Nucleotides & Nucleic Acids
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What elements do nucleic acids contain?
Carbon
Hydrogen
Oxygen
Nitrogen
Phosphorus
Nucleic Acids
Large polymers formed from many nucleotides (monomers) linked together in a chain
Structure of RNA nucleotide
Ribose pentose sugar, phosphate group, & 1 of the 4 nitrogenous bases
Uracil replaces thymine
RNA molecule made up of a single polynucleotide chain
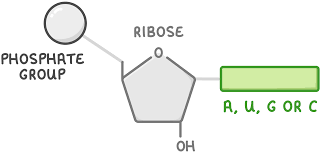
Structure of DNA nucleotide?
Deoxyribose pentose sugar
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous group (A-T, C-G)
Amount of H bonds formed between complementary base paris
Thymine & Adenine form 2
Cytosine & Guanine form 3
Pyrimidine bases
Thymine & Cytosine & Uracil
Smaller bases containing single carbon-nitrogen ring structures
Purine bases
Adenine & Guanine
Larger bases, containing double carbon-nitrogen ring structures
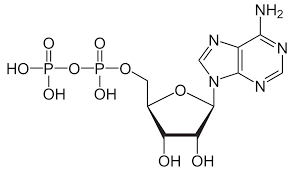
What is ADP & its structure as a phosphorylated nucleotide?
Adenosine Diphosphate
Contains the nitrogenous base adenine, the pentose sugar ribose & 2 phosphate groups
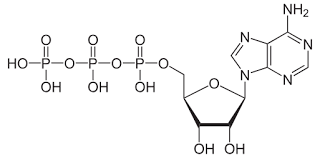
What is ATP & its structure as a phosphorylated nucleotide?
Adenosine triphosphate
Contains nitrogenous base adenine, pentose sugar ribose & 3 phosphate groups
How are polynucleotides synthesized?
Nucleotides linked together by condensation reactions
Phosphate group at 5th carbon of pentose sugar of 1 nucleotide forms a covalent bond w. OH group at 3rd carbon of pentose sugar of adjacent nucleotide
These bonds = phosphodiester bonds
Forms a long, strong sugar-phosphate backbone w. a base attached to each sugar
Breakdown of polynucleotides into nucleotides
Breaking phosphodiester bonds using hydrolysis reactions
DNA structure
Double helix, consisting of 2 anti-parallel polynucleotide strands joined together by hydrogen bonding between complementary bases
2 anti-parallel strands twist to form a double helix shape
How is DNA purified? (6)
Grind sample in mortar & pestle
Breaks down cell walls
Mix sample w. detergent
Breaks down cell membrane, releasing cell contents into solution
Add salt
Breaks H bonds between DNA & water molecules
Add protease enzyme
Breaks down proteins associated w. DNA in nuclei
Add layer of ethanol on top
Causes DNA to precipitate out of solution
Will be seen as white strands between layer of sample & alcohol
DNA can be picked up by spooling it onto glass rod
DNA replication (5)
DNA helicase breaks H bonds between 2 polynucleotide strands, forming 2 single strands
Free floating DNA nucleotides join to exposed bases on each orig. template strand by complementary base pairing
Nucleotides on new strand join together by DNA polymerase, forming the sugar-phosphate backbone & complete polynucleotide chain
Strands twist to form double helix
Each new DNA molecule contains 1 strand from orig. DNA molecule & 1 new strand
Why is it important to replicate DNA? (2)
So each new cell has full amount of DNA
Important for passing genetic info from generation to generation
Whys it important DNA replication is accurate?
To conserve genetic info
What is the occurrence of random, spontaneous mutations?
Often, although they don’t always have an affect but alter the sequence of amino acids
May cause abnormal protein to be produced
Genetic Code
Sequence of base triplets (codons) in DNA or mRNA which codes for specific amino acids
Nature of genetic code? (3)
Non overlapping
Triplets don’t share bases
Degenerate
Are more possible combinations of triplets than there are amino acids
Universal
Same base triplets code for same amino acids in all living things
How many possible combinations of triplets are there?
64
How many amino acids are there?
20
How does a gene determine the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (the primary structure of a protein)?
A gene is a sequence of DNA nucleotides that codes for a polypeptide
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide which is the primary structure that forms a protein
Order of protein synthesis
Transcription
Translation
Transcription (5)
DNA helicase moves along DNA & unzips strands by breaking H bonds
Exposes DNA bases on template DNA strand
DNA polymerase binds & free RNA nucleotides enter 1 by 1 forming temporary H bonds w. complementary base pairs
mRNA forms as RNA polymerase makes phosphodiester bonds
H bonds break & mRNA moves to ribosome via a nuclear pore
DNA double helix reforms
Antisense Strand
Complementary copy of the sense strand & doesn’t code for a protein
Acts as a template strand during transcription
Ensures complementary RNA strand formed carries same base sequence as sense strand
From 3’ to 5’
Sense strand
DNA strand that has to code for protein to be synthesized
Runs from 5’ to 3’
Translation (7)
Mature mRNA binds to small ribosome unit ; large ribosome unit sits on top
Codons presented 1 at a time
tRNA enters & anti codon binds temporarily to complementary codon, bringing the corresponding amino acid
Peptidyl transferase binds adjacent amino acids using peptide bonds, forming a polypeptide
H bonds break
Peptidyl transferase catalyzes release from tRNA
Process continues until a stop codon on mRNA is reached eventually forming a polypeptide chain
What occurs post translation?
As the amino acids are joined together forming the primary structure of the protein, they fold into secondary & tertiary structures
This folding & bonds that are formed are determined by the sequence of amino acids in the primary stucture
Protein may be further modified in Golgi Apparatus before it is fully functional & able to carry out specific role
What is mRNA & its role?
A single polynucleotide strand made in nucleus during transcription
Carries genetic code from RNA in nucleus to cytoplasm
Groups of 3 adjacent bases = codons
What is tRNA & what is its role?
Transfer RNA
Carries amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis
What is rRNA & what is its role?
Ribosomal RNA ; is in the ribosome
Combines w. proteins to form ribosomes which are responsible for protein synthesis in cells
Forms 2 subunits in a ribosome
Helps to catalyze formation of peptide bonds between amino acids