Comprehensive Biology Midterm Review: Cell Types, Macromolecules, Genetics, and Biotechnology
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Prokaryotes
Simple cells with no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles. Example: Bacteria.
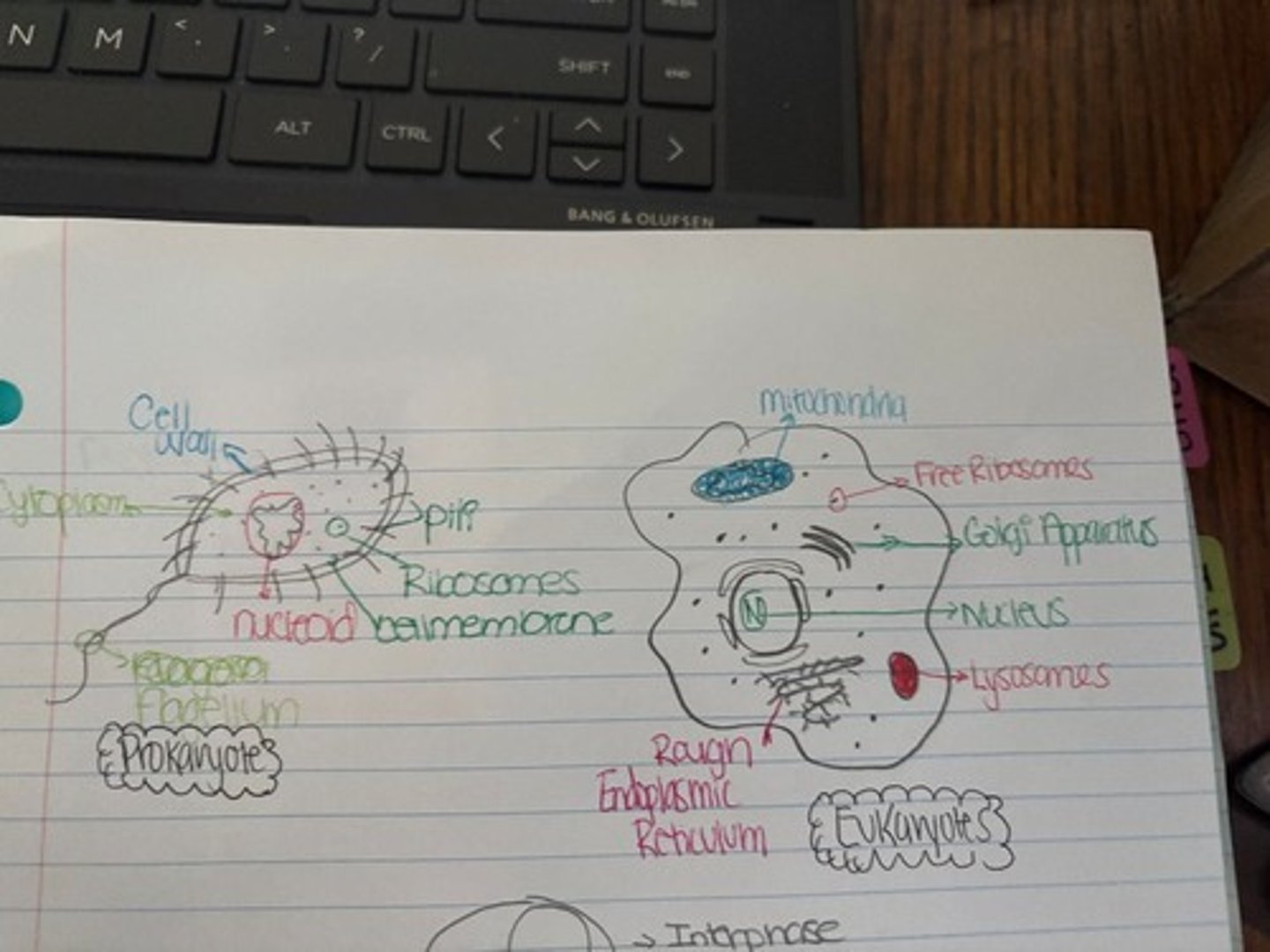
Eukaryotes
Complex cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (like mitochondria). Example: Plants, animals, fungi.
Lipids
Made from fatty acids and glycerol. Examples: Oils, Cholesterol, fatty acids.
Carbohydrates
Made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Examples: sucrose, fructose, and glucose.
Proteins
Made from amino acids. Function: muscle builder and help with regulating hormones. Example: eggs, yogurt, lean meats.
Nucleic Acids
Made up of nitrogen-containing bases, phosphate groups, and sugar molecules. Includes DNA & RNA.
DNA
Double helix structure that stores genetic information. (Adenine & Thymine -> Guanine & Cytosine)
RNA
Acts as a messenger to read DNA's instructions and direct protein synthesis. Structure: single strand.
Monera
Single-celled, prokaryotic organisms (bacteria).
Protista
Mostly single-celled, eukaryotic organisms (algae, amoeba).
Fungi
Absorb nutrients, eukaryotic organisms (mushrooms, yeast).
Plantae
Multicellular organisms that make food by photosynthesis (plants).
Animalia
Multicellular organisms that eat food (animals, humans).
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
Explains how genetic information flows: DNA → RNA → Protein.
Diploid
Cells with two sets of chromosomes. Example: body cells.
Haploid
Cells with one set of chromosomes. Example: sperm or eggs.
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles (HH or hh).
Heterozygous
Having two different alleles (Hh).
Recessive
Traits that are hidden unless two copies are present (aa).
Dominant
Traits that show when at least one copy is present (A).
Allele
A form of a gene (R or r for hair color).
Genotype
Genetic makeup (AA, Aa, or aa).
Phenotype
The physical trait seen (blue or brown eyes).
Prophase
Chromosomes become visible, nuclear membrane breaks down.
Metaphase
Chromosomes line up in the middle.
Anaphase
Chromosomes pull apart to opposite sides.
Telophase
Two new nuclei form.
Cytokinesis
Cell splits into two identical cells.
Pros of Biotechnology
Helps cure diseases (gene therapy), makes GMOs that grow faster and resist pests, produces insulin for diabetics.
Cons of Biotechnology
Raises ethical questions (gene editing, cloning), possible environmental risks (crossbreeding of GMOs), can cause unequal access to new technology.
Examples of Biotechnology
CRISPR gene editing, GMO crops like pest-resistant corn, insulin made using bacteria.