4.3.1: Marketing
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
global marketing strategy
for businesses operating outside their country of origin
aim to sell products beyond national market
planning, producing, placing and promoting a business in a worldwide market
various offices and facilitations
global localisation (glocalisation)
differs from having a common strategy for all countries
adapting local expectations in order to succeed
‘think global, act local’
businesses should aim for potential customers worldwide, but consider local tastes, customs and tradition
should be sensitive to specific preferences of different markets
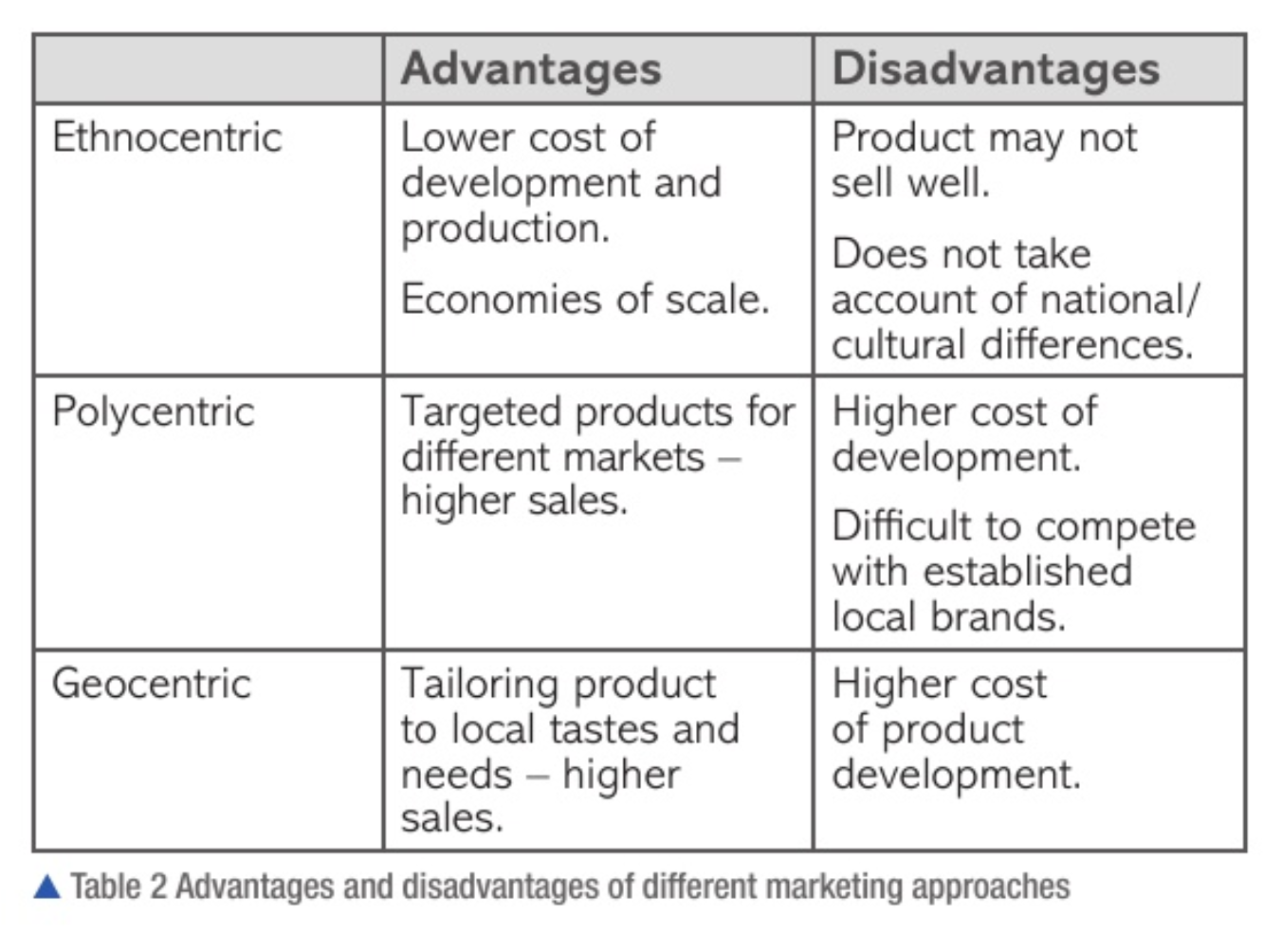
different marketing approaches
ethnocentric domestic approach:
overseas markets are idential to domestic markets
assumes what’s good for the domestic market will be good for global markets
make little or no attempt to adapt products to different markets
advantages:
economies of scale = standardised
no development costs for adaptation
reduced average costs due to ethnocentric marketing
lower prices
increased competitiveness
disadvantages:
may not sell well if not adapted
risky
polycentric international approach:
adapt products to local markets
developing and marketing different products for the demands of local customers
advantages:
product sells well
specific customer needs
targeted precisely
easier to gain acceptance in new markets
reduced ads and promotional costs
less effort to push products
higher sales and revenue
disadvantages:
costly
risky
geocentric mixed approach:
combination of the ethnocentric and polycentric
geocentric glocalisation
used by MNCs
maintains and promotes global brand name while tailoring products to local markets
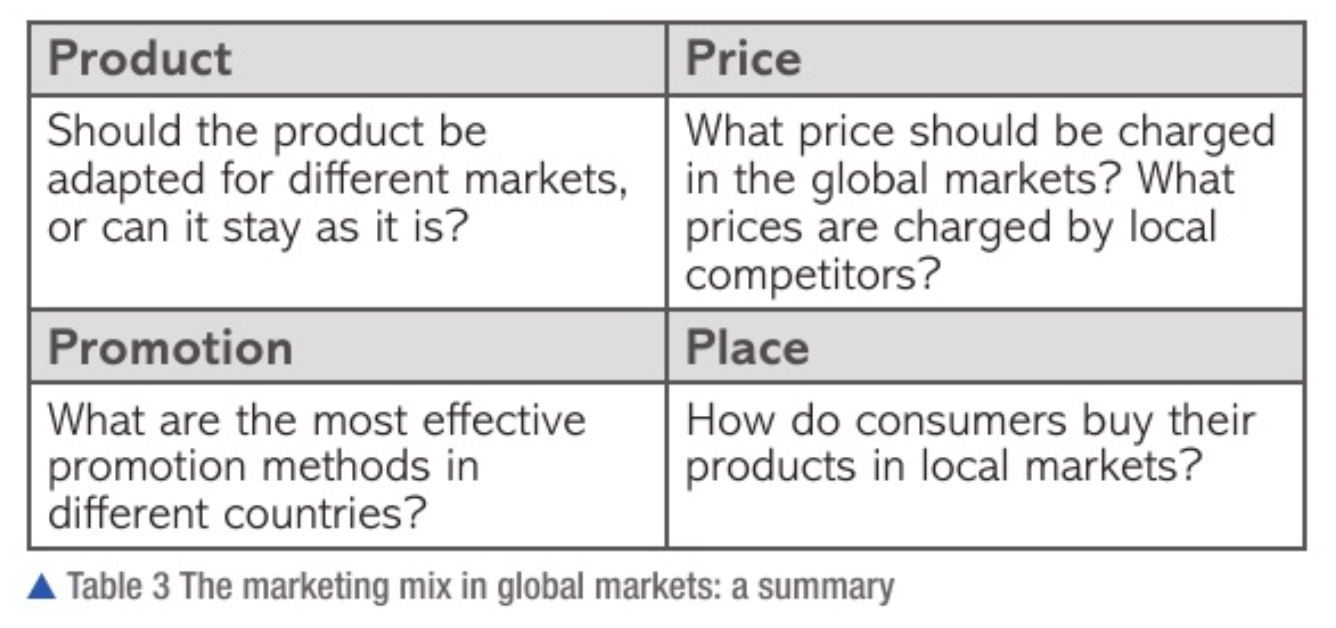
application and adaptation of the marketing mix to global markets
price
need to consider local factors (income, tax, rent)
a business is unlikely to charge the same price in all markets
reflects various local factors
product
modification
adaptation
ethnocentric, polycentric, geocentric approach
promotion
conscious of language differences
values, beliefs, perceptions, legal and sociocultural aspects
identify target custimers
attract foreign customers
place
how local consumers buy products
online selling and retailing
application of ansoff’s matrix to global marketing decisions
market penetration
business adapts products for markets in which it already operates
market development
marketing of existing products in new markets
not always straightforward
varying tastes and preferences
relies heavily on understanding local habits, tastes and needs
slight modifications necessary i.e. language, labelling
refinement of existing product to fit in a new overseas market
glocalisation
product development
business promotes new or modified products in existing markets
appropriate for businesses that markets products with short PLCs
diversification
occurs when new products are developed for entirely new markets
riskiest
little to no experience
application of porter’s strategic matrix to global marketing decisions
cost leadership - attempting to be the lowest cost supplier
differentiation - business sucessfully distinguishes products from those of rivals
focus - business targets a narrow range of customers through:
cost focus
differentiation focus
used in domestic and global markets, mass markets, may be able to transfer competitive advantage from domestic market to global market