Ella Kulman GU
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
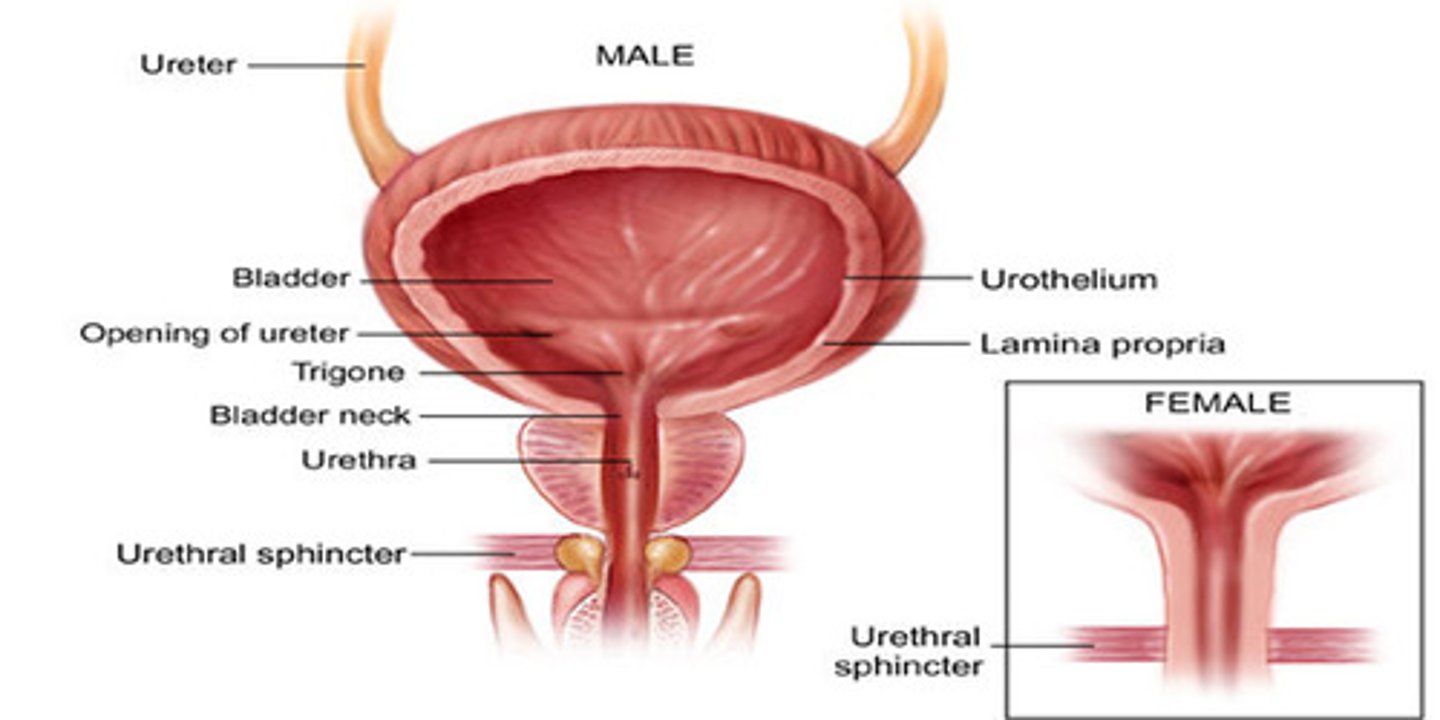
What anatomical structures make up the LUT?
Bladder → bladder neck → prostate gland > urethra → urethral sphincter
3 functions of the LUT
1. Storage of urine
2. converts the continuous process of excretion to an intermittent, controlled and volitional process
3. Allows rapid, low pressure voiding
Is the detrusor muscle relaxed or contracted during storage?
relaxed
Is the detrusor muscle relaxed or contracted during voiding?
contracted
Is the urethral sphincter relaxed or contracted during storage?
contracted
Is the urethral sphincter relaxed or contracted during voiding?
relaxed
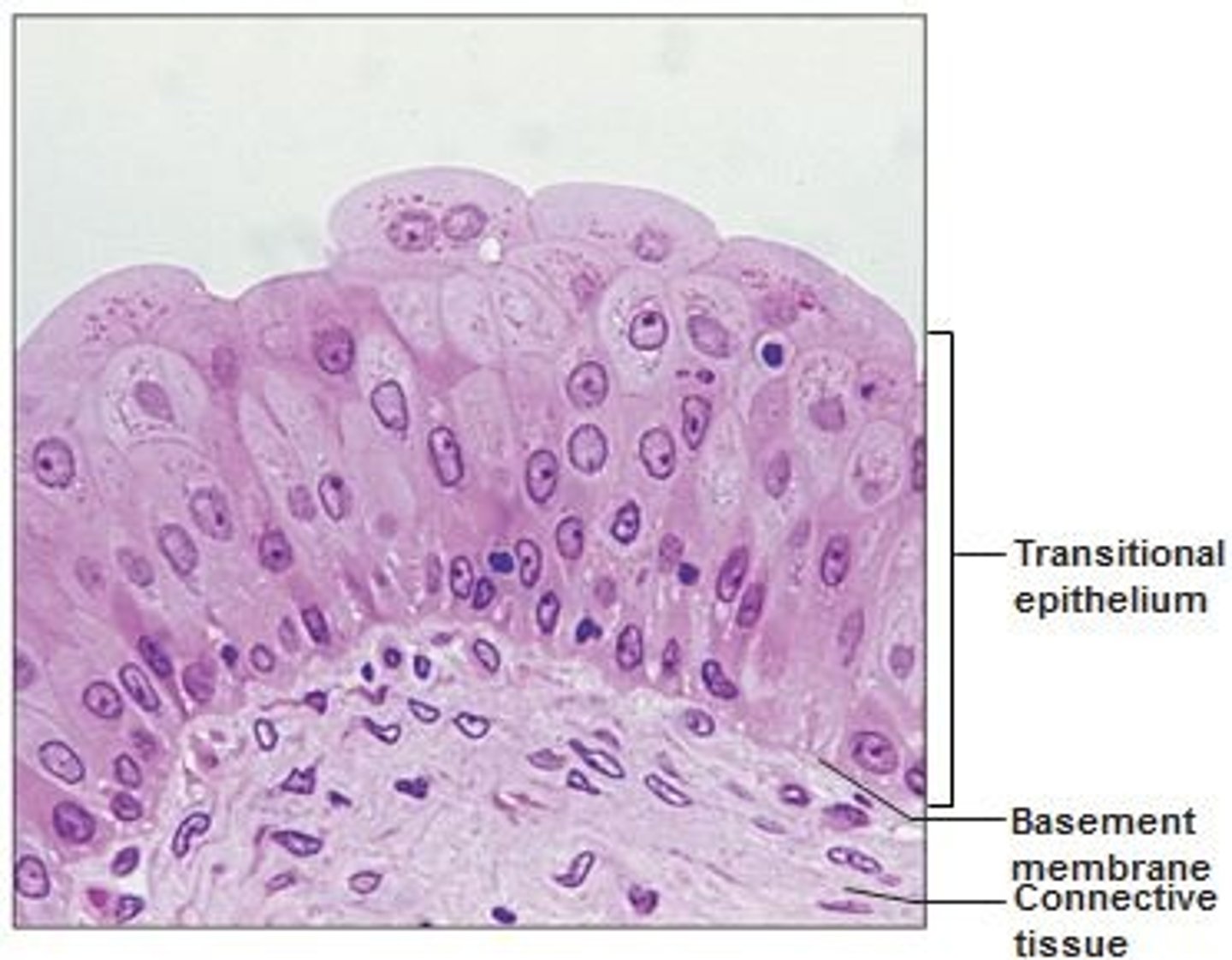
What type of epithelium lines the bladder?
urothelium (transitional epithelium) - pseudo stratified
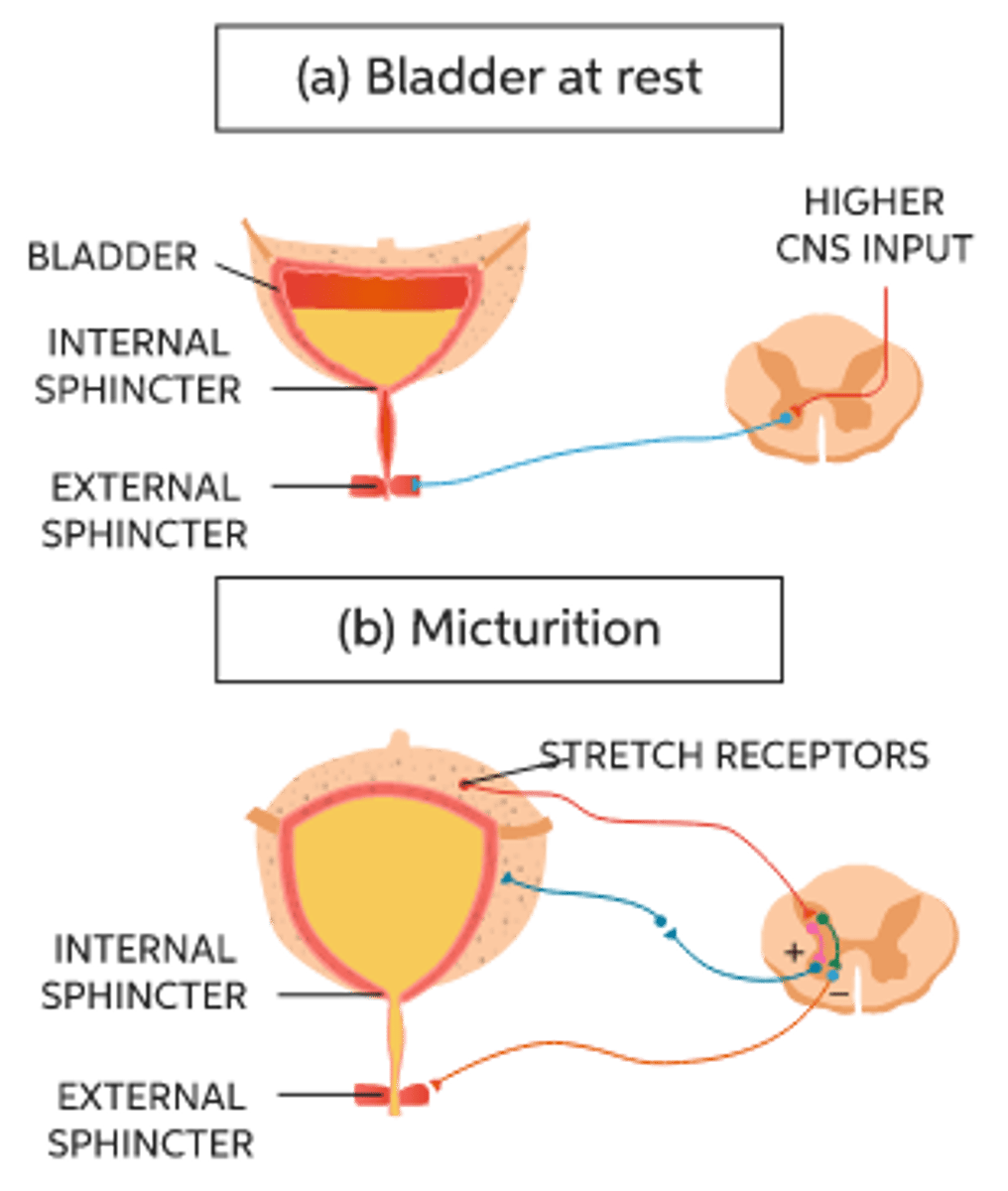
Describe the physiology of micturition
The bladder fills and stretch receptors are stimulated. Afferent impulses stimulate parasympathetic action of detrusor muscle - it contracts. Urethral sphincters relax
What are LUTS in men > 50 likely to be due to?
benign prostatic enlargement/hyperplasia
LUTS: Give 3 symptoms of storage problems
1. Frequency
2. Urgency
3. Nocturia
LUTS: Give 4 symptoms of voiding problems
1. Straining
2. Hesitancy
3. Incomplete emptying
4. Poor fIow
What might dysuria suggest?
Inflammation
What investigations might you do on someone who presents with LUTS?
1. Urinary tests eg. dipstick
2. Urinary flow: maximum flow rate and residual vol. are important
3. Symptom assessment: international prostate scoring system
4. Blood tests e.g. PSA, U+E
Describe treatment for pt with mild LUTS
reassurance, watch and wait
Describe treatment for someone with moderate LUTS
1. Fluid management, avoid caffeine
2. Bladder drill
2 pharmacological therapies used to treat moderate to severe LUTS
1. Alpha-1-blockers e.g tamulosin
2. 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors
2 potential side effects of tamulosin
hypotension and retrograde ejaculation
surgical treatment for BPE/BPH
TURP- transurethral resection of the prostate
5 potential consequences of untreated LUTS
1. Bladder calculi (stones)
2. UTI
3. Urinary incontinence
4. Reduced QOL
5. Acute urinary retention
Name a rare but serious cause of acute urinary retention
spinal cord compression
What investigations might you do in someone with acute urinary retention?
1. Clinical examination: palpable bladder?
2. MRI
3. Bloods
4. Neurological tests (spinal cord compression)
Treatment for acute urinary retention
catheter, pain relief
2 main causes of erectile dysfunction
1. Organic ( e.g. vasculogenic, neurogenic, hormonal, anatomical)
2. Psychogenic
4 risk factors for erectile dysfunction
1. Obesity
2. Lack of exercise
3. Smoking
4. Diabetes mellitus
What is priapism?
prolonged erection lasting >4 hours
What is a potential consequence of priapism?
permanent ischaemic damage
Where might a transitional cell carinoma arise?
1. Bladder (50%)
2. Ureter
3. Renal pelvis
5 risk factors for transitional epithelium
1. Smoking
2. Occupational exposure (e.g. working in rubber factories - aromatic amines)
3. Increasing age
4. Male
5. Family history
5 symptoms of a transitional cell carcinoma
1. Painless haematuria!!!
2. Frequency
3. Urgency
4. Dysuria
5. Urinary tract obstruction
What test is diagnostic in transitional cell carcinoma?
flexible cystoscopy
Give 5 functions of the kidney
1. Filters and excretes waste products from the blood
2. Regulates BP
3. Retains albumin
4. Reabsorption of Na, Cl, K, glucose, H2O, amino acids
5. Synthesises EPO
Typical GFR value in ml/min
120 ml /min
Give an example of a substance used for estimating GFR
Creatinine
What is the effect on GFR of afferent arteriole vasoconstriction?
deceased GFR
what is the effect on GFR of efferent arteriole vasoconstriction?
increased GFR
where in the nephron does the bulk of reabsorption occur?
proximal convoluted tubule
What 7 things are reabsorbed at the PCT?
1. Sodium
2. Chlorine
3. Potassium
4. Glucose
5. Water
6. Amino acids
7. Bicarbonate
What part of the loop of Henle is permeable to water?
descending limb
What hormone is responsible for regulating sodium reabsorption?
Aldosterone
What is the effect of NSAIDs on the afferent arteriole of glomeruli, and therefore GFR?
NSAIDs inhibit prostaglandins and so lead to AA vasoconstriction = reduced GFR
what is the effect of ACEi on the efferent arteriole of glomeruli, and therefore GFR?
they cause EA vasodilation = reduced GFR
Name 2 hormones that increase sodium reabsorption
Aldosterone and angiotensin 2
Name a hormone that decreases sodium reabsorption
ANP
What is the function of EPO
stimulates bone marrow → RBC maturation
What triggers PTH secretion?
low serum calcium
Give 3 ways that PTH increases serum calcium
1. Increased bone resorption
2. Increased reabsorption of calcium at the kidneys
3. Increased calcium absorption from intestine
2 hormones secreted from the posterior pituitary
1. ADH
2. Oxytocin
3 factors that stimulate renin release
1. Sympathetic stimulation
2. Decreased BP
3. Decreased Na detected by macula densa
Define urinary tract infection
inflammatory response of the urothelium to bacterial invasion, usually associated with bacteriruria and pyuria
2 things that can facilitate bacterias descent into the urinary tract via the urethra
1. Sexual intercourse
2. Catheterisation
The vagina is heavily colonised with lactobacilli. What is the function of this?
helps maintain low pH = host defence mechanism
Give 2 reasons why a post menopausal woman is more susceptible to a UTI
1. pH rises - increased colonisation
2. Reduced mucus secretion
What is pyuria?
presence of leukocytes in urine
What investigations might you do on someone who you suspect has a UTI?
1. Take a good history
2. Urinalysis - multistix SG
3. Microscopy, culture, and sensitivity of mid-stream urine
4. In recurrent/complicated UTI renal imaging is important
What determines if a UTI is complicated or uncomplicated?
complicated if:
- someone with an abnormal urinary tract
- a man
- a pregnant lady
- children
- the immunocompromised
- if it is recurrent
What is cystitis?
inflammation of the bladder secondary to infection
3 symptoms of cystitis
1. Dysuria
2. Frequency
3. Urgency
what investigations might you do in someone with prostatis?
1. Urinalysis and MSU
2. Semen cultures
3. STI cultures
4. Bloods including MCS
What can cause urethritis?
STI's e.g. gonorrhoea, chlamydia
What is epididymo-orchitis?
inflammation of the epididymis and testicle
Define pyelonephritis
inflammation secondary to infection of the renal parenchyma and soft tissues of the renal pelvis
3 symptoms of pyelonephritis
1. Loin pain
2. Fever
3. Pyuria
What is the function of the prostate?
secretes proteolytic enzymes into the semen which break down clotting factors in the ejaculate
Where can prostate cancer commonly metastasise to?
lymph nodes and bone
Other than prostate cancer, what can cause elevated PSA levels?
1. Benign prostate enlargement/hyperplasia
2. UTI
3. Prostatis
What is the treatment for metastatic prostate cancer?
palliative treatment e.g. hormone therapy - androgen deprivation
What is septic shock?
severe sepsis with persistent hypotension
What can cause raised urinary tract pressure?
1. stone in lumen of UUT
2. Tumour in the wall
3. LUT outflow obstruction: BPH, tumour, stone
4. Bladder dysfunction
What age/gender is more at risk of renal cell carcinoma?
incidences increase in males, and over >60 yrs
3 risk factors for renal cell carcinoma
1. Smoking
2. Obesity
3. Hypertension
3 classic signs of renal cell carcinoma
1. Haematuria
2. Flank mass
3. Loin pain
3 places renal cell carcinoma might metastasise to?
1. Lymph nodes
2. Lungs
3. Bones
what is a varicocele?
An abnormal enlargement of the pampiniform venous plexus in the scrotum
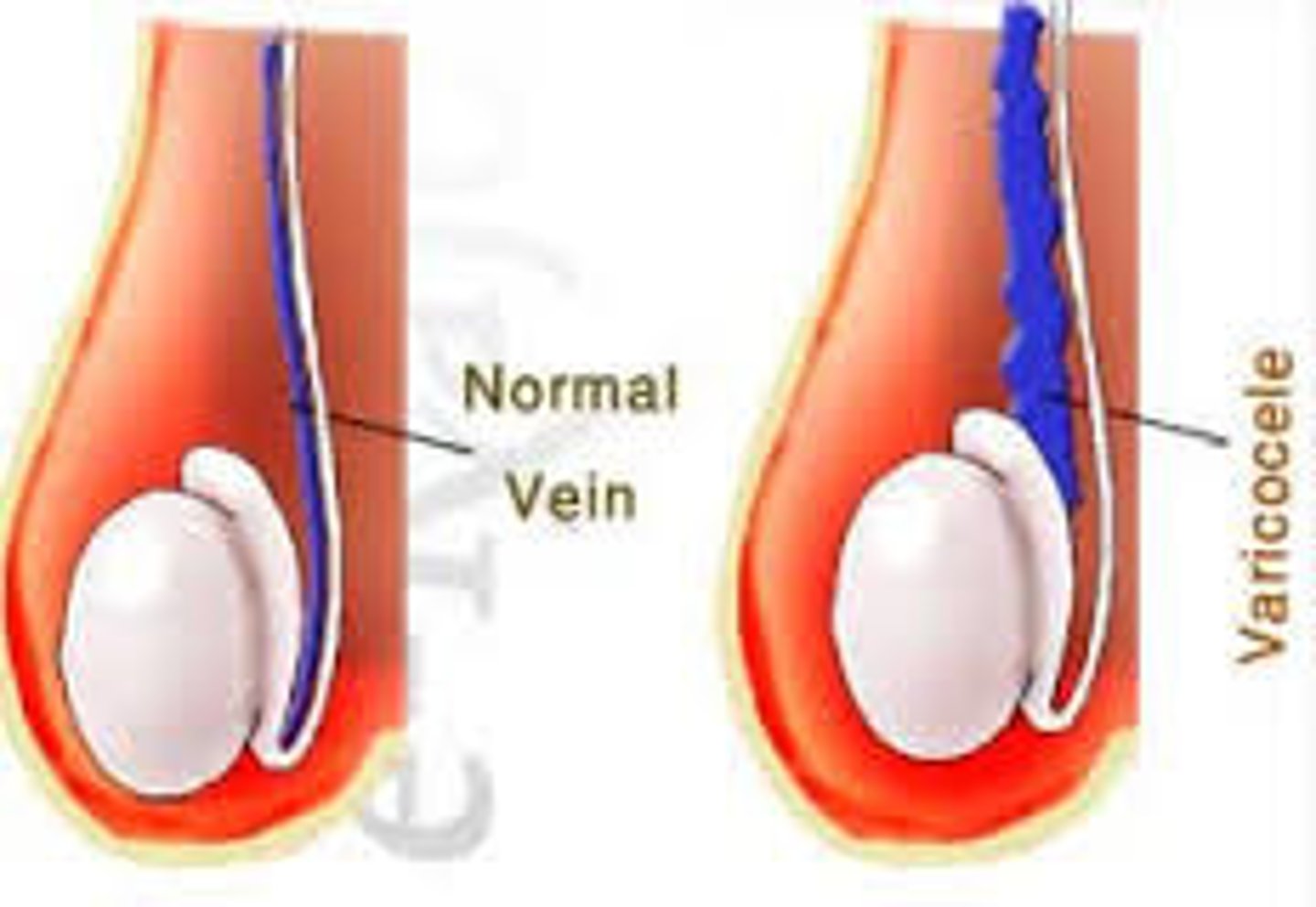
Why might RCC cause left sided varicocele?
If the renal tumour obstructs where the gonadal vein drains into the renal vein, blood can back up and so you may see left sided varicocele
What investigations might you do in someone with suspected RCC?
- ultrasound
- bloods: FBC, U+E, LFT, Ca profile
- abdo CT scan with contrast
-bone scan for boney metastases
Treatment for RCC: localised/metastasised
localised - surgical excision (partial nephrectomy)
metastatic - palliative nephrectomy, radiotherapy
Give a reason why incontinence in men is less common than it is in women
men have a bladder neck mechanism and a strong urethral sphincter, whereas women have only a weak urethral sphincter
3 types of incontinence
1. Stress - associated with coughing/sneezing
2. Urgency
3. Continuous - due to fistula
4. Mixed- stress and urgency
What is the main cause of stress incontinence in women?
usually secondary to birth trauma
Give 4 causes of haematuria
1. kidney tumour, trauma, stones, cysts
2. Ureteric stones or tumour
3. Bladder injection, stones or tumour
4. BPH or prostate cancer
ICF
28 L, 40% of body weight
ECF
14L, 20% body weight
interstitial fluid
11L
Plasma fluid
3 L
What happens to HR in hypovolaemia?
increases - tachycardia
What happens to BP in hypovolaemia?
decreases - hypotension
3 groups of people at risk of hypovolaemia
1. Elderly
2. Those who have had an ileostomy
3. Short bowel syndrome/bowel obstruction
3 groups of people at risk of hypervolaemia
1. AKI/CKD pts
2. HF pts
3. Liver failure pts
What happens to BP in hypervoIaemia?
BP is high/normal
What happens to urine output in hypervolaemia?
normal
2 symptoms of hypervolaemia
1 shortness of breath
2. Peripheral oedema
2 potential causes of rising creatinine
1. Too many diuretics
2. Progression of CKD
What is PSA?
prostate-specific antigen → a glycoprotein secreted by the prostate into the blood stream
4 symptoms of BPH
1. Increased frequency of micturition
2. Nocturia
3. Hesitancy
4. Post-void dribbling
Give 4 symptoms of prostate carcinoma
(same as BPH)
1. Increased frequency of micturition
2. Nocturia
3. Hesitancy
4. Post-void dribbling
Investigations for suspected prostate carcinoma
1. Trans-rectal ultrasound of prostate
2. Serum PSA - will be elevated
3. Trans-rectal prostate biopsy
Describe the pathophysiology of stone formation in the upper urinary tract
stones form from crystals in supersaturated urine -80% are calcium based
5 symptoms of upper urinary tract stones
1. loin pain → groin pain
2. 'renal colic' - pain caused by a blockage in the urinary tract
3. UTI symptoms (eg. dysuria, urgency, frequency)
4. Recurrent UTI's
5. Haematuria
Treatment for renal colic
1. Analgesia (e.g. NSAIDs - diclofenac)
2. Anti-emetics
3. Check for sepsis
What is the access point in haemodialysis?
AV fistula
