Bonding and thermodynamics
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Ionic =
metal (left side) + nonmetal (right side) - opposite sides of periodic table
If you see NH₃ or H₂O
its probs a coordinate covalent bond
Which of the following molecules CANNOT participate in hydrogen bonding with water?
a hydrogen bond has to be bonded to N, O, or F
what are these examples of:
NH₃ + H⁺ → NH₄⁺
BF₃·NH₃
[Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺
[Cu(NH₃)₄]²⁺
coordinate covalent bonds
covalent bond =
nonmetal + nonmetal
Double or triple bonds count as
one electron group
one lone pair =
1 group
what is the hybridization of this BF3
sp2 because Boron is electron deficient and has no lone pairs
work through how to do this:
What is the hybridation of the central atom in PCl3?
-draw it out (lone pairs = 1. single, double, triple = 1)
2- sp, 3- sp2, 4- sp3
Answer: sp3
ALWAYS electron-deficient = no lone pairs = sp
beryllium (Be)
Which of the following correctly describes the molecular shape of CS2?
linear
how do you determine what goes in the middle of the lewis structure
CS2
the one with the lowest electronegativity
so C
list the hybridzation rules
sp - 2 electron groups, linear
sp2- 3 electron groups, trigonal plannar
sp3 - 4 electron groups, tetrahedral
Which of the following bonds is the most polar?
the bigger the difference in electronegativity the in a covalent bond, the more polar it is
3 bonds + 0 lone pairs =
Ex. BF₃
trigonal planar (120)
2 bonds + 1 lone pair =
Ex. SO₂
bent (120)
4 bonds + 0 lone pairs =
Ex. CH4
tetrahedral (109.5)
3 bonds + 1 lone pair
Ex. NH₃, PCl₃
Trigonal pyramidal (107)
what is one of the most polar bonds you will see
Si - O
when is something most likely polar
when bonded to oxygen
what are these molecules
CO₂
CH₄
O₂
N₂
CCl₄
nonpolar (symmetric) - london dispersion
what are these molecules
H₂O
NH₃
SO₂
HCl
CH₃OH
polar (assymetric) - dipole dipole
how would i solve this: London dispersion forces are the primary intermolecular forces in which of the following molecules?
first look what hydrogen bonds: H bonded go N, O, or F
then see if its polar (assymetric)- dipole dipole
then nonpolar (symmetric) - london dispersion forces
how would I do this
Given the following data:
NO2(g) ΔHf° = +33.2 kJ/mol
N2O4(g) ΔHf° = +11.1 kJ/mol
Which statement is true for the reaction below?
2 NO2(g) → N2O4(g)
product - reactants
11.1 - 2(33.3)
DO NOT FORGET THE 2 OUT IN FRONT
Is SO2 polar or nonpolar
polar
which one is more nonpolar SO2 or BCl3
BCl3 because it has no oxygen, oxygen makes something more polar
what increases entropy (ΔS)
solid → liquid → gas
increase in moles
breaking bonds
does this reaction show an increase or decrease in entropy?
2 C3H8O(l) + 9 O2(g) → 6 CO2(g) + 8 H2O(l)
decrease in entropy because the moles of gas goes from 9 to 6
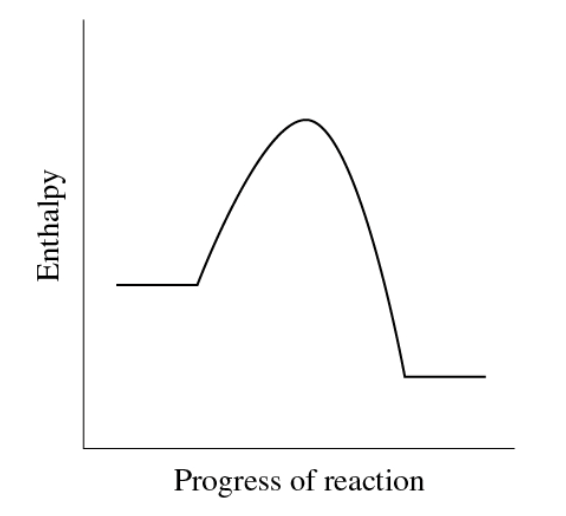
How would you do this:
The decomposition of sodium azide, 2 NaN3(s) → 2 Na(s) + 3 N2(g), has the following reaction coordinate diagram:
products is lower then reactants: H = negative
solid → gas: S = + (increase in entropy = +)

how do I do this
What is the ΔH° for the conversion of one mole of C2H6O(l) to C2H4O(l)?
2 (C2H4O) make -2334, so you have to divide it by 2 and then subtract (reactant - product; top - bottom)
answer: -200
polar -
covalent bond