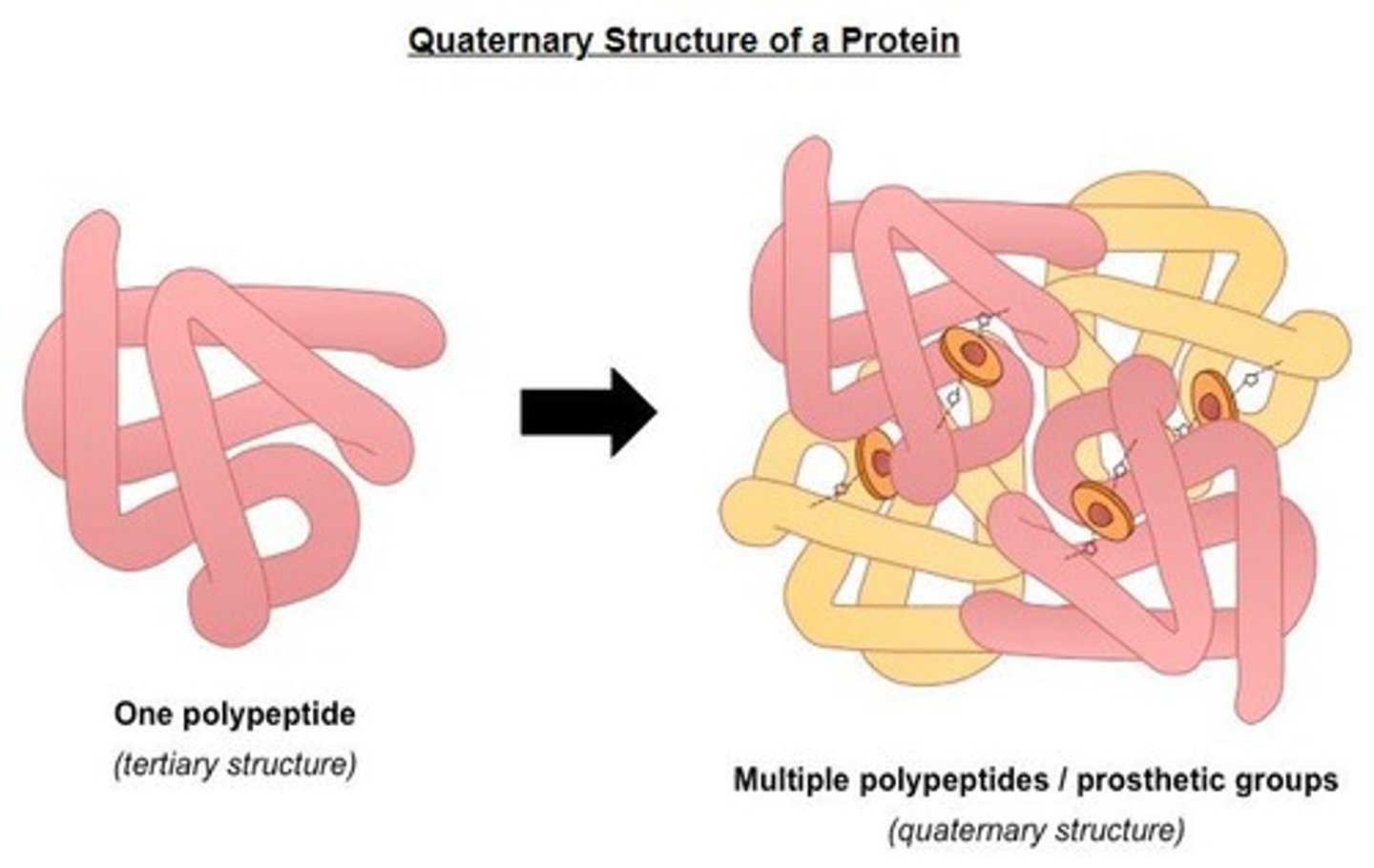
Quaternary Structure
Structure formed by multiple polypeptide chains.
Essential Amino Acids
Amino acids that must be obtained through diet.
Non-Essential Amino Acids
Amino acids synthesized by the body.
Conditional Amino Acids
Amino acids required during specific physiological conditions.
Protein Deficiency Malnutrition
Health issues from lack of essential amino acids.
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bonds crucial for protein secondary and tertiary structures.
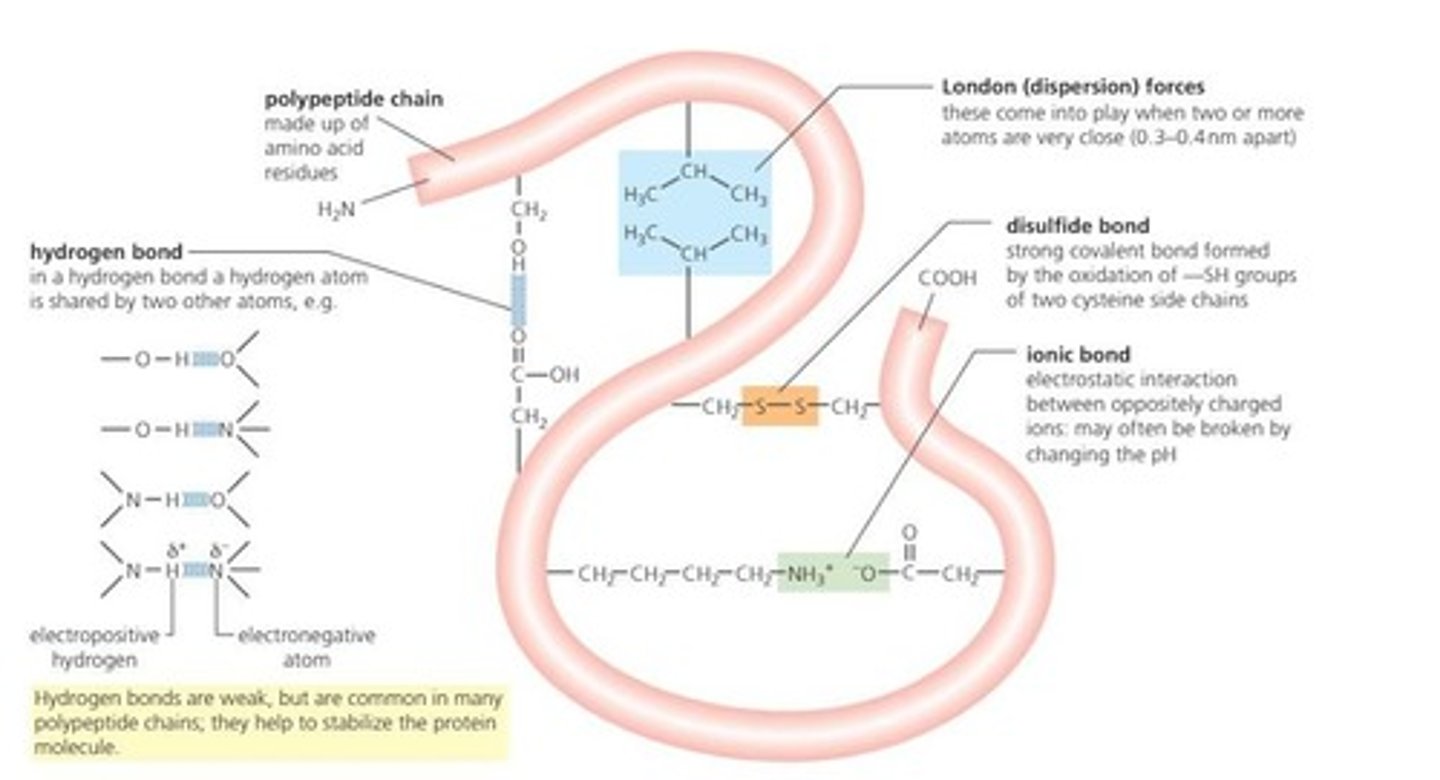
Ionic Bonds
Electrostatic attractions between charged side chains.
Disulfide Bridges
Covalent bonds between cysteine side chains stabilizing structure.
Hydrophobic Interactions
Non-polar side chains cluster to avoid water.

Alpha Helices
Coiled structure formed in protein secondary structure.
Beta-Pleated Sheets
Staggered strand configuration in protein secondary structure.
Denaturation
Loss of protein structure and function due to stress.
Optimal Temperature
Temperature at which proteins function best (~37ºC).
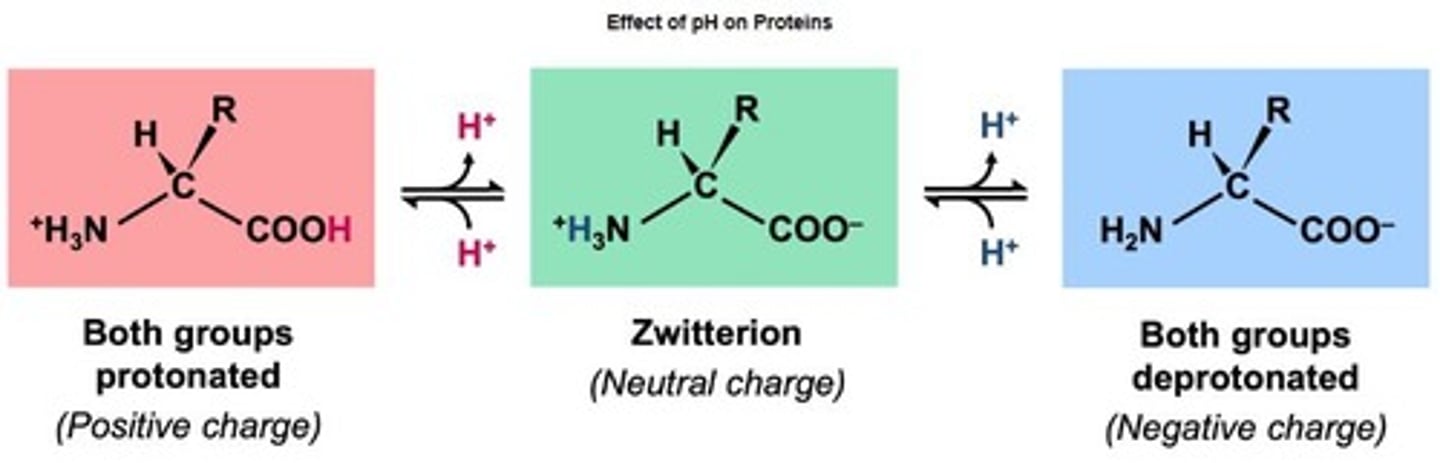
Optimal pH
pH level where proteins maintain proper structure.
Globular Proteins
Compact proteins with functional roles in cells.
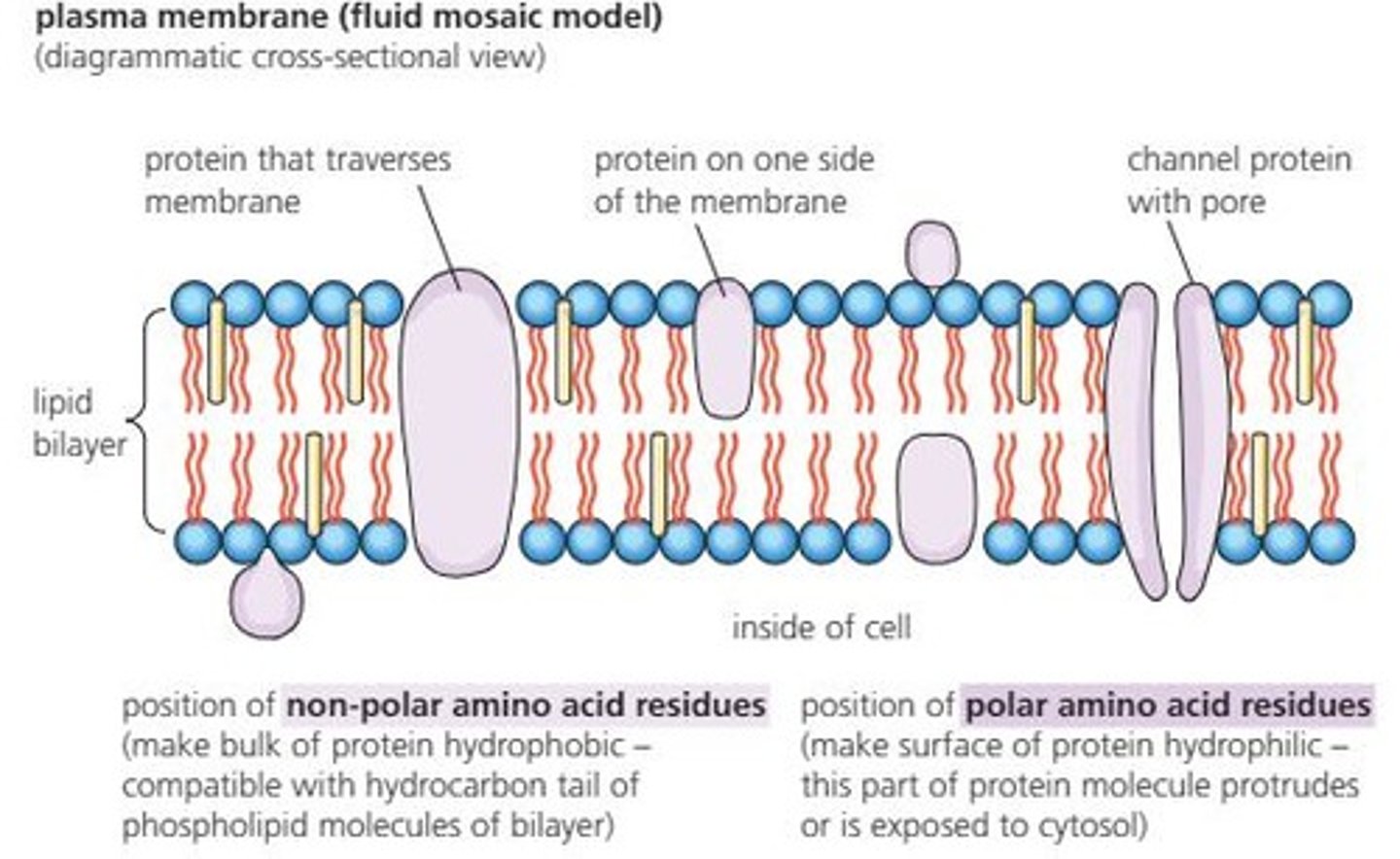
Fibrous Proteins
Structural proteins providing support and strength.
R-groups
Variable side chains that determine amino acid properties.
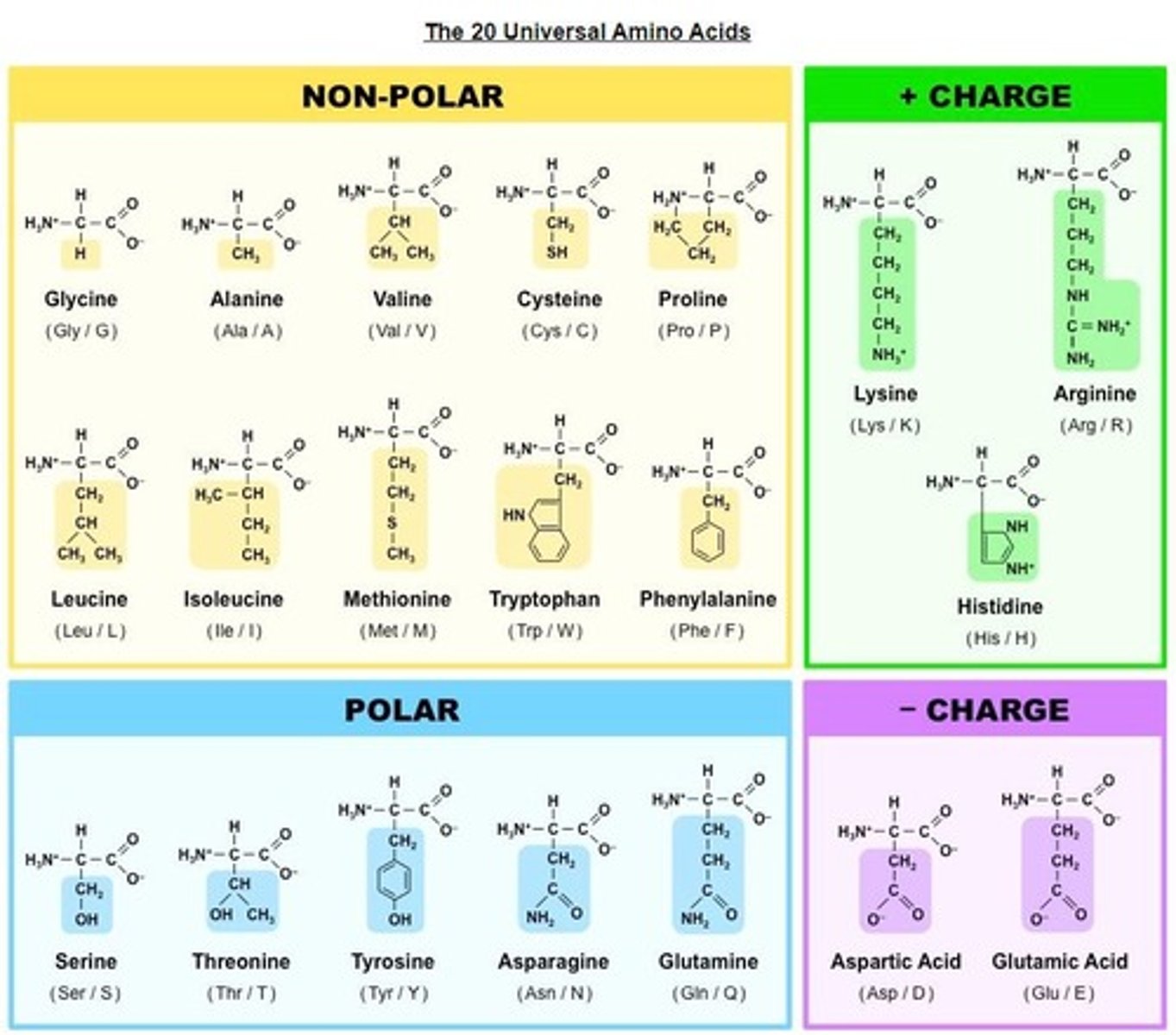
Hydrophilic Properties
Attraction to water, affecting protein solubility.
Hydrophobic Properties
Repulsion from water, influencing protein folding.
Vegan Diet Considerations
Need for careful amino acid intake to avoid deficiency.
Chemical Diversity
Variety in R-groups leading to diverse protein functions.